Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
Use the NOT function, one of the logical functions, when you want to make sure one value is not equal to another.
Example
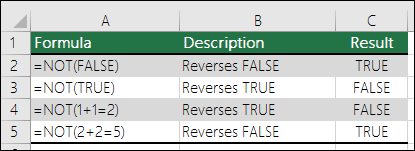
The NOT function reverses the value of its argument.
One common use for the NOT function is to expand the usefulness of other functions that perform logical tests. For example, the IF function performs a logical test and then returns one value if the test evaluates to TRUE and another value if the test evaluates to FALSE. By using the NOT function as the logical_test argument of the IF function, you can test many different conditions instead of just one.
Syntax
NOT(logical)
The NOT function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Logical Required. A value or expression that can be evaluated to TRUE or FALSE.
Remarks
If logical is FALSE, NOT returns TRUE; if logical is TRUE, NOT returns FALSE.
Examples
Here are some general examples of using NOT by itself, and in conjunction with IF, AND and OR.
|
Formula |
Description |
|---|---|
|
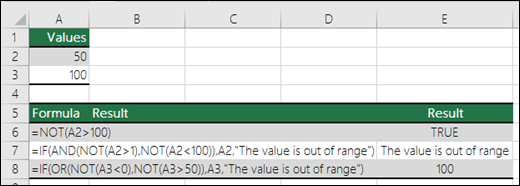
=NOT(A2>100) |
A2 is NOT greater than 100 |
|
=IF(AND(NOT(A2>1),NOT(A2<100)),A2,»The value is out of range») |
50 is greater than 1 (TRUE), AND 50 is less than 100 (TRUE), so NOT reverses both arguments to FALSE. AND requires both arguments to be TRUE, so it returns the result if FALSE. |
|
=IF(OR(NOT(A3<0),NOT(A3>50)),A3,»The value is out of range») |
100 is not less than 0 (FALSE), and 100 is greater than 50 (TRUE), so NOT reverses the arguments to TRUE/FALSE. OR only requires one argument to be TRUE, so it returns the result if TRUE. |
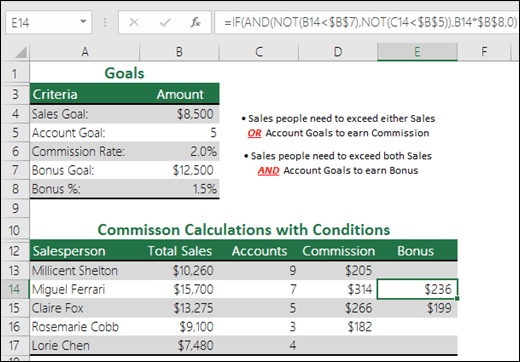
Sales Commission Calculation
Here is a fairly common scenario where we need to calculate if sales people qualify for a bonus using NOT with IF and AND.
-
=IF(AND(NOT(B14<$B$7),NOT(C14<$B$5)),B14*$B$8,0)— IF Total Sales is NOT less than Sales Goal, AND Accounts are NOT less than the Account Goal, then multiply Total Sales by the Commission %, otherwise return 0.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Related Topics
Video: Advanced IF functions
Learn how to use nested functions in a formula
IF function
AND function
OR function
Overview of formulas in Excel
How to avoid broken formulas
Use error checking to detect errors in formulas
Keyboard shortcuts in Excel
Logical functions (reference)
Excel functions (alphabetical)
Excel functions (by category)
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
NOT in Excel
NOT function is an inbuilt function that is categorized under the Logical Function; the logical function operates under a logical test. It is also called Boolean logic or function. Boolean functions are most commonly used along with or in conjunction with other functions, specifically along with conditional test functions (“IF’’ FUNCTION), to create formulas that can evaluate multiple parameters or criteria and produce desired results depending on that criteria. It is used as an individual function or part of the formula and other excel functions in a cell. E.G. with AND, IF & OR function. It returns the opposite value of a given logical value in the formula, NOT function is used to reverse a logical value. If the argument is FALSE, then TRUE is returned and vice versa.
Note: Use NOT function when you want to make sure a value is not equal to one Specific or particular value
It’s a worksheet function; it is also used as part of the formula in a cell along with other excel function
- If given with the value TRUE, the Not function returns FALSE
- If given with the value FALSE, the Not function returns TRUE
NOT Formula in Excel
Below is the NOT Formula in excel:
=NOT (logical) logical – A value that can be evaluated to TRUE or FALSE
The only parameter in the NOT function is a logical value.
The logical test or argument can be either entered directly, or it can be entered as a reference to a cell that contains a logical value, and it always returns the Boolean value (“TRUE” OR “FALSE”) only.
How to Use the NOT Function in Excel?
NOT Function in Excel is very simple and easy to use. Let us now see how to use the NOT function in excel with the help of some examples.
You can download this NOT function Excel Template here – NOT function Excel Template
Example #1 – Excel NOT Function
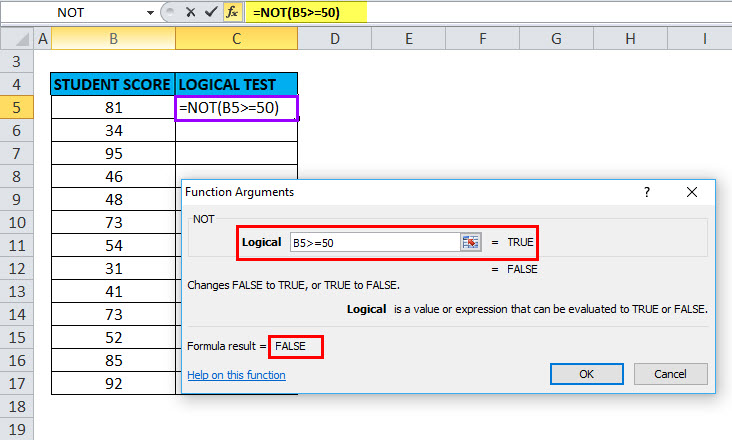
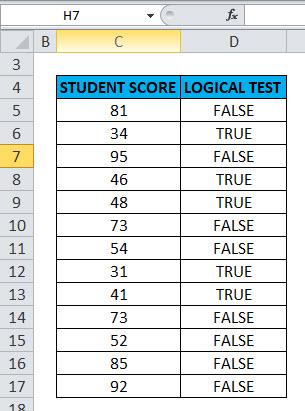
Here a logical test is performed on the given set of values (Student score) by using the NOT function. Here, we will check which value is greater than or equal to 50.
In the table, we have 2 columns, the first column contains student score & the second column is the logical test column, where the NOT function is performed.
Result: It will return the reverse value if the value is greater than or equal to 50, then it will return FALSE and if the lesser than or equal to 50, it will return TRUE as output.
The result will be as given below:
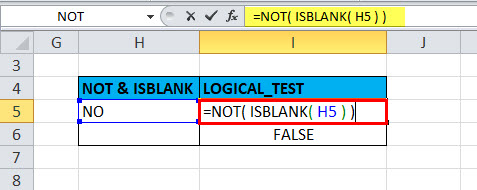
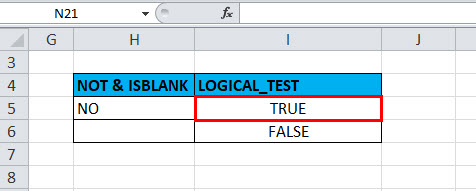
Example #2 – Using NOT Function with ISBLANK
the logical test is performed on the H5 & H6 Cells by using the NOT Function along with ISBLANK function; here will check if cells H5 & H6 is blank OR not using NOT function along with ISBLANK in excel
OUTPUT will be TRUE.
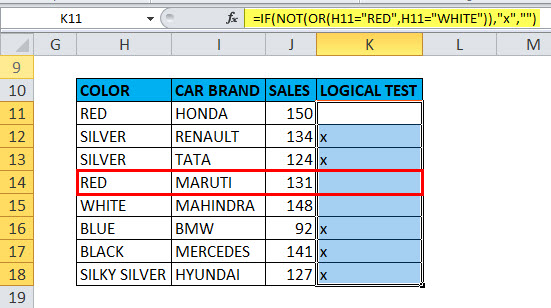
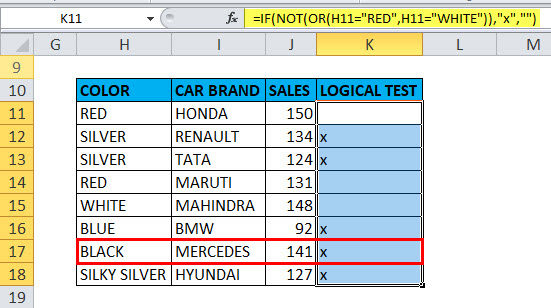
Example #3 – NOT Function along with “IF” and “OR” Function
Here the color check is performed for the cars in the below-mentioned table by using NOT Function along with “if” and “or” function
Here we have to sort out color “WHITE” or “RED” from the given set of data
=IF(NOT(OR(H11=”RED”,H11=”WHITE”)),”x”,””) formula is used
This logical condition is applied on a Color column containing any car with color “RED” or “WHITE”,
if the condition is true, then it will return blank as output,
if not true, then it will return x as output
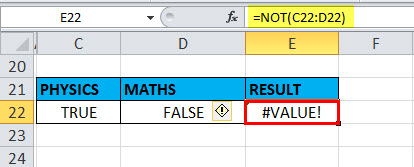
Example #4 – VALUE! Error
It Occurs when the supplied argument is not a logical or numeric value.
Suppose, if we give a range in the logical argument
Selected the range C22:D22 in the logical argument, i.e. =NOT (C22:D22)
a function returns a #VALUE error because the NOT function does not allow any range and can take only a logical test or argument or one condition.
Example #5 – NOT Function for an empty cell or blank or “0”
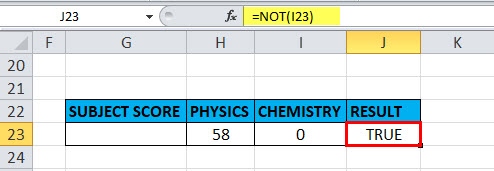
An empty cell or blank or “0” are treated as false, therefore “NOT” function returns TRUE
Here in the cell “I23”, the stored value is “0” suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “0” or “I23”, Output will be TRUE.
Example #6 – NOT Function for Decimals
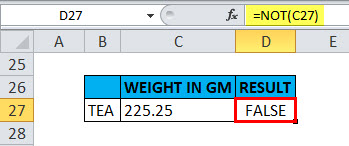
When the value is decimal in a cell
Suppose if we take the argument as decimals, i.e. suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “225.25” or “c27”, Output will be FALSE.
Example #7 – NOT Function for Negative Number
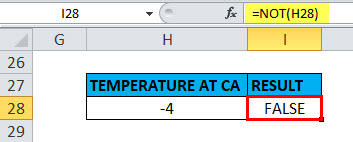
When the value is a negative number in a cell
Suppose if we take the argument as a negative number, i.e. suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “-4” or “H27”, Output will be FALSE.
Example #8 – When the value or Reference is Boolean Input in NOT Function
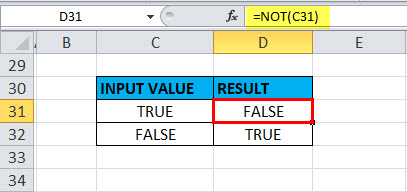
When the value or reference is Boolean input (“TRUE” OR “FALSE”) in a cell.
Here in the cell “C31”, the stored value is “TRUE” suppose if I apply the “NOT” function with logical argument or value as “C31” or “TRUE”, Output will be FALSE. It will be vice versa if the logical argument is “FALSE”, i.e. the NOT function returns the “TRUE” value as output.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to NOT Function. Here we discuss the NOT Formula and how to use the NOT function along with practical examples and downloadable excel templates. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- FV Function in Excel
- LOOKUP in Excel
- MINVERSE in Excel
- Write Formula in Excel
If you’re familiar with logical functions in Excel, you’ve probably used IF statements to execute different actions based on variable input criteria. In the majority of these scenarios, it’s likely that you’ve used Excel’s «=» logical operator to determine whether two values in your formula are equivalent to each other.
But there are some situations in which you may need to figure out whether two values are not equal to one another. This is possible using the NOT function, but there’s an even easier way: use the «does not equal» operator to determine whether two statements are not equal. Read on to find out how.
This tutorial will assume that you know how to use Excel’s
TRUE
and
FALSE
boolean functions. If you’re not familiar with those, stop by our
TRUE and FALSE tutorials
before proceeding.
The «does not equal» operator
Excel’s «does not equal» operator is simple: a pair of brackets pointing away from each other, like so: «<>«. Whenever Excel sees this symbol in your formulas, it will assess whether the two statements on opposite sides of these brackets are equal to one another. If they are not equal, it will output TRUE, and if they are equal, it will output FALSE. This is the exact opposite functionality of the equals sign (=), which will output TRUE if the values on either side of it are equal and FALSE if they are not.
Let’s take a look at the «does not equal» operator in action to see how we can use it in a simple formula:
=6<>8
Output: TRUE
The above formula outputs TRUE, because 6 does not equal 8. Let’s take a look at another simple example using integers:
=45<>45
Output: FALSE
This formula outputs FALSE, because 45 is equal to 45.
Of course, «<>» doesn’t have to be used on numbers. It can also be used on strings of text. Can you tell why the following formulas output the given results?
="Boston"<>"San Francisco"
Output: TRUE
="New York"<>"New York"
Output: FALSE
=RIGHT("Boston, MA", 2)<>"MA"
Output: FALSE
Hint: For the last example above, you’ll have to read up on how the RIGHT function works if you don’t already know it!
Combining <> with IF statements
The «does not equal» operator is useful on its own, but it becomes most powerful when combined with an IF function. Let’s take a look at a practical example to see how this works.
The following example uses the
IF
function. If you haven’t used
IF
statements yet, check out our
IF statement tutorial
first.
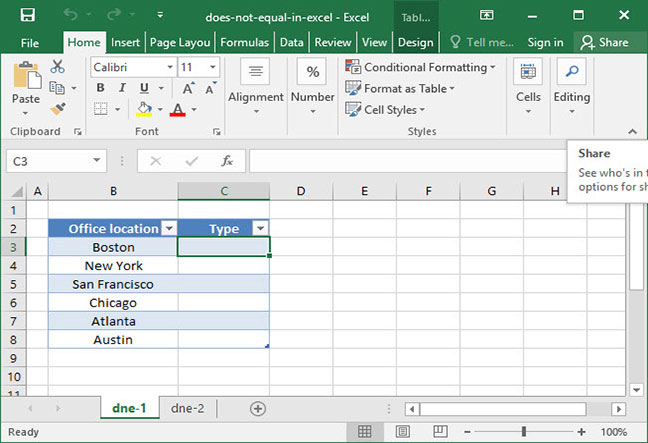
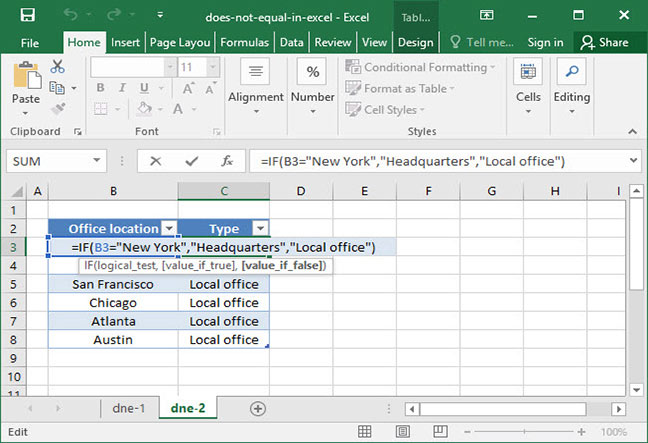
The spreadsheet above shows a list of SnackWorld’s office locations around the country. The company’s headquarters is in New York, and all of the other offices are local. A SnackWorld manager wants to add a column to the spreadsheet that dynamically outputs whether a given office is the company headquarters or a local office.
To do so, we could use the following formula:
=IF(B3<>"New York","Local office","Headquarters")
Output: "Local office"
Note that this formula outputs «Local office» for all the offices names that do not equal «New York»; but, it outputs «Headquarters» when it sees that the office name is equal to «New York».
Note that the above formula could be rewritten as follows, using the equals operator (=) but switching the order of the IF statement’s value_if_true and value_if_false arguments:
=IF(B3="New York","Headquarters","Local office")
Output: "Local office"
Is there any advantage to using the «<>» operator instead of the equals sign? Definitely. When you’re using IF statements, you can swap around the order of arguments and generally use either «=» or «<>» in your formulas. But when working with more advanced conditional formulas — in particular, SUMIF and COUNTIF — you’ll likely bump into scenarios in which only «<>» is sufficient (for example, if you want to sum up sales for all offices for which the office name is not «New York»).
Other logical operators
If you found this article useful, consider taking a look at our full article on logical operators. We’ll teach you how to use the full range of logical operators, including «greater than» and «less than», in your formulas.
Save an hour of work a day with these 5 advanced Excel tricks
Work smarter, not harder. Sign up for our 5-day mini-course to receive must-learn lessons on getting Excel to do your work for you.
- How to create beautiful table formatting instantly…
- Why to rethink the way you do VLOOKUPs…
- Plus, we’ll reveal why you shouldn’t use PivotTables and what to use instead…
Comments
We can use the “Not equal to” comparison operator in Excel to check if two values are not equal to each other. In Excel, the symbol for not equal to is <>. When we check two values with the not equal to formula, our results will be Boolean values which are either True or False. In this tutorial, we will explore the ways to use the Not Equal to Boolean operator in Excel.

Using the “Not Equal to” to test numeric values and text values
We will prepare a data table and then test values from our data table using the <> symbol.

- In Cell D4, we will enter the formula below and press OK
=C4<>B4
- Our result will be displayed as either TRUE or FALSE.
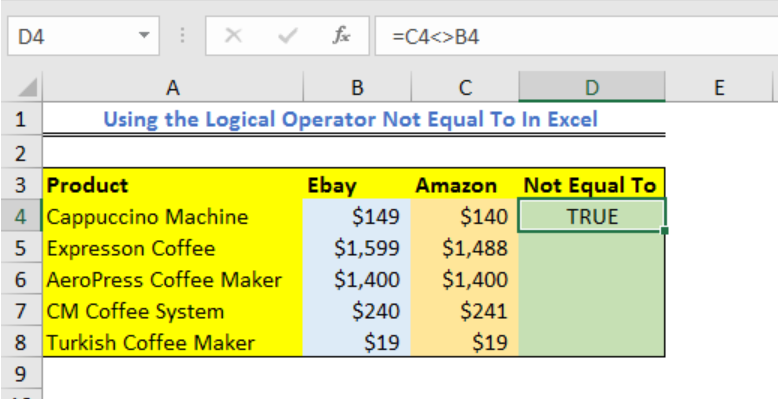
- If we drag down the formula into other cells in Column C, we will have:

Using a “Not Equal To” in Excel IF Formula
We can write IF Statements with the not equal to operator to show specific results when particular conditions are met or not.
- Again, we will prepare a data table

- In Cell C4, we will insert the formula and press the enter key
=IF(A4<>B4,"Product Not Matching", "Product Matching")

- We will copy down the formula into other cells.

Using the Not Equal to in Excel COUNTIF formula
We can use the not equal to operator to count the number of cells that contain values not equal to a particular value. In this section, we will use the COUNTIF function and the not equal to operators to count other items in our list except the specified item.
- We will prepare a data table

- To count all items except Cereal. In Cell E4, we will enter the formula below and press the enter key.
=COUNTIF(A4:A20,"<>Cereal")

- To Count all other items except Soda, we will click on Cell E5, and enter the formula below.
=COUNTIF(A4:A20,"<>Soda")

- To Count all items except Snacks, we will click on Cell E6, and enter the formula below
=COUNTIF(A4:A20,"<>Snacks")

Instant Connection to an Excel Expert
Most of the time, the problem you will need to solve will be more complex than a simple application of a formula or function. If you want to save hours of research and frustration, try our live Excelchat service! Our Excel Experts are available 24/7 to answer any Excel question you may have. We guarantee a connection within 30 seconds and a customized solution within 20 minutes.
What is “Not Equal To” Sign in Excel?
The “not equal to” is a logical operator in excel that helps compare two numerical or textual values. It is written (like <>) using a pair of angle brackets pointing away from each other. The “not equal to” excel sign returns either of the two Boolean values (true and false) as the outcome
- True implies that the two compared values are different or not equal.
- False implies that the two compared values are the same or equal.
For example, “=2<>4” (ignore the double quotation marks) returns “true” since the numbers 2 and 4 are not equal to each other.
The “not equal to” is used in the arguments of several Excel functions. The purpose of using the “not equal to” is to assess whether two values are different or not. However, the magnitude of difference is not conveyed by this operator.
Table of contents
- What is “Not Equal To” Sign in Excel?
- How is the “Not Equal To” Sign Used in Excel?
- Example #1–Compare two Numeric Values with the “Not Equal To” Operator
- Example #2–Compare two Textual Values with the “Not Equal To” Operator
- Example #3–Obtain Defined Results with the IF Function and the “Not Equal To” Condition
- Example #4–Count Specific Cells with the COUNTIF Function and the “Not Equal To” Condition
- Example #5–Sum Particular Cells with the SUMIF Function and the “Not Equal To” Condition
- The Key Points Related to the “Not Equal To” Operator of Excel
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
- How is the “Not Equal To” Sign Used in Excel?
How is the “Not Equal To” Sign Used in Excel?
Let us consider some examples to understand the working of the “not equal to” operator in Excel.
You can download this Not Equal to Excel Template here – Not Equal to Excel Template
Example #1–Compare two Numeric Values with the “Not Equal To” Operator
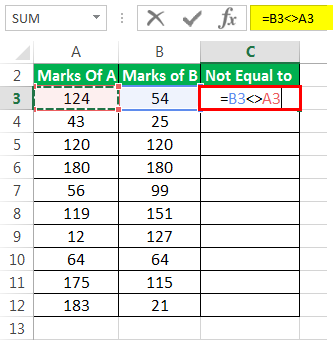
The succeeding image shows the marks of students A and B (columns A and B) in 10 subjects. The total marks of each subject are 200. We want to find those rows for which the marks of the two students are unequal. Use the “not equal to” signof Excel.
The steps to find if a difference exists between the two marks are listed as follows:
Step 1: In cell C3, type the “equal to” symbol followed by the cell reference B3. Since the difference between cells B3 and A3 needs to be assessed, insert the “not equal to” sign between these two cell references.
The formula should look like the expression “=B3<>A3.” This expression is also known as a statement or a condition.
Note: A condition in Excel is an expression that evaluates to either true or false. At a given time, a condition cannot be assessed as both true and false.
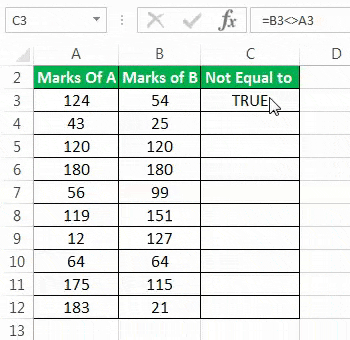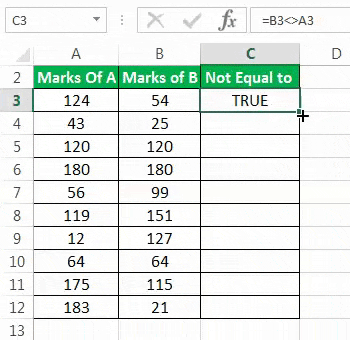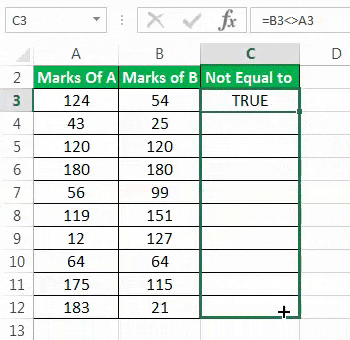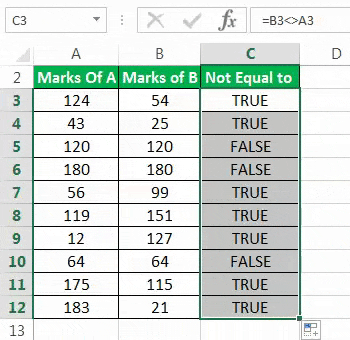
Step 2: Press the “Enter” key. The output in cell C3 is “true.” This is shown in the following image.
Step 3: Drag the formula of cell C3 till cell C12 by using the fill handle. This is shown in the following image.
Step 4: The outputs for the entire column C are shown in the following image. The outputs which are false have been colored yellow. The inferences from this dataset are stated as follows:
- If the output is “true,” the values of column A and column B for a given row are not equal. This means that the “not equal to” excel condition for that particular row is met. For instance, the “not equal to” condition for row 3 is “=B3<>A3.” In other words, 124 is not equal to 54.
- If the output is “false,” the values of column A and column B for a given row are equal. This means that the “not equal to” condition for that particular row is not met. For instance, the “not equal to” condition for row 5 is “=B5<>A5.” In other words, 120 is certainly equal to 120.
Overall, for three rows (rows 5, 6, and 10), the marks of students A and B are equal. Except for these rows, the marks are unequal in all the remaining rows (rows 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 11, and 12). Without knowing the magnitude of difference, one cannot conclude whose performance (from students A and B) is better.
Example #2–Compare two Textual Values with the “Not Equal To” Operator
In the dataset of example #1, we have substituted random grades (from A to J) in place of numbers. We want to find the rows for which the grades of students A and B are unequal. Use the “not equal to” operator of Excel.
The steps to find if a difference exists (between the grades) are listed as follows:
Step 1: Enter the formula “=B3<>A3” in cell C3. Press the “Enter” key. The output in cell C3 is “true.” So, for row 3, the “not equal to” excel operator has validated that the values in the first and second cell (A3 and B3) are not equal.
Step 2: Drag the formula of cell C3 till cell C12. The outputs for the entire column C are shown in the following image. The single false output has been colored yellow.
The output in cell C3 meets the “not equal to” excel condition, which is “=B3<>A3.” In contrast, the output in cell C11 does not meet the “not equal to” condition, which is “=B11<>A11.” Hence, the grades of all rows, except row 11, are unequal. The grades of the two students are equal for row 11.
Example #3–Obtain Defined Results with the IF Function and the “Not Equal To” Condition
The succeeding image shows the names of a few candidates and their native places in columns A and B respectively. From these candidates, an organization wants to hire those candidates whose city of origin is “A.”
We want to differentiate candidates who need to be contacted and who need not be contacted for the further hiring process. For this, display the status as either “please call” or “don’t call” (in column C), depending on whether the hometown of a candidate is “A” or not.
Use the IF function and the “not equal to” operator of Excel.
The steps to use the IF functionIF function in Excel evaluates whether a given condition is met and returns a value depending on whether the result is “true” or “false”. It is a conditional function of Excel, which returns the result based on the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the given criteria.
read more and the “not equal to” operator are listed as follows:
Step 1: Enter the following formula in cell C2.
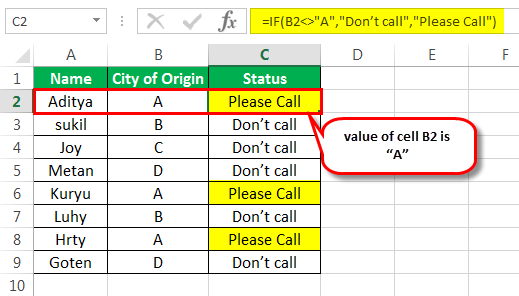
“=IF(B2<>”A”,”Don’t call”,”Please Call”)”
Press the “Enter” key. Drag the formula till cell C9. The outputs of column C are shown in the succeeding image. The candidates whose city of origin is “A” have been assigned the “please call” status in column C.
Note: In the given IF formula, the condition [B2<>“A”] is the logical test. The string “don’t call” is “value_if_true” and the string “please call” is “value_if_false.”
So, the IF formula returns “don’t” call” for a given row, if the value of column B is not equal to “A” (i.e., the condition is true). It returns “please call” for a given row, if the value of column B is equal to “A” (i.e., the condition is false).
With the help of the IF function, Excel can display different results for the matched and unmatched conditions. For more details related to the IF function of Excel, click the hyperlink given immediately before step 1 of this example.
Step 2: The candidates whose hometown is other than “A” have been assigned the “don’t call” status in column C. This is shown in the following image.
Hence, only candidates “Aditya,” “Kuryu,” and “Hrty” should be called for the further round of interviews. The remaining candidates need not be contacted.
So, with the IF function and the “not equal to” excel operator, we have successfully differentiated the candidates who can be hired from those who cannot be hired.
Note: Notice that this step has been added only for the purpose of understanding. The preceding step (step 1) is complete in itself for the given task of hiring candidates.
Example #4–Count Specific Cells with the COUNTIF Function and the “Not Equal To” Condition
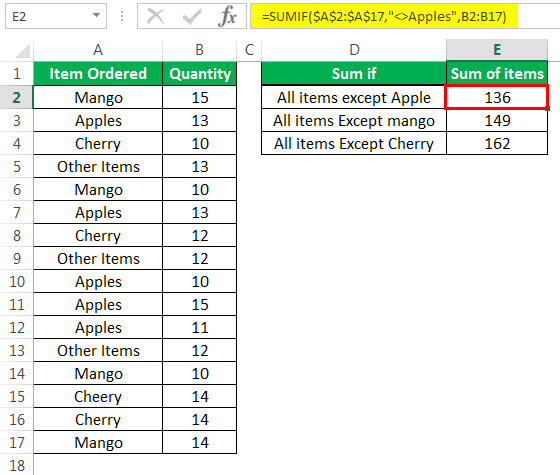
The succeeding image shows certain fruits (or items) in column A and their quantities ordered in column B. Apart from apples, mangoes, and cherries, the remaining fruits have been clubbed under “other items” in column A.
We want to count the number of cells (of column A) that are not equal to:
- “Apples”
- “Mango”
- “Cherry”
There should be three outputs, one output excluding one fruit. Use the COUNTIF function and the “not equal to” operator of Excel.
The steps to use the COUNTIF functionThe COUNTIF function in Excel counts the number of cells within a range based on pre-defined criteria. It is used to count cells that include dates, numbers, or text. For example, COUNTIF(A1:A10,”Trump”) will count the number of cells within the range A1:A10 that contain the text “Trump”
read more and the “not equal to” operator are listed as follows:
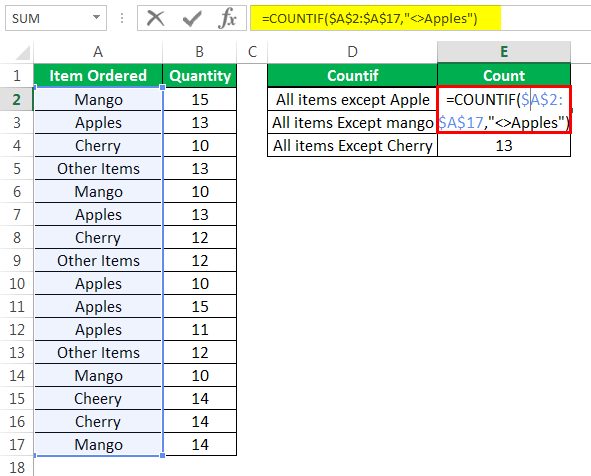
Step 1: Enter the following formulas in cells E2, E3, and E4 respectively.
- “=COUNTIF($A$2:$A$17,”<>Apples”)”
- “=COUNTIF($A$2:$A$17,”<>Mango”)”
- “=COUNTIF($A$2:$A$17,”<>Cherry”)”
Press the “Enter” key after entering each formula.
The first formula counts the number of cells in the range A2:A17, which do not contain the string “apples.” Likewise, the second formula counts the number of cells in this range that do not contain the string “mango.” The third formula helps count the number of cells in the given range (A2:A7), which do not contain the string “cherry.”
Notice that the succeeding image shows the formula in cell E2 and the result of the third formula in cell E4.
Note: “$A$2:$A$17” is the “range” argument of the preceding COUNTIF formulas. The condition “<>Apples” is the “criteria” argument of the first formula. In all the preceding formulas, the range is the same, but the criterions are different.
The COUNTIF counts the cells of a range, which satisfy a single criterion. For more details related to the COUNTIF function, click the hyperlink given before step 1 of this example.
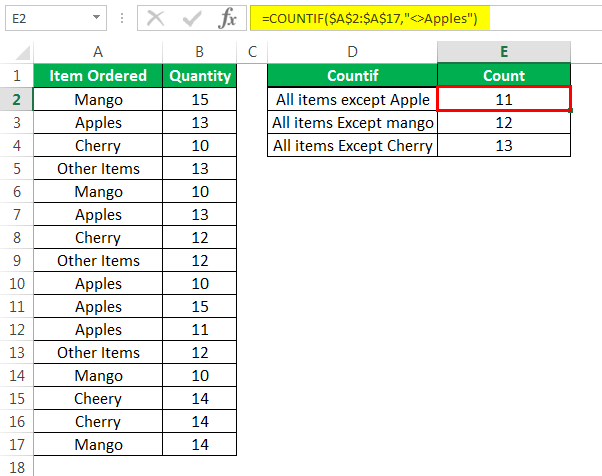
Step 2: The following image shows the three outputs (in cells E2, E3, and E4) of the three formulas entered in the preceding step.
Notice that “cherry” has been deliberately misspelled as “cheery” in cell A15. As a result, this cell has also been counted (as a cell not containing “cherry”) by the third COUNTIF formula.
Had the word been correctly spelled in cell A15, the output in cell E4 would have been 12. In this case, cell A15 would have been excluded from the count (as a cell containing “cherry”).
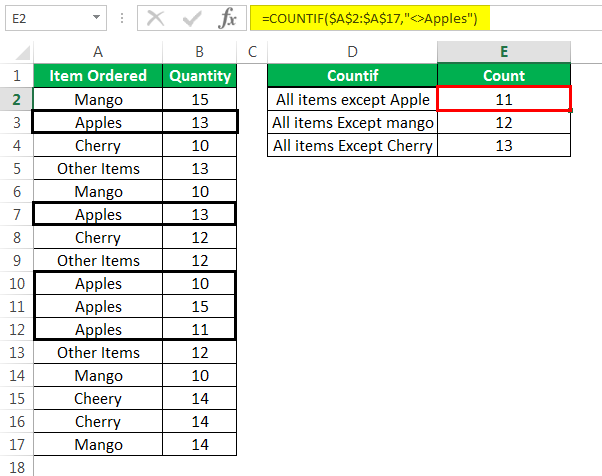
Step 3: The rows containing “apples” are displayed in black boxes in the following image. These rows are excluded while counting the cells not containing “apples.” Hence, 11 cells (in the range A2:A17) do not contain the string “apples.”
Likewise, in the given range, 12 cells do not contain the string “mango” and 13 cells do not contain the string “cherry.”
Note: This step has been added only for notifying the readers, the cells that are counted and the cells that are left out by the first COUNTIF formula (entered in step 1).
Example #5–Sum Particular Cells with the SUMIF Function and the “Not Equal To” Condition
Working on the data of example #3, we want to sum the quantities of column B that are not equal to:
- “Apples”
- “Mango”
- “Cherry”
There should be three summed outputs where each output excludes one fruit. Use the SUMIF function and the “not equal to” sign of Excel.
The steps to use the SUMIF functionThe SUMIF Excel function calculates the sum of a range of cells based on given criteria. The criteria can include dates, numbers, and text. For example, the formula “=SUMIF(B1:B5, “<=12”)” adds the values in the cell range B1:B5, which are less than or equal to 12.
read more and the “not equal to” operator are listed as follows:
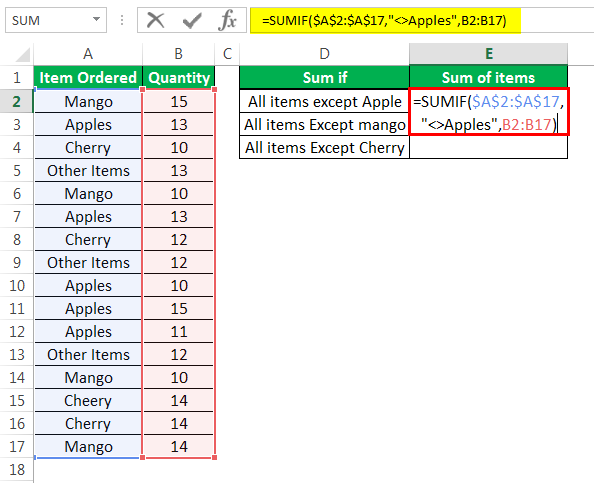
Step 1: Enter the following formulas in cells E2, E3, and E4 respectively.
- “=SUMIF($A$2:$A$17,”<>Apples”,B2:B17)”
- “=SUMIF($A$2:$A$17,”<>Mango”,B2:B17)”
- “=SUMIF($A$2:$A$17,”<>Cherry”,B2:B17)”
The first formula is shown in the following image.
In all three formulas, the SUMIF function evaluates the range A2:A17. For cells not equal to “apples” (in range A2:A17), the first formula sums the numbers of the range B2:B17. Likewise, for cells not equal to “mango” in the given range (A2:A17), the second formula also sums the numbers of the range B2:B17. Similar summing is carried out by excluding cells containing “cherry.”
Note: “$A$2:$A$17” is the “range” argument of the SUMIF function. The condition “<>Apples” is the “criteria” argument. The range “B2:B17” is the “sum_range” argument of the SUMIF function.
With the SUMIF function, we have applied the given condition (in each formula) to the range A2:A17 and summed up the corresponding values of the range B2:B17. Usually, the SUMIF works with a single criterion. For more details related to the SUMIF function, click the hyperlink given before step 1 of this example.
Step 2: Press the “Enter” key after entering each of the preceding formulas. The three summed outputs are shown in the following image.
Hence, the sum of all the fruit quantities except “apples” is 136. Excluding the cells containing “mango,” this sum is 149. Likewise, leaving the cells containing “cherry,” this sum is 162.
Notice that the value of cell B15 has also been included in the sum returned (in cell E4) by the third SUMIF formula (entered in step 1). This is because in cell A15, the spelling of “cherry” has been misspelled as “cheery.” Hence, Excel considers A15 as a cell not containing “cherry.”
The important points governing the usage of the “not equal to” operator of Excel are listed as follows:
- The “not equal to” is the converse of the “equal to” operator. This implies that the interpretation of “true” and “false” is exactly the opposite with these two logical operators.
- The results produced by the “not equal to” operator are similar to those returned by the NOT function of Excel. The NOT function reverses the “true” and “false” outcomes of a condition. For instance, if the output of a condition is “false,” the formula “=NOT(false)” returns “true.”
- The “not equal to” operator is case-insensitive. This means that it ignores the casing of the two text strings that are compared. For instance, if “rose” and “ROSE” are compared using the “not equal to” operator, the output is “false.” This is because these two values mean the same to the “not equal to” excel operator.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Define the “not equal to” operator and state how is it used in Excel.
The “not equal to” excel operator checks whether two values (numeric or textual) being compared are different from each other or not. If the values are different, the output is “true.” If the values are the same, the output is “false.” The “not equal to” operator is the easiest method to ensure that a difference exists between two values.
In Excel, the “not equal to” operator is used as follows:
“=value1<>value2”
“Value1” is the first value to be compared and “value2” is the second value to be compared.
Note: Exclude the beginning and ending double quotation marks while entering the “not equal to” condition in Excel. For more details related to the usage of this operator, refer to the examples of this article.
2. How to use the “not equal to” operator with the conditional formatting feature of Excel?
The steps to use the “not equal to” with the conditional formatting feature of Excel are listed as follows:
a. Select the range on which a conditional formatting rule is to be applied.
b. From the Home tab, click the “conditional formatting” drop-down from the “styles” group. Next, click “new rule.”
c. The “new formatting rule” window opens. Under “select a rule type,” choose the option “use a formula to determine which cells to format.”
d. Under “format values where this formula is true,” enter the desired formula. For instance, if cells (in the range A1:A6) not equal to 2 are to be formatted, enter the formula as “=A1<>2” (without the beginning and ending double quotation marks).
e. Click “format” and select a color from the “fill” tab. Click “Ok” in the “format cells” window.
f. Click “Ok” again in the “new formatting rule” window.
The chosen color (selected in step “e”) is applied to the selected range (selected in step “a”). If the formula given in step “d” is applied, the cells of the range A1:A6, which do not contain 2, are colored. No formatting is applied to the remaining cells.
Note: To conditionally format a range of text values by using the “not equal to” operator, keep the string of the formula in double quotation marks. For instance, the formula [=A1<>“rose”] formats those cells of the selected range which do not contain the string “rose.” Exclude the beginning and ending square brackets while applying this formula.
3. How to use the “not equal to” operator to find blanks in a range of Excel?
The steps to find blanks in Excel by using the “not equal to” operator are listed as follows:
a. Enter the formula containing the cell reference (to be evaluated), “not equal to” operator, and an empty text string. For instance, if blanks in the range A1:A6 are to be found, enter the formula =A1<>“” in cell B1.
b. Press the “Enter” key. Drag the formula to the remaining range (of column B) to obtain outputs for the entire column (column A).
The cells containing blanks have been identified. The formula entered in step “a” returns “true” for all values which are not blanks. For all blank values, this formula returns “false.”
Since the double quotation marks of the formula represent an empty string, a “false” implies that the cell value is equal to an empty string. Conversely, a “true” implies that the cell contains some value, which is not equal to an empty string.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the “not equal to” operator/sign of Excel. Here we discuss how to use the “not equal to” formula in Excel along with step-by-step examples and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles–
- VBA IF NOT In VBA, IF NOT is a comparison function that compiles statements and provides inverted outcomes. The function returns “FALSE” if the logical test is correct, and “TRUE” if the logical test is incorrect.read more
- NOT Excel FunctionNOT Excel function is a logical function in Excel that is also known as a negation function and it negates the value returned by a function or the value returned by another logical function.read more
- VBA OR FunctionOr is a logical function in programming languages, and we have an OR function in VBA. The result given by this function is either true or false. It is used for two or many conditions together and provides true result when either of the conditions is returned true.read more
- How to use OR in Excel?