You will often see that “coursework” is written in one or two words. It would help to know all the rules associated with using it correctly. Don’t worry. This article will run you through everything there is to know.
“Coursework” is most commonly written as one word. It’s commonly written in this way because “course” and “work” are easily distinguishable from each other, even in the one-word variation. “Course work” is correct, but it’s not as common to see in English writing.
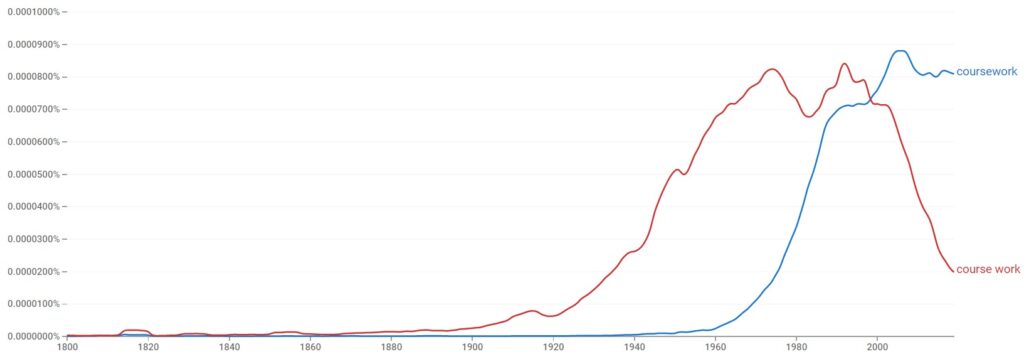
According to Google Ngram Viewer, “coursework” is the most common spelling variation of the two options. With that said, “course work” as two words is still fairly common, showing that both are correct.
The Oxford Dictionary lists “coursework” as the main variation, but there is a note that says “also course work,” showing that the two-word variation is acceptable.
The Cambridge Dictionary only has an entry for “coursework” as one word. There is no mention of the two-word variation in The Cambridge Dictionary.
Is “Coursework” One Word?
“Coursework” is almost always written as one word. Most native speakers recognize it in this form because it’s commonly written together. “Course” and “work” can combine to show that you are working on something for your course.
Spaces between words like “course work” are often dropped when they do not add anything of use to the meaning of the word. This is the case with “coursework” since removing the space still shows a clear difference between “course” and “work.”
It goes from needing “course” to act as an adjective to “coursework” being a compound noun. Compound nouns contain an adjective and noun in the same word, allowing the modification to take place without thinking about it.
You will often hear people refer to AP Style rules when they remove spaces like this. AP Style encourages people to keep their writing simplistic, and removing spaces when they are unnecessary is a good way to go about this.
These examples will help you understand more about it:
- I have a lot of coursework to get on with. Do you mind giving me some time to get it all sorted?
- What about all of the coursework they set? Do you think you’ll be able to do it before the deadline?
- I’m not sure if this coursework is right for me. I really don’t think I fancy answering all these questions.
- That’s a lot of coursework! How are we ever going to be able to get it all done?
Is “Course work” Two Words?
You can use “course work” as two words, but it’s not a very common option. Most people avoid writing it like this because the one-word variation already makes the meaning of the word clear. You do not have to isolate “course” from “work” to show the modification.
“Course” modifies “work,” which is why it’s still acceptable for the words to be separated. The modification is made clear when it’s written in this form.
You can refer to AP Style guidelines to show that adjectives come before nouns when modifications take place. If you treat “course” as the adjective and “work” as the noun, these guidelines still make sense for the two-word variation.
These examples will enlighten you:
- What can you tell me about the course work? Do I need to know anything before going into it?
- I haven’t done the course work yet, but I’m working on it. I hope you don’t mind waiting for a bit.
- It’s not course work unless it’s challenging. You can’t just go around making everything look easy.
- I’ll have to set them new course work to tide them over. I hope they don’t mind these options.
Tip to Remember Which to Use
“Coursework” is best used as one word, so it would help to remind yourself of that.
“Coursework” is easy to remember if you say it out loud. When spoken, “coursework” is uttered quickly, showing that there is no need for a space between the words. This indicates that the one-word variation is the best spelling choice.
Final Thoughts
You will only ever need “coursework” in your writing if you want to be grammatically correct every time. While there may not be any English rules that say that “course work” is incorrect, it’s best to avoid using the two-word variation in most cases.
Martin holds a Master’s degree in Finance and International Business. He has six years of experience in professional communication with clients, executives, and colleagues. Furthermore, he has teaching experience from Aarhus University. Martin has been featured as an expert in communication and teaching on Forbes and Shopify. Read more about Martin here.
For example, home is the only strong syllable in homework, but one of two in home rule. I write coursework as one word because course- is stronger than work.
What is the meaning of course work?
Coursework is work performed by students or trainees for the purpose of learning. In universities, students are usually required to perform coursework to broaden knowledge, enhance research skills, and demonstrate that they can discuss, reason and construct practical outcomes from learned theoretical knowledge.
What is another word for coursework?
What is another word for coursework?
| homework | project |
|---|---|
| prep | assignments |
| assignment | task |
| schoolwork | exercise |
| lesson | study |
How do you write coursework?
Seven Tips to Help You Produce Excellent Coursework
- Understand the objective before you begin.
- Research, research, research.
- Plan your essay or report carefully.
- Manage your time.
- Do not plagiarise.
- Review and edit your work.
- Make sure it fits all presentation requirements.
How is coursework marked?
All coursework is evaluated by three examiners. The First Marker (normally although not exclusively the Module Convener), the Second Marker who checks all marks or Moderator who checks a selection of marks and External Examiner. The First marker reads all of the papers, and makes commentary and awards a grade to each.
How do you put coursework on a resume?
When creating a resume, consider adding a section called “Relevant Coursework.” In it, include the courses directly related to the position you are applying for. For example, if you are applying for work as a paralegal, list any classes you took related to law or politics.
Should I put coursework on my resume?
Should you include relevant coursework on your resume? Some people will tell you yes, others will advise against it. The best answer is: it depends. If you have relatively little experience in the field, including a list of relevant courses can be a good way to demonstrate your interest and exposure to a topic area.
What do I put for skills on a resume?
What are the best skills to put on a resume?
- Communication skills.
- Computer skills.
- People skills.
- Leadership skills.
- Organizational skills.
- Time management skills.
- Collaboration skills.
- Problem-solving skills.
Can you put CPD on your CV?
The research found that CPD is directly linked to employability, and adding a CPD section to a CV can improve job prospects significantly, with the opportunity of securing a dream job increased by 10% (the CPD Research Project 2010).
Can I put a MOOC on my CV?
Fortunately, there is no single right way to put MOOCs on your resume. My high school English teacher used to say, “All writing is creative.” While your resume should be based in fact, not fiction, you can absolutely use some creativity when highlighting your MOOC-based business education.
How do you list courses taught on CV?
To the right of each course, in parentheses, give the terms and years taught. This allows you to show the number of times you’ve taught a course without listing it over and over. Give course titles BUT NEVER GIVE COURSE NUMBERS! Course numbers are meaningless outside your campus.
Is a CV or a resume better?
As stated, three major differences between CVs and resumes are the length, the purpose, and the layout. A resume is a brief summary of your skills and experience over one or two pages, a CV is more detailed and can stretch well beyond two pages.
Do you include scholarships on CV?
DO INCLUDE AWARDS – List any awards, scholarships, or related commendations under the appropriate section of your resume. But you should not change or enhance your job titles on the resume.
How do I write a CV with no experience?
7 tips for writing a great CV when you have no work experience
- Tailor your CV to the job.
- Make the most of your personal statement.
- Think outside the job.
- Leverage your transferable skills.
- Add a cover letter.
- Use the right keywords.
- Show your personality.
- Recommended Reading:
How do I write my first CV?
What to put in your first CV
- Full name.
- Contact details: Address, telephone, email.
- Personal statement: (see below)
- Key skills (see below)
- Education: Where you’ve studied, for how long, and what grades you got. If you haven’t got any results yet, you can put what grades you’ve been predicted.
- Work experience.
Can you get a job without a CV?
Even though constructing a CV will increase your chances of getting a job, and it is advisable by many career professionals, there is a possibility you could still get hired by just demonstrating your passion and interest in the company effectively!
Do you need a CV for a part time job?
Include contact details so the employer knows how to reach you if they want to offer you a job. Use your resume or CV to outline your experience, skills and qualifications. You may not need them at all, depending on the job you are applying for, but it’s a good idea to have them handy in case you need them.
What is an example of a part time job?
Part time is defined as working a portion of a regular time period. An example of part time is when a person works for 20 hours and not the customary 40 hours per week. An example of a part-time job is a job where you work less than the customary 40 hours per week.
How do I write a CV for a part time job?
Here are our top tips.
- Mentioning your motives for going part-time in the personal statement.
- Always highlight your achievements.
- Match skills to the job where relevant.
- Edit and proofread.
What do you put on your first resume for a part time job?
Write a Part-Time Job Resume Objective or Resume Summary Highlight the knowledge and skills you’ve gathered to date and how well you’d fit in the offered position. Think of transferable skills and quantifiable achievements from other gigs you’ve had that are relevant to the open position and vouch for you.
Do you need a resume for your first part time job?
You probably won’t need a resume for a basic first part-time job unless the position is an internship. However, it will be useful for you to have a document in hand to promote your background as you network with contacts or make in-person prospecting visits with employers.
What should a 16 year old put on a resume?
For instance, a 16-year-old’s resume can include volunteering, hobbies, school activities, academic honors and relevant course work. All of these experiences say a lot about you and your well-rounded interests.
What is a good objective for a part time job?
1. Seeking a position as a part time sales associate at ABC Company that necessitates strong interpersonal skills, sales experience, and occupational flexibility. 2. Looking for a part time sales associate position with ABC Company that will require communication, customer service, and marketing skills.
What is a good objective for a resume with no experience?
Objective (Not a Summary) for a Resume with No Experience—Examples
- Start with your strong character traits (motivated, personable).
- Say who you are (student pursuing a BA in… ).
- Mention the company you’re applying to by name to personalize your resume.
- Say what you want to do for the company.
What skills does a part-time job give you?
Ten shop work skills that will help students get a graduate job
- Customer service and communication skills.
- Commercial awareness.
- Working under pressure.
- Working in a busy team.
- Time management.
- Problem-solving and initiative.
- Attention to detail.
- Responsibility.
What should I put for objective?
How to Write an Objective for a Resume
- Keep it short. Don’t add fluff!
- Be clear and detailed about the job you want. State the position you are applying for and describe your goals only as they pertain to the job and industry for which you’re applying.
- Explain what you can do for them.
What are the 5 smart objectives?
By making sure the goals you set are aligned with the five SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-Bound), you have an anchor on which to base all of your focus and decision-making.
How do you write an objective example?
5 Steps to Writing Clear and Measurable Learning Objectives
- Identify the Level of Knowledge Necessary to Achieve Your Objective. Before you begin writing objectives, stop and think about what type of change you want your training to make.
- Select an Action Verb.
- Create Your Very Own Objective.
- Check Your Objective.
- Repeat, Repeat, Repeat.
What are the 5 performance objectives?
The key to having good all-round performance is five performance objectives: quality, speed, dependability, flexibility and cost.
Last Update: Jan 03, 2023
This is a question our experts keep getting from time to time. Now, we have got the complete detailed explanation and answer for everyone, who is interested!
Asked by: Elinore Hammes
Score: 4.3/5
(9 votes)
min·i·course
A short, usually intensive course on a subject of study.
Is mini course one word or two?
Meaning of «mini-course» in the English dictionary
Mini-Course is a noun. A noun is a type of word the meaning of which determines reality.
What does mini course mean?
noun. a short, intensive course of study, usually a few weeks long.
Is course work one or two words?
For example, home is the only strong syllable in homework, but one of two in home rule. I write coursework as one word because course- is stronger than work.
Is Mini a word or a prefix?
word-forming element meaning «miniature, minor,» abstracted from miniature, with sense perhaps influenced by minimum. The vogue for mini- as a prefix in English word coinage dates from c. 1960; minicam for «miniature camera» (1937) is an early use.
28 related questions found
What is a mini dictionary called?
A mini-dictionary is a little dictionary, also called a pocket dictionary.
Is Mini a root word?
Definition & Meaning: Mini Root Word
What does Mini Root Word mean? … The name ‘minion’ is derived from the Root Word Mini which means ‘small, less’. It is usually used to make something smaller.
Is courseworks a word?
«Coursework» is a mass noun, which means it is uncountable and used in similar ways to other mass nouns you might be more familiar with. Think water, love, or ass-kicking. Similarly, words such as «schoolwork» and «homework» are also mass nouns. You can’t count them or pluralize them.
Is Town Hall one or two words?
AP’s online Ask the Editor section says “town hall” is:
Two words not one (“town hall” not “townhall”). … Not hyphenated before “meeting” (town hall meeting). Correct as a noun (meaning a public forum: “The town hall is tonight.”) or as an adjective before a noun (as in “town hall meeting”).
How do you spell course work?
the work required of a student in a particular course of study; classroom work.
What is the meaning of crash course?
: a rapid and intense course of study also : an experience that resembles such a course has been given a crash course in diplomacy in his first weeks in office.
What is a school town hall meeting?
A town hall meeting is an informal arena where citizens can voice their opinions on issues that affect the community at large. … We will host a town hall meeting before a hypothetical district school board and debate the superintendent’s proposal to eliminate high school sports.
Why is the City Hall important?
City halls exist in almost every city across America. They serve the same purpose in each place: they are portals through which we interact with local leaders and conduct our bureaucratic business with the government.
Why is coursework better than exams?
In contrast to exams, coursework enables students to demonstrate they can work on a task over a period of time and bring it to completion. It’s more inclusive, catering for different learning styles. For practical subjects such as drama, it’s a much more suited method of assessment.
What a coursework means?
: work that is assigned or performed as part of a course of study The rigorous program combines coursework in …
What’s the root word of smallest?
#70 micro → small.
What root means many?
Quick Summary. The English prefix multi- means “many.” Examples using this prefix include multivitamin and multiplication.
What do Mini Me mean?
/ (ˈmɪnɪˌmiː) / noun informal. a person who resembles a smaller or younger version of another person. a person who adopts the opinions or mannerisms of a more powerful or senior person in order to win favour, achieve promotion, etc.
Is Mini a word in the dictionary?
anything of a small, reduced, or miniature size.
How do you spell Mimi?
Mimi is a feminine given name and a shorter form (hypocorism) of the given names Miriam, Emilia or Naomi.
What is a town hall for?
town hall: «A building used for the administration of local government, the holding of court sessions, public meetings, entertainments, etc.; (in early use also) a large hall used for such purposes within a larger building or set of buildings. …
What is another name for all hands meeting?
An all-hands meeting, sometimes called a «town hall» or «forum,» gathers the whole organization in person or virtually for company updates.
Coursework. Coursework is work performed by students or trainees for the purpose of learning. Coursework may be specified and assigned by teachers, or by learning guides in self-taught courses. Coursework can encompass a wide range of activities, including practice, experimentation, research, and writing.
Frontyard is coursework one word two words.
Subsequently, What does coursework mean in college?
College coursework is study taken for college credit, completed at or transferred to a degree-granting institution of higher education approved by the New York State Commissioner of Education or a regional accrediting agency. … Unacceptable coursework is that which is not credit-bearing or not applicable toward a degree.
Also, What Does completed coursework mean?
“Relevant coursework” is an optional entry-level resume section that includes coursework you’ve completed related to the job you’re applying to. … If you are a student or have just graduated, relevant coursework is a good way to demonstrate your expertise even if you don’t yet have professional experience.
Is coursework one word or two?
Frontyard is coursework one word two words.
Last Review : 13 days ago.
Related Contents
- 1 How do you use coarse and course in a sentence?
- 2 Is coursework singular or plural?
- 3 What is another word for coursework?
- 4 Which is correct of coarse or of course?
- 5 Is it of course or of coarse?
- 6 What is college coursework?
- 7 Which is correct of course or ofcourse?
- 8 How do you use ofcourse?
- 9 What are the basic college classes?
- 10 What is course of study for college?
- 11 Do you say of course or of coarse?
- 12 What’s the difference between of course and of course?
- 13 What should be included in coursework on resume?
- 14 How do you use coarse in a sentence?
- 15 How do you spell of course not?
How do you use coarse and course in a sentence?
– A coarse painting was drawn on the cave wall. ( meaning rough or crude)
– The blacksmith’s coarse language shocked Ma. ( …
– She dusted the tops of the candies with coarse sugar. ( …
– She took a course in welding at the local community college. ( …
– The yacht’s pilot set a course for the open sea. (
Is coursework singular or plural?
“Coursework” is a mass noun, which means it is uncountable and used in similar ways to other mass nouns you might be more familiar with. Think water, love, or ass-kicking. Similarly, words such as “schoolwork” and “homework” are also mass nouns. You can’t count them or pluralize them.
What is another word for coursework?
In this page you can discover 14 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for coursework, like: course-work, dissertation, assignment, summative, written examination, , courseworks, , practicals, unassessed and end-of-course.
Which is correct of coarse or of course?
“Coarse” is always an adjective meaning “rough, crude.” Unfortunately, this spelling is often mistakenly used for a quite different word, “course,” which can be either a verb or a noun (with several different meanings).
Is it of course or of coarse?
“Coarse” is always an adjective meaning “rough, crude.” Unfortunately, this spelling is often mistakenly used for a quite different word, “course,” which can be either a verb or a noun (with several different meanings).
What is college coursework?
College coursework is study taken for college credit, completed at or transferred to a degree-granting institution of higher education approved by the New York State Commissioner of Education or a regional accrediting agency. … Unacceptable coursework is that which is not credit-bearing or not applicable toward a degree.
Which is correct of course or ofcourse?
“Of course” is always 2 words, and is a shorter form of “As a matter of course”. Furthermore, Google Fight says of course wins at 75 900 000 vs ofcourse which has only 521 000. If you Google it, half of the results on the first page are in the url, and the first result is another forum where this was asked.
How do you use ofcourse?
You use of course as a polite way of giving permission. “Can I just say something about the game on Saturday?”—”Yes, of course you can.” You use of course in order to emphasize a statement that you are making, especially when you are agreeing or disagreeing with someone. “I guess you’re right.”—”Of course I’m right!”
What are the basic college classes?
– English: English 1-4, American Literature, creative writing.
– Math: Algebra 1-3, Geometry, statistics.
– Natural of physical science: biology, chemistry, physics.
– Social science: American History, civics, government.
– Additional: comparative religion, Spanish 1-4.
What is course of study for college?
1. course of study – an integrated course of academic studies; “he was admitted to a new program at the university” curriculum, syllabus, programme, program. course of lectures – a series of lectures dealing with a subject.
Do you say of course or of coarse?
Additionally, “course” is always a noun or verb, while “coarse” is always an adjective. The words “coarse” and “adjective” both contain an “a.” So if you have a flair for grammar, this might be a good way to remember how to use “coarse” (an adjective) instead of “course” (a noun or verb).
What’s the difference between of course and of course?
“Of course” is always 2 words, and is a shorter form of “As a matter of course”. Furthermore, Google Fight says of course wins at 75 900 000 vs ofcourse which has only 521 000.
What should be included in coursework on resume?
Relevant coursework is a list of subjects and courses you took at school that are pertinent to the position you’re applying for. You can include relevant coursework on your resume in the education section. Any courses, subjects, and projects you list have to be related to the job opening.
How do you use coarse in a sentence?
– My clothes were made of coarse cloth.
– His coarse habits have gradually fined away.
– The yarn is woven into a coarse fabric.
– The soldiers did not bother to moderate their coarse humour in her presence.
– The coarse language on TV was bleeped out. …
– The man was brutish and coarse.
How do you spell of course not?
—used informally to say no in a way that shows one is very definite “Are you angry with me for being late?” “Of course not!””Did you take the money?” “Of course not!”
- Reference 1
- Reference 2
- Reference 3
Spread the word ! Don’t forget to share.
.
There are some rules for joining two different words into one, but they do not cover all cases
AREAS OF UNCERTAINTY ABOUT JOINING WORDS TOGETHER
Is it correct to write bath tub, or should it be the single word bathtub? Is every day a correct spelling, or everyday? Uncertainties like this are widespread in English, even among proficient users. They are made worse by the fact that in some cases both spellings are correct, but mean different things.
Are there any guidelines for resolving such uncertainties? It seems that in some cases there are and in some there are not. I wish here to indicate some of these guidelines. They mostly involve combinations that can make either one word or two, depending on meaning or grammar.
.
ORDINARY COMPOUNDS
Ordinary compounds are the area with the fewest guidelines. They include words like coursework, which I like to write as a single word but my Microsoft Word spellchecker tells me should be two. As a linguist, I usually disregard computer advice about language (see 68. How Computers Get Grammar Wrong), but the question of why ordinary compound words give especial problems is interesting. First, these words need to be defined.
One can think of a compound as two or more words joined together. Linguists, though, like to speak of joined roots or stems rather than words, partly because the joining into a compound stops them being words (a few are not even words by themselves, e.g. horti- in horticulture).
Another problem with “joined words” is that some, such as fearless, are not considered compounds at all. The -less ending is called not a “root” but an “affix”, a meaningful word part added to a root to modify its meaning. Most affixes (some named suffixes, e.g. -less, -ness, -tion, -ly, -ing; some prefixes, e.g. -un-, in-, mis-, pre-) cannot be separate words, but a few like -less can (see 106. Word-Like Suffixes and 146. Some Important Prefix Types). Thus, words like fearless, unhappy and international are not compounds because they have fewer than two roots. Other compounds are swimsuit, homework and eavesdrop.
Suggestions for recognising a compound are not always very helpful. The frequency of words occurring together is no guide because it ignores the fact that many frequent combinations are not compounds (e.g. town hall and open air). The grammatical classes of the words and the closeness of the link between them are sometimes mentioned, but are unreliable. The age of a combination is also suggested, the claim being that compounds originate as two separate words, and gradually evolve through constant use first into hyphenated expressions (like fire-eater or speed-read – see 223. Uses of Hyphens), and eventually into compounds. However, some quite recent words are already compounds, such as bitmap in computing.
Much more useful is the way compounds are pronounced. Single English words generally contain one syllable that is pronounced more strongly than the others (see 125. Stress and Emphasis). This means compounds should have just one strong syllable, while non-compounds should have more. The rule applies fairly universally (see 243. Pronunciation Secrets, #3). For example, home is the only strong syllable in homework, but one of two in home rule. I write coursework as one word because course- is stronger than work.
The only problem with this approach is that you have to know pronunciations before you start, which is not always the case if English is not your mother tongue. The only other resort is a dictionary or spellcheck!
.
NOUNS DERIVED FROM PHRASAL VERBS
Happily, some compound words have some other helpful features. Most are words whose roots, if written as two words, are also correct but have different meaning and grammar, so that the meaning indicates the spelling or vice versa. A particularly large category of such words is illustrated by the compound noun giveaway (= “obvious clue”). If its two roots are written separately as give away, they become a “phrasal” verb – a combination of a simple English verb (give) with a small adverb (away) – meaning “unintentionally reveal” (see 244. Special Uses of GIVE, #12).
There are many other nouns that can become phrasal verbs, e.g. takeover, takeaway, makeup, cutoff, breakout, setdown, pickup, washout, login and stopover. In writing there is always a need to remember that, if the two “words” are going to act as a verb, they must be spelled separately, but if they are going to act as a noun, they must be written together.
.
OTHER CHOICES THAT DEPEND ON WORD CLASS
In the examples above, it is the choice between noun and verb uses that determines the spelling. Other grammatical choices can have this effect too. The two alternative spellings mentioned earlier, every day and everyday, are an example. The first (with ev- and day said equally strongly) acts in sentences like a noun or adverb, the second (with ev- the strongest) like an adjective. Compare:
(a) NOUN: Every day is different.
(b) ADVERB: Dentists recommend cleaning your teeth every day.
(c) ADJECTIVE: Everyday necessities are expensive.
In (a), every day is noun-like because it is the subject of the verb is (for details of subjects, see 12. Singular and Plural Verb Choices). In (b), the same words act like an adverb, because they give more information about a verb (cleaning) and could easily be replaced by a more familiar adverb like regularly or thoroughly (see 120. Six Things to Know about Adverbs). In (c), the single word everyday appears before a noun (necessities), giving information about it just as any adjective might (see 109. Placing an Adjective after its Noun). It is easily replaced by a more recognizable adjective like regular or daily. For more about every, see 169. “All”, “Each” and “Every”.
Another example of a noun/adverb contrast is any more (as in …cannot pay any more) versus anymore (…cannot pay anymore). In the first, any more is the object of pay and means “more than this amount”, while in the second anymore is not the object of pay (we have to understand something like money instead), and has the adverb meaning “for a longer time”.
A further adverb/adjective contrast is on board versus onboard. I once saw an aeroplane advertisement wrongly saying *available onboard – using an adjective to do an adverb job. The adverb on board is needed because it “describes” an adjective (available). The adjective form cannot be used because there is no noun to describe (see 6. Adjectives with no Noun 1). A correct adjective use would be onboard availability.
Slightly different is alright versus all right. The single word is either an adjective meaning “acceptable” or “undamaged”, as in The system is alright, or an adverb meaning “acceptably”, as in The system works alright. The two words all right, on the other hand, are only an adjective, different in meaning from the adjective alright: they mean “100% correct”. Thus, Your answers are all right means that there are no wrong answers, whereas Your answers are alright means that the answers are acceptable, without indicating how many are right.
Consider also upstairs and up stairs. The single word could be either an adjective (the upstairs room) or an adverb (go upstairs) or a noun (the upstairs). It refers essentially to “the floor above”, without necessarily implying the presence of stairs at all – one could, for example, go upstairs in a lift (see 154. Lone Prepositions after BE). The separated words, by contrast, act only like an adverb and do mean literally “by using stairs” (see 218. Tricky Word Contrasts 8, #3).
The pair may be and maybe illustrates a verb and adverb use:
(d) VERB: Food prices may be higher.
(e) ADVERB: Food prices are maybe higher.
In (e), the verb is are. The adverb maybe, which modifies its meaning, could be replaced by perhaps or possibly. Indeed, in formal writing it should be so replaced because maybe is conversational (see 108. Formal and Informal Words).
My final example is some times and sometimes, noun and adverb:
(f) NOUN: Some times are harder than others.
(g) ADVERB: Sometimes life is harder than at other times.
Again, replacement is a useful separation strategy. The noun times, the subject of are in (f), can be replaced by a more familiar noun like days without radically altering the sentence, while the adverb sometimes in (g) corresponds to occasionally, the subject of is being the noun life.
.
USES INVOLVING “some”, “any”, “every” AND “no”
The words some, any, every and no generally do not make compounds, but can go before practically any noun to make a “noun phrase”. In a few cases, however, this trend is broken and these words must combine with the word after them to form a compound. Occasionally there is even a choice between using one word or two, depending on meaning.
The compulsory some compounds are somehow, somewhere and somewhat; the any compounds are anyhow and anywhere, while every and no make everywhere and nowhere. There is a simple observation that may help these compounds to be remembered: the part after some/any/every/no is not a noun, as is usually required, but a question word instead. The rule is thus that if a combination starting with some, any, every or no lacks a noun, a single word must be written.
The combinations that can be one word or two depending on meaning are someone, somebody, something, sometime, sometimes, anyone, anybody, anything, anyway (Americans might add anytime and anyplace), everyone, everybody, everything, everyday, no-one, nobody and nothing. The endings in these words (-one, -body, -thing, -way, -time, -place and –day) are noun-like and mean the same as question words (who? what/which? how? when? and where? – see 185. Noun Synonyms of Question Words).
Some (tentative) meaning differences associated with these alternative spellings are as follows:
SOME TIME = “an amount of time”
Please give me some time.
SOMETIME (adj.) = “past; old; erstwhile”
I met a sometime colleague
.
SOMETHING = “an object whose exact nature is unimportant”.
SOME THING = “a nasty creature whose exact nature is unknown” (see 260. Formal Written Uses of “Thing”, #2).
Some thing was lurking in the water.
.
ANYONE/ANYBODY = “one or more people; it is unimportant who”
Anyone can come = Whoever wants to come is welcome; Choose anyone = Choose whoever you want – one or more people.
ANY ONE = “any single person/thing out of a group of possibilities”.
Any one can come = Only one person/thing (freely chosen) can come; Choose any one = Choose whoever/whichever you want, but only one.
ANY BODY = “any single body belonging to a living or dead creature”.
Any body is suitable = I will accept whatever body is available.
.
ANYTHING = “whatever (non-human) is conceivable/possible, without limit”.
Bring anything you like = There is no limit in what you can bring; Anything can happen = There is no limit on possible happenings.
ANY THING = “any single non-human entity in a set”.
Choose any thing = Freely choose one of the things in front of you.
.
EVERYONE/EVERYBODY = “all people” (see 169. “All”, “Each” and “Every” and 211.General Words for People).
Everyone/Everybody is welcome.
EVERY ONE = “all members of a previously-mentioned group of at least three things (not people)”.
Diamonds are popular. Every one sells easily.
EVERY BODY = “all individual bodies without exceptions”.
.
EVERYTHING = “all things/aspects/ideas”.
Everything is clear.
EVERY THING = “all individual objects, emphasising lack of exceptions”.
Every thing on display was a gift.
.
NO-ONE/NOBODY = “no people”
No-one/Nobody came.
NO ONE = “not a single” (+ noun)
No one answer is right.
NO BODY = “no individual body”.
.
NOTHING = “zero”.
Nothing is impossible.
NO THING = “no individual object”.
There are other problem combinations besides those discussed here; hopefully these examples will make them easier to deal with.