Last Update: Jan 03, 2023
This is a question our experts keep getting from time to time. Now, we have got the complete detailed explanation and answer for everyone, who is interested!
Asked by: Braden Ritchie
Score: 4.4/5
(30 votes)
Because is a subordinating conjunction, which means that it connects a subordinate clause
subordinate clause
A subordinate clause is a clause that cannot stand alone as a complete sentence; it merely complements a sentence’s main clause, thereby adding to the whole unit of meaning. Because a subordinate clause is dependent upon a main clause to be meaningful, it is also referred to as a dependent clause.
to an independent clause
independent clause
An independent clause (or main clause) is a clause that can stand by itself as a simple sentence. An independent clause contains a subject and a predicate and makes sense by itself.
; good style dictates that there should be no comma between these two clauses.
Is because a conjunction example?
because Definitions and Synonyms
Because can be used in the following ways: as a conjunction (connecting two clauses): We went by bus because it was cheaper. in the preposition phrase because of (followed by a noun): The game was cancelled because of the snow.
What type of conjunction is because?
Subordinating conjunctions
This type of conjunction includes words like because, if, although, since, until, and while. A subordinating conjunction is used to introduce a dependent clause.
Should I use a comma before because?
A comma before “because”
Most of the time, a comma is appropriate before because, given that the information in the clause that starts with because is not essential to the main thought. You could remove that clause without changing the meaning of the sentence, so it is considered secondary, or nonessential.
What type of word is because?
As detailed above, ‘because’ can be an adverb, an interjection or a conjunction. Adverb usage: I ruined my life because of you!
31 related questions found
What is because called in grammar?
Linguists are recognizing the delightful evolution of the word «because.» … The word «because,» in standard English usage, is a subordinating conjunction, which means that it connects two parts of a sentence in which one (the subordinate) explains the other. In that capacity, «because» has two distinct forms.
What is without in grammar?
from English Grammar Today. The preposition without means ‘not having something’ or ‘lacking something’: I can’t drink tea without milk.
How can I use because in a sentence?
Because sentence example
- I think he felt included because he was helping as much as we were. …
- They were angry because their plans had been discovered. …
- Because you are sorry for him! …
- Is it because winning the award gives them more confidence? …
- He was in trouble because his scholars would not study.
Is if a conjunction word?
If is a conjunction.
What are the 10 examples of conjunctions?
Examples of Conjunctions
- I tried to hit the nail but hit my thumb instead.
- I have two goldfish and a cat.
- I’d like a bike for commuting to work.
- You can have peach ice cream or a brownie sundae.
- Neither the black dress northe gray one looks right on me.
- My dad always worked hard so we could afford the things we wanted.
What is conjunction and examples?
A conjunction is a word that joins words, phrases, clauses, or sentences. e.g., but, and, because, although, yet, since, unless, or, nor, while, where, etc. Examples.
Is due to in a sentence?
Simple Example 1: The traffic jam was due to a terrible accident at the intersection. In the above-mentioned sentence, the phrase due to has been used to present the reason for the noun traffic jam. The reason for traffic jam, grammatically a noun entity, is a terrible accident.
What are 10 examples interjections?
Here are some more interjections, this time used in the context of an accompanying sentence:
- Ahh, that feels wonderful.
- Alas! I’m lost in the wilderness.
- Bah! That was a total waste of time.
- Bless you! I couldn’t have done it without you.
- It’s time for me to go. Cheerio!
- Congrats! …
- Crikey! …
- Gesundheit!
How do you use yet conjunction in a sentence?
as a conjunction (connecting two words, phrases, or clauses): The weather was cold, yet bright and sunny. Her advice seems strange, yet I believe she’s right. I’m amazed that you haven’t told him anything yet. She hasn’t yet decided if she wants to come or not.
What are the 7 conjunctions?
The seven coordinating conjunctions are for, and, nor, but, or, yet, and so.
What type of ID is if?
The word “if” is categorized under conjunctions because it connects the clauses “you can walk” and “the rain stops.”
What is the word if in a sentence?
You use if in conditional sentences to introduce the circumstances in which an event or situation might happen, might be happening, or might have happened. She gets very upset if I exclude her. You’ll feel a lot better about yourself if you work on solutions to your upsetting situations. You can go if you want.
Do we put comma after as?
Common starter words for introductory clauses that should be followed by a comma include after, although, as, because, if, since, when, while. While I was eating, the cat scratched at the door. Because her alarm clock was broken, she was late for class.
Do you put a comma after but?
According to editors and grammarians, there is no comma after the word but at the beginning of a sentence. … There is really only one comma rule that mentions conjunctions: a comma goes before a coordinating conjunction that separates two independent clauses.
Can a sentence start with as?
In that case, it is generally OK to start a sentence with «as,» particularly in informal writing. Some purists would argue that one should never start a sentence with a conjunction in formal writing, but the tide is beginning to turn on that former truism.
How do you use without in a sentence?
[M] [T] He left without saying goodbye. [M] [T] I did that without consulting anyone. [M] [T] He left the room without saying a word. [M] [T] Without your help, I would have drowned.
What is the difference between with no and without?
«Without» would have a different meaning. «With no» here has the meaning that the fellow put a lot of effort. «Without» couldn’t have been used here. That’s the only difference I could point out.
What does it mean when you say someone is without?
—used to say that someone is not with or is not involved with another person or group. : not using (something specified) without. adverb. English Language Learners Definition of without (Entry 2 of 2)
There are various types and kinds of conjunctions that are used in the English Language. Let us explore the usage of “because” as a conjunction.
“Because” is a conjunction and it is used as a way to provide reason or cause of a certain situation or circumstance.
Here are two examples of “because” as a conjunction-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 1. | He asked for another spoon because he dropped the first one. | The word ‘because’ in this statement can be termed a conjunction as it is used to join two clauses. |
| 2. | She was picked for the team because she is the best player.. | ‘Because’ in this example can be called a conjunction as it is seen linking two clauses. |
Let us take a deeper dive into “because” as a conjunction with the help of facts and examples.
Let us take a look at when is “because” a conjunction.
“Because” is a conjunction when it is used to link two clauses. Specifically speaking, subordinating clauses.
Here are a two examples of when “because” functions as a conjunction-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 3. | They finally bought the small cottage because they loved it so much. | In this case, the word ‘because’ can be termed a conjunction as it links subordinating clause of the sentence to the main clause. |
| 4. | The students cried because their favorite teacher was retiring. | In this particular case the term ‘because’ is also a conjunction as it links the second clause to the first one. |
How is “because” a conjunction?
Let us explore as to how “because” can be considered a conjunction.
“Because” is considered a conjunction due to the fact that that it helps combine two clauses.
Here are a couple examples of how “because” can be used as a conjunction-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 5. | We went to watch the ballet because it was the most anticipated show being put up in our city. | The word ‘because’ in this specific sentence functions as a conjunction as it joins two clauses together. |
| 6. | We reached early because we wanted good concert seats. | The term ‘because’ in this mentioned example is a conjunction as it joins the second clause to the first one. |
Is “because” always a conjunction?
Let us look into whether “because” always functions as a conjunction or not.
“Because” may not always be a conjunction. Sometimes it can be functional in different grammatical forms and that depends on its placement in a sentence and also on particular words that follow it.
Here are a two examples of “because” not being used as a conjunction-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 7. | My friends and I have not been in touch for two and a half years because of our extremely busy schedules. | In this case, the words ‘because of’ is a two-word preposition as it is used to mark the causal relationship between the second clause to the first clause. The usage of the word ‘of’ after ‘because’ tends to make it a prepositional term. |
| 8. | Because I got a better job, my lifestyle has also been updated. | Here, the word ‘because’ is an adverb as it is not used in the beginning of the sentence and does not combine the two clauses. |
When is “because” not considered as conjunction?
There are exceptional times when “because” may not be considered a conjunction. Let us explore that fact.
“Because” is not always used as it depends on when, where and how that word is placed in a sentence. “Because” can, in some cases, be used as a preposition and in some cases as an adverb.
Here is one example each of “because” functioning as a preposition and adverb-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 9. | We had to leave the school premises because of a pranks that the students pulled on the staff. | In this case, the words ‘because of’ is a two-word preposition as it is used to mark the causal relationship between the second clause to the first clause. The usage of the word ‘of’ after ‘because’ tends to make it a prepositional term. |
| 10. | Because she likes ice-cream, her father bought three tubs of it. | Here, the word ‘because’ is an adverb as it is not used in the beginning of the sentence and does not combine the two clauses. |
What kind of conjunction is the word “because”?
Let us explore as to what sort of a conjunction is “because”.
“Because” comes under the sub-type of a subordinating conjunction.
Here are a two examples “because” as subordinating conjunctions-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 11. | The most experienced worker will be asked to take over the assignment because the company needs the outcome to be perfect. | The word ‘because’ in this sentence as well can be termed a conjunction as it joins two clauses together, consequently making it a subordinating conjunction. |
| 12. | The college professors walked out because they wanted the higher ups to increase their pay. | In this particular example also ‘because’ is a subordinating conjunction as it links two clauses together, namely, the second one to the first one. |
Why is “because” a subordinating conjunction?
Let us try to figure why “because” is considered a subordinating conjunction.
“Because” is considered a subordinating conjunction as it connects a subordinating clause to a main clause.
Let us look at some more examples of “because” as conjunctions for better understanding-
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 13. | The toddler called her mother because she missed her on the one-day field trip her and her dad had taken. | In this case, the word ‘because’ can be termed a conjunction as it links subordinating clause of the sentence to the main clause. |
| 14. | Our entire group went to the best restaurant in town because we had wanted to go there for months now.. | The word ‘because’ in this statement can be termed a conjunction as it is used to join two clauses. |
Examples of ‘because’ as conjunctions.
Let us look at a few more exampled of ‘because as a conjunction.
| Sl. No. | Examples | Explanations |
| 15. | My son has been studying for hours now because his exams start from tomorrow. | The word ‘because’ in this sentence as well can be termed a conjunction as it joins two clauses together, consequently making it a subordinating conjunction. |
| 16. | The man bought a boat for himself because he won a good fortune with the lottery ticket. | ‘Because’ in this example can be called a conjunction as it is seen linking two clauses. |
| 17. | She quit her job because she wanted to start a business of her own. | The term ‘because’ in this mentioned example is a conjunction as it joins the second clause to the first one. |
| 18. | Mark wanted to become an architect as well as interior because it was his childhood dream. | In this particular case the term ‘because’ is also a conjunction as it links the second clause to the first one. |
| 19. | She asked for some loose cash because she only had her credit card. | ‘Because’ in this example can be called a conjunction as it is seen linking two clauses. |
| 20. | I love baking bread every Sunday because it helps me wind down after a long week. | In the written statement over here example also ‘because’ is a subordinating conjunction as it links two clauses together, namely, the second one to the first one. |
Conclusion
Hence, it’s proven that the word “because” more often than not is a conjunction, a subordinating conjunction at that, and in some cases can be used in different forms as well.
Home / Part of Speech by Word / What Part of Speech is “BECAUSE”


The word “because” is always used as a conjunction in English texts and verbal communication.
- Conjunction
This word is categorized under conjunctions because it can connect two clauses to form a single sentence. In the sample sentence:
I rested because I was tired.
The word “because” is considered as a conjunction that links together the clauses “I rested” and “I was tired.”
Definition:
a. for the reason that; since
- Example:
- She did it because she felt it was her duty.
Is because a conjunction word?
Because is a subordinating conjunction, which means that it connects a subordinate clause to an independent clause; good style dictates that there should be no comma between these two clauses.
Is the word because a pronoun?
Why Do Dictionaries Insist That Because Is a Conjunction? It Is Not. The classic subordinating conjunction is that (that can also be a pronoun, an adjective, or an adverb, but those are different usages).
Is because an adverb or a conjunction?
Because can be an adverb, an interjection or a conjunction.
What kind of word is furthermore?
adverb – Word
What is furthermore an example of?
Furthermore is defined as in addition to or besides. When furniture you are considering buying is beautiful and also cheap, this is an example of a situation where you might say “Its beautiful and furthermore, it’s cheap.” In addition; besides; moreover. In addition; moreover.
Is furthermore a formal word?
Moreover and furthermore are essentially interchangeable synonyms. They’re formal substitutes for additionally, also, as well, in addition to, likewise, and too.
What is furthermore in grammar?
“Furthermore” is similar to “in addition.” Use “furthermore” to add more information in your sentence. It’s a little formal, but you can use it when speaking English. Sometimes, the second part of the sentence that follows “furthermore” contains information more pertinent (important) than the first part. examples.
What comes first Furthermore or moreover?
Moreover is the next level up from furthermore. Also is simple addition, furthermore is addition and advancing an argument, whereas moreover is addition, advancing an argument, and indicating that the added reason is of a different kind than previously furnished reasons.
How do you use the word furthermore?
Furthermore is a useful word when you have an additional point to make in an argument or explanation. It is often used at the beginning of a sentence and followed by a comma.
What is another word for additionally?
Additionally Synonyms – WordHippo Thesaurus….What is another word for additionally?
| also | in addition |
|---|---|
| furthermore | further |
| too | as well |
| in addition to that | in addition to this |
| moreover | what’s more |
Is moreover a transition word?
To Add An Idea. again, also, and, as well as, besides, for one thing, further, furthermore, in addition to, last, likewise, more, moreover, next, similarly, too. To Illustrate or Explain an Idea. for example, for instance, in other words, in particular, namely, specifically, such as, that is, thus, to illustrate.
What do you say after furthermore?
Common Transitional Words and Phrases
- cause and effect: consequently, therefore, accordingly, as a result, because, for this reason, hence, thus.
- sequence: furthermore, in addition, moreover, first, second, third, finally, again, also, and, besides, further, in the first place, last, likewise, next, then, too.
Is firstly a good transition word?
Is “Firstly” a Real Word? Dictionary giants Samuel Johnson and Noah Webster did not recognize firstly as a word at all. Native English speakers naturally warm to the word firstly as an ordinal adverb because most adverbs end in -ly. Not all adverbs do; consider fast, well, and often, for example.
Can I use furthermore to start a new paragraph?
Of course, you can also use link words and phrases in the middle of a paragraph to start a new sentence. However, make sure you don’t over-use words such as ‘furthermore’, ‘moreover’, ‘additionally’, ‘nonetheless’ and ‘similarly’ to start either new paragraphs or new sentences.
How do you start a new paragraph?
At the beginning of each supporting paragraph, start with a topic sentence. This is a way to introduce the ideas that you’re going to discuss in that paragraph. You can elevate your topic sentence by using a transition word or phrase to show that you’re switching to a new idea.
When should you start a new paragraph examples?
You should start a new paragraph when:
- When you begin a new idea or point. New ideas should always start in new paragraphs.
- To contrast information or ideas.
- When your readers need a pause.
- When you are ending your introduction or starting your conclusion.
What is the new paragraph symbol?
Symbols
| Symbol Name | Image | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Pilcrow (Unicode U+00B6) | ¶ | Begin new paragraph |
| Pilcrow (Unicode U+00B6) | ¶ no | Remove paragraph break |
| Caret (Unicode U+2038, 2041, 2380) | ‸ ⁁ ⎀ | Insert |
| # | Insert space |
What is proper paragraph format?
A paragraph discusses one idea in detail and aids the development of an overall topic for the essay. Paragraph length will vary depending on the purpose of the paragraph. The basic paragraph consists of three parts: a topic sentence, supporting details, and a concluding sentence.
Do you start a new paragraph every time someone speaks?
Even with dialogue that is clearly attributed, start a new paragraph with each new speaker. The reader shouldn’t have to wait until after the dialogue is spoken to understand who is saying it. Readers form ideas and draw conclusions as they read.
How do you break up dialogue?
Breaking up dialogue with a tag Sometimes, writers choose to interrupt a speaker’s line with a dialogue tag before allowing them to continue. If the dialogue tag takes place between sentences, cap it off with a period. After the tag, resume the quote with the next sentence (which begins with a capital letter).
Should quotes be their own paragraph?
8. Each to its own: In conversation or dialogue, place each speaker’s quotes in separate paragraphs. Do not run two or more speakers’ quotes into the same paragraph, no matter how short.
How do you use multiple quotes in a sentence?
When multiple quotation marks are used for quotations within quotations, keep the quotation marks together (put periods and commas inside both; put semi-colons, colons, etc., outside both).
How do you break a quote into two?
Whenever you want to leave out material from within a quotation, you need to use an ellipsis, which is a series of three periods, each of which should be preceded and followed by a space. So, an ellipsis in this sentence would look like . . . this.
What type of word is because?
conjunction
What part of grammar is the word because?
In Standard English, the word “because” can be used two ways. One of them is to introduce a clause, as in “Aardvark was late because he was waiting for the repairman to show up.” Used this way, “because” is a subordinating conjunction. The other is to team up with “of” to form what’s called a compound preposition.
What is another word for addiction?
In this page you can discover 28 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for addiction, like: compulsion, craving, habit, bent, enslavement, dependence, habituation, obsession, addictedness, alcoholism and inclination.
What word can you use instead of so?
so
- accordingly,
- consequently,
- ergo,
- hence,
- therefore,
- thereupon,
- thus,
- wherefore.
What can I say instead of as?
What is another word for as?
| although | though |
|---|---|
| conversely | then again |
| by contrast | instead |
| despite that | just the same |
| except that | but still |
What is a word for righting a wrong?
Some common synonyms of rectify are amend, correct, emend, redress, reform, remedy, and revise. While all these words mean “to make right what is wrong,” rectify implies a more essential changing to make something right, just, or properly controlled or directed.
What is the meaning of could ve?
The definition of could’ve is something that potentially might have happened if it weren’t for another alternative. An example of could’ve is for a student to say that he had the potential to do his homework instead of choosing to go to the basketball game.
What type of word is could ve?
Could’ve is the usual spoken form of ‘could have,’ when ‘have’ is an auxiliary verb.
What type of word is would ve?
Would’ve is a spoken form of ‘would have,’ when ‘have’ is an auxiliary verb. I knew deep down that my mom would’ve loved one of us to go to college.
Is could’ve formal?
Because they are informal, most style guides—which tend to be guides for formal styles of written English—advise against using them. The Corpus of Historical American English has incidences of should’ve dating to 1910, could’ve dating to 1880, and would’ve dating to 1830.
Is could’ve proper?
And yes, could’ve is an acceptable contraction. Contractions are abbreviations of words blending together. Can’t is a contraction of “cannot.” Won’t is a contraction of “will not.” The proper contracted forms of could/would/should have look like could’ve/would’ve/should’ve.
Is might’ve a real word?
Might’ve is the usual spoken form of ‘might have,’ especially when ‘have’ is an auxiliary verb. Collins!
Is should’ve a real word?
should’ve | Intermediate English. contraction of should have: I should’ve known better.
A conjunction is a word that grammatically connects two words, phrases, or clauses together. The most common examples are words like “and” and “but.”
For example, “I took the subway, and got off at 96th Street.” Or, “I took the subway, but there was a delay.” However, conjunctions can come in many forms with many different functions.
They’re a part of speech that can be broken down into several categories, and we’ll explore each one in depth with examples.
Conjunctions can primarily be broken down into three categories:
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Correlative conjunctions
- Subordinating conjunctions
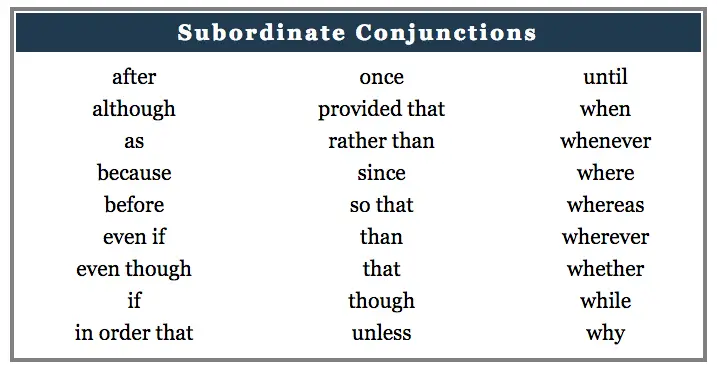
While we’ve so far seen some extremely common conjunctions, most conjunctions fall under the category of subordinating conjunctions. These conjunctions are used to join two clauses together that are grammatically unequal.
In other words, the clause without a conjunction (the independent clause) is able to stand alone, while the clause that contains the conjunction (the subordinate clause) cannot. Subordinating conjunctions examples:
- I don’t like cake because it’s too sweet.
This sentence consists of two clauses, “I don’t like cake” and “it’s too sweet,” both connected by the subordinating conjunction “because.”
The clause that stands alone is “I don’t like cake” and can form its own separate sentence. The clause “because it’s too sweet,” however, cannot stand alone and instead subordinates to the first clause.
This is why we call the word “because” a subordinating conjunction. You’ll notice that subordinating conjunctions are some of the most common and useful words in English. Below is a list of the most common ones.
Note that unlike with coordinating conjunctions, subordinate clauses can appear before or after the independent clause.
For example, while you could say, “I don’t like cake because it’s too sweet,” you could also say, “Because cake is too sweet, I don’t like it.”
BECAUSE
Used to introduce a cause or a reason
- I didn’t answer your messages because I was out of the country.
- I’m not going to apologize just because you told me to.
- Because my lower back kept hurting, I decided to finally go see a chiropractor.
SINCE
Can be used to introduce a cause or a reason
- I decided to bake cupcakes, since it was Marjorie’s birthday.
- Since you’re always late, I’m going to start showing up late too.
Can also be used to indicate that something has been true starting from a certain point in time.
- I’ve been broke since my last vacation to Puerto Rico.
- Ever since I was young, I’ve always wanted to become a scientist.
- What have you been up to since school ended?
UNTIL
Can be used to indicate that an event only happens up to a certain point in time.
- I usually sit around in my office until my boss gives me work to do.
- Until you came into my life, I wasn’t quite sure where I would find love.
- When I was in college, I would study until I passed out at 3 or 4 in the morning.
WHEN
Can be used to indicate that two events happened simultaneously
- When it started to snow, everyone started posting statuses on Facebook.
- When the clock struck three, all the students immediately evacuated the classroom.
- I don’t know how to react when you yell at me like that.
WHENEVER
Can be used to indicate that when one event happens at any point, so does another
- Whenever I try to comfort people, I somehow make things worse.
- I hate it whenever I run into coworkers outside of work.
- Whenever you start feeling anxious, just try to breathe.
WHILE
Can be used to indicate that two things happen simultaneously. It emphasizes the continuousness of an action more than the conjunction “when.”
- I often get distracted while trying to study.
- It’s hard trying to take classes while also working two jobs.
- While my parents were away for the weekend, my brother and I decided to throw a house party.
Can also be used to switch from one idea to another
- While puppies are cute, they can be incredibly annoying to take care of.
- Neutral colors tend to go together easily, while other colors are harder to pair up well.
AS
Can be used as an alternative to “while”
- We can see what logistical problems come up as we move on with the project.
- As the night drew on, the crowd became noisier and noisier.
- My dad entered the driveway right as I called to see where he was.
Can also be used as an alternative to “since” or “because”
- You should be careful going to the gym, as your ankle is still a little weak.
Can also be used to mean something like “in the manner of.” Can be emphasized by the word “just”
- I wrote my essay with five paragraphs just as my professor told me to do in the instructions.
- I took the dog out three times a day just as you told me to.
- Just as you requested, here’s your coffee with soy milk instead of regular milk.
ONCE

- I only started to seriously rethink my life once I graduated college.
- Once I actually started going to museums, I realized that I really liked them.
- I don’t know how Jared is so charismatic. Once he starts a trend, everyone else quickly follows.
IF
Can be used to set up a condition in a hypothetical situation.
- If I lived alone, I’d be blasting my music 24/7.
- I’ll scratch your back if you scratch mine.
- If something’s bothering you, don’t hesitate to tell me.
The conjunction “if” can be emphasized with the word “even.”
- I wouldn’t tell you his secret even if you begged me.
- Even if I’m having a bad day, I try to be nice to people.
AS IF
Can be used to mean something like “pretending that something were true”
- He treats me as if I were his sister, not his girlfriend.
- Don’t try to lecture me as if you actually knew what you were talking about.
- You tend to brush most things off as if they’re no big deal.
LIKE
Can be used as an alternative to “just as.” Can be emphasized by the word “just.”
- I did the dishes like you told me to.
- The dish that was served looked just like it did in the menu.
Can also be used as an informal alternative to “as if”
- Sometimes I feel like Keira ignores me on purpose.
- Don’t treat me like I’m an idiot.
UNLESS
Can be used to introduce an exception to a statement
- The professor said not to email her unless you have a logistical question.
- I personally won’t date you unless I find you attractive.
- The visiting team is going to win unless the tables somehow turn last minute.
IN CASE
Can be used to mean something like “for the possibility that something might happen”
- I sent the message twice in case the first one didn’t go through.
- In case you’re wondering, the performance doesn’t end for another two hours.
- Can you double check the document just in case there aren’t any errors?
WHETHER
A shortened form of “whether or not”
- I’m not sure whether we’ll be able to hit everything on the itinerary.
- Can you tell whether this was handwritten?
- Do you care whether I’m in the room while you’re on the phone?
ALTHOUGH
Can be used to mean “despite the fact that” or “regardless of the fact that”
- Although he was a bit rude, people still found him funny and hung out with him.
- Although the party was dull, I was still happy to see you guys.
- My dad claims that he’s German and Dutch, although he’s also a compulsive liar.
THOUGH
- I finally finished the video, though the editing is a bit choppy.
- Even though I hate rollercoasters, I went on one after my friends forced me.
- I tried escargot for the first time in Paris, though I can’t quite say that I enjoyed it.
AS SOON AS
Can be used to indicate that one event happened at the same time as or directly after another event. It’s similar to the correlative conjunctions “no sooner…than” and “hardly…when.”
- As soon as you’re all packed, we’ll put everything in the car and go.
- Can you let me know as soon as you’re done with the assignment?
- I saw your eyes light up as soon as I said the word “ice cream.”
AS LONG AS
Can be used to indicate that one thing is true only under the condition that another thing is true.
- I’ll be happy as long as you remember to call me when you’re gone.
- As long as it’s below 60 degrees, you won’t catch me wearing short sleeves.
- I’ll always tip a waiter as long as they’re a decent server.
Another alternative is “so long as.”
- You should be able to do whatever you want so long as you’re happy and healthy.
PROVIDED (THAT)
A more formal alternative to “as long as”
- The manager will give you a day off work provided you give a valid reason for it.
- Provided that you worked hard and participated all semester, the professor might cut your final grade some slack.
BEFORE
Used to introduce the earlier event in a pair of events
- We should meet up and grab lunch before this week is over.
- Before we move on any further, do you have any questions?
- I told you to use the bathroom before we left the rest stop.
AFTER
Used to introduce the later event in a pair of events
- My friend fell into a coma after he got in a car accident.
- After the movie is over, do you want to grab food somewhere?
- We decided to order pizza after you fell asleep.
IN THAT
Can be used to specify the respect to which something is true
- He’s peoplesmart in that he knows how to act around different people.
- I was extremely lucky in that the police decided not to check my belongings.
- The stage setting was excellent in that it really caught the eye yet with a minimalist design.
NOW THAT
Can be used to indicate that a situation has changed with the occurrence of an event
- Now that I’m eighteen, I can finally vote in my first election.
- I can think a bit clearer now that I’ve had my coffee.
- We should think about going to the park now that the weather is a bit nicer.
SO (THAT)

- I took some pictures on my vacation so you could see.
- If you see an ambulance behind you, always pull over so that it can get through.
- Can you make the link shareable so I can view it?