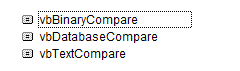Определение первого вхождения одной строки в другую с помощью функции InStr из кода VBA Excel. Синтаксис функции, параметры, примеры использования.
InStr – это функция, которая предназначена для определения номера позиции первого вхождения одной строки в другую. Она возвращает значение типа Variant (Long).
Функция InStr ищет первое вхождение одной строки в другую с начала исходной строки. Для поиска первого совпадения с конца исходной строки используется функция InStrRev.
Функция InStr часто незаменима при определении параметров функций Left, Mid и Right. Также ее можно использовать для определения наличия искомой подстроки в заданной строке.
Еще есть в VBA Excel функция InStrB, которая работает с байтовыми данными, содержащимися в строке. Она возвращает позицию байта, а не символа первого вхождения одной строки в другую. Смотрите ниже Пример 3.
Синтаксис, параметры, значения
Синтаксис функции InStr
Полный вариант:
|
InStr([start], string1, string2, [compare]) |
Сокращенный вариант:
Чаще всего в VBA Excel используется сокращенный вариант функции со значениями необязательных параметров по умолчанию.
Параметры функции InStr
| Параметр | Описание | Значение по умолчанию |
|---|---|---|
| start | Необязательный аргумент.* Числовое выражение, которое задает начальную позицию для поиска. | 1 |
| string1 | Обязательный аргумент. Строковое выражение, в котором выполняется поиск. | – |
| string2 | Обязательный аргумент. Искомое строковое выражение. | – |
| compare | Необязательный аргумент. Задает тип сравнения строк. | –1** |
* Если задан аргумент compare, аргумент start является обязательным.
** Если аргумент compare не указан, используется значение инструкции Option Compare, заданное на уровне модуля. Если инструкция Option Compare в начале модуля отсутствует, используется ее значение по умолчанию – 0 (двоичное сравнение).
Если параметр start или параметр compare содержит значение NULL, возникает ошибка.
Значения аргумента «compare»
| Константа | Значение | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | Сравнение с помощью параметра инструкции Option Compare. |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | Двоичное (бинарное) сравнение.* |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | Текстовое сравнение.* |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | Сравнение на основе сведений из базы данных. Только для Microsoft Access. |
* При двоичном сравнении учитывается регистр букв, при текстовом – не учитывается.
Значения функции InStr
| Если | Возвращаемое значение |
|---|---|
| string2 найдена в string1 | Позиция первого найденного соответствия. |
| string2 не найдена в string1 | 0 |
| string2 является пустой | start |
| string2 равна Null | Null |
| string1 является пустой | 0 |
| string1 равна Null | Null |
| start больше длины string1 | 0 |
Примеры использования в VBA Excel
Пример 1
Самый простой пример:
|
Sub Test1() Dim x As Variant x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «Фернандо») MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 9 End Sub |
Пример 2
В этом примере, используя одинаковые строки, в которых выполняется поиск, и искомые подстроки, применим разные виды сравнения – двоичное (бинарное) и текстовое, и посмотрим на результаты.
|
Sub Test2() Dim x As Variant x = InStr(10, «На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «по», 0) MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 36 (поиск с учетом регистра символов) x = InStr(10, «На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «по», 1) MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 18 (поиск без учета регистра символов) End Sub |
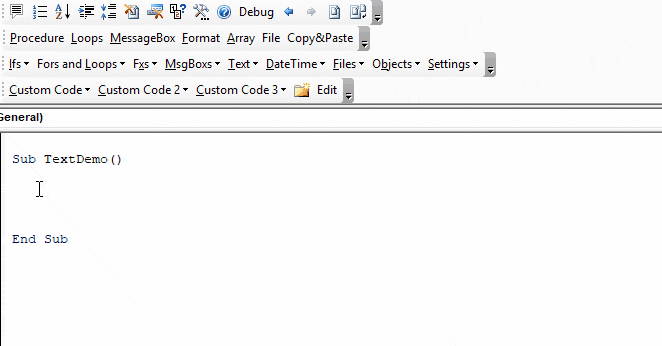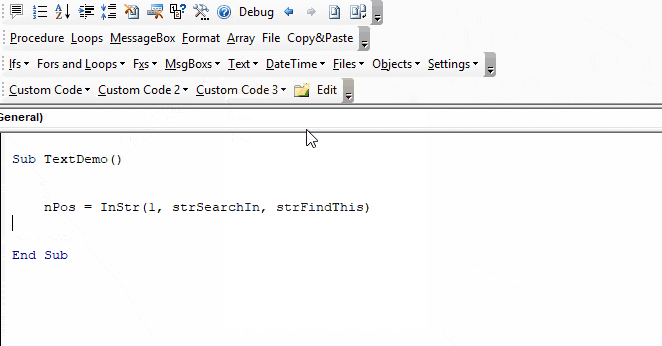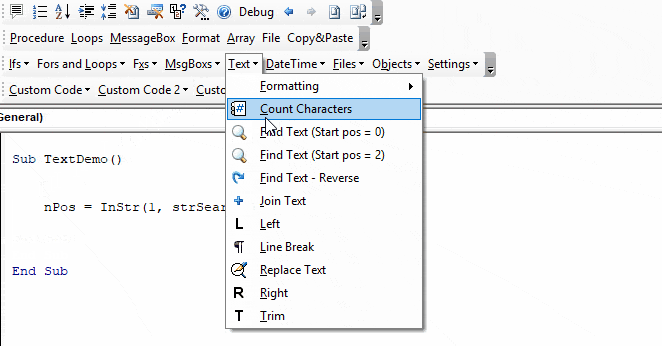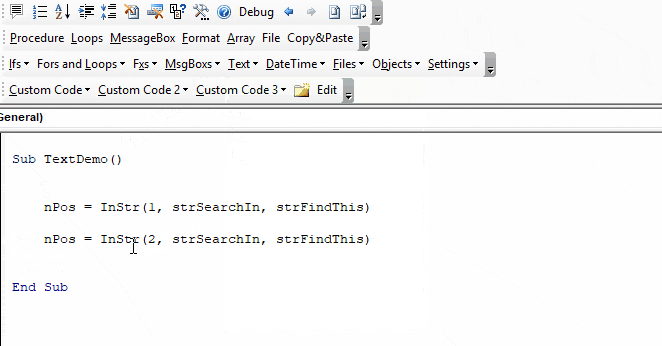
Обратите внимание: несмотря на то, что начало поиска мы задали с 10 символа, номер позиции первого вхождения считается с начала строки, в которой выполняется поиск.
Пример 3
В этом примере посмотрим на результаты посимвольного и побайтового сравнения, опять же используя одинаковые строки и искомые подстроки.
|
Sub Test3() Dim x As Variant x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «гор») MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 4 x = InStrB(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «гор») MsgBox x ‘Здесь x будет равен 7 End Sub |
Результат 7 при побайтовом сравнении получен для кодировки, у которой один символ составляет 2 байта.
In this Article
- INSTR Function
- Instr Example
- Instr Syntax
- Instr Start Position
- Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
- InstrRev Function
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- InString Examples
- If String Contains Substring
- Find Text String in a Cell
- Find Position of a Character in a String
- Search String for Word
- If Variable Contains String
- Instr and the Left Function
- Using Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
INSTR Function
The VBA Instr Function checks if a string of text is found in another string of text. It returns 0 if the text is not found. Otherwise it returns the character position where the text is found.
The Instr Function performs exact matches. The VBA Like Operator can be used instead to perform inexact matches / pattern matching by using Wildcards.
Instr Example
The following code snippet searches the string “Look in this string” for the word “Look”. The Instr Function returns 1 because the text is found in the first position.
Sub FindSomeText()
MsgBox InStr("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubThis second example returns 7 because the text is found starting in the 7th position:
Sub FindSomeText2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "Look")
End SubImportant! The Instr Function is case-sensitive by default. This means “look” will not match with “Look”. To make the test case-insensitive read below.
Instr Syntax
The syntax for the Instr function is as follows:
Instr( [start], string, substring, [compare] )[start] (optional) – This optional argument is the starting position of the search. Enter 1 to start searching from position 1 (or leave blank). Enter 5 to start searching from position 5. Important! The INSTR function calculates the character position by counting from 1 NOT from the [start] position.
string – The string of text to search in.
substring – The string of text to find in the primary string.
[compare] (optional) – By default, Instr is case-sensitive. By setting this argument you can make Instr Case insensitive:
|
Argument vb Value |
Argument Integer | Description |
| vbBinaryCompare |
0 |
(Default) Case-sensitive |
|
vbTextCompare |
1 |
Not Case-sensitive |
|
vbDatabaseCompare |
2 |
MS Access Only. Uses information in the database to perform comparison. |
Instr Start Position
The Instr start position allows you to indicate the character position where you will begin your search. Keep in mind however, the Instr output will always count from 1.
Here we set the start position to 3 to skip the first B:
Sub Instr_StartPosition()
MsgBox InStr(3, "ABC ABC", "B")
End SubThe result is 6 because the second B is the 6th character in the string.
Case-Insensitive INSTR Test
By default, VBA treats “L” different from “l”. In other words, VBA is case-sensitive. This is true of all text functions. To make VBA case-insensitive, set the [compare] argument to 1 or vbTextCompare.
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase()
MsgBox InStr(1, "Don't Look in this string", "look", vbTextCompare)
End SubAlternatively, you can add Option Compare Text to the top of your code module:
Option Compare TextOption Compare Text
Public Sub FindText_IgnoreCase2()
MsgBox InStr("Don't Look in this string", "look")
End SubOption Compare Text will impact all of the code in that module. I personally place this at the top of any module that deals with text because I never care about case differences.
InstrRev Function
The Instr Function searches from the left. Instead you can search from the right using the InstrRev Function. The InstrRev Function works very similarly to the Instr function.
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string", "Look")
End SubJust like the Instr function this will return 1 because there is only one instance of “Look” in the text. But if we add a second “Look”, you’ll see that it returns the position of the right-most “Look”:
Sub FindSomeText_FromRight()
MsgBox InStrRev("Look in this string Look", "Look")
End SubNext we will review more Instr examples.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
InString Examples
If String Contains Substring
Here we will use an If statement to test if a string contains a a substring of text:
Public Sub FindSomeText()
If InStr("Look in this string", "look") = 0 Then
MsgBox "No match"
Else
MsgBox "At least one match"
End If
End SubFind Text String in a Cell
You can also find a string in a cell:
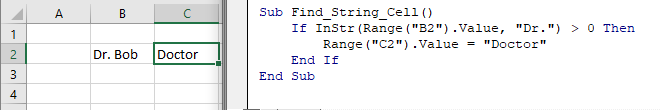
Sub Find_String_Cell()
If InStr(Range("B2").Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
Range("C2").Value = "Doctor"
End If
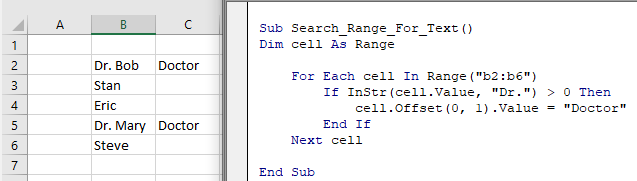
End SubOr loop through a range of cells to test if the cells contain some text:
Sub Search_Range_For_Text()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("b2:b6")
If InStr(cell.Value, "Dr.") > 0 Then
cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Doctor"
End If
Next cell
End SubVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Find Position of a Character in a String
This code will find the position of a single character in a string and assign the position to a variable:
Sub Find_Char()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "L")
End SubSearch String for Word
This code will search a string for a word:
Sub Search_String_For_Word()
Dim n As Long
n = InStr("Here Look Here", "Look")
If n = 0 Then
MsgBox "Word not found"
Else
MsgBox "Word found in position: " & n
End If
End SubIf Variable Contains String
This code will test if a string variable contains a string of text:
Sub Variable_Contains_String()
Dim str As String
str = "Look Here"
If InStr(str, "Here") > 0 Then
MsgBox "Here found!"
End If
End SubInstr and the Left Function
Instr can be used along with other text functions like Left, Right, Len, and Mid to trim text.
With the Left function you can output the text prior to a string of text:
Sub Instr_Left()
Dim str As String
Dim n As Long
str = "Look Here"
n = InStr(str, "Here")
MsgBox Left(str, n - 1)
End SubUsing Instr in Microsoft Access VBA
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
To learn more, read our article: VBA text functions
<<Return to VBA Examples
InStr Function in Excel VBA
The VBA InStr function helps find the position of a given substring within a string. It returns the first occurrence of the substring in the form of an integer (output). A string is a series of characters or text supplied to the function in double quotation marks.
For example, the InStr can extract a substring from a sentence, apply the desired font to a particular string, find the position of a character within the string, and so on.
The VBA InStr function in excel begins searching from left to right.
Table of contents
- InStr Function in Excel VBA
- The Syntax of the VBA InStr Function
- VBA InStr Examples
- Example #1–“Start” Argument is Omitted
- Example #2–“Start” Argument is Specified
- Example #3–Case-sensitive Search
- Example #4–Case-insensitive Search
- Example #5–Advanced Level
- Properties of VBA InStr Function
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA InStr (wallstreetmojo.com)
The Syntax of the VBA InStr Function
The syntax of the function is shown in the following image:
The function accepts the following arguments:
- Start: This is the position from which the function begins to search. For example, if “start” is set at 3 and the character “a” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,” the output is 5.
- String 1: This is the actual string within which the substring is to be found. For example, if the character “a” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,” “string 1” is “Bangalore.”
- String 2: This is the substring to be found. For example, if the character “a” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,”“string 2” is “a.”
- Compare: This is the type of comparison to be performed. The types of comparison methods are shown in the following image.
The three comparison methods are explained as follows:
1. vbBinaryCompare: This is a binary comparison and can be entered as zero (0). It is a case-sensitive search of the substring (string 2) in the actual string (string 1).
For example, if 0 is specified in the argument and:
a. The character “a” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,” the output is 2.
b. The character “A” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,” the output is 0. This is because the supplied string is in uppercase which is not found in “string 1.”
2. vbTextCompare: This is a textual comparison and can be entered as one (1). It is a case-insensitive search of the “string 2” in the “string 1.”
For example, if 1 is specified in the argument and:
a. The character “a” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,” the output is 2.
b. The character “A” is to be found in the word “Bangalore,” the output is 2. This is because this comparison method ignores the casing of the substring.
3. vbDatabaseCompare: This can be entered as two (2). It compares based on the information of the Microsoft Access database.
The “string 1” and “string 2” are required arguments, while “start” and “compare” are optional.
Note 1: If the “start” parameter is omitted, the default is 1, implying that the search begins from the first position.
Note 2: If the “compare” parameter is omitted, the default method is “vbBinaryCompare.”
VBA InStr Examples
You can download this VBA Instr Function Excel Template here – VBA Instr Function Excel Template
Example #1–“Start” Argument is Omitted
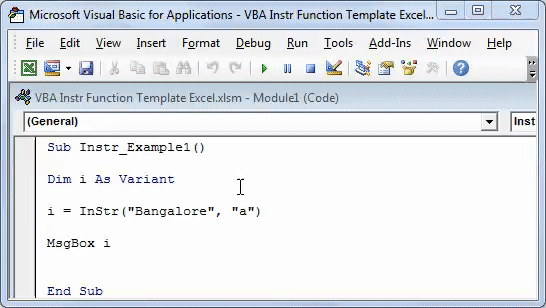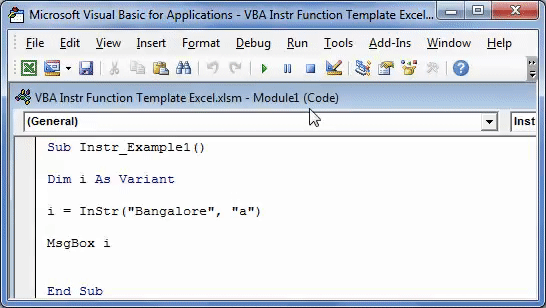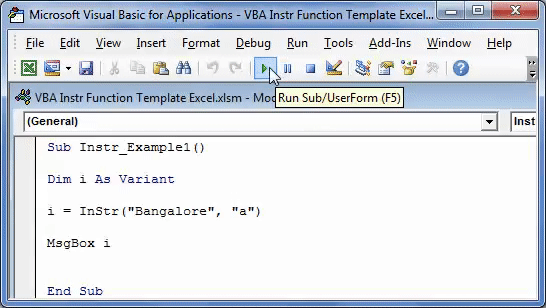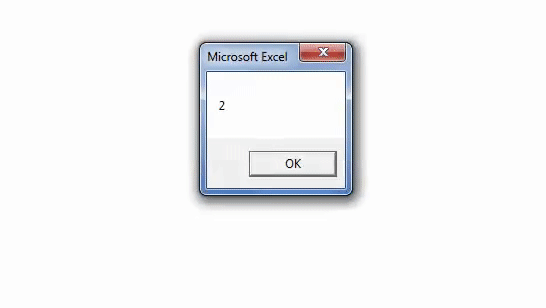
We have to find the position of character “a” in the word “Bangalore.”
Step 1: Enter the following code.
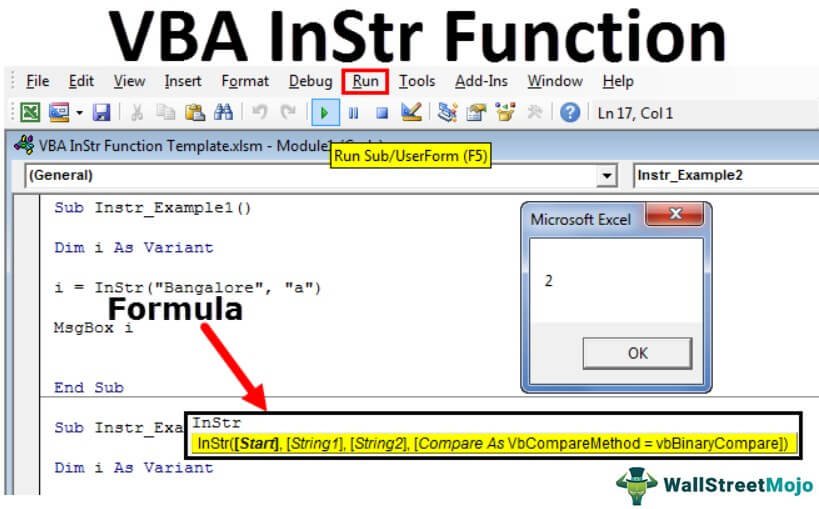
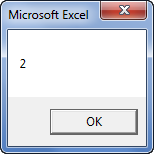
Sub Instr_Example1() Dim i As Variant i = InStr("Bangalore", "a") MsgBox i End Sub
Step 2: Press F5 or run the VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more manually, as shown in the following image.
Step 3: The output is 2, as shown in the following image. Hence, the character “a” is at the second position in the word “Bangalore.”
Example #2–“Start” Argument is Specified
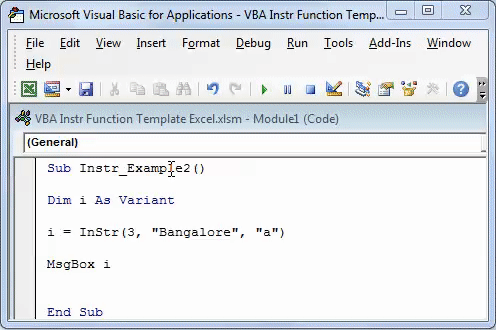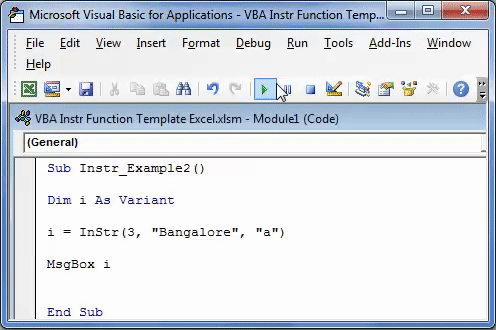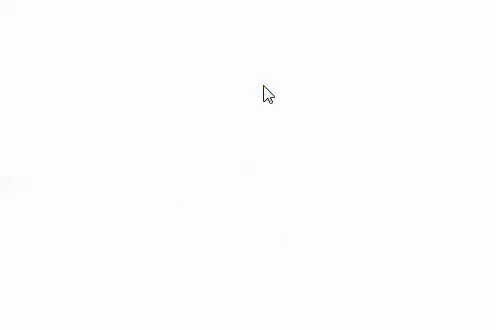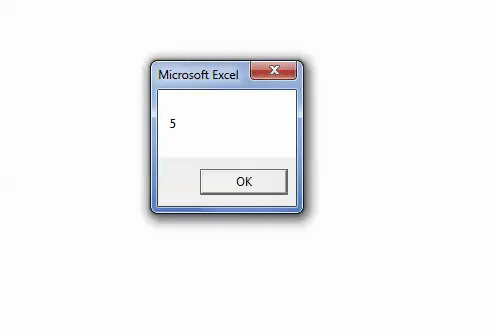
We have to find the position of character “a” in the word “Bangalore.” The search should begin from the third position.
Step 1: Enter the following code.
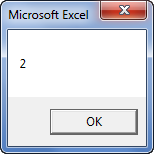
Sub Instr_Example2() Dim i As Variant i = InStr(3, "Bangalore", "a") MsgBox i End Sub
Step 2: Press F5 or run the VBA code manually, as shown in the following image.
Step 3: The output is 5, as shown in the following image. Since the search begins from the third letter (n), the VBA InStr function in excel ignores the first occurrence (second position) of the character “a.”
Hence, in this case, the character “a” is at the fifth position in the word “Bangalore.”
Example #3–Case-sensitive Search
We have to find the character “A” in the word “Bangalore.”
Let us supply the compare argument “vbBinaryCompare” to the VBA InStr function.
Step 1: Enter the following code.
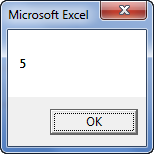
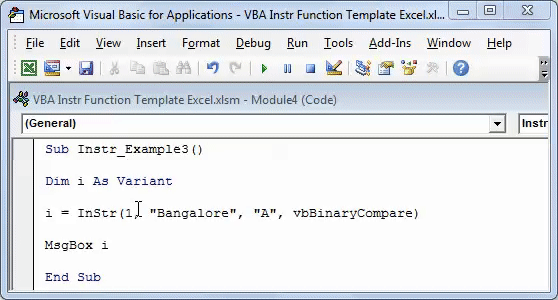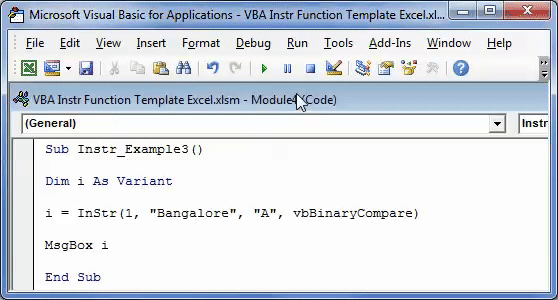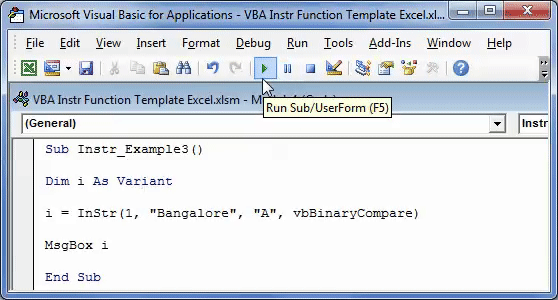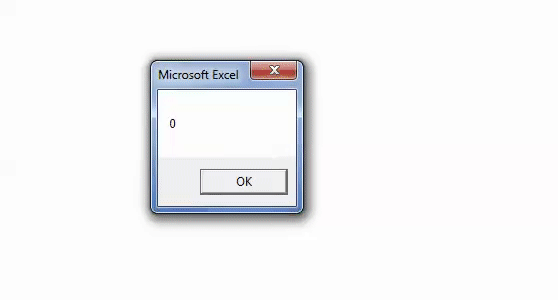
Sub Instr_Example3() Dim i As Variant i = InStr(1, "Bangalore", "A", vbBinaryCompare) MsgBox i End Sub
Step 2: Press F5 or run the VBA code manually, as shown in the following image.
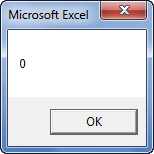
Step 3: The output is 0, as shown in the following image. Since the argument “vbBinaryCompare” is supplied, the VBA InStr function in excel searches for the uppercase letter “A.”
Hence, the function returns 0 because it could not find the uppercase letter “A” in the word “Bangalore.”
Example #4–Case-insensitive Search
We have to find the character “A” in the word “Bangalore” using the case-insensitive approach.
Let us supply the compare argument “vbTextCompare” to the VBA InStr function.
Step 1: Enter the following code.
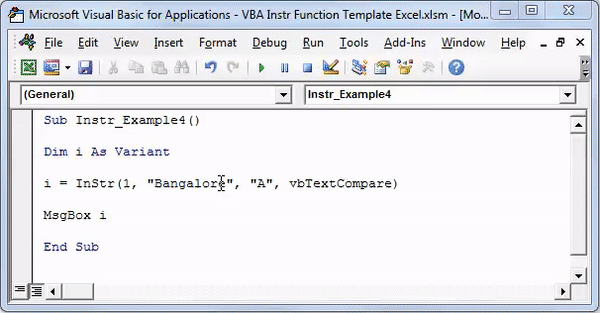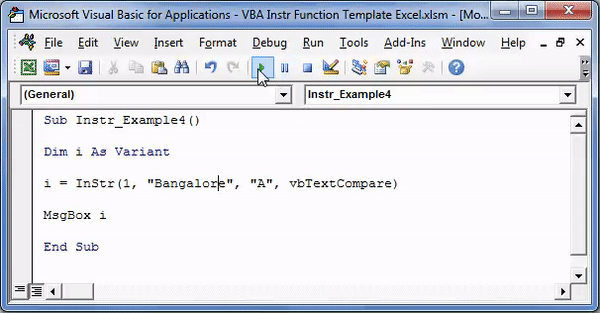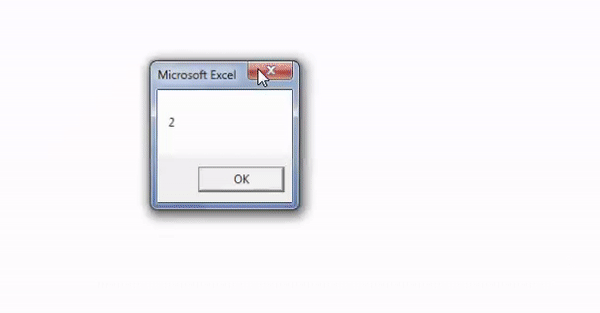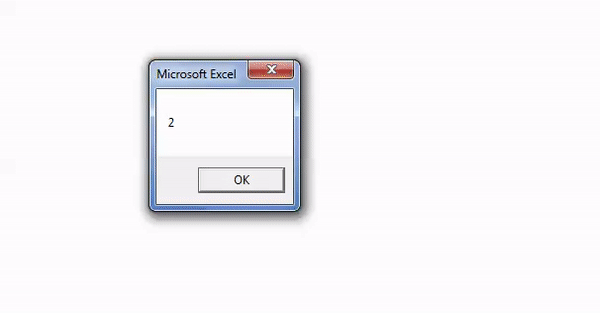
Sub Instr_Example4() Dim i As Variant i = InStr(1, "Bangalore", "A", vbTextCompare) MsgBox i End Sub
Step 2: Press F5 or run the VBA code manually, as shown in the following image.
Step 3: The output is 2, as shown in the following image. Since the argument “vbTextCompare” is supplied, the InStr function ignores the casing of the substring “A.”
Hence, the function returns 2 because the letter “A” or “a” is present at the second position in the word “Bangalore.”
Example #5–Advanced Level
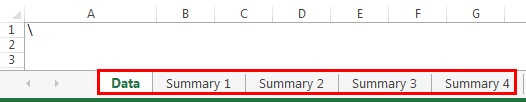
Let us consider an example of the advanced level of VBA InStr function in excel.
The succeeding image shows five worksheets in Excel with the names, “Data,” “Summary 1,” “Summary 2,” “Summary 3,” and “Summary 4.”
We want to hide all worksheets except for the sheet “Data.”
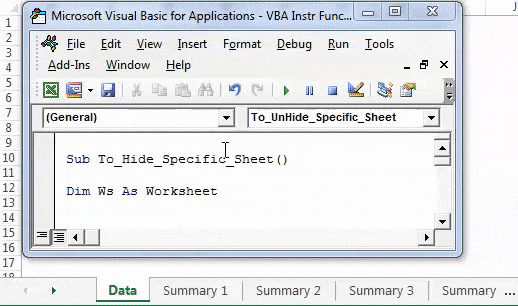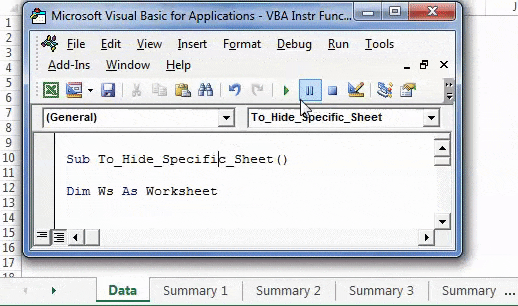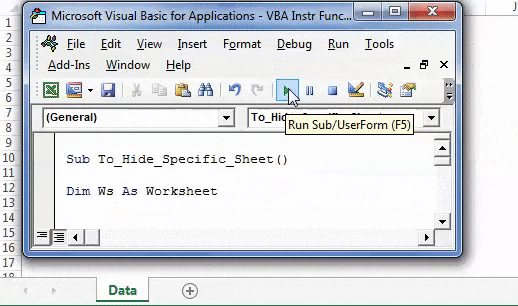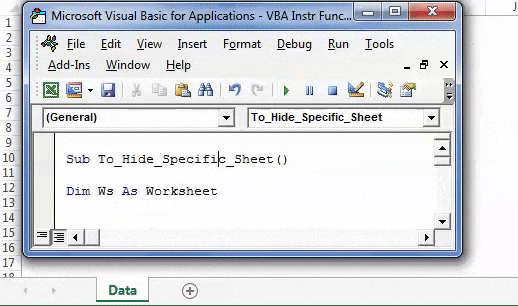
Step 1: Enter the following code to hide all those sheets which contain the word “Summary” in their name.
Sub To_Hide_Specific_Sheet() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If InStr(Ws.Name, "Summary") > 0 Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden End If Next Ws 'InStr function looks for word or phrase in the sheet name 'If it finds then it will be hidden End Sub
Step 2: Press F5 or run the VBA code manually, as shown in the following image. In the output, only the sheet “Data” is visible. The remaining four sheets are hidden.
Likewise, we can unhide those sheetsThere are different methods to Unhide Sheets in Excel as per the need to unhide all, all except one, multiple, or a particular worksheet. You can use Right Click, Excel Shortcut Key, or write a VBA code in Excel. read more which contain the word “Summary” in their name.
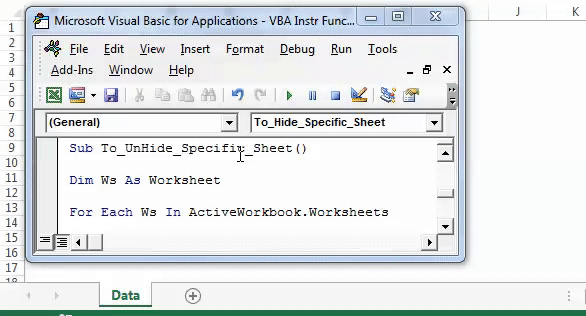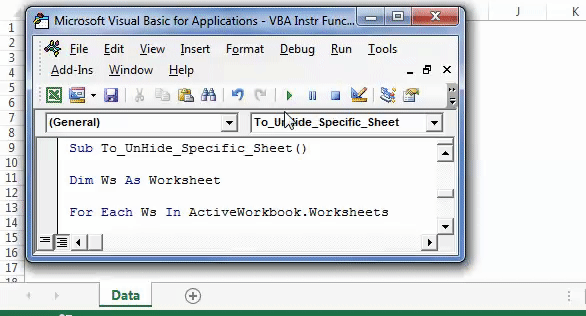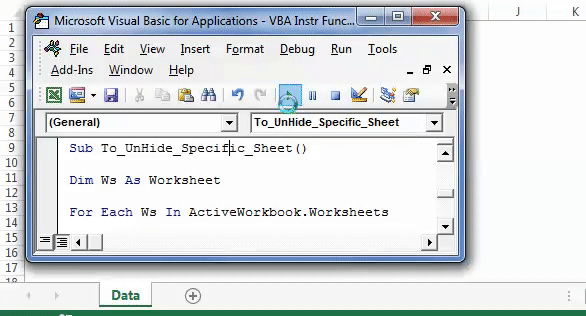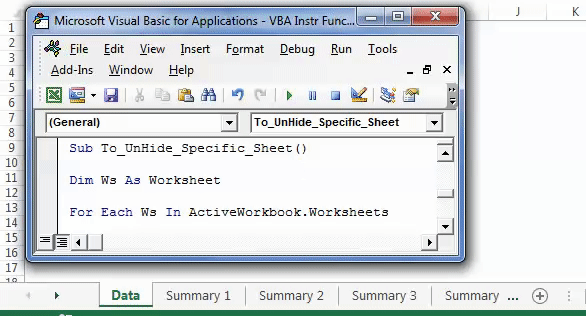
Step 1: Enter the following code to unhide all the sheets.
Sub To_UnHide_Specific_Sheet() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets If InStr(Ws.Name, "Summary") > 0 Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible End If Next Ws 'InStr function looks for word or phrase in the sheet name 'If it finds then it will be hidden End Sub
Step 2: Press F5 or run the VBA code manually, as shown in the following image. In the output, all the five sheets are unhidden.
Properties of VBA InStr Function
The properties of the function are listed as follows:
- It is a case-sensitive function. To eliminate this issue, supply the “compare” argument “vbTextCompare.”
- It is a VBA functionVBA functions serve the primary purpose to carry out specific calculations and to return a value. Therefore, in VBA, we use syntax to specify the parameters and data type while defining the function. Such functions are called user-defined functions.read more and cannot be used like other in-built formulas of Excel.
- It returns zero if it cannot find “string 2” in “string 1.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Define the VBA InStr function.
The VBA InStr function returns the position of one string within another string. This position corresponds to the first occurrence of the substring. The function returns an integer as the output. It returns zero (0) if the substring is not found within the string.
The syntax and the arguments of the function are listed as follows:
“InStr([start],string1,string2,[compare])”
• Start: It specifies the position from which search should begin. The default value is 1.
• String 1: It is the actual string within which the substring is to be searched.
• String 2: It is the substring to be searched.
• Compare: It specifies the comparison method to be used. The methods are stated as follows:
a. vbBinaryCompare or 0: It is used for a case-sensitive search of the substring within the string.
b. vbTextCompare or 1: It is used for a case-insensitive search of the substring within the string.
c. vbDatabaseCompare or 2: It is used for comparison with Microsoft Access database.
The arguments “string 1” and “string 2” are mandatory, while “start” and “compare” are optional.
What is the difference between the InStr and the InStrRev functions of VBA?
How to use the VBA InStr function in excel with wildcards?
With the usage of wildcards, the InStr function returns “true” or “false” depending on whether it has found the specified substring within the string or not.
The function supports the usage of the following wildcards:
1. Asterisk (*): It represents one or more characters of a string and works as follows:
• “a*” refers to the text that begins with the character “a.”
• “*a” refers to the text that ends with the character “a.”
• “*a*” refers to the text that has the character “a” in the middle.
2. Question mark (?): It represents one character of a string and works as follows:
• “a?” refers to two characters beginning with “a.”
• “?a” refers to two characters ending with “a.”
• “?a?” refers to three characters having “a” in the middle.
Likewise, the VBA InStr function can be used with the tilde (~) as well.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to VBA InStr Function in Excel. Here we learn how to use the InStr function along with step by step examples and a downloadable excel template. Below you can find some useful Excel VBA articles-
- VBA FileCopy Function
- Excel VBA FileDialog
- Excel VBA String Functions
- Excel VBA SubString
- VBA Name Worksheet
VBA InStr function in Excel is categorized as a Text/String function in VBA. It is a built-in function in MS Office Excel. Finds the position of specified sub-string with the given string. Returns the first occurrence position as a integer value. If it doesn’t find specified sub string, It returns a value ‘0’. Performs a case sensitive search. It has four parameters.
The VBA InStr function use in either procedure or function in a VBA editor window in Excel. We can use this VBA InStr function any number of times in any number of procedures or functions. In the following section we learn what is the syntax and parameters of the InStr function, where we can use this VBA InStr function and real-time examples.
Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Syntax of VBA InStr Function in Excel:
- Parameters or Arguments:
- Where we can apply or use the InStr Function?
- Example 1: Search specified substring in given string, starting at position 1
- Example 2: Search specified substring within string, starting at position 3
- Example 3: InStr Function using ‘vbBinaryCompare’ (Case Sensitive Search)
- Example 4: InStr Function using vbTextCompare (Avoid Case Sensitive Search)
- Example 5: Search for ‘@’ symbol in specified email
- Example 6: Search for ‘.’ and file extension within specified file name
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
The syntax of the VBA InStr function is
InStr ([start], string, substring, [compare])
In the above syntax the second and third arguments are mandatory (string & substring) parameters. And the first and last two parameters are optional (start & compare) Arguments.
Parameters or Arguments:
Where
Start: The start is an optional argument, and its default value is ‘1’. It represents the starting position for the search. It accepts integer type input value. If we don’t specify any value, default it considers default value as one.
String: The string is a mandatory argument. The string in which we want to search.
Substring: The substring is a mandatory argument. The substring that you want to find within string.
Compare: The compare is an optional argument. It represents which type of comparison needs to perform. It has four numeric values. It we don’t specify any value, default it considers a binary comparison. Here are the different four comparisons, which are shown in the below table.
| VBA Compare | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| vbUseCompareOption | -1 | Performs a comparision using the ‘option compare’ |
| vbBinaryCompare | 0 | Performs a Binary comparison |
| vbTextCompare | 1 | Performs a Textual comparison |
| vbDatabaseCompare | 2 | Microsoft Access only. Performs a comparison based on information in your database. |
Where we can apply or use the VBA InStr Function in Excel?
We can use this VBA InStr function in MS Office 365, MS Excel 2016, MS Excel 2013, 2011, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel 2016 for Mac, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel Online, Excel for iPhone, Excel for iPad, Excel for Android tablets and Excel for Android Mobiles.
Example 1: Search specified substring in given string, starting at position 1
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring in within given string, starting at position 1
'Search for "if" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex1()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'if' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "if")
'or
iPosition = InStr(sWord, "if")
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F8") = "The text 'if' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'if' position: " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
In the above example ‘iPosition & sWord’ are declared as an integer and string data type. This variable ‘iPosition’ now contains the starting position of substring.
Output: Here is the screen shot of first example output.
Example 2: Search specified substring within string, starting at position 3
Here is another example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring in within given string, starting at position 3
'Search for "if" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 3.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex2()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'if' in given string
iPosition = InStr(3, sWord, "if")
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F11") = "The text 'if' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'if' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of second example output.
Example 3: InStr Function using ‘vbBinaryCompare’ (Case Sensitive Search)
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds ‘b’ substring in within given string, starting at position 1. Where ‘b’ is a small letter. It returns ‘0’ as an output. Notice fourth argument in InStr function. It performs a binary comparison.
'Search for "b" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex3()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'b' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "b")
‘or
‘iPosition =InStr(1, sWord, "b", vbBinaryCompare)
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F14") = "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Note: VBA InStr is a Case sensitive search.
Output: Here is the screen shot of third example output.
Example 4: InStr Function using vbTextCompare (Avoid Case Sensitive Search)
Here is one more example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds ‘b’ substring in within given string, starting at position 1. Where ‘b’ is a small letter, but It avoids case sensitive search and returns ‘9’ as an output. Notice fourth argument in InStr function. It performs a textual comparison.
'Search for "b" in string "Life is Beautiful", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex4()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "Life is Beautiful"
'Search for 'b' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "b", vbTextCompare)
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("F17") = "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The text 'b' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of fourth example output.
Example 5: Search for ‘@’ symbol in specified email
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring in within given string, starting at position 1. We can also search special characters within string. Sometimes we want to search ‘@’ position in email. Let’s see.
'Search for "@" in string "abcde@gmail.com", starting at position 1.
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex5()
'Variable declaration
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
sWord = "abcde@gmail.com"
'Searh for '@' in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, "@")
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("I8") = "The Special Character '@' position : " & iPosition
'Display output message
MsgBox "The Special Character '@' position : " & iPosition, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of fifth example output.
Example 6: Search for ‘.’ and file extension within specified file name
Here is a simple example of the VBA InStr function. This below example macro uses the InStr function and finds specified substring(.) in within given string, starting at position 1. Most of the time while writing VBA codes we try to extract file extension or file name. Before that we need to identify ‘.’ Position In file name.
'Search for '.' and file extension in the file name "xyz.xlsm"
Sub VBA_InStr_Function_Ex6()
'Variable declarations
Dim iPosition As Integer
Dim sWord As String
Dim sFileExtn As String
sWord = "xyz.xlsm"
'Search file extension in given string
iPosition = InStr(1, sWord, ".")
'Get File Extension
sFileExtn = Right(sWord, Len(sWord) - iPosition)
'You can see answer in the Worksheet
Sheets("VBAF1.com").Range("I11") = "Specified File Extension is : " & sFileExtn
'Display output message
MsgBox "Specified File Extension is : " & sFileExtn, vbInformation, "Example of InStr Function"
End Sub
Output: Here is the screen shot of sixth example output.
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays in Excel Blog
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers
Если часто приходится работать с электронными таблицами, то настоятельно рекомендуется ознакомиться с макросами. Это микропрограммы, настроенные на автоматизацию выполнения определенных действий. Они позволяют значительно расширить возможности как самого Excel, так и конкретного пользователя.
Одно из ключевых понятий языка программирования VBA (а именно на нем осуществляется написание макросов) является функция. Это блок программы, который обрабатывает определенные данные и возвращает какой-то конкретный результат.
Одной из таких функций является InStr. Давайте подробно рассмотрим ее основные аргументы, а также реальные примеры, описывающие ее использование в реальной жизни.
Но давайте сначала узнаем, зачем макросы нужны? Потому что многие начинающие пользователи Excel нередко ошибочно считают, что эта функция излишняя. Но на самом деле, они просто очень мало работали с этой программой. Как только увеличить продолжительность взаимодействия с электронными таблицами, оказывается, что мы часто выполняем тысячи однотипных действий, которые компьютерная программа может выполнить буквально за несколько секунд. Это здорово экономит время и силы, а также разгружает мозг.
Итак, давайте разберем функцию InStr более подробно.
Содержание
- Описание функции InStr
- Синтаксис функции InStr, параметры, значения
- Синтаксис функции InStr
- Параметры функции InStr
- Значения аргумента «сравнение»
- Примеры использования функции InStr в VBA Excel
- Пример 1
- Пример 2
- Пример 3
- Выводы
Описание функции InStr
С помощью функции InStr пользователь может находить местонахождение первого вхождения какого-то текста в другой. Возвращаемый тип данных, осуществляемый этой функцией – Variant.
Сфера применения этой функции очень широкая, и без нее невозможно обойтись при использовании других функций, таких как Left, Mid, Right. Кроме этого, она может применяться для поиска какого-то текста.
Есть похожая функция в языке VBA, которая называется InStrB. Ее отличие заключается в том, что обрабатываются байтовые данные. С ее помощью можно узнать расположение байта, а не символа. Более подробно вы можете ознакомиться с этой функцией в третьем примере.
Преимущества функции InStr следующие:
- Возможность быстро обрабатывать огромные массивы данных буквально за несколько секунд. Когда человек осуществляет поиск вручную, только кажется, что все делает компьютер. НА самом деле, он выполняет лишь часть работы. Но все основное делается самим человеком. например, нужно вбить строку поиска, нажимать на стрелочки, чтобы искать определенное по счету вхождение и так далее. Это очень затратно. В случае же с функцией VBA InStr можно добиться этой цели с помощью макросов: с помощью формулы передать в функцию аргументы, а потом дальше использовать получившийся результат в другой функции. Таким образом автоматизируется огромное количество действий, которые при прочих равных пришлось бы выполнять вручную.
- Экономия времени. Есть сотрудники, которые за счет макросов смогли значительно увеличить эффективность своей работы и фактически не работать большую часть времени. Все, что им потребовалось – один раз написать скрипт, а потом просто передавать ему нужные параметры. И функция InStr является важной составляющей этого процесса, поскольку со строками приходится иметь дело постоянно, если человек активно использует электронные таблицы.
- Экономия ресурсов, в том числе, и интеллектуальных. Это тоже очень важный пункт. Ни для кого не секрет, что постоянное выполнение однотипных действий невероятно утомляет. Следовательно, функция InStr позволяет избавиться от бренной ноши постоянного поиска значений вручную, особенно если для этого используется формула.
Кстати! Использование функции InStr дает возможность значительно улучшить творческие способности!
Как? Очень просто. Исследователи доказали, что основной фактор, который мешает творческому процессу – это излишнее количество рутинных действий. В определенных пределах они помогают сосредоточиться (например, когда человек рисует что-то на автомате), но через некоторое время соответствующие нейронные связи начинают терять в скорости проведения нервных импульсов. Следовательно, на другие задачи уже сил не хватает. А творчество – это интеллектуально затратный процесс.
Если же использовать функцию InStr, можно освободить себя от этой бренной участи и уделить внимание другим важным вещам и создать не просто красивую, а функциональную таблицу, которая работает полностью автоматически и при этом содержит все необходимые данные.
А теперь давайте после лирического отступления все же перейдем к рассмотрению синтаксиса функции InStr.
Синтаксис функции InStr, параметры, значения
Синтаксис функции InStr
Если говорить об этой функции в общем, она записывается таким образом.
InStr([начало], строка1, строка2, [сравнение])
Но этот вариант полный, но очень часто используется сокращенная разновидность этой функции, содержащая всего два аргумента.
InStr(строка1, строка2)
Как правило, именно сокращенный вариант используется на практике. Нельзя сказать, что в ней вообще нет первого и последнего аргумента, просто автоматически применяются те значения, которые определены как «по умолчанию».
Параметры функции InStr
Давайте более подробно опишем, что означает каждый из аргументов:
- Начало. Этот параметр не является обязательным. В него записывается число, которым записывается изначальная позиция, с которой начинается поиск.
- Строка1. Этот аргумент нужно не забывать указывать. Это непосредственно тот текст, в котором нужно искать.
- Строка 2. Это то, что мы ищем.
- Сравнение. С помощью этого аргумента пользователь может задать способ, которым будут анализироваться и сопоставляться строки.
Важно учесть некоторые нюансы:
- Если пользователь записал последнее значение, то первое вводить обязательно.
- Если же параметр «Сравнение» в функции не прописан, то Эксель применяет значение по умолчанию (0 или другое при условии наличия инструкции Option Compare).
- Если пользователь укажет значение NULL в необязательные аргументы, то формула выдаст ошибку. Это нужно держать в уме.
Ну как? Сложно? Наверно, все же все просто. На первый взгляд может показаться, что запомнить все это довольно тяжело. Но в практике мастерство оттачивается. Поэтому настоятельно рекомендуется потренироваться «в песочнице».
Значения аргумента «сравнение»
С помощью аргумента «сравнение» человек может задавать тип сравнения. Делается это через указание значения, выраженного в цифровом формате. Если в качестве значения этого аргумента используется 1, то параметр означает сравнивание двух показателей с использованием инструкции Option Compare.
Если этому аргументу присвоить значение 1, то функция осуществляет бинарное сравнение. Простыми словами, при этом типе осуществляется поиск значения с учетом регистра. В случае же с текстовым сравнением регистр не учитывается.
Каждое значение, возвращаемое функцией, говорит о выполнении одного из возможных условий:
- Позиция первого найденного соответствия. Если возвращается строка, аналогичная тому, что было обнаружено в самом первом случае, то поиск оказался успешным.
- 0. Это значение говорит о том, что поиск оказался неудачным. Простыми словами, не получилось в первой строке отыскать вторую. Также нередко можно встретить такую ошибку в ситуациях, когда при попытке поиска оказывается, что первая строка не содержит никаких значений или же значение, передающееся аргументу «начало», оказывается большим, чем длина первой строки.
- Такое же значение, которое передается аргументу «начало». Это говорит о том, что вторая строка не содержит никаких значений.
- NULL. Эта проблема возникает в ситуациях, когда или строка 1, или строка 2 содержит аналогичную ошибку. Чаще всего эта проблема случается, если пользователь неправильно указал диапазон (например, указал неправильный оператор диапазона). Также если вводится несколько пересекающихся диапазонов, то эта ошибка может возникать, если человек неправильно применил оператор диапазона (коим служит символ пробела).
В последнем случае нужно удостовериться в том, что для указания диапазона был использован знак двоеточия. Например, если используется диапазон от А1 до А10, то нужно его записывать, как А1:А10.
Если же нужно указать несколько непересекающихся друг между другом наборов ячеек, то используется символ точки с запятой (некоторые говорят, что используется запятая, но это неправильно). Например, правильный ввод такой: А1:А10;С1:С10.
Если же используется пробел, нужно убедиться в том, что диапазоны действительно пересекаются. Если они расположены независимо друг от друга, это может породить множество проблем. Поэтому нужно или заменить знак, разделяющий диапазоны, на точку с запятой, или изменить диапазоны так, чтобы они пересеклись в том или ином месте.
Ну и простой пример для наглядности. Предположим, у нас есть диапазоны a1: A5 C1: C3.
В этом случае ячейки никак не пересекаются. Соответственно, будет возвращено значение NULL. Следовательно, пользователь увидит после вычисления по формуле с использованием аргументов, возвращающих это значение, также NULL. Ведь невозможно выполнять поиск в тех ячейках, где нет нормального значения пусть даже числового (хотя формула InStr лучше подходит для поиска именно текстовых соответствий).
Если в Excel включена функция автоматической проверки ошибок, то рядом с ошибочной ячейкой будет находиться восклицательный знак. Если на него нажать, появится возможность выбрать подходящую под текущую проблему ситуацию.
Примеры использования функции InStr в VBA Excel
Существует множество применений функции InStr при разработке макросов. Давайте разберем три простых примера, чтобы было более наглядно, как можно использовать ее в реальных (или воображаемых) условиях
Пример 1
Этот пример создан специально для новичков, поскольку демонстрирует чисто использование функции InStr. Следовательно, он является наиболее простым.
Sub Test1()
Dim x As Variant
x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «Фернандо»)
MsgBox x
‘Здесь x будет равен 9
End Sub
Пример 2
Этот пример показывает, как можно использовать текстовое и бинарное сравнение для поиска соответствий, в которых регистр символов важен и нет. В этом кейсе для примера были использованы две строки с одинаковым содержимым, чтобы было проще наглядно показать, как Excel учитывает регистр символ или не учитывает его в макросах.
Sub Test2()
Dim x As Variant
x = InStr(10, «На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «по», 0)
MsgBox x
‘Здесь x будет равен 36 (поиск с учетом регистра символов)
x = InStr(10, «На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «по», 1)
MsgBox x
‘Здесь x будет равен 18 (поиск без учета регистра символов)
End Sub
Здесь мы видим, что в качестве начального значения обозначен десятый символ. Но несмотря на это первое вхождение анализируется, стартуя той строкой, в которой осуществляется анализ информации на предмет соответствия заданному значению.
Пример 3
А в этом случае осуществляется сравнение сравнений посимвольного и побайтового типов. Здесь также для большей наглядности мы использовали одинаковые строки и подстроки, которые будем искать. А вот и сам пример.
Sub Test 3()
Dim x As Variant
x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «гор»)
MsgBox x
‘Здесь x будет равен 4
x = InStr(«На горе Фернандо-По, где гуляет Гиппо-по», «гор»)
MsgBox x
‘Здесь x будет равен 7
End Sub
Выводы
Таким образом, функция InStr в языке программирования VBA, который используется в макросах, имеет очень много применений. Она полезна, когда есть оромный массивы данных, который невозможно проанализировать вручную, а встроенные средства автоматизации типа поиска также отнимают много времени и сил.
По сути, эта функция и являет собой тот же самый поиск за тем лишь исключением, что можно заранее задать Excel, при каких условиях и как он будет осуществляться.
Есть еще множество других волшебных функций, используемых для написания макросов, и мы обязательно познакомим вас с ними в следующий раз.
Оцените качество статьи. Нам важно ваше мнение: