Андрей Тихонов
Пользователь
Сообщений: 119
Регистрация: 01.01.1970
#3
06.03.2013 17:12:56
Спасибо за ответ, Sergei_A, я понял, просто странно,что vba не отличает [a1] от a1.
Лично мне удобно называть переменные так: a1, a2, a3, вместо превычного: a,b,c.
Буду знать 2 вещи:
1.Если у меня есть переменная, например: a1 ,то к ячейке нужно обращаться через: Cells(y,x), а не [a1].
2.Переменные лучше называть: a01, a02, … , a012 вместо: a1,a2,a3.
Тема закрыта!
I use this technique when I get confused about the type of object I have created by stringing properties.
Within Excel’s Visual Basic Editor, create a new module if you do not have an existing one that you wish to use in this way. If you select the module in Project Explorer and click F4, you can change the module’s name to «Experiments» say.
Type or copy:
Option Explicit
Sub TestA()
End Sub
I always start my modules with Option Explicit. Look Option Explicit up in VBA Help and it will tell you why this is a good idea.
I have also created an empty sub-routine into which I will type some statements.
Start typing a new statement so you have:
Sub TestA()
Debug.Print Range("B:B").
End Sub
When you type the period at the end of this new line, a pop-up window will show you the available methods and properties. This list will show, as expected, all the methods and properties of a Range. Type «Address» or select Address from the list to get:
Sub TestA()
Debug.Print Range("B:B").Address
End Sub
Click F5 to run this macro and the following will appear in the Immediate Window:
$B:$B
This is the address of all rows in column B which is what you would expect.
Now add two further statements to the macro:
Debug.Print Range("F:F").Address
Debug.Print Union(Range("B:B"), Range("F:F")).Address
Run this macro again and you will get:
$B:$B
$F:$F
$B:$B,$F:$F
Again this is what was expected.
Now add:
Debug.Print Union(Range("B:B"), Range("F:F")).Rows.
The pop-up window that appears will be unchanged because Range.Rows is still a range.
Complete the statement by adding or selecting «Address» and run the macro again to get:
$B:$B
$F:$F
$B:$B,$F:$F
$B:$B,$F:$F
This may not be what you expected but think about it. $B:$B,$F:$F is all rows in columns B and F so adding the property Rows does not change the address.
Now add the following statements to the macro:
Debug.Print Union(Range("B:B"), Range("F:F")).Count
Debug.Print Union(Range("B:B"), Range("F:F")).Rows.Count
Run the macro and these statements will each output an integer. I am using Excel 2003 so I get:
131072
65536
If you are using a later version of Excel, you will get larger integers. The second integer is the number of rows in a worksheet for your version of Excel. The first integer is the number of cells in two columns of a worksheet for your version of Excel.
Now add:
Debug.Print Union(Range("B:B"), Range("F:F")).Rows.Count.
When you type the final period, no pop-up window will appear because an integer has no method or property that you can select in this way. Method .End(xlUp) operates on a range; it is not a property of Count which is why you get «Invalid qualifier».
It is very easy to get oneself confused when stringing properties together. Personally I avoid stringing properties because even if it is faster to run, it takes longer for me to understand and debug. There are situations in which minimising runtime is the top priority but is this one of those cases? How many hours have you wasted with this approach?
Consider:
Dim Rng1 As Range
Dim Rng2 As Range
Dim Rng3 As Range
Dim RowMax As Long
Set Rng1 = Range("B:B")
Set Rng2 = Range("F:F")
Set Rng3 = Union(Rng1, Rng2)
RowMax = Rng3.Count
Debug.Print RowMax
Debug.Print Rng3.Find("*", Range("B1"), xlValues, xlWhole, xlByRows, xlPrevious).Row
You do not need RowMax but I have included it so you are absolutely clear what Rng3.Count returns. I have also gone OTT with the ranges. I would be happy to type: Set Rng3 = Union(Range("B:B"), Range("F:F")) because I find it easy to understand.
Method .End(xlUp) operates on a cell. MultiCellRange.End(xlUp).Row is valid syntax but I cannot get it to return useful information. If you want to use .End(xlUp) consider:
Dim RowMaxColB As Long
Dim RowMaxColF As Long
RowMaxColB = Cells(Rows.Count, "B").End(xlUp).Row
RowMaxColF = Cells(Rows.Count, "F").End(xlUp).Row
I agree with Siddharth, Find appears to be the best approach in this situation. However, you should look at this answer of mine, https://stackoverflow.com/a/20849875/973283, to a different question. It includes a macro that demonstrates a selection of methods of finding last rows and columns and shows the situations in which they fail.
Return to VBA Code Examples
This article will explain the VBA invalid qualifier error.
The VBA invalid qualifier error occurs when trying to use properties or methods on a variable or object that do not actually exist for that variable or object.
String Variables and Properties
A simple example is when trying to assign a value to a string variable.
For example:
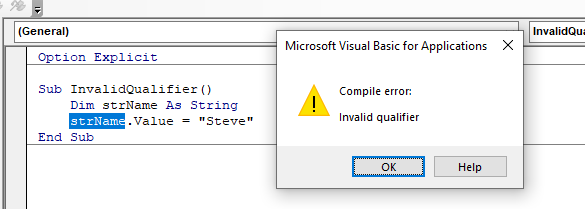
Sub InvalidQualifier()
Dim strName As String
strName.Value = "Steve"
End SubWhen we run this code, we would get the following error:
A simple alteration will fix our code:
Sub InvalidQualifier()
Dim strName As String
strName= "Steve"
End SubThe value property is not available to a string variable and is not required to populate the variable.
Object and Methods
Another example could be when trying to work with an Object.
Take the following code for example:
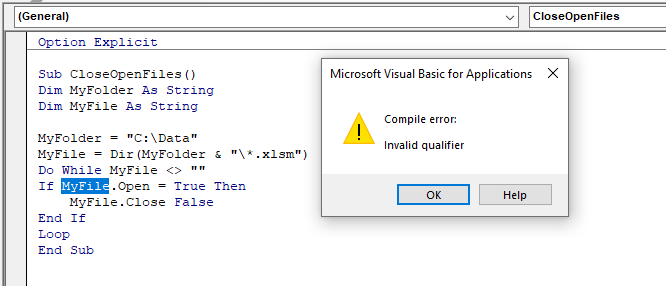
In the above code, the variable MyFile has been declared as a String variable. The code is trying to close the file if the file is open – but as a string variable is not an Object, you cannot assign it any properties or methods and therefore you will get this error.
To fix this error, you need to use an Object. We can declare a variable for a workbook and then create a second For Each Loop to check if the workbook name is equivalent to the string variable MyFile. If the workbook name is equivalent to this variable, we can use the Close method of the workbook object to close the file.
Sub CloseOpenFiles()
Dim MyFolder As String
Dim MyFile As String
Dim wkb As Workbook
MyFolder = "C:Data"
MyFile = Dir(MyFolder & "*.xlsm")
Do While MyFile <> ""
For Each wkb In Workbooks
If wkb.Name = MyFile Then
wkb.Close False
End If
Next wkb
MyFile = Dir
Loop
End Sub|
pasha7598 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 12.03.2020 Сообщений: 9 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
Excel 12.03.2020, 09:35. Показов 7033. Ответов 11 Метки vba (Все метки)
Значит, ситуация обстоит следующая. Имеется одна книга, в которой есть форма, помимо неё может быть несколько параллельно открытых книг. В пользовательской форме имеется два комбобокса, в первом из них нужно выбрать книгу, а во втором уже должны быть показаны листы выбранной книги в предыдущем комбобоксе.
0 |
|
223 / 134 / 45 Регистрация: 08.09.2012 Сообщений: 283 Записей в блоге: 1 |
|
|
12.03.2020, 10:13 |
2 |
|
pasha7598, и вам здравствуйте!
Имеется одна книга а у нас этой книги нет. Предлагаете за Вас создать книгу, вставить туда форму, создать контролы, вставить код?
1 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 12.03.2020 Сообщений: 9 |
|
|
12.03.2020, 10:39 [ТС] |
3 |
|
Я бы с удовольствием прикрепил бы файл, но ведь вба сохраняется только в формате .xlsm, а здесь такой прикрепить нельзя, либо я чего-то недопонимаю. По делу: почему Вы решили, что строковая переменная kniga должна вести себя как объект и иметь свойство Name? То есть ошибка в том, что неправильный тип у переменной? Прошу у вас помощи, ибо сам не сильно шарю за это все. Просто если я даю ей As Object, оно тоже выдает ошибку «Object veriable or With block variable not set». Какой тип тогда нужно дать этой переменной? Либо может это как-то можно реализовать по-другому?
0 |
|
Модератор 11337 / 4656 / 748 Регистрация: 07.08.2010 Сообщений: 13,487 Записей в блоге: 4 |
|
|
12.03.2020, 10:41 |
4 |
|
только в формате .xlsm, а здесь такой прикрепить нельзя, либо я чего-то недопонимаю. зазипуйте .xlsm и выкладывайте архив
1 |
|
pashulka 4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
||||
|
12.03.2020, 10:45 |
5 |
|||
2 |
|
bite 3693 / 3126 / 692 Регистрация: 13.04.2015 Сообщений: 7,315 |
|
|
12.03.2020, 10:45 |
6 |
|
kniga.Name Уберите Name
1 |
|
amd48 779 / 461 / 79 Регистрация: 18.05.2016 Сообщений: 1,242 Записей в блоге: 4 |
||||
|
12.03.2020, 10:48 |
7 |
|||
|
в строке 9 И вообще эта kniga не очень-то и нужна:
Ну а задавать вопросы на форуме следует в таком стиле: апаздал…
1 |
|
1811 / 1134 / 345 Регистрация: 11.07.2014 Сообщений: 3,999 |
|
|
12.03.2020, 10:50 |
8 |
|
aequit, да и в ComboBox1.Text при инициализации ничего ещё нет
1 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 12.03.2020 Сообщений: 9 |
|
|
12.03.2020, 23:43 [ТС] |
9 |
|
Спасибо большое, практически то, что я и хотел, не ожидал таких быстрых ответов, вообще впервые оказался на форуме этом. Но имеется еще один вопрос. Книг может быть несколько, но как реализовать так, чтобы при выборе книги, были видны листы именно из неё, а из остальных книг не высвечивались.
0 |
|
779 / 461 / 79 Регистрация: 18.05.2016 Сообщений: 1,242 Записей в блоге: 4 |
|
|
13.03.2020, 07:11 |
10 |
|
ActiveWorkbook
0 |
|
pashulka 4131 / 2235 / 940 Регистрация: 01.12.2010 Сообщений: 4,624 |
||||
|
13.03.2020, 08:44 |
11 |
|||
|
Решение
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 12.03.2020 Сообщений: 9 |
|
|
13.03.2020, 09:03 [ТС] |
12 |
|
Хорошо, а как сделать тогда, чтобы была выбрана книга, а потом из нее был выведен список листов? То есть как мне сделать выбранную через комбобокс книгу активной? Добавлено через 6 минут
0 |
Permalink
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Invalid qualifier |
vblr6.chm1040094 |
vblr6.chm1040094 |
office |
5e109dee-e5f2-60e7-e89f-3d81d511a582 |
06/08/2017 |
medium |
Qualifiers are used for disambiguation. This error has the following cause and solution:
-
The qualifier does not identify a project, module, object, or a variable of user-defined type within the current scope.
Check the spelling of the qualifier. Make sure that the qualifying identifier is within the current scope. For example, a variable of user-defined type in a Private module is visible only within that module.
For additional information, select the item in question and press F1 (in Windows) or HELP (on the Macintosh).
[!includeSupport and feedback]




 Сообщение было отмечено pasha7598 как решение
Сообщение было отмечено pasha7598 как решение