Is back a preposition?
The word “Back” is not a preposition but it is used as 1) a noun 2) an adjective 3) a verb and 4) an adverb. 1) USED AS A NOUN: the rear surface of the human body from the shoulders to the hips.
Is back an adverb of place?
An adverb of place can indicate an object’s position in relation to another object. Many adverbs of place indicate movement in a particular direction and end in the letters “-ward or -wards”. For example: Toward, forward, backward, homeward, westward, eastwards onwards.
How do you use back as a verb?
There are two uses of “back” as a verb:
- To support someone or something.
- To reverse or move backwards (opposite of forwards).
Is return verb or noun?
noun. the act or fact of returning as by going or coming back or bringing, sending, or giving back: the return of the Jews from the Diaspora;We should appreciate your return of the book immediately.
What is the verb of back?
intransitive/transitive to move backwards, or to make someone move backwards. back into/onto/out of etc: She backed out of the room carrying a tray. He backed me into a corner at the party.
Where do you place an adverb in a sentence?
When modifying an entire sentence, adverbs can be placed in four positions:
- at the beginning;
- at the end;
- after the verb to be and all auxiliary verbs: can, may, will, must, shall, and have, when have is used as an auxiliary (for example in I have been in Spain twice);
- before all the other verbs.
Which comes first verb or adverb?
Adverbs of manner are usually placed after the main verb. He swims fast. She sings beautifully. It is possible to place the adverb before the verb.
What is a example of a adverb?
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Lots of adverbs end “-ly.” For example: She swims quickly. (Here, the adverb “quickly” modifies the verb “swims.”)
What is adverb give 5 examples?
Examples
- He swims well.
- He ran quickly.
- She spoke softly.
- James coughed loudly to attract her attention.
- He plays the flute beautifully. ( after the direct object)
- He ate the chocolate cake greedily. ( after the direct object)
How do you identify a adverb?
An adverb is “a word that modifies or describes verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.” Adverbs typically answer questions like how or when in relation to the action of a sentence. Many common adverbs end in -ly, like quickly, usually, and completely, but not all adverbs do, such as very, now, here, and sometimes.
Is down a adverb?
Down can be used in the following ways: as a preposition (followed by a noun): She was walking down the street. as an adverb (without a following noun): She lay down and fell asleep. after the verb ‘to be’: Oil prices are down.
Is was an adverb or verb?
Examples of verbs that relate a state of being are: am, are, is, will, was, were. An adverb is used to show degree, manner, place, or time of the verb, adjective, or another adverb that it modifies. Examples of adverbs are: very, slowly, nearly, often, never, strangely, not.
What is the difference between verb and adjective?
Verbs are words used to describe an action, state, or occurrence, and form the main part of the predicate of a sentence, such as hear, become, happen etc; while Adjectives are words that describe or modify another person or thing in the sentence.
What is the verb example?
A verb is the action or state of being in a sentence. Verbs can be expressed in different tenses, depending on when the action is being performed. Example: Jennifer walked to the store. In this sentence, the verb is “were.” It shows a state of being that was in the past, so it is a past tense verb.
Is had a verb or noun?
The verb have has the forms: have, has, having, had. The base form of the verb is have. The present participle is having. The past tense and past participle form is had.
What are the 50 verbs?
50 verbs in english, Verb 1,2,3 Forms
| V1 Base Form | V2 Past Simple | V3 Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| drive | drove | driven |
| dwell | dwelt | dwelt |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
What are basic verbs?
In the English language, there are three basic types of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and auxiliary verbs, sometimes called helping verbs.
What are the 10 example of verb?
Examples of Action Verbs in Sentences
- Anthony is throwing the football.
- She accepted the job offer.
- He thought about his stupid mistake in the test.
- John visited his friend for a while and then went home.
- The dog ran across the yard.
- She left in a hurry.
- She yelled when she hit her toe.
- The cat sat by the window.
How many types of verb are there?
three types
What are adjectives give 10 examples?
Examples of adjectives
- They live in a beautiful house.
- Lisa is wearing a sleeveless shirt today. This soup is not edible.
- She wore a beautiful dress.
- He writes meaningless letters.
- This shop is much nicer.
- She wore a beautiful dress.
- Ben is an adorable baby.
- Linda’s hair is gorgeous.
What are some verb sentences?
Verb Phrase Examples
- She was walking quickly to the mall.
- He should wait before going swimming.
- Those girls are trying very hard.
- Ted might eat the cake.
- You must go right now.
- You can’t eat that!
- My mother is fixing us some dinner.
- Words were spoken.
I was strangely conscious of something not altogether unfamiliaras though something stirred in the back of my mind.
I knew that Darrow would hurry as fast as he could back to the valley by way of the upper hills; I knew that he had there several sporting rifles; and I hoped greatly that he and Dr. Schermerhorn might accomplish something before the men had recovered their wits to the point of foreseeing his probable attack.
He turned his back on Mary and walked away.
Any Stick Will Do To Beat A Dog Reader, possibly on one of your country walks you have come upon a man with his back against a hedge, tormented by a fiend in the likeness of a dog.
He turned to me with so beautifully casual an air that I wanted to clap him on the back with the joy of it.
The stranger, who was a youngster of about their own age, with a pleasant, good—natured—looking face, patted Diggory on the back in a fatherly manner, and addressing the group said, «Well, my boys, we‘re a large family at Ronleigh, but fresh additions are always welcome.
«Here is CÆSAR with his back toward us, fighting the German‘s hordes.
I know a preparation that will turn the sauerkraut and sausages, that Oswald eats so much of, into degluted fire and brimstone, warranted to keep him on the broad of his back for ten days or a fortnight.
I hopped over the wall at the back into the field, and waited there for about a quarter of an hour, and then, as no one came, I made tracks home.
I got so used to bein‘ kicked down stairs, that evry time a man come in the door, I would place my back towards him and sing out: «Kick away, my friend, I‘m in the Editorial biziness to—dayto—morrow I go hentsthere‘s rather too much exsitement runnin‘ a noosepaper, and I shall resine this evenin.
«We couldn’t back out of it at the last minute, you know; they‘d think we were afraid.
I was as dirty as a collier, my coat was half off my back from my handling on the moor, and there were long rents at the knees of my breeches.
The yellow of his coat darkened, and there was a whitish—gray streak along his back like that along Kazan‘s.
The door was closed and the windows shuttered, but half a dozen negroes came running from the back at the sound of our wheels and took us in out of the storm.
he asked, holding them behind his back by way of challenge.
Scowlyou know that scowl of hisit freezes the very sentries on the wall if he looks at their backs through the window!
The valet backed before the pale and desperate—looking young man, with terrified and wondering glances, and disappeared into his master‘s apartment, whence the Major put out his head as soon as he had his wig on.
«Put it on the floor at the back under the rug,« he said.
The little man with the cold blue eyes and the gray—blond hair stroked his back without fear.
He did not sleep a wink, did not even try, but lay on his back across the bed, hands locked over his hair while «visions of sugar plums danced through his head.«
They would push, they would shove, they would «boost,« they would arch both their straight backs as pedestals for her tiptoe; and at the same time, by some sweet prodigy of mechanics, she would pull them up and up with her.
The distance from the tips of the hoofs of the fore—feet, stretched out, to the top of the back between the shoulders, was seven feet and five inches.
«I will destroy all the people to whom thou shalt come, and I will make all thine enemies turn their backs unto thee.
Then, quickly, it began to back along the sill; until, reaching the wall at the end, it could go no further.
At last she went off, looking behind ‘er, to the ship, and then I went outside and put my back up agin the gate and waited.
FumbleFingers comment on EdGuiness answer is, I think, the real answer. When you are describing a destination, using a verb such as «go», you use the preposition «to». When you are describing a «state of being», using a verb such as «to be», you use the preposition «in».
I go to Detroit.
I am in Detroit.
I travelled to Detroit.
I live in Detroit.
Note that if you do use a non-proper noun like «city» or «town», you need to include an article.
I live in a city.
I went to the town.
Side note: «Town» without an article has a varity of special meanings. «I live in town» means that I live within the city limits, as in:
Bob: I live in the suburbs.
Alice: Oh, I live in town.
«I am/was/will be in town» means that I am in the city under discussion as opposed to travelling somewhere else. Like:
«I was on a business trip last weekend, but this weekend I’m staying in town.»
«We went to town» can mean that we went to the city under discussion, but it is also a slang term meaning we had a wild party or had sexual relations.
Back is an adverb, noun, adjective or verb.
Back can mean ‘returning to an earlier starting point or situation’ or ‘moving to a point further away’ or ‘replying to something’. Back also means ‘at the rear of’ or ‘the part of a person or thing that is opposite the front’.
Back as an adverb
Olga’s not looking forward to going back to school in September.
[taking a photograph]
Don’t move too far back or you’ll fall in the swimming pool.
Sorry, I’m just finishing a meeting. Can I ring you back in ten minutes?
Back as a noun
There’s a new restaurant at the back of our office building.
Will Hoskins is unlikely to play as he hurt his back badly playing in the Rugby World Cup semi-final and is still receiving treatment.
Back as an adjective
The reporters were chasing her and, in order to avoid the cameras, she had to use the back door of the theatre.
Unfortunately she’s spilt coffee over the back seat of the car.
Back as a verb
[talking about a pet dog]
He’s got a lovely temperament but he may panic and bite you if you back him into a corner.
Did you know that during his driving test he backed his car into a bicycle?
In this post, we are covering preposition, its types with examples and rules. Following points will be covered.
- What is a preposition?
- List of Prepositions
- Types of Preposition
- Simple Preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Types of Prepositions According to Function
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments/devices
- Preposition of direction/movement
- Preposition of agent
- Rules of Preposition
A preposition is an important part of the English language and grammar. Prepositions are common but they seem complicated when we use them. These are the words used to link the noun and pronoun or other words.
Preposition is used to prove a correlation between nouns and pronouns in a sentence.
Examples
- She is going to school.
- He put the flowers by the door.
- The jug was placed on the table.
In above sentences the bold words are prepositions.
Preposition + Noun
I gave the jug to Alan.
Preposition + Pronoun
I gave the wallet to him.
Preposition + Gerund
I devoted my time to stitching.
2 – List of Prepositions
- Above
- About
- Absent
- Across
- After
- Along
- Among
- Around
- As
- Before
- Behind
- Below
- Beside
- Beneath
- Between
- Beyond
- By
- Considering
- Despite
- During
- Except
- For
- From
- Given
- In
- Inside
- Into
- Minus
- Of
- Off
- On
- Onto
- Opposite
- Outside
- Over
- Per
- Plus
- Round
- Since
- Than
- Through
- To
- Towards
- Under
- Until
- Up
- Upon
- Via
- Without
- Within
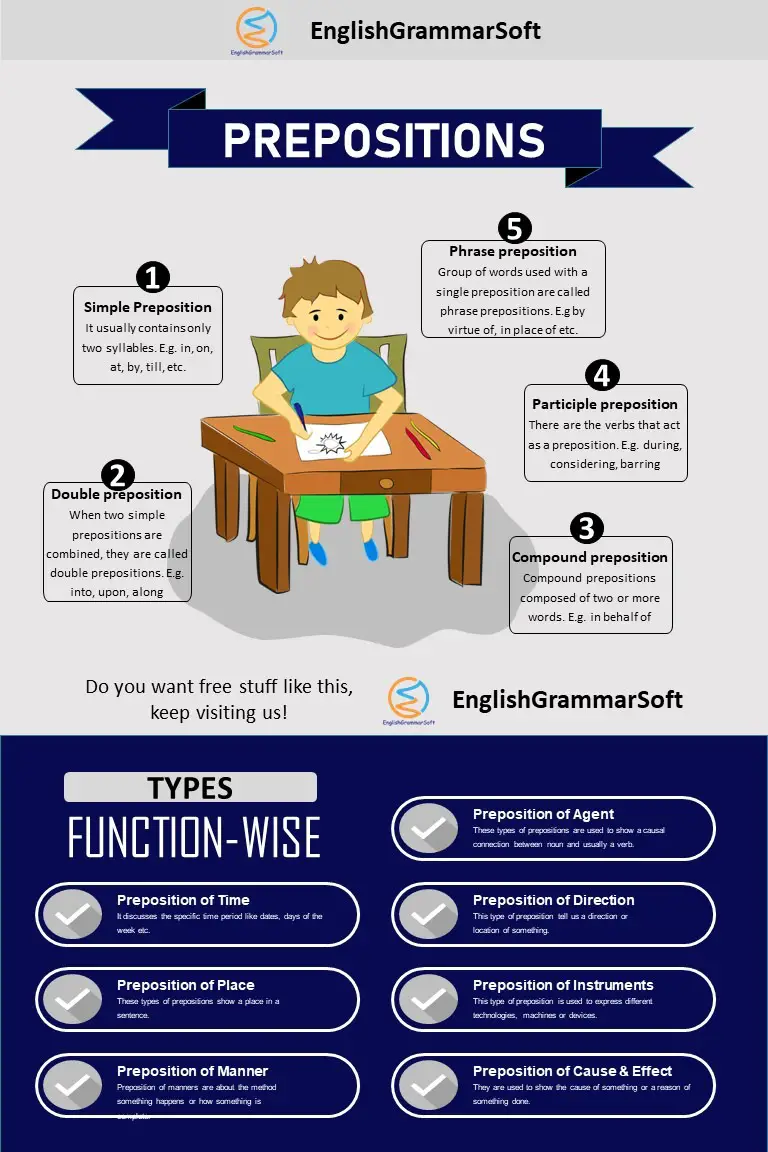
3 – Types of Preposition
There are different types of prepositions
- Simple preposition
- Double preposition
- Compound preposition
- Participle preposition
- Phrase preposition
3.1 – Simple Preposition
It usually contains only two syllables.
Simple prepositions are; by, at, in, of, off, out, till, up, to, with, on, etc.
Simple Preposition Examples
- Cat sat on the bed.
- There is some water in the jug.
- He is working hard to pass the exam.
- My baby is suffering from flu.
- I am from Islamabad.
- She is working at grocery store.
- This book belongs to Tom.
3.2 – Double preposition
When two simple prepositions are combined, they are called double prepositions. They habitually indicate directions.
Double prepositions are
- into
- upon
- along
- onto
- out of
- behind
- without
- within
- next to
Double preposition examples
- Once upon a time, there was a lion.
- The cat climbed onto the table.
- The dog is sitting behind the chair.
- Hira never goes out without her mobile.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- The bank is next to the post office.
3.3 – Compound preposition
Compound prepositions composed of two or more words. They are easy to known because the last word of a compound preposition is always simple preposition.
Compound preposition = Prefix + Noun / adjective / adverb
Compound prepositions are
- In behalf of
- According to
- Beyond
- In front of
- Beneath
- Besides
- Between
- Without
- Around
Compound preposition examples
- The children ran around the table.
- His personality is beyond imagination.
- There is a station beneath this area.
- There is a show inside the box.
- The dog is jumping around the seat.
- The auto pulled along the drive way.
- She is picked in front of bank.
3.4 – Participle preposition
There are the verbs that act as a preposition. Frequently, such words end in –ing and –ed.
Participle prepositions are
- During
- Considering
- Barring
- Provided
- Laughing
- Concerning
- Frustrated
Participle prepositions examples
- The teacher, sometimes gets frustrated with her class.
- Everyone, please keep quiet during the class.
- The kept following her home.
- Considering his education, he did a great job.
- Sara is interested in anything concerning novels.
- All the brothers were there including the mother.
3.5 – Phrase preposition
Group of words used with a single preposition is called phrase preposition.
For example,
- On the behalf
- On time
- At home
- Before class
- By virtue of
- Inspite of
- In place of
- On the floor
Sometimes they are used as an adverb and sometimes as a preposition.
- A word is preposition when it adds noun or pronoun. For example, The knife lies in the basket.
- A word is an adverb when it adds verb. For example, Let’s move on.
Phrase preposition = Preposition + object + modifier
- Jon received the trophy on the behalf of his friend.
- The match got canceled because of heavy rain.
- I will get to the class on time.
- Teacher met to discuss lecture before class.
- In course of time, the wounds healed.
4 – Types of Prepositions According to Function
There are many types of prepositions according to function.
- Preposition of time
- Preposition of place
- Preposition of manner
- Preposition of cause and effect
- Preposition of instruments / devices
- Preposition of direction / movement
- Preposition of agent
4.1 – Preposition of time
These types of prepositions show time in a sentence. It discusses the specific time period like dates, days of the week etc.
Preposition of time
- At: Used for precise time.
- In: Used for months, years, centuries and long periods.
- On: Used for days and dates.
Table
| AT | IN | ON |
| At 9 o’clock | In June | On Monday |
| At night | In the spring | On 8 February |
| At breakfast | In 1991 | On Sunday |
| At dinner | In December | On a summer eve |
| At noon | In the age | On independence day |
| At school | In the past | On my birthday |
| At college | In the future | On new year’s eve |
| At university | In the summer | On the way |
| At home | In a row | On a ship |
| At sunrise | In the garden | On a radio |
| At the moment | In the sky | On 30th June 2010 |
| At the cinema | In winter | On the wall |
Uses of at
- We have a meeting at 9 a.m.
- I went home at lunch time.
- We have a party at midnight.
- The shop closes at 6 o’ clock
- The stars shine at night.
At is used to express
- Exact time at 5 o’ clock
- Meal time at lunch
- Festivals at New Year
- With age at the age of 20
- Time at this time
Uses of in
- I shall return in an hour.
- In this town, it often rain in July.
- Would you think we will go to Greece in the future?
- I shall be successful in the next year.
- We will go to hill station in the summer.
In is used to express
- Parts of the day in the morning
- Months in December
- Centuries in 20th Century
- Years in 2013
- Season in Autumn
- Time period in those days
Uses of on
- I work on Monday.
- His birthday on 1st April.
- Vacations end on Tuesday.
- We are going to Texas on 1st June.
- We will meet on Friend’s Day
On is used to express
- Festivals on independence day
- Dates on 1st May
- Days of the week on Monday
- Occasion on that day
- Anniversaries on wedding day
4.2 – Preposition of Place
These types of prepositions show a place in a sentence.
- At: It is used to discuss a certain point.
- In: It is used an enclosed space.
- On: It is used to discuss a surface.
Examples of Preposition of Place
Uses of In
- I live in Multan
- She is in the bus.
- He is the most famous artist in the world.
- She watches TV in the room.
- Google is the best search engine in the world.
Uses of At
- I met him at the bust stop.
- We are going to watch the movie and we met him at cinema.
- Sun rises at 05:30 a.m.
- There is a rod at the roof.
Uses of On
- Look at the lizard on the wall.
- There is a book on the table.
- There is a smile on her face.
- My room is on the first floor of the hotel.
- There is a beautiful picture of my father on the wall.
4.3 – Preposition of Manners
Preposition of manners are about the method something happens or how something is complete. Commonly used words are “by” and “with”. Some other words are also used (in, like, on).
Examples
- She will dies by the cancer.
- Teacher faces students with big courage.
- My baby sings like a cuckoo bird.
- We are going by taxi.
- The tourist arrived on the island on a bus.
4.4 – Prepositions of cause and effect
They are used to show the cause of something or a reason of something done.
Commonly used words are; due to, because of, from hence, on account, therefore through etc.
Examples
- He cannot run the bicycle because of his leg.
- He is sick from fever.
- Her sales increased repeatedly through good marketing.
- The quarrel was increased due to discourtesy of both sides.
- She does not eat meal regularly on account of her disease.
4.5 – Preposition of Devices / Instrument
This type of preposition is used to express different technologies, machines or devices. Some words are used for, by, with and on.
On, with = describe the use of machines and devices.
For examples,
- My aunt is back home by taxi.
- Bob opened the lock with an old key.
- May I do my work on your computer?
- We are going on a trip by ferry.
- My work is done with the use of your cell phone.
4.6 – Preposition of Direction / Movement
This type of preposition tell us a direction or location of something.
Some words used are
- Across
- Along
- Among
- At
- Behind
- Below
- Into
- Towards
- Onto etc.
Examples
- Supervisor walked towards the examination hall.
- Sana was sitting among her family.
- Meet me at the bus stop.
- The ducks are eating along the river.
- I have the poster below the mirror.
4.7 – Preposition of agent
These types of prepositions are used to show a causal connection between noun and usually a verb. Words used as preposition of agent are:
- By
- With
Examples
- A literature book was written by John Keats.
- This work was done by me.
- Some institutes were closed by government.
- Hira graduated with a public administration degree.
Some commonly used prepositions are:
In front of
It is used to show that someone is standing in front of other person. For example,
The teacher stands in front of the class.
Behind
It is used to show that at the back of something.
Example
There is a shoe behind the table.
Between
It is used to show that two things or boejcts
Example
There is a strong relationship between Tom and Alice.
Across from
It is used to show an opposite direction.
Example
She lives across from school.
Next to
It is used to show that a person that is at the side of another thing.
Example
A guard stands next to the entrance gate.
Under
It is used to show low level of something.
Example
There are boxes under the bed.
5 – Rules of prepositions
There are three rules
- Pair them accurately.
- Watch what follows them.
- Avoid using them at the end of sentences
5.1 – Pair them properly
Determining which preposition to exercise be a capable of tricky prepositions. It is notably difficult when dealing with idioms. Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just give birth to memorize, and at what time errors are made.
That’s why you need to write them accurately with their places and easy to understand.
5.2 – Watch what follows them
Prepositions are always be followed by a noun / pronouns. The noun is called the object of preposition. Note that a verb can’t be the object of a preposition.
Example
The bone was for the dog. (correct)
The bone was for walked. (incorrect)
5.3 – Avoid using them at the end of sentences
Because prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be sited at the end of sentences.
Example
The table is where I put my books on. (incorrect)
I put my books on the table. (correct)
Further Reading:
- 50 sentences of prepositions
- Preposition Usage and Examples
- Learn Prepositions