Wiki User
∙ 7y ago
Best Answer
Copy
No. The word put is a verb, and rarely a noun. It cannot be a
preposition.
Wiki User
∙ 7y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
More answers
Wiki User
∙ 8y ago
Copy
No. The word «put» is a verb. It is an action word— you put a thing in a certain place, which requires some action.Any word which required action of some sort is a verb.
This answer is:
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: Is the word put a preposition?
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
Both entrances were arranged and the old elevator (which had not worked for years) was put in order.
It had something in its talons, which it put to its mouth and tore at….
He was remarkably intelligent and absolutely unscrupulous, didn’t hesitate to put into the mouths of people what he wished them to say, so he naturally had a great pull over the ordinary simple—minded journalist who wrote simply what he saw and heard.
The grand piano, which had been standing well out toward the middle of the room, open, with music on it (I dare say some of Liszt‘s ownbut I didn’t have time to examine), was being pushed back into a corner, all the music hidden away, and the instrument covered with photographs, vases of flowers, statuettes, heavy books, all the things one doesn’t habitually put on pianos.
The same seed becomes a very different plant when sowed in one soil or another, and put under this or that mode of cultivation.
In entering the Christian life, one must put out of his heart the expectation that it is to be an easy life, or one removed from toil and danger.
The aborigines of this far away country have no written language, and this work aims to put before the traveler or trader a means of communication with this people which it is hoped will be of mutual benefit to both.
In recognition of this general fear, the unmuzzled Cerberus was put at the gate of Hades.
We turned our horses and ran, the bullets flying after us thick and fastmy whip being shot from my hand and daylight being put through the crown of my hat.
«Let‘s put for the village.
Boys who were taken to gaol for the first time were put with old and hardened criminals; the prisons were dirty and ill—smelling; the dungeons were dark and unhealthy; and, unless prisoners could afford to pay for comforts, they were obliged to sleep on cold bare floors, even delicate women not being exempted from such cruel treatment.
If she was kept late at the hospital, Mavity put by a bite of cold supper for her, and Mandy always waited to see that she had what she wanted.
Tapp was still putting after him.
Education is not a thing of books alone, or schools; it is a process of intellectual assimilation of what is about us, or what we put about ourselves.
The Lunarians write as we do, from left to right; but when their words consist of more than one syllable, all the subsequent syllables are put over the first, so that what we call long words, they call high ones: which mode of writing makes them more striking to the eye.
Unless you break down the bar you put between us, I never want to see your face again,never, living or dead!
He put from him the knowledge of how her charm wrought upon himbound him the faster every time he spoke to her.
I have triedah, how often!to put behind me the memory of her face as I saw it then, but it is before me now and again, even yet.
I am utterly against those confused Olios into which men put almost all kinds of meats and Roots, and especially against putting of Oyle, for it corrupts the Broath, instead of adding goodnesse to it.
Jarvis felt satisfied that his veracity had been put beyond question.
It is, however, in the double aisled transepts that we can best appreciate how very glorious that first Norman church must have been; there is nothing in England more wonderful; and so far as I know there is nothing in Europe quite to put beside them.
The buffalo were put within a wire fence, which, when it was built, was found to have included both black—tail and white—tail deer.
It has, doubtless, found its way into your state—room, and has been put among your effects by your man, through mistake.
This is put as a question, and Shelley does not supply an answer to it here, though the terms in which his enquiry is couched seem intended to suggest a reply to the effect that the mind shall not die.
Behind them, at least four hundred people packed and waiting with their possessions at their feet, ready to be put aboard the instant the Oklahoma made fast.
Asked
6 years, 4 months ago
Viewed
8k times
Is there a serious difference between the following three sentences:
I put the toys in the box.
I put the toys into the box.
I put the toys inside the box.
Jasper
24k4 gold badges53 silver badges86 bronze badges
asked Dec 3, 2016 at 0:17
SovereignSunSovereignSun
24.7k36 gold badges139 silver badges258 bronze badges
0
No significant difference between them — in this context.
It is a matter of choice and personal style. Nevertheless, people prefer the shorter way as usual: «he is putting the toys in the box».
In other contexts may be differences between them. Be aware that normally the word «into» is a preposition for movement or transformation while inside is preposition for location. Also see that and this.
answered Dec 3, 2016 at 1:23
Virtuous LegendVirtuous Legend
26.6k189 gold badges392 silver badges577 bronze badges
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
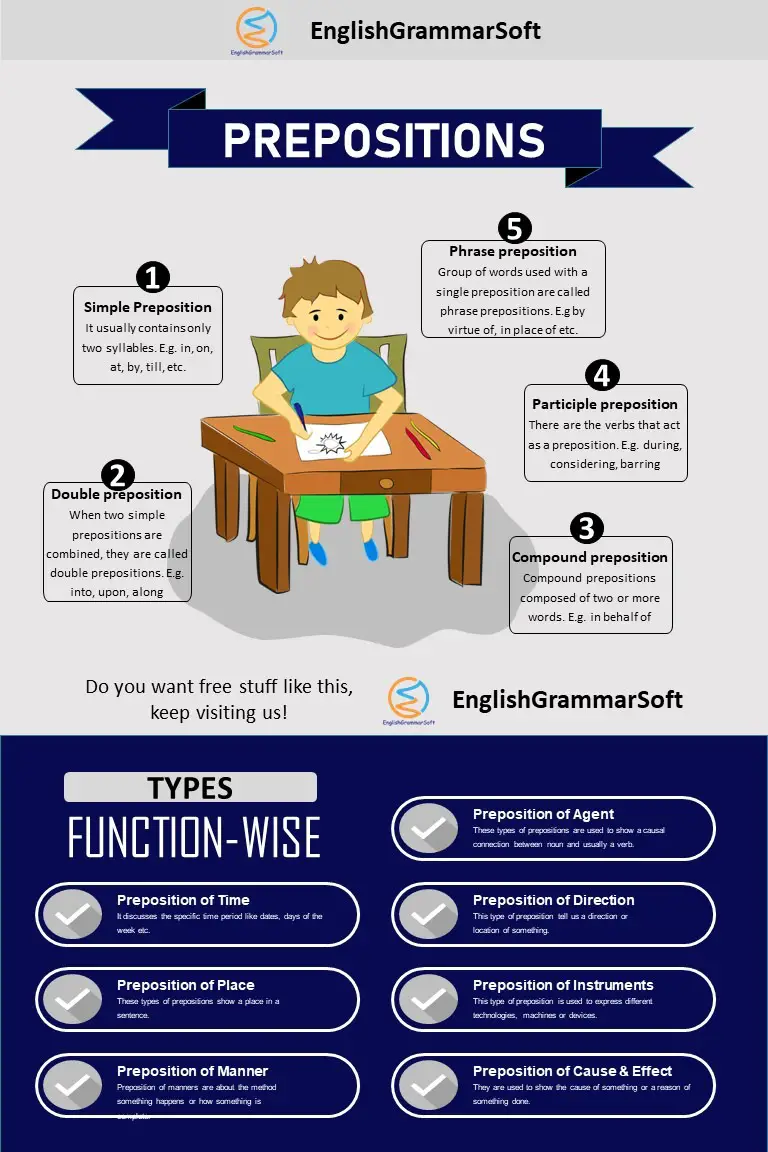
Types of Prepositions
There are several types of prepositions such as: Simple Prepositions, Double Prepositions, Compound Prepositions, Phrasal prepositions, Participle Prepositions, Disguised preposition, and Detached Prepositions.
1. Simple Prepositions:
Simple prepositions are used to denote a relation between nouns or pronouns. These can even be used to join different parts of sentences and clauses. Simple prepositions are one word prepositions. These are also called Single Prepositions. Common words used that come under the category of Simple Prepositions are as follows:
In, out, on, up, at, for, from, by, of, off, through, till, etc.
Examples of Simple Prepositions in sentences:
Keep your phones in your pockets.
Staring at people is not considered a good gesture.
In the above two examples, both prepositions consist of one simple word and hence are Single or Simple Prepositions.
2. Double Prepositions:
Double Prepositions are made by putting together two Single Prepositions. That is why they are called Double Prepositions. Common words used as Double Prepositions are as follows:
Onto, into, throughout, up till, up to, within, without, upon, etc.
Examples of Double Prepositions in sentences:
Complete this essay within two hours.
I am going to turn this scrap into a masterpiece.
In the first example, the Preposition within is made by combining two Single Prepositions with and in.
In the second example, the Preposition into is formed by putting together two Simple Prepositions in and two. These are hence Double Prepositions.
3. Compound Prepositions:
Compound Prepositions are those types of preposition that are usually formed by prefixing a preposition to nouns, adjectives or adverbs. They are different from double prepositions because they are not formed by two single prepositions. Common words, which come under the category of compound prepositions, are stated below:
Above, about, across, along, before, behind, beside, inside, outside, etc.
Examples of preposition in sentences:
He was going about his business.
The person beside Ali is my brother.
In the first example, the prefix ‘a’ is added to a root word ‘bout’ to make a preposition. In the second example, the prefix be is added to the root word side to make a preposition. Thus, these words are Compound Prepositions.
4. Phrasal Prepositions:
Phrasal Prepositions are groups of words or phrases that join the noun or pronoun in a sentence, to the remainder of the sentence. These groups of words express a single idea by coming together as a unit. Words that come under the category of Phrasal Prepositions are as follows:
In addition to, by means of, in spite of, according to, owing to, in favour of, etc.
Examples of Phrasal Prepositions in sentences:
He couldn’t pass the test, owing to his lack of knowledge of English Grammar.
She made it to the other side of the world, in spite of all the difficulties.
In the first example, the group of words ‘owing to’ is joining the two sentences with each other and is a phrase. Likewise, the group of words ‘in spite of’ is also a phrase and is working as a preposition. Hence, these are Phrasal Prepositions.
5. Participle Prepositions:
Participle Prepositions, indicating from their name, are the Present Participle forms of Verbs. These are used without any noun or pronoun attached with them. The words that are distinguished as Participle Prepositions are as follows:
Concerning, considering, barring, notwithstanding, touching, pending, during, etc.
Examples of Participle Prepositions in sentences:
Notwithstanding his efforts, he was still fired from the job.
Touching this matter, I do not have much information.
In above examples, both the verbs notwithstanding and touching are in Present Participle which is apparent from the ‘ing’ at the end of both words. These words are therefore Participle Prepositions.
6. Disguised Prepositions:
Disguised prepositions are those prepositions which are not used in the sentences directly, but we use them in a disguised way. Their shorter forms are used. The examples of Disguised Prepositions are ‘a’ and ‘o’.
Disguised preposition ‘a’ is shortened form of the preposition ‘on’ and similarly ‘o’ is the shortened form of the preposition ‘of’.
Examples of disguised prepositions in sentences:
The ceremony will be held at 5 o’ clock.
We all went to a party.
In the first example, instead of saying ‘5 of the clock’, we have used disguised form of the preposition of.
In the second example, instead of saying ‘went on partying’, we have used abbreviation of the preposition on and disguised the preposition as ‘a’. Hence these are Disguised Prepositions.
7. Detached Prepositions:
A preposition is called a detached preposition when it does not come before its object. It is detached from its object. When the object of a preposition is an interrogative pronoun or a relative pronoun, the preposition comes at the end of the sentence.
Look at the following examples of detached prepositions for further understanding.
She is the woman whom I was talking about.
Here are the books that you asked for.
Which of the houses were you working in?
In the first two of the above examples, we can see that because of relative pronouns whom and that, the prepositions about and for are being detached from their objects.
In the third example, the interrogative pronoun ‘which’ is detaching the preposition ‘in’ from its object.
Hence these are all detached prepositions.
In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions
Most English speaking people recall only a handful of common prepositions, but in reality, there are about 150 different prepositions. Three of these prepositions are in the top ten most commonly used words in the English language: of, to, and in. What are prepositions, are there more than one type, and if there are prepositions, are there postpositions? Finally, what can you do to understand prepositions better, especially when studying for an English proficiency test?
What are prepositions?
According to Merriam-Webster, the technical definition of a preposition is “a word or group of words that is used with a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, location, or time, or to introduce an object.” Simply put, prepositions are connector words. These connectors customarily tie a noun to an idea. An example of this is in the sentence, “I went to the store.” “To” connects the location of “store” to where the person went.
Often a preposition is a short word such as on, in, or to. This standard is not the only option; it can also be a longer word, multiple words, or a short phrase. “In front of” is an example of a short phrase. She parked her bike in front of the school.
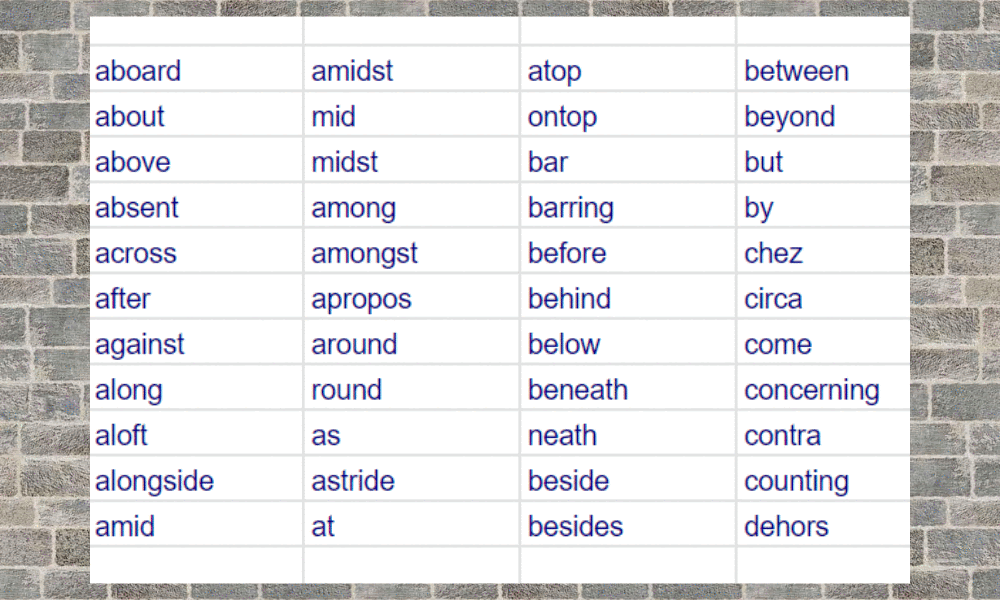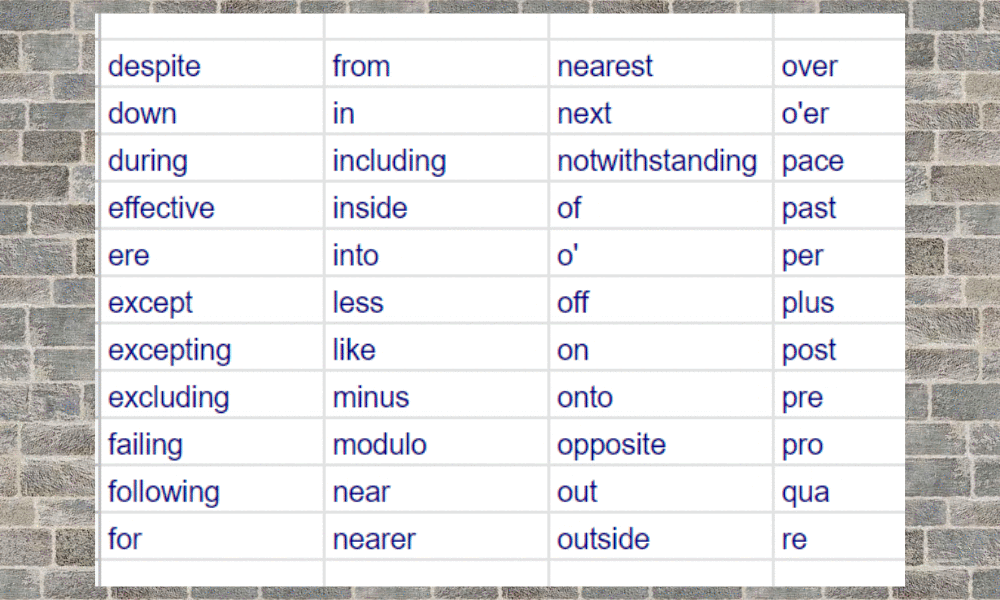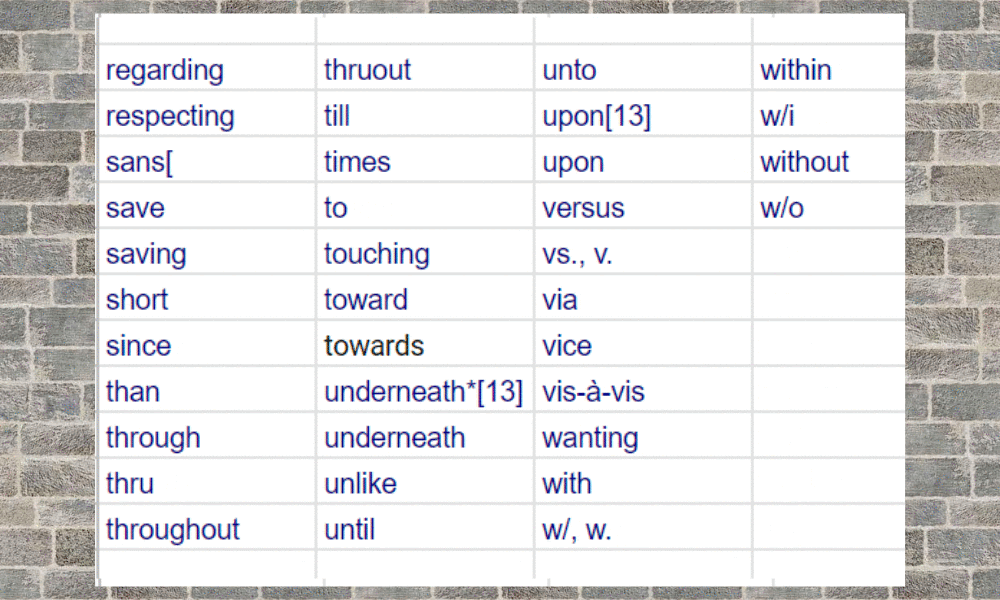
Prepositions are common in the English language. There are about 150 used with the most common being: above, across, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, by, down, from, in, into, near, of, off, on, to, toward, under, upon, with and within.
Types of prepositions
Because there are so many prepositions, differentiating them helps to understand when and how to use them properly. The word directly following a preposition is called its complement, and how it relates to the preposition determines what type of preposition you are using.
Transitive Prepositions
A transitive preposition always uses a complement with a preposition. For example, the word “amongst” is a transitive preposition. You cannot write “she lived amongst the wildflowers” without the complement “the wildflowers.” Some traditional grammars believe transitive prepositions are the only true prepositions.
Intransitive Prepositions
Intransitive prepositions do not need to use the complement to complete the thought. For example, “outside” can be used in the following sentence without a complement, “she lived outside.” You could add a complement to this, “She lived outside the city limits,” but it is unnecessary when using it. Traditional grammars believe intransitive prepositions are actually adverbs. The argument for intransitive prepositions parallels the use of transitive or intransitive verbs. “He runs” versus “he runs a marathon.”
Conjunctive Preposition
This type of preposition uses a clause as the complement. Traditional grammar may categorize these are subordinating conjunctions instead of conjunctive prepositions. One common example of a conjunctive preposition is the word “because.”
Complex Preposition
When two or more words form a preposition, they are a complex preposition. This type of preposition is also referred to as a compound preposition. Aside from being more than one word, it functions essentially the same as any other preposition. “In light of” is an example of a complex preposition. “In light of the recent traffic reports, the man drove a different way to work.” Other examples are in addition to, on behalf of, in the middle of, or across from.
Complex prepositions are mostly found at the beginning and the middle of a sentence, but rarely at the end. To find the correct complex preposition to use, focus on the relationship between the beginning and the end of the sentence. When you have determined this relationship, you can identify the proper complex preposition much easier.
Phrase propositions
Sometimes called prepositional phrases, phrase prepositions contain the preposition, the object, and the optional object’s modifier (extra details about the object such as “smooth” to describe a table). Some examples of these are “at home, with a little help, according to their wishes.”
Difference between prepositions and postpositions
As mentioned earlier, a preposition is a word connecting an idea or action to a noun. The example “I went to the store” describes where one went. The preposition “to” came before its complement “store.” The word “pre” means before, so the preposition (to) comes before the complement.
When this comes after the complement, instead of being called a PREposition, this is called a POSTposition. Post means “after,” and the postposition comes after the complement. English does not often use postpositions, although there are a few. Ago, as in “that was many years ago,” or through, as in “We slept the whole night through,” are two of the few postpositions English uses.
English postpositions
- Ago
- Apart
- Aside
- Aslant
- Away
- Hence
- Notwithstanding
- On
- Over
- Short
- Through
- Withal
List of prepositions
Lists of prepositions like the picture above are overwhelming to study. They provide limited context as to how to apply the prepositions. If you are looking for a list of prepositions, these lists offer prepositions by category. Don’t forget to check out this preposition song used to help American kids when memorizing prepositions.
Even advanced English learners struggle with using prepositions in the proper context. Some of the ways native English speakers use prepositions do not translate well to other languages. Sometimes the only way to learn these is by forcing yourself to begin using them in your practice. The lists below describe using prepositions for place and time.
Prepositions – Place |
||
| English | Usage | Example |
| in | room, building, street, town, country
book, paper, etc. transportation picture, world |
We sleep in our bedroom. We live in Texas.
I live in the United States. I read about it in Harry Potter. We are going in a bus to the sports game. You look great in that picture. Where in the world were you? |
| at | next to or by an object
for sitting at a table for events place where you are to doing something |
Leave your shoes at the door.
We have dinner at the table. I told him I would meet him at school. We are studying at the library. |
| on | attached
being on an object for a certain side for a floor in a house for public transportation for media |
The mirror is on the wall.
The keys are on the desk. The stage is on the right side. We live on the first floor. I talked to him on the bus. I saw it on Twitter. |
| by, next to, beside | left or right of an object or person | The school is next to the church. |
| under | on the ground or lower than something else | The ants are under the rock. |
| below | lower than something else | The glasses go below the cups in the pantry. |
| over | covered by something else
meaning more than getting to the other side overcoming an obstacle |
Put a blanket over your lap.
You can drive if you are over 16 years of age. Drive over the bridge. Climb over the wall. |
| above | higher than something else, but not directly over it | The plates go above the glasses in the pantry. |
| across | go to the other side | Walk across the bridge.
Swim across the pool. |
| through | to move from one place to another by entering the inside of something | Drive through the tunnel.
Enter through the breezeway. |
| to | movement to person, building, place or country
can also indicate bedtime |
Go to the restaurant.
Go to California. Go to bed. |
| into | enter a room or a building | Go into the house. Once there, go into the bedroom. |
| towards | movement in the direction of something, as opposed to away from it | She walked towards the house. |
| onto | moving to the top of something | Jump onto the bench. |
| from | where did object come from | We bought a fruit from the grocery store. |
| English | Usage | Example |
| on | days of the week | on Friday |
| in | months / seasons
time of day year after a certain period of time (when?) |
in September / in autumn
in the evening in 2020 in thirty minutes |
| at | for night
a certain point of time |
at night
at half past seven |
| since | from a certain point of time in the past | since 1999 |
| for | a certain past time until present | for 10 years |
| ago | a time in the past | 4 years ago |
| before | earlier than a specified date | before 2020 |
| to | telling the time | ten to 10 (9:50) |
| past | telling the time | ten past five (5:10) |
| to / till / until | the beginning and end of a period of time | from Wednesday to/till Friday |
| till / until | how long something is going to last | He is on vacation until Sunday |
| by | indicating the latest something will happen by
up to a certain time |
I will be done with work by 6 o’clock.
By 7 pm, I had finished my chores. |
Preposition Exercises
You must practice using prepositions to better your understanding of them. Simply reading through the information will not allow it to commit to memory for speaking, let alone an English proficiency test. Only by practicing preposition exercises will you acquire the skills to feel comfortable.
Ending with a preposition
Before you put yourself to the test, become familiar with spotting out incorrect usage of prepositions. See if you can spot out the mistake in the below sentences:
Where did he go to? Do you know where it is at?
In each of these, the question ends with a preposition. Remember, you ordinarily want to place the preposition before the object. There are some exceptions to this rule, but for the most part, it applies. Try instead the changes below:
Where did he go? Do you know where it is?
Like or as
Another hiccup is often the words “like” and “as.” Use “like” when saying something is similar to something else. Use “as” when comparing something to a verb. Which of the following sentences is the proper use of “like?”
You look like your mother.
You look like you are angry.
If you said the first one, you are correct. Again, think of replacing “like” with “similar.” Which sentence makes sense?
You look similar to your mother.
You look similar to angry.
The first one makes sense. Moreover, if you add “do” or “does” to the end of the sentence, the preposition may no longer be modifying the same subject. For example, in the first sentence, if you wrote, “you look like your mother does,” you would need to change “like” to “as” because no one says, “you look similar to your mother does.”
When not to use of and from
“Of” is often misused. When using the preposition of, make sure the verb “have” is not really what you are requiring. For example, “I should of taken the money to the bank,” should be written as “I should have taken the money to the bank.”
“From” is another tricky one. Skilled linguists will insist the phrase “different than” is rewritten as “different from” when at all possible. For example, “that shirt is different than the others,” should instead be, “that shirt is different from the others.”
In verses into
This rule is often one that is mixed up in the speech of even most native English speakers. When using “into,” pair it with movement towards something. In contrast, “in” is used when talking about a location.
Compare the two sentences below and their meanings:
She is walking on the street.
She walked into the street.
The first sentence means she is going for a walk on the street. The second says she has walked onto the street, maybe from her yard or out of the car.
Exercises to practice prepositions
With so many different types of prepositions and rules, it can be overwhelming to imagine taking an English proficiency test. Not to worry, there are plenty of places to pull up sample exercises for practice.
The English Page has numerous online practice preposition tests. English Grammar Online is another resource. Downloadable, amusing worksheets can be found at English-grammar.at. Englishpage.com is an extra resource for online practice problems.
If you are studying for an English proficiency test and need your skills to be in the best shape possible, start with the common prepositions and work up to the more advanced skills. Practice with worksheets a few times a week until you feel comfortable and as if prepositions were nothing more than a walk in the park. Did you catch the preposition there?
Preposition definition: A preposition is a part of speech that shows the relation of a noun or pronoun to another word.
What are prepositions? Prepositions show the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word. These relationships include where, when, who, or what.
Examples of Prepositions:
- above (where?)
- before (when?)
- for (whom?)
- with (what?)
Let’s look closer at a preposition example.
A preposition can be understood as anywhere a dog can be in relation to its doghouse.
A dog can be:
- in the doghouse
- around the doghouse
- near the doghouse
- on the doghouse
Each of these prepositions describe the relation between the dog and its doghouse. The dog can be inside the doghouse, it can be around the doghouse, it can be near the doghouse, it can be on the doghouse, etc.
All of these preposition examples show where the dog is in relation to its doghouse.
What is the Role of a Preposition?

Most often prepositions are used to introduce prepositional phrases.
Prepositions serve to modify and generally function in prepositional phrases as adjectives or adverbs.
Examples of prepositions indicating where:
- along (the path)
- amid (torment)
- throughout (the garden)
- within (men)
Examples of prepositions indicating when:
- since (the storm)
- after (the party)
- before (noon)
- until (tomorrow)
Examples of prepositions indicating who:
- besides (Petra)
- except (the children)
- with (everyone)
- for (the teacher)
Examples of prepositions indicating what:
- besides (the essay)
- of (the few)
- like (the dog)
- with (chocolate)
Preposition List

aboard
about
above
across
after
against
along
amid
among
anti
around
as
at
before
behind
below
beneath
beside
besides
between
beyond
but
by
concerning
considering
despite
down
during
except
excepting
excluding
following
for
from
in
inside
into
like
minus
near
of
off
on
onto
opposite
outside
over
past
per
plus
regarding
round
save
since
than
through
to
toward
towards
under
underneath
unlike
until
up
upon
versus
via
with
within
without
For a more full list of prepositions, see our full page on the subject. Prepositions list here.
Object of Prepositions

Examples:
- along (the path)
- The path is the object of the preposition.
- amid (torment)
- Torment is the object of the preposition.
- throughout (the colorful garden)
- The colorful garden is the object of the preposition.
Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions

The prepositions that can function in subordinate conjunctions include: after, as, before, since, until.
Prepositions together within subordinate conjunctions function as adverbs.
Preposition Examples:
- Since the movie premiered, the star has received much attention.
- We could not make an appointment until the office opened the following day.
- The student did not think before he asked a question.
What are Prepositional Phrases?
What does prepositional phrase mean? Almost always a preposition will function in a prepositional phrase.
A prepositional phrase is any preposition and its object (a noun). A prepositional phrase may also include any modifiers in the phrase.
Prepositional phrases clarify the relationship of the preposition to other words.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
- along the path
- along (prep.) + the (article) + path (noun) = prepositional phrase
- amid torment
- amid (prep.) + torment (noun) = prepositional phrase
- throughout (the colorful garden)
- throughout (prep.) + the (article) + colorful (adj.) + garden (noun) = prepositional phrase
Multiple prepositional phrases may exist within one larger prepositional phrase.
Prepositional Phrase Examples:
- within all of the men
- within all + of the men = prepositional phrase
- by the lake in the forest
- by the lake + in the forest = prepositional phrase
- on the table at the restaurant
- on the table + at the restaurant = prepositional phrase
Summary: What are Prepositions?
Define preposition: To clarify, prepositions:
- show the relationship of a word to a noun or pronoun
- are almost always used in prepositional phrases
- sometimes begin subordinate conjunctions
Contents
- 1 What is a Preposition?
- 2 What is the Role of a Preposition?
- 3 Preposition List
- 4 Object of Prepositions
- 5 Some Prepositions Also Function as Subordinate Conjunctions
- 6 What are Prepositional Phrases?
- 7 Summary: What are Prepositions?
The preposition of is used when we want to say that someone or something belongs to someone or something, directly refers to him. I don’t like the smell of this perfume. I don’t like the smell of this perfume. She was a friend of mine.
under — under.
- close to — close to, near;
- in — in, inside;
- in front of — in front, in front;
- next to — next to next;
- on — on;
- opposite — opposite;
- over — over;
- past — for, on the other side.
When are prepositions not used in English?
In English, prepositions are never put if there are:
— Tom could not remember what he was doing that day. My friend spent last Sunday in Vegas playing roulette. — My friend spent last Sunday in Vegas playing roulette. Next spring Maria is going to enter a sports school.
What are the articles in English?
In English, the two articles are indefinite (a / an) and definite (the). The article is a sign of a noun and is placed either directly before the noun, or before the adjective that defines it.
When are prepositions used in English?
Direction prepositions are used to indicate the direction of movement of a person or object. For example: «She left the house.» Here are the main prepositions of this group. Someone is moving from one side of something to the other.
Memorization tips:
- Learn prepositions in sentences or at least in phrases, i.e. …
- Start with the simplest prepositions: the most popular, with the fewest meanings. …
- Write out sentences where there is a preposition in Russian, but not in English, and vice versa.
When are prepositions not used?
When we don’t use prepositions of time
These include: all, any, each, every, last, next, one, some, this, that (that). Compare the following examples: She’ll come in the morning. — She will come in the morning.
How do prepositions work in English?
Prepositions in English are service words that show the relationship of a pronoun or noun to other words in a sentence. As in Russian, these relationships can be spatial (on the top — at the top), temporary (in time — in time), causal (because of you — because of you) and others.
Why isn’t to put before Home?
Before the word ‘home’ when referring to direction, the preposition to is not used: go home / come home / get back home / return home / visit home (not “to home”). The preposition into is used to mean «to get inside»: go into, get into. As soon as you get into the room, you’ll see a huge box on the floor.
Where should you put articles in English?
General rules for the use of articles in English
- The indefinite article a / an is used with singular countable nouns.
- The definite article the can be used with countable nouns (regardless of their number) and uncountable nouns.
How easy is it to understand articles in English?
An article is a «part» of a noun. If there is an article in a sentence, then there must be a noun or a word next to it that takes the meaning of a noun. But if the noun has a definition (adjective), then the article is placed before the adjective.
What is an article in simple terms?
In simple terms, the article is a kind of «label», a companion of a noun. He stands in front of him, and makes it clear that this is a noun, and not a verb or adverb. … Because there is no article in Russian, and therefore it is not translated into Russian in any way.
What preposition is used over time in English?
Prepositions of time in English: at, in, on, since, for, during, by, until, till and others ‹Inglex
What preposition is used with months in English?
So, we use the preposition ‘in’ before months, seasons, years, decades or periods of time. For example: I was born in September.
What kinds of prepositions are there?
So, prepositions do not change and are not members of the sentence, but they express different relationships:
- spatial — about, in, among, on, etc .;
- temporary — during, in continuation, etc.;
- causal — due to, due, due, in connection, due to, etc .;
- target — for, etc.;
- object — about and others;