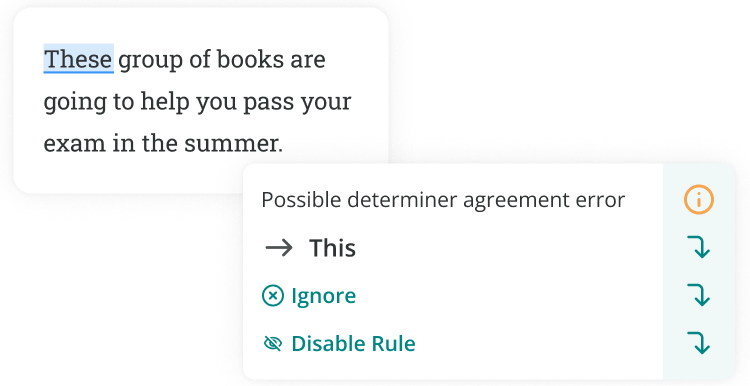
This and these are demonstratives, which means they indicate a specific noun in a sentence. They’re both important words in the English language.
Many people mix up this and these because they both refer to nouns that are near in space and time.
So what exactly is the difference between this vs these?
The short answer is that this is used with singular or uncountable nouns (e.g. this egg), while these refers to plural nouns (e.g. these cookies).
This article will explain the difference between this vs these and help you remember how to use these words correctly in your writing.
Quick Definition and Meaning of “This”
This refers to a singular noun that is near in time or space, such as a lamp or a desk.
If you say “I know this song,” for example, you’re most likely talking about the song that’s currently playing within earshot.
We also use this for uncountable nouns that we treat as singular, such as water, sugar, or happiness. For example, you might say “This water tastes funny” to talk about the water you’re currently drinking.
This is often used with words describing time, such as morning, week, and year. When used with these words, this can be used to talk about time in the present or in the near past or near present. For example, you could use the phrase “this afternoon” to refer to the afternoon of the present day.
It’s also important to remember that when the noun is omitted after this, it becomes a singular pronoun. If you say “I enjoyed eating this,” the word this refers to whatever singular dish you just ate.
Quick Definition and Meaning of “These”
These also refers to nouns that are near in time or space, but it is used for plural countable nouns. The noun that follows these must always be plural.
If you say “I don’t know any of these people,” you’re referring to more than one person, all of whom are near in time or space.
Just like this, these can be used as a plural pronoun if you omit the noun afterwards. If you say “Wow, I like these,” the word these most likely refers to whatever plural noun you’re referring to in the present moment.
What’s the Difference Between This and These?
The main difference between this and these is that this is used to refer to singular and uncountable nouns, while these is used to refer to plural countable nouns.
You would say “this necklace” to refer to a single necklace, and “these necklaces” to refer to multiple necklaces. It would be incorrect to say “these necklace” or “this necklaces.”
Let’s take a look at some more examples of how to use this and these in a sentence.
Examples of These in a Sentence
Here are some examples of these used to refer to a plural countable noun:
- Where did these papers come from?
- Let me hand you these boxes.
- These musicians are talented.
- These shoes are really beautiful.
Here are some examples of these used as demonstrative pronouns, with the noun omitted:
- These are organic.
- Let me give you these.
- What are these?
- I don’t want any of these.
One of the best ways to learn a word is to see examples from literature in the real world. Here are some examples of these from popular English books:
- “Some of these women have had so much work done their words come out all mushy because they can’t move their lips.”—Maggie Shipstead, Great Circle
- “The long route took us through all these old neighborhoods and shopping streets and finally past a tiny little temple in the middle of a bunch of ugly concrete office buildings.”—A Tale for the Time Being
- “But these days, inside my closet, poetry is as real to me as an ax. I need it more than food.”—Amity Gaige, Sea Wife
- “But the nostalgia didn’t hit. These weren’t my memories.”—Ottessa Moshfegh, My Year of Rest and Relaxation
- “Places like these were already suffocating. It did naught to add more weight upon the pillow pressed to their faces.”—Chloe Gong, These Violet Delights
- “These are the times that try men’s souls.”—Thomas Paine, The American Crisis
Examples of This in a Sentence
Here are some examples of this used to refer to a singular noun or uncountable noun:
- This cupcake is delicious. (singular noun)
- I told my parents that I want this necklace for Christmas. (singular noun)
- What is this music you’re listening to? (uncountable noun)
- Get a grip on all this anger. (uncountable noun)
Here are some examples of this used to talk about time:
- My friends called me this morning. (near past)
- What’s for dinner this evening? (near future)
- I had three cancellations this week. (present)
- This year has been difficult for my family. (present)
Here are some examples of this used as demonstrative pronouns, with the noun omitted:
- Don’t forget to turn this off when you leave.
- Can you please heat this on the stove over a low flame?
- This is delicious!
-
I like this.
Finally, here are some examples of this from popular English books:
-
“This morning I had poison for breakfast.”—Lemony Snicket, Poison for Breakfast
- “She stared at him as though he were another architectural marvel of this strange new world.”—Shelley Parker-Chan, She Who Became the Sun
- “Was I alive? I hoped so, but only because if this was the location of the afterlife, I’d be lodging an appeal immediately.”—Gail Honeyman, Eleanor Oliphant Is Completely Fine
- “The kids stared at me, awestruck. Why had their parents not explained this to them? Probably because they didn’t understand it themselves.”—Andy Weir, Project Hail Mary
- “This is my first experience of a heartfelt apology from Marcus, and so far it has involved six clichés, two butchered literary references and no eye contact.”—Beth O’Leary, The Road Trip
Conclusion on This vs These
There you have it—a complete guide to this vs these. Here’s a quick recap:
- Use this to refer to singular nouns that are near in time and space
- Use these to refer to plural nouns that are near in time and space
- Both this and these can be used as pronouns if you omit the noun afterwards
If you’re worried about mixing up this and these, you can always run your work through ProWritingAid, which will show you which one is correct. Our grammar checker will point out confused words and misspellings.
We hope this article helped you learn the difference between these two words!

Demonstrative pronouns in English
In order not to miss new useful materials, subscribe to site updates
Demonstrative pronouns in English (demonstrative pronouns / demonstratives) indicate a person, object, or their signs. There are several demonstrative pronouns in English.
Single number The many number
| this — this, this, this | these — these |
| that — that, that, that | those — those |
| such — such, similar | such — such like |
| the same — the same | the same — the same |
| it is | it is |
Now you know what demonstrative pronouns are in English. Next, we will consider the cases when each of them is used.
Demonstrative pronouns this and these
This is used with singular nouns, the pronoun these — with plural nouns. These pronouns should be used in the following cases:
- When we talk about people or things that are near us. Sometimes in sentences with this and these, the adverb here (here) is used, which also indicates the proximity of the subject to us.
- When a situation occurs in the present or future tense, we describe this situation using this / these.
- When we talk about the same thing several times and want to avoid repetition.
- When we introduce people or introduce ourselves in a telephone conversation.
This table is wooden. — This table wood. (the table is nearby, and we point to it)
These books belong to me. — These books belong to me. (several books are next to me)
this girl is here and she is waiting for you. — This girlhereand she is waiting for you.
We are going to meet this week… — We are going to meet at this week.
This month you are making a great progress. — V this month you are making tremendous progress.
I don’t want to discuss this but I have to. — I do not want it discuss, but I have to. (it is assumed that this event has already been called before, thus avoiding repetition)
Look at this! He seems to be looking for his money. — Look at it! He seems to be looking for his money. (the pronoun indicates the situation described in the second sentence)
This is the main goal in my life. — This is the main goal in my life.
Jim, These are my brothers, Tom and Carl. — Jim, it my brothers, Tom and Karl.
Hello! This is Kate speaking! Can I speak to Mary? — Hey. This is Kate. Can I talk to Mary?
Demonstrative pronouns that and those
The demonstrative that is used with singular nouns, the pronoun those with plural nouns. Let’s see when we can use the demonstrative pronouns that and those:
- When we talk about people or things that are far away from us. Sometimes the adverb there is used in sentences with the demonstrative pronouns that and those.
I don’t this piece of cake. Give me That one, please. — I don’t like this piece of cake. Give me that, please. (the piece of cake that the speaker liked is farther from him)
Source: https://engblog.ru/demonstrative-pronouns
Demonstratives this, that, these and those
| Singular | Plural | ||
| This — this, this, this | What color is this shirt? What color is this skirt? | These — these | Thesis buildings are new. |
| That is that, that, that | I don’t know That girl. I don’t know this girl. | Those — those | Who broght Those cakes? Who brings em cakes? |
- This and these only indicate close objects or moments in time.
Let’s sit on These chairs, they are the closest.
Let’s sit on these chairs, they are the closest to us.
I’m too tired this weekend.
I am very tired this week.
If the pronoun this is used with the words government, city, country, etc., it means the country, city, place to which the speaker belongs. When translated, instead of the obscure Russian pronoun «this», you can name a city or a country.
This country is very interesting. — The person is in the UK
Great Britain is very interesting.
- That and those indicate objects that are distant in time or distance.
They can also be translated into Russian as «this», since the pronoun «that» is used much less often than that or those in English.
Let’s sit on Those chairs next to the stage. — Let’s sit on those chairs next to the stage.
Don’t got ill on Saturday. That day was the most difficult for him. — Don got sick on Saturday. That (this) day was the most difficult for him.
These pronouns can be put together with nouns and serve as a definition:
He owns this car. — He owns this car.
Or replace nouns and be used separately:
This is what John was searching for. “This is what John was looking for.
Pronoun such
Demonstrative pronouns in English include such — such. Its form does not change depending on the number, but the singular requires the use of the indefinite article if the noun is countable.
It is Such a boring book. — It’s such a boring book.
I don’t Such boring books. — I don’t like such boring books.
Pronoun same
Source: https://lingua-airlines.ru/kb-article/ukazatelnye-mestoimeniya-v-anglijskom-yazyke/
LESSON 17 English
Abstract of the 17th lesson in PDF format can be viewed, printed and downloaded at this link
Do you know what is the most frequently used word in English? This is the article the! There is also an article a/an, and in some cases the article should not be used at all.
The topic of the correct arrangement of articles, despite its apparent simplicity, remains one of the «stumbling blocks» even for those who have been studying English for a long time.
In this lesson we will try to understand why this interesting part of speech is needed, in which cases it is necessary to use articles and how to do it correctly.
The meaning and use of articles
In English before everyone noun, as a rule, the article is put. Of course, there are cases when the article is not used (the so-called Article zero). But in general, the rule remains in force — this part of speech goes along with the noun «in conjunction». If a noun is used with adjective, the article is placed before the adjective, and all article placement rules remain in effect.
This topic seems difficult to us because in the Russian language there is no such part of speech as the article. However, we still have words that seem to play his role. Let’s look at how the definite and indefinite articles differ, and with what words they can be replaced in Russian.
Use of the indefinite article ‘a / an’
Article a/an in English comes from the word one — «one«. The analogue of this article in Russian will be the word “one”, But not in the meaning of quantity, but in the meaning of“ one of many ”. For example: “I knew one doctor «.
If the article is followed by a word that begins with a consonant, we put the article a, if with a vowel — use an… If a noun is used with an adjective, the rule applies to the adjective preceded by the article. For example: to book (book), an actress (actress), a nice girl, an interesting film (interesting film).
Pay attention! This rule is determined by phonetics (pronunciation), not spelling. For example, the word an hour [auə] («Hour») begins with a consonant, but with a vowel, so we put the article an. The words a university
Source: http://en1632.com/d/1635634/d/lesson32_17_synopsis.html
Demonstrative pronouns in English: what does it mean?
In today’s English, demonstrative pronouns are those pronouns that denote a person or object located near or at a distance, as well as their signs.
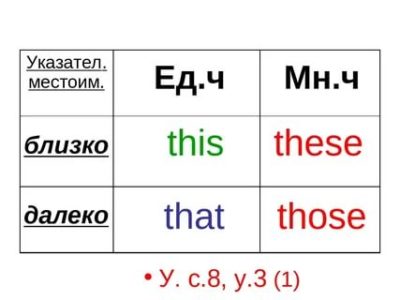
There are several demonstrative English pronouns: this — this, this, this; That — that, that, that; Such — such, similar; same — the same. In pl. number of pronouns such and the same does not change, but the form of the pronouns this and that in plural. number changes to these and those.
The demonstrative pronouns
In unit. number number of
| This (this, this, this) | These (these) |
| That (that, that, that) | Those |
Let’s look at the possible uses of all demonstrative pronouns, as well as determine what they have in common, and what are the differences between them.
This is a rhino.
Pronouns this — these
This — these are used when we mean persons or objects that are at close range from us.
In sentences with this (this, singular) or These (these, plural) can be used here —here, so that there is no doubt that a certain object or person is in the vicinity of the speaker.
Pronoun this in singular form. numbers are used when an action or situation is implied that occurs in a given period of time, or that will occur in the near future: this year (this year), this month (this month), etc.
The demonstrative pronoun this usually used when talking on the phone or meeting another person:
Usually this / these are used when discussing objects or places that are near us.
Those bears are very funny!
Pronouns that — those
That — those are used when they mean things or persons located at a distance from the interlocutor, therefore the adverb «there — there» is sometimes used together with that.
In the case when a situation from the past is implied.
During a telephone conversation, when we specify who we are talking to.
look! Those are monkeys.
Pronouns the same and such
Rules for using demonstrative pronouns same (the same) and Such (such) are identical.
It is enough just to remember that in the case of using such with nouns (countable) in singular. number, it is correct to use it with an indefinite article, and with uncountable nouns or plural nouns after such an article is not needed.
Anchoring test
1 is my friend.
- a) There
- b) This
- c) These
2 are fish.
Source: https://crownenglishclub.ru/dlya-nachinayushhih/ukazatelnye-mestoimeniya-v-anglijskom-yazyke-kakoj-chto-oznachaet.html
This, That, These, Those — demonstrative pronouns in English
The demonstrative pronouns in English, they do not name a person or an object, but indicate it. Usually, demonstrative pronouns include this, that and their plural forms these, those.
Demonstrative pronouns This — That and the difference between them
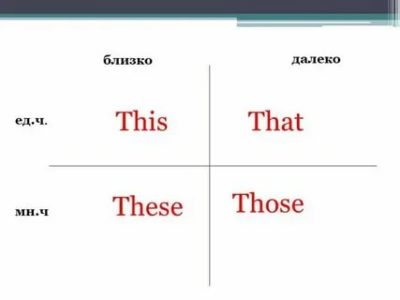
Pronoun this used to indicate an object or person in the vicinity, like “this” in Russian. Pronoun That indicates an object, a person in the distance, like “that” or “that” in Russian. This plural is these, that the plural is those:
Single number The many number
| Close | This | Thesis |
| Far | That | Those |
This and that refer to noun determinants, words that clarify the meanings of nouns.
examples:
I hold the book in my hands, looking at the pictures.
I this book. — I like this book.
I don’t These pictures. — I do not like these Pictures.
At the bookstore, I point to the books on the shelf:
I That book. — I like and book.
I don’t Those books. — I do not like those books.
Pronoun That It is far from always appropriate to translate into Russian as “that, that”. More often «this, this» is suitable. For example, I’m talking about a book that the other person mentioned in the conversation. There is no book nearby, it is only mentioned.
I That book. — I like this book.
This is That as pronouns-nouns
The pronouns this and that can act not as determinants of a noun, but in roles characteristic of the nouns themselves. For example:
As a subject:
This is what we wanted. — This is what we wanted.
That was a good show. — It was a good show.
As an add-on:
I don’t this. — I do not like this.
Can you see that? — You it see?
Demonstratives Such, Same
Demonstrative pronouns also include Such и same… Both pronouns do not have special plural forms.
1. Pronoun Such
The pronoun such means «such», «this type, kind». If such comes before a singular noun, the article “a an” is placed between them:
It was such a moment interesting movie. — It was such an interesting film.
beer? At such as time? — Beer? At this hour?
The pronoun such is often used in surprised exclamations — happy or not:
Such a wonderful place! — What a wonderful place!
Such a mess! — What a mess!
If such comes before a plural noun, the article is not needed:
I don’t know Such people. — I don’t know such people.
Why would she ask me Such questions? — Why would she ask me such questions?
2. Pronoun Same
The pronoun same means “the same”, “the same”. Since same identifies a specific noun, it is always preceded by the definite article the.
I have same jacket. — I have the same jacket.
they had same idea. — They had the same idea.
Source: https://langformula.ru/english-grammar/this-that/
Pronouns in English. Exercises for beginners
The «Pronouns» section is one of the most important sections of the grammar of any language and to start pronouns in English it is necessary already at the first level of study.
In this article, I publish exercises for beginners on the most important pronoun groups. References are given to theoretical material on the topic «Pronouns in English».
Pronoun exercises for beginners are arranged as the difficulty increases and contain only the most common vocabulary.
:
* * *
1. Personal pronouns. Exercises for beginners
Exercise 1. Select words from the list that can be replaced with “He”, “she”, “it”, “they”.
Children, a cat, animals, Mary, parents, Oleg, friends, a pen, books, a family, rain, a house, mice, February, summer, a river, Peter and Mike. a dog, windows, tuesday
* * *
Exercise 2. Replace the highlighted words with personal pronouns.
1. Nick is from Great Britain. 2. Iren is a student. 3. Bert and his brother live in London. four. Helen and me are good friends. 5. Are you and your sister twins? 6. The cat is drinking milk.
* * *
2. Demonstrative pronouns: this, these, that, those
Exercise 3. Build sentences by reference. Use the imperative of the verb cool and demonstrative pronouns this — this (this) and These -these.
Imperative verb stands in the first form (from a dictionary). look — look Look at — Look at
SAMPLE
- man / fat — Look at this man. He is fat. — Look at this man. He’s fat.
- hat / new — Look at these hats. They are new. — Look at these hats. They are new.
1.woman / thin2. sportsman / tall3. sportswoman / short4. children / noisy5. feet / clean6. hands / dirty7. dogs / spotty
8. cats / old
* * *
Exercise 4. Choose English Pronoun Equivalents this, these, that,Those.
1. What color are (those) pens? 2. (That) boy is my friend. 3. I want to read (that) book. 4. (Those) children are my friends. 5. What is (this)? 6. (This) table is round. 7. (These) cats are white.
8. (Those) flowers are roses.
* * *
Exercise 5. Make the sentences plural.
SAMPLE. This is a spider. — These are spiders.
1. This is a spider. 2. That is a snail. 3. This is a star. 4. This is a boy. 5. This is a baby. 6. That is a flower. 7. That is a shelf. 8. Is this a sofa? 9. Is this a bookcase? 10. Is this a man? 11. Is that a woman? 12. Is that a train? 13. Is that a plane? 14. Is the window open? 15. Is the door closed? 16. That is not a king. 17. That is not a queen. 18. That is not a bus. 19. This isn’t a mountain. 20. This isn’t a mouse.
* * *
Exercise 6. Translate sentences with turnover «It«Into English.
SAMPLE
- This is a child. — This is a child.
- These are kids. — These are children.
1. This is a hat. 2. It’s a car. 3. These are toys. 4. This is a pen.
5. These are pencils.
* * *
3. Personal and possessive pronouns
Exercise 7. Fill in the blanks with pronouns my, your, his, her, our, their.
REMEMBER: I would = I’d — I would like to
- I’d some ice in orange juice.
- We’d to have breakfast in.room.
- The children would to watch TV in. room.
- He’d some milk in .. cereal.
- She’d lemon in ..tea.
* * *
* * *
Exercise 8. Fill in the gaps with possessive pronouns.
Source: http://englishinn.ru/mestoimeniya-v-angliyskom-yazyike-uprazhneniya-dlya-nachinayushhih.html
The use of the pronoun both in English
Pronoun both in English can be used in different situations in different ways. Both translated as «both«,»both«, etc.
For example:
I want both books.
I want both books.
Both shirts are good.
Both shirts are good.
Following pronoun both possessive pronoun or definite article the often omitted.
For example:
You can take both shirts… (NOT both the shirts.) You can take both shirts.
He lost both parents when he was a child. (NOT both his parents)
He lost both parents when he was a child.
Both and both of
Before a noun with a determinative (for example: the, this, my, your, those, etc.), can be used as bothAnd both of… In American English, the more commonly used both of.
For example:
I want both of these books… = I want both these books.
I want both of these books.
Before the personal pronoun is used both of.
For example:
Both of them are good. They are both good. Both of us want to go. We both want to go.
If a pronoun is used as an object in a sentence, both can be used after it.
For example:
She has invited us both… She invited both of us.
She has sent you both her love.
She says hello to both of you.
Both and neither
In negative sentences instead of both is used neither.
For example:
Neither of them came. (NOT Both of them did not come.)
Both of them are not have come.
Place both in a sentence
When the pronoun both used to describe the subject in a sentence, it is used together with the predicate, and is placed after the auxiliary verb, but before the semantic verb. When there are two auxiliary verbs, both usually placed after the first one.
For example:
They are both good. They are both good.
We both want to go.
We both want to go.
We have both been invited.
We were both invited.
They have both gone home.
They both went home.
Note that in such cases, the same value can be passed using the construction both (of) + noun / pronoun.
For example:
Both of them are good. They are both good.
Both of us want to go.
We both want to go.
Both of us have been invited.
We were both invited.
Both of them have gone home.
They both went home.
Both and
Pay attention to the use both in this construction, which is a relational union. This construction translates as “both «,»and, and «.
For example:
She is both Beautiful and smart.
It as smart and beautiful.
She both sings and dances.
It и sings, и dancing.
Source: http://www.correctenglish.ru/mistakes/features/both/
Demonstrative pronouns. Demonstrative Pronouns
In English, there are four demonstrative pronouns (demonstrative pronouns): this (These), That (Those), Such и same.
Demonstrative pronouns indicate a person, an object or their signs and serve to distinguish them from other persons, objects, signs.
Demonstrative pronouns
| Singular | this [ðis] this, this, thisThat [ðæt] that, that, that (sometimes this, this, this) |
| Plural | These [ði: z] theseThose [ðəuz] those |
| Pronouns such and the same categories do not have numbers | Such [sʌtʃ] such, suchsame [seim] the same, the same |
Demonstratives this, these, that, those
1. Demonstrative pronouns this / these indicate items that are near with the speaker. And pronouns that / those indicate items that removed from the speaker.
Examples: Take this plum. It looks very ripe. — Take this plum. She looks very ripe. (This refers to a plum that the speaker sees directly in front of him or holds in his hand)
That house is very beautiful. — The one (this) the house is very beautiful. (We are talking about a house located at some distance from the speaker)
2. Before the noun to which the demonstrative pronoun belongs this, these, that, those, the article is not used.
Examples: I have read That book twice. — I’ve read that book twice.
Those houses are rather new. — Those the houses are quite new.
3. In expressions of time, demonstrative pronouns this / these refer to moment of speech or to current time period. A that / those to the past moment or the future.
Examples: Louie, I think this is the beginning of a beautiful friendship. — Louis, I think it the beginning of a wonderful friendship.
I remember that he woke up early That morning. — I remember that he woke up the early in the morning.
4. After pronouns this и That pronoun is often used one, in order not to repeat the previously mentioned noun twice.
Examples: Will you give me another cola? I don’t this one… — Give me another cola. I do not like this.
5. In the meaning of the demonstrative pronoun instead of That the pronoun is sometimes used it. It in this case translates as it.
Examples: What is That? — What it? (singular)
It is my cocktail dress. — This is my cocktail dress.
But!
What are These? — What is it? (plural)
They are my dresses. — These are my dresses.
6. Demonstrative pronouns That и this are often part of established expressions of the English language.
That’s right… — It’s right. Everything is correct. Exactly.
That’s a bit of all right… — Fine.
Not at all! That’s all right… “Please don’t be grateful.
this… — Thus.
before… — Thus.
To know better that that… — Be smarter.
Oh, hardly that… — No, not really. Not at all about that.
And all that… — Etc.
That’s why… — That’s why.
After that… — After that.
So that’s that… — That’s it.
Such and such things.
etc.
Demonstrative pronouns such and same
1. Demonstrative pronoun Such translated as such, such.
Examples: There are Such interesting people here! — There is such interesting people!
Why don’t all Chinese restaurants serve Such delicious food? — Why not all Chinese restaurants serve such a yummy?
2. Pronoun Such defines a noun. If it comes before a countable noun in the singular, then after Such the indefinite article is used.
Examples: It is such a moment honor to be nominated for this award. — It a honor to be nominated for this award.
3. Demonstrative pronoun same has the meaning the same, same… Front same the definite article is always used.
Examples: Don’t tell me same… — Do not tell me то же самое.
She bought same perfumes. — She bought the same perfume.
Source: http://englishstyle.net/grammar/pronoun/demonstrative-pronouns/
TOP 13 mistakes that prevent learning English grammar
: 14.11.2014
Is it easy for you to learn English grammar? In fact, every student periodically has some kind of learning difficulties. This is completely normal: you are improving your knowledge, which is why such moments arise. Today we will talk about what difficulties with grammar most often arise in the process of learning English and how to cope with them.
We advise you to watch the webinar of our methodologist Maria on the topic «Learning English from the mistakes of others.»
The main difficulties in learning English grammar and methods of getting rid of them
Do not be afraid of grammar: with our tips you will cope with all the difficulties. Russian students are often afraid of grammar in a foreign language. Let’s take a look at the most popular «hacks» and formulate some tips to help you cope with them.
1. Absence of the verb to be
Beginners often forget about the verb to be in an affirmative sentence. We are used to speaking Russian «I am free«,»She is at school now«And so on. Therefore, in English I just want to say»I free» instead of «I’m free«And»She at school now» instead of «She is at school now”. How to train yourself to use an auxiliary verb?
- Remember the main point: there is ALWAYS a verb in a sentence in English.
- Learn the most common uses of the verb to be, it is used:
- when you need to tell WHO you or another person (for example, by name or profession): “My name is Sam«;
- when you need to tell WHERE you or someone is: “He is at the hospital«;
- when you need to tell WHAT you or another person (quality): “You are beautiful«.
2. The absence of the auxiliary verb do / does
The next mistake is the absence of the auxiliary verb do / does in a negative or interrogative sentence in the present simple tense.
We are speaking «She does not go to school«, That’s why I just want to say»She didn’t go to school» instead of «She doesn’t go to school«.
And the sentence “Do you know Jim?«I want to translate»You know Jim?«, And the correct option is»Do you know Jim?”. How not to forget about the verb?
- Remember an easy rule: in general questions and negative sentences, there is ALWAYS an auxiliary verb (an exception if there is a modal verb in the sentence), even if it was not in the affirmative sentence.
- Another «foundation» of English grammar is word order: in the general question, the auxiliary (or modal) verb ALWAYS comes first, followed by the subject (subject) and only after that the predicate (action), for example: “Does she go to school?”(“She goes to school?») — in the first place is the auxiliary verb — does, then the subject — she (she), then the predicate — go (walks).
3. Wrong word order in an affirmative sentence
The great Russian language allows us to speak and “I love English«, And»I love English«, And»I love english«. And this most beloved English language does not spoil us with such a variety of options. Therefore, instead of “Love I English«We have to make do with the unoriginal and the only correct»I love english«.
- In this case, you need to forever remember the scheme for constructing a sentence in English: subject — predicate — the rest of the sentence. Therefore, if you are translating a sentence from Russian into English, first determine WHAT is the subject and WHAT is the predicate.
- Grammar and translation exercises are a great opportunity to hone your English sentence construction skills. Do these exercises as often as possible.
4. Lack of -s / -es
It is also often forgotten about -s / -es in verbs used after pronouns and nouns in the third person and the singular (he, she, it, Tom, car, park, cat, etc.) in the present simple tense (Present Simple ).
It’s not just those who recently started learning English grammar make this mistake: colloquially, we are so focused on WHAT to say that we sometimes forget HOW to say. Example: we say “I play chess» and «She plays chess».
We translate as “I play chess«, I just want to say similarly»She play chess«, Instead of the correct option»She plays chess”. How not to lose the ending?
- First, take your time to speak. As a rule, students remember very well to add the ending -s / -es, but they are in such a hurry to express their idea that they forget about it. You will still have time to acquire fluency, but grammatical errors need to be corrected as they appear.
- Secondly, we recommend installing the Polyglot application (iOS, Android) on your tablet or smartphone. It is free and does not require an Internet connection. Of course, you won’t be able to learn English in 16 hours, as the authors of the program of the same name promise. But you will hone your skills in using the Simple tenses and the ending -s / -es will be pronounced automatically.
5. Incorrect use of demonstrative pronouns
Another common mistake is the misuse of the demonstrative pronouns that (that, that, that), this (this, this, this), these (these), those (those). The only reason why we admit confusion is ignorance of these words and their rare use in speech.
- The advice will be simple and reliable: you just need to remember what this and these say about objects that are next to us, in close proximity to the speaker. And that and those we are talking about distant objects. This and that speak of things in the singular, and these and those in the plural.
- Practice on the surrounding objects, accustom yourself to say these words so that when talking with an English-speaking interlocutor, you no longer think about which pronoun to speak, but pronounce the right word automatically.
6. Absence of articles
They are not in Russian, so it seems that the cunning Englishmen invented them on purpose, so that we puzzled over when to say a dog, and when the dog. Even at levels like Pre-Intermediate or Intermediate, students forget about articles. They often explain this by the fact that “I don’t want to put it here”, “the instinct of the language did not suggest”.
Some people consider articles to be a trifle, an optional part of speech. This is a misconception: a native speaker will, of course, understand what you are talking about, but he will have to guess if there is a specific subject or something in common.
In addition, if you miss the article, some words (for example, hand or fly) from nouns can turn into verbs, which is completely unacceptable.
- To make it easier to learn the use of articles, you can memorize simple associations. The article a / an comes from the English numeral one, which is why it is placed only before a countable noun (one that can be counted) in the singular. Some philologists suggest associating it with the word any, that is, a / an means «any, any» subject. The article the evolved from the word that, so it means a specific object that is well known to the interlocutors.
- To check how well you have learned the rules, take the tests on the use of articles in English, presented in our blog.
For information on how to use articles correctly in English, see the video.
7. Incorrect use of words any / some, a few / little, many / much
It would seem that these pairs of words are similar. But if we want to ask “How much tea do you drink?«, offer «How many teas do you drink?«Will be incorrect, but it would be correct to say»How much tea do you drink?
Source: https://englex.ru/13-most-common-grammar-mistakes/
Demonstrative pronouns in English. Use of demonstrative pronouns in English
There are not so many demonstrative pronouns in the English language, but they play an important role, indicating the subject of conversation. Already in grade 3, students are taught to actively use these elements and understand the difference between them. Since demonstrative pronouns are very common in colloquial speech, you need to know the rules for their use.
Introduction to demonstrative pronouns
The task of this class of pronouns is to indicate an object, a person, or their signs. In Russian, the following pronouns correspond to them: this (this, this, these), that (that, that, those), such (such, such, such), the same.
Demonstrative pronoun table in English
These pronouns change in numbers, with the exception of such, the same… Let’s consider separately the use cases of these words.
Features this, that, these, those
These pronouns are used when the speaker’s goal is not only to indicate the object in question, but also to show how far the object is in relation to the interlocutor. The following table makes it clear when to use each of these pronouns.
So, if the narrator points to one close object, we use this, if there is an indication of many objects, then these are set. Pay attention to the following suggestions:
- This is my new T-shirt.
- These boots are very dirty.
In both versions, it is said about objects that are in the speaker’s field of vision.
Accordingly, we will talk about physically distant objects, using that for one object and those for several. For example:
- I would to buy that parrot (I would like to buy that parrot).
- We don’t know those guys (We don’t know those guys).
In addition, these pronouns can indicate the temporal proximity of events. In this case, this and these are used in relation to the present time, and that and those — to the past or future.
Those days were nice.
The use of demonstrative pronouns in relation to people is considered appropriate only for acquaintance. In other situations, this shows a dismissive attitude towards the person under discussion.
Demonstrative pronoun such
The role of this pronoun is to indicate the quality of the object or the object itself. It can be translated into Russian as «such» or «similar». Moreover, if after such there is an object in the singular, be sure to put an indefinite article! Naturally, it will not be in the plural.
- Such a silly outfit!
- I have never seen such amazing creatures.
Pronoun the same
As for the pronoun the same, which translates as «similar», «the same», it is always used with the definite article the. In this case, it does not matter in what number the subsequent part of the speech is. Here’s an example:
We with friends have the same interests.
Along with the pronoun this (this), you can use it, the difference will be only in logical stress — highlighting a certain word in intonation.
Take a look at the following examples:
- THIS is my classmate (This particular person, and not someone else, is my classmate).
- It is my CLASSMATE (This person is my classmate, not my brother or best friend).
When using several demonstrative pronouns in a choice situation, in order not to repeat the corresponding noun, the second time it is replaced by one or ones (for plural):
- He has chosen this coat, not that one.
Source: https://ik-ptz.ru/fizika/ukazatelnye-mestoimeniya-angl-upotreblenie-ukazatelnyh-mestoimenii-v.html
When it is written these and when those. Using this, that, these, and those: rules and examples. When the pronoun that is used
This, that, these, those are demonstrative or demonstrative pronouns in English. Typically, this, that, these, and those are used to refer to a specific object, creature, or phenomenon. When should you refer to these pronouns? What is the difference between them? Read more in the article.
Fundamental rules
So, the rule about this, that, these and those testifies: in English speech, these words can play the role of not only pronouns, but also determinatives. Consider the following table.
It’s also worth noting that these is the plural form of this and those are the plural form of that.
Thus, this and that should be used with singular nouns, and these and those should be used with plural nouns.
Using the pronouns this, that, these and those: rule
The first thing to remember is that we use this and that with uncountable nouns as well as singular nouns.
Try to repeat this exercise every morning and evening.What does this music make you think.I’ve never been to that part of France.Can I have some of that juice, please?
- Try to repeat this exercise every morning and evening.
- What does this music make you think about?
- I have never been to this part of France.
- Can I have some of this juice, please?
The English rule of thumb about this, that, these and those indicates that these and those should only be used with plural nouns:
You can use any one of these computers.
- You can use any of these computers.
- I need to paint those windows.
Interestingly, according to the rules of the English language, this, that, these and those are used in the context of time.
Demonstrative pronouns and tense
So, for example, we often use this with words describing the time and date (morning, afternoon, evening, week, month, year).
In this case, it is important to refer to the time in which the speaker speaks directly, or the time that comes. For example:
I’ll be with you some time this evening.Johan seemed very happy this afternoon.Ian is in Germany all this week.
- I’ll be with you tonight.
- Johan seemed very happy this afternoon.
- Jan is in Germany this week.
This, that, these, those is the rule of using further pronouns.
This, that, these, those — pronouns
We use the above words as pronouns, referring to things or phenomena:
Put the butter, chocolate and sugar in a saucepan. Heat this over a low flame until it melts.
Add butter, chocolate, and sugar to the saucepan. Heat it (this / container with the mixture) over low heat until the food is melted.
What color are those? Black or dark blue. I can’t see.
What color are they? Black or blue. I do not understand.
You can use this and that if you want to point to a person:
Linda, this is my mother, Anne. Is that your brother over there?
- Linda, this is my mother, Ann.
- Is that your brother over there?
Demonstrative pronouns are often used in telephone conversations.
Hello, is that Ken Orm? This is Jane Bromham here.
Hi, is this Ken Orme? This is Jane Bromham calling.
Use cases for this and these, that and those
In many ways, the selection of the correct pronoun is determined by the physical proximity of the object / person / phenomenon to the speaker. Those and these, this, that and the spelling rules are presented in the following examples:
Translation: Should I use this knife?
Source: https://my-kross.ru/porody/kogda-pishetsya-these-a-kogda-those-ispolzovanie-this-that-these-i-those/
Wiki User
∙ 11y ago
Best Answer
Copy
‘These’ is the plural form of ‘this’.
Wiki User
∙ 11y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: Is these singular or plural
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
It has less to do with the actual number, and more to do with how the number is said or written.
Singular nouns:
Any time the number is «one», or a fraction with «one» in the numerator, the result is singular. This also applies to negatives. See Is -1 followed by a singular or plural noun?
- One apple
- 1 apple («one apple»)
- Half an apple
- One half of an apple
- 1/2 apple («one half apple» or «half of an apple»)
- 1/4 apple («one quarter apple» or «one quarter of an apple» or «one fourth of an apple»)
- -1 volt («minus one volt», «negative one volt»)
Plural nouns:
Any decimal number, including 1.0, is plural. See Should we use plural or singular for a fraction of a mile?
- 1.0 apples («one point zero apples», «one point oh apples»)
- 0.5 apples («zero point five apples», «oh point five apples»)
Complicated cases:
Fractions with numerators larger than one can be handled both ways. This also applies to percentages. The plural form is used for countable objects, and the singular form is used for non-countable objects. See Is two-thirds plural?
- 2/3 of the people are here. (We are counting people.)
- 2/3 of the soda was left over. (We are not counting soda.)
- 75% of the computers are broken. (countable)
- 75% of the rice was eaten. (not countable)
Complex and imaginary numbers:
Complex and imaginary numbers only appear in technical contexts. I can only think of examples with units, for example:
- 5.7+3.1j kΩ at 500 Hz
- -1.0+0.9j mV at 10 kHz
Note that engineers usually use «j» instead of «i» to avoid confusion with I, the symbol for current. Mathematicians use «i».
In technical contexts, quantities for should be written with numerals and units should be written with abbreviations, which do not take plural. So «5 V» is okay, but «five volts» is only okay in non-technical contexts.
What is singular noun?
The singular nouns are words that only refer to one person or thing. They can be used as a subject, direct object, indirect object, predicate nominative, or appositive.
For example: “I went to the store.” This sentence is about the speaker and their experience at the store. It’s also possible for a singular noun to be an appositive such as in this sentence: “Tina was wearing her best dress.”
Here, Tina is being described by what she was wearing which is called an appositive.
What is plural noun?
Plural nouns are words that refer to more than one person, place or thing. They are often used in sentences where we want to talk about a group of people, animals, or things.
Let’s take the sentence “I am teaching a class this semester.” We can change it around and say “The students have been working hard all semester long.” In the first sentence, “class” is singular and in the second sentence, “students” is plural. That means you need to use a proper noun (singular or plural) according to the situation.
It may not seem like much of a difference at first but it will make your writing sound awkward if you don’t get it right! The best way is to learn the rules of plural nouns.
We’ll break down the rules so you’ll never get your plural nouns wrong again.
Rule-1
We add ‘-s’ to the end of regular nouns to make them plurals. For examples,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Chair | Chairs |
| Table | Tables |
| Pencil | Pencils |
| Book | Books |
| Cat | Cats |
Rule-2
In some cases, we add suffix “-es” to the nouns ending in “o”. See examples below.
Examples
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Tomato | Tomatoes |
| Potato | Potatoes |
| Mosquito | Mosquitoes |
| Echo | Echoes |
| Zero | Zeroes |
Rule-3
In some Latin or Greek words (foreign words) ending in “-o”, we add suffix ‘-s’. For example,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Avocado | Avocados |
| Photo | Photos |
| Video | Videos |
| Studio | Studios |
| Radio | Radios |
Rule-4
When singular noun ends in ‘-us’, we replace ‘-us’ with ‘-i’. Examples are,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Cactus | Cacti |
| Fungus | Fungi |
| Focus | Foci |
| Nucleus | Nuclei |
Rule-5
In singular noun ending on ‘-y’ (when the letter before -y is vowel), we add ‘-s’ to the end to make the noun plural, for example,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Boy | Boys |
| Alloy | Alloys |
| Day | Days |
| Ray | Rays |
| Guy | Guys |
Rule-6
In singular noun ending on ‘-y’ (when the letter before -y is consonant), we replace ‘-y’ with ‘-ies’ to make the noun plural, for example
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Lady | Ladies |
| City | Cities |
| Spy | Spies |
| Penny | Pennies |
| Army | Armies |
Rule-7
In some cases, the singular nouns ending in ‘-s’ or ‘-z’, the last letter is doubled plus we add ‘-es’ to the end. See the examples,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Gas | Gasses |
| Quiz | Quizzes |
| Fez | Fezzes |
Rule-8
In many cases, the singular noun ending in ‘-f’ or ‘-fe’, we replace the ‘-f’ or ‘-fe’ with ‘-ves’. For example,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Thief | Thieves |
| Wife | Wives |
| Loaf | Loaves |
| Half | Halves |
| Knife | Knives |
There are some exceptions where the rule does not apply, Examples are roof -> roofs, belief -> beliefs, cliff -> cliffs
Rule-9
In case the noun ends in ‘-on’, we replace ‘-on’ with ‘-a’ to make it plural, for example
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Criterion | Criteria |
| Phenomenon | Phenomena |
Rule-10
In case the singular noun is ending in ‘-is’, to make the noun plural, ‘-is’ is replaced with ‘-es’. For examples
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Oasis | Oases |
| Thesis | Theses |
| Basis | Bases |
| Crisis | Crises |
| Diagnosis | Diagnoses |
Rule-11
If the nouns ends in ‘-um’, last letters ‘-um’ are replaced with ‘-a’ in plural form. Examples are
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Datum | Data |
| Agendum | Agenda |
| Medium | Media |
| Bacterium | Bacteria |
| Memorandum | Memoranda |
Rule-12
In some case, the singular noun is ending in ‘-ex’ or ‘-ix’, the plural will end in ‘-ices’ Examples are given below:
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Matrix | Matrices |
| Index | Indices |
| Vertex | Vertices |
| Codex | Codices |
Rule-13
There are several singular nouns which do not follow any of the above rules while making them plural
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Foot | Feet |
| Child | Children |
| Mouse | Mice |
| Louse | Lice |
| Man | Men |
| Woman | Women |
| Goose | Geese |
| People | Person |
| Alumnus | Alumni |
| Genus | Genera |
Rule-14
Many nouns have the same singular and plural form. Fro example, plural nouns for sheep is ‘sheep’. See some more examples.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Fish | Fish |
| Tuna | Tuna |
| Salmon | Salmon |
| Deer | Deer |
| Gross | Gross |
| Ice | Ice |
| Species | Species |
Rule-15
Some nouns do not have plural forms. Examples are
- Love
- Hatred
- Lust
- Happiness
- Kindness
Types of Plurals
A lot of people don’t know about the types of plural nouns, but it’s important to understand that there are three types of plurals:-
- Regular Plurals
- Irregular Plurals
- Compound Words
The plural noun rule is one of those things that can trip you up when you’re writing sentences
Regular Plurals
Regular plurals end in s or es. For example, bag -> bags, toy -> toys, pen -> pens etc.
Irregular Plurals
Irregular plurals have a different spelling for their endings than they do for singulars. For example ox -> oxen, goose -> geese etc.
Compound Plurals
Compound words are made up of two words put together to make one word. For example, “bookcase” is a compound word with two parts – book and case. To form the plural form of this word, we would simply add an ‘s’ at the end (bookcases).
It’s easy to remember these rules if you think about them like this – just add an ‘es’ for regular plurals and an ‘s’ for irregular ones!
You can read here further: Regular and Irregular Nouns Rules with Examples
Singular Noun Example Sentences
- Fungus is vicious for human health.
- I need a knife to cut the apple.
- There is only one chair in the hall.
- Runabout is the most popular boat in the United States.
- Tom has been driving the same car for the last ten years.
- Do you think life is so easy?
- I love to eat continental food.
- Tina bought a new house in a colony near the forest.
- My room is spacious and well furnished.
- The chef baked a pie cake for the guests.
- Do you have a camera to record the action?
- The cat is sitting on the roof.
- I avoid junk food because it is unhealthy.
- They booked a table in the restaurant.
- The baby is crying with hunger.
- Do you still listen to radio programs?
- The rug was so dirty that I had to vacuum it.
- I can’t believe you left your clothes on the floor!
- You’re going to have to clean up after yourself if you want dinner tonight.
- In this game, players are given a singular noun and must use it in a sentence.
- It’s time to go home now, so I’ll see you later!
- The most common type of security system is a door alarm that will sound when someone opens your front door.
- I’m going to a party this weekend.
- Who is watching television?
- Our school was founded by a man named John Smith who wanted to create a safe space for children and teenagers who were bullied at their old schools.
Plural Nouns Example Sentences
The plural noun example sentences are often used when you want to refer to a group of people or things.
- Fungi are vicious for human health.
- There are fifty chairs in the hall.
- I avoid oily and high-calorie foods.
- Pakistan is the largest exporters of footballs all over the world.
- Jackson has a great collection of coins and stamps.
- All the friends agreed to spend a day in the jungle camp.
- There are many ways to whiten teeth naturally.
- A fleet of boats was sailing in the river.
- There are 195 countries in the world.
- Men and women are born with 12 pairs of ribs.
- She cut the pizza into equal halves.
- How many subjects have you completed in this syllabus?
- The costs of the new house are high.
- It’s important that you know what the words mean and when they can be used.
- The pencils are sharpened.
- The students have their assignments due tomorrow.
- I think both the computers need to be fixed.
- There is a lot of food for everyone to eat.
- We’ve been waiting on you guys forever!
- As a result of the recent increase in crime rates, many people are opting to buy home security systems.
- These alarms can be easily installed on existing doors with just a few screws and some wiring.
- You don’t need any special tools or equipment – all you’ll need is an electric drill and some patience.
- There are three cats in the yard.
- How many people work for your company?
- A group of students is waiting at the bus stop 30 minutes before school starts.
Worksheet for Singular and Plural Nouns
Following is a worksheet for singular and plural nouns. Answers are given at the end. Mention against each sentence whether highlighted/bold word is a singular or plural noun.
- This is my favorite pizza topping because they give me one every time I order one. (singular/plural)
- The sun is shining. (singular/plural)
- My mom’s favorite color is red. (singular/plural)
- A house has four walls, a roof, and a door. (singular/plural)
- Cars are typically rectangular in shape with sharp corners and flat surfaces. (singular/plural)
- A dog has fur on its back legs to keep it warm during winter months. (singular/plural)
- The cat is under the table. (singular/plural)
- My phone is on my desk. (singular/plural)
- The apple fell from the tree and landed in a pile of leaves. (singular/plural)
- I need to go back to my house because I left my wallet there. (singular/plural)
- That’s an interesting idea, but it won’t work for me. (singular/plural)
- I have two hands and five fingers. (singular/plural)
- You should come over to my place sometime, we’ll have fun together. (singular/plural)
- The books are on the desk. (singular/plural)
- Three dogs were playing outside. (singular/plural)

Answers
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Plural Noun
Read also
- Singular and Plural Nouns for Kids
- Types of Noun with Examples
- Regular and Irregular Nouns
- Material Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns