Table of Contents
- What does rode mean?
- What is the root form of Rode?
- What kind of verb is rode?
- Do you say rode or ridden?
- What is another word for rode?
- What is the opposite of Rode?
- What is another word for amazed?
- Is amazed positive or negative?
- Is dumbfounded negative or positive?
- Is flabbergasted good or bad?
- What is another word for very shocked?
- How do you describe a shocked person?
- How do you explain being overwhelmed?
- How do you respond to being overwhelmed?
- What does a messy house say about a person?
- How do you clean yourself when you’re overwhelmed?
- How do you declutter when overwhelmed?
verb. a simple past tense of ride. Nonstandard. a past participle of ride.
What does rode mean?
Rode is defined as to have taken a ride. The definition of a rode is the rope or chain attached to the anchor used with a small boat. An example of a rode is a cable attached to an anchor which is used to keep a boat from moving in the water.
What is the root form of Rode?
The verb “ride” does not follow a regular conjugation pattern. In the past tense, the root changes, with the “i” swapping out for “o,” to form the verb “rode.” The past participle is “ridden,” as in: “He has ridden the bike.”
What kind of verb is rode?
Rode definition: Rode is the simple past tense conjugation of the verb to ride, which means to travel inside or on top of something.
Do you say rode or ridden?
Rode is in the simple past form. Ridden is the past participle. When you use the word rode, you are talking about riding something in the immediate or distant past.
What is another word for rode?
Rode Synonyms – WordHippo Thesaurus….What is another word for rode?
| went | travelledUK |
|---|---|
| motored | rolled |
| toured | hitched a ride |
| thumbed a ride | spun |
| span | steered |
What is the opposite of Rode?
Near Antonyms for rode. dived. (or dove), lunged, plunged.
What is another word for amazed?
In this page you can discover 45 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for amazed, like: astonished, astounded, stunned, dumbfounded, astonied, flabbergast, posed, surprised, overwhelmed, mystified and vexed.
Is amazed positive or negative?
Both can be used in both contexts. Effectively, when given a negative connotation, it is similar to the word ‘Stunned’ as in “I will be amazed when he finally gets a job” or “I’m astonished by your lack of commitment”.
Is dumbfounded negative or positive?
Dumbfounded: “greatly astonish or amaze: they were dumbfounded at his popularity.” (New Oxford American Dictionary) Although it doesn’t necessarily suggest a negative outcome, I think it does generally carry connotations of nonplussed bemusement. As others have already mentioned, there’s also appalled and nonplussed.
Is flabbergasted good or bad?
Use the adjective flabbergasted to describe someone who’s astounded or surprised for any reason, good or bad. You could be flabbergasted at how astonishingly expensive a parking ticket is, or at how incredibly delicious pineapple pizza is.
What is another word for very shocked?
What is another word for shocked?
| stunned | astonished |
|---|---|
| astounded | amazed |
| dumbfounded | flabbergasted |
| dumbstruck | stupefied |
| thunderstruck | surprised |
How do you describe a shocked person?
There are other ways to show shock. Their heart stops or skips or catches. They’re frozen or rooted to their place. Stomach twists.
How do you explain being overwhelmed?
Emotional overwhelm is a state of being beset by intense emotion that is difficult to manage. It can affect your ability to think and act rationally. It could also prevent you from performing daily tasks. Emotional overwhelm may be caused by stress, traumatic life experiences, relationship issues, and much more.
How do you respond to being overwhelmed?
If the person is able to describe feeling (overwhelmed), use good eye contact and empathic listening to affirm what s/he says. That could sound like… “So you’re feeling like things are just too much for you now.”
What does a messy house say about a person?
Some people simply do not place a high priority on having everything clean, organized, and in its place. In this case, messiness is simply a normal state of affairs. If the house is cluttered and it’s just fine with you, then it’s probably more a sign of your personality and preferences.
How do you clean yourself when you’re overwhelmed?
How to Start Cleaning if You’re Overwhelmed
- Set a timer for 20 minutes.
- Spend those 20 minutes cleaning.
- Take a 10-minute break from cleaning.
- Repeat.
How do you declutter when overwhelmed?
15 SIMPLE WAYS TO START DECLUTTERING WHEN FEELING OVERWHELMED
- #1 – JUST GET STARTED! I know, I know.
- #2 – START SMALL.
- #3 – CREATE A HABIT.
- #4 – CREATE A PLAN.
- #5 – FOCUS YOURSELF.
- #6 – START IN THE PLACE THAT WILL MAKE A DIFFERENCE THE MOST.
- #7 – KEEP IT SHORT AND SWEET.
- #8 – DO A RUBBISH AMNESTY.
English has a wide array of homophones that confuse both native and non-native speakers alike. What’s confusing about them is that many of us will use words in everyday conversation but give little thought to their spelling or purpose in a sentence. Most words come to us as sort of second nature, or we gradually pick them up as time goes by. But when we go to write them down on paper, it’s a little more difficult to remember which is which. The difference between road vs. rode is a good example of two popular words that hang people up.
So, in today’s post, I want to discuss the definitions of these words, their functions in a sentence, and give you a few tips on how to keep track of them in the future. Once you finish reading this post, you shouldn’t have any trouble remember which word to use and when.
When to Use Road

- What road do I turn on to get to your house?
- Slow down, you are almost to my road.
Road also has a more metaphorical sense meaning a “course or path.”
- If you go to a good school, you’ll be on the road to a good paying job.
- He was on the road to riches and no one could stop him.
It is clear in both of these examples that the subject was not literally on “road to riches.” It is a metaphorical pathway referring to the direction his life was headed.
When to Use Rode

- President Ronald Reagan enjoyed riding horseback.
- She and I rode together in her car.
Ride has a few other definitions, mostly having to do with travel, movement, or being supported/carried.
- We rode highways the entire trip.
- He rode a giant wave while surfing.
- He rode his motorcycle to work.
Remember the Difference
It’s actually quite easy to distinguish between these two words when you’re writing your sentence because they are two different parts of speech.
As I mentioned above, “road” is a noun. This means that it could appear just about anywhere in your sentence.
- Roads are dangerous around here. (Beginning of sentence and subject)
- In order to get there on time, we really need to take the correct road. (End of sentence and direct object)
“Rode,” on the other hand, is a verb. This means that you should expect the subject of your sentence to be very close.
- We rode the bike in tandem. (Subject directly beside “rode”)
Another great mnemonic tool to keep track of these two words is that Roads are made with Asphalt, and both of these words contain the letter “a.”
Summary
Mixing up rode vs. road can be an embarrassing mistake, but it is entirely avoidable.
Road is a way for passage for vehicles or bicycles. It is a noun and is commonly made from asphalt.
Rode is the past tense of the verb “ride.”
Contents
- 1 When to Use Road
- 2 When to Use Rode
- 2.1 Remember the Difference
- 2.2 Summary
|
WordReference Random House Learner’s Dictionary of American English © 2023 rode1 /roʊd/USA pronunciation
WordReference Random House Unabridged Dictionary of American English © 2023 rode1
rode2
Collins Concise English Dictionary © HarperCollins Publishers:: rode /rəʊd/ vb
WordReference Random House Learner’s Dictionary of American English © 2023 ride /raɪd/USA pronunciation
n. [countable]
Idioms
WordReference Random House Unabridged Dictionary of American English © 2023 ride
v.t. n.
Collins Concise English Dictionary © HarperCollins Publishers:: ride /raɪd/ vb (rides, riding, rode, ridden)
n
Etymology: Old English rīdan; related to Old High German rītan, Old Norse rītha ˈridable, ˈrideable adj ‘rode‘ also found in these entries (note: many are not synonyms or translations): |
|
Definitions For Rode
Verb
rodt , grodt
(transitive, reflexive) to move, stir
Etymology 1
Verb
Simple past tense of ride
(now, colloquial, nonstandard) Past participle of ride
Etymology 2
Noun
RODE (plural RODEs)
(nautical) The line from a vessel to its anchor.
Synonyms
warp
Translations
Dutch: reed, reden
Finnish: ankkuriköysi (rope), ankkurikettinki (chain)
Icelandic: reið
Norwegian: red
Etymology 3
See road.
Noun
RODE (plural RODEs)
(obsolete) A raid; an incursion.
: (Edmund Spenser)
(obsolete) A roadstead.
Anagrams
Dore, EDRO, Oder, dero, doer, orde, redo, roed
Alemannic German
English International (SOWPODS)
YES
Points in Different Games
Scrabble
Words with Friends
The word Rode is worth 5 points in Scrabble and 5 points in Words with Friends
Asked by: Mr. Van Streich
Score: 5/5
(51 votes)
v.tr. To clean or put in order: tidied up the house. To make things clean or orderly: tidied up after dinner.
What does tidied up mean?
Synonyms & Antonyms of tidied (up)
1 to make a place neat and orderly by removing extraneous stuff. just give me a minute to tidy up before you bring company over.
How do you use tidied in a sentence?
Tidied sentence example
- The room there has not been tidied up. …
- After a shower and breakfast, she tidied the cabin and wandered around. …
- When they came in to tea, having taken off their outdoor things and tidied themselves up after their journey, Marya Dmitrievna kissed them all in due order.
What does tidier mean in English?
neat, orderly, or trim, as in appearance or dress: a tidy room; a tidy person.
What does tidy mean in slang?
Tidy – Great, fantastic, brilliant etc…
21 related questions found
What is a fancy word for clean?
pure, flawless, fresh, immaculate, impeccable, spotless, unblemished, unsullied. hygienic, antiseptic, decontaminated, purified, sterile, sterilized, uncontaminated, unpolluted.
Are tidied up?
To make something or some place cleaner, neater, or more organized in appearance. In this usage, a noun or pronoun can be used between «tidy» and «up.» You really need to tidy up your room.
What do you call a person who cleans?
A janitor (American English, Scottish English), custodian, porter, cleanser, cleaner or caretaker is a person who cleans and maintains buildings.
What does impulsive mean in English?
: doing things or tending to do things suddenly and without careful thought : acting or tending to act on impulse. : done suddenly and without planning : resulting from a sudden impulse. See the full definition for impulsive in the English Language Learners Dictionary. impulsive.
What’s the meaning of shipshape?
: clean, neat, and tidy : organized and in good condition. See the full definition for shipshape in the English Language Learners Dictionary. shipshape. adjective.
How do you say ride in past tense?
Rode is in the simple past form. Ridden is the past participle. When you use the word rode, you are talking about riding something in the immediate or distant past.
Is past perfect tense?
The formula for the past perfect tense is had + [past participle]. It doesn’t matter if the subject is singular or plural; the formula doesn’t change.
Can we use tidy as a verb?
verb (used with or without object), ti·died, ti·dy·ing. to make tidy or neat (often followed by up). noun, plural ti·dies.
How do you describe a very clean person?
fastidious – very concerned about matters of cleanliness (Oxford Dictionaries Online)is a particular sense strongly associated with that way of referring to “fussiness”. Clean freak someone who has to constantly clean; someone who obsessively cleans. Neatnik (n) A stickler for neatness or cleanliness.
Is cleaned up a word?
If it’s an action or process, «clean up» can take a tense: A «cleanedup» isn’t grammatically correct, but «cleaned up» is.
What are 3 synonyms for clean?
- washed, scrubbed, cleansed, cleaned, polished.
- spotless, unsoiled, unstained, unspotted, unsullied, unblemished, immaculate, pristine, speckless, dirt-free.
- hygienic, sanitary, disinfected, sterilized, sterile, aseptic, decontaminated, healthy.
- pure, white, whiter than white.
- laundered.
What’s a better word for beautiful?
admirable, adorable, alluring, angelic, appealing, beauteous, bewitching, captivating, charming, classy, comely, cute, dazzling, delicate, delightful, divine, elegant, enthralling, enticing, excellent, exquisite, fair, fascinating, fetching, fine, foxy, good-looking, gorgeous, graceful, grand, handsome, ideal, inviting …
How do you say very clean?
very clean
- clean.
- fresh.
- hygienic.
- immaculate.
- neat.
- polished.
- pure.
- sanitary.
Does tidy mean good looking?
The definition of tidy is someone or something that is neat and well put together. An example of someone who would be described as tidy is a clean and well-dressed person.
What does Chopsy mean?
Chopsy means cocky and talkative.
Is tidy a bad word?
Use the adjective tidy for something that is neat and clean. … A less informal use is as an adjective, meaning “large.” If you can put the word tidy before your profit or the sum in your bank account, it’s a good thing.
One of the common challenges faced by non-native English speakers is English Grammar. The English language comes with an extensive library of words, slangs, phrases, idioms, etc. The foundation of being strong in your English vocabulary is your mastery of the words in the English language.
It is estimated that there are over 1 million words in the English language. However, if you are taking an English language test such as the Duolingo English test — you don’t have the time and energy to learn and know all the words. Frankly, nobody can.
The truth is you don’t need to learn every single word in the English dictionary. You need to familiarize yourself with the most common real words in the language. These common words are the building blocks of your language skills which you can apply to the various test sections of the DET. You can also confidently use these common words in your day-to-day life, whether you are a student, a career-minded professional, or someone visiting an English-speaking country.
Here, in this article, we will share some of the most common words in the English language that you need to learn and know to pass the Duolingo English test successfully.
We will also discuss the test sections where you will have the opportunity to use them. Finally, we’ll also share some sample practice questions to help you understand where they will appear on your Duolingo English test.
Most Common Real Worlds on the Duolingo English Test
Which Duolingo English Test Sections Test Your English Vocabulary?
The variation on the “yes/no” vocabulary exam is very common in many English tests, including Duolingo English Test. These exams have been used to measure vocabulary proficiency across the CEFR levels or other English Proficiency tests.
The text variation of the “yes/no” question type requires you to distinguish between a collection of written English words and pseudo-words made to seem English-like. Studies show that the text yes/no vocabulary item type predicts listening, reading, and writing ability.
Traditional yes/no vocabulary exams concurrently provide a huge number of stimuli of varying degrees of difficulty. The format is made computer-adaptive by displaying many smaller sets, each containing a handful of stimuli of similar complexity.
This test activity is available in two formats: text and audio. These types of questions will appear in the following test sections of the DET:
- Read and Select
- Listen and Select
Read and Select
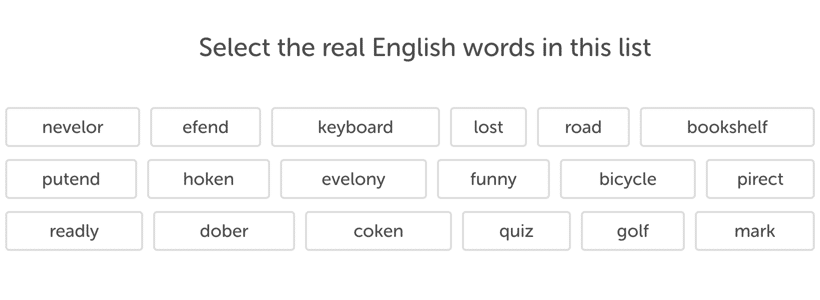
In this test section, you will work on a list of terms, some of which are genuine and others are pseudo-words, and you must choose just the proper ones.
Be cautious while selecting the right word, and double-check the spelling since some words seem accurate but are made up!
Listen and Select
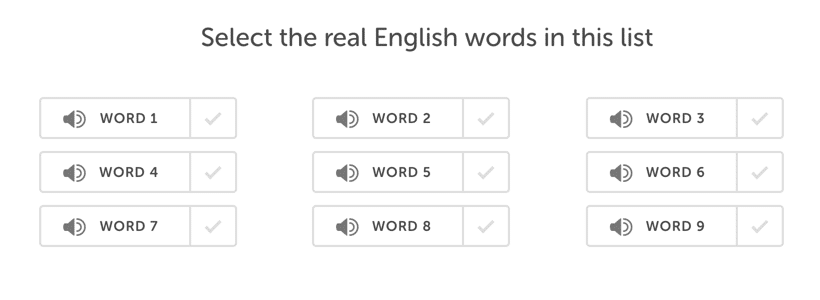
Unlike Read and Select, you must listen to the words before picking the correct ones.
The same advice applies to this test problem as the previous one. The pronunciation may sound like a legitimate term, but it isn’t, so pay attention!
Here are some valuable tips that we can give you in answering these test types:
- Only use phrases that you are certain are true! Trust yourself.
- There might be an unlimited amount of genuine terms in the list, so don’t be concerned if one question contains more than another.
- Please read the paragraphs carefully. Some words seem to be authentic, although they vary somewhat from actual English terms.
- Pay close attention to each syllable of each word since some bogus words may change slightly from actual ones.
- Only use terms that you are certain are true.
- Before pressing the NEXT button, double-check the words you’ve chosen.
How to Improve Your Vocabulary And Spelling for the Duolingo English Test?
Adding new terms to your written vocabulary is one of the simplest methods to improve your writing abilities. To learn and apply English vocabulary, you will never run out. A strong vocabulary is beneficial to all writing genres, including fiction, journalism, essays, poetry, etc. Defined as time put in writing, learning new words improves your vocabulary.
- Make reading a habit: Contextual vocabulary development is the easiest.
- Use the dictionaries: Correct usage of online dictionaries and thesaurus is beneficial.
- Word games: Classic games like Scrabble and Boggle may help you learn new words in English.
- Take notes: Using flashcards is a quick technique to learn a vast vocabulary.
- Subscribe to daily word feeds: Some websites, apps, or email services will send you a word a day to help you develop your vocabulary.
- Mnemonics:; Associating words helps you recall their meanings and their use.
- Experiment with new terms in speech: Unable to utilize words, one might build up a large vocabulary.
- 30+ Tips to Speak English Without Grammar Mistakes
What Are the Common English Words You Need to Learn for the Duolingo English Test?
Here is a list of real English words that you can get yourself be familiar with:
Days of the Week
| Sunday | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday |
| Friday | Saturday | weekdays | weekend |
Months of the Year
| January | February | March | April | May | June |
| July | August | September | October | November | December |
Numbers
| one | twenty-one | forty-one | sixty-one | eighty-one |
| two | twenty-two | forty-two | sixty-two | eighty-two |
| three | twenty-three | forty-three | sixty-three | eighty-three |
| four | twenty-four | forty-four | sixty-four | eighty-four |
| five | twenty-five | forty-five | sixty-five | eighty-five |
| six | twenty-six | forty-six | sixty-six | eighty-six |
| seven | twenty-seven | forty-seven | sixty-seven | eighty-seven |
| eight | twenty-eight | forty-eight | sixty-eight | eighty-eight |
| nine | twenty-nine | forty-nine | sixty-nine | eighty-nine |
| ten | thirty | fifty | seventy | ninety |
| eleven | thirty-one | fifty-one | seventy-one | ninety-one |
| twelve | thirty-two | fifty-two | seventy-two | ninety-two |
| thirteen | thirty-three | fifty-three | seventy-three | ninety-three |
| fourteen | thirty-four | fifty-four | seventy-four | ninety-four |
| fifteen | thirty-five | fifty-five | seventy-five | ninety-five |
| sixteen | thirty-six | fifty-six | seventy-six | ninety-six |
| seventeen | thirty-seven | fifty-seven | seventy-seven | ninety-seven |
| eighteen | thirty-eight | fifty-eight | seventy-eight | ninety-eight |
| nineteen | thirty-nine | fifty-nine | seventy-nine | ninety-nine |
| twenty | forty | sixty | eighty | hundred |
Subjects or General Topics
| Science | Politics | Architecture | Law |
| Physics | Psychology | Anthropology | Economics |
| Statistics | Mathematics | Performing Arts | Visual Arts |
| Archaeology | Business Management | Logic | Literature |
| History | Biology | Humanities | Chemistry |
| Geography | Philosophy | Agriculture | Engineering |
Continents
| Antarctica | Europe | Oceania | Arctic |
| Asia | North America | South America |
Countries
Countries in Asia
| Afghanistan | Georgia | Kyrgyzstan | Pakistan | Taiwan |
| Armenia | India | Laos | Palestine | Tajikistan |
| Azerbaijan | Indonesia | Lebanon | Philippines | Thailand |
| Bahrain | Iran | Malaysia | Qatar | Timor-Leste |
| Bangladesh | Iraq | Maldives | Russia | Turkey |
| Bhutan | Israel | Mongolia | Saudi Arabia | Turkmenistan |
| Brunei | Japan | Myanmar | Singapore | United Arab Emirates (UAE) |
| Cambodia | Jordan | Nepal | South Korea | Uzbekistan |
| China | Kazakhstan | North Korea | Sri Lanka | Vietnam |
| Cyprus | Kuwait | Oman | Syria | Yemen |
Countries in Europe
| Albania | Cyprus | Iceland | Moldova | San Marino |
| Andorra | Czechia | Ireland | Monaco | Serbia |
| Armenia | Denmark | Italy | Montenegro | Slovakia |
| Austria | Estonia | Kazakhstan | Netherlands | Slovenia |
| Azerbaijan | Finland | Kosovo | North Macedonia | Spain |
| Belarus | France | Latvia | Norway | Sweden |
| Belgium | Georgia | Liechtenstein | Poland | Switzerland |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Germany | Lithuania | Portugal | Ukraine |
| Bulgaria | Greece | Luxembourg | Romania | United Kingdom |
| Croatia | Hungary | Malta | Russia | Vatican City |
Countries in North and South America
| Antigua and Barbuda | Bahamas | Barbados | Belize | Canada |
| Dominica | Dominican Republic | El Salvador | Grenada | Guatemala |
| Jamaica | Mexico | Nicaragua | Panama | Colombia |
| Bolivia | Brazil | Paraguay | Uruguay | Venezuela |
| Costa Rica | Cuba | Trinidad and Tobago | Argentina | Haiti |
| Honduras | United States of America (USA) | Ecuador | Guyana | Suriname |
| Saint Lucia | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Peru | Chile |
Countries in Africa
| Algeria | Chad | Ethiopia | Madagascar | Rwanda |
| Angola | Comoros | Gabon | Malawi | Sao Tome and Principe |
| Benin | Zambia | Ghana | Mauritania | Seychelles |
| Botswana | Cote d’Ivoire | Guinea | Mauritius | Sierra Leone |
| Burkina Faso | Djibouti | Guinea-Bissau | Morocco | Somalia |
| Burundi | Egypt | Kenya | Mozambique | South Africa |
| Cabo Verde | Equatorial Guinea | Lesotho | Namibia | South Sudan |
| Cameroon | Eritrea | Liberia | Niger | Sudan |
| Mali | Eswatini | Libya | Nigeria | Tanzania |
| Togo | Tunisia | Uganda | Zambia | Senegal |
| Zimbabwe | Congo | Gambia | Mali |
Countries in Australia and Oceania
| Australia | Fiji | Kiribati | Marshall Islands |
| Palau | Papua New Guinea | Samoa | Solomon Islands |
| Micronesia | Nauru | New Zealand | Tonga |
| Tuvalu | Vanuatu |
| air conditioner | doorknob | greenhouse | painting | swimming pool |
| appliances | doorway | gutters | paneling | threshold |
| attic | dormer | hall | pantry | throw rug |
| awning | downspout | hall closet | patio | toilet |
| back door | downstairs | hallway | picture | trash can |
| backyard | drain | hamper | picture frame | trellis |
| baluster | drapes | heater | plumbing | trim |
| barbecue | driveway | hinge | pool | tub |
| baseboard | dryer | home | porch | upstairs |
| basement | duct | hose | portico | vacuum cleaner |
| bathroom | dustpan | house | quilt | vase |
| bathtub | eaves | inglenook | railing | Venetian blinds |
| beam | electrical outlet | insulation | rake | vent |
| bedroom | electrical system | jamb | range | wainscoting |
| blinds | entrance | key | recreation room | walkway |
| broom | entry | kitchen | roof | wall |
| bunk bed | entryway | ladder | room | carpet |
| carpet | family room | lamp | rug | washer |
| carport | fan | lanai | sash | toilet |
| ceiling | faucet | laundry | screen door | wastebasket |
| cellar | fence | laundry room | shed | water heater |
| chimney | fenced yard | lawnmower | shelf | weather stripping |
| closet | fireplace | library | shelves | welcome mat |
| clothes dryer | floor | light | shingle | window |
| clothes washer | foundation | light switch | shower | windowpane |
| column | frame | linen closet | shutters | window sill |
| concrete | front door | lintel | siding | wood stove |
| cornice | front stoop | living room | sill | yard |
| counter | furnace | lock | sink | door |
| crib | furniture | loft | skylight | doorbell |
| cupboard | fuse box | lumber | sliding door | door jamb |
| curtain rod | gable | mailbox | soffit | garden shed |
| curtains | garage | mantle | staircase | gate |
| dining room | garage door | mat | stairs | girder |
| dishwasher | garage opener | mirror | stairway | storage shed |
| doggie door | garbage can | mop | steps | storm door |
| doghouse | garden | newel | stoop | stove |
Places
| city | town | capital | metropolis | village |
| health resort | seaside resort | winter resort | mountain resort | ski resort |
| big city | large city | small town | city | hamlet |
| city center | downtown | suburb | outskirts | slums |
| region | district | neighborhood | borough | block |
| place | location | site | locality | vicinity |
| intersection | crossroads | junction | traffic light | red light |
| street corner | overpass | underpass | traffic circle | bridge |
| school | hospital | supermarket | store | restaurant |
| bank | post office | museum | library | movie theater |
| church | cathedral | temple | chapel | mosque |
| crosswalk | station | attractions | landmarks | airport |
| ghetto | city limits | environment | yellow light | tunnel |
| hotel | factory | synagogue | port | resort |
Transportation
| bus | bicycle | train | taxi | ship | wheel |
| boat | bike | automobile | vehicle | speedboat | tire |
| airplane | helicopter | auto | tram | vessel | trail bike |
| ferry | chopper | cab | taxicab | trailer | tricycle |
| motorboat | delivery truck | driver | sports car | tugboat | scooter |
| ocean liner | lorry | motor | sedan | steamship | ride |
| car | riverboat | pilot | race car | steamboat | semi |
| passenger | yacht | plane | carriage | school bus | motorcycle |
| railroad | sail | unicycle | engine | kayak | mountain bike |
| railway | sailboat | Vespa | jet boat | truck | car |
Colors
| amber | dark | pale | tan | cream |
| amethyst | denim | pastel | tangerine | crimson |
| apricot | desert sand | peach | taupe | cyan |
| aqua | ebony | periwinkle | teal | silver |
| aquamarine | ecru | persimmon | terracotta | slate |
| auburn | eggplant | pewter | thistle | spectrum |
| azure | emerald | pink | tint | slate |
| beige | fuchsia | primary | tomato | orchid |
| black | gold | puce | topaz | scarlet |
| blue | goldenrod | pumpkin | turquoise | sea green |
| bronze | gray | purple | ultramarine | secondary |
| brown | green | rainbow | umber | sepia |
| buff | grey | red | vermilion | shade |
| burnt umber | hue | rose | violet | shamrock |
| cardinal | indigo | ruby | viridian | silver |
| carmine | ivory | russet | wheat | orange |
| celadon | khaki | rust | white | mauve |
| cerise | lavender | saffron | wisteria | mustard |
| cerulean | lemon | salmon | yellow | olive |
| charcoal | light | sapphire | coral | maroon |
| chartreuse | lilac | lime | magenta | mahogany |
| chocolate | cinnamon | sienna | complementary | copper |
Technology
| design | desktop | download | net | network | paste |
| disk | document | file | online | password | |
| enterprise | format | podcast | pop-up | programmer | |
| flash drive | font | upload | printer | program | screenshot |
| gigabyte | home page | Internet | save | screen | software |
| shift key | spreadsheet | trash | username | web | wireless |
| virus | storage | undo | website | network | window |
Food
| wheat | rye | oats | corn | rice |
| bakery goods | bread | rolls | cakes | cookies |
| cereal | corn flakes | oat flakes | popcorn | pies |
| pasta | macaroni | noodles | spaghetti | muffin |
| sesame roll | cinnamon roll | hamburger bun | hot dog bun | lamb chops |
| oatmeal | cookie | crackers | biscuits | toast |
| apple pie | meat pie | pizza | pancake | doughnut |
| beef | pork | veal | lamb | plum |
| beefsteak | roast beef | ground beef | hamburgers | pork chops |
| salmon | trout | cod | tuna | sole |
| fish steak | fish fillet | smoked fish | caviar | grapes |
| shrimp | crab | oysters | melon | cherry |
| apple | pear | apricot | peach | nectarine |
| lemon | orange | tangerine | grapefruit | corn |
| banana | kiwi | pineapple | watermelon | mineral water |
| hazelnuts | walnuts | almonds | peanuts | soft drinks |
| peas | green peas | beans | string beans | kidney beans |
| tea | coffee | milk | cocoa | hot chocolate |
Animals
| amphibians | butterflies | fox | blindworm |
| frog | silkworm | gazelle | boa |
| frogspawn | swallowtail | gerbil | chameleon |
| newt | barbel | giraffe | constrictor snake |
| tadpole | carp | goat | copperhead |
| toad | cod | grizzly bear | coral snake |
| arachnids | crab | guinea pig | cottonmouth |
| harvestman | eel | hamster | crocodile |
| scorpion | goldfish | hare | diamondback |
| spider | haddock | hare | gecko |
| tarantula | halibut | hedgehog | iguana |
| birds | jellyfish | horse | lizard |
| albatross | lobster | hyena | rattlesnake |
| biddy | perch | lion | venomous snake |
| blackbird | pike | llama | python |
| canary | plaice | lynx | salamander |
| crow | ray | mammoth | saurian |
| cuckoo | salmon | marmot | sea snake |
| dove, | sawfish | mink | sidewinder |
| pigeon | scallop | mole | snake |
| duck | shark | mongoose | turtle |
| eagle | shell | mouse | tortoise |
| falcon | shrimp | mule | bullock |
| finch | trout | otter | camel |
| flamingo | ant | panda | chimpanzee |
| goose | aphid | pig, hog | dachshund |
| gull | bee | platypus | elephant |
| hawk | beetle | polar bear | turkey |
| jackdaw | bumblebee | polecat | vulture |
| jay | caterpillar | pony | woodpecker |
| kestrel | cockroach | porcupine | wren |
| kookaburra | dragonfly | prairie dog | dolphin |
| mallard | flea | puma | swift |
| nightingale | fly | raccoon | bear |
| nuthatch | gadfly | rat | roundworm |
| ostrich | grasshopper | reindeer | tit |
| owl | harvestman | rhinoceros | beaver |
| parakeet | ladybug | seal | millipede |
| parrot | larva | seal | tapeworm |
| peacock | louse | sheep | leech |
| pelican | maggot | skunk | earthworm |
| penguin | midge | sloth | roundworm |
| pheasant | moth | squirrel | millipede |
| piranha | nymph | tiger | armadillo |
| raven | wasp | weasel | badger |
| robin | mammals | whale | bat |
| rooster | anteater | wolf | bear |
| sparrow | antelope | zebra | beaver |
| stork | swallow | swan | swift |
| abatement | acid rain | air pollution | air quality |
| algae | amoeba | algal blooms | algae land |
| biofuels | biomass | biosphere | carbon count |
| bring bank | brown bin | carbon emissions | turbine |
| toxin | carbon dioxide | carbon offset | carbon tax |
| carbon monoxide | carbon-neutral | climate change | compost |
| carpooling | climate | conservation | cryptosporidium |
| civic amenity site | composting | dioxins | disposal |
| compostable | development plan | draught-proofing | dumping |
| deforestation | domestic waste | environmental | green bin |
| domestic charges | emissions projections | electric vehicle | emissions |
| ecosystem | effluent | fuel poverty | global warming |
| ecotourism | fossil fuels | greenhouse gases | groundwater |
| flora and fauna | greenhouse effect | organic food | household waste |
| greener | hazardous waste | particulate matter | organic |
| habitat | insulation | planning permission | pay by weight |
| incinerator | litter | radioactive | plastic bag levy |
| landfill | noise pollution | refuse | radon |
| municipal waste | oil spill | river basin | renewable energy |
| noxious gases | ozone layer | solar panel | sewage |
| organism | permits | sustainable tourism | toxic |
| pesticides | radiation | zero emissions | tidy towns |
| post-consumer waste | reforestation | atmosphere | ventilation |
| recycle | reuse | biodiversity | backyard burning |
| renewable resource | smokeless fuel | energy efficiency | bioenergy |
| smog | sustainable | amenities | energy rating |
| surface water | traffic calming | biodegradable waste | wind |
Work and Jobs
| accountant | butler | cryptographer | exporter | illustrator |
| actor | cab driver | custodian | exterminator | importer |
| actress | calligrapher | dancer | extra | instructor |
| actuary | captain | dentist | falconer | intern |
| advisor | cardiologist | deputy | farmer | internist |
| aide | caregiver | dermatologist | financier | interpreter |
| ambassador | carpenter | designer | firefighter | inventor |
| animator | cartographer | detective | fisherman | investigator |
| archer | cartoonist | dictator | flutist | jailer |
| artist | cashier | director | football player | janitor |
| astronaut | catcher | disc jockey | foreman | jester |
| astronomer | caterer | diver | game designer | jeweler |
| athlete | cellist | doctor | garbage man | jockey |
| attorney | chaplain | doorman | gardener | journalist |
| auctioneer | chauffeur | driver | gatherer | judge |
| author | chef | drummer | gemcutter | laborer |
| babysitter | chemist | dry cleaner | general | landlord |
| baker | clergyman | ecologist | geneticist | landscaper |
| ballerina | clergywoman | economist | geographer | laundress |
| banker | clerk | editor | geologist | lawyer |
| barber | coach | educator | golfer | lecturer |
| bellhop | concierge | empress | guide | librettist |
| biologist | consul | engineer | hairdresser | lifeguard |
| blacksmith | contractor | entertainer | handyman | linguist |
| bookkeeper | cook | entomologist | harpist | lobbyist |
| bowler | cop | entrepreneur | Highway patrol | locksmith |
| builder | coroner | executive | hobo | lyricist |
| butcher | courier | explorer | hunter | magician |
| maid | muralist | painter | physicist | private detective |
| mail carrier | musician | paleontologist | pianist | producer |
| manager | navigator | paralegal | pilot | professor |
| manufacturer | negotiator | park ranger | pitcher | programmer |
| marine | notary | pathologist | plumber | psychiatrist |
| marketer | novelist | pawnbroker | poet | psychologist |
| mason | nun | peddler | police | publisher |
| mathematician | nurse | pediatrician | policeman | quarterback |
| mayor | oboist | percussionist | policewoman | quilter |
| mechanic | operator | performer | politician | radiologist |
| messenger | ophthalmologist | pharmacist | president | rancher |
| midwife | optician | philanthropist | prince | ranger |
| miner | oracle | philosopher | princess | real estate agent |
| model | orderly | photographer | principal | receptionist |
| monk | ornithologist | physician | private | referee |
| registrar | sailor | scuba diver | socialite | student |
| reporter | salesperson | seamstress | soldier | surgeon |
| representative | samurai | security guard | spy | surveyor |
| researcher | saxophonist | senator | star | swimmer |
| restaurateur | scholar | sheriff | statistician | tailor |
| retailer | scientist | singer | stockbroker | tax collector |
| retiree | scout | smith | street sweeper | taxi driver |
| taxidermist | toolmaker | treasurer | usher | waiter |
| teacher | trader | truck driver | valet | waitress |
| technician | trainer | tutor | veteran | warden |
| tennis player | translator | typist | veterinarian | warrior |
| test pilot | trash collector | umpire | vicar | watchmaker |
| tiler | travel agent | undertaker | violinist | weaver |
| welder | woodcarver | workman | wrangler | writer |
Common Adjectives
| adorable | adventurous | aggressive | ugliest |
| agreeable | alert | alive | unsightly |
| amused | angry | annoyed | uptight |
| annoying | anxious | arrogant | vivacious |
| ashamed | attractive | average | wicked |
| awful | bad | beautiful | witty |
| better | bewildered | black | wrong |
| bloody | blue | blue-eyed | ugly |
| blushing | bored | brainy | unusual |
| brave | breakable | bright | vast |
| busy | calm | careful | wandering |
| cautious | charming | cheerful | wide-eyed |
| clean | clear | clever | worried |
| cloudy | clumsy | colorful | zany |
| combative | comfortable | concerned | outrageous |
| condemned | confused | cooperative | perfect |
| courageous | crazy | creepy | poised |
| crowded | cruel | curious | precious |
| cute | dangerous | dark | putrid |
| dead | defeated | defiant | real |
| delightful | depressed | determined | rich |
| different | difficult | disgusted | shiny |
| distinct | disturbed | dizzy | sleepy |
| doubtful | drab | dull | sore |
| eager | easy | elated | spotless |
| elegant | embarrassed | enchanting | stupid |
| encouraging | energetic | enthusiastic | talented |
| envious | evil | excited | tender |
| expensive | exuberant | fair | thankful |
| faithful | famous | fancy | tired |
| fantastic | fierce | filthy | outstanding |
| fine | foolish | fragile | plain |
| frail | frantic | friendly | poor |
| frightened | funny | gentle | prickly |
| gifted | glamorous | gleaming | puzzled |
| glorious | good | gorgeous | relieved |
| graceful | grieving | grotesque | scary |
| grumpy | handsome | happy | shy |
| healthy | helpful | helpless | smiling |
| hilarious | homeless | homely | sparkling |
| horrible | hungry | hurt | stormy |
| ill | important | impossible | successful |
| inexpensive | innocent | inquisitive | tame |
| itchy | jealous | jittery | tense |
| jolly | joyous | kind | thoughtful |
| lazy | light | lively | tough |
| lonely | long | lovely | panicky |
| lucky | magnificent | misty | pleasant |
| modern | motionless | muddy | powerful |
| mushy | mysterious | nasty | proud |
| naughty | nervous | nice | quaint |
| nutty | obedient | obnoxious | repulsive |
| odd | old-fashioned | open | selfish |
| silly | smoggy | splendid | strange |
| super | tasty | terrible | thoughtless |
| alter | stability | energy | aware | license |
| amendment | logic | rejected | expansion | objective |
| area | approach | role | legislation | income |
| assume | theory | benefit | evidence | consistent |
| categories | perceived | sought | acquisition | features |
| circumstances | instance | considerable | shift | deduction |
| code | investigation | phase | prior | apparent |
| comments | convention | published | framework | implies |
| communication | ethnic | hypothesis | professional | status |
| community | resident | range | construction | strategies |
| component | constraints | technical | emphasis | sequence |
| concept | formula | section | data | research |
| conference | attributed | annual | obvious | commitment |
| consent | proportion | demonstrate | reaction | criteria |
| contact | network | facilitate | welfare | transition |
| create | derived | factors | procedure | environment |
| debate | dimensions | promote | sum | integration |
| elements | previous | conclusion | security | text |
| enforcement | draft | styles | precise | marginal |
| equivalent | liberal | notion | pursue | symbolic |
| established | authority | major | issues | labor |
| evolution | conflict | image | discretion | target |
| export | source | assessment | policy | identified |
| external | psychology | fundamental | adjustment | capacity |
| final | positive | evaluation | assistance | commission |
| focus | purchase | injury | site | journal |
| generation | exposure | decline | academic | modified |
| hence | occupational | internal | goals | mechanism |
| impact | consequences | chapter | equation | appropriate |
| imposed | despite | job | parameters | approximate |
| justification | funds | reliance | physical | partnership |
| label | concentration | principal | series | parallel |
| location | link | coordination | alternative | specified |
| minorities | technology | philosophy | removed | corresponding |
| negative | dominant | illustrated | outcomes | ensure |
| occur | economic | involved | percent | structure |
| overall | emerged | regime | implementation | project |
| primary | complex | institute | investment | select |
| regulations | computer | items | consumer | achieve |
| relevant | distinction | region | traditional | transfer |
| required | constitutional | analysis | distribution | function |
| resources | participation | survey | potential | credit |
| sector | available | financial | process | individual |
| specific | principle | estimate | variables | contract |
| statistics | option | domestic | output | access |
| substitution | generated | trend | revenue | compounds |
| sufficient | corporate | interaction | contribution | immigration |
| summary | attitudes | undertaken | cycle | implications |
| validity | task | techniques | excluded | compensation |
| whereas | enable | version | perspective | prime |
| energy | lethargy | pink | verdure |
| fitness | weakness | prime | vigor |
| strength | disease | robustness | wholeness |
| well-being | illness | salubriousness | clean bill |
| bloom | infirmity | salubrity | eupepsia |
| complexion | sickness | shape | fine feather |
| constitution | hardihood | soundness | good condition |
| euphoria | hardiness | stamina | top form |
| fettle | healthfulness | state | complaint |
| form | healthiness | tone | condition |
| haleness | lustiness | tonicity | illness |
| ailment | indisposition | malady | infirmity |
| disease | queasiness | nausea | diseasedness |
| disorder | unhealthfulness | syndrome | unhealth |
| ill health | unwellness | bug | affliction |
| pastiche | cantilever | taxonomy | generative |
| sustainability | curvilinear | hierarchy | ambiguity |
| ergonomy | rectilinear | scale | catalyst |
| genius loci | Miesian | section | penetrate |
| facade | Corbusian | formal | appropriate |
| charette | permaculture | nodes | inspiration |
| regionalism | blobitecture | pods | contemporary |
| threshold | exurbia | grain | amalgamation |
| massing | walkability | extrapolate | performative |
| enfilade | pilotis | device | hegemony |
| materiality | verticality | elevation | curate |
| poché | rebate | iconic | bifurcate |
| post-industrial | mullion | organic | superimpose |
| diagrammatic | muntin | dichotomy | confluences |
| vernacular | gentrification | eclectic | gestalt |
| modular | stylobate | kitsch | zeitgeist |
| deconstruction | obscure | sequence | banal |
| parametric | space | interstitial | motifs |
| program | fabric | iteration | procession |
| skin | metaphor | juxtapose | homogenous |
| building envelope | legibility | stereotomic | palimpsest |
| vault | dimension | tectonics | paradigm |
| arcade | moment | liminal | dissonance |
| fenestration | celebrate | articulate | adjacencies |
| truncated | negotiate | ephemeral | parallax |
| parti | dynamic | domesticity | assemblage |
| flâneur | language | anthropogenic | aesthetic |
| phenomenology | context | regenerate | monolithic |
| brutalism | gesture | hybrid | uniformity |
| morphology | duality | nuance | transient |
| redundancy | robust | bespoke | holistic |
Business/Workplace
| accounts | build | company | leader | partner |
| achievement | business | competition | leadership | partnership |
| advantage | capital | concept | management | passion |
| advertising | capitalism | confidence | market leader | performance |
| agreement | career | consultant | marketing | persistence |
| ambition | chairman | consultation | marketplace | pioneer |
| appreciation | client | consumer | mastery | planning |
| approach | clincher | contract | meeting | portfolio |
| authority | co-op | incentive | mentor | position |
| benefits | co-worker | industry | merger | potential |
| boss | colleague | jet-setter | milestone | price |
| bottom line | commerce | job | raise | priorities |
| brainstorm | responsibility | job security | money | pro |
| branch | scope | labor force | negotiation | product |
| brand | stability | laborer | prosperity | productivity |
| experience | expert | expertise | finances | firm |
| growth | hard sell | hard work | ideas | impact |
| proprietorship | coaching | investment | messaging | power |
| resource | team | launch | open doors | profit |
| satisfaction | work | results | opportunity | cooperative |
| solution | sales | sector | organization | corporation |
| talent | skill | staff | owner | revenue |
| vision | supplier | teamwork | return | shareholder |
| growth | hard sell | ideas | impact | implementation |
| referral | program | assessment | promotion | proprietorship |
| goal | growth | hard sell | ideas | impact |
| costs | customer | deal | department | departments |
| desk | desktop | determination | division | drive |
| effort | employee | employment | enterprise | entrepreneur |
| fortune | implementation | economy | excellence | executive |
| expansion | expectation | sale | program | prosperity |
Sample Practice Questions from the Duolingo English Test that Test Your “Yes/No” Vocabulary
They’ve developed these activities to assist students like you in practicing for the Duolingo English Test for free. You may also prepare for the Duolingo English Test by going to Duolingo Test Free Practice – Exercises and Information.
What English Spelling Skills Do You Need to Improve for the Duolingo English Test?
A common challenge for non-English speakers is that a few words in English sound and look familiar but have a different meaning. Or on other occasions, a few words are commonly misspelled. And usually, the misspelling happens with a single alphabet, “i” or “e”. There are many nuances to the English language that confuses and leads to spelling mistakes.
And the rarest form is extremely long multi-syllable words, and in some cases, these words are foreign even to native and fluent English speakers.
Let’s look at both these scenarios with multiple examples.
Commonly Confused English Words
The difficulty with spellcheck is that it might misspell words. English is full of similar-sounding but differently written terms.
Usually, English learners misinterpret many words with similar (but not identical) meanings due to confusing structures or even multiple meanings. Here are some of the most frequently misunderstood English terms.
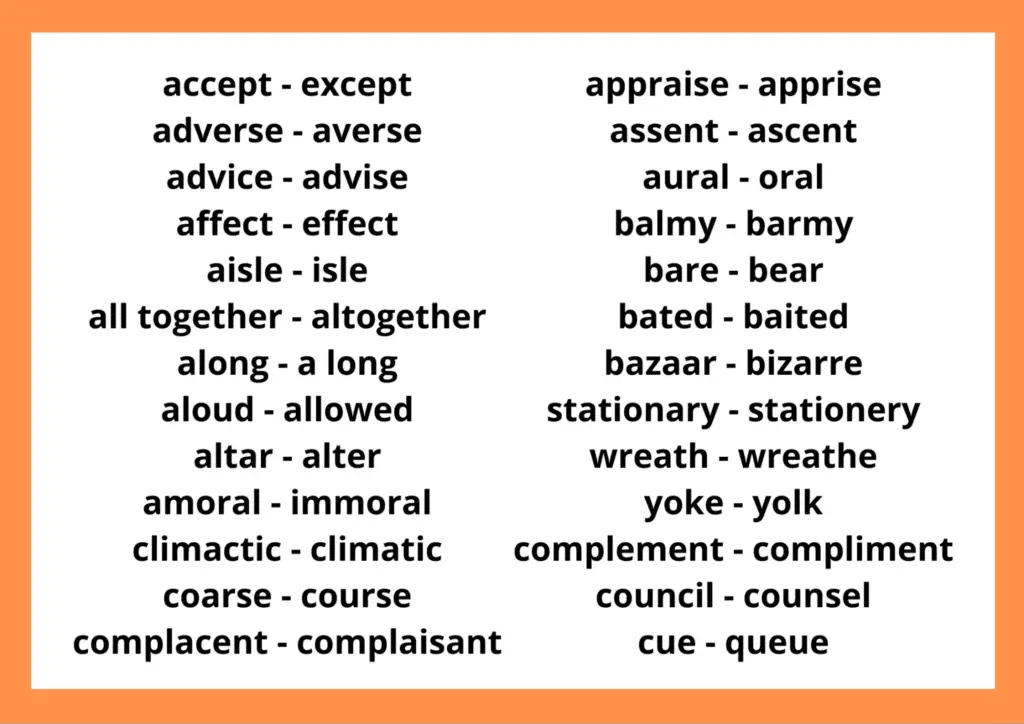
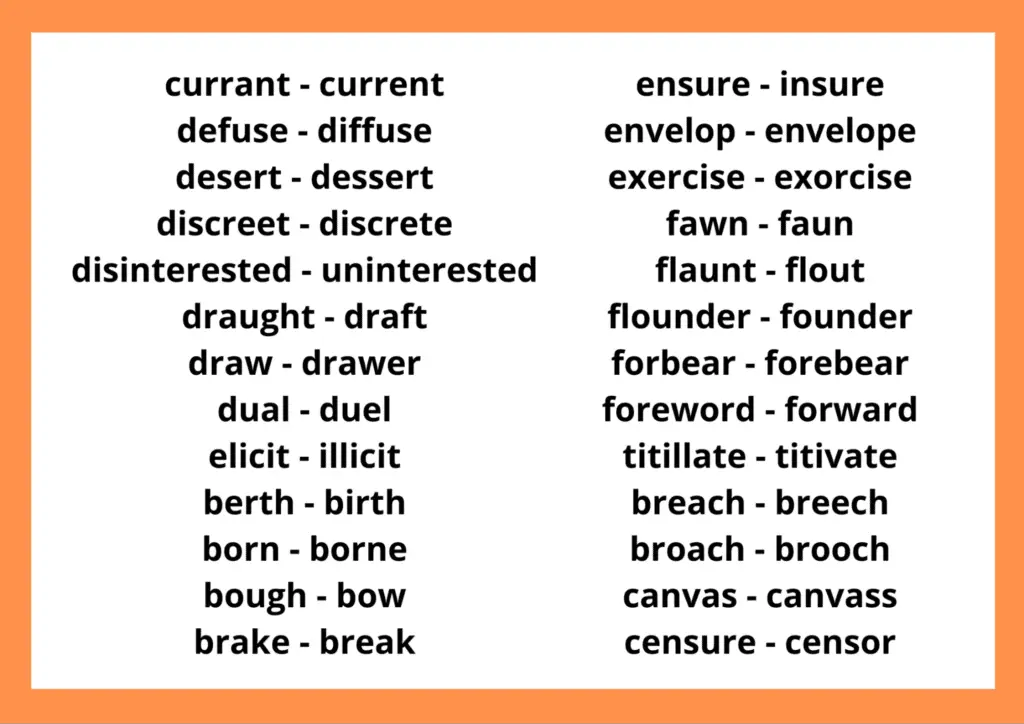
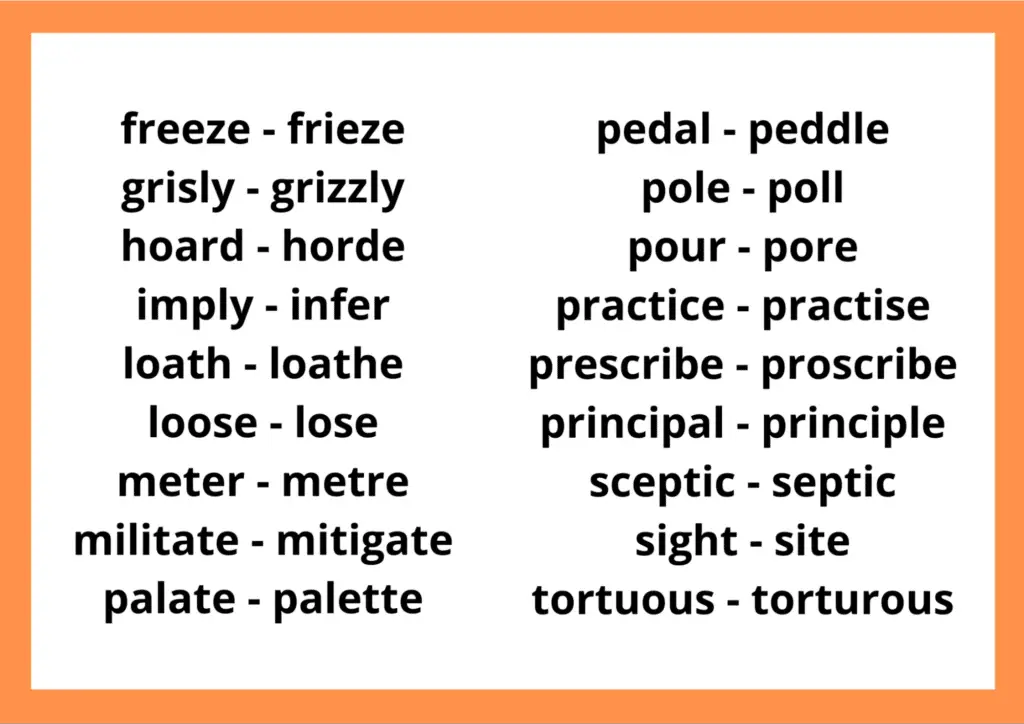
English Words with Troublesome Spelling
The ever-evolving English language may be challenging to spell because of its quirks and exceptions.
It is only since the advent of the printing machine that they have standardized the terms in American English. While spellcheck apps are excellent, understanding and being competent in spelling are crucial both at school and at the workplace.
People will evaluate you based on your misspelled words, fair or not. That may harm your grades or professional growth.
i – e and e – i
“i before e unless after c” is one of the first English spelling rules students learn in school. This only works when the word with a long ee, like in shield.
| i – e | e – i |
| piece relief believe niece chief priest thief |
conceive conceit receive receipt eight heigh feign |
Silent Letter
When writing a word, don’t forget to spell it with its silent letter even though it is not spoken. In other words, more than half of the alphabet may occur as silent letters.
At times, you may find them at the beginning, end, or center of the words, and you wouldn’t know they were there based on the word’s sound.
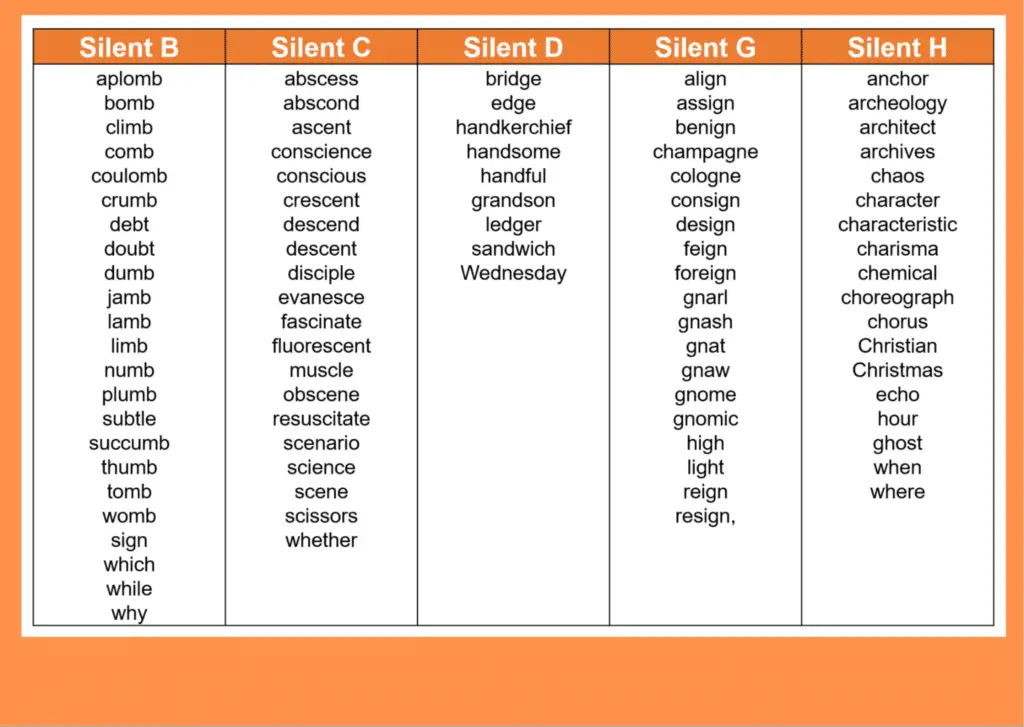
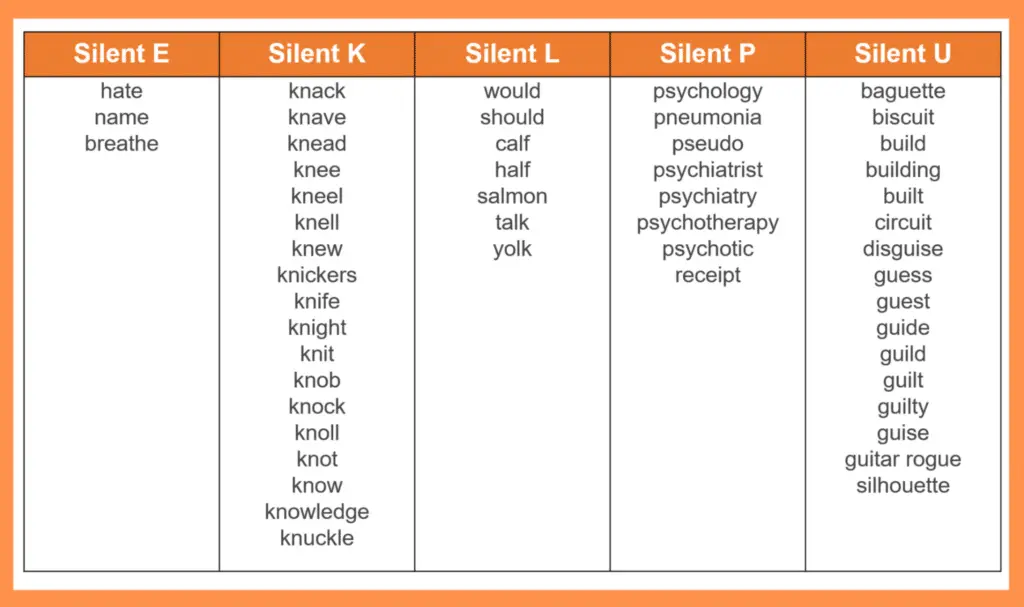
Lengthy Words
When you break them down into their component pieces, they’re not as terrifying as they seem. This is how most lengthier words function and many of them are scientific or medical phrases. You’ll have a good start if you understand the most frequent Latin and Greek roots (there are many lists online, such as this one).
Examples:
- antidisestablishmentarianism
- supercalifragilisticexpialidocious
Is the Word British or American?
The majority of the spelling changes between the two forms are common and well-known. There’s undoubtedly a lot to say about it, but one of the main reasons is that British English has sought to maintain the spelling of the terms it has taken from other nations for the most part. To simplify spelling, American English has attempted to confirm the spelling of specific terms to the way they are spoken in English.
| American | British |
| labor | labour |
| color | colour |
| favor | favour |
| favorite | favourite |
| realize | realise |
| apologize | apologise |
| license | licence |
| defense | defence |
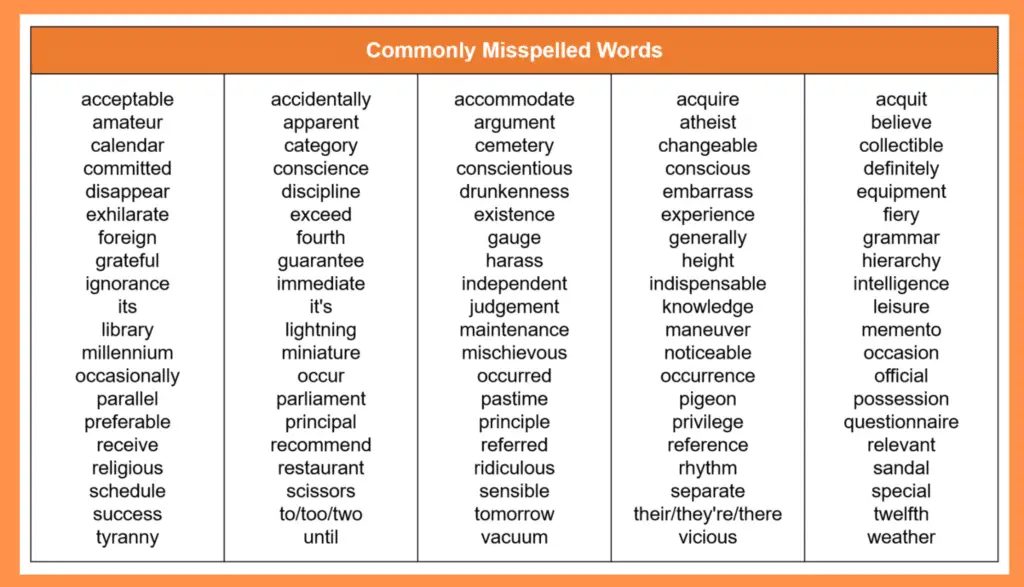
Common Misspelled English Words
Below is a list of commonly misspelled words. Get yourself familiar with it to avoid committing mistakes:
What are a Few Tips to Improve Your English Spelling?
These suggestions for improving your spelling are based on professional guidance. Take a look at the fundamentals listed below:
- Keep a list of difficult terms. Underline the word’s most difficult section.
- Don’t use a spell-checker! Don’t trust a spell-checker. The most often misspelled terms I’ve seen online are there and there.
- Learn words’ prefixes and suffixes.
- Don’t depend on the rules. As previously said, every rule has an exception.
Additional FAQs — Duolingo Enlgish Test Vocabulary
What is the Best Way to Prepare for the Duolingo English Test?
The Duolingo English Test is a test that assesses and evaluates real-world language proficiency.
Take a free practice exam on their preparedness page.
They have a detailed guide that includes information on the test questions and test-taking tips and strategies.
What is A Real English word?
A real word has meaning in the English language. As a point of reference, the term ‘real word’ is often used in conjunction with the teaching of nonsensical words.
Nonsense words are made-up words that are used to aid in the teaching of important phonetic sounds.
What is the Duolingo English Exam Passing Score?
The range of Duolingo scores is 10-160. You will view their total result rather than the sub-scores for each ability since the scores are holistic.
Universities often demand a minimum score of 110; however, this is not always the case and might vary from institution to university.
- Top Definitions
- Quiz
- Related Content
- More About Ride
- Examples
- British
- Idioms And Phrases
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
verb (used without object), rode or (Archaic) rid; rid·den or (Archaic) rid; rid·ing.
to sit on and manage a horse or other animal in motion; be carried on the back of an animal.
to be borne along on or in a vehicle or other kind of conveyance.
to move or float on the water: the surfboarders riding on the crests of the waves.
to move along in any way; be carried or supported: He is riding along on his friend’s success. Distress is riding among the people.
to have a specified character for riding purposes: The car rides smoothly.
to be conditioned; depend (usually followed by on): All his hopes are riding on getting that promotion.
Informal. to continue without interruption or interference: He decided to let the bet ride.
to be carried on something, as a litter, a person’s shoulders, or the like.
to work or move up from the proper place or position (usually followed by up): Her skirt rode up above her knees.
to extend or project over something, as the edge of one thing over the edge of another thing.
to turn or rest on something: the great globe of the world riding on its axis.
to appear to float in space, as a heavenly body: A blood-red moon rode in the cloudless sky.
to lie at anchor, as a ship.
verb (used with object), rode or (Archaic) rid; rid·den or (Archaic) rid; rid·ing.
to sit on and manage (a horse, bicycle, etc.) so as to be carried along.
to sit or move along on (something); be carried or borne along on: The ship rode the waves. We ride a bus.
to ride over, along, or through (a road, boundary, region, etc.); traverse.
to ridicule or harass persistently: The boys keep riding him about his poor grades.
to control, dominate, or tyrannize over: a man ridden by fear; a country that is ridden by a power-mad dictator.
to cause to ride.
to carry (a person) on something as if on a horse: He rode the child about on his back.
to execute by riding: to ride a race.
to rest on, especially by overlapping.
to keep (a vessel) at anchor or moored.
Jazz. to play improvisations on (a melody).
noun
a journey or excursion on a horse, camel, etc., or on or in a vehicle.
a means of or arrangement for transportation by motor vehicle: We’ll handle rides to be sure everyone gets home quickly.
the vehicle used for transportation: I’ve got to hang up now—my ride’s here.
a vehicle or device, as a Ferris wheel, roller coaster, or merry-go-round, on which people ride for amusement.
a way, road, etc., made especially for riding.
Verb Phrases
ride out,
- to sustain (a gale, storm, etc.) without damage, as while riding at anchor.
- to sustain or endure successfully.
QUIZ
CAN YOU ANSWER THESE COMMON GRAMMAR DEBATES?
There are grammar debates that never die; and the ones highlighted in the questions in this quiz are sure to rile everyone up once again. Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates?
Which sentence is correct?
Idioms about ride
- to trample or overturn by riding upon or against.
- to ride up to; overtake; capture: The posse rode down the escaping bank robber.
- Nautical. to bear down upon (a rope of a tackle) with all one’s weight.
ride down,
ride for a fall, to conduct oneself so as to invite misfortune or injury.
- to murder, especially by abducting the victim for that purpose.
- to deceive; trick: It was obvious to everyone but me that I was being taken for a ride.
ride the beam, Aeronautics. to fly along the course indicated by a radio beam.
take for a ride, Slang.
Origin of ride
before 900; 1915–20 for def. 17; Middle English riden (v.), Old English rīdan; cognate with Old Frisian rīda,German reiten,Old Norse rītha; akin to Old Irish ríad journey (cf. palfrey, rheda). See road
synonym study for ride
Words nearby ride
ridable, riddance, ridden, riddle, riddled, ride, rideable, Rideau Canal, Rideau Hall, ride down, ride for a fall
Other definitions for ride (2 of 2)
noun
Sally, 1951–2012, U.S. astronaut and astrophysicist: first U.S. woman to reach outer space 1983.
Dictionary.com Unabridged
Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2023
MORE ABOUT RIDE
What is a basic definition of ride?
Ride is a verb that means to sit on the back of a moving animal or to travel in or on a vehicle, like a car. A ride is a journey made on an animal or using a vehicle. Ride has many other senses as a verb and a noun.
When someone rides an animal, they are usually sitting on the animal’s back while it moves. In general, the word ride is used even if the animal is uncooperative or is trying to get rid of the person sitting on them. The person sitting on the animal is called a rider. Its past tenses are rode and ridden.
- Real-life examples: Horses are the most common animal that people ride. Cowboys attempt to ride angry bulls at rodeos. In many Asian countries, people ride camels.
- Used in a sentence: I like to ride horses with my mom.
In a similar sense, ride is used to mean to travel using a vehicle. This can include a vehicle you stand or sit on, like a bicycle.
- Real-life examples: People ride bikes, motorcycles, and skateboards. Airplanes, submarines, boats, cars, trains, buses, and subway cars are vehicles that people ride in.
- Used in a sentence: Grant rides the subway to get to work.
A ride is also the journey or trip you take on an animal or using a vehicle. This sense of ride is also used figuratively to mean any journey or experience that a person has embarked on.
- Real-life examples: Petting zoos often offer pony rides to children. A trip from Tokyo to Berlin would be a long ride, no matter what kind of vehicle you used. People who are afraid of heights probably won’t be fans of airplane rides.
-
Used in a sentence: My college years were a wild ride.
Where does ride come from?
The first records of ride come from before the 900s. It comes from the Old English verb rīdan. It is related to similar words with the same meaning, such as the Old Frisian rīda, the German reiten, and the Old Norse rītha.
Did you know … ?
How is ride used in real life?
Ride is a very common word that most often means to travel on the back of an animal or to travel on or in a vehicle.
Who would have thought, one month ago, that I would be here after finishing my 11th Dakar on a row and in P17. Many days I could not ride at my normal pace, but I can assure you that this has been a great personal victory! Thanks to the team, the sponsors and every single
+ pic.twitter.com/f6mGs9fUQX— Laia Sanz (@LaiaSanz_) January 15, 2021
I’m riding the bus and a whole grip of climate protestors just got on.
It’s pretty clear they never ride the bus, which is pretty ironic when you think about it.
— Lawrence Sonntag (@SirLarr) September 20, 2019
I am about to board a train for a long ride so if anyone has a dramatic reason to halt me at the platform do it now before I spend the next five hours wistfully staring out the window
— JP (@jpbrammer) February 2, 2020
Try using ride!
Which of the following is a person most likely to ride?
A. bench
B. horse
C. road
D. shower
Words related to ride
drive, excursion, expedition, jaunt, outing, tour, transportation, cruise, drift, float, go, go with, guide, move, sit, travel, airing, commute, hitch, joyride
How to use ride in a sentence
-
Germs like the flu virus can also hitch a ride on dust and other airborne particles that we shed.
-
If you’re a crime junkie, clear your schedule, because this one is going to take you on a ride.
-
Uber may also try to push more drivers to work for both its rides and food delivery services to reduce costs, Shmulik said.
-
Along for the ride are the real people whose lives and livelihoods are, to some degree, linked to it.
-
Meanwhile, ride demand has been rebounding from the sharp drop-off that accompanied the start of lockdowns across the US.
-
I told them it was back where I parked my car, so they offered me a ride.
-
I mean, the reality of it was, I had to go out and get on a horse, and ride in, shoot the gun — how hard was that, right?
-
“They just walk around, they ride in their patrol cars, and they just pass by,” he said.
-
In “Sleigh Ride,” the narrator is painting a scene so perfect that it could be featured on an iconic Currier and Ives print.
-
My bike ride that mid-October day starts like so many others.
-
Possibly, he would not shy at such monstrosities after twenty miles of a lathering ride.
-
The other day an excursion was arranged to Sondershausen, a town about three hours’ ride from Weimar in the cars.
-
The truth is, it is not safe to trot down such mountains and hardly to ride down them at all.
-
The farmer told him it was six miles; «but,» he added, «you must ride sharp, or you will get a wet jacket before you reach it.»
-
Coppy, in a tone of too-hastily-assumed authority, had told her over night that she must not ride out by the river.
British Dictionary definitions for ride
verb rides, riding, rode or ridden
to sit on and control the movements of (a horse or other animal)
(tr) to sit on and propel (a bicycle or similar vehicle)
(intr ; often foll by on or in) to be carried along or travel on or in a vehicleshe rides to work on the bus
(tr) to travel over or traversethey rode the countryside in search of shelter
(tr) to take part in by ridingto ride a race
to travel through or be carried across (sea, sky, etc)the small boat rode the waves; the moon was riding high
(tr) US and Canadian to cause to be carriedto ride someone out of town
(intr) to be supported as if floatingthe candidate rode to victory on his new policies
(intr) (of a vessel) to lie at anchor
(tr) (of a vessel) to be attached to (an anchor)
(esp of a bone) to overlap or lie over (another structure or part)
Southern African informal
- (intr) to drive a car
- (tr) to transport (goods, farm produce, etc) by motor vehicle or cart
(tr) (of a male animal) to copulate with; mount
(tr) slang to have sexual intercourse with (someone)
(tr; usually passive) to tyrannize over or dominateridden by fear
(tr) informal to persecute, esp by constant or petty criticismdon’t ride me so hard over my failure
(intr) informal to continue undisturbedI wanted to change something, but let it ride
(tr) to endure successfully; ride out
(tr) to yield slightly to (a blow or punch) in order to lessen its impact
(intr often foll by on) (of a bet) to remain placedlet your winnings ride on the same number
(intr) jazz to play well, esp in freely improvising at perfect tempo
ride roughshod over to domineer over or act with complete disregard for
ride to hounds to take part in a fox hunt on horseback
ride for a fall to act in such a way as to invite disaster
ride again informal to return to a former activity or scene of activity
riding high confident, popular, and successful
noun
a journey or outing on horseback or in a vehicle
a path specially made for riding on horseback
transport in a vehicle, esp when given freely to a pedestrian; liftcan you give me a ride to the station?
a device or structure, such as a roller coaster at a fairground, in which people ride for pleasure or entertainment
slang an act of sexual intercourse
slang a partner in sexual intercourse
take for a ride informal
- to cheat, swindle, or deceive
- to take (someone) away in a car and murder him
Derived forms of ride
ridable or rideable, adjective
Word Origin for ride
Old English rīdan; related to Old High German rītan, Old Norse rītha
Collins English Dictionary — Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition
© William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins
Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Other Idioms and Phrases with ride
In addition to the idioms beginning with ride
- ride for a fall
- ride hellbent for leather
- ride herd on
- ride high
- ride out
- ride roughshod over
- ride shotgun
- ride up
also see:
- along for the ride
- go along (for the ride)
- gravy train, ride the
- hitch a ride
- let ride
- take someone for a ride
The American Heritage® Idioms Dictionary
Copyright © 2002, 2001, 1995 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
What makes one word more “real” than another? Are there degrees of “realness” for words?
Totally “real”
“Real” words can be defined in a few different ways. The most obvious and restrictive definition is a word accepted as being “standard,” which means it appears in the dictionary and is recognized as valid by prescriptive grammarians—grammarians who prefer that the written word follow the rules of formal Standard English, the term used to describe the type of English that’s considered to be the norm for educated speakers. (For a good look at prescriptive vs. descriptive grammar, see this excellent entry by 
Sort of “real”
A second definition, more forgiving than the first, describes words that are recognized by the dictionary but considered nonstandard—words which are accepted through common, frequent usage, especially in dialects, other casual speech, and the less formal types of writing, but which aren’t considered grammatical or proper by a wider audience. Words in this category include irregardless, which is likely a combination of “irrespective” and “regardless”; ain’t; and alright, which is the nonstandard spelling of “all right.” In many cases, the nonstandard word is a portmanteau—a word created by blending the sounds and meanings of two other words. Over time, words like these might become standard by virtue of having been used so often and for so long that they’re accepted by even the most prescriptive of grammarians. Motel (motor + hotel), chortle (chuckle + snort), and smog (smoke + fog) are all portmanteaus that were once considered informal or nonstandard, but which are now accepted as standard. Similarly, trademarks and jargon from certain professions or interests can become mainstream—think jazzercise (jazz + exercise), palimony (pal + alimony), and breathalyzer (breath + analyzer).
Other words considered sort of “real” are contracted versions of longer words, like “mobile” for mobile phone or “cell” for cellular phone. These contractions can also become standard over time, as has happened with “flu” for influenza, “phone” for telephone, and even “TV” for television.
But until words in this category lose their “nonstandard” label in the dictionary, like the examples above, most grammarians would encourage you not to use them except in more casual writing and speech.
Not “real”
A third definition includes slang and words that are just being coined and used by various groups. Most people, grammarians or otherwise, would consider these words to be a level or two below nonstandard and therefore definitely not “real.” However, these words have a certain currency, thanks to their ability to proliferate rapidly via the internet and casual conversation as they’re picked up and used by more and more people. Phat, ginormous, and conversate are just a few examples of words we could consider to be “real” in the sense that they’re understood by those who use them, but they’re not “real” in the sense that they’re neither recognized by a wider audience, nor are they recognized as belonging to Standard English. It wouldn’t be appropriate to use them in an essay for school, in a resume, in an email to a work colleague, or in most other types of written communication, but you might use them in things like emails among friends or very casual blog posts.
Most slang terms and similar words enjoy a brief popularity, falling in and out of fashion very quickly (almost nobody uses “groovy” seriously anymore), so it’s probably a good idea to use them sparingly. Not only might several groups of people not understand what they mean, but they also tend to date the works they’re in. Likewise, you’ll want to avoid modern slang in fandoms set in the past—Sherlock Holmes wouldn’t take a “phat case,” and nobody in Arthur Conan Doyle’s works would describe the Hound of the Baskervilles as “ginormous.” You could always do some research and use some slang from the appropriate period to help your fics feel authentic, but be careful not to go overboard since that could backfire by confusing or annoying your readers.
Even though slang isn’t considered “real” or even “sort of real,” some of it might eventually become mainstream. Many slang terms have made the transition to “real” words over time—jazz is one that immediately comes to mind.
Really not “real”
And then there are words that are really not “real,” like the fantastic nonsense words in Lewis Carroll’s poem “Jabberwocky.” Nearly all of them are portmanteaus. In fact, Carroll’s the one who first began using the word portmanteau in the way it’s being used in this feature—the word originally meant a sort of a large suitcase, but he appropriated it to describe the words he created: slithy is a combination of “slimy” and “lithe,” mimsy comes from “miserable” and “flimsy,” and so on.
Other words that fall into this category are malapropisms, or words used incorrectly, usually in a comical way:
“Shh! Hakkai said we had to aggravate our voices in the library,” said Goku.
“That’s moderate, you stupid monkey,” Gojyo said, rolling his eyes.
The term malapropism comes from the play The Rivals by Richard Brinsley Sheridan, whose character Mrs. Malaprop loves using big words—even though she uses them incorrectly all the time (such as when she substitutes “allegory” for “alligator” in the famous line, “she’s as headstrong as an allegory on the banks of Nile”). While the words in malapropisms themselves aren’t wrong, the meanings being attributed to them are, so in a sense malapropisms can count as being really not “real.”
General nonsense words or made-up terms would also fall under this definition. Phasers in Star Trek, the vorpal blade in “Jabberwocky,” and naquadah reactors from Stargate: SG1 are just a few examples of clearly made-up words. Words like these would be obviously wrong if used in contexts other than the fandoms to which they belong.
Because they’re really not “real,” nonsense words and malapropisms should be used as features of either a narrative or character voice only.
So is this a “real” word or not?
If you’re not sure, the best way to decide if you’re using a “real” word or not is to look it up in either a dictionary or a usage guide—Dictionary.com is useful because they compile definitions from multiple sources, and they’ll often tell you if a word is used or spelled differently in American versus British English. They also label particular words or definitions as nonstandard or slang where appropriate, so you won’t have to guess. As for usage guides, any decent writing handbook should have a section on the more commonly used idioms, colloquialisms, and nonstandard words and phrases to help you decide whether you’re using a “real” word or not. (For a short list of usage guides and writing handbooks that have been reviewed by members of this community, you can go here.)
Practical application
As always, it’s up to you to decide what tone and flavor you want to give your writing. Nonstandard words are most likely to occur (and more likely to be accepted by readers) in the dialog, which is meant to reflect natural speech patterns, while the narrative portion of many stories is written paying more attention to the rules of Standard English than not—particularly if it’s a neutral third-person narration. A third-person narration that focuses on one particular character’s point of view will probably use at least some of that character’s nonstandard vocabulary. A first-person narration, though, draws entirely from the speech patterns of the character doing the narrating.
For instance, Sha Gojyo of Saiyuki, a gambler with little formal education, would be more likely to use slang and loose, informal grammar in both his speech and thoughts, while Cho Hakkai, a former schoolteacher, would stick to more proper grammar in both his dialog and narrative written from his point of view. So while Gojyo might say,
“Yeah, sorry. It was kind of a spur-of-the moment thing, leaving like that.” Gojyo shrugged, casual-like, to show he wasn’t worried about what Sanzo might say.
Hakkai’s point of view for the same incident would probably be something more like,
“My apologies, but the decision to leave had to be made quickly.” Hakkai raised his shoulder in a casual shrug, showing he wasn’t concerned about what Sanzo might say.
If you’re focusing on what sounds most authentic for your characters and your story, that particular consideration easily trumps any concern over whether you should be using “real” words or not.
Sources:
Dictionary.com
Fowler’s Modern English Usage by R. W. Burchfield
Garner’s Modern American Usage by Bryan A. Garner
“Jabberwocky” on Wikipedia
Rules for Writers, 6th ed. by Diana Hacker
