Is the word everywhere a preposition?
Everywhere is an adverb of place, and adverbs cannot be object of prepositions, as it is in your sentence: in everywhere.
Which type of pronoun is everywhere?
Indefinite pronouns
| Person | Place | |
|---|---|---|
| All | everyone everybody | everywhere |
| Part (positive) | someone somebody | somewhere |
| Part (negative) | anyone anybody | anywhere |
| None | no one nobody | nowhere |
What is the plural form of everyone?
Normally, everyone doesn’t have a plural. You treat it as a singular that refers to multiple people. Though Alice and Bob run home, everyone runs home. If you’d rather use something that conjugates as though it is a plural, you could use “they all” or some similar construction.
What type of word is everyone’s?
indefinite pronouns
What is used with everybody is or are?
The right answer is Everyone is. ‘Everyone’ is a single pronoun. We use everyone as a single group, so everyone takes a single verb.
Is it you’ll or Y all?
The only right way to spell the contraction of “you” and “all” is “y’all.” “Ya’ll” is incorrect and a misspelling of the word, so don’t use it. When you think about it, though, “y’all” makes the most sense for how this contraction should be correctly spelled.
How are you all is correct sentence?
“How are all of you?” is correct English. In the USA, it would be considered somewhat formal. “How are you all?” (or in the South “How are y’all?”) is more common and less formal.
What can I say instead of you all?
What is another word for you all?
| you | cha |
|---|---|
| y’all | ye |
| you gals | you guys |
| you lot | you-uns |
| all y’all | all of you |
What word can replace yall?
What is another word for y’all?
| all of you | all y’all |
|---|---|
| you guys | you lot |
| youse | cha |
| chu | yah |
| youz | yer |
How do you say yall formally?
While “y’all” is actually a contraction for “you all” and is therefore technically correct, it is most commonly used in place of the plural form of “you.” The apostrophe after the “y” represents the lost “ooo” sound from the letters O and U. This explains why the sometimes-seen “ya’ll” spelling is wrong.
Whats another word for all?
What is another word for all?
| everybody | everyone |
|---|---|
| the whole lot | every one |
| every single one | each and every one |
| one and all | all and sundry |
| each one | public |
Wiki User
∙ 9y ago
Best Answer
Copy
No. Everywhere is an adverb (in all places). It cannot be a
preposition.
Wiki User
∙ 9y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: Is everywhere a preposition
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
Everywhere
Everywhere adverb — In every place or in all places.
Usage example: freedom and happiness are the goals of people everywhere
Throughout
Throughout adverb — In every place or in all places.
Usage example: a cake studded throughout with raisins
Everywhere is a synonym for throughout in all over topic. You can use «Everywhere» instead the word «Throughout» as an adverb or an adjective or a preposition, if it concerns topics such as during the whole of. popular alternative
Google Ngram Viewer shows how «everywhere» and «throughout» have occurred on timeline
Is the sentence below grammatical?
There are a lot of people, with many wearing tuxedos.
There are some cute teenage girls in the club, with many of them being PhD graduates in topological field theory.
I check through my dictionary and don’t see a definition of with that makes the above sentence legit.
with wɪð preposition preposition: with
accompanied by (another person or thing). «a nice steak with a bottle of red wine» synonyms: accompanied by, in the company of,
escorted by «she’s gone out with her boyfriend»having or possessing (something). «a flower-sprigged blouse with a white collar» wearing or carrying. «a small man with thick glasses»
indicating the instrument used to perform an action. «cut the fish with a knife» indicating the material used for a purpose. «fill the
bowl with water»in opposition to. «a row broke out with another man»
indicating the manner or attitude in which a person does something. «the people shouted with pleasure»
indicating responsibility. «leave it with me»
in relation to. «my father will be angry with me» affected by (a particular fact or condition). «he’s in bed with the flu» indicating
the cause of (a condition). «he was trembling with fear» because of
(something) and as it happens. «wisdom comes with age»employed by. «she’s with the Inland Revenue now» using the services of. «I bank with the TSB»
in the same direction as. «marine mammals generally swim with the current»
indicating separation or removal from something. «to part with one’s dearest possessions»
cf. ODO
So my questions are:
1] can I use «with» this way?
There are partial differential equations on this paper, with many of them having no real solutions.
2] or with an adjective?
There are deuterium atoms in this jar, with many/some of them ionized.
3] or without «of them»?
There are grey goos everywhere, with many/some consuming the haemocoels of tardigrades.
asked Aug 14, 2014 at 23:51
THE COMMENT GUYTHE COMMENT GUY
7375 gold badges12 silver badges30 bronze badges
While RHK Webster’s lists the above usage of ‘with’ as a prepositional one, it flags the peculiar usage, calling it a ‘function word’. Though this is rather misleading (all prepositions lie somewhere along the lexical word — function word continuum, their actual location dependent on the actual context they’re used in), RHKW are right to imply that this is a very marginal use even for a preposition. They don’t even attempt to give a definition of this sense of ‘with’ other than an explanation of the use to which it is put in a context:
(17.) (used as a function word to specify [introduce] an additional
circumstance or condition): We climbed the hill, with Jeff following
behind.
It is almost always more idiomatic to drop the ‘with’ and use the remaining absolute construction. The RHKW example is unusual in that the inclusion of the ‘with’ sounds slightly more natural, if anything; this is probably due to the lack of semantic cohesion between the main clause and the absolute clause. Two sentences would (unless previous context linked the clauses more closely) be equally appropriate, with little change even in emphasis: We climbed the hill. Jeff followed behind. Of course, stylistically, this is more staccato.
answered Aug 15, 2014 at 9:02
Edwin AshworthEdwin Ashworth
74.3k11 gold badges138 silver badges235 bronze badges
The manner of with used in your sentences is
2. having or possessing (something). «a flower-sprigged blouse with a white collar» wearing or carrying. «a small man with thick glasses»
You write:
There are a lot of people, with many wearing tuxedos.
I find this construction a little bit odd, but I doubt that it’s ungrammatical. More commonly I’d expect to hear
There are a lot of people, many in tuxedos.
Andrew Leach♦
98.3k12 gold badges188 silver badges306 bronze badges
answered Aug 15, 2014 at 0:01
anongoodnurseanongoodnurse
54.9k16 gold badges125 silver badges204 bronze badges
2
In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
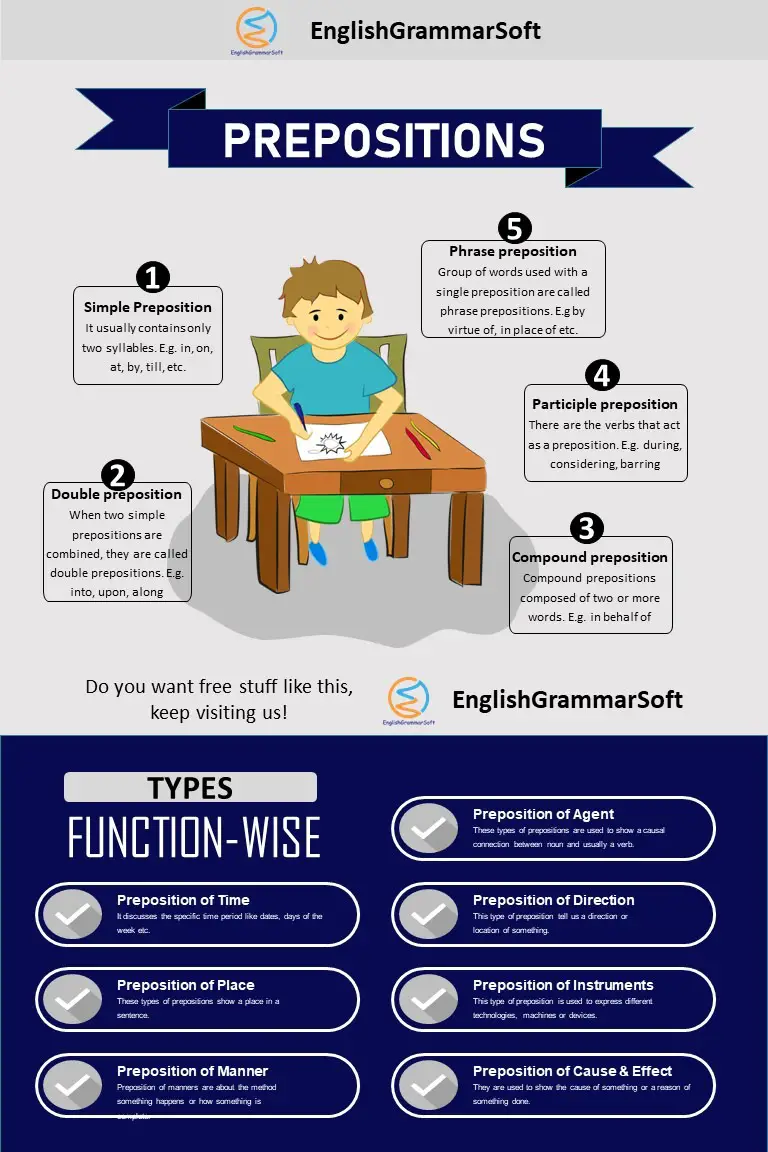
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions