In the English language, the word “but” is also used for multiple purposes. It can serve as a conjunction, a preposition, an adverb, or a noun in sentences.
- Conjunction
This word is commonly categorized under conjunctions because it can connect two clauses together and form a single sentence. In the sample sentence below:
She stumbled but didn’t fall.
The word “but” links together the clauses “she stumbled” and “didn’t fall,” and is therefore considered as a conjunction.
Definition:
a. used to introduce something contrasting with what has already been mentioned
- Example:
- He was called, but he did not answer.
b. used to indicate the impossibility of anything other than what is being stated
- Example:
- One cannot but sympathize with the old man.
2. Preposition
Sometimes, the word “but” is classified as a preposition that means “except.” It is commonly used after the words all, any, no, every, none, nothing, etc. In the sample sentence below:
This is nothing but an insult.
The word “but’ is considered as a preposition that means “other than.”
Definition:
a. except; apart from; other than.
- Example:
- She teaches nothing but ballet all day long.
3. Adverb
In some cases, the word “but” can be used as an adverb that means “merely,” and can modify a verb or an adjective. For instance, in the sample sentence below:
She is but a shadow of her old self.
The word “but” is an adverb that can also mean “nothing but” or “only.”
Definition:
a. no more than; only
- Example:
- He is but a child.
4. Noun
Other times, this word is also categorized as a noun that refers to an argument against something. Take for example, the sentence below:
There are no buts when it comes to regulations.
In this sentence, the word “but” is used as a noun that also means “objection.”
Definition:
a. a reason someone gives for not doing or agreeing with something
- Example:
- I told you, no buts.
Table of Contents
- What part of speech is the word but?
- Is the word but a conjunction?
- What part of speech is not?
- What is only in parts of speech?
- What is the word not in grammar?
- How do you say no and not in English grammar?
- What does the word NOT MEAN?
- What word type does not?
- What is the meaning of did?
- What is the full form of did?
- What does did mean in text?
- What type of word is did?
- Did is used with singular or plural?
- Which verb form used with did?
- Did he give or gave?
- Which tense to use after did?
- What we use with did?
- What tense to use after did not?
- Can we use did in present tense?
- Why do we use present tense with did?
- What is the present tense of have?
- What is the present tense for start?
* But is very seldom a preposition. When it is used as a preposition, but means the same as except—Everyone ate frog legs but Jamie. Usually, but functions as a coordinating conjunction.
What part of speech is the word but?
Preposition. Sometimes, the word “but” is classified as a preposition that means “except.” It is commonly used after the words all, any, no, every, none, nothing, etc. In the sample sentence below: This is nothing but an insult. The word “but’ is considered as a preposition that means “other than.”
Is the word but a conjunction?
The conjunctions but and although/though connect ideas that contrast. Whereas is also used but it is not as common: … But is a coordinating conjunction used to connect ideas that contrast. Even though and even if are also used as subordinating conjunctions in the same way as although/though.
What part of speech is not?
adverbs
What is only in parts of speech?
Only is a versatile word, functioning as an adverb, an adjective and a conjunction. As an adverb it can generally be replaced by the word just, as in the following examples: It’s only an idea; She was only 18 when she had her first child; I only hope we can finish this on time.
What is the word not in grammar?
from English Grammar Today. Not is one of the most common words we use to indicate negation. It is often shortened to n’t and joined to an auxiliary verb or modal verb: She’s not coming with us.
How do you say no and not in English grammar?
2: We use ‘no’ before a noun. We don’t use ‘a / an / the’. It means ‘not any’. There is no bread left….Not
- It’s used to make a verb negative.
- It’s used with an adjective without a noun.
- It’s used with an adverb.
- It’s used with any / much / many / enough.
What does the word NOT MEAN?
Not is defined as a word used with a verb to make a negative. An example of not used as an adverb is in the phrase “not happy,” which means unhappy. Used to express negation, denial, refusal, or prohibition. I will not go.
What word type does not?
As detailed above, ‘not’ can be an adverb, a conjunction, an interjection or a noun.
What is the meaning of did?
Dissociative identity disorder
What is the full form of did?
| DID | Dissociative identity disorder Academic & Science » Psychology — and more… | Rate it: |
|---|---|---|
| DID | Dissociative Identity Disorder Dissociative identity disorder Miscellaneous » Unclassified | Rate it: |
| DID | Dissociate Identity Disorder Miscellaneous » Unclassified | Rate it: |
| DID | Discrete IDentifier Governmental » Military | Rate it: |
What does did mean in text?
DID. Dudes in Dresses. showing only Slang/Internet Slang definitions (show all 45 definitions)
What type of word is did?
verb
Did is used with singular or plural?
In the simple present tense, do will function as an auxiliary to express the negative and to ask questions. (Does, however, is substituted for third-person, singular subjects in the present tense. The past tense did works with all persons, singular and plural.)
Which verb form used with did?
The present participle is doing. The past participle is done. The present simple tense do and the past simple tense did can be used as an auxiliary verb. As an auxiliary, do is not used with modal verbs….Do – Easy Learning Grammar.
| I did not want it. | We did not want it. |
|---|---|
| She did not want it. | They did not want it. |
Did he give or gave?
Which is correct, did he give or did he gave? “Did he give” is grammatically correct because if the helping (auxiliary) verb is in past tense, the main verb should be in present tense.
Which tense to use after did?
present tense
What we use with did?
To make a question in the Past Tense in English we normally put the auxiliary DID at the beginning of the question or before the main subject. DID is used with regular AND irregular verbs in English. Both Do and Does in present tense questions become Did in past tense questions.
What tense to use after did not?
past tense
Can we use did in present tense?
The quick answer is you cannot use “did” in the present tense. The past tense for “do” is “did.” Its present tense forms are “do” and “does.” Its past participle is “done.” The verb “to do” is irregular.
Why do we use present tense with did?
So that is how you can understand why the “did” is there. It’s an auxiliary which is inserted to replace a null auxiliary once subject-aux inversion takes place (do affixing), and at the same time “steals” the past tense from the main verb, because auxiliaries have to carry the tense when they are present!
What is the present tense of have?
Present. The present form of “to have” is mainly used to form the simple present of a sentence. Since this verb is irregular, there are two ways of writing it in the present: “have” or “has”, and deciding to use one or the other depends on the subject of the sentence.
What is the present tense for start?
The third-person singular simple present indicative form of start is starts. The present participle of start is starting. The past participle of start is started.
For those interested in a little info about this site: it’s a side project that I developed while working on Describing Words and Related Words. Both of those projects are based around words, but have much grander goals. I had an idea for a website that simply explains the word types of the words that you search for — just like a dictionary, but focussed on the part of speech of the words. And since I already had a lot of the infrastructure in place from the other two sites, I figured it wouldn’t be too much more work to get this up and running.
The dictionary is based on the amazing Wiktionary project by wikimedia. I initially started with WordNet, but then realised that it was missing many types of words/lemma (determiners, pronouns, abbreviations, and many more). This caused me to investigate the 1913 edition of Websters Dictionary — which is now in the public domain. However, after a day’s work wrangling it into a database I realised that there were far too many errors (especially with the part-of-speech tagging) for it to be viable for Word Type.
Finally, I went back to Wiktionary — which I already knew about, but had been avoiding because it’s not properly structured for parsing. That’s when I stumbled across the UBY project — an amazing project which needs more recognition. The researchers have parsed the whole of Wiktionary and other sources, and compiled everything into a single unified resource. I simply extracted the Wiktionary entries and threw them into this interface! So it took a little more work than expected, but I’m happy I kept at it after the first couple of blunders.
Special thanks to the contributors of the open-source code that was used in this project: the UBY project (mentioned above), @mongodb and express.js.
Currently, this is based on a version of wiktionary which is a few years old. I plan to update it to a newer version soon and that update should bring in a bunch of new word senses for many words (or more accurately, lemma).
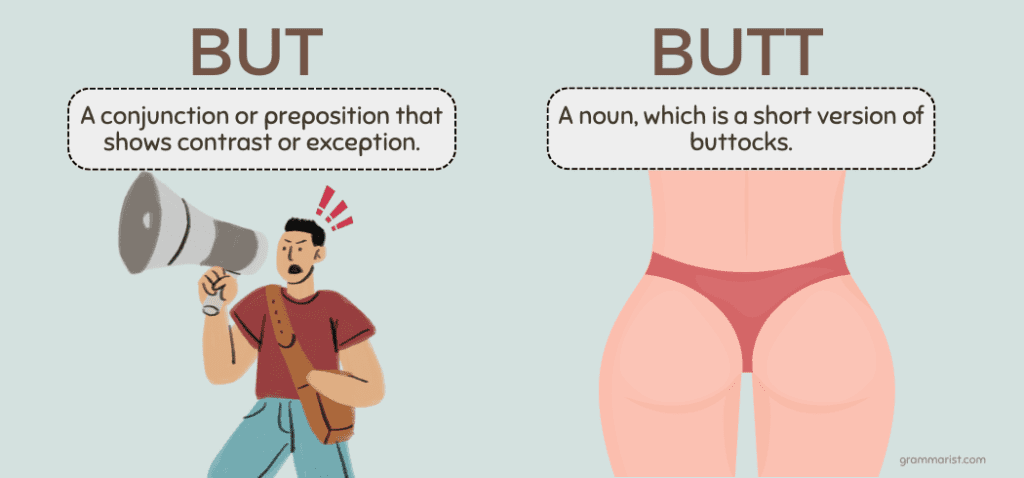
But and butt are similar-sounding terms with very different meanings and spellings. One is a conjunction that connects clauses, while the other is an informal abbreviation for buttocks. I’ll show you the difference between but vs. butt in this guide with various, easy-to-understand sentence examples.
But vs. Butt
But and butt sound the same way when spoken. But when written, their spellings differ. Their meanings are also different from each other. These words are called homophones.
- But is a conjunction or preposition that shows contrast or exception.
- Butt is a noun, which is a short version of buttocks.
What Does But Mean?
As a conjunction, but introduces clauses to show contrast with something previously mentioned. For example:
- I like cake, but carrot cake is not my favorite.
It can also be a preposition that means except or apart from.
- I eat any cake but carrot cake.
What Does Butt Mean?
Butt is a short and informal version of buttocks. For example:
- My butt hurt from sitting too much.
It can also be a noun that refers to a person or thing at which criticism or humor is directed. Other words for butt include target or victim. For example:
- She dislikes being the butt of a joke.
Examples of But in a Sentence
Here are some sentence examples showing how to properly use the word but.
- But this was the mess I had made, and I couldn’t regret the choices that led me here because they brought all of you into my life.
- I was going to stop for ice cream after work, but my husband called and said the house was on fire.
- We accept all forms of payment here but not checks.
- I love you, but I love myself more.
- But without the proper tools, we can’t finish this job, and the client will be left without a finished deck.
- I don’t care what you take with you in the divorce, but please leave my collection of antique cherubs.
Examples of Butt in a Sentence
Take a look at these examples I found using the word butt in a sentence.
- I can’t believe Michael did that and showed everyone in the office his butt!
- I’m tired of the way you all treat men; I’m always the butt of the jokes around here!
- I’m getting those butt implants next year; I just need to save up a few more thousand dollars.
- I have been going to the gym each day for six weeks and really focusing on my butt and glutes.
- Don’t forget to put powder on the baby’s butt after you change its diaper; it helps with chafing.
Final Word on But vs. Butt
Many people get confused between but and butt. Hopefully, this guide helps you differentiate between the two. Remember:
- But with one T is more commonly used because it’s a conjunction that shows contrast.
- Butt with two Ts refers to buttocks or a person at which humor is directed.
Main Difference – But vs Yet
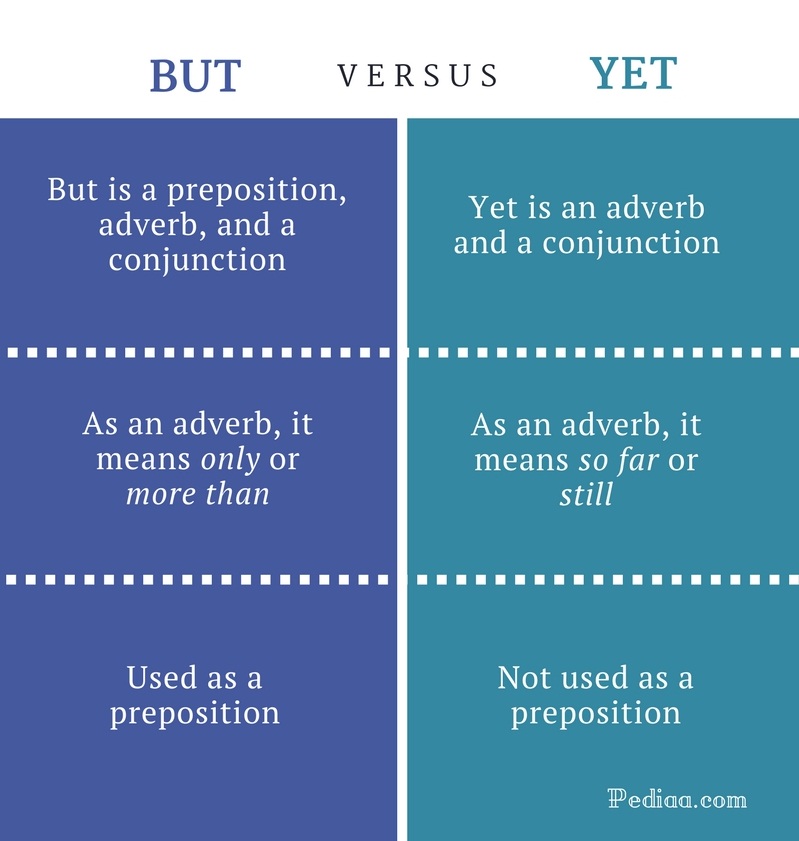
But and yet are two words that have many functions. Yet can function as an adverb and a conjunction whereas but can function as a conjunction, preposition, and an adverb. Although but and yet can be used interchangeably as conjunctions, they cannot be used interchangeably in other contexts. This is because these two words have different meanings as adverbs. As an adverb, but means no more than or only whereas yet means until now or so far. This is the main difference between but and yet.
This article covers,
1. What Does mean – Grammar, Meaning and Usage
2. What Does Yet Mean – Grammar, Meaning and Usage
3. Difference Between But and Yet
What Does But Mean – Grammar, Meaning and Usage
But can be used as a conjunction, preposition, and adverb. The following section describes these functions by explaining the different meanings of but and their examples.
But as a Conjunction
But is used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way. In other words, but connects two statements that have opposite meanings.
Her mother told her to stay quiet, but she started shouting.
The dress is cheap but elegant.
Many didn’t agree with her, but she didn’t let that discourage her.
But as an Adverb
The adverb but means no more than or only.
He is but a shadow of his strong brother.
He is but a child.
You have but two days to get ready.
But as a Preposition
As a preposition, but means or is equivalent to except or apart from.
You have no choice but to leave.
He had no one but his mother.
I didn’t tell anyone but my wife.
She didn’t tell anyone but her friend.
What Does Yet Mean – Grammar, Meaning and Usage
Yet can be used as an adverb as well as a conjunction. As a conjunction, yet can connect two contrasting ideas. In this sense, it is quite similar to but. The two conjunctions but and yet are interchangeable.
Her mother told her to stay quiet, yet she started shouting.
The dress is cheap yet elegant.
Many didn’t agree with her, yet she didn’t let that discourage her.
As an adverb, yet means up until the present or a specified or implied time. It is equivalent to so far or still. For example,
I haven’t watched it yet.
Have you told anyone else yet?
He is yet to be convinced of her innocence.
If you look at the meaning of the above examples carefully, you’ll note that yet in these examples cannot be replaced by but. The easiest way to remember the difference between but and yet is to remember that but and yet can only be used interchangeably when they are conjunctions.
The bus is not here yet.
Grammatical Category
But is a preposition, adverb, and a conjunction.
Yet is an adverb and a conjunction.
As an Adverb
But means only or more than.
Yet means so far or still.
As a Preposition
But is used as a preposition.
Yet is not used as a preposition.
Image Courtesy:
“One girl whispering secrets to another little girl” by Personal Creations (CC BY 2.0)
“WAITING FOR THE BUS-ON NICOLLET MALL – NARA – 551448” By Donald Emmerich, Photographer (NARA record: 3045077) – U.S. National Archives and Records Administration (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia