In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
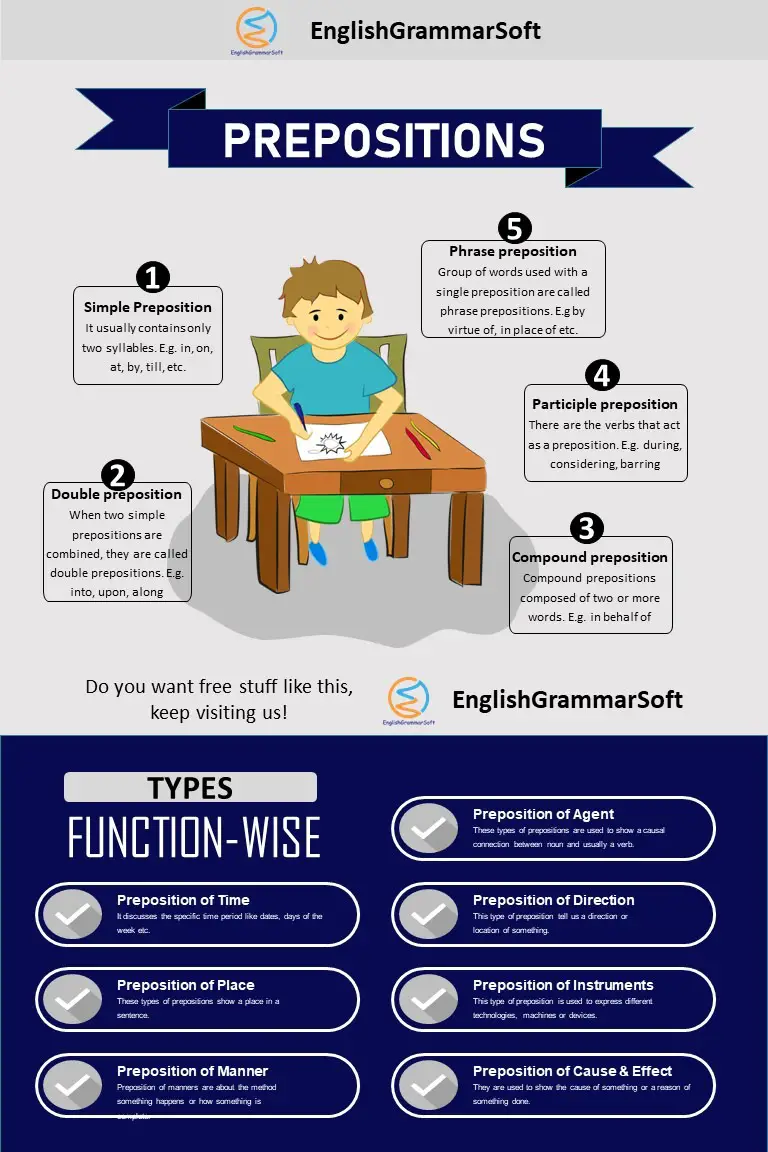
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions
This list of prepositions will help you understand what a preposition is. But let’s start by having you learn the preposition song. Singing this song is an easy way to help you memorize some of the prepositions. I’ll sing it for you in the video below. 
The Preposition Song
above, across, after, at, around, before, behind,
below, beside, between, by, down, during, for, from,
in, inside, onto, of, off, on, out, through,
to, under, up, with
And that’s the preposition song!
This list contains one-word, two-word, and three-word prepositions. Sometimes, words act together to form one preposition.
WARNING: Keep in mind that the words on this list have the potential to be prepositions. Many of these words can also function as adverbs and other fun things. How can you tell the difference? I’ll teach you all the secrets below this list. 
A aboard, about, above, according to, across, after, against, ahead of, along, amid, amidst, among, around, as, as far as, as of, aside from, at, athwart, atop
B barring, because of, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, between, beyond, but (when it means except), by, by means of
C circa, concerning
D despite, down, due to, during
E except, except for, excluding
F far from, following, for, from
I
in, in accordance with, in addition to, in case of, in front of, in
lieu of, in place of, in spite of, including, inside, instead of, into
L like
M minus
N near, next to, notwithstanding
O of, off, on, on account of, on behalf of, on top of, onto, opposite, out, out of, outside, over
P past, plus, prior to
R regarding, regardless of
S save, since
T than, through, throughout, till, to, toward, towards
U under, underneath, unlike, until, up, upon
V versus, via
W with, with regard to, within, without
Would you like to download these word lists?

- Word Lists for the 8 Parts of Speech (Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, & Interjections)
- 17 Pages
- Printable
- 100% Money-Back Guarantee
- Only $2.99
If you’d like to see even more prepositions, check out Wikipedia’s list of English prepositions page.
The Mean Thing About This List
(The Secret About Prepositions)
Many times, words on this list of prepositions don’t act as prepositions.
That’s not very nice, is it? You probably feel a bit like you were tricked. I’m sorry about that. I would change the rules of language if I could so that it would be easier for you to figure all of this out.
Of course, I can’t do that, but I can help you use that powerful brain of yours to tell when a word is a preposition and when it’s not a preposition. Are you ready? Good.
Here is the one thing that you need to remember: prepositions are ALWAYS in prepositional phrases.
Look at these examples of prepositional phrases with the eye of a detective. What do you notice about them?
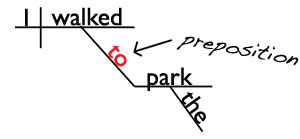
I walked to the park.
The cat climbed up the tree.
They biked around the block.
All three of those prepositional phrases begin with a preposition (to, up, around) and end with a noun (park, tree, block), and that sums up what a prepositional phrase is.
Prepositional phrases begin with a preposition (to, up, around) and end with a noun or pronoun called the object of the preposition (park, tree, block).
But why? Why do prepositions need to be in prepositional phrases?
The answer comes to us when we look at the definition of a preposition.
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun/pronoun and some other word in the sentence.
In order for a preposition to do its job (to show the relationship between a noun/pronoun and another word in a sentence), it needs to be followed by that noun or pronoun.
I sense that you may be furrowing your brow in a state of confusion right now, so it’s the perfect time for us to look at some sentence diagrams, which will make all of this visual.
Sentence diagrams are pictures of sentences that show us how the words are grammatically related.
In the diagram, the preposition to, which is on a slanted line, is connecting the noun park with the verb walked. It almost looks like a little bridge, doesn’t it? You can think of a preposition as a noun bridge if that helps.
to the park = prepositional phrase
to = preposition
park = noun (object of the preposition)
Prepositional phrases are always diagrammed like that. The preposition goes on a slanted line between the object of the preposition (the noun or pronoun at the end of a prepositional phrase) and a word in the rest of the sentence.
Why? Because the preposition is telling us how that special noun called the object of the preposition relates to the rest of the sentence. It acts as a little noun bridge.
Psst! You can learn more about how to diagram prepositions and prepositional phrases here if you’d like.
Preposition or Adverb?
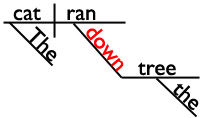
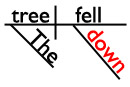
Did you know that words on the preposition list are often used as adverbs rather than prepositions? It’s true! I’m going to use that fact to see if you’ve been paying attention. Are you ready for a tiny quiz? Great! In which sentence is down a preposition?
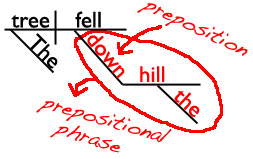
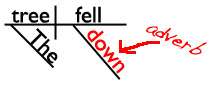
A. The cat ran down the tree.
B. The tree fell down.
I’ll give you a hint and show you the sentence diagrams of those sentences. (In which diagram is down a bridge between a noun and the rest of the sentence? That’s the diagram with the preposition!)
The cat ran down the tree.
The tree fell down.
Are you ready for the answer?
In sentence A, down is a preposition. It’s in the prepositional phrase down the tree.
In sentence B, the word down isn’t in a phrase, so it’s not a preposition. (In this sentence, down is an adverb telling us where the tree fell.)
The cat ran down the tree.
The tree fell down.
If you wanted to, you could change sentence B so that down was a preposition instead of an adverb. Can you think of how you would do that?
HINT: Add at least a noun (and probably an adjective as well) after down so that you create a prepositional phrase.
The tree fell down. (adverb)
The tree fell down the hill. (preposition)
Here are two other examples of words from this list functioning as adverbs and as prepositions. I’ll bet that you can see the difference now, right?
My sister just walked past. (adverb)
My sister just walked past us. (preposition)
Carefully crawl inside. (adverb)
Carefully crawl inside the tent. (preposition)
The moral of the story is that in order for a word to be a preposition, it must be in a prepositional phrase.
Preposition or Phrasal Verb?
As you saw above, words on this list of prepositions are only potential prepositions. We need to look at how each word-in-question is functioning within a sentence in order to say what part of speech it actually is.
I’m sure you remember that the words on this list are only prepositions when they are in prepositional phrases.
In our last example above (The tree fell down.), you saw how words from the list of prepositions could also function as adverbs.
Another common function of words on this list is for them to be a part of something called phrasal verbs. (I’ll underline the phrasal verbs below.) Notice that the words out, up, and off are not prepositions in these sentences.
I work out every Saturday.
He dressed up for the concert.
I was so tired that I nodded off during the class.
Phrasal verbs are two-word or three-word phrases that function as the verb in the sentence. They are made up of a verb (word, dressed, nodded) and a word from the preposition list (out, up, off), and they form a meaning that’s different from the meaning that the words have all by themselves.
When words like out, up, and off are in phrasal verbs, they have a special name. They’re called particles.
Let’s look at a sentence diagram with a phrasal verb. That way, you can see that particles (words from the preposition list that are functioning in phrasal verbs) are not prepositions.
We were tired, and we turned in early.
Look at the sentence diagram and notice that the word in isn’t on a little noun bridge. If in were a preposition, it would be diagrammed on a noun bridge like the word to in the diagram below.
Preposition or Conjunction?
I have a feeling that you already know where I’m going with this. 
A. I’m looking for bananas. (preposition)
B. He felt energized, for he had just won the competition. (conjunction)
In sentence A, for is in the prepositional phrase for bananas.
In sentence B, for is connecting the two clauses he felt energized and he had just won the competition.
Summary
Sometimes it helps to have a summary of everything you’ve learned. For your learning pleasure, here are the main points we covered on this page.
- Singing some of the prepositions to the tune of «Yankee Doodle» can help you memorize a handful of words from the preposition list.
- Words on the preposition list are not always used as prepositions.
- They are only prepositions when they are in prepositional phrases (preposition + noun).
- Words from the preposition list often act as adverbs. They can also be in phrasal verbs or function as conjunctions. In these cases, they are not prepositions.
Would you like to download these word lists?

- Word Lists for the 8 Parts of Speech (Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, & Interjections)
- 17 Pages
- Printable
- 100% Money-Back Guarantee
- Only $2.99
This is original content from https://www.english-grammar-revolution.com/list-of-prepositions.html
What is a preposition?
A preposition is a word used to link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They act to connect the people, objects, time and locations of a sentence. Prepositions are usually short words, and they are normally placed directly in front of nouns. In some cases, you’ll find prepositions in front of gerund verbs.
A nice way to think about prepositions is as the words that help glue a sentence together. They do this by expressing position and movement, possession, time and how an action is completed.
Indeed, several of the most frequently used words in all of English, such as of, to, for, with, on and at, are prepositions. Explaining prepositions can seem complicated, but they are a common part of language and most of us use them naturally without even thinking about it.
In fact, it’s interesting to note that prepositions are regarded as a ‘closed class’ of words in the English language. This means, unlike verbs and nouns, no new words are added to this group over time. In a way, it reflects their role as the functional workhorse of the sentence. They are unassuming and subtle, yet vitally important to the meaning of language.
There are two very important rules to remember when using prepositions. Because they are somewhat vague, learning about prepositions and using them correctly in sentences takes practice. Because 1:1 translation is often impossible when dealing with prepositions, even the most advanced English students have some difficulty at first.
- The first rule is that to make sentences clear, specific prepositions are needed. For example, the preposition in means one thing and the preposition on cannot substitute for it in all cases. Some prepositions are interchangeable but not always. The correct preposition means one particular thing and using a different proposition will give the sentence a very different meaning. I want to see you in the house now, Bill! means something very different from I want to see you on the house now, Bill! In the house means Bill should go through the door, walk inside, and stand in the hall or living room. On the house means Bill would need to get a ladder and climb to the roof where he would be on top of the house.
- The second rule for using prepositions is that prepositions are generally followed by nouns or pronouns. There was a time in the past when teachers held strictly to this rule, but it made for some clunky sentences. I am seeking someone I can depend on ends with the preposition on, so people who insisted that sentences shouldn’t end with a preposition would be forced to use convoluted and unnatural phrasing. To avoid ending that sentence above with a preposition, you’d have to say, someone I can depend on is whom I am seeking.
- There are more than 100 prepositions in the English language. In addition, there are endless possibilities for creating prepositional phrases, phrases that begin with a preposition and end with a noun or pronoun. In the following sections, you will find examples of prepositions, types of prepositions, a comprehensive list of prepositions, and some helpful preposition exercises. As you read the examples and study the list, remember that prepositions usually convey concepts such as comparison, direction, place, purpose, source possession, and time.
In the following sentences, examples of prepositions have been italicized. As you read, consider how using different prepositions or even different types of prepositions in place of the examples might change the relationship between the rest of the words in the sentence.
- I prefer to read in the library.
- He climbed up the ladder to get onto the roof.
- Please sign your name on the dotted line after you read the contract.
- Go down the stairs and through the door.
- He swam across the pool.
- Take your brother with you.
Types of Prepositions
There are three types of prepositions, including time prepositions, place prepositions, and direction prepositions.
Time prepositions are those such as before, after, during, and until; place prepositions are those indicating position, such as around, between, and against; and direction prepositions are those indicative of direction, such as across, up, and down. Each type of preposition is important.
Type of Prepositions
Prepositions of Time
Basic examples of time prepositions include: at, on, in, before and after. They are used to help indicate when something happened, happens or will happen. It can get a little confusing though, as many different prepositions can be used.
Prepositions of time examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
For example:
- I was born on July 4th, 1982.
- I was born in 1982.
- I was born at exactly 2am.
- I was born two minutes before my twin brother.
- I was born after the Great War ended.
The above makes it seem quite difficult, with five different prepositions used to indicate when something happened. However, there is a set of guidelines that can help decide which preposition to use:
For years, months, seasons, centuries and times of day, use the preposition in:
- I first met John in 1987.
- It’s always cold in January
- Easter falls in spring each year.
- The Second World War occurred in the 20th century.
- We eat breakfast in the morning.
For days, dates and specific holiday days, use the preposition on.
- We go to school on Mondays, but not on Sunday
- Christmas is on December 25th.
- Buy me a present on my birthday.
For times, indicators of exception and festivals, use the preposition at:
- Families often argue at Christmas time.
- I work faster at night.
- Her shift finished at 7pm.
Before and after should be much easier to understand than the other examples of prepositions of time. Both are used to explain when something happened, happens or will happen, but specifically in relation to another thing.
- Before I discovered this bar, I used to go straight home after work.
- We will not leave before 3pm.
- David comes before Bryan in the line, but after Louise.
Other prepositions of time could include: During, about, around, until and throughout.
- The concert will be staged throughout the month of May.
- I learned how to ski during the holidays.
- He usually arrives around 3pm.
- It was about six in the morning when we made it to bed.
- The store is open until midnight.
Prepositions of Place
To confuse matters a bit, the most common prepositions to indicate time – on, at, in – are also the most common prepositions to indicate position. However, the rules are a little clearer as place prepositions are a more rigid concept than time prepositions.
Prepositions of place examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- The cat is on the table.
- The dogs are in the kennel.
- We can meet at the crossroads.
The guidelines can be broken down as follows:
On is used when referring to something with a surface:
- The sculpture hangs on the wall.
- The images are on the page.
- The specials are on the menu, which is on the table.
In is used when referring to something that is inside or within confined boundaries. This could be anything, even a country:
- Jim is in France, visiting his aunt in the hospital.
- The whiskey is in the jar in the fridge.
- The girls play in the garden.
At is used when referring to something at a specific point:
- The boys are at the entrance at the movie theater.
- He stood at the bus stop at the corner of Water and High streets.
- We will meet at the airport.
Lot’s of other prepositions of place, such as under, over, inside, outside, above and below are used in English. There is, however, a lot less confusion as they refer to rigid positions rather than abstract ones.
- The cat is under the table.
- Put the sandwich over there.
- The key is locked inside the car.
- They stepped outside the house.
- Major is ranked above corporal.
- He is waving at you from below the stairs.
Prepositions of Movement
Prepositions of movement are quite easy to understand as they are less abstract than prepositions of place and time. Essentially, they describe how something or someone moves from one place to another. The most commonly used preposition of movement is to, which usually serves to highlight that there is movement towards a specific destination.
Prepositions of movement examples in the following sentences are in bold for easy identification.
- He has gone on vacation to France.
- She went to the bowling alley every Friday last summer.
- I will go to bed when I am tired.
- They will go to the zoo if they finish their errands.
Other more specific prepositions of movement include: through, across, off, down and into. These prepositions can sometimes get mixed up with others. While they are similar, they have individual meanings that add context to the movement.
Across refers to moving from one side to another.
- Mike travelled across America on his motorcycle.
- Rebecca and Judi are swimming across the lake.
Through refers to moving directly inside something and out the other end.
- The bullet Ben shot went through the window.
- The train passes through the tunnel.
Into refers to entering or looking inside something.
- James went into the room.
- They stare into the darkness.
Up, over, down, past and around indicate directions of movement:
- Jack went up the hill.
- Jill came tumbling down after.
- We will travel over rough terrain on our way to Grandma’s house.
- The horse runs around the track all morning.
- A car zoomed past a truck on the highway
How to Recognize a Preposition?
Recognizing prepositions can be challenging as they do not always follow a consistent pattern in terms of their position in a sentence, nor do they have a discernible structure or spelling. We do know, however, that prepositions are almost always short words, with the majority having less than six letters. One technique people use to identify a preposition is to think of a preposition as anywhere a mouse can go. Above, below, next to, between, beyond, through, by, with…It won’t cover them all, but it can be a useful question to ask when trying to identify and recognize a preposition. While there are over 100 prepositions, there are around 500,00-700,000 nouns in English! It is unlikely anyone will learn so many nouns, but recognizing and then mastering prepositions might be a worthwhile and attainable goal.
Prepositions with Nouns
There are lots of different nouns that carry specific prepositions to consolidate their meaning. These are called dependent prepositions. Again, there isn’t a set rule that says a particular type of noun will take a dependent preposition, although they normally follow the noun. Moreover, there are many possible combinations. Essentially, it’s case of familiarizing yourself with the different possibilities of nouns and dependent prepositions. Examples:
- He displayed cruelty towards his dog.
- She had knowledge of physics.
- The trouble with Jack.
- 21 is the age at which you are allowed to drink.
- Bolt made another attempt at the world record.
- The police held an inquiry into the murder.
Prepositions with Verbs
Prepositional verbs – the phrasal combinations of verbs and prepositions – are important parts of speech. The prepositions again act as links between the verb and noun or gerund, giving extra meaning to the sentence. The prepositions most commonly used with verbs are: to, for, about, of, in, at and from. The good news is that these will always come after the verb in the sentence. However, it should also be noted that the prepositional verbs can have slightly different meaning compared to the original verb. For example, to relate a story simply means to tell a story, to relate to a story means you identify with it, find some personally meaning in that story.
Verb + to:
- He admitted to the charge.
- I go to Vancouver on vacation twice a year.
- William can relate to the character in the play.
Verb + for:
- He must apologize for his actions.
- We searched for ages before we found the perfect apartment.
- I provide for my family by working two jobs.
Verb + with:
- I don’t agree with your claim.
- The lawyer said he will meet with your representatives.
- They began with a quick warm-up.
Verb + of:
- I dream of a better life.
- Have you heard of Shakespeare?
- The bread consists of dough, raisins and a little honey.
Verb + in:
- Does Rick believe in miracles?
- Fallon lives in New York.
- The bus accident resulted in my being late to work.
Verb + at
- We arrived at our destination.
- Ilene excels at singing.
- Will the baby smile at her mother?
Verb + on:
- We should really concentrate on our studies now.
- Helen insisted on Brenda’s company.
- Morris experimented on some canvas.
Verb + from:
- Since turning 80, she suffers from lapses in concentration.
- Dad retired from the navy in the 1970s.
- Billy Bob, please refrain from doing that.
Prepositions with Adjectives
Prepositions can form phrases with adjectives to give further context to the action, emotion or thing the adjective is describing. Like verbs and nouns, adjectives can be followed by: to, about, In, for, with, at and by.
- I am happily married to David.
- Ellie is crazy about this movie.
- Michelle is interested in politics.
- We are sorry for your loss.
- Jane will be delighted with her results.
- Is he still angry at the world?
- The entire room was astonished by the election results.
There can sometimes be a pattern in deciding which prepositions go with adjectives, for example, when adjectives have the same or very similar meaning to each other, they might take the same preposition:
- Frightened of, afraid of, scared of, terrified of
Indeed, when adjectives have opposite meaning they might also take the same preposition:
- Good at, great at, superb at, wonderful at
- Bad at, terrible at, woeful at, inept at
There are always many exceptions to the above, but it can help that there seems to be some
consistency when adjectives have the same meaning or opposite meaning.
Nevertheless, perhaps a more general rule is that English speakers simply need to learn which prepositions go with which adjectives, as meaning can change significantly by using a different preposition.
- I am good at sports means I have some athletic talent.
- The nurse was good to my mother means she took care of her and was nice, kind, and helpful.
- I am good with animals means I get along with them and handle them well.
- Swimming is good for your health.
- That was good of you to come means you were begin nice and good to visit.
- My little brother is good inside (his body) means even though you can’t see how he thinks and feels, he is good. Even if his behavior is bad.
- The blueberry jam will be good on toast.
Prepositions Exercises
The following exercises will help you gain greater understanding about how prepositions work. Choose the best answer to complete each sentence.
1. The bone was _______ the dog.
a. About
b. For
c. After
d. Considering
Answer: b. The bone was for the dog.
2. We are going on vacation _______ August.
a. On
b. At
c. In
d. Since
Answer: c. We are going on vacation in August.
3. Please put the vase ________ the table.
a. In
b. On
c. For
d. Over
Answer: b. Please put the vase on the table.
4. I received a present ________ Janet.
a. From
b. Of
c. By
d. About
Answer: a. I received a present from Janet.
5. School begins ________ Monday.
a. In
b. On
c. From
d. Since
Answer: b. School begins on Monday.
List of Prepositions
While there are only about 150 prepositions in the English language, these words are among the most important. Without them, the sentences we speak, read, and write would be difficult to understand. The following list of prepositions is not a complete one, however it is among the most comprehensive lists of prepositions available anywhere.
Aboard
About
Above
Absent
Across
After
Against
Along
Alongside
Amid
Among
Amongst
Anti
Around
As
At
Before
Behind
Below
Beneath
Beside
Besides
Between
Beyond
But
By
Circa
Concerning
Considering
Despite
Down
During
Except
Excepting
Excluding
Failing
Following
For
From
Given
In
Inside
Into
Like
Minus
Near
Of
Off
On
Onto
Opposite
Outside
Over
Past
Per
Plus
Regarding
Round
Save
Since
Than
Through
To
Toward
Towards
Under
Underneath
Unlike
Until
Up
Upon
Versus
Via
With
Within
Without
Worth
What is preposition
A preposition is a word that indicates the relationship between a noun and the other words of a sentence. They explain relationships of sequence, space, and logic between the object of the sentence and the rest of the sentence. They help us understand order, time connections, and positions.
Example:
- I am going to Canada.
- Alex threw a stone into the pond.
- The present is inside the box.
- They have gone out of the town.
There are a few interesting linguistic facts about prepositions.
First, they are a closed class of words which means no new preposition gets added to the language. We use a fixed set of prepositions.
Second, prepositions do not have any other form. They cannot be plural, possessive, inflection, or anything else.
Third, most of the prepositions have many different contextual and natural uses. So, it is easy to be confused about it.
Fourth, sometimes a preposition works as nouns, adjectives, and adverbs.
Prepositions can be of one, two, three, or even more words. Prepositions with two or more words are called phrasal prepositions.
There are some commonly used phrasal prepositions:
because of, in case of, instead of, by way of, on behalf of, on account of, in care of, in spite of, on the side of, etc.
Types of Preposition
Most of the prepositions have many uses. There are some prepositions which are common in every type of preposition as they function in a versatile way.
- Simple Preposition
- Double Preposition
- Compound Preposition
- Participle Preposition
- Disguised Preposition
- Detached Preposition
- Prepositions of Time
- Prepositions of Place and Direction
- Prepositions of Agents or Things
- Phrasal Prepositions
Simple Preposition
These are among the most common type of prepositions. The prepositions used to express the relationship the Nouns and Pronouns of a sentence have with the rest of the words in it are called Simple Prepositions. They are often used to join two clauses in terms of Complex Sentence and Compound Sentence.
Examples:
| Most Popular Prepositions | |||||
| and | but | at | to | on | in |
| for | of | up | off | from | out |
| with | during | down | below | beside | over |
| by | near | behind | inside | among | along |
Double Preposition
Two Simple Prepositions joining together to form one which connects the Noun(s) or Pronoun(s) to the rest the words in a sentence.
Examples:
- Are you out of your mind?
- I was allowed the inside of the temple.
- She’s sandwiched in between two of her cousins.
Compound Preposition
Compound Prepositions are composed of prepositions as well as other words. Compound Prepositions are easily confused with Double Prepositions since they both require other prepositions or words to help with acting like a preposition.
Examples:
- According to my calculations, this color should work just fine.
- I started for home, with a view to celebrating Eid with my family.
- On behalf of our family, my father attended the family reunion.
Participle Preposition
Present Participles (-ing) and Past Participles (-ed and -en) that are used as Prepositions instead of Verbs, are called Participle Prepositions. These are participles as well as prepositions.
Examples:
| Present Participle Prepositions | Past Participles Prepositions |
| Assuming | Respected |
| Barring | Given |
| Considering | Gone |
| During | Barred |
| Notwithstanding | Provided |
| Regarding | Taken |
Participle Prepositions Used in Sentences:
- Barred from the entrance, he threw a fit.
- I was happy given the fact that I got great marks.
- Assuming the possibility of rain, she carried an umbrella.
Disguised Preposition
These prepositions are usually disguised as some other element in the English language. Often these prepositions are disguised as «a» and «o» in sentences.
Examples:
- I wake up at 5 o‘clock. (Of the clock)
- Keep striding ahead. (on the head)
- Pope went ashore. (onshore)
- Rimi visits the riverbank once a day. (in a day)
Detached Preposition
A preposition that has been detached and sent to the very end of the sentence is called Detached Preposition. These prepositions are detached from the interrogative or relative pronouns and adverbs but get detached for the sake of the integrity of sentences.
Examples:
- Where are you coming from?
- Is that the neighborhood you are headed to?
- I won’t tolerate being screamed at.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time show the relationship of time between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, from, to, for, since, ago, before, till/until, by, etc. are the most common preposition of time.
Example:
- He started working at 10 AM.
- The company called meeting on 25 October.
- There is a holiday in December.
- He has been ill since Monday.
Read More: Prepositions of Time Usage
Prepositions of Place and Direction
Prepositions of place show the relationship of place between the nouns to the other parts of a sentence.
On, at, in, by, from, to, towards, up, down, across, between, among, through, in front of, behind, above, over, under, below, etc. are the most common prepositions of place/direction.
Example:
- He is at home.
- He came from England.
- The police broke into the house.
- I live across the river.
Read More: Prepositions of Places & Direction Usage
Prepositions of Agents or Things
Prepositions of agents or things indicate a causal relationship between nouns and other parts of the sentence.
Of, for, by, with, about, etc. are the most used and common prepositions of agents or things.
Example:
- This article is about smartphones.
- Most of the guests have already left.
- I will always be here for you.
- He is playing with his brothers.
Phrasal Prepositions
A phrasal preposition is not a prepositional phrase, but they are a combination of two or more words that function as a preposition.
Along with, apart from, because of, by means of, according to, in front of, contrary to, in spite of, on account of, in reference to, in addition to, in regard to, instead of, on top of, out of, with regard to, etc. are the most common phrasal prepositions.
Example:
- They along with their children went to Atlanta.
- According to the new rules, you are not right.
- In spite of being a good player, he was not selected.
- I’m going out of the city.
When you start breaking it down, the English language is pretty complicated—especially if you’re trying to learn it from scratch! One of the most important English words to understand is the.
But what part of speech is the word the, and when should it be used in a sentence? Is the word the a preposition? Is the a pronoun? Or is the word the considered a different part of speech?
To help you learn exactly how the word the works in the English language, we’re going to do the following in this article:
- Answer the question, «What part of speech is the?»
- Explain how to use the correctly in sentences, with examples
- Provide a full list of other words that are classified as the same part of speech as the in the English language
Okay, let’s get started learning about the word the!
In the English language the word the is classified as an article, which is a word used to define a noun. (More on that a little later.)
But an article isn’t one of the eight parts of speech. Articles are considered a type of adjective, so «the» is technically an adjective as well. However, «the» can also sometimes function as an adverb in certain instances, too.
In short, the word «the» is an article that functions as both an adjective and an adverb, depending on how it’s being used. Having said that, the is most commonly used as an article in the English language. So, if you were wondering, «Is the a pronoun, preposition, or conjunction,» the answer is no: it’s an article, adjective, and an adverb!
While we might think of an article as a story that appears in a newspaper or website, in English grammar, articles are words that help specify nouns.
The as an Article
So what are «articles» in the English language? Articles are words that identify nouns in order to demonstrate whether the noun is specific or nonspecific. Nouns (a person, place, thing, or idea) can be identified by two different types of articles in the English language: definite articles identify specific nouns, and indefinite articles identify nonspecific nouns.
The word the is considered a definite article because it defines the meaning of a noun as one particular thing. It’s an article that gives a noun a definite meaning: a definite article. Generally, definite articles are used to identify nouns that the audience already knows about. Here’s a few examples of how «the» works as a definite article:
We went to the rodeo on Saturday. Did you see the cowboy get trampled by the bull?
This (grisly!) sentence has three instances of «the» functioning as a definite article: the rodeo, the cowboy, and the bull. Notice that in each instance, the comes directly before the noun. That’s because it’s an article’s job to identify nouns.
In each of these three instances, the refers to a specific (or definite) person, place, or thing. When the speaker says the rodeo, they’re talking about one specific rodeo that happened at a certain place and time. The same goes for the cowboy and the bull: these are two specific people/animals that had one kinda terrible thing happen to them!
It can be a bit easier to see how definite articles work if you see them in the same sentence as an indefinite article (a or an). This sentence makes the difference a lot more clear:
A bat flew into the restaurant and made people panic.
Okay. This sentence has two articles in it: a and the. So what’s the difference? Well, you use a when you’re referring to a general, non-specific person, place, or thing because its an indefinite article. So in this case, using a tells us this isn’t a specific bat. It’s just a random bat from the wild that decided to go on an adventure.
Notice that in the example, the writer uses the to refer to the restaurant. That’s because the event happened at a specific time and at a specific place. A bat flew into one particular restaurant to cause havoc, which is why it’s referred to as the restaurant in the sentence.
The last thing to keep in mind is that the is the only definite article in the English language, and it can be used with both singular and plural nouns. This is probably one reason why people make the mistake of asking, «Is the a pronoun?» Since articles, including the, define the meaning of nouns, it seems like they could also be combined with pronouns. But that’s not the case. Just remember: articles only modify nouns.
Adjectives are words that help describe nouns. Because «the» can describe whether a noun is a specific object or not, «the» is also considered an adjective.
The as an Adjective
You know now that the is classified as a definite article and that the is used to refer to a specific person, place, or thing. But defining what part of speech articles are is a little bit tricky.
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. The thing about these eight parts of speech in English is that they contain smaller categories of types of words and phrases in the English language. Articles are considered a type of determiner, which is a type of adjective.
Let’s break down how articles fall under the umbrella of «determiners,» which fall under the umbrella of adjectives. In English, the category of «determiners» includes all words and phrases in the English language that are combined with a noun to express an aspect of what the noun is referring to. Some examples of determiners are the, a, an, this, that, my, their, many, few, several, each, and any. The is used in front of a noun to express that the noun refers to a specific thing, right? So that’s why «the» can be considered a determiner.
And here’s how determiners—including the article the—can be considered adjectives. Articles and other determiners are sometimes classified as adjectives because they describe the nouns that they precede. Technically, the describes the noun it precedes by communicating specificity and directness. When you say, «the duck,» you’re describing the noun «duck» as referring to a specific duck. This is different than saying a duck, which could mean any one duck anywhere in the world!
When «the» comes directly before a word that’s not a noun, then it’s operating as an adverb instead of an adjective.
The as an Adverb
Finally, we mentioned that the can also be used as an adverb, which is one of the eight main parts of speech we outlined above. Adverbs modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, but never modify nouns.
Sometimes, the can be used to modify adverbs or adjectives that occur in the comparative degree. Adverbs or adjectives that compare the amounts or intensity of a feeling, state of being, or action characterizing two or more things are in the comparative degree. Sometimes the appears before these adverbs or adjectives to help convey the comparison!
Here’s an example where the functions as an adverb instead of an article/adjective:
Lainey believes the most outrageous things.
Okay. We know that when the is functioning as an adjective, it comes before a noun in order to clarify whether it’s specific or non-specific. In this case, however, the precedes the word most, which isn’t a noun—it’s an adjective. And since an adverb modifies an adjective, adverb, or verb, that means the functions as an adverb in this sentence.
We know that can be a little complicated, so let’s dig into another example together:
Giovanni’s is the best pizza place in Montana.
The trick to figuring out whether the article the is functioning as an adjective or an adverb is pretty simple: just look at the word directly after the and figure out its part of speech. If that word is a noun, then the is functioning as an adjective. If that word isn’t a noun, then the is functioning like an adverb.
Now, reread the second example. The word the comes before the word best. Is best a noun? No, it isn’t. Best is an adjective, so we know that the is working like an adverb in this sentence.
How to Use The Correctly in Sentences
An important part of answering the question, «What part of speech is the word the?» includes explaining how to use the correctly in a sentence. Articles like the are some of the most common words used in the English language. So you need to know how and when to use it! And since using the as an adverb is less common, we’ll provide examples of how the can be used as an adverb as well.
Using The as an Article
In general, it is correct and appropriate to use the in front of a noun of any kind when you want to convey specificity. It’s often assumed that you use the to refer to a specific person, place, or thing that the person you’re speaking to will already be aware of. Oftentimes, this shared awareness of who, what, or where «the» is referring to is created by things already said in the conversation, or by context clues in a given social situation.
Let’s look at an example here:
Say you’re visiting a friend who just had a baby. You’re sitting in the kitchen at your friend’s house while your friend makes coffee. The baby, who has been peacefully dozing in a bassinet in the living room, begins crying. Your friend turns to you and asks, «Can you hold the baby while I finish doing this?»
Now, because of all of the context surrounding the social situation, you know which baby your friend is referring to when they say, the baby. There’s no need for further clarification, because in this case, the gives enough direct and specific meaning to the noun baby for you to know what to do!
In many cases, using the to define a noun requires less or no awareness of an immediate social situation because people have a shared common knowledge of the noun that the is referring to. Here are two examples:
Are you going to watch the eclipse tomorrow?
Did you hear what the President said this morning?
In the first example, the speaker is referring to a natural phenomenon that most people are aware of—eclipses are cool and rare! When there’s going to be an eclipse, everyone knows about it. If you started a conversation with someone by saying, «Are you going to watch the eclipse tomorrow?» it’s pretty likely they’d know which eclipse the is referring to.
In the second example, if an American speaking to another American mentions what the President said, the other American is likely going to assume that the refers to the President of the United States. Conversely, if two Canadians said this to one another, they would likely assume they’re talking about the Canadian prime minister!
So in many situations, using the before a noun gives that noun specific meaning in the context of a particular social situation.
Using The as an Adverb
Now let’s look at an example of how «the» can be used as an adverb. Take a look at this sample sentence:
The tornado warning made it all the more likely that the game would be canceled.
Remember how we explained that the can be combined with adverbs that are making a comparison of levels or amounts of something between two entities? The example above shows how the can be combined with an adverb in such a situation. The is combined with more and likely to form an adverbial phrase.
So how do you figure this out? Well, if the words immediately after the are adverbs, then the is functioning as an adverb, too!
Here’s another example of how the can be used as an adverb:
I had the worst day ever.
In this case, the is being combined with the adverb worst to compare the speaker’s day to the other days. Compared to all the other days ever, this person’s was the worst…period. Some other examples of adverbs that you might see the combined with include all the better, the best, the bigger, the shorter, and all the sooner.
One thing that can help clarify which adverbs the can be combined with is to check out a list of comparative and superlative adverbs and think about which ones the makes sense with!
3 Articles in the English Language
Now that we’ve answered the question, «What part of speech is the?», you know that the is classified as an article. To help you gain a better understanding of what articles are and how they function in the English language, here’s a handy list of 3 words in the English language that are also categorized as articles.
|
Article |
Type of Article |
What It Does |
Example Sentence |
|
The |
Definite Article |
Modifies nouns by giving them a specific meaning |
Please fold the laundry. Do you want to go to the concert? |
|
A |
Indefinite Article |
Modifies a noun that refers to a general idea; appears before nouns that begin with a consonant. |
Do you want to go to a concert? |
|
An |
Indefinite Article |
Modifies a noun that refers to a general idea; appears before nouns that begin with a vowel. |
Do you want to go to an arcade? Let’s get an iguana. |
What’s Next?
If you’re looking for more grammar resources, be sure to check out our guides on every grammar rule you need to know to ace the SAT (or the ACT)!
Learning more about English grammar can be really helpful when you’re studying a foreign language, too. We highly recommend that you study a foreign language in high school—not only is it great for you, it looks great on college applications, too. If you’re not sure which language to study, check out this helpful article that will make your decision a lot easier.
Speaking of applying for college…one of the most important parts of your application packet is your essay. Check out this expert guide to writing college essays that will help you get into your dream school.
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.
Have friends who also need help with test prep? Share this article!
About the Author
Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.