Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the RATE function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity. RATE is calculated by iteration and can have zero or more solutions. If the successive results of RATE do not converge to within 0.0000001 after 20 iterations, RATE returns the #NUM! error value.
Syntax
RATE(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess])
Note: For a complete description of the arguments nper, pmt, pv, fv, and type, see PV.
The RATE function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Nper Required. The total number of payment periods in an annuity.
-
Pmt Required. The payment made each period and cannot change over the life of the annuity. Typically, pmt includes principal and interest but no other fees or taxes. If pmt is omitted, you must include the fv argument.
-
Pv Required. The present value — the total amount that a series of future payments is worth now.
-
Fv Optional. The future value, or a cash balance you want to attain after the last payment is made. If fv is omitted, it is assumed to be 0 (the future value of a loan, for example, is 0). If fv is omitted, you must include the pmt argument.
-
Type Optional. The number 0 or 1 and indicates when payments are due.
|
Set type equal to |
If payments are due |
|
0 or omitted |
At the end of the period |
|
1 |
At the beginning of the period |
-
Guess Optional. Your guess for what the rate will be.
-
If you omit guess, it is assumed to be 10 percent.
-
If RATE does not converge, try different values for guess. RATE usually converges if guess is between 0 and 1.
-
Remarks
Make sure that you are consistent about the units you use for specifying guess and nper. If you make monthly payments on a four-year loan at 12 percent annual interest, use 12%/12 for guess and 4*12 for nper. If you make annual payments on the same loan, use 12% for guess and 4 for nper.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Data |
Description |
|
|
4 |
Years of the loan |
|
|
-200 |
Monthly payment |
|
|
8000 |
Amount of the loan |
|
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=RATE(A2*12, A3, A4) |
Monthly rate of the loan with the terms entered as arguments in A2:A4. |
1% |
|
=RATE(A2*12, A3, A4)*12 |
Annual rate of the loan with the same terms. |
9.24% |
Need more help?
Purpose
Get the interest rate per period of an annuity
Return value
The interest rate per period
Usage notes
The RATE function returns the interest rate per period of an annuity. You can use RATE to calculate the periodic interest rate, then multiply as required to derive the annual interest rate. The RATE function calculates by iteration. If the results of RATE do not converge within 20 iterations, RATE returns the #NUM! error value.
The RATE function takes six separate arguments, three of which are required as explained below.
nper (required) — The total number of payment periods in the annuity. For example, a 5-year car loan with monthly payments has 60 periods. You can enter nper as 5*12 to show how the number was determined.
pmt (required) — The payment made each period. This number cannot change over the life of the annuity. In annuity functions, cash paid out is represented by a negative number. Note: If pmt is not provided, the optional fv argument must be supplied.
pv (optional) — The present value. This is the cash balance required after all payments have been made.
fv (optional) — The future value, or a cash balance required after the last payment is made. When fv is omitted, it defaults to zero (0) and pmt must be provided.
type (optional) — type is a boolean that controls when when payments are due. Use 0 for payments due at the end of the period (regular annuities) and 1 for payments due at the end of the period (annuities due). Type defaults to 0 (end of period).
guess (optional) — guess is a seed value to use for iteration. When omitted, guess defaults to 10%. Ordinarily, you can safely omit guess. If RATE does not converge, RATE will return a #NUM! error. Try different values for guess between 0 and 1.
Example
To calculate the annual interest rate for a $5000 loan with payments of $93.22 per month over 5 years, you can use RATE in a formula like this:
=RATE(60,-93.22,5000)*12 // returns 4.5%
In the example shown, the formula in C10 is:
=RATE(C7,-C6,C5)*C8 // returns 4.5%
Notice the value for pmt from C6 is entered as a negative value.
Notes
You must use consistent values for for guess and nper. If you make monthly payments on a five-year loan at 10 percent annual interest, use 10%/12 for guess and 5*12 for nper. If you make annual payments on the same loan, use 10% for guess and 5 for nper.
The effective rate of interest on the loan (as with almost on any other financial instrument) – this is the expression of all future cash payments (incomes from a financial instrument), which are included in the treaty provision of the contract, in the figure annual interest. That is the real interest that the debtor will pay for using of money in the Bank (investor – to obtain). Here is taken into account the rate of interest designated in the contract, all fees, repayment schemes, loan term (of deposit).
The calculation of the effective rate on the loan in Excel
There are the range of built-in functions in Excel, that allow you to compute the effective rate of interest, with taking into account additional charges and fees, and excluding (relying only on the nominal interest and the loan term).
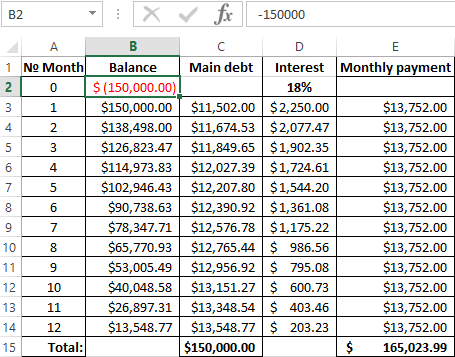
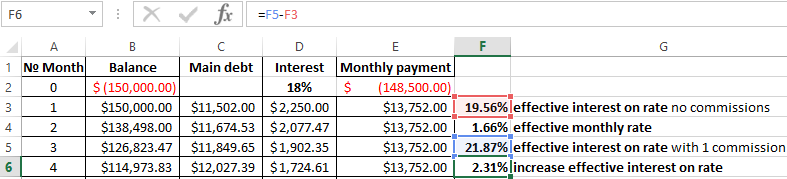
The debtor took a credit in the sum of 150 000$ on the term of 1 year (12 months). The nominal annual rate — is 18%. Payments on the loan specify in the table below:
Since this example does not include the additional fees and charges, we determine to the annual effective rate using the function EFFECT.
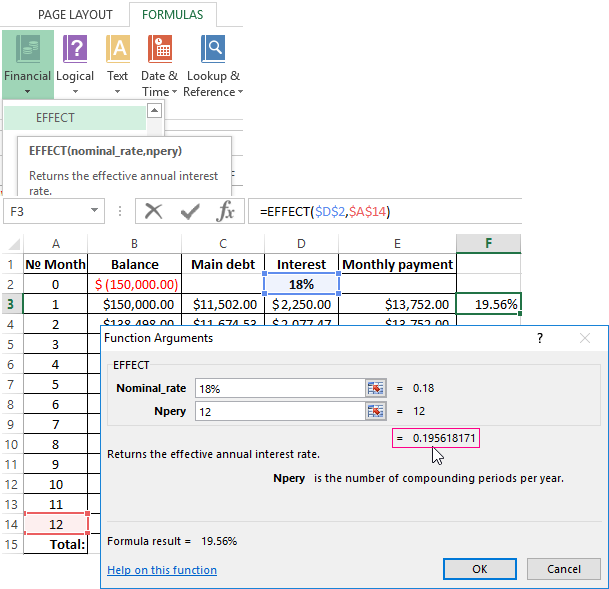
We are calling: «FORMULAS»-«Function Library»-«Financial» finding the function EFFECT. The arguments:
- «Nominal rate» — is the annual rate of interest on the credit, which is designated in the agreement with the Bank. In this example – is 18% (0, 18).
- «Number of periods» — the number of periods in a year, for which interests are charged. In this example – there are 12 months.
The effective interest on rate — is 19. 56%.
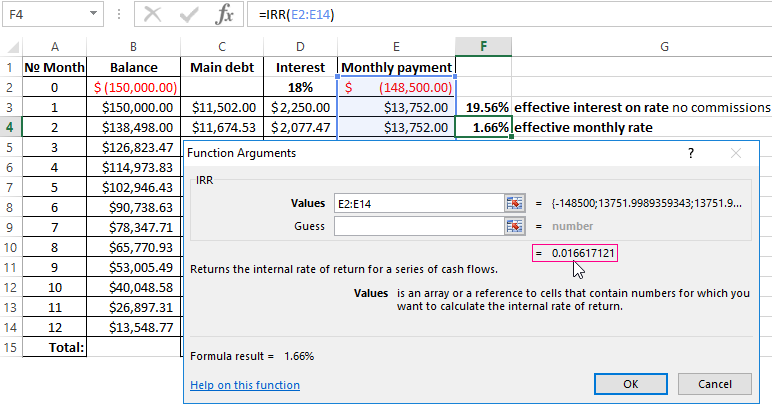
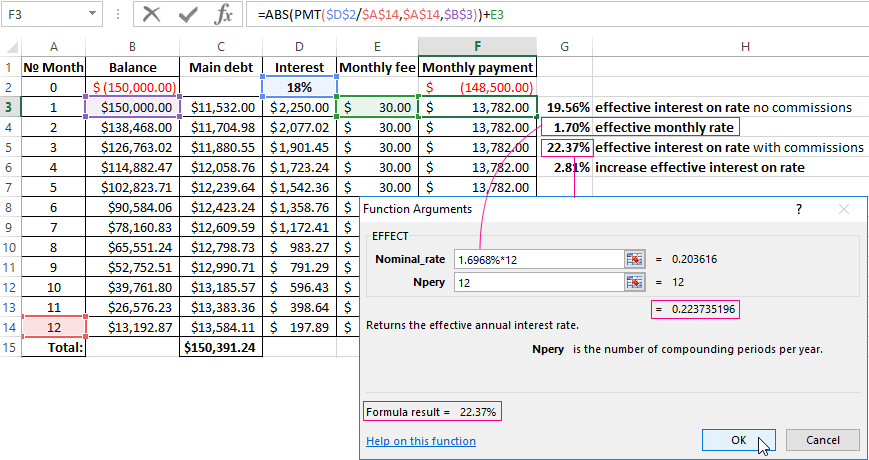
Let’s complicate the task by adding the one-time commission loan at the amount of 1% of the sum of 150 000$. In monetary terms – is 1500$. So, the borrower to get on his hands is the sum of 148 500$.
For calculating to the effective monthly rate, we need use the IRR function (return to the internal rate of return for cash flow):
We have made the column with monthly payments 148 500 with the sign «-», because the money the Bank first gives. Payments which the debtor will make in the cashier subsequently are positive for the bank. The internal rate of return we consider from the Bank’s point of view: it acts as an investor.
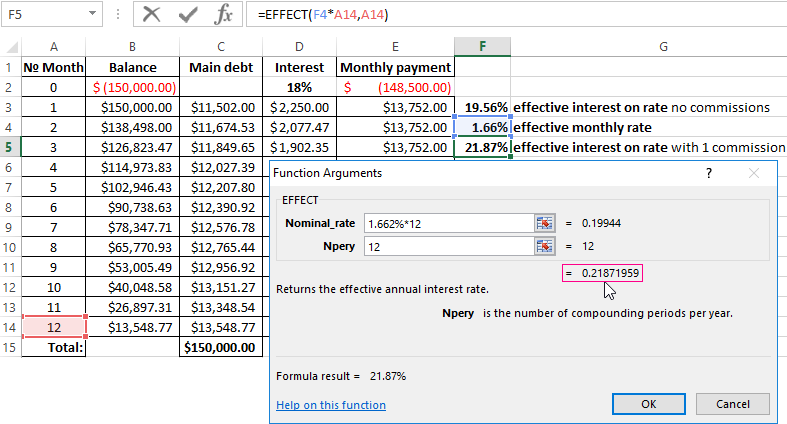
The function has given to the effective monthly rate of 1.6617121%. For the calculating of the nominal rate to the result need multiply by 12 (the term of loan): 1.662% * 12 = 19.94%. Let`s recalculate the effective interest percent:
The one-time fee in amount of 1% increased the actual annual interest on 2.31%. It was: 21, 87%.
We add in the scheme of payments on the loan to the monthly fee for account maintenance in the amount of 30$. Monthly effective rate will be equal to 1.6968%.
The nominal percent is 1.6968% * 12 = is 20.3616%. The effective annual rate is:
The monthly fees increased till 22, 37%. But in the loan contract will continue to be the figure of 18%. However, the new law requires banks to specify in the loan agreement to the effective annual interest rate. However, the borrower will see this figure after the approval and signing of the contract.
What distinguishes a lease from a loan
Leasing – this is the long-term rental of vehicles, real estate, equipment, with the possibility of their future redemption. The lessor acquires to the property and transfers it under the contract to a physical / legal person under certain conditions. The lessee uses to the property (in personal/ business purposes) and pays to the lessor for the right of using.
In the essen, it`s the same loan, only to the property will belong to the lessor until the lessee is fully repaid to the asset purchased plus interest.
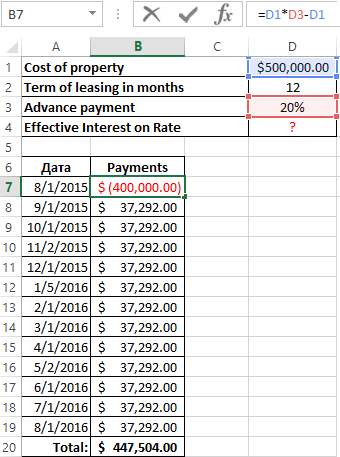
The computation of the effective percent on leasing in Excel is followed on the same scheme as the computation of the annual interest rate on the credit. There is the example with another function.
The data input:
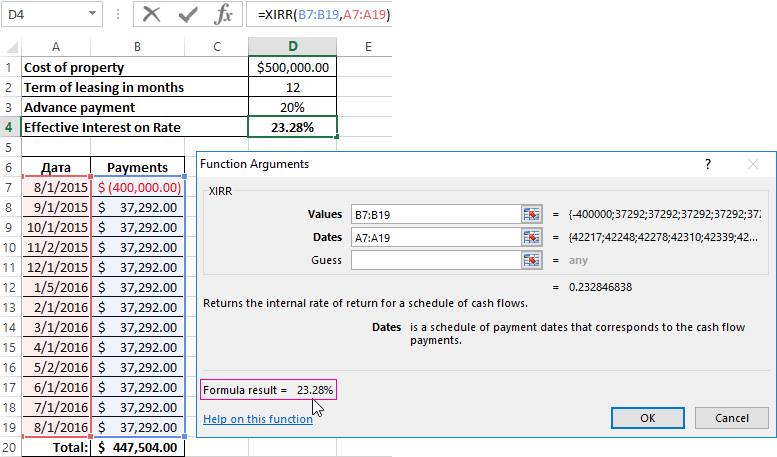
You can go on already blazed way: to computation the internal rate of return, and then multiply the result by 12. But we using the function =XIRR(it returns to the internal percent of return for the schedule of cash flows).
The function arguments:
The effective interest on the lease was % to 23. 28%.
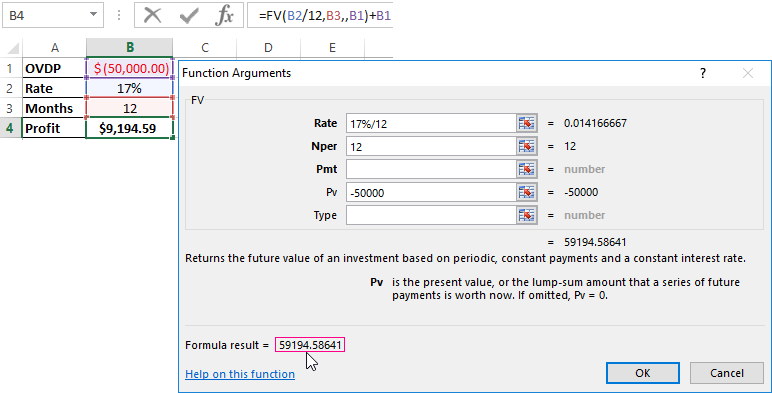
Calculation of the effective interest rate on OVDP in Excel
OVDP — domestic government loan bonds. They can be compared with the deposits in a bank. So how exactly the investor gets to a refund of the full amount of invested funds plus additional income as a percentage. The guarantor of the safety of funds is the National Bank.
The effective interest allows estimate to the real income, because it takes into account to capitalization of interest. For example, «acquire» one-year bonds in the sum of 50 000 at 17%. To calculate your income, using the function =FV():
Suppose that the interest to capitalize by monthly. Therefore, we divide 17% by 12. The result as a decimal insertion we put in the field «Bet». In the «Nper» we enter to the number of periods of compounding. Monthly fixed payments we will not get, so the field «Pmt» leaving free. In the column «Pv» we put the deposit invested funds with the sign «-».
Download calculation effective interest rates in Excel
In the window, we immediately see to the sum, which you can get for the bonds in the end of the term. This is the monetary value of accrued compound interest.
What is the “RATE Function”?
The RATE function is a financial function in Excel that calculates the interest rate per period of an annuity. The function is used to calculate the periodic interest rate, which can then be multiplied as required to calculate the annual interest rate. The function calculates by iteration.
The function can be used to calculate the interest rate charged by a loan or offered by an investment for a given period. The RATE function’s output can help decide whether to borrow at a particular interest rate or invest in a security, such as bonds, at the rate of return offered.
Key Learning Points
- The RATE function is a financial function in Excel used for calculating the interest rate of a loan or an investment for a given period. The function can be applied to loans to calculate the percentage of interest charged or to investments to calculate the percentage of return offered
- While interest rate can also be calculated without the RATE function, it makes the calculation more efficient
- The RATE function gives its output through trial and error. If the results do not converge within 20 iterations, it presents a #NUM! error in Excel
- The function returns a #Value! error if any of the supplied arguments are non-numeric
Syntax
The syntax for the RATE function is shown as:
Rate(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess]
The syntax includes the following arguments:
- Nper represents the number of payment periods for which the interest rate is being calculated. The periods can be in months, quarters, or years. The output of the RATE function (the interest rate) is based on the period included in this argument. The annualized return can be calculated from the period return.
- Pmt is the amount of payment in each period. This number must be constant over the loan’s/investment’s life. If Pmt is omitted, the FV value should be entered.
- PV is the present value of the future payments. For example, if it is a loan, the PV is the amount borrowed. If it is an investment, the PV is the amount invested today.
Optional Arguments
- FV is the future value or the cash balance after the last payment is made. If it is a loan, the FV will be 0. If it is an investment, the FV will be the desired amount of cash flow resulting from the payments. If FV is omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
- Type indicates the payment due dates. If the payment is to be made at the end of each period, the type is 0. If payment is due at the beginning, the type is 1.
- Guess is a guess of what the interest rate is likely to be. If omitted, the rate is assumed to be 10%.
Important Points about the RATE Function
- The RATE function calculates the rate with an iterative process (trial and error). It will return a #NUM! error value if the results do not converge within 20 iterations. The guess provides a starting point for the rate function to converge an answer sooner before reaching 20 iterations. If RATE does not converge, try and input other values in the guess argument.
- #NUM! error value may also be returned due to errors related to cash flow conventions. Typically, cash outflows are input with a negative sign.
- #VALUE! error happens if any of the arguments are non-numeric.
- The Nper argument should be consistent with the payment. For example, if it is a 5-year loan with an interest payment of 200 per month, the NPER should 60 (5 years x 12 months). Also, the units used for Nper and guess should be consistent.
- The output given by the RATE function depends on the period input for loan payments. For example, if the NPER is 12 and the input in PMT is monthly payments, the RATE function’s output will be a monthly interest rate. If you want the annual interest rate, you need to multiply the monthly rate by 12.
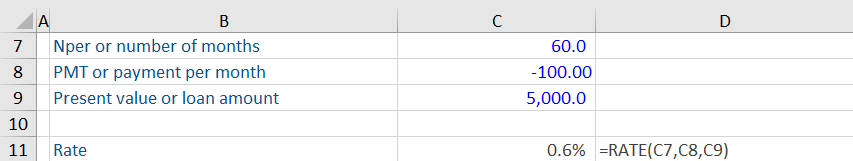
Example 1:
Based on the information below, we have been asked to calculate the interest rate for this loan using Excel’s RATE function. Download this free rate function workout from our blog and practice yourself.
The RATE function has calculated the interest rate for this loan as 0.6%. The payment per month is entered as a negative number to reflect a cash outflow. This output is the monthly interest rate as the Nper and payments are monthly. If you want the annual interest rate, you need to multiply this output by 12.
Example 2:
Calculate the yield to maturity or the return rate offered by the bond below. Coupon payments are made at the end of each year.
The bond gives an annualized return of 4.4%. Notice we have also included the optional arguments, including a guess of the interest rate as 4%. The present value is a negative number as investing in the bond today will lead to a cash outflow. Investing in a bond is different from taking a loan, where first there is a cash inflow, followed by outflows towards interest and principal repayment. In a bond, in the beginning, there is a cash outflow (the investment), followed by cash inflows (interest payments and eventually the original investment).