DO – DOES – DID – DONE
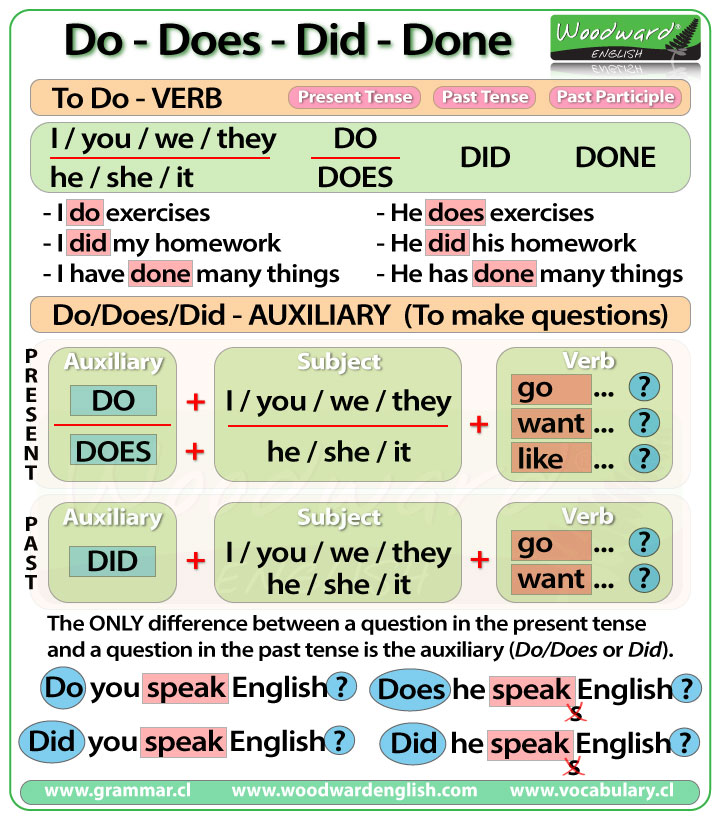
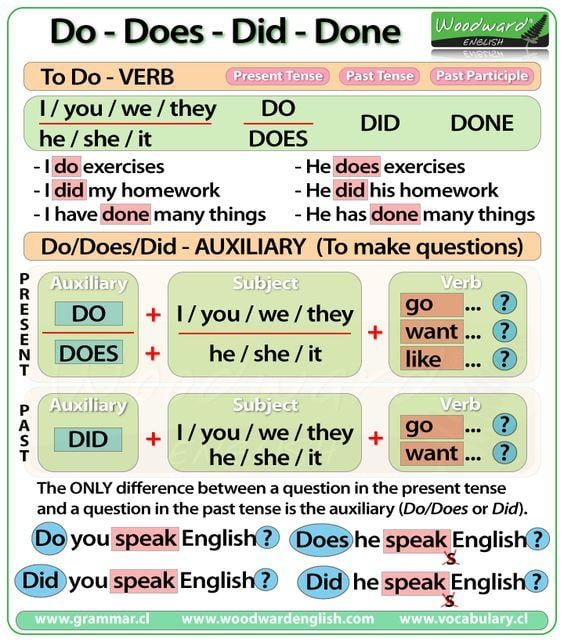
The word DO appears a lot in English.
This is because it can be a verb, as in the verb TO DO which can be conjugated as Do and Does in the present tense, Did in the past tense and Done as a past participle.
DO can also be an AUXILIARY verb in the form of Do / Does to make questions in the present tense and Did to make questions in the past tense.
Let’s look at each one in more detail. We will start with the verb TO DO.
As we have seen, the verb TO DO has four forms: Do / Does / Did and Done
Lets look at its form in the simple present tense.
TO DO – Present Tense
With the verb TO DO in the Present Tense…
We say: I do / you do / we do / they do
But we say: he does / she does / it does
Let’s look at some example sentences:
- I do my laundry on Saturdays.
(Do my laundry means I wash my clothes, well, I put in the washing machine)
- They do their chores when they arrive home.
(Chores is the housework you need to do like washing the dishes, doing the vacuuming, etc.)
- He does nothing all day. (That’s right… he is quite lazy, he does absolutely nothing.)
- She does charity work when she has time. (People that do charity work are superheroes)
TO DO – Past Tense
The simple past tense of DO is DID for all subjects:
I did / you did / we did / they did / he did / she did / it did
Notice how there is only one form of the verb in the past tense…. DID.
- He did a magic trick. (Yes, and everyone was amazed… wooow!)
- The baby did a fart. (Yes, and the smell made everyone cry. How can such a cute thing produce something so rotten.)
- I did my homework in record time. (Yes, it only took me 5 hours instead of 10)
- She did ballet after school last year. (This year she is doing something different)
TO DO – Past Participle
The past participle of DO is DONE. Remember that past participles are accompanied by a conjugation of the verb TO HAVE or TO BE (which means it is in the correct tense according to the subject)
In general Have + past participle is used with a perfect tense and BE + past participle is with the passive voice.
Let’s look at some examples:
- I have done my homework.
- He has done a good job.
These two sentences are in the present perfect tense because they have have or has before the past participle done.
- The video will show you how it is done.
- The report was done on time.
Here we used a conjugation of the verb To Be before the past participle done.
TO DO – To replace a verb
We sometimes use the verb DO to replace a verb when the meaning is clear or obvious. This replacement is more common in informal spoken English:
- Have you done the dishes yet?
(Here done means washed)
- I’ll do the kitchen if you do the lawns
(The first do means clean – The second do means mow)
Sometimes Do, Does, and Did are used as auxiliaries to make questions in English.
Let’s start with DO and DOES:
DO / DOES – For Questions
To make a question in the simple present tense in English we normally put the auxiliary Do or Does at the beginning of the question before the subject.
After the subject is the verb in its base form which means the infinitive without TO at the beginning.
Look at this affirmative sentence:
- You speak English.
How can we make this a question? We add DO at the beginning so it becomes:
- Do you speak English?
You will see that we add DO at the beginning when the subject is I, you, we or they.
But look at this affirmative sentence:
- He speaks Arabic.
To make this a question we say:
- Does he speak Arabic?
You can see that we add DOES at the beginning when the subject is he, she or it.
Notice how the letter S at the end of the verb in the affirmative sentence (because it is in third person) disappears in the question. That is because the verb is in the base form of the infinitive.
NOTE: We DON’T use Do or Does in questions that have the verb To Be or Modal Verbs (can, must, might, should etc.)
DID – For Questions
Let’s look at the auxiliary DID.
To make a question in the Simple Past Tense in English we normally put the auxiliary DID at the beginning of the question before the subject.
And just like in the present tense, After the subject is the verb in its base form which means the infinitive with TO at the beginning.
Look at this affirmative sentence:
- You lived in Spain.
How can we make this a question? We add DID at the beginning so it becomes:
- Did you live in Spain?
We use the verb form Live and NOT lived because the auxiliary DID show that the question is in the past tense.
Did is also used with He, She and It. So with this affirmative sentence:
- She lived in Japan.
To make it a question in the past tense we say:
- Did she live in Japan?
Again we use DID for questions in the past EXCEPT with To Be and Modal Verbs such as Can.
Compare these questions:
- Do you speak English?
- Did you speak English?
The only difference between a question in the present tense and the past tense is the first part… DO or DID.
And look at these two questions
- Does he speak Italian?
- Did he speak Italian?
The only difference between a question in the present tense and the past tense when it refers to third person (he, she, or it) is the first part… DOES or DID.
Auxiliary and Verb together
Look at this question:
- Do you do exercises every day?
Why are there two DOs in this question?
The first DO is necessary because we are making a question in the simple present tense.
The second DO is from the verb TO DO. You DO exercises.
What happens if instead of YOU we are asking about another person?
- Does she do exercises every day?
We use DOES because it is necessary for simple present tense questions for third person, in this case for SHE. Does she….?
Again DO appears because you DO exercises. It appears as DO and not DOES because the verb needs to be in the base form of the infinitive.
Of course in the past tense you would say:
- Did you do exercises yesterday?
Did is an auxiliary which is needed to make a question.
Do is from the verb To Do.
DO and DOES – For Emphasis
Sometimes Do / Does / Did are used in positive sentences to give special emphasis that what you say is true, despite what the other person thinks. Note that when speaking, the word (do/does/did) is stressed.
- I do want to go. (We put stress on the word DO to emphasize that we really want to go, even if you think it is not true.)
- I did study for the test. (Contrary to what you may believe… yes, I studied)
Notice that Did is used for positive sentences in the past tense and that the main verb is in its base form.
- Yes, he does like broccoli. (You may be surprised but yes, he likes broccoli)
- You do need tickets for the event. (I am emphasizing that fact that tickets ARE needed despite what you think.)
Summary Chart
| 1. | Base Form (Infinitive): | Do |
| 2. | Simple Past: | Did |
| 3. | Past Participle: | Done |
| 4. | Present Participle: | Doing |
| 5. | 3rd Person Singular: | Does |
| Did |
| Did is the past tense of the word do. |
Do past participle
| Done |
| Done is the past participle of the word do. |
Do verb forms V1 V2 V3 V4
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle | Present Participle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do | Did | Done | Doing |
Conjugation of Do
| Simple / Indefinite Present Tense |
| I do homework. |
| He/She/It does homework. |
| You/We/They do homework. |
| Simple Past Tense |
| I did homework. |
| He/She/It did homework. |
| You/We/They did homework. |
| Simple Future Tense |
| I will/shall do homework. |
| He/She/It will do homework. |
| You/We/They will/shall do homework. |
| Present Continuous Tense |
| I am doing homework. |
| He/She/It is doing homework. |
| You/We/They are doing homework. |
| Past Continuous Tense |
| I was doing homework. |
| He/She/It was doing homework. |
| You/We/They were doing homework. |
| Future Continuous Tense |
| I will be doing homework. |
| He/She/It will be doing homework. |
| You/We/They will be doing homework. |
| Present Perfect Tense |
| I have done my homework. |
| He/She/It has done my homework. |
| You/We/They have done my homework. |
| Past Perfect Tense |
| I had done my homework. |
| He/She/It had done my homework. |
| You/We/They had done my homework. |
| Future Perfect Tense |
| I will have done my homework. |
| He/She/It will have done my homework. |
| You/We/They will have done my homework. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
| I have been doing my homework. |
| He/She/It has been doing my homework. |
| You/We/They have been doing my homework. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
| I had been doing my homework. |
| He/She/It had been doing my homework. |
| You/We/They had been doing my homework. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense |
| I will have been doing my homework. |
| He/She/It will have been doing my homework. |
| You/We/They will have been doing my homework. |
More verb past tense
- Drag
- Draw
- Dream
- Drink
- Drive
Таблица неправильных глаголов
В английском языке глаголы делятся на правильные и неправильные. Неправильные глаголы — это такие глаголы, у которых форма прошедшего времени ( Past tense form ), а также форма причастия прошедшего времени ( Past participle ) образуется не так, как у правильных глаголов. Правильные глаголы образуют эти формы путём прибавления –ed к первой форме. Подробнее про глаголы.
Нет общего правила для неправильных глаголов. Их нужно просто выучить.
| Base form | Past simple | Past participle | Перевод |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | |||
| arise | arose | arisen | возникать, появляться |
| awake | awakened / awoke | awakened / awoken | будить, проснуться |
| B | |||
| backslide | backslid | backslidden / backslid | отказываться от прежних убеждений |
| be | was, were | been | быть |
| bear | bore | born / borne | родить |
| beat | beat | beaten / beat | бить |
| become | became | become | становиться, делаться |
| begin | began | begun | начинать |
| bend | bent | bent | сгибать, гнуть |
| bet | bet / betted | bet / betted | держать пари |
| bind | bound | bound | связать |
| bite | bit | bitten | кусать |
| bleed | bled | bled | кровоточить |
| blow | blew | blown | дуть |
| break | broke | broken | ломать |
| breed | bred | bred | выращивать |
| bring | brought | brought | приносить |
| broadcast | broadcast / broadcasted | broadcast / broadcasted | распространять, разбрасывать |
| browbeat | browbeat | browbeaten / browbeat | запугивать |
| build | built | built | строить |
| burn | burned / burnt | burned / burnt | гореть, жечь |
| burst | burst | burst | взрываться, прорываться |
| bust | busted / bust | busted / bust | разжаловать |
| buy | bought | bought | покупать |
| C | |||
| can | could | could | мочь, уметь |
| cast | cast | cast | бросить, кинуть, вышвырнуть |
| catch | caught | caught | ловить, хватать, успеть |
| choose | chose | chosen | выбирать |
| cling | clung | clung | цепляться, льнуть |
| clothe | clothed / clad | clothed / clad | одевать (кого-либо) |
| come | came | come | приходить |
| cost | cost | cost | стоить, обходиться (в какую-либо сумму) |
| creep | crept | crept | ползать |
| cut | cut | cut | резать, разрезать |
| D | |||
| deal | dealt | dealt | иметь дело |
| dig | dug | dug | копать |
| dive | dove / dived | dived | нырять, погружаться |
| do | did | done | делать, выполнять |
| draw | drew | drawn | рисовать, чертить |
| dream | dreamed / dreamt | dreamed / dreamt | грезить, мечтать |
| drink | drank | drunk | пить |
| drive | drove | driven | управлять (авто) |
| dwell | dwelt / dwelled | dwelt / dwelled | обитать, находиться |
| E | |||
| eat | ate | eaten | есть, кушать |
| F | |||
| fall | fell | fallen | падать |
| feed | fed | fed | кормить |
| feel | felt | felt | чувствовать |
| fight | fought | fought | драться, сражаться, бороться |
| find | found | found | находить |
| fit | fit | fit | подходить по размеру |
| flee | fled | fled | убегать, спасаться |
| fling | flung | flung | бросаться, ринуться |
| fly | flew | flown | летать |
| forbid | forbade | forbidden | запрещать |
| forecast | forecast | forecast | предсказывать, предвосхищать |
| foresee | foresaw | foreseen | предвидеть |
| foretell | foretold | foretold | предсказывать, прогнозировать |
| forget | forgot | forgotten | забывать |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven | прощать |
| forsake | forsook | forsaken | покидать |
| freeze | froze | frozen | замерзать |
| G | |||
| get | got | gotten / got | получать, достигать |
| give | gave | given | давать |
| go | went | gone | идти, ехать |
| grind | ground | ground | молоть, толочь |
| grow | grew | grown | расти |
| H | |||
| hang | hung / hanged | hung / hanged | вешать, развешивать |
| have, has | had | had | иметь |
| hear | heard | heard | слышать |
| hew | hewed | hewn / hewed | рубить |
| hide | hid | hidden | прятаться, скрываться |
| hit | hit | hit | ударять, поражать |
| hold | held | held | держать, удерживать, фиксировать |
| hurt | hurt | hurt | ранить, причинить боль |
| I | |||
| inlay | inlaid | inlaid | вкладывать, вставлять, выстилать |
| input | input / inputted | input / inputted | входить |
| interweave | interwove | interwoven | воткать |
| K | |||
| keep | kept | kept | держать, хранить |
| kneel | knelt / kneeled | knelt / kneeled | становиться на колени |
| knit | knitted / knit | knitted / knit | вязать |
| know | knew | known | знать, иметь представление (о чем-либо) |
| L | |||
| lay | laid | laid | класть, положить |
| lead | led | led | вести, руководить, управлять |
| lean | leaned / leant | leaned / leant | опираться, прислоняться |
| leap | leaped / leapt | leaped / leapt | прыгать, скакать |
| learn | learnt / learned | learnt / learned | учить |
| leave | left | left | покидать, оставлять |
| lend | lent | lent | одалживать, давать взаймы |
| let | let | let | позволять, предполагать |
| lie | lay | lain | лежать |
| light | lit / lighted | lit / lighted | освещать |
| lose | lost | lost | терять |
| M | |||
| make | made | made | делать, производить, создавать |
| may | might | might | мочь, иметь возможность |
| mean | meant | meant | значить, иметь ввиду |
| meet | met | met | встречать |
| miscast | miscast | miscast | неправильно распределять роли |
| misdeal | misdealt | misdealt | поступать неправильно |
| misdo | misdid | misdone | делать что-либо неправильно или небрежно |
| misgive | misgave | misgiven | внушать недоверия, опасения |
| mishear | misheard | misheard | ослышаться |
| mishit | mishit | mishit | промахнуться |
| mislay | mislaid | mislaid | класть не на место |
| mislead | misled | misled | ввести в заблуждение |
| misread | misread | misread | неправильно истолковывать |
| misspell | misspelled / misspelt | misspelled / misspelt | писать с ошибками |
| misspend | misspent | misspent | неразумно, зря тратить |
| mistake | mistook | mistaken | ошибаться |
| misunderstand | misunderstood | misunderstood | неправильно понимать |
| mow | mowed | mowed / mown | косить |
| O | |||
| offset | offset | offset | возмещать, вознаграждать, компенсировать |
| outbid | outbid | outbid | перебивать цену |
| outdo | outdid | outdone | превосходить |
| outfight | outfought | outfought | побеждать в бою |
| outgrow | outgrew | outgrown | вырастать из |
| output | output / outputted | output / outputted | выходить |
| outrun | outran | outrun | перегонять, опережать |
| outsell | outsold | outsold | продавать лучше или дороже |
| outshine | outshone | outshone | затмевать |
| overbid | overbid | overbid | повелевать |
| overcome | overcame | overcome | компенсировать |
| overdo | overdid | overdone | пережари(ва)ть |
| overdraw | overdrew | overdrawn | превышать |
| overeat | overate | overeaten | объедаться |
| overfly | overflew | overflown | перелетать |
| overhang | overhung | overhung | нависать |
| overhear | overheard | overheard | подслуш(ив)ать |
| overlay | overlaid | overlaid | покры(ва)ть |
| overpay | overpaid | overpaid | переплачивать |
| override | overrode | overridden | отменять, аннулировать |
| overrun | overran | overrun | переливаться через край |
| oversee | oversaw | overseen | надзирать за |
| overshoot | overshot | overshot | расстрелять |
| oversleep | overslept | overslept | проспать, заспаться |
| overtake | overtook | overtaken | догонять |
| overthrow | overthrew | overthrown | свергать |
| P | |||
| partake | partook | partaken | принимать участие |
| pay | paid | paid | платить |
| plead | pleaded / pled | pleaded / pled | обращаться к суду |
| prepay | prepaid | prepaid | платить вперед |
| prove | proved | proven / proved | доказывать |
| put | put | put | класть, ставить, размещать |
| Q | |||
| quit | quit / quitted | quit / quitted | выходить, покидать, оставлять |
| R | |||
| read | read | read | читать |
| rebind | rebound | rebound | перевязывать |
| rebuild | rebuilt | rebuilt | перестроить |
| recast | recast | recast | изменять, перестраивать |
| redo | redid | redone | делать вновь, переделывать |
| rehear | reheard | reheard | слушать вторично |
| remake | remade | remade | переделывать |
| rend | rent | rent | раздирать |
| repay | repaid | repaid | отдавать долг |
| rerun | reran | rerun | выполнять повторно |
| resell | resold | resold | перепродавать |
| reset | reset | reset | возвращать |
| resit | resat | resat | пересиживать |
| retake | retook | retaken | забирать |
| retell | retold | retold | пересказывать |
| rewrite | rewrote | rewritten | перезаписать |
| rid | rid | rid | избавлять |
| ride | rode | ridden | ездить верхом |
| ring | rang | rung | звонить |
| rise | rose | risen | подняться |
| run | ran | run | бегать |
| S | |||
| saw | sawed | sawed / sawn | пилить |
| say | said | said | сказать, заявить |
| see | saw | seen | видеть |
| seek | sought | sought | искать |
| sell | sold | sold | продавать |
| send | sent | sent | посылать |
| set | set | set | ставить, устанавливать |
| sew | sewed | sewn / sewed | шить |
| shake | shook | shaken | трясти |
| shave | shaved | shaved / shaven | бриться |
| shear | sheared | sheared / shorn | стричь |
| shed | shed | shed | проливать |
| shine | shined / shone | shined / shone | светить, сиять, озарять |
| shoot | shot | shot | стрелять, давать побеги |
| show | showed | shown / showed | показывать |
| shrink | shrank / shrunk | shrunk | сокращаться, сжиматься |
| shut | shut | shut | закрывать, запирать, затворять |
| sing | sang | sung | петь |
| sink | sank / sunk | sunk | тонуть, погружаться (под воду) |
| sit | sat | sat | сидеть |
| slay | slew / slayed | slain / slayed | убивать |
| sleep | slept | slept | спать |
| slide | slid | slid | скользить |
| sling | slung | slung | бросать, швырять |
| slink | slunk | slunk | красться, идти крадучись |
| slit | slit | slit | разрезать, рвать в длину |
| smell | smelled / smelt | smelled / smelt | пахнуть, нюхать |
| sow | sowed | sown / sowed | сеять |
| speak | spoke | spoken | говорить |
| speed | sped / speeded | sped / speeded | ускорять, спешить |
| spell | spelled / spelt | spelled / spelt | писать или читать по буквам |
| spend | spent | spent | тратить, расходовать |
| spill | spilled / spilt | spilled / spilt | проливать, разливать |
| spin | spun | spun | прясть |
| spit | spit / spat | spit / spat | плевать |
| split | split | split | расщеплять |
| spoil | spoiled / spoilt | spoiled / spoilt | портить |
| spread | spread | spread | распространиться |
| spring | sprang / sprung | sprung | вскочить, возникнуть |
| stand | stood | stood | стоять |
| steal | stole | stolen | воровать, красть |
| stick | stuck | stuck | уколоть, приклеить |
| sting | stung | stung | жалить |
| stink | stunk / stank | stunk | вонять |
| strew | strewed | strewn / strewed | усеять, устлать |
| stride | strode | stridden | шагать, наносить удар |
| strike | struck | struck | ударить, бить, бастовать |
| string | strung | strung | нанизать, натянуть |
| strive | strove / strived | striven / strived | стараться |
| sublet | sublet | sublet | передавать в субаренду |
| swear | swore | sworn | клясться, присягать |
| sweep | swept | swept | мести, подметать, сметать |
| swell | swelled | swollen / swelled | разбухать |
| swim | swam | swum | плавать, плыть |
| swing | swung | swung | качать, раскачивать, вертеть |
| T | |||
| take | took | taken | брать, взять |
| teach | taught | taught | учить, обучать |
| tear | tore | torn | рвать |
| tell | told | told | рассказать |
| think | thought | thought | думать |
| throw | threw | thrown | бросить |
| thrust | thrust | thrust | колоть, пронзать |
| tread | trod | trodden / trod | ступать |
| U | |||
| unbend | unbent | unbent | выпрямляться, разгибаться |
| underbid | underbid | underbid | снижать цену |
| undercut | undercut | undercut | сбивать цены |
| undergo | underwent | undergone | испытывать, переносить |
| underlie | underlay | underlain | лежать в основе |
| underpay | underpaid | underpaid | оплачивать слишком низко |
| undersell | undersold | undersold | продавать дешевле |
| understand | understood | understood | понимать, постигать |
| undertake | undertook | undertaken | предпринять |
| underwrite | underwrote | underwritten | подписываться |
| undo | undid | undone | уничтожать сделанное |
| unfreeze | unfroze | unfrozen | размораживать |
| unsay | unsaid | unsaid | брать назад свои слова |
| unwind | unwound | unwound | развертывать |
| uphold | upheld | upheld | поддерживать |
| upset | upset | upset | опрокинуться |
| W | |||
| wake | woke / waked | woken / waked | просыпаться |
| waylay | waylaid | waylaid | подстерегать |
| wear | wore | worn | носить (одежду) |
| weave | wove / weaved | woven / weaved | ткать |
| wed | wed / wedded | wed / wedded | жениться, выдавать замуж |
| weep | wept | wept | плакать, рыдать |
| wet | wet / wetted | wet / wetted | мочить, увлажнять |
| win | won | won | победить, выиграть |
| wind | wound | wound | заводить (механизм) |
| withdraw | withdrew | withdrawn | взять назад, отозвать |
| withhold | withheld | withheld | воздерживаться, отказывать |
| withstand | withstood | withstood | противостоять |
| wring | wrung | wrung | скрутить, сжимать |
| write | wrote | written | писать |
Simple past tense (past simple tense) is a verb tense that describes completed actions or past habits before now. It is also used to talk about a series of events in the past. “Did” is the helping verb of simple past tense. For affirmative (positive) sentences we use past simple form of a verb.
Table of Contents
- ⬤ Formation of simple past tense
- ⬤ Which auxiliary (helping verb) to use for simple past tense?
- ⬤ Positive (Affirmative) sentences
- ⬤ Negative sentences
- ⬤ Interrogative sentences
- ⬤ Sentence forms in simple past tense
- ⬤ What are the regular verbs?
- ⬤ What are the irregular verbs?
- ⬤ Explanations and usages of Simple Past Tense
- ⬤Using “was”, “were” to talk about past states.
- ⬤ What are the time expressions in simple past tense?
- ⬤ Time adverbs exercise
- ⬤ Images and example sentences
- ⬤ A conversation example
- ⬤ Translate these sentences
- ⬤ Sentence scramble game
- ⬤ Example sentences about simple past tense
- ⬤ Questions and with answers
⬤ Formation of simple past tense
For affirmative sentences we use the formation of “verb + ed”. For negative sentences and questions we use the auxiliary “did” or “did not”. See the chart below to learn the structure of simple past tense.
Did Why didWhere did
Alex
arrivedworkedhelpdid not playplaygo
yesterday
QUICK LINKS IN THIS PAGE
| (+) Affirmative form | (-) Negative form | (?) Question form |
|---|---|---|
| I watched. | I didn’t watch. | Did you watch? |
| You watched. | You didn’t watch. | Did you watch? |
⬤ Which auxiliary (helping verb) to use for simple past tense?
The auxiliary verb in simple past tense is “did“. However we use “was-were” to talk about a state in the past.
Examples:
- I walked in the park.
- I didn’t walk in the park.
- Did you walk in the park?
- I was in the park.
- I wasn’t in the park.
- Were you in the park?
⬤ Positive (Affirmative) sentences
For the formation of positive sentences in simple past tense we add “-ed“, “-ied” or just “-d” to the verb. We do not use “did” for the positive sentences.
- I asked a question.
- She studied maths.
- She cleaned her room.
- Jack repaired the car last week.
- A traffic accident happened yesterday.
⬤ Negative sentences
For the formation of negative sentences in simple past tense we use “not” together with “did“. The short form is “didn’t”
- He did not want tea.
- We didn’t wait for the bus.
- I didn’t use your pen.
- Susan didn’t lie.
⬤ Interrogative sentences
For the formation of question sentences (interrogative) in simple past tense we put “did” before the subject.
- Did you enjoy your holiday.
- Did she write an email.
- Where did Yuto go?
- What did Ali want?
⬤ Sentence forms in simple past tense
| (+) Affirmative sentences | (-) Negative sentences | (?) Interrogative sentences |
|---|---|---|
| I played | I didn’t play | Did I play? |
| You played | You didn’t play | Did you play? |
| He played | He didn’t play | Did he play? |
| She played | She didn’t play | Did she play? |
| It played | It didn’t play | Did it play? |
| We played | We didn’t play | Did we play? |
| They played | They didn’t play | Did they play? |
⬤ What are the regular verbs?
Regular verbs are the verbs that gets “-ed“, “-ied” or “-d” for the the past simple forms.
| Infinitive | Past simple | Past participle |
|---|---|---|
| clean | cleaned | cleaned |
| play | played | played |
| study | studied | studied |
⬤ What are the irregular verbs?
Irregular verbs are the verbs which don’t get “-ed“, “-ied” or “-d” to form past simple form or past participle form. There are a number of irregular verbs which needs to be memorized. Because the formation has no standard rule. Some verbs have the same form as bare form, past simple form or past participle form. For example “cut, put, let, hit”.
| Infinitive | Past simple form | Past participle form |
|---|---|---|
| find | found | found |
| go | went | gone |
| break | broke | broken |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| put | put | put |
Examples:
- (+) I visited my uncle.
- (-) I didn’t visit my uncle yesterday.
- (?) Did you visit your uncle yesterday?
- (+) They found the cat.
- (-) They didn’t find the cat.
- (?) Did they find the cat?
SIMILAR PAGES:
❯❯ Learn verb to be here
❯❯ Learn simple present tense here
❯❯ Learn present continuous tense here
❯❯ Learn future simple tense (will) here
❯❯ Learn be going to future tense here
❯❯ Learn past continuous tense here
❯❯ Learn present perfect tense here
⬤ Explanations and usages of Simple Past Tense
Let’s go on with the explanations, usages and time adverbs of simple past tense:
⬤ 1- Finished actions in the past
Simple Past Tense is used to describe a finished action in a specific time in the past.
Examples:
I watched a film yesterday.
I didn’t watch a film yesterday.
Last year, I traveled to Italy.
Last year, I didn’t travel to Italy.
She washed her hands.
She didn’t wash her hands.
I bought a hat yesterday.
Did you like your cake?
Where did you go?
What did Ethan say?
How did she get 100 points in the exam?
⬤ 2- A series of finished actions.
Simple Past Tense is also used to describe past actions that happen one after the other. The series of actions are all expressed in simple past tense.
Examples:
I went out, walked to the park, and watched the sky silently.
He arrived from the airport at 11:00, looked for someone to ask the way, and called a taxi.
⬤ 3- Past habits
We can also use simple past tense to talk about habits in the past.
Examples:
I always played basketball when I was a child.
He often played the guitar.
They never went to school, they always skipped.
She worked at the hospital after school.
⬤Using “was”, “were” to talk about past states.
If you want to talk about a past state or condition we use “was, were”. The negative form is “was not, were not” or “wasn’t weren’t”. To make questions we use “was/were” before the subject.
⬤ I lived in London.
⬤ I was in London.
Examples (did)
Sally worked at the hospital.
Sally didn’t work at the hospital.
Did Sally work at the hospital?
Where did Sally work?
Examples (was-were)
Sally was at the hospital.
Sally wasn’t at the hospital.
Was Sally at the hospital?
Where was Sally?
⬤ What are the time expressions in simple past tense?
⬤ yesterday
I went to the cinema yesterday.
⬤ last week, last year, last Sunday, last month etc.
He bought a car last week.
⬤ two years ago, four days ago, three minutes ago etc.
I saw her five minutes ago.
⬤ in 1995, in 2003 etc.
I had an accident in 2014.
⬤ Time adverbs exercise
You can see the simple past tense time adverbs below. Click on the cards and tell the meaning of them in your native language..
⬤ Images and example sentences
You can learn simple past tense with images and example sentences below.
⬤ A conversation example
Here is a dialogue to learn simple past tense. You can make similar conversations.
-
Hi? Harry
Did you win the match yesterday?
-
-
-
-
What do you mean?
Didn’t you play?
-
Actually I didn’t.
I had a traffic accident
so I spent the night at a hospital.
We won the match.
My teammates dedicated the goals to me.
-
How nice!
Well. Your team needs you. Get well soon.
⬤ Translate these sentences
You will see random examples of simple past tense below. Try to translate them into your own language.
⬤ Sentence scramble game
You will see scrambled words of simple past tense sentences. Click on them in order to make a sentence.
⬤ Example sentences about simple past tense
You can see many sentences below to learn simple past tense.
➔ 10 examples of about simple past tense
- I listened to the new pop album yesterday. It’s great.
- She liked the film but she didn’t like the music.
- There was a problem with the plug.
- I was happy to see her with a smile in her face.
- Her parents travelled by train from Istanbul to Moscow.
- I phoned you four times last night but you were out.
- There were many workers waiting outside.
- We walked along the beach yesterday. It was lovely.
- I had a problem. So I asked to my mother about it.
- Last week I was in Paris. I stayed in a hotel.
⬤ Questions and with answers
Read the questions and the answers below to learn how to use about simple past tense.
➔ 10 questions and answers about simple past tense
- Did you like the film?
Yes, I liked it very much. - Did they give her a present after the ceremony?
Yes, they gave her a new camera. - When did you start playing the guitar?
I started playing the guitar when I was nine. - Was there a guard at the door?
No. They let us in. - When did you leave school?
I left school when I was sixteen. - Who invented the radio?
Guglielmo Marconi invented it. - When did you give your first concert?
We gave our first concert in a wedding in Liverpool. - How many sandwiches did he eat?
He ate 3 sandwiches. - Were you with Sally when she had an accident?
Yes, I was. - What did she do with the book?
She sat on a bench and started reading.
External resources:
You can go to British Council page and study simple past tense, or watch a video from the popular movies about past simple tense.
Ask the Editor
Question
did + main verb: base form or past tense form?
—
Umer
,
India
Answer
The short answer to your question is that the verb that follows did should be used in its base form. Read below for more information.
The verb did, the past tense form of do, commonly appears before another verb in these two sentence types:
1. Questions about the past
- What did you eat? (The two verbs are did and eat.)
- Did you eat pizza? (did, eat)
2. Negative statements about the past
- I didn’t stay late.(didn’t, stay)
- Julia didn’t come at all last night. (didn’t, come)
In both of these sentence types, did is an auxiliary verb (or “helping verb”) that is followed by a main verb, which carries the real verb meaning.
The auxiliary verb (did) is marked for past tense, but the main verb is not. It appears in its base form. A helpful way to remember this is that when there is an auxiliary verb, the main verb does not need to be marked for tense, because the tense is shown in the auxiliary. However, in a sentence about the past without an auxiliary verb, the main verb does need to be in the past tense form, as in this sentence:
- He ate a whole pizza. (ate, the only verb, is in the past tense form)
I hope this helps.
You can read more articles in the archive.
Do V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 has five different forms: base form, past simple form, past participle form, present perfect form, and present perfect participle form. So what is Do‘s past? How to conjugate verbs with the verb Do?
Let’s find with English tivi more details in this article.
See more at: Verbs
Do of Definition and Meaning
Do is a verb. It means to perform an action.
| Base Form (V1) | do |
| Past Form (V2) | did |
| Past Participle Form (V3) | done |
| s / es/ ies (V4) | does |
| ‘ing’ form (V5) | doing |
Do of Past Simple V2
The verb do is also employed in its V2 form as “did”’. It is used to indicate the past tense in sentences.
Do of Past Participle V3
This verb’s V3 form is ‘ done ‘ In the case of past perfect tense or present perfect tense, the word ‘ done ‘ is used.
+ In the present perfect tense, the word do is used ‘have + done ‘ or ‘has + done.’
- I, you, and we are used as ‘have + done ‘ subjects.
- He, she, and it are used as ‘has + done ‘ subjects.
+ If you need to use the past perfect tense, use ‘had + done ‘ regardless of the subject.
You might also like: ALL the English Grammar Basics You Need
Conjugation of Do V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
| Conjugation table: Do | |||
| Number | Singular | ||
| Present Simple of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| do | do | does | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| do | do | do | |
| Present Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| am doing | are doing | is doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| are doing | are doing | are doing | |
| Present Perfect of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| have done | have done | has done | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| have done | have done | have done | |
| Present Perfect Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| have been doing | have been doing | has been doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| have been doing | have been doing | have been doing | |
| Past Simple of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| did | did | did | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| did | did | did | |
| Past Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| was doing | were doing | was doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| were doing | were doing | were doing | |
| Past Perfect of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| had done | had done | had done | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| had done | had done | had done | |
| Past Perfect Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| had been doing | had been doing | had been doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| had been doing | had been doing | had been doing | |
| Future Simple of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall do | will/shall do | will/shall do | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall do | will/shall do | will/shall do | |
| Future Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall be doing | will/shall be doing | will/shall be doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall be doing | will/shall be doing | will/shall be doing | |
| Future Perfect of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall have done | will/shall have done | will/shall have done | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall have done | will/shall have done | will/shall have done | |
| Future Perfect Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| will/shall have been doing | will/shall have been doing | will/shall have been doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| will/shall have been doing | will/shall have been doing | will/shall have been doing | |
| Conditional Present of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| would do | would do | would do | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would do | would do | would do | |
| Conditional Perfect of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| would have done | would have done | would have done | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would have done | would have done | would have done | |
| Conditional Present Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| would be doing | would be doing | would be doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would be doing | would be doing | would be doing | |
| Conditional Perfect Continuous of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| would have been doing | would have been doing | would have been doing | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| would have been doing | would have been doing | would have been doing | |
| Present Subjunctive of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| do | do | do | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| do | do | do | |
| Past Subjunctive of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| did | did | did | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| did | did | did | |
| Past Perfect Subjunctive of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| had done | had done | had done | |
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| had done | had done | had done | |
| Imperative of do | I | You | She/He/It |
| do | |||
| Plural | |||
| We | You | They | |
| Let’s do | do |
See more at: Vocabulary
Example Sentences with Do V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
In this section, we will learn about do sentence examples.
Example:
+ She does love this game.
+ He does want to come over now.
+ How do you do that?
+ They do my hair before school.
+ He wants to do his best in this race.
Synonym Words For Do
Synonym of the do word list. Here are a variety of words whose meaning is nearly the synonym of do:
- satisfy
- suffice
- function
- work
Opposite Words For Do
The antonym of the do word list. Here are some words that have nearly the opposite meaning as do.
- idle
- bum
- dawdle
- dillydally
- laze
- loll
- lounge
- sit
- back
- slack
- slouch
- stagnate
You might also like: Best List of Irregular Verbs in English
Some Frequently Asked Questions About Do (Verb)
What is the V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 of do?
The past tense of do is did. The third-person singular simple present indicative form of do is does. The present participle of do is doing. The past participle of do is done.
| Base Form (V1) | do |
| Past Form (V2) | did |
| Past Participle Form (V3) | done |
| s / es/ ies (V4) | does |
| ‘ing’ form (V5) | doing |
What is the V2 and V3 form of do?
+ The V2 and V3 form of do is “did and done“.
What is the sentence of do?
What is the past tense V2 of do?
+ The past tense of do is “did“.
What is the past participle V3 of do?
+ The past participle of do is “done“.
What is the present participle V5 of do?
+ The present participle of do is “doing“.
Conclusion
There are three types of Do V1 V2 V3 V4 V5: Base Form, Past Simple, and Present Continuous and Present Continuous. We know all about them. English is easier and more fun to learn if we make it easier and more fun to use.
You should follow the English TV YouTube channel to learn more about English and improve your skills.
Here are other verbs V1 V2 V3 List
| Base Form V1 | Past Form V2 | Past Participle Form V3 |
| abide | abode/abided | abode/abided |
| arise | arose | arisen |
| awake | awoke | awoken |
| backslide | backslid | backslidden/backslid |
| be | was/were | been |
| bear | bore | borne |
| beat | beat | beaten/beat |
| become | became | become |
| befall | befell | befallen |
| begin | began | begun |
| behold | beheld | beheld |
| bend | bent | bent |
| beset | beset | beset |
| bespeak | bespoke | bespoken |
| bet | bet/betted | bet/betted |
| bid | bid | bid |
| bind | bound | bound |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| bleed | bled | bled |
| blow | blew | blown |
| break | broke | broken |
| breed | bred | bred |
| bring | brought | brought |
| broadcast | broadcast | broadcast |
| browbeat | browbeat | browbeaten/browbeat |
| build | built | built |
| burn | burnt/burned | burnt/burned |
| burst | burst | burst |
| bust | busted/bust | busted/bust |
| buy | bought | bought |
| cast | cast | cast |
| catch | caught | caught |
| chide | chid/chided | chid/chidden/chided |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| cleave | clove/cleft/cleaved | cloven/cleft/cleaved |
| cleave | clave | cleaved |
| cling | clung | clung |
| clothe | clothed/clad | clothed/clad |
| come | came | come |
| cost | cost | cost |
| creep | crept | crept |
| crossbreed | crossbred | crossbred |
| crow | crew/crewed | crowed |
| cut | cut | cut |
| daydream | daydreamed daydreamt |
daydreamed daydreamt |
| deal | dealt | dealt |
| dig | dug | dug |
| disprove | disproved | disproved/disproven |
| dive | dove/dived | dived |
| do | did | done |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| dream | dreamt/dreamed | dreamt/dreamed |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| drive | drove | driven |
| dwell | dwelt | dwelt |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feed | fed | fed |
| feel | felt | felt |
| fight | fought | fought |
| find | found | found |
| fit | fitted/fit | fitted/fit |
| flee | fled | fled |
| fling | flung | flung |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forbear | forbore | forborne |
| forbid | forbade/forbad | forbidden |
| forecast | forecast/forecasted | forecast/forecasted |
| forego (also forgo) | forewent | foregone |
| foresee | foresaw | foreseen |
| foretell | foretold | foretold |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven |
| forsake | forsook | forsaken |
| freeze | froze | frozen |
| frostbite | frostbit | frostbitten |
| get | got | got/gotten |
| gild | gilt/gilded | gilt/gilded |
| gird | girt/girded | girt/girded |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| grind | ground | ground |
| grow | grew | grown |
| hand-feed | hand-fed | hand-fed |
| handwrite | handwrote | handwritten |
| hang | hung | hung |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| heave | hove/heaved | hove/heaved |
| hew | hewed | hewn/hewed |
| hide | hid | hidden |
| hit | hit | hit |
| hurt | hurt | hurt |
| inbreed | inbred | inbred |
| inlay | inlaid | inlaid |
| input | input | input |
| inset | inset | inset |
| interbreed | interbred | interbred |
| interweave | interwove interweaved |
interwoven interweaved |
| interwind | interwound | interwound |
| jerry-build | jerry-built | jerry-built |
| keep | kept | kept |
| kneel | knelt/kneeled | knelt/kneeled |
| knit | knit/knitted | knit/knitted |
| know | knew | known |
| lay | laid | laid |
| lead | led | led |
| lean | leaned/leant | leaned/leant |
| leap | leapt /leaped | leapt /leaped |
| learn | learnt/learned | learnt/learned |
| leave | left | left |
| lend | lent | lent |
| let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain |
| light | lit/lighted | lit/lighted |
| lip-read | lip-read | lip-read |
| lose | lost | lost |
| make | made | made |
| mean | meant | meant |
| meet | met | met |
| miscast | miscast | miscast |
| misdeal | misdealt | misdealt |
| misdo | misdid | misdone |
| mishear | misheard | misheard |
| mislay | mislaid | mislaid |
| mislead | misled | misled |
| mislearn | mislearned mislearnt |
mislearned mislearnt |
| misread | misread | misread |
| misset | misset | misset |
| misspeak | misspoke | misspoken |
| misspell | misspelt | misspelt |
| misspend | misspent | misspent |
| mistake | mistook | mistaken |
| misteach | mistaught | mistaught |
| misunderstand | misunderstood | misunderstood |
| miswrite | miswrote | miswritten |
| mow | mowed | mown/mowed |
| offset | offset | offset |
| outbid | outbid | outbid |
| outbreed | outbred | outbred |
| outdo | outdid | outdone |
| outdraw | outdrew | outdrawn |
| outdrink | outdrank | outdrunk |
| outdrive | outdrove | outdriven |
| outfight | outfought | outfought |
| outfly | outflew | outflown |
| outgrow | outgrew | outgrown |
| outleap | outleaped/outleapt | outleaped/outleapt |
| outlie | outlied | outlied |
| output | output | output |
| outride | outrode | outridden |
| outrun | outran | outrun |
| outsell | outsold | outsold |
| outshine | outshined/outshone | outshined/outshone |
| outshoot | outshot | outshot |
| outsing | outsang | outsung |
| outsit | outsat | outsat |
| outsleep | outslept | outslept |
| outsmell | outsmelled/outsmelt | outsmelled/outsmelt |
| outspeak | outspoke | outspoken |
| outspeed | outsped | outsped |
| outspend | outspent | outspent |
| outswear | outswore | outsworn |
| outswim | outswam | outswum |
| outthink | outthought | outthought |
| outthrow | outthrew | outthrown |
| outwrite | outwrote | outwritten |
| overbid | overbid | overbid |
| overbreed | overbred | overbred |
| overbuild | overbuilt | overbuilt |
| overbuy | overbought | overbought |
| overcome | overcame | overcome |
| overdo | overdid | overdone |
| overdraw | overdrew | overdrawn |
| overdrink | overdrank | overdrunk |
| overeat | overate | overeaten |
| overfeed | overfed | overfed |
| overfly | overflew | overflown |
| overhang | overhung | overhung |
| overhear | overheard | overheard |
| overlay | overlaid | overlaid |
| overpay | overpaid | overpaid |
| override | overrode | overridden |
| overrun | overran | overrun |
| oversee | oversaw | overseen |
| oversell | oversold | oversold |
| oversew | oversewed | oversewn/oversewed |
| overshoot | overshot | overshot |
| oversleep | overslept | overslept |
| overspeak | overspoke | overspoken |
| overspend | overspent | overspent |
| overspill | overspilled/overspilt | overspilled/overspilt |
| overtake | overtook | overtaken |
| overthink | overthought | overthought |
| overthrow | overthrew | overthrown |
| overwind | overwound | overwound |
| overwrite | overwrote | overwritten |
| partake | partook | partaken |
| pay | paid | paid |
| plead | pleaded/pled | pleaded/pled |
| prebuild | prebuilt | prebuilt |
| premake | premade | premade |
| prepay | prepaid | prepaid |
| presell | presold | presold |
| preset | preset | preset |
| preshrink | preshrank | preshrunk |
| proofread | proofread | proofread |
| prove | proved | proven/proved |
| put | put | put |
| quick-freeze | quick-froze | quick-frozen |
| quit | quit/quitted | quit/quitted |
| read | read | read |
| reawake | reawoke | reawaken |
| rebid | rebid | rebid |
| rebind | rebound | rebound |
| rebroadcast | rebroadcast rebroadcasted |
rebroadcast rebroadcasted |
| rebuild | rebuilt | rebuilt |
| recast | recast | recast |
| recut | recut | recut |
| redeal | redealt | redealt |
| redo | redid | redone |
| redraw | redrew | redrawn |
| refit | refitted/refit | refitted/refit |
| regrind | reground | reground |
| regrow | regrew | regrown |
| rehang | rehung | rehung |
| rehear | reheard | reheard |
| reknit | reknitted/reknit | reknitted/reknit |
| relay | relaid | relaid |
| relearn | relearned/relearnt | relearned/relearnt |
| relight | relit/relighted | relit/relighted |
| remake | remade | remade |
| rend | rent | rent |
| repay | repaid | repaid |
| reread | reread | reread |
| rerun | reran | rerun |
| resell | resold | resold |
| resend | resent | resent |
| reset | reset | reset |
| resew | resewed | resewn/resewed |
| retake | retook | retaken |
| reteach | retaught | retaught |
| retear | retore | retorn |
| retell | retold | retold |
| rethink | rethought | rethought |
| retread | retread | retread |
| retrofit | retrofitted/retrofit | retrofitted/retrofit |
| rewake | rewoke/rewaked | rewaken/rewaked |
| rewear | rewore | reworn |
| reweave | rewove/reweaved | rewoven/reweaved |
| rewed | rewed/rewedded | rewed/rewedded |
| rewet | rewet/rewetted | rewet/rewetted |
| rewin | rewon | rewon |
| rewind | rewound | rewound |
| rewrite | rewrote | rewritten |
| rid | rid | rid |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| ring | rang | rung |
| rise | rose | risen |
| roughcast | roughcast | roughcast |
| run | ran | run |
| sand-cast | sand-cast | sand-cast |
| saw | sawed | sawn |
| say | said | said |
| see | saw | seen |
| seek | sought | sought |
| sell | sold | sold |
| send | sent | sent |
| set | set | set |
| sew | sewed | sewn/sewed |
| shake | shook | shaken |
| shave | shaved | shaved/shaven |
| shear | sheared | shorn |
| shed | shed | shed |
| shine | shone | shone |
| shit | shit/shat/shitted | shit/shat/shitted |
| shoot | shot | shot |
| show | showed | shown/showed |
| shrink | shrank | shrunk |
| shut | shut | shut |
| sight-read | sight-read | sight-read |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sink | sank | sunk |
| sit | sat | sat |
| slay | slew | slain |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| slide | slid | slid |
| sling | slung | slung |
| slink | slunk | slunk |
| slit | slit | slit |
| smell | smelt | smelt |
| smite | smote | smitten |
| sneak | sneaked/snuck | sneaked/snuck |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| speed | sped/speeded | sped/speeded |
| spell | spelt/spelled | spelt/spelled |
| spend | spent | spent |
| spill | spilt/spilled | spilt/spilled |
| spin | spun/span | spun |
| spoil | spoilt/spoiled | spoilt/spoiled |
| spread | spread | spread |
| stand | stood | stood |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| stick | stuck | stuck |
| sting | stung | stung |
| stink | stunk/stank | stunk |
| stride | strode | stridden |
| strike | struck | struck |
| string | strung | strung |
| sunburn | sunburned/sunburnt | sunburned/sunburnt |
| swear | swore | sworn |
| sweat | sweat/sweated | sweat/sweated |
| sweep | swept | swept |
| swell | swelled | swollen/swelled |
| swim | swam | swum |
| swing | swung | swung |
| take | took | taken |
| teach | taught | taught |
| tear | tore | torn |
| telecast | telecast | telecast |
| tell | told | told |
| think | thought | thought |
| throw | threw | thrown |
| thrust | thrust | thrust |
| tread | trod | trodden/trod |
| typewrite | typewrote | typewritten |
| unbend | unbent | unbent |
| unbind | unbound | unbound |
| unclothe | unclothed/unclad | unclothed/unclad |
| undercut | undercut | undercut |
| underfeed | underfed | underfed |
| undergo | underwent | undergone |
| underlie | underlay | underlain |
| understand | understood | understood |
| undertake | undertook | undertaken |
| underwrite | underwrote | underwritten |
| undo | undid | undone |
| unfreeze | unfroze | unfrozen |
| unhang | unhung | unhung |
| unhide | unhid | unhidden |
| unlearn | unlearned/unlearnt | unlearned/unlearnt |
| unspin | unspun | unspun |
| unwind | unwound | unwound |
| uphold | upheld | upheld |
| upset | upset | upset |
| wake | woke/waked | woken/waked |
| wear | wore | worn |
| wed | wed/wedded | wed/wedded |
| weep | wept | wept |
| wet | wet/wetted | wet/wetted |
| win | won | won |
| wind | wound | wound |
| withdraw | withdrew | withdrawn |
| withhold | withheld | withheld |
| withstand | withstood | withstood |
| work | worked | worked |
| wring | wrung | wrung |
| write | wrote | written |
Post Views: 5,145
STARTBODY
Home /
Grammar Corner /
Verbs /
DO – DOES – DID – DONE
Register now & get certified to teach english abroad!
The word «do» comes up a lot in English. This is because it can be used in a variety of ways and tenses. Let’s look at each one in more detail below.
TO DO – Present Tense
With the verb «to do» in the Present Tense…
We say: I do / you do / we do / they do
But we say: he does / she does / it does
For example:
- I do my laundry on Saturdays.
- They do their homework when they arrive home from school.
- He does nothing all day.
- She does her best every day at work.
TO DO – Past Tense
The simple past tense of «do» is «did» for all subjects:
I did / you did / we did / they did / he did / she did / it did
- He did a magic trick.
- The dog did a spin.
- I did my homework in my bedroom.
- She did ballet after school last year.
TO DO – Past Participle
The past participle of «do» is «done». It’s important to remember that past participles are accompanied by a conjugation of the verb «to have» or «to be».
In general «have + past participle» is used with a perfect tense and «be + past participle» is with the passive voice.
Let’s look at some examples:
- I have done my homework.
- He has done a good job.
These two sentences are in the present perfect tense because they have «have» or «has» before the past participle «done».
- The video will show you how it is done.
- The report was done on time.
In the two examples above, the conjugation of the verb «to be» is used before the past participle done. This indicates that the sentence is in the passive voice.
TO DO – To replace a verb
Sometimes the verb «do» can be used to replace a verb when the meaning is clear or obvious. This replacement is more common in informal and spoken English:
Have you
done
the laundry yet?
I’ll
do
the kitchen if you do the lawns.
DO / DOES / DID – For Questions
To make a question in the simple present tense in English we normally put the auxiliary «do» or «does» and for questions in the past tense «did» at the beginning of the question before the subject.
Look at this affirmative sentence:
- You speak English.
How can we turn this into a question? We add «do» at the beginning so it becomes:
- Do you speak English?
Another example would be:
- He speaks Korean.
To make this a question we say:
- Does he speak Korean?
For sentences in the past tense, it works very similar:
- You lived in France.
How can we make this a question? We add «did» at the beginning so it becomes:
- Did you live in France?
As you an see, the only difference between a question in the present tense and the past tense is when it refers to third person (he, she, or it) is the first part… «does» or «did».
DO and DOES – For Emphasis
Sometimes «do», «does» and «did» are used in positive sentences to give special emphasis that what you say is true, despite what the other person thinks. Note that when speaking, the word (do/does/did) is stressed with the voice.
For example:
- I do really want to go.
- I did study for the test.
One thing to note here is that «did» is used for positive sentences in the past tense and that the main verb is in its base form.
Are you interested in teaching English as a foreign language?
Get your TESOL certification with ITTT.
Register now & get certified to teach english abroad!
ENDBODY