Wiki User
∙ 7y ago
Best Answer
Copy
No, was is a past tense verb.
«Was» is not a preposition. It is a verb. The word «was» has an original verb form, known as «to be». «To be» is broken down, as shown below.
Present tense:
She/he is
You are
I am
Past tense:
She/he was
You were
I was
Wiki User
∙ 7y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: Is was a preposition
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
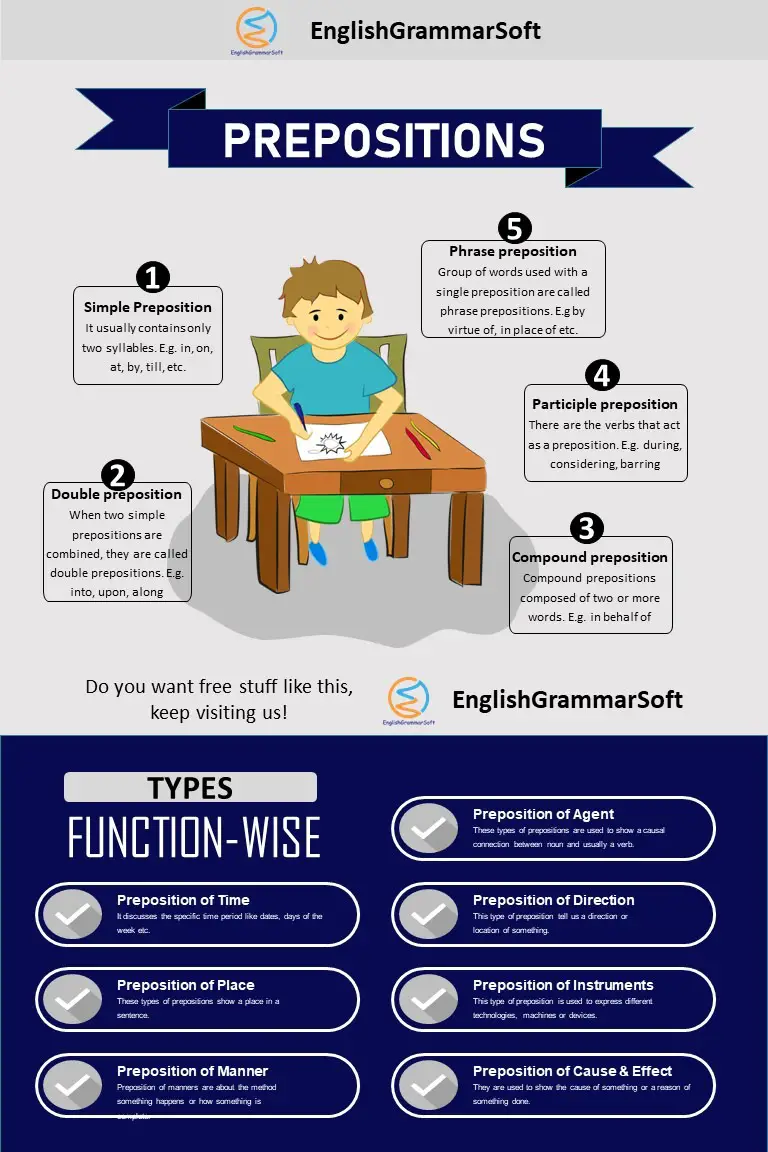
In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions
This list of prepositions will help you understand what a preposition is. But let’s start by having you learn the preposition song. Singing this song is an easy way to help you memorize some of the prepositions. I’ll sing it for you in the video below. 
The Preposition Song
above, across, after, at, around, before, behind,
below, beside, between, by, down, during, for, from,
in, inside, onto, of, off, on, out, through,
to, under, up, with
And that’s the preposition song!
This list contains one-word, two-word, and three-word prepositions. Sometimes, words act together to form one preposition.
WARNING: Keep in mind that the words on this list have the potential to be prepositions. Many of these words can also function as adverbs and other fun things. How can you tell the difference? I’ll teach you all the secrets below this list. 
A aboard, about, above, according to, across, after, against, ahead of, along, amid, amidst, among, around, as, as far as, as of, aside from, at, athwart, atop
B barring, because of, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, but (when it means except), by, by means of
C circa, concerning
D despite, down, due to, during
E except, except for, excluding
F far from, following, for, from
I
in, in accordance with, in addition to, in case of, in front of, in
lieu of, in place of, in spite of, including, inside, instead of, into
L like
M minus
N near, next to, notwithstanding
O of, off, on, on account of, on behalf of, on top of, onto, opposite, out, out of, outside, over
P past, plus, prior to
R regarding, regardless of
S save, since
T than, through, throughout, till, to, toward, towards
U under, underneath, unlike, until, up, upon
V versus, via
W with, with regard to, within, without
Would you like to download these word lists?

- Word Lists for the 8 Parts of Speech (Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, & Interjections)
- 17 Pages
- Printable
- 100% Money-Back Guarantee
- Only $2.99
If you’d like to see even more prepositions, check out Wikipedia’s list of English prepositions page.
The Mean Thing About This List
(The Secret About Prepositions)
Many times, words on this list of prepositions don’t act as prepositions.
That’s not very nice, is it? You probably feel a bit like you were tricked. I’m sorry about that. I would change the rules of language if I could so that it would be easier for you to figure all of this out.
Of course, I can’t do that, but I can help you use that powerful brain of yours to tell when a word is a preposition and when it’s not a preposition. Are you ready? Good.
Here is the one thing that you need to remember: prepositions are ALWAYS in prepositional phrases.
Look at these examples of prepositional phrases with the eye of a detective. What do you notice about them?
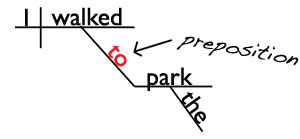
I walked to the park.
The cat climbed up the tree.
They biked around the block.
All three of those prepositional phrases begin with a preposition (to, up, around) and end with a noun (park, tree, block), and that sums up what a prepositional phrase is.
Prepositional phrases begin with a preposition (to, up, around) and end with a noun or pronoun called the object of the preposition (park, tree, block).
But why? Why do prepositions need to be in prepositional phrases?
The answer comes to us when we look at the definition of a preposition.
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun/pronoun and some other word in the sentence.
In order for a preposition to do its job (to show the relationship between a noun/pronoun and another word in a sentence), it needs to be followed by that noun or pronoun.
I sense that you may be furrowing your brow in a state of confusion right now, so it’s the perfect time for us to look at some sentence diagrams, which will make all of this visual.
Sentence diagrams are pictures of sentences that show us how the words are grammatically related.
In the diagram, the preposition to, which is on a slanted line, is connecting the noun park with the verb walked. It almost looks like a little bridge, doesn’t it? You can think of a preposition as a noun bridge if that helps.
to the park = prepositional phrase
to = preposition
park = noun (object of the preposition)
Prepositional phrases are always diagrammed like that. The preposition goes on a slanted line between the object of the preposition (the noun or pronoun at the end of a prepositional phrase) and a word in the rest of the sentence.
Why? Because the preposition is telling us how that special noun called the object of the preposition relates to the rest of the sentence. It acts as a little noun bridge.
Psst! You can learn more about how to diagram prepositions and prepositional phrases here if you’d like.
Preposition or Adverb?
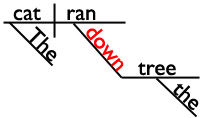
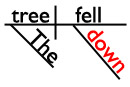
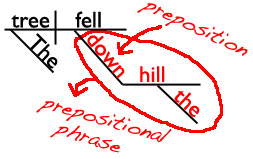
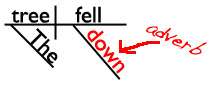
Did you know that words on the preposition list are often used as adverbs rather than prepositions? It’s true! I’m going to use that fact to see if you’ve been paying attention. Are you ready for a tiny quiz? Great! In which sentence is down a preposition?
A. The cat ran down the tree.
B. The tree fell down.
I’ll give you a hint and show you the sentence diagrams of those sentences. (In which diagram is down a bridge between a noun and the rest of the sentence? That’s the diagram with the preposition!)
The cat ran down the tree.
The tree fell down.
Are you ready for the answer?
In sentence A, down is a preposition. It’s in the prepositional phrase down the tree.
In sentence B, the word down isn’t in a phrase, so it’s not a preposition. (In this sentence, down is an adverb telling us where the tree fell.)
The cat ran down the tree.
The tree fell down.
If you wanted to, you could change sentence B so that down was a preposition instead of an adverb. Can you think of how you would do that?
HINT: Add at least a noun (and probably an adjective as well) after down so that you create a prepositional phrase.
The tree fell down. (adverb)
The tree fell down the hill. (preposition)
Here are two other examples of words from this list functioning as adverbs and as prepositions. I’ll bet that you can see the difference now, right?
My sister just walked past. (adverb)
My sister just walked past us. (preposition)
Carefully crawl inside. (adverb)
Carefully crawl inside the tent. (preposition)
The moral of the story is that in order for a word to be a preposition, it must be in a prepositional phrase.
Preposition or Phrasal Verb?
As you saw above, words on this list of prepositions are only potential prepositions. We need to look at how each word-in-question is functioning within a sentence in order to say what part of speech it actually is.
I’m sure you remember that the words on this list are only prepositions when they are in prepositional phrases.
In our last example above (The tree fell down.), you saw how words from the list of prepositions could also function as adverbs.
Another common function of words on this list is for them to be a part of something called phrasal verbs. (I’ll underline the phrasal verbs below.) Notice that the words out, up, and off are not prepositions in these sentences.
I work out every Saturday.
He dressed up for the concert.
I was so tired that I nodded off during the class.
Phrasal verbs are two-word or three-word phrases that function as the verb in the sentence. They are made up of a verb (word, dressed, nodded) and a word from the preposition list (out, up, off), and they form a meaning that’s different from the meaning that the words have all by themselves.
When words like out, up, and off are in phrasal verbs, they have a special name. They’re called particles.
Let’s look at a sentence diagram with a phrasal verb. That way, you can see that particles (words from the preposition list that are functioning in phrasal verbs) are not prepositions.
We were tired, and we turned in early.
Look at the sentence diagram and notice that the word in isn’t on a little noun bridge. If in were a preposition, it would be diagrammed on a noun bridge like the word to in the diagram below.
Preposition or Conjunction?
I have a feeling that you already know where I’m going with this. 
A. I’m looking for bananas. (preposition)
B. He felt energized, for he had just won the competition. (conjunction)
In sentence A, for is in the prepositional phrase for bananas.
In sentence B, for is connecting the two clauses he felt energized and he had just won the competition.
Summary
Sometimes it helps to have a summary of everything you’ve learned. For your learning pleasure, here are the main points we covered on this page.
- Singing some of the prepositions to the tune of «Yankee Doodle» can help you memorize a handful of words from the preposition list.
- Words on the preposition list are not always used as prepositions.
- They are only prepositions when they are in prepositional phrases (preposition + noun).
- Words from the preposition list often act as adverbs. They can also be in phrasal verbs or function as conjunctions. In these cases, they are not prepositions.
Would you like to download these word lists?

- Word Lists for the 8 Parts of Speech (Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, & Interjections)
- 17 Pages
- Printable
- 100% Money-Back Guarantee
- Only $2.99
This is original content from https://www.english-grammar-revolution.com/list-of-prepositions.html
Before writing about the List of Prepositions, we have to know about the prepositions.
What is Preposition?
The preposition is a word that correlates between two different words or phrases, usually about the time or position. It places before the noun or a pronoun in a sentence that relates to the rest of the sentence and makes it meaningful by telling us what is exactly happening in the sentence.
In the English Language, there are various prepositional words, and each of these is used according to their use in a sentence.
There are certain varieties of the preposition, based on their use like,
Basic examples of prepositions
A] One-word Prepositions:
- Common Prepositions
- Seldom used Prepositions
B] Complex Prepositions:
- Prepositional Phrases
- Prepositions with verbs
- Prepositions with Idioms.
One word Common prepositions:
Common prepositions are those prepositional words that are used mostly in sentences.
Here is the list of some common prepositional words,
- About, above, across, after, against, among, around, at
- Before, behind, below, beside, between, by
- Down, during
- For, from
- In, inside, into
- Near
- Of, off, on, out, over
- Through, towards, to
- Under, up
- With
Examples
- About:
- What about your health
- We are about to reach our destination.
- Above:
- An eagle is flying above the clouds.
- The water level goes above the marking line due to heavy rainfall.
- Across:
- There is a huge mountain across the river.
- A baby is going across the road
- After:
- We went home after the party was over.
- I will go to sleep after 10 o’clock.
- Against:
- What do you have against me?
- The man is running against the train.
- Among:
- He is the eldest son among all.
- He is not comfortable sitting among us.
- Around:
- We all are sitting around the table.
- Her age was around 80.
- At:
- We are at the party.
- Come to my home at 8 o’clock.
- Before:
- He came before any other.
- The train was left before its time
- Behind:
- He is doing something behind my house.
- She is coming from behind.
- Below:
- He is swimming below the surface.
- I will not decrease its price below the cost price.
- Beside:
- She lives beside this colony.
- He was sitting beside my aunt.
- Between:
- I will catch you between 1 to 4 PM.
- He overtakes his bike between two trucks.
- By :
- She was murdered by any sharp metal object.
- We will provide you with the rest part by this evening.
- Down:
- He fell down on the ground.
- You go straight, then step down the hill and continue your walk.
- During
- Nobody is allowed to go out during the lecture.
- He was sleeping during the day.
- For:
- Let us go out for a trek.
- Smoking is bad for your health.
- From:
- I wish her a happy new year from my side too.
- He bought this shirt from supermart.
- In:
- He is working in this location.
- We are in the zoo now.
- Inside:
- The puppy is sitting inside the box.
- I have some cash inside my pocket.
- Into:
- Water turns into ice at 0-degree celsius.
- Jayson cut the eraser into two and gave them one each.
- Near:
- His office is just near my school.
- She stands near the statue.
- Of:
- She came to meet me at the end of the month.
- I am in the middle of something.
- Off:
- This shop is giving a 30% off sale on clothes.
- Please take off your shirt.
- On:
- We started our project on that site.
- He is sitting on the table.
- Out:
- He scored 79 marks out of 100 marks.
- She is out of the world.
- Over:
- That airplane is flying over the buildings.
- The village is situated just over the mountain.
- Through:
- The bullet is passing through this hole.
- We had gone through bad situations.
- Towards:
- She is looking towards me for the last hour.
- He has some responsibilities towards his family.
- To:
- You are coming to London.
- This little girl waited for a long time to wish you personally.
- Under:
- He knows how to swim under-water.
- He escaped from the cops on a boat under the bridge.
- Up:
- Jack and Jill both went up the hill.
- He strikes a ball up the sky.
- With:
- Are you coming with us?
- I pulled her out with the help of this rope.
Seldom used Prepositions:
Seldom used prepositions are those prepositional words that are rarely used in sentences.
Here is the list of some seldom-used prepositional words,
Examples:
- Aboard:
- She climbed aboard the ship.
- Welcome aboard this flight to Mumbai.
- Along:
- We traveled along with the boat in the Arabian Sea.
- The bedroom is along with the kitchen.
- Amid:
- She hadn’t listened to her amid the voice.
- We were lost amidst the world cup this year.
- As:
- My brother is working as a manager at this hotel.
- Sugarcane is as sweet as sugar.
- Astride:
- He sat astride the Terries.
- She slept astride on the sofa.
- Alongside:
- Their car is standing alongside our car.
- My roll number is alongside my friend in the exam hall.
- Beneath:
- She hides beneath the bed.
- He stands beneath the building.
- Beyond:
- This difficult stunt is beyond my limits.
- Nobody can break the record beyond him.
- But:
- Everyone was present, but my friend didn’t.
- He agreed to work here, but he has certain conditions.
- Bar:
- She stood on the table bar her friend did not.
- I will come to the bar after 8 o’clock.
- Concerning:
- Your parents came to my house, and they discussed with us concerning your sister’s marriage.
- I want to make some changes because I am concerned about you.
- Considering:
- Considering the demand, I will increase production.
- This race is finished, considering the rules.
- Counting:
- If we start counting now, it will take 2 hours to finish.
- The net cash is only $20k after counting.
- Cum:
- He invented a bicycle-cum-bike.
- His mind is so sharp that he can sleep-cum-talk at the same time.
- Despite:
- We went on a picnic despite any arrangement.
- He finished the race despite filling petrol in it.
- Except:
- You can purchase any other cell phone except Vivo. That is out of stock.
- I will go anywhere for dinner except for this restaurant.
- Exclude:
- The total amount is 470$, excluded taxes.
- He attends every seminar excluding Sundays.
- Following:
- The red t-shirt guy is following me.
- Write down the following sentences.
- Given:
- She has given all her money to the kidnapper already.
- All students will have to finish their paper at a given time.
- Gone:
- Let us go now; some of them have already gone away.
- Your turn is gone earlier; now, it is my turn.
- Including:
- We provide you with special treatment in our hotel, including VIP services.
- Like:
- His behavior is like his brother.
- I want a refreshing juice like Lemon soda.
- Less:
- Its qualities are less than the previous one.
- 100 less 20 equals 80.
- Minus:
- Today’s temperature is minus 12 degrees Celsius.
- Eighty minus ten equals’ seventy.
- Next:
- The next candidate is absent.
- Call the cops standing next to you.
- Notwithstanding:
- Notwithstanding the quality, I refuse to buy it.
- The hot iron is notwithstanding the strokes of the hammer.
- Onto:
- He jumped onto the trampoline from Terries.
- The dog jumped onto the fence.
- Opposite:
- Opposite poles of a magnet repel each other.
- She sat opposite my seat on the bus.
- Outside:
- He has not escaped outside the city.
- The hot lava came outside from volcanoes.
- Past:
- The time half-past ten.
- After an accident, I forgot my past memories.
- Per:
- His vehicle runs at a speed of 120 miles per hour.
- She charges $50 per photo.
- Plus:
- Twenty-five plus seven equals thirty-two.
- We won the match, and this is our plus point for qualifying for the finals.
- Pro:
- This phone is a pro version of my old phone.
- We are playing a pro league match in this tournament.
- Pending:
- My payment is still pending.
- She had completed all her pending works on this holiday.
- Regarding:
- I will discuss this with the management regarding your promotion.
- Regarding this situation, I purchased a new machine for our work.
- Round:
- He stands outside the 30 yards round.
- The bullet motions round, not straight.
- Respecting:
- I am talking too politely with you respecting your age.
- Are you still respecting your teachers?
- Save:
- We all present here because he saves all of us at that moment.
- The superhero is always ready to save the world.
- Since:
- We have been friends since 1980.
- The museum had been closed since 1800 AD.
- Than:
- My brother is stronger than his brother.
- I have an expensive toy car than anyone.
- Till:
- The shop will open till Saturday.
- Throughout:
- We have done nothing throughout the day.
- Touching:
- He still starts his morning touching his parents’ feet.
- Your voice is touching my soul.
- Underneath:
- The money is hidden underneath the cushion.
- The transformer is fixed underneath the poles.
- Upon:
- The spaceship needs extra force to go upon the earth.
- An author has started writing a book upon his struggle.
- Until:
- You have to wait until I come.
- The match will be continued until one loses.
- Unlike:
- You have so many, unlike characteristics.
- He is working hard, unlike his younger brother.
- Versus:
- The match of David versus Jayul will start on time.
- You have to select Range Rover versus Land Rover.
- Via:
- This ship travels to South Africa via Cambodia.
- The International flight to Dubai ready to take off from Chennai, taking a route via Delhi.
- Within:
- Accessories also come within the box.
- We are taking off our jet within two minutes.
- Without:
- I wore this blazer without a waistcoat inside.
- Please do not leave without eating food.
- Worth
- I bought an Apple iPhone X worth USD 2565$ only.
- Your good behavior is worth it.
Complex Prepositions or Prepositional phrases:
A complex preposition is a combination of two words. It may be a combination of
- a preposition and a phrase, Prepositional Phrases:
- A preposition and a verb, Prepositions with verbs:
- preposition with an idiom, Prepositions with Idioms, respectively.
Examples
Here is a list of complex prepositions,
- According to:
- According to my father, I don’t know how to eat.
- Ahead of:
- She was seated ahead of my seat on the bus.
- Along with:
- Have some biscuits or snacks along with Tea.
- Apart from:
- He has parked his car apart from his house.
- As for:
- As for me, this one is outstanding.
- Aside from:
- We have another day aside from this evening.
- As per:
- The exam will start on time as per the rules.
- As well as:
- He read as well as writing at the same time.
- Away from:
- The thief ran away from the cops and escaped.
- Because of:
- We failed to enjoy it because of the poor weather.
- But for:
- Usually, I refused to work with him, but for you, I agreed.
- By means of:
- You can climb the mountain by means of ropes.
- Close to:
- Your vehicle stands very close to my car.
- Contrary to:
- Contrary to desires, he failed the competitive exam.
- Depending on:
- We will go for a picnic by bus, depending on the strength.
- Due to:
- Due to the rain, the match was delayed.
- Except for:
- All are present at the party except for Shong,
- Forward of:
- He is driving his vehicle just forward of our vehicle.
- Further to:
- Further to this topic, I have to talk with your guardian.
- In addition to:
- There are a total of twelve players in addition to me in the team.
- In the face of:
- He looks at me like a stranger in the face of a big question mark for him.
- In favor of:
- All members are in favor of this decision.
- In between:
- His bike is in between the two-sport cars.
- In front of:
- No one will stand in front of the door.
- In spite of:
- We chose these curtains in spite of those ones.
- Instead of:
- He went on the road by walking instead of a car.
- In view of:
- In view of the celebration, we have decided to stay here.
- Irrespective of:
- Don’t try to judge me irrespective of my behavior.
- Near to:
- There is a workshop near to my school.
- Next to:
- His roll number is next to my seat in the hall.
- On account of:
- We are going to announce a holiday on account of the boss’s wedding celebration.
- On behalf of:
- You are appointed here on behalf of your colleague.
- On top of:
- We are sitting on top of the building.
- Opposite to:
- Your friend is standing opposite to the music system.
- Other than:
- You can order anything other than Tequila.
- Out of:
- Pick one cloth out of these ones.
- Outside of:
- Throw the ball outside of the stadium.
- Owing to:
- We can afford one AC owing to the monthly income.
- Preparatory to:
- We made a presentation preparatory to the seminar.
- Prior to:
- He never dares to go to the basement prior to living in the hostel.
- Regardless of:
- I won’t help you, regardless of our relationship, even if you pay for help.
- Save for:
- This is money that I have saved for a long time.
- Thanks to:
- We are in good condition, thanks to our Manager for his kindness.
- Together with:
- He would like to have some water together with the whiskey.
- Up against:
- China is fighting back up against the powerful nation of America.
- Up to:
- I will work in this building for up to ten years.
- Up until:
- We played up until they lost the game.
- With regard to:
- We would like to speak about your father with regard to his bravery in the Army.
- With reference to:
- With reference to your mail, I’m sending you the details of our company.
A Preposition is a word placed before a noun or a pronoun to show the relationship between the person or the thing denoted by it and something else as:
Example:
-
We saw a dog on the road.
-
I am fond of chocolates.
-
The boy jumped off the table.
In the first example, the preposition word ‘on’ joins a noun to another noun.
In the second example, the preposition word ‘of’ joins a noun to an adjective.
In the third example, the preposition word ‘off’ joins a noun to a verb.
A preposition is used with its object, which is either a noun or a pronoun. In a sentence, a preposition can have more than one object. Prepositions alludes to direction, time, place, location, spatial relationships, or to introduce an object when placed before a noun or pronoun. In addition to «in,» «at,» «on,» and «of,» prepositions also include «at» and «to.»
There are a lot of idiomatic expressions in English prepositions. Most prepositions are used based on fixed expressions, though there are some rules for usage. Instead of memorizing a single preposition, your best bet is to memorize the phrase.
Prepositions are often thought of as the tools that bind sentences together. In order to achieve this, they convey place and movement, possession, time, and how an action is completed.
As a matter of fact, many of the most commonly used words in the English language are prepositions, including of, to, for, with, on, and at. Even though it may seem complex to explain prepositions, they are commonly used parts of language and we generally use them without even noticing.
Prepositions are regarded as a subset of English words that do not belong to any other group. It follows that, unlike verbs and nouns, this category does not develop new words over time. Their role as the functional backbone of the sentence is reflected here. Language relies on them for its meaning, even though they are subtle and unassuming.
Some Examples
Example: The children ran across the hill and the plain.
Note: The word, ‘preposition’ is placed before its object; but sometimes it is placed after its object.
Example:
-
Please give me the phone that I asked for.
-
What are you looking at?
-
That is the student (whom) I was speaking of.
In the first example, a preposition word is placed at the end when the object is the relative pronoun that.
In the second example, when its object is interrogative, then the preposition word is placed at the end of the sentence.
In the third example, the preposition word is placed at the end of the sentence because its object is a relative pronoun.
Note: Sometimes, when a preposition word needs to be emphasized, then the object is placed at the beginning of the sentence.
Example: Sachin Tendulkar is known all the world over.
That he insists on.
To learn the correct usage of prepositions in a sentence, you must do ample reading, listening, speaking and writing. However, there are certain rules, which are worth knowing.
Kinds of Preposition
i) Simple Preposition: The preposition words that are used along with its object is called simple preposition. Ex: at, by, for, in, of, off, on, out, through, till, to, up, with, etc.
Example:
-
I saw a man at the corner of the street.
-
My parents live in the countryside.
-
The train moved through the dark tunnel.
ii) Compound Preposition: These are usually formed by prefixing a preposition (a or be) to a noun, adjective or adverb. Ex: above, across, along, around, before, beyond, inside, within, without, etc.
Example:
-
The children were hiding behind the tree.
-
The dog went around the bush.
-
I reached the mall before my friend.
iii) Phrasal/ Group Preposition: Joining two or more words forms this preposition. Ex: according to, in addition to, away from, by means of, in order to, instead of, with regard to, etc.
Example:
-
I live 5kms away from my mother’s house.
-
According to the latest news, the elections will be postponed.
-
I watched the news instead of a movie.
iv) Participle Preposition: When present participles are used without any noun or pronoun attached to them, these are called participle prepositions. Ex: barring, concerning, passing, considering, during, pending, regarding, touching, etc.
Example:
-
Notwithstanding his ill health, he took the final examination.
-
Considering the quality, the price is not high.
-
Concerning his involvement in the incident, locals differ.
Classes of Preposition
To make a distinction, simple prepositions can be divided into three classes:
I. Prepositions of Time and Date: These include at, on, in by, to, till, until, during, for, since, from, within, before, after, afterwards, then, etc.
Example:
-
We have been living in this apartment for ten years.
-
Our relatives arrived in the morning.
-
Bring the file to the office by nine o’clock.
II. Prepositions of Place: These include at, in, on, to, behind, etc.
Example:
-
My parents live in Kolkata.
-
We are going to Shimla for a vacation.
-
The teacher is standing behind the desk.
III. Prepositions of Travel and Movement: These include from, to, by, on, into, at, out, out of, off, etc.
Example:
-
We are travelling by bus.
-
Give me the book from the shelf.
-
We are going from Bangalore to Delhi.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Solved Solutions
Q1. Apply for, since, at, in, on, by where required in the following sentences.
-
She drinks a lot of tea _______________ the evenings.
-
It is usually much warmer ___________________ two o’ clock in the afternoon than __________ the morning.
-
The new session starts ___________ June.
-
They have lived in this city __________ 2015.
-
I have been waiting for you ____________ 6 o’clock.
-
We will finish our exams ____________ two days’ time.
-
They have lived in Bangalore ___________ six months.
-
Hari went home ______________ sunset.
-
We have been waiting ___________ over an hour.
Solution:
-
She drinks a lot of tea in the evening.
-
It is usually much warmer by two o’clock in the afternoon than in the morning.
-
The new session starts in June.
-
They have lived in this city since 2015.
-
I have been waiting for you since 6 o’clock.
-
We will finish our exams in two days’ time.
-
They have lived in Bangalore for six months.
-
Hari went home at sunset.
-
We have been waiting for over an hour.
Q2. Correct the following sentences.
-
She met me in last evening.
-
Rita is not home.
-
We drove to home early this morning.
-
The man faced the danger by courage.
-
I reached at the mall a little late.
-
The shopkeeper deals with rice.
-
The river flows through the bridge.
-
The police will investigate into the matter.
-
We met with each other in Diwali evening.
Solution:
-
She met me last evening. (delete ‘in’ before last)
-
Rita is not at home. (place ‘at’ before home)
-
We drove home early this morning (delete ‘to’ before home)
-
The man faced the danger with courage. (replace ‘by’ with ‘with’)
-
I reached the mall a little late. (delete ‘at’ after reached)
-
The shopkeeper deals in rice. (deals in)
-
The river flows under the bridge. (under the bridge)
-
The police will investigate the matter (delete ‘into’)
-
We met with each other on Diwali evening. (replace ‘in’ with ‘on’)
Q3. Use the appropriate prepositions in the following sentences.
-
Does the headmaster live _______ the school campus? (on / in / at/ between)
-
The ground is wet. It must have rained ___________ the night. (during / at / for / through)
-
There is no cure _____________ cancer. ( of / with / for / about)
-
Students should concentrate _____________ studies (to / at / on / with)
-
The hotel is adjacent _________ the police station. ( into / to / at / by )
Solution:
-
Does the headmaster live on the school campus?
-
The ground is wet. It must have rained during the night.
-
There is no cure for cancer.
-
Students should concentrate on studies.
-
The hotel is adjacent to the police station.
Which Prepositions Can Be Recognized?
In general, prepositions are hard to recognize because their placement in sentences is not always consistent, nor do they follow a distinctive structure or spelling. Prepositions, however, have typically short words, with most of them containing fewer than six letters. Among the methods people use to identify prepositions, one is to see them as locations where a mouse could go. There are many different types of prepositions; this can be a helpful question to ask when identifying and recognizing them. They include: above, below, next to, between, beyond, through, by, with… The English language contains about 500,00-700,000 nouns, whereas there are over 100 prepositions! No one is likely to learn so many nouns, but probably is able to master prepositions once they identify them and master them.
The preposition of is used when we want to say that someone or something belongs to someone or something, directly refers to him. I don’t like the smell of this perfume. I don’t like the smell of this perfume. She was a friend of mine.
under — under.
- close to — close to, near;
- in — in, inside;
- in front of — in front, in front;
- next to — next to next;
- on — on;
- opposite — opposite;
- over — over;
- past — for, on the other side.
When are prepositions not used in English?
In English, prepositions are never put if there are:
— Tom could not remember what he was doing that day. My friend spent last Sunday in Vegas playing roulette. — My friend spent last Sunday in Vegas playing roulette. Next spring Maria is going to enter a sports school.
What are the articles in English?
In English, the two articles are indefinite (a / an) and definite (the). The article is a sign of a noun and is placed either directly before the noun, or before the adjective that defines it.
When are prepositions used in English?
Direction prepositions are used to indicate the direction of movement of a person or object. For example: «She left the house.» Here are the main prepositions of this group. Someone is moving from one side of something to the other.
Memorization tips:
- Learn prepositions in sentences or at least in phrases, i.e. …
- Start with the simplest prepositions: the most popular, with the fewest meanings. …
- Write out sentences where there is a preposition in Russian, but not in English, and vice versa.
When are prepositions not used?
When we don’t use prepositions of time
These include: all, any, each, every, last, next, one, some, this, that (that). Compare the following examples: She’ll come in the morning. — She will come in the morning.
How do prepositions work in English?
Prepositions in English are service words that show the relationship of a pronoun or noun to other words in a sentence. As in Russian, these relationships can be spatial (on the top — at the top), temporary (in time — in time), causal (because of you — because of you) and others.
Why isn’t to put before Home?
Before the word ‘home’ when referring to direction, the preposition to is not used: go home / come home / get back home / return home / visit home (not “to home”). The preposition into is used to mean «to get inside»: go into, get into. As soon as you get into the room, you’ll see a huge box on the floor.
Where should you put articles in English?
General rules for the use of articles in English
- The indefinite article a / an is used with singular countable nouns.
- The definite article the can be used with countable nouns (regardless of their number) and uncountable nouns.
How easy is it to understand articles in English?
An article is a «part» of a noun. If there is an article in a sentence, then there must be a noun or a word next to it that takes the meaning of a noun. But if the noun has a definition (adjective), then the article is placed before the adjective.
What is an article in simple terms?
In simple terms, the article is a kind of «label», a companion of a noun. He stands in front of him, and makes it clear that this is a noun, and not a verb or adverb. … Because there is no article in Russian, and therefore it is not translated into Russian in any way.
What preposition is used over time in English?
Prepositions of time in English: at, in, on, since, for, during, by, until, till and others ‹Inglex
What preposition is used with months in English?
So, we use the preposition ‘in’ before months, seasons, years, decades or periods of time. For example: I was born in September.
What kinds of prepositions are there?
So, prepositions do not change and are not members of the sentence, but they express different relationships:
- spatial — about, in, among, on, etc .;
- temporary — during, in continuation, etc.;
- causal — due to, due, due, in connection, due to, etc .;
- target — for, etc.;
- object — about and others;
What is preposition
A preposition is a word that indicates the relationship between a noun and the other words of a sentence. They explain relationships of sequence, space, and logic between the object of the sentence and the rest of the sentence. They help us understand order, time connections, and positions.
Example:
- I am going to Canada.
- Alex threw a stone into the pond.
- The present is inside the box.
- They have gone out of the town.
There are a few interesting linguistic facts about prepositions.
First, they are a closed class of words which means no new preposition gets added to the language. We use a fixed set of prepositions.
Second, prepositions do not have any other form. They cannot be plural, possessive, inflection, or anything else.
Third, most of the prepositions have many different contextual and natural uses. So, it is easy to be confused about it.
Fourth, sometimes a preposition works as nouns, adjectives, and adverbs.
Prepositions can be of one, two, three, or even more words. Prepositions with two or more words are called phrasal prepositions.
There are some commonly used phrasal prepositions:
because of, in case of, instead of, by way of, on behalf of, on account of, in care of, in spite of, on the side of, etc.
Types of Preposition
Most of the prepositions have many uses. There are some prepositions which are common in every type of preposition as they function in a versatile way.
- Simple Preposition
- Double Preposition
- Compound Preposition
- Participle Preposition
- Disguised Preposition
- Detached Preposition
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Place and Direction
- Prepositions of Agents or Things
- Phrasal Prepositions
Simple Preposition
These are among the most common type of prepositions. The prepositions used to express the relationship the Nouns and Pronouns of a sentence have with the rest of the words in it are called Simple Prepositions. They are often used to join two clauses in terms of Complex Sentence and Compound Sentence.
Examples:
| Most Popular Prepositions | |||||
| and | but | at | to | on | in |
| for | of | up | off | from | out |
| with | during | down | below | beside | over |
| by | near | behind | inside | among | along |
Double Preposition
Two Simple Prepositions joining together to form one which connects the Noun(s) or Pronoun(s) to the rest the words in a sentence.
Examples:
- Are you out of your mind?
- I was allowed the inside of the temple.
- She’s sandwiched in between two of her cousins.
Compound Preposition
Compound Prepositions are composed of prepositions as well as other words. Compound Prepositions are easily confused with Double Prepositions since they both require other prepositions or words to help with acting like a preposition.
Examples:
- According to my calculations, this color should work just fine.
- I started for home, with a view to celebrating Eid with my family.
- On behalf of our family, my father attended the family reunion.
Participle Preposition
Present Participles (-ing) and Past Participles (-ed and -en) that are used as Prepositions instead of Verbs, are called Participle Prepositions. These are participles as well as prepositions.
Examples:
| Present Participle Prepositions | Past Participles Prepositions |
| Assuming | Respected |
| Barring | Given |
| Considering | Gone |
| During | Barred |
| Notwithstanding | Provided |
| Regarding | Taken |
Participle Prepositions Used in Sentences:
- Barred from the entrance, he threw a fit.
- I was happy given the fact that I got great marks.
- Assuming the possibility of rain, she carried an umbrella.
Disguised Preposition
These prepositions are usually disguised as some other element in the English language. Often these prepositions are disguised as «a» and «o» in sentences.
Examples:
- I wake up at 5 o‘clock. (Of the clock)
- Keep striding ahead. (on the head)
- Pope went ashore. (onshore)
- Rimi visits the riverbank once a day. (in a day)
Detached Preposition
A preposition that has been detached and sent to the very end of the sentence is called Detached Preposition. These prepositions are detached from the interrogative or relative pronouns and adverbs but get detached for the sake of the integrity of sentences.
Examples:
- Where are you coming from?
- Is that the neighborhood you are headed to?
- I won’t tolerate being screamed at.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time show the relationship of time between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, from, to, for, since, ago, before, till/until, by, etc. are the most common preposition of time.
Example:
- He started working at 10 AM.
- The company called meeting on 25 October.
- There is a holiday in December.
- He has been ill since Monday.
Read More: Prepositions of Time Usage
Prepositions of Place and Direction
Prepositions of place show the relationship of place between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, by, from, to, towards, up, down, across, between, among, through, in front of, behind, above, over, under, below, etc. are the most common prepositions of place/direction.
Example:
- He is at home.
- He came from England.
- The police broke into the house.
- I live across the river.
Read More: Prepositions of Places & Direction Usage
Prepositions of Agents or Things
Prepositions of agents or things indicate a causal relationship between nouns and other parts of the sentence.
Of, for, by, with, about, etc. are the most used and common prepositions of agents or things.
Example:
- This article is about smartphones.
- Most of the guests have already left.
- I will always be here for you.
- He is playing with his brothers.
Phrasal Prepositions
A phrasal preposition is not a prepositional phrase, but they are a combination of two or more words that function as a preposition.
Along with, apart from, because of, by means of, according to, in front of, contrary to, in spite of, on account of, in reference to, in addition to, in regard to, instead of, on top of, out of, with regard to, etc. are the most common phrasal prepositions.
Example:
- They along with their children went to Atlanta.
- According to the new rules, you are not right.
- In spite of being a good player, he was not selected.
- I’m going out of the city.
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word or element in a sentence.
If there are two or more words (a preposition and a non-preposition word), it is a compound preposition.
They can consist of two-word combinations (instead of) or three-word (in addition to) combinations.
Here are some examples of compound prepositions:
- In front of
- According to (meaning: as stated by)
- Instead of (meaning: as an alternative)
- Ahead of (meaning: in front of or before)
- In view of (meaning: because of)
- As of (meaning: indicates the time/date when something starts)
- On top of
- On account of (meaning: because of)
- In lieu of (meaning: instead)
- In accordance with (meaning: something we are complying to)
- Because of
- Along with (meaning: together with)
- By means of (meaning: a particular method or process of)
- In addition to (meaning: when you want to say another item connected to what you are talking to)
- Rather than (meaning: a contrary choice or wish)
- Relating to
- As a result of
- Out of (meaning: from)
- In spite of (meaning: despite; without being affected by something)
- Next to
- Apart from (meaning: except for; when you are making an exception)
- On behalf of (meaning: used when speaking for someone)

Examples of Compound Prepositions in Sentences
- My house is in front of the supermarket.
- According to the weather report, it is going to rain tomorrow.
- Instead of going to the beach, we went shopping.
- The plane is ahead of schedule.
- She was sick, so her friend stood in place of her.
- The store is open as of today.
- She stacked the heavy boxes on top of each other.
- She bought a new dress in addition to the shoes.
- In spite of his parents’ protests, he went to the concert.
- I couldn’t go to school on account of the blizzard.
- The business gave their employees bonuses in lieu of holiday time.
- The project was completed in accordance with the guidelines.
- The show was cancelled because of the snowstorm.
- The date was postponed on account of the speaker’s illness.
- We went to the movies along with our friends.
- She paid the bills by means of snail mail.
- He bought the new video game in addition to the old ones.
- He enjoys meeting friends rather than staying home.
- My assignment is related to geometry.
- The examinations have been rescheduled as a result of the extreme weather conditions.
- He stood out of his friend’s way.
- In spite of the weather, they went out.
- In addition to studying hard, he played video games all night long.
- Instead of going to the movies, we stayed home and watched TV.
- I bought the book on account of it being cheap.
- The book is next to the table.
- Apart from the high prices, it was an enjoyable experience.
- On behalf of the students, I would like to say thank you for everything you’ve done.
Useful Links
- 45 Pronoun Examples in Sentences
- 55 Official Symbol Names in English
- 41 Flower Names in English with Pictures (Flower List)
- 3D Shape Names in English (Beginner Friendly)
- 103 Common Nouns List in English You Should Know (Alphabetized)
Other Common Questions
Some other useful things to know related to our topic on compound preposition examples.
Compound Preposition Vs Double Preposition
There is a small difference between compound and double prepositions.
A double preposition consists of two or more preposition words made into one word, for example, inside, upon, into and throughout.
A compound preposition consists of a simple preposition and a non-preposition word as discussed.
Compound Prepositions Test with Answers
- We went outside __________ the rain.
Ahead of
In spite of
In place of
2. I’ll have tea __________ coffee, please.
In lieu of
Apart from
Instead of
3. The car is parked __________ the station.
In front of
Along with
By means of
4. __________ going to the movies, we stayed home and watched TV.
Rather than
In spite of
As a result of
5. They teach the course __________ live weekly classes and continuous expert support.
According to
On account of
By means of
Answers:
- in spite of
- instead of
- in front of
- rather than
- by means of
Find this post helpful? Let me know in the comments section below if you learned something new and I will add more questions to the test!
I’m an Irish tutor and founder of TPR Teaching. I started teaching in 2016 and have since taught in the UK, Spain, and online.
I love learning new things about the English language and how to teach it better. I’m always trying to improve my knowledge, so I can better meet the needs of others!
I enjoy traveling, nature walks, and soaking up a new culture. Please share the posts if you find them helpful!