I have created an Excel Sheet that does some lookups to format data that needs to be inserted into another table. This Excel Workbook needs to be given to some users that are free to add some new rows, and then need to be able to hit an «Insert Into Database» button and have the records transformed and inserted as new records into a SQL Table. I am using Excel 2010 and SQL Server 2008. I have a connection to the DB as I am using it to pull some data back in order to verify the new rows being added, but I’m not sure how to then insert the data back.
Excellll
5,5494 gold badges38 silver badges55 bronze badges
asked Sep 22, 2010 at 9:24
You can do a lot with ADO:
Dim cn As New ADODB.Connection
''You should probably change Activeworkbook.Fullname to the
''name of your workbook
strCon = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" _
& ActiveWorkbook.FullName _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1"";"
cn.Open strCon
s = "INSERT INTO [ODBC;Description=TEST;DRIVER=SQL Server;" _
& "SERVER=Server;Trusted_Connection=Yes;" _
& "DATABASE=test].SomeTable ( Col1, Col2, Col3, Col4 ) " _
& "SELECT a.Col1, a.Col2, a.Col3, a.Col4 " _
& "FROM [Sheet2$] a " _
& "LEFT JOIN [ODBC;Description=TEST;DRIVER=SQL Server;" _
& "SERVER=Server;Trusted_Connection=Yes;" _
& "DATABASE=test].SomeTable b ON a.Col1 = b.Col1 " _
& "WHERE b.Col1 Is Null"
cn.Execute s
You can also use the ACE connection: http://www.connectionstrings.com/ or OPENROWSET and an SQL Server connection. In all cases, you may have problems with mixed data types in columns, depending on your registry settings (http://forum.lessthandot.com/viewtopic.php?f=17&t=12043&p=59669&hilit=excel#p59669)
answered Sep 22, 2010 at 10:28
FionnualaFionnuala
90.1k7 gold badges110 silver badges148 bronze badges
1
I have found out that within a macro, you can create an ADO connection by adding a reference to the «Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 6.0 Library». Once you have opened a connection within the Macro, you can create your insert statement and execute it via using the connection.Execute(statement) method:
Dim item as String = "Insert Into MyTable(ColA,ColB) VALUES('Foo', 'Bar')"
Dim thisCon As New ADODB.Connection
thiscon.Open("ConnectionString")
thisCon.Execute (item)
SeanC
15.6k5 gold badges45 silver badges65 bronze badges
answered Sep 22, 2010 at 10:29
BenBen
3,92612 gold badges53 silver badges87 bronze badges
After modifying the data in excel, need to generate Update statements, which will be executed by pressing the button «update». As a result, will be executed Update and Insert statements. Then have to send a query to refresh the data in Excel.(imho)
answered Sep 22, 2010 at 9:42
Zoitc2014Zoitc2014
2991 silver badge8 bronze badges
Добрый день!
У меня такой вопрос.
Мне нужно из хранимой процедуры одного сервера SQL записать данные в таблицу на другой сервер SQL.
Я попробовал
Sub Test()
Dim conn As String
Dim data_base As String
Dim period As String
Dim datasource As String
Dim object_id As String
Dim dt As Integer
Dim day_start As String
Dim date_beg As String
Dim date_end As String
conn = «Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Password=Knpz_asrmb;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=USER_ASRMB;Initial Catalog=TCD_Work;Data Source=Sam-knpz-app24»
conn1 = «Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Password=ASRMB;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=ASRMB;Initial Catalog=dbm_asrmb_knpz_20190129;Data Source=KNPZ-ASRMB-N1MSSQLASRMB1»
JS_params = «{» + Chr(34) + «id_object» + Chr(34) + «:» + Chr(34) + object_id + Chr(34) + «,» _
+ Chr(34) + «period» + Chr(34) + «:» + Chr(34) + period + Chr(34) + «,» _
+ Chr(34) + «datasource» + Chr(34) + «:» + Chr(34) + CStr(dt) + Chr(34) + «,» _
+ Chr(34) + «date» + Chr(34) + «:» + Chr(34) + day_start + Chr(34) + «,» _
+ Chr(34) + «date_beg» + Chr(34) + «:» + Chr(34) + date_beg + Chr(34) + «,» _
+ Chr(34) + «date_end» + Chr(34) + «:» + Chr(34) + date_end + Chr(34) + «}»
Query conn, JS_params
End Sub
Sub Query(connStr As String, jsonParams As String)
Dim cnDB As New ADODB.Connection
Dim rc As New ADODB.Recordset
cnDB.CommandTimeout = 360
cnDB.Open connStr
Dim params As Object
Set params = JsonConverter.ParseJson(jsonParams)
Dim period As String
Dim object_id As String
Dim day_start As String
Dim date_beg As String
Dim date_end As String
Dim data_source As String
Dim dataseg As String
Dim day1 As String
Dim month1 As String
Dim year1 As String
Dim dt As String
dataseg = Date
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(2).Cells(1, 2).Value = dataseg
day1 = Day(dataseg)
month1 = Mid(dataseg, 4, 2)
year1 = year(dataseg)
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(2).Cells(2, 1).Value = day1
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(2).Cells(3, 1).Value = month1
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(2).Cells(4, 1).Value = year1
dt = year1 + month1 + day1
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(2).Cells(5, 1).Value = dt
period = params(«period»
object_id = params(«id_object»
data_source = params(«datasource»
date_beg = params(«date_beg»
date_end = params(«date_end»
day_start = params(«date»
Dim ws As Worksheet
‘Set ws = Sheets(«Áàëàíñ ïî çàâîäó»
‘ws.UsedRange.Clear
Dim sql As String
sql = «set nocount on EXEC spTCD__KNPZ_shipment ‘» + dt + «‘,1»
rc.Open sql, cnDB
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Cells(1, 1).CopyFromRecordset rc
rc.Close
cnDB.Close
Dim cn1DB As New ADODB.Connection
Dim rc1 As New ADODB.Recordset
cn1DB.CommandTimeout = 360
cn1DB.Open «Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Password=ASRMB;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=ASRMB;Initial Catalog=dbm_asrmb_knpz_20190129;Data Source=KNPZ-ASRMB-N1MSSQLASRMB1»
Dim sql2 As String
sql2 = «Insert INTO [dbm_asrmb_knpz_20190129].[dbo].[tsd] (id_prod, prod_name, prod_okp,prod_ksm, id_transType, transtype, id_owner, owner, m_netto, shipDT) From rsADO»
rc1.Open sql2, cn1DB
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(3).Cells(1, 1).CopyFromRecordset rc1
rc1.Close
cn1DB.Close
В один рекордсет я записал данные. Но не могу записать из него в таблицу
seun asked in an old post of mine, Interfacing with MySQL via Excel; whether it’s possible to submit data from Excel into MySQL.
Yes, it is very much possible to do this. In fact, I’ve written a tutorial on how to do this with the help of VBA.
First, we create the table that we will use to store the data. The SQL statement below will create our sample table called tutorial. Just copy and paste it into your favourite MySQL IDE or phpMyAdmin.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tutorial` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment,`title` varchar(255) NOT NULL,`author` varchar(255) NOT NULL,`price` float(4,2) NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 AUTO_INCREMENT=1 ;
Now that we’ve created the table, it’s time to store some data in it. The data must come from a source. In this example, I’ve created a list of book titles, along with the author and price of each book. Just copy the table below and paste it into an Excel worksheet.
| Title | Author | Price |
|---|---|---|
| How to Win Friends and Influence People | Dale Carnegie | 7.99 |
| The Magic of Thinking Big | David Schwartz | 10.17 |
| The Richest Man in Babylon | George S. Clason | 6.99 |
| As a Man Thinketh | James Allen | 9.95 |
| The Power of Your Subconcious Mind | Dr. Joseph Murphy | 7.49 |
| The Magic of Believing | Claude M. Bristol | 6.99 |
| It Works | R.H. Jarrett | 3.00 |
| Write It Down, Make It Happen: Knowing What You Want and Getting It | Henriette Anne Klauser | 10.52 |
| The Attractor Factor: 5 Easy Steps For Creating Wealth (Or Anything Else) From the Inside Out | Joe Vitale | 11.53 |
| The Science of Getting Rich | Wallace D. Wattles | 11.20 |
Now rename that sheet as Books. If you haven’t displayed your Visual Basic and Control Toolbox toolbars yet, now is a good time to do so. Go to the View top menu and navigate to Toolbars. Make sure Visual Basic and Control Toolbox are checked.
I prefer to place the toolbars at the top panel area so they’re out of the way of my Excel spreadsheet. You might want to do the same.
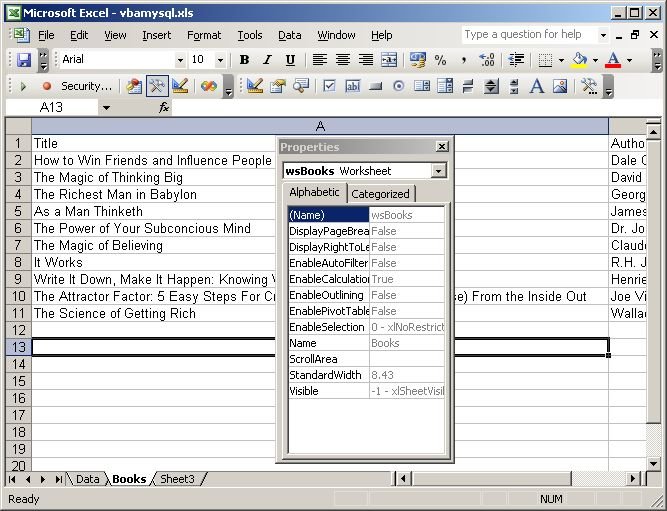
Next, click on the Properties icon of the Control Box toolbar and set the name of the Booksworksheet as wsBooks. You’ll get something like the screenshot below:
Now it’s on to some programming. But before we even start typing a single line of code, we need to understand what we’re trying to achieve with our code:
- Connect to the local MySQL database server
- Use the demo database
- Insert each line of the Books table into the tutorial database we created earlier
Connecting to the Database Server and Selecting the Correct Database
As we will be using VBA to perform our data insertion, we need a method to connect to the database server and ensure we’ve selected the correct database where the data will be inserted into.
There are three components necessary for us to perform MySQL database manipulation using VBA:
- MySQL Connector/ODBC
- Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) Library
- The correct connection string to access the MySQL database
For this tutorial, I’m using MySQL Connector/ODBC 5.1. You can download it here. For Windows users, grab the MSI Installer version and just double click the file and go through the installation screen.
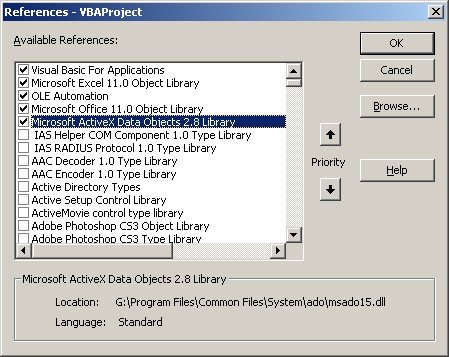
You’ll also need to reference to the Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects Library in your Excel Workbook. Fire up the Visual Basic Editor using Alt-F11. Go to the Tools top menu item of the Visual Basic Editor and choose References.
In the list of references, check the Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.8 Library. Refer to the following screenshot:
Next, we will then start coding. The first thing we should do is to write a Sub procedure to connect to the database. This will be done using an ADODB connection.
First we need to declare the variable for the ADODB connection. Make sure you’ve double-clicked the wsBooks worksheet in the Project Explorer (if you can’t see it, press Ctrl-R). It should bring out a code window for that sheet.
In that sheet, enter the following code:
Dim oConn As ADODB.ConnectionPrivate Sub ConnectDB()Set oConn = New ADODB.ConnectionoConn.Open "DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 5.1 Driver};" & _"SERVER=localhost;" & _"DATABASE=yourdatabase;" & _"USER=yourdbusername;" & _"PASSWORD=yourdbpassword;" & _"Option=3"End Sub
You should replace yourdatabase, yourdbusername and yourdbpassword with your database name, your database username and the database password accordingly.
Test your ConnectDB Sub procedure by putting the cursor anywhere between the Sub statement and press F5 (this runs the Sub procedure). If an error popup appears, check that your MySQL service is running and that you’ve referenced to the Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.8 Library.
Once the ConnectDB Sub procedure is working, we will code the Sub procedure to perform data insertion. Before that, we need to create a data sanitizing function to escape single quotes before inserting them into the database. This is necessary because improper quote escaping will cause data insertion to fail.
Here are the codes for the esc function that will escape single quotes from data to be inserted:
Function esc(txt As String)esc = Trim(Replace(txt, "'", "'"))End Function
And now for the Sub procedure to perform data insertion:
Dim rs As ADODB.RecordsetPrivate Sub InsertData()Set rs = New ADODB.RecordsetConnectDBWith wsBooksFor rowCursor = 2 To 11strSQL = "INSERT INTO tutorial (author, title, price) " & _"VALUES ('" & esc(.Cells(rowCursor, 1)) & "', " & _"'" & esc(.Cells(rowCursor, 2)) & "', " & _esc(.Cells(rowCursor, 3)) & ")"rs.Open strSQL, oConn, adOpenDynamic, adLockOptimisticNextEnd WithEnd Sub
Now run the InsertData Sub procedure and you will see that it will insert the data from line 2 to line 11 of the Books worksheet into the tutorial table.
Hope this tutorial has given you a basic understanding on how to insert data into a MySQL database from Microsoft Excel using VBA. If you have any questions, just drop a comment below.
Tags: Microsoft, MySQL, Smoking
Hi ,
I am new to excel vba and i have absolutely no idea of how to achieve this.
i want to insert and update a sql server table using excel macro.
currently i have done it for the update can someone please help me in adding the insertion code.
here is the update code below:-
‘General variables we’ll need
Public con As ADODB.Connection
Public bIgnoreChange As Boolean
Dim pk As New Collection
Dim oldValue As Variant
Dim nRecordCount As Integer
Private Sub Workbook_Deactivate()
If Not (con Is Nothing) Then
con.Close
Set con = Nothing
End If
End Sub
Function IsInPrimaryKey(name As String)
For Each pki In pk
If (pki = name) Then
IsInPrimaryKey = True
Exit Function
End If
Next pki
IsInPrimaryKey = False
End Function
Function MakeSQLText(data As Variant)
If (IsNumeric(data)) Then
MakeSQLText = data
Else
MakeSQLText = «‘» & Replace(data, «‘», «»») & «‘»
End If
End Function
Private Sub Workbook_SheetActivate(ByVal Sh As Object)
‘ Let’s retrieve the data from the SQL Server table with the same name as the sheet
bIgnoreChange = True
Set con = New ADODB.Connection
con.Provider = «sqloledb»
sConnectionString = «Server=D90SC6Q1SQLEXPRESS;Database=BIClients;UID=BIClients;Pwd=Rumbl31nJungl3»
con.Open sConnectionString
‘ Clean up old Primary Key
While (pk.Count > 0)
pk.Remove 1
Wend
‘ Try to retrieve the primary key information
On Error GoTo NoCon
Set rs = con.Execute(«SELECT COLUMN_NAME FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLE_CONSTRAINTS AS tc INNER JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.KEY_COLUMN_USAGE AS kcu ON tc.CONSTRAINT_NAME = kcu.CONSTRAINT_NAME WHERE tc.CONSTRAINT_TYPE = ‘PRIMARY KEY’ AND tc.TABLE_NAME
= ‘» & Sh.name & «‘»)
‘ Fill up the primary key infomration
While (Not rs.EOF)
pk.Add CStr(rs(0))
rs.MoveNext
Wend
‘ Clean up the sheet’s contents
Sh.UsedRange.Clear
‘ Now get the table’s data
Set rs = con.Execute(«SELECT fkGroupID,fkProjectID,[Outage Start Date],[Outage Stop Date],[Man Hour Lost],[Outage Cost],[fkReasonCategoryId] FROM » & Sh.name)
‘ Set the name of the fields
Dim TheCells As Range
Set TheCells = Sh.Range(«A1»)
For i = 0 To rs.Fields.Count — 1
TheCells.Offset(0, i).Value = rs.Fields(i).name
Next i
‘ Get value for each field
nRow = 1
While (Not rs.EOF)
For i = 0 To rs.Fields.Count — 1
TheCells.Offset(nRow, i).Value = rs(i)
Next
rs.MoveNext
nRow = nRow + 1
Wend
nRecordCount = nRow — 1
bIgnoreChange = (pk.Count = 0) And (nRecordCount > 0)
Exit Sub
NoCon:
con.Close
Set con = Nothing
End Sub
Private Sub Workbook_SheetChange(ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range)
‘ No loops, and don’t do nothing if there’s no connection
If bIgnoreChange Or con Is Nothing Then
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Is something different?
If (Target.Value = oldValue) Then
‘ No change
oldValue = Application.ActiveCell.Value
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Don’t allow changes in the column names or outside of the table borders
‘If Target.Row < 2 Or Sh.Cells(1, Target.Row).Text = «» Or Sh.Cells(1, Target.Column) = «» Or (Target.Row > nRecordCount + 1) Then
‘ Target.Value = oldValue
‘oldValue = Application.ActiveCell.Value
‘MsgBox «You can only edit items inside the table»
‘Exit Sub
‘End If
‘ Is this change is in a primary key column — if so, we can’t edit it
If (IsInPrimaryKey(Sh.Cells(1, Target.Column).Text)) Then
Target.Value = oldValue
oldValue = Application.ActiveCell.Value
MsgBox «This column is a part of the primary key, so it cannot be changed»
Exit Sub
End If
‘ Build the primary key from the data in this row
Dim Names As Range
Set Names = Sh.Range(«A1»)
nColumn = 0
sWhere = «»
While (Names.Offset(0, nColumn).Text <> «»)
If (IsInPrimaryKey(Names.Offset(0, nColumn).Text)) Then
If (sWhere <> «») Then
sWhere = sWhere & » AND «
End If
sWhere = sWhere & Sh.Cells(1, nColumn + 1).Text & » = » & MakeSQLText(Sh.Cells(Target.Row, nColumn + 1))
End If
nColumn = nColumn + 1
Wend
‘ Update the server!
sSQL = «UPDATE » & Sh.name & » SET » & «[» & Sh.Cells(1, Target.Column).Text & «]» & » = » & MakeSQLText(Target.Text) & » WHERE » & sWhere
con.Execute sSQL
oldValue = Application.ActiveCell.Value
End Sub
Private Sub Workbook_SheetSelectionChange(ByVal Sh As Object, ByVal Target As Range)
If (Not bIgnoreChange) Then
‘ Remember the old value
oldValue = Application.ActiveCell.Value
End If
End Sub
Santt
Приведенный ниже код предназначен для простого добавления строк информации из листа Excel в таблицу в SQL Server. Это утомительно написано там, где идет строка за строкой и ячейка за ячейкой. Он работает без всплывающих окон с ошибками, но когда я проверяю таблицу на предмет своих данных, там ничего нет.
Я выполнял запрос в SQL для проверки с помощью предложения WHERE, и поле «Аналитик» должно соответствовать моему имени. Ничего не всплывает.
Почему мои данные не отображаются в таблице? А ТАКЖЕ Я открыт для любых предложений о лучших способах сделать это. Спасибо!
Public Sub ConnectToDB()
Dim DBCONT As Object
Dim strConn As String
Dim Server_Name As String
Dim Database_Name As String
Dim Table_Name As String
Dim User_ID As String
Dim Password As String
Dim strSQL As String
Dim rs As Object
Dim Fields As String
Dim LastRowAudit As Long
Dim i As Long
Dim sAuditType, sClaimeReceivedDate, sDateAssigned, sDateCompleted, sAnalyst, sCustomer, sID, sAffiliate, sFacility, sDEA, sAcctNumber, sWholesaler, sVendor, sProduct, sNDC, sRef, sClaimedContract, sClaimedContractCost, sContractPriceStartDate, sContractPriceEndDate, sCatalogNumber, sInvoiceNumber, sInvoiceDate, sChargebackID, sContractIndicator, sUnitCost, sWAC, sPotentialCreditDue, sQTY, sSpend, sIpDshIndicator, sDSHorHRSANumber, sUniqueGPOCode, sComment, sResCode, sCorrectCost, sCRRBCM, sCRRBRebill, sCRRBDate As String
' SET ALL VARIABLES
Server_Name = "I have this in my actual code" ' Enter your server name here
Database_Name = "I have this in my actual code" ' Enter your database name here
Table_Name = "I have this in my actual code"
User_ID = "I have this in my actual code" ' enter your user ID here
Password = "I have this in my actual code" ' Enter your password here
WkbName = ThisWorkbook.Name
SheetName = "Audit Data" ' WHERE RS IS
'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
' SET SQL STRING
strSQL = "INSERT INTO " & Database_Name & ".[dbo]." & Table_Name & _
" ([Audit],[Audit Type],[Claim Received Date],[Date Assigned],[Date Completed]," & _
" [Analyst],[Customer],[ID],[Affiliate],[Facility],[DEA],[Acct Number],[Wholesaler],[Vendor],[Product],[NDC],[Ref],[Claimed Contract]," & _
" [Claimed Contract Cost],[Contract Price Start Date],[Contract Price End Date],[Catalog Number],[Invoice Number],[Invoice Date]," & _
" [Chargeback ID],[Contract Indicator],[Unit Cost],[WAC],[Potential Credit Due],[Qty],[Spend],[IP-DSH indicator Y/N]," & _
" [DSH and/or HRSA Number],[Unique GPO Code],[Comment],[ResCode],[Correct Cost],[CRRB CM],[CRRB Rebill],[CRRB Date])" & _
" VALUES ('" & sAudit & "', '" & sAuditType & "', '" & sClaimeReceivedDate & "', '" & sDateAssigned & "', '" & sDateCompleted & "', '" & sAnalyst & "', '" & sCustomer & "', '" & sID & "', '" & sAffiliate & "', '" & sFacility & "', '" & sDEA & "', '" & sAcctNumber & "', '" & sWholesaler & "', '" & sVendor & "', '" & sProduct & "', '" & sNDC & "', '" & sRef & "', '" & sClaimedContract & "', '" & sClaimedContractCost & "', '" & sContractPriceStartDate & "', '" & sContractPriceEndDate & "', '" & sCatalogNumber & "', '" & sInvoiceNumber & "', '" & sInvoiceDate & "', '" & sChargebackID & "', '" & sContractIndicator & "', '" & sUnitCost & "', '" & sWAC & "', '" & sPotentialCreditDue & "', '" & sQTY & "', '" & sSpend & "', '" & sIpDshIndicator & "', '" & sDSHorHRSANumber & "', '" & sUniqueGPOCode & "', '" & sComment & "', '" & sResCode & "', '" & sCorrectCost & "', '" & sCRRBCM & "', '" & sCRRBRebill & "', '" & sCRRBDate & "')"
Debug.Print strSQL
' SET TO CONNECTION VARIABLES
Set DBCONT = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
Set rs = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
' LOOP THROUGH AND APPEND TO TABLE
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Audit Data").Select
LastRowAudit = Cells(Cells.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
With ActiveSheet
DBCONT.Open "Driver = {SQL Server};Server = " & Server_Name & ";Database = " & Database_Name & _
";Uid = " & User_ID & ";Pwd = " & Password & ";"
For i = 2 To LastRowAudit
sAudit = Cells(i, 1)
sAuditType = Cells(i, 2)
sClaimeReceivedDate = Cells(i, 3)
sDateAssigned = Cells(i, 4)
sDateCompleted = Cells(i, 5)
sAnalyst = Cells(i, 6)
sCustomer = Cells(i, 7)
sID = Cells(i, 8)
sAffiliate = Cells(i, 9)
sFacility = Cells(i, 10)
sDEA = Cells(i, 11)
sAcctNumber = Cells(i, 12)
sWholesaler = Cells(i, 13)
sVendor = Cells(i, 14)
sProduct = Cells(i, 15)
sNDC = Cells(i, 16)
sRef = Cells(i, 17)
sClaimedContract = Cells(i, 18)
sClaimedContractCost = Cells(i, 19)
sContractPriceStartDate = Cells(i, 20)
sContractPriceEndDate = Cells(i, 21)
sCatalogNumber = Cells(i, 22)
sInvoiceNumber = Cells(i, 23)
sInvoiceDate = Cells(i, 24)
sChargebackID = Cells(i, 25)
sContractIndicator = Cells(i, 26)
sUnitCost = Cells(i, 27)
sWAC = Cells(i, 28)
sPotentialCreditDue = Cells(i, 29)
sQTY = Cells(i, 30)
sSpend = Cells(i, 31)
sIpDshIndicator = Cells(i, 32)
sDSHorHRSANumber = Cells(i, 33)
sUniqueGPOCode = Cells(i, 34)
sComment = Cells(i, 35)
sResCode = Cells(i, 36)
sCorrectCost = Cells(i, 37)
sCRRBCM = Cells(i, 38)
sCRRBRebill = Cells(i, 39)
sCRRBDate = Cells(i, 40)
DBCONT.Execute strSQL
Next i
End With
Call CloseDB
MsgBox i & " Lines Imported."
End Sub
Sub CloseDB()
On Error Resume Next
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
DBCONT.Close
Set DBCONT = Nothing
End Sub