Last Updated: February 19, 2022 | Author: lewisbloom
What type of noun is her?
language note: Her is a third person singular pronoun. Her is used as the object of a verb or a preposition. Her is also a possessive determiner. You use her to refer to a woman, girl, or female animal.
Is her common noun or proper noun?
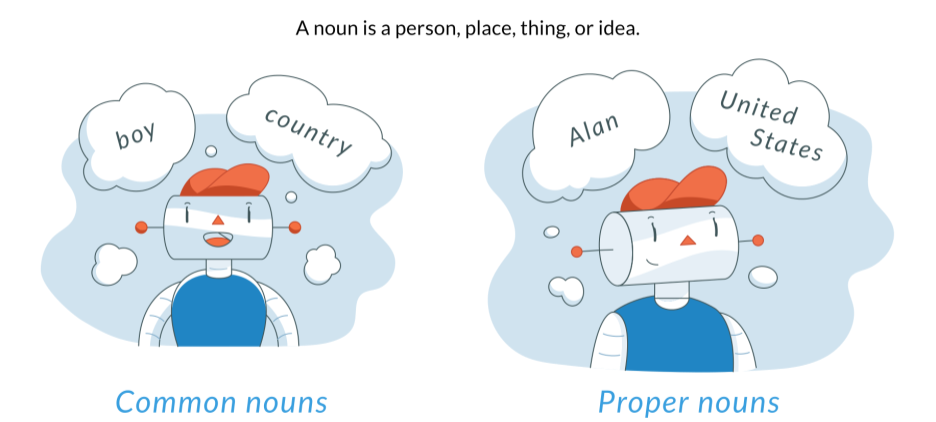
Proper nouns are always capitalized. Common nouns are those which name a person, place, thing, or idea in general, such as holiday, girl, and city.
Can a common noun be a person’s name?
Each is a common noun because they name a thing, place, or person: People: mother, father, baby, child, toddler, teenager, grandmother, student, teacher, minister, businessperson, salesclerk, woman, man.
What is common noun and examples?
A common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence. In this example, stage, sleep, repeat, times, and night are all general common nouns.
Is mother a common noun?
Many common nouns may be used as proper nouns; for example, mother is a common noun, as in “His mother just turned sixty-five”, but may be used as a proper noun, as in “Have you seen Mother today?”. As in this example, common nouns are traditionally capitalized when used as proper nouns.
– A common noun is a non-specific person, place or thing. … For example: dog, house, oven. – A proper noun is a specific person, place or thing.
What is the common noun?
Kids Definition of common noun
: a noun that names a class of persons or things or any individual of a class and that may occur with a limiting modifier (as a, the, some, or every) The words “child,” “city,” and “day” are common nouns. More from Merriam-Webster on common noun.
What is a common noun proper noun?
proper noun. The difference between a common noun and a proper noun is what type of thing they are referring to. Common nouns refer to generic things while proper nouns refer to specific things. For example, the noun country is a common noun because it refers to a general, non-specific place.
What are the types of common noun?
Common or generic nouns can be broken down into three subtypes: concrete nouns, abstract nouns, and collective nouns.
Which is not a common noun in the following?
Childhood is not a common noun.
Common noun is something represents a whole community of people or a group of objects. It a name commonly used for the entire group. King is a common noun as king can be used for any king and does not specifically mention any.
What is common noun of school?
The word ‘school’ can be either a common or proper noun, depending upon its usage. In this sentence, it is the name of a specific school, so it is a…
Is the word he a common noun?
The word ‘he’ is not a common noun or a proper noun. It is not a noun at all. Instead, ‘he’ is a pronoun.
How many common nouns are there?
100 Common Nouns in English.
Is girl a proper noun?
The word ‘girl’ is a common noun. It refers to a person but not by her specific name.
Is she a noun or pronoun?
Today, she is the only feminine pronoun in English. It is occasionally used as a gender neutral, third-person, singular pronoun (see also singular they).
Is the word she a proper noun?
The word ‘she’ is not a proper noun because it is not a noun at all. It is a pronoun. It takes the place of a noun in a sentence. For example, you…
Are girls noun?
A young female (in contrast to boy), usually a child or adolescent. “Amanda is a girl of 16.” Any woman, regardless of her age.
Are boy and girl nouns?
There are four types of gender nouns in English. Masculine gender nouns are words for men, boys, and male animals. Feminine gender nouns are words for women, girls and female animals.
Is it her or her?
Her second compilation album, I Used to Know Her, was nominated for five Grammy Awards, including Album of the Year and Song of the Year for “Hard Place”.
…
| H.E.R. | |
|---|---|
| Birth name | Gabriella Sarmiento Wilson |
| Also known as | Gabi Wilson |
| Born | June 27, 1997 Vallejo, California, U.S. |
| Genres | R&B |
What is the noun form of SHE?
pronoun, singular nominative she,possessive her or hers,objective her;plural nominative they,possessive their or theirs,objective them. the female person or animal being discussed or last mentioned; that female. the woman: She who listens learns.
Does her or do her?
If there is only one word in the verb, we use a form of to do to add a word to the verb, then move the added do: Statement: She does her homework. Two-word verb: She does do her homework.
At some point, everyone has the same question: What is a common noun? Here, we’ll take a look at common nouns and provide some common noun examples so you can easily recognize common nouns when you see them. Don’t worry, this will be painless.
What is a Common Noun
A noun is a word that names a person, animal, place, thing, or idea. All nouns can be further classified as a proper or common noun. Common nouns are words used to name general items rather than specific ones. Go into your living room. What do you see? A lamp, chair, couch, TV, window, painting, pillow, candle – all of these items are named using common nouns.
Common nouns are everywhere, and you use them all the time, even if you don’t realize it. Wherever you go, you’ll find at least one common noun. Street, closet, bathroom, school, mall, gas station, living room; all of these places are things, and thus they are common nouns.
What is the difference between common and proper nouns?
When we look at the two main types of noun – proper and common – we can differentiate between the two by saying that a common noun is a general way of classifying something, and a proper noun is a specific way of classifying something, So, for example, the word dog is a common noun; but if your dog was called Fido, the word Fido is a proper noun:
- Dog = common noun
- Dog’s name (Fido, in this case) = proper noun
More examples of the difference between common and proper nouns:
- My favorite newspaper (common noun) is the Washington Post (proper noun).
- Her husband (common noun) is called Frank (proper noun).
- The award-winning Babe Ruth (proper noun) is the greatest baseball player (common noun) in history.
You may have noticed from the examples that common nouns are not usually capitalized, unless they begin a sentence, whereas proper nouns are normally capitalized. You will also notice that both types of nouns can be more than a single word.
When to use common nouns?
We use common nouns to denote a class of objects or a concept. Consider the word star, as in the stars we see in the sky. Star is used as a common noun, used to denote the class of objects that we view in the night sky, i.e. the luminescent bodies that are spread across the universe, twinkling overhead. The Sun, however, is a proper noun, used to describe the specific star that is at the center of our solar system.
So, anything that is a thing can be generally classified as a common noun:
Professions: lawyer, doctor, teacher, nurse, politician, football player.
People: People in general are named using common nouns, though their official titles in certain cases or given names are proper nouns. When we refer to people using common nouns, we use words like teacher, clerk, police officer, preacher, delivery driver, boyfriend, girlfriend, grandma, cousin, and barista.
For example, when talking about your mother, mother is a common noun.
- My mother is an actress.
- Barbara’s mother was the best cook in the city.
But when speaking to your mother, or using mother as her name, mother is used as a proper noun.
- “Mother, can you bake your brownies for the party?”
- I asked Mother Thompson to join us at dinner.
Objects: car, newspaper, boat, potato chip, shoe, house, table, sword.
However, common nouns can also be more abstract concepts, not things but ideas, emotions and experiences, for example:
Abstract ideas: Culture, love, democracy, time, hatred, peace, war, empathy, anger, laughter.
How to recognize a common noun?
Considering what we have laid out above, it should be pretty easy to recognize a common noun. However, there are some cases when it can be tricky. Consider these sentences:
- Queen Elizabeth II welcomed President Donald Trump to Buckingham Palace.
- Donald Trump visited many queens and palaces during his tenure as the president of the United States.
In the first sentence, Queen Elizabeth II, President Trump and Buckingham Palace are proper nouns. They are specific titles for a specific person. In the second sentence, queens, palaces and president are common nouns. Queens and palaces refer to queens and palaces in general, and president refers to the job title and not the specific person.
We mentioned earlier that job titles and general titles fall under the category of common nouns – attorney, actor, comedian, truck driver, sergeant, officer, secretary. However, if these become specific titles referring to a specific person, they sometimes become proper nouns as in the examples above. Normally, this means the words are capitalized when placed directly in front of that person’s name:
- Attorney General William Barr was appointed by President
But look how we can use the same words with common nouns:
- Each US president must appoint an attorney general while in office.
So, you can recognize the common noun by the fact it is not capitalized. But remember that common nouns can also be identified because they are referring to non-specific things or classifications.
The takeaway is this: common nouns are general names and unless they are part of a title like Postmaster General or begin a sentence, they’re not usually capitalized.
Common Noun Examples
The following common noun examples will help you to recognize common nouns. In the sentences that follow, common noun examples are italicized. Notice that the examples providing proper nouns name specific versions of the same type of person, animal, place, thing, or idea.
- Common Noun: You broke my favorite mug. Proper Noun: I can’t believe you broke my Snoopy mug.
- Common Noun: I really want a new pair of jeans. Proper Noun: I really want to buy a new pair of Levis.
- Common Noun: I wish I could remember the name of that painter. Proper Noun: I really love art by Van Gogh.
- Common Noun: They’re all waiting for us at the restaurant. Proper Noun: Everyone else is at Bill’s Burgers.
- Common Noun: I really want to live in the city Proper Noun: Of all the places I’ve lived, Denver was best.
- Common Noun: Let’s go to watch a live game at the stadium. Proper Noun: Let’s try to get good seats at Wrigley Field
Do you get confused about the difference between a common noun and a proper noun? Would practice help you become a master?
Read on to learn about the difference between common and proper nouns, how they are used, and when to use them.
When you feel like you’ve got it, test yourself with a quiz and practice with our high-quality, standards-aligned questions here.
The Basics of Common and Proper Nouns
What is a common noun?
A common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
For example, as you work on your homework, think about the things you are using. You might be using a computer, a textbook, or a pencil. All of these are generic items that we encounter on a regular basis and are common nouns.
What is a proper noun?
A proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized. This is true whether they begin a sentence or not.
Let’s consider the same example from above, but instead, now we will be more specific about the resources necessary to complete your homework.
As you work, you may be using a Pearson Algebra 1 textbook, a Google Chromebook, and a Ticonderoga pencil. You are better able to visualize this scenario if proper nouns are provided since they are more specific and unique.
What is the relationship between common and proper nouns?
Common and proper nouns are closely related. The most straightforward way of understanding the relationship between common and proper nouns is to think about proper nouns as specific examples of common nouns.
For example, the word building is a common noun. Examples of buildings include The White House, The Art Institute of Chicago, and Memorial Hall at Harvard University.
These examples are all proper nouns since they are specific, unique examples of the common noun building. Generally, we can more vividly picture or understand a text when the author uses examples of proper nouns since there is less room for interpretation.
How do you use common and proper nouns?
Common and proper nouns can be used in relation to each other or separately. Typically, authors use common nouns when they are describing something broad or ambiguous.
Proper nouns are used to describe a person, place, thing, or idea that is specific and concrete. Common and proper nouns are often used together in sentences.
Take the following sentence as an example: The doctor worked long hours at Memorial Hospital to help contain the spread of the common cold.
In this sentence, we see examples of common nouns, such as doctor, hours, and common cold. Additionally, the sentence has an example of a proper noun– Memorial Hospital.
If the sentence were not to name the hospital specifically, then it would have remained a common noun (hospital).
Return to the top
3 Tips for Understanding Common vs. Proper Nouns
Here are some important tips to help you determine the difference between common and proper nouns:
Tip #1: If it’s a noun and it’s capitalized, then it’s probably a proper noun.
- Remember, proper nouns are specific people, places, things, or ideas. Since they represent a concrete or specific person, place, thing, or idea, they are capitalized.
- For example, book is a generic common noun.
- The Scarlet Letter is a specific book and, as a result, is a proper noun.
- There is an exception to this rule, however– if a common noun begins a sentence, then it should be capitalized since the first word of every sentence should be capitalized.
- For example, Lampshades come in many different colors, varieties, and shapes. Even though lampshades is capitalized in this sentence, it is not a specific brand or size of lampshade.
- Lampshade is capitalized because it begins the sentence, not because it is a proper noun.
Tip #2: Make sure it’s a noun.
- Do not rely solely on the capitalization of words to determine whether or not the word (or words) in question is a common or proper noun.
- There are other examples of words that can be capitalized in a sentence, such as proper adjectives. Before you classify a word as a common or proper noun, ask yourself whether or not the word or phrase in question is a person, place, thing, or idea. If it’s not, then it is not a noun.
- For example, consider the following sentence: It can be difficult for young people to read complicated, Shakespearian language. At first glance, you may quickly classify Shakespearian as a proper noun. Upon further inspection, however, Shakespearian merely describes the common noun language.
- Therefore, in this instance, Shakespearian is NOT a proper noun even though it is capitalized. Instead, it is a proper adjective.
Tip #3: When writing, ask yourself, “what message am I trying to communicate?”
- If you are using common and proper nouns in your own writing, it is important to consider what it is that you want the reader to take away from your writing.
- If you are trying to paint a clear, vivid picture for the reader, then it is important to use more proper nouns.
- However, if you are attempting to create a more general, vague scene, then using more common nouns is appropriate.
Remember, if you are trying to figure out whether a word is a common or proper noun, ask yourself if the word in question is a noun and whether or not it’s capitalized.
If you are writing, ask yourself what message you are trying to communicate before using common or proper nouns.
Return to the top
Applying the Basics: Common and Proper Noun Review & Practice
Now that you understand what common and proper nouns are, let’s review how and when to use them, and how to tell them apart! Remember, every proper noun has a common noun counterpart, but not every common noun has a related proper noun.
The Ultimate List of Common and Proper Nouns
Refer to the graphic below for an extensive list of example common and proper nouns:
This list, obviously, does not include all common and proper nouns and is meant to be used as a guide while identifying other nouns.
Common Noun Exercises & Review
Now that you know the difference between common and proper nouns, test your ability to accurately identify common nouns.
Select the common noun(s) in the sentences below. Remember, these are generic items that we encounter on a regular basis. They are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
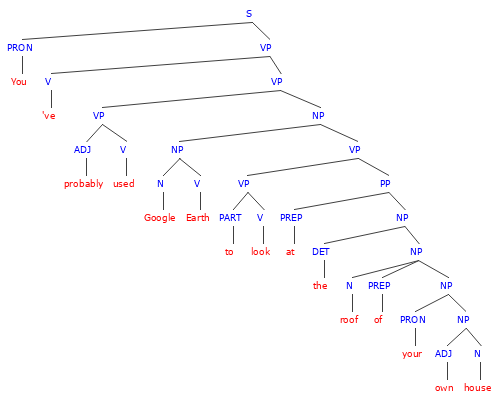
1. You’ve probably used Google Earth to look at the roof of your own house.
- In this sentence, roof and house are both common nouns because they are not specific names or titles. They are just general, making them common nouns.
2. In New York City, for example, subways chug along 500 miles of underground track.
- In this sentence, example, subways, miles, and track are common nouns because they are not specific names or titles. They are just general, making them common nouns.
3. Some people argue that the government should control what goes on underground, and private companies should not be able to profit from the land beneath your house.
- In this sentence, people, government, underground, companies, land, and house are all common nouns because they are not specific names or titles. They are just general, making them common nouns.
4. How would you feel about a public road going under your porch?
- In this sentence, road and porch are common nouns because they are not specific names or titles. They are just general, making them common nouns.
5. The way we answer these questions will help determine how our society grows and changes in the future.
- In this sentence, way, questions, society, and future are all common nouns because they are not specific names or titles. They are just general, making them common nouns.
Pro tip: When evaluating whether a noun is common, ask yourself, “Is it general, and is it in lower case?”
Return to the top
Proper Noun Exercises & Review
Complete the quick exercise below to assess your mastery of proper nouns.
Select the proper noun(s) in the sentences below. Remember, a proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized. This is true whether they begin a sentence or not.
1. In 1890, long before your great-grandparents were born, the U.S. Congress established Yosemite National Park.
In this sentence, U.S Congress and Yosemite National Park are proper nouns because they are specific names or titles. When a noun is specific like this, it is proper and must be capitalized.
2. Before becoming a national park, the Yosemite area was home to the Ahwahneechee and Miwok people for many generations.
In this sentence, Yosemite, Ahwahneechee, and Miwok are proper nouns because they are specific names or titles. When a noun is specific like this, it is proper and must be capitalized.
3. Disney’s “Pocahontas” has a similar happy tone, but the actual life of Pocahontas was more interesting than what we saw on screen.
In this sentence, Disney’s and Pocahontas are proper nouns because they are specific names or titles. When a noun is specific like this, it is proper and must be capitalized.
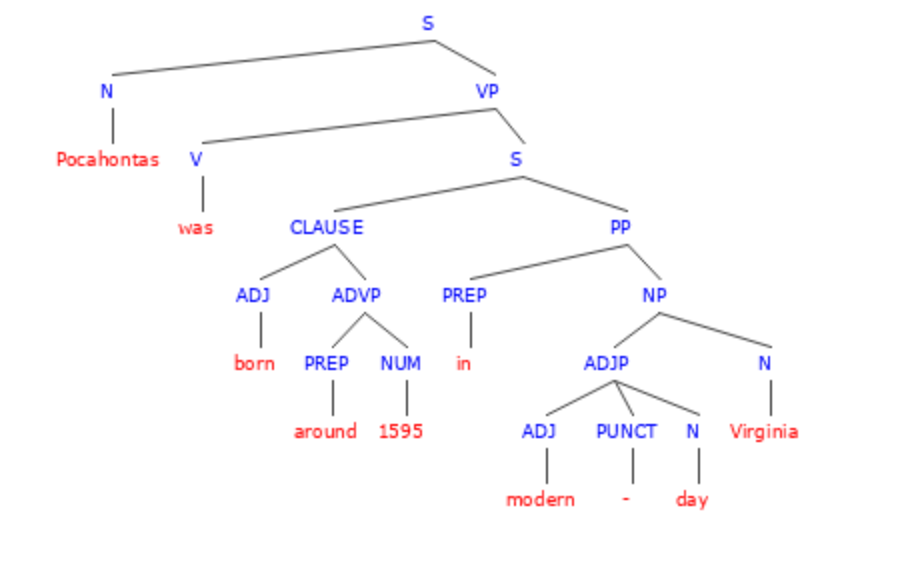
4. Pocahontas was born around 1595 in modern-day Virginia.
In this sentence, Pocahontas and Virginia are proper nouns because they are specific names or titles. When a noun is specific like this, it is proper and must be capitalized.
5. Heralded as an example of the possibilities in the “New World”, Pocahontas and John Rolfe traveled to England with their son in 1616.
In this sentence, New World, Pocahontas, John Rolfe, and England are all proper nouns because they are specific names or titles. When a noun is specific like this, it is proper and must be capitalized.
Pro tip: When evaluating whether a noun is proper, ask yourself, “Is it specific, and is it capitalized?”
For additional practice, check out Common and Proper Nouns content on Albert.
Return to the top
Try for Yourself: Common and Proper Nouns Quiz
Feeling confident in your understanding of common and proper nouns?
Take this short six-question quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Is a common noun general or specific?
- Answer: General
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
2. Is a proper noun general or specific?
- Answer: Specific
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized.
3. In this sentence, are the underlined words common or proper nouns?
Adolescent brains are constantly rewiring and retraining to prune skills that are not being used to make room for the skills being used often.
- Answer: Common
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence. Brains, skills, room, and skills are not capitalized in this example.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
4. In this sentence, are the underlined words common or proper nouns?
We enter our REM stage within the first 90 minutes of sleep and repeat this cycle several times throughout the night.
- Answer: Common
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence. In this example, stage, sleep, repeat, times, and night are all general common nouns.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a common noun is the general, non-specific term for a person, place, thing, or idea. Usually, common nouns are not capitalized unless they begin a sentence.
5. In this sentence, are the underlined words common or proper nouns?
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, plastic litter is of the greatest concern as it has the most widespread and harmful impacts on animal populations.
- Answer: Proper
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized. In this example, the Environmental Protection Agency refers to a specific government entity.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized.
6. In this sentence, are the underlined words common or proper nouns?
What does NASA’s space program cost each of the 328 million people that currently live in the USA?
- Answer: Proper
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized. In this example, NASA and USA refer to a specific organization and nation.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a proper noun is a specific, unique person, place, thing, or idea. Unlike common nouns, proper nouns are almost always capitalized.
For additional practice with common and proper nouns, check out our practice on Albert.io: Common and Proper Nouns.
Return to the top
Teacher’s Corner
While it’s true that common and proper nouns are a foundational grammar skill, the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that even elementary-level skills “require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking.”
For specific standards addressing common and proper nouns, check out the Common Core State Standards site!
Albert’s common and proper nouns practice can be used for much more than homework! Our assessments can be used as pre-and post-tests to measure student progress. Our pre-made quizzes can be used as bell-ringers, exit tickets, and more!
In addition to our pre-made assessments, you can also use our assignments feature to create your own quizzes and assessments.
Summary on Common and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are general, non-specific people, places, things, or ideas.
Proper nouns are specific, concrete people, places, things, and ideas.
In writing, proper nouns generally provide the reader with a more clear, tangible image of what the author describes.
Common and proper nouns can be used in tandem with one another or separately. Be sure to check out our grammar course for more common and proper noun practice.
You can also access over 3,400 high-quality questions that address nearly every grammatical concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.
The Standard Definition of a Noun
Many people define a noun simply as a word that names a person, place, thing, or concept (e.g., Tom, library, monkey, and freedom).
However, not all such words are always nouns.
For example, depending on how it is used in a sentence, monkey might not be a noun. In the phrase, “The kids often monkey around,” monkey is a verb. And if someone asks you to pass them a monkey wrench, they’ve used monkey as an adjective.
Three Types of Nouns
A good place to begin discussion about what actually makes a word a noun is with a quick explanation of the three types of nouns. Nouns can be categorized into three basic groups: common nouns, proper nouns, and pronouns.

A common noun is a word used to identify a person, place, or thing (e.g., girl, tower, movie). However common nouns do not give the name of one specific person, place, or thing. That is the job of a proper noun (e.g., Rosie, the Eiffel Tower, Back to the Future). A person, place, or thing can also be identified by using a pronoun. A pronoun is a single word that substitutes for either a common noun or a proper noun (e.g., I, he, she, it, they).
Properties of Nouns
It is not entirely accurate to classify a word as a noun simply because it names something. A more precise definition is needed. A noun should be thought of as a word that, given its purpose in a sentence, has most or all of the properties of nouns,¹ which are as follows:
A noun can be pluralized without making a sentence confusing.
The sentences, “The monkey climbed up the tree,” and “The monkeys climbed up the tree,” both make perfect sense. This is an indicator that monkey is a noun as it is used in this sentence.
Monkey cannot be pluralized in “The kids often monkey around.” “The children continued to monkeys around” is an ungrammatical expression.
A noun can be preceded by the articles “the” or “a.”
Our example, “The monkey climbed up the tree,” shows this property in action. If a word cannot be preceded by the in a phrase, that word is probably not a noun. Monkey cannot be a noun in “The kids often monkey around” because “The kids often the monkey around” is not proper English.
It is important to note that the word the or a does not need to immediately precede a noun for the noun to have this property. Often, adjectives are placed between articles and their corresponding nouns, such as in “The short, hairy monkey climbed up the tree.”
This property is sometimes tricky to spot. For instance, in the phrase, “The monkey wrench was too small for the job,” it might appear as though monkey is a noun because it is preceded by the. However, monkey is an adjective in this sentence. Notice that the first property of nouns does not apply to monkey this phrase — “The monkeys wrench were too small for the job” is incorrect.
A noun can be preceded by adjectives.
We will again look at the sentence, “The monkey climbed up the tree.” Monkey is a noun because it can be modified by adjectives, as in the example we saw earlier: “The short, hairy monkey climbed up the tree.” Monkey cannot be a noun in “The kids often monkey around” because it is not grammatically correct to put adjectives in front of it. “The kids often short, hairy monkey around” is nonsense.
As with the previous property, this one can be deceiving sometimes, as words that are not nouns occasionally appear to be preceded by adjectives. In the sentence, “They would slow dance to their favorite song,” it looks like dance follows an adjective (slow). However, dance is a verb in this sentence because “They would a slow dance to their favorite song” and “They would slow dances to their favorite song” are improper English. Because dance is not a noun in this sentence, slow is not an adjective but rather an adverb.
A noun functions as the head of a noun phrase.
An example of a noun phrase is “the small, funny monkeys” as it appears in “We watched the small, funny monkeys.” We can be sure the underlined string of words in this sentence is a noun phrase because all of these words describe the noun monkeys (which we know is a noun because it is pluralized and preceded by adjectives and the word the).
If we strip all the words except for monkey from the phrase, the sentence retains its meaning, simply with less detail: “We watched monkeys.” Sentences that contain other segments from the noun phrase do not make sense: “We watched the funny.” Thus, it is without question that the string of words revolves around the word monkeys. For this reason, we say that monkeys is the head of this noun phrase.
Any word that serves as the head of a noun phrase is always a noun even if it does not have all of the other characteristics of a noun. Conversely, if a word does not head a noun phrase, it is not a noun even if has other characteristics of a noun. Because of this, proper nouns and pronouns are considered nouns even though they often do not have all the properties of nouns.
Proper Nouns vs.Pronouns
Proper nouns have only the third and fourth properties of nouns from the list given above. Meanwhile, pronouns have only the fourth property. Nonetheless, this is enough to make these words nouns according to most grammarians.
The proper noun John is a noun in “Big John plays baseball.” John is the head of a noun phrase in this sentence, and so John is a noun even though “The big John plays baseball” and “Big Johns play baseball” are not grammatical.
The pronoun he, by itself, is a noun phrase in the sentence, “He plays baseball.” Therefore, he is a noun in this sentence even though “The he plays baseball,” “Hes play baseball,” and “Big he plays baseball” are all incorrect.
Because pronouns share so few properties with nouns, some view pronouns as being a part of speech of their own rather than being a subgroup of the noun word class. The next article in this series discusses pronouns in detail.
Nouns that Don’t Look Like Nouns
We now have a more accurate idea of what a noun is, and we can classify more words as nouns than we would if we were to use the standard definition given at the beginning of this article. For instance, consider the word run, which as an “action word” is generally thought to be a verb.
Prior to reading this article, you may have thought the word run is a verb in the sentence, “I will not have time for a run.” However, run is a noun in this sentence. Notice that it has all the properties of a noun:
-
Run can be pluralized without creating an ungrammatical sentence: “I will not have time for runs.”
-
Run is preceded by an article: “I will not have time for a run.”
-
Run could have adjectives placed in front of it: “I will not have time for a long, grueling run.”
-
Run is the head of the noun phrase, “a run.”
To simply define a noun as a word that names a person, place, thing, or concept is not always accurate. Hopefully, this article has shown you how to identify nouns in any sentence and how to avoid misidentifying other kinds of words as nouns.
¹Pronouns and proper nouns are exceptions — they are nouns despite not having most of these properties
Reference:
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Classification of Nouns :
A Noun is a word used for naming some person or thing.
Book
Computer
Abraham
Holiness
River
Letters
Country
India
America
England
Mouse
House
School
Teacher
Road
These are nouns which denote either persons or things or concepts.
Nouns are of five different kinds.
1. Proper
2. Common
3. Collective
4. Material
5. Abstract
Proper Nouns
A Proper Noun is used for one particular person or thing as different from every other as
James (a person)
Ganges (a river)
Lucknow (a city)
India (a country)
The writing of a Proper Noun should always be commenced with a capital letter.
Common Nouns
A Common Noun denotes no one person or thing in particular, but is common to any and every person or thing of the same kind as man, book and country.
Thus…
The word Man need not be used to point out any particular man, such as Kaja but could be used for any and every man.
River does not point out any particular river such as Ganges, but can be used for any and every river.
Country does not point out any particular country, such as India, but can be used for
any country in any part of the world.
A Proper Noun becomes a Common Noun when it denotes a class of persons or things and is used in a descriptive sense.
He is the Newton of the age. That is…the greatest astronomer of the age.
Collective Nouns
A Collective Noun denotes a group or collection of similar individuals, considered as one complete whole. For instance, there may be many sheep in a field, but only one flock. Here sheep is a Common Noun, because it may stand for any and every sheep. But FLOCK is a Collective Noun. Because, it stands for all the sheep at once and not
for any one sheep taken separately.
Every Collective Noun is also a kind of Common Noun.
Thus the term FLOCK may stand for many different flocks (or groups of sheep).
CLASS may stand for many classes (or groups of students).
Nouns of Multitude
There is a difference between a Collective Noun and a Noun of Multitude.
A Collective Noun denotes one undivided whole and hence the Verb following is Singular.
A jury consists of twelve persons.
Nouns of Multitude denote the individuals members of the group and hence the Verb is taking Plural, although the Noun is Singular.
The jury (the men on the jury) were divided in their opinions.
Material Nouns
A Noun of Material denotes the matter or substance of which things are made.
Thus sheep is a Common Noun. But mutton (or the flesh of sheep) is a Material Noun.
The same word can be a Material Noun or a Common Noun according to the context.
Fish live in water.
Fish is good for food.
In the first sentence the Noun denotes individual fish or fishes and is therefore a Common Noun.
In the second it denotes the matter of which the bodies of fish are made and is therefore a Material Noun.
Abstract Nouns
An Abstract Noun speaks of the condition of quality, state or action, apart from anything possessing the quality, etc.
She has beauty. Here the word SHE is a noun where as BEAUTY is an abstract noun.
Quality — Cleverness, height, humility, roguery, colour….
State — Poverty, manhood, bondage, pleasure, youth….
Action — Laughter, movement, flight, choice, revenge…..
The kinds of nouns (four types) described above all speak about the objects of sense, that
is, to things which can be seen, touched, heard, smelt or tasted in a word perceived by the senses.
But an Abstract Noun speaks about the qualities and states which cannot be seen or touched and which are thought of apart from any object of sense.
We know that a stone is hard. We also know that iron is hard. We also know that a hammer is hard. We can therefore speak of hardness apart from stone or iron or hammer or any other object having the same quality.
Abstract means drawn off (abstracted in thought) from the object.
Hence hardness is an Abstract Noun while stone or brick or iron is a Material Noun.
The names of Arts and Sciences (e.g., philosophy, music, chemistry, etc.) are also Abstract Nouns.
RELATED PAGES :
- The Noun
- Kinds of Nouns
- Kinds of Nouns in English
- Types of Nouns in English
- Correct Usage of Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Nouns of Multitude
- Material Nouns
- Compound Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
- Count Nouns
- Mass Nouns
- Pronouns
- Abstract Nouns formed from Adjectives
- Abstract Nouns formed from Common Nouns
- Abstract Nouns formed from Verbs
- Abstract Nouns of the same form as Verbs
- Absolute Phrases
- Noun and Gender
- Nouns and Gender
- Masculine Nouns and Feminine Nouns
- Masculine Nouns
- Feminine Nouns
- Ways of forming the feminine of nouns
- Exceptional Masculine Nouns and Feminine Nouns
- Exceptional Feminine Nouns
- Foreign Feminine Nouns
- Nouns in Common Gender
- Common Gender Nouns
- Neuter Pronouns
- Neuter Gender Nouns
- Gender of Personified Things
- Noun and Case
- Kinds of Cases in English
- Noun and Number
- Singular and Plural
- Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns
- Ways of forming plurals
- Formation of Plurals
- Compound Nouns and Plurals
- Noun Infinitive
- Noun to Verb
- The Noun
Classification of Nouns :
Classification of Nouns To HOME PAGE
The Sentences Index
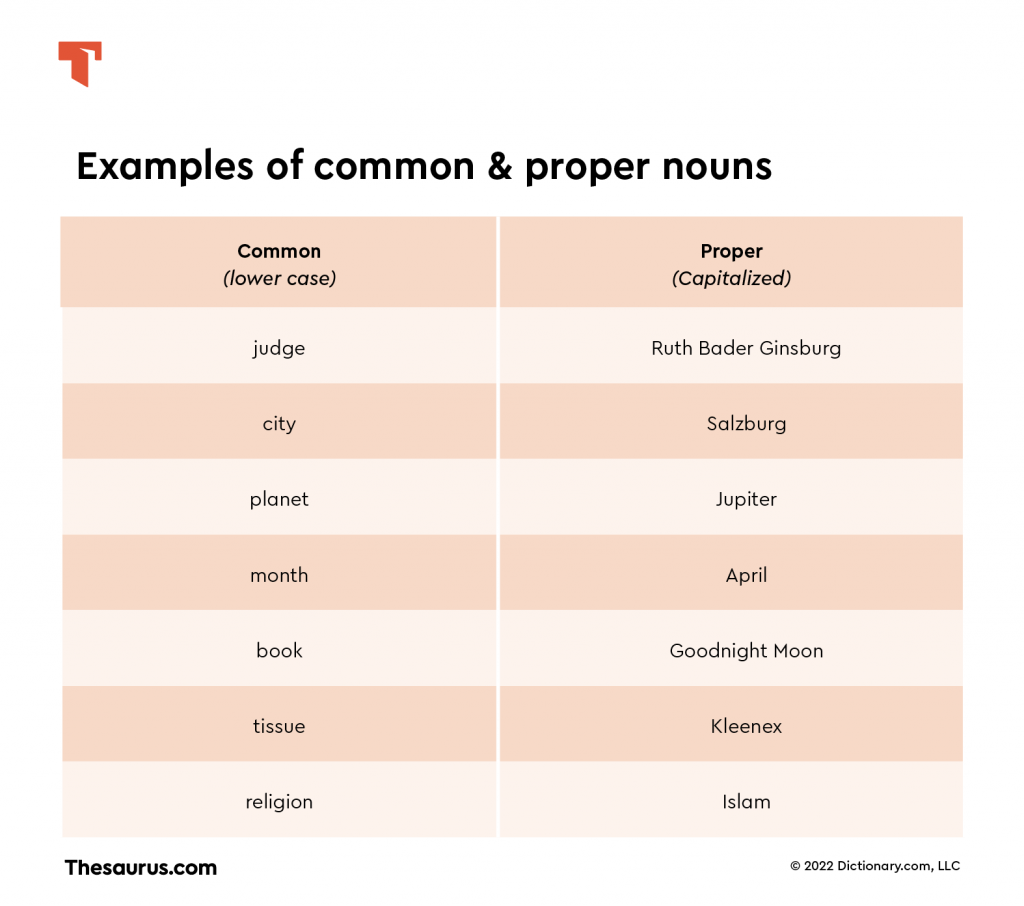
A noun is a word that refers to a person, place, thing, or idea. We use nouns to refer to general things like friends or pizza and specific things like Leonardo Da Vinci or Canada. We use a lot of different nouns like these to describe everything around us, but all of the nouns we use can be separated into just two different types: common nouns and proper nouns.
Common noun vs. proper noun
The difference between a common noun and a proper noun is what type of thing they are referring to. Common nouns refer to generic things while proper nouns refer to specific things. For example, the noun country is a common noun because it refers to a general, non-specific place. On the other hand, the noun Spain is a proper noun because it refers to a specific country located in Europe (another proper noun). Grammatically, there is one main difference between common and proper nouns: proper nouns are always capitalized whereas common nouns are only capitalized in very specific situations.
Common nouns
As has been said, common nouns refer to generic people, places, and things. You’ll more easily understand what we mean by this with some examples.
Examples of common nouns
Common nouns can refer to people, places, things, and ideas.
- People: man, woman, child, cop, criminal, butcher, baker, neighbor, friend, enemy, person, stranger, judge, jury, executioner, knights, bishops, kings, queens
- Places: city, town, country, neighborhoods, islands, beaches, province, state, outside, upstairs, basement, hallway, lobby, rooms, alleys, campsites
- Things: guitar, drums, apples, oranges, snow, rain, ice, fire, dirt, cars, trucks, knee, elbows, food, water, sky, stars, day, weeks, month, years
- Ideas, emotions, concepts: happiness, sadness, fear, courage, questions, answers, government, chaos, hunger, confusion, doubt, loneliness, friendship, science
Want a closer look at common nouns? Set your sights on this handy article about them!
Proper nouns
Proper nouns can also refer to people, places, things, and ideas. However, proper nouns refer to more specific people and things.
Examples of proper nouns
As you read each of these proper nouns, you can test your understanding of common nouns. Can you think of a common noun that could also refer to each item referred to by a proper noun?
- People: Harriet Tubman, King Richard the Lionheart, Miles Davis, Emily Dickinson, Helen of Troy, Superman, Lady Gaga, Captain Crunch
- Places: New York City, Moscow, Cairo, Portugal, Zimbabwe, Peru, Europe, Asia, Australia, Main Street, Rocky Mountains, Colorado River, Sahara Desert
- Things: Jupiter, Google, Twitter, Kawasaki Ninja, Playstation 5, Star Wars, Band-aids, Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, Apollo 13, Great Wall of China
- Ideas and Concepts: Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Romanticism, Cubism, Industrial Revolution, Dark Ages, Monday, November
How do you use common and proper nouns?
Grammatically, the biggest difference between common and proper nouns has to do with capitalization. Proper nouns are always capitalized no matter where they appear in a sentence. One exception to this rule is brand names that use lowercase letters for stylistic reasons: the word iPad is a proper noun even though the first letter is lowercase.
Common nouns, on the other hand, are only capitalized at the beginning of sentences or when used in the title or name of something. For example, the word captain is a common noun and will be lowercase in most sentences. However, it has a capital letter when it is used in a title such as in the name Captain Hook.
Both common and proper nouns are used in most of our sentences. For the most part, it is pretty easy to use them, but you should be careful to always capitalize proper nouns and to only capitalize a common noun when it is appropriate to do so.
Visit the full discussion on proper nouns at our article dedicated to them here.
Tips for differentiating common vs. proper nouns
If you are trying to determine if a word is a common or proper noun, look at the capitalization. Is the noun capitalized in the middle of a sentence? If so, you most likely have a proper noun. Things are trickier if the noun is the first word in the sentence. In that case, ask yourself if the noun is referring to a specific person or thing. If it is, you have a proper noun again. If it isn’t, you are instead looking at a common noun. A good rule of thumb is that all names and titles are proper nouns and will always be capitalized.
Let’s test to see if you have mastered common and proper nouns. Read the following sentences and see if you can figure out if the nouns are common or proper nouns.
- We went to school yesterday.
- We learned about the history of France.
- Jennifer is my older sister.
- She likes to read novels by Stephen King.
Finally, look at these example sentences and see if you can find the three mistakes involving common and proper nouns. (You can find the answers at the end of this article.)
- My favorite American president is theodore roosevelt.
- I like all kinds of animals. dogs are the cutest of them all.
- When we went to Arizona, I took tons of pictures of the Grand canyon.
No more grammar errors
We’ve got a noun for you: genius! And that’s what you’ll be when you check your writing on Thesaurus.com’s Grammar Coach™. This uncommon tool can definitely spot the difference between your proper and common nouns—and more! Grammar Coach™ uses machine learning technology uniquely designed to catch grammar and spelling errors. Its Synonym Swap will find the best nouns, adjectives, and more to help say what you really mean, guiding you toward clearer, stronger, writing.
Whether you’re writing about a person, place, or thing, perfect grammar has never been easier!
Answers: Theodore Roosevelt, Dogs, Grand Canyon
If you want more of a challenge, head over to our quiz on common vs. proper nouns.
In this post, you will learn about common noun definition, examples, lists, and exercises.
Let’s take a dive into it!
- Definition
- Common Noun Examples
- Types of Common Noun
- Common Nouns List
- Common Noun Vs Proper Noun
- Exercise
Definition
A common noun is a generic word used to denote a thing, a place or a person.
The common noun is capitalized if it comes at the start of the sentence. It can be abstract, collective or concrete.
You can see it every where around you like, house, road, bike etc.
For example,
- A car is moving on the road.
- My house is located in the mid of the city.
- I am sitting on a chair.
A noun is categorized into two main types i.e. common noun and proper noun.
The common noun denotes things generally while proper nouns are the specific names of the things, places, or person.
Common Noun Examples
Look at the following examples. The bold word indicates a common noun in each example.
- I bought a laptop yesterday.
- Michael lives in Sydney. He is my fast friend.
- Fiji is a beautiful island. It is a great place to visit.
- I see a lot of people in the park every morning.
- She bought some new utensils.
- He is a humble man.
- The sailor is rowing the boat.
- My house is one kilometer away from the park.
- Santah is reading a novel.
- He has been living in this city for 10 years.
Types of Common Noun
Possessive common noun
Possessive common noun shows the ownership of a common noun, it can be quality, thing or idea. We use apostrophe and ‘s’ with the common noun. For example, man’s fate, bike’s color.
Singular common noun
A singular common noun indicates a single person, thing, or place. For example, a desk, a chair, or a man.
Plural common noun
Plural common noun shows plural items like chairs, desks, persons or places.
Common Nouns List
Here is a category wise list of common nouns
People
- aunt
- businessman
- daughter
- son
- brother
- sister
- mother
- father
- president
- salesman
- man
- woman
Animals
- bird
- elephant
- lion
- cat
- dog
- reptile
- mammal
Places
- forest
- park
- road
- countryside
- sea-shore
- city
- state
- house
- office
Things
- bed
- chair
- fan
- table
- bottle
- glass
- pencil
- book
- computer
- laptop
- utensils
Feelings
- love
- hate
- angry
- pride
Common Noun Vs Proper Noun
It is very easy to distinguish between a common noun and a proper noun. By reading these easy to understand the difference, you will be able to distinguish between a common noun and a proper noun.
| Common Noun | Proper Noun |
|---|---|
| The generic word used to name a thing, a person, or a place. | The specific name of a person, a place, or a thing. |
| A common noun is a lowercase word. It is capitalized only when comes at the start of the sentence. | Proper nouns are always capitalized whether we write at the start of a sentence or at the beginning. |
| These are general names. | These are specific names. |
| Not every common noun has a proper noun. For example, hate ->? |
Every proper noun has a common noun. For example, Jon->Man |
| Examples: man, women, city, country | Examples: Washington DC, Diana, Michael |
Exercise
Find the common noun in the given sentences.
- Laura baked the cookies. ( __________ )
- The cat was sitting under the table. ( __________ )
- I have a large collection of books. ( __________ )
- She takes fresh juice every morning. ( __________ )
- Tom loves to ride the horse. ( __________ )
- He reads the newspaper every morning. ( __________ )
- In which country do you live? ( __________ )
- Her mother bought him a beautiful present. ( __________ )
- Bob is a very good painter. ( __________ )
- I was flying the kite yesterday. ( __________ )
Answers
- cookies
- cat, table
- books
- juice
- horse
- newspaper
- country
- mother, present
- painter
- kite

Further Reading
- What is a noun? Types of nouns with examples
- 50 Sentences of Nouns
- Common and proper nouns
- Parts of Speech Guide for Beginners