How to determine the initial form of a verb
For the correct spelling of verbs in Russian, it is important to be able to determine their initial form.
A verb is a part of speech that denotes an action or indicates a state.
The initial (indefinite) form is a special grammatical form of the verb, the infinitive, and it stands out from the rest of the speech. The infinitive answers verb questions what to do? what to do?.
The name of this part of speech (infinitive) originates from the Latin language and is translated as «indefinite». This word (infinitivus), or rather its derivative «infinitive» indicates a special verb form. The situation is similar to nouns and their initial nominative form, which is always given in explanatory dictionaries.
If you ask these questions (what to do? What to do?) To any form of action, then you can get an initial view, which will be considered indefinite or zero.
Ordinary verbs can be conjugated by face and number, time, mood. The bottom line is that by the infinitive it is impossible to determine neither the time, nor the number, nor any other grammatical category of the taken verb (for example, he cuts (n.v, singular), what to do? — cut (?,?.). Always indefinite ends in -T, -ti or –Night.
Determining the initial form of a verb
Any verb indicating the performance of an action or a state can have an indefinite form, for example:
- Swam (what did you do?) — swim (what to do?);
- You go (what are you doing?) — go (what to do?);
- Hit (what will I do?) — hit (what to do?);
- Welcome (what am I doing?) — to greet (what make?).
It is not difficult to determine the initial form of the verb, it is enough just to ask one of the specified questions to the word. The ending (-t, -ti). For example:
- I will come — heyyou;
- Sew — sewthe;
- I run — runthe;
- Reads — readsthe;
- Gives — yesthe;
- Writes — Pisathe.
It is worth noting that some of the verbs have no (zero) ending at all (they end in –Night), eg:
- We take care — we take carewhose (root, no ending);
- Attracts — attractswhose (prefix, root, no ending);
- Lay down — lay downwhose (prefix, root, no ending);
- Bake — newhose (root, null ending).
You also need to pay special attention to some null verbs, which have the letter «Y» at the root of the word. For example:
- Walked around — aboutйty;
- Let’s go — forйty;
- Passed — transйty;
- Let’s go out — youйti.
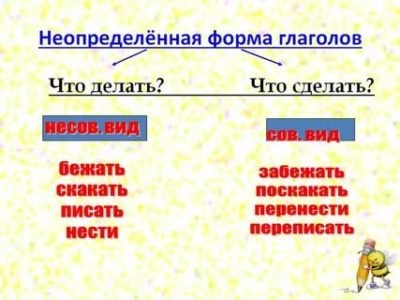
It is noteworthy that the infinitive can answer two questions. This diversity speaks of different lexical types of the word, which are called the perfect and imperfect form. The view speaks of the compliance of the action with the limit (occurs at the beginning or at the end).
For example, an imperfect form of action is not limited to any framework. This is a constant action that is periodically repeated (for example, eating, hitting, sleeping, guessing — what to do?).
The perfect form indicates an action that was completed, but retained the result at the time of the conversation (for example, swim, sleep, go — what to do?).
What is the verb infinitive for?
One of the reasons for using the infinitive is that in some words the endings are not stressed. This happens when people have doubts about the spelling of the letters «e» and «and» in word forms:
- Build or build;
- Glues or glues;
- We are healthy or healthy.
For the correct spelling of such words, you need to determine the conjugation of these verbs using the infinitive form. Everything is simple enough.
Another point is that verbs often get unstressed suffixes in the past tense. For example:
- Glue — glued;
- Sow — sow;
- To hate — hated.
- Depend — depended.
Based on the indefinite form, other word forms of verbs are created, for example:
To cherish — lele-yal, lele-yu, lele-jav (only the ending changes, the base remains exactly the same as in the infinitive).
That is why it is so important to accurately determine the initial view and highlight the unstressed suffix in it. Without this knowledge, it will not be possible to correctly write verbs in the past tense, past participles, gerunds.
Morphological characteristics of the infinitive form of verbs in Russian
Indefinite verbs are needed to indicate the action or state of what is being said. However, they do not have any changeable characteristics that are inherent in other parts of speech and forms. Infinitives received only immutable morphological definitions:
- View.
- Recoverability.
- Conjugation and transitivity.
Consider the sentence: They began to light the lights little by little. Let’s single out the morphological characteristics using the example of the initial form «ignite».
Ignite — answers the question what to do?
- It is a verb indicating action;
- Infinitive form;
- Imperfect species;
- Non-returnable;
- Intransitive;
- First conjugation.
Syntactic purpose — part of the compound verb predicate «started to light up».
Consider another proposal: She had a dream to be freed from captivity.
Free — answers the question of what to do?
- A verb indicating an action;
- Infinitive form;
- Perfect view;
- Intransitive;
- Returnable;
- First conjugation.
Syntactic purpose — inconsistent definition.
It is important to remember that the initial form of the verb answers the questions “what to do? what to do?» and can be any member in the proposal.
Source: https://nach-shkola.ru/kak-opredelit-nachal-nuyu-formu-glagola.html
Undefined verbs are used in dictionaries. What is an infinitive? The features are as follows:
- Verbs in an indefinite form answer the questions «what to do?» and «what to do?»
- Endowed with grammatical features of the type (perfect or imperfect).
- It is returnable and irrevocable.
- It is saved.
- When shaping, suffixes of the indefinite form of the verb -ty, -ty, -ch are used. For some verbs, it is ––––––––––––––––––––.
Important!Any verb word form can be initialized using the question «what to do?» or «what to do?»
Such word forms are called indefinite because it is impossible to determine their main grammatical features: time, face, mood, gender and number, how they differ from the rest.
Indefinite form of the verb: signs
Signs of the indefinite form of the verb
The main signs are the endings of the verbs in -ti, -ty and -ch. The questions «what to do?» Will help to determine this. and «what to do?»
Examples of education
The infinitive ends with the suffix -ty if it is preceded by a consonant: come, crawl, shake. The suffix –ty is used after the vowels: write, fly, shoot, pull.
In some words ending in -ch, the ending is missing in the initial form, and -ch is included in the root structure. For example, attract, bake, protect, crush.
How to use the indefinite form of a verb
The infinitive is required to form other verb forms and to check spelling.
Often the endings of verbs in personal word forms are unstressed, which raises doubts about their writing… To check your spelling, you need to know how to indefinate a verb.
For example:
- Build — What to do? build. This means that the correct ending is -you.
- Glues, glued — What to do? glue. The correct spelling is -it and -il.
- Hated — What to do? hate. Correctly write the vowel -e.
An unstressed suffix in an infinitive indicates its spelling in the past tense, in participial and participial forms.
To glue — to glue — to glue — to glue — to glue.
What is a reflexive or non-reflexive verb
Sometimes after the word-forming suffix -ty, -ty, -ch, an additional postfix -sy or -s is used. For example, pray, beware, ask, take cover.
Postfix allows you to define a returnable and non-returnable form.
The rule explains that word forms with -sya (-s) are considered reflexive and mean the action of someone or something directed at oneself, contact or position of an object. For example, topple over, deteriorate, equip, make your way.
Irretrievable infinitives express an action to someone, something. For example, reeling, eavesdropping, ironing.
Reflexive verb
Signs of a transitional and intransitive infinitive
Transition in an indefinite form allows you to identify an additional word indicating an object or phenomenon participating in the action.
As an additional word is used:
- A noun or pronoun used in the accusative case and without a preposition. For example, putting on a coat, cooking dinner.
- A noun (accusative or genitive) that expresses a relation or fraction of something and is used without a preposition. For example, pouring tea, waiting for guests.
- In a negative expression with an infinitive, a noun or pronoun in the genitive is used. For example, not having a chance not to hurt her.
Additional words give meaning to the infinitive, and without them the essence of what is happening is lost. Some part of the action is transferred to objects or circumstances, they acquire a clear semantic load.
In an intransitive infinitive, an action denotes one word.
Perfect and imperfect views
Verb words are classified into perfect and imperfect.
Imperfect ones characterize an action that lasts without a specific time frame. These actions can be called eternal, there is no indication of their completeness or incompleteness. The question «What to do?» Approaches them.
- I’m going to go on a trip.
- The street lights began to go out.
Perfect infinitives point to action taken or whatever will happen. The result can already be observed or it is still expected. The question «What to do?» Is used.
- After opening the can, the contents must be transferred.
- Did you receive instructions on what to report?
Known insignificant part of dual infinitives… They are used in both forms in one word form. They are defined by meaning. A standard question can be posed for dual verbs in the infinitive.
- The whole area should be cleaned up tomorrow. — «What to do?».
- Clean up trash on your desk and in your room. — «What to do?».
- It is necessary to explore the city. — «What to do?».
- They were to explore the city at dawn. — «What to do?»
Perfect and imperfect view
Knowledge of any language is unthinkable without knowledge of the basic units of speech. No less important are grammatical rules that allow all parts of speech to be harmoniously connected with each other using cases, prepositions, conjugation. Russian is a predicative language, it often uses categories of action or verb constructions. When familiar with this part of speech, students will learn how it is formed and what the indefinite form of the verb is.
In the textbook for grade 4, when children get acquainted with this concept, a rule is given.
The indefinite form of the verb is the initial and unchanging form from which all the verbal parts of speech (participles, verbal adjectives) and the forms of the verb formed during conjugation are formed.
What questions does the indefinite form answer: what to do? (what to do?).
The indefinite form in linguistics is called the term «infinitive» (from Lat. Infinitus). It is impossible to say by the infinitive who and when performs any action (for example, “to walk”: it is not clear who did it and when, there is no indication of either the number or the time). Its morphological features are suffixes -t (s) (for example, idyou, skazathe) or the ending of the root in -night (for example, lewhose,cewhose).
Features
The indefinite form of the verb does not change. This is the peculiarity of the infinitive, so it cannot be conjugated or otherwise changed.
The initial form of a verb can only have constant signs:
- Conjugation (1st, 2nd, multi-conjugate).
- Returnable (returnable, non-returnable).
- Transition (transient or intransitive).
- View (imperfect or perfect).
The infinitive is devoid of signs of a person, time or number, so it is impossible to tell from it who is performing an action and when.
How to find the infinitive
For those who learn Russian as a foreign language or for children who do not read enough, the question of finding an infinitive can present some difficulties. How to find the indefinite form of a verb.
Those who know Russian at the native level, as a rule, do not experience any particular difficulties with this. How to put a verb in an indefinite form: mentally ask questions of the infinitive — «what to do?» or «what to do?»
Also, the infinitive can be defined in another way:
- Find out what kind of verb in a sentence belongs to.
- «Cut off» personal endings that appear during conjugation, and (if necessary) the past tense suffix -l-.
- Substitute the infinitive suffix -ty (s) to the rest of the part, or simply ask the appropriate question.
Let’s take the following example: «They diligently wrote letters in a notebook.» The initial form in this case will be «prescribe».
How we defined it:
- We ask the question: They (what did they do?) Prescribed.
- The question «what did you do?» indicates that the verb is imperfect (without the prefix «s»), which means that to define the infinitive, you also need to ask without the prefix «s»: «what to do?».
- Removing the ending -and and the suffix of the past tense –L-.We have: prescription-.
- Substitute the infinitive suffix -ty to the rest of the word: (what to do?) — register.
Note that in this case you can make a mistake and name it as an answer “register”, it will be wrong, since “register” answers the question “what to do?”, That is, it stands in perfect form.
Important!When determining the initial form, you need to put a question to the verb in the sentence itself in order to determine its form.
A tip on how not to be mistaken in determining the (im) perfect form: all prefixes and suffixes (except for the past tense suffix -l-) of the verb form with which you are working in the text are preserved in the infinitive.
Pay attention! In the process of searching N.F. you can go in two ways: ask the question — «what to do?» or «what to do?», or follow the above method.
Syntactic function
What is the role of the indefinite form of the verb in the sentence. It can perform various syntactic functions. A summary of the possible members of the sentence, expressed by the infinitive, is given in the table:
The infinitive almost never occurs as a complement. Nevertheless, in the sentence “He ordered coffee to be served”, one can interpret “serve” as an addition (ordered about what?).
Definitiononline
If you find it difficult to determine the initial form yourself or are not sure that you did it correctly, you can test yourself using online services for.
Since the definition of the infinitive is an obligatory part of it, you can go to any website that offers this service and enter the desired verb in the form in which it is used in the sentence.
The first word that will be indicated will be N.f. verb ..
Note that, in general, the ability to identify parts of speech, change them by faces, numbers, times, largely depends on innate literacy and linguistic instinct. But even if this is not all right, it is not so difficult to learn which questions the indefinite form answers. For the rest, you should adhere to the above schemes and tips.
To consolidate (or form) knowledge on this topic, a number of tasks and exercises can be recommended:
- Distinguishing parts of speech with similar endings (put a cast iron in the oven (noun) — bake pies (ch.), Sing, come here! (Proper name) — sing songs (ch.)).
- Converting the imperfective verb to the perfect verb and vice versa.
- Formation of a verb from a noun (for example, travel — travel, food — eat, trip — travel).
With practice, the necessary skills will come.
Source: https://vorota21vek.ru/neopredelennaya-forma-glagola-zabotimsya-chto-takoe-neopredel-nnaya-forma-glagola.html
Indefinite verb form (initial form, infinitive)
Any verb can be put in such a form, which is called the initial form. It is also called indefinite verb or infinitive… The indefinite form of the verb received such a name due to the fact that it does not show either time, number, person, or gender, that is, these signs are not defined.
Verbs in an indefinite form answer the questions of what to do? what to do? The verbs that answer the question what to do? Are imperfective verbs. The verbs that answer the question what to do? Are perfective verbs.
The indefinite form of the verb most often ends in —the or —you (sing, dance, walk, get out, find, carry, crawl). These are suffixes. An indefinite form can be obtained with the help of other inflectional suffixes: -is (to steal), -to carry (to carry, to row).
Sometimes the indefinite form of the verb ends in -ch, but these letters are part of the root: they guard — guard (the root guard-, guard-), lie down — lie down (root lie-, lie-). In some textbooks for elementary school -ch is considered a suffix, and in high school they teach that -ch is included in the root.
In the indefinite form of verbs, if it does NOT end in –ti, it is always written ь. It is also written after the letter h (-ch) — this is a spelling for the rule: ь in the indefinite form of the verb.
The letters of the vowels in the indefinite form of the verbs before -ty are most often suffixes. They can be different: -a, -e, -i, -i, -o.
If they are unstressed, then in their place there is always a spelling. These letters-suffixes cannot be determined by the rule, they can only be recognized by the dictionary and memorized.
Suffix -a: hear, swim, jump, listen Suffix -e: see, offend, depend Suffix -i: build, iron, cook, glue, set, build
Suffix — I: bark, melt, blow, sow
Verbs often contain a special suffix -sy or -s… It is special because it is after. To distinguish it from other suffixes, scientists gave it their name — postfix («Attached after»). Examples: swim, listen.
There is confusion about the indefinite form of the verb and the verbs used in the complex future tense.
The future difficult tense is formed just from the imperfective verbs and answers the questions what will I do? What will they do ?, formed from the verb to be (I will write, will smile).
Although the infinitive remains the infinitive, elementary school teachers teach that this is the future tense, not the initial form. In the future difficult tense, only the verb «to be» changes in persons and numbers.
Morphological signs of the infinitive
The infinitive or indefinite form of the verb is the unchangeable, unconjugated form of the verb. It has only constant grammatical features of verbs:
View — perfect, denoting a completed action (rewrite, wash), imperfect (cook, give).
Recurrence — returnable (to be heard, to wrap up), irrevocable (to fold, close).
Transitivity — transitional (read a book, see a picture), intransient (have fun, live).
Conjugation — I conjugation (do, mix) and II conjugation (love, draw).
Also, the infinitive of the verb is inherent inflectional sign of a pledge: active voice (Mom decided to make lasagna); passive voice (Lasagna should be ready soon).
We train in the formation of verbs of an indefinite form
Let’s find verbs in an indefinite form in the text.
It’s good in the summer early (what to do?) To get up and (what to do?) Go to the lake. It’s nice (what to do?) Sunbathe in the sun, (what to do?) Swim in clear water, (what to do?) Pick mushrooms and berries in the forest, (what to do?) Listen to birdsong.
It is interesting (what to do?) To observe the behavior of insects, (what to do?) To play football with friends. It is useful (what to do?) To work in the garden and in the garden, (what to do?) To help the elders with the housework.
I (what will I do?) Will have a great (difficult future time, singular, not n.f.) time in the summer.
Let’s put the verbs in an indefinite form.
Let’s take — what shall we do ?, what shall we do? take
Let’s add — what shall we do? What shall we do? add
Shake it up — what shall we do? What shall we do? whip
Pour out — what shall we do? What shall we do? pour out
Let’s add — what shall we do ?, what shall we do? add
Let’s mix — what shall we do? What shall we do? mix
We bake — what do we do? What do we do? bake
Flowed — what did you do ?, last century, what to do? leak (root tech-leak)
I cut — what am I doing ?, present, what should I do ?, cut (root cut-cut)
I will save — what will I do ?, bud.v., what to do?
I will captivate — what will I do ?, bud.v., what to do ?, captivate (root attract)
Form indefinite verbs using these suffixes and prefixes.
Prefixes VZ-, PO-, PRI-, OT-. Roots -SLEEP-, -CASHL-, -PLYAS-. Suffixes -ИВА-, -НУ-, -ИВА-, -А-, -Я-, -СЯ.
Take a nap — prefix vz-, suffix -nu-,
nap — prefix po, suffix -а,
cough — the prefix is po, the suffix is -ya-,
to clear your throat — prefix from-, suffix -я-,
to dance — prefix po, suffix -a-,
to dance — prefix prefix-, suffix -yva-,
to dance — the prefix from-, suffix -yva-.
Source: https://7gy.ru/shkola/russkij-yazyk/1231-neopredelennaya-forma-glagola.html
The indefinite form of the verb in English
›Verbs› Grammar of the Verb ›Indefinite Form of the Verb in English: the Infinitive and Its Usage
The English verb, as a grammatical concept, is very complex and diverse. To study all the moments of its use, it is necessary to learn more than a dozen rules and hundreds of exceptions (if we are talking, for example, about irregular verbs).
But today we will turn to the very basics of verb grammar, because the topic of the material is the indefinite form of the verb in English.
Let’s consider what is hidden behind the dictionary form of the verb, find out how the meaning of the infinitive can change depending on the place in the sentence and figure out what indefinite forms are distinguished in the English language.
How is the vagueness of the verb expressed?
Everyone knows that verbs express the course of any event. The personal forms of the verb, due to the fact that they change the ending, help us determine the time of the action and the person performing it. But the indefinite form is unchanged in its purpose, it can only indicate the execution of an action, without going into any details.
For example, take sentence I to read (I love to read), where to read is the infinitive that answers the question «what to do?» Try to determine which person the action belongs to.
This is impossible, since the infinitive is unchanged, no matter what pronoun it is used: he (he) s to read, they to read.
Also, nothing can be said about the time of action: I like to read, but that does not mean that I am reading now, I read yesterday, or I will read tomorrow. Therefore, infinitive verbs are called indefinite.
How is the indefinite form of the verb used in English?
The infinitive (as the indefinite form is called in another way) is the basis for the formation of personal forms. This is what we study when meeting new vocabulary. Remember the beginning of your classes? You were probably explained to write — write, to speak — speak, talk, to study — study, etc. The to particle is a distinctive feature inherent only to the infinitive (it is important not to confuse it with the preposition to, which refers to pronouns or nouns).
But, since English is the language of exceptions, there are several situations in which the infinitive form is used without the to particle. The table below will help us to consider these cases.
| Using the infinitive without to | ||
| Situation | Example | Transfer |
| Use of modal verbs in a sentence (except for ought to) | She can drive very well. I must go home. It may be true. | She can drive very well. I have to go home. That may be true. |
| The following words are used in the statement: make (force), help (help), let (allow), dare (dare). | They always help their father wash the car. Let me answer. | They always help their dad wash the car. Let me answer. |
| The sentence uses the verb will or shall. | Jack will visit |
Source: https://speakenglishwell.ru/neopredelennaya-forma-glagola-v-anglijskom-yazyke/
The indefinite form of the verb in English in detail
Good afternoon friends! Today I will tell you about what the indefinite form of the verb is in English. What do you remember when you hear the phrase «indefinite verb»? Exactly! The initial form of the word, answering the question «what to do?», «What to do?»
Generally speaking, this general description holds true for the British language as well. But, here it should be noted that different sources distinguish in the English language several varieties of an indefinite form of a word expressing an action, namely:
- The initial, from which actions are formed in consequence in all times.
- The participle is a verbal adjective.
- Gerund is a verbal noun.
And yet, proceeding from the meaning of the term itself, it is more correct to consider the first of the proposed options as «an indefinite form of the verb» (Infinitive). Such «initial action words» are called the infinitive, which translates as Infinitive. We see a complete coincidence of the translations of these grammatical terms. Our today’s conversation will go about the infinitive.
When do we use it?
Most often, you can find the infinitive as part of a complex predicate, translated in such a way that it answers the questions «what to do?», «What to do?»:
Robert s to collect coins. Robert loves collecting coins.
Ann wanted to catch a taxi. Anna wanted to catch a taxi.
Sometimes you can find the initial form of a verb in a different role in a sentence, for example:
Have you noticed that there is an unchangeable «to» part in the selected words? This is the particle that points to the infinitive. When you see it in a statement before a word denoting an action, be sure that it answers one of the above questions.
We skip but don’t forget
But in some cases we omit this particle in sentences. Consider the table below. It contains words that oblige us to use «shortened infinitive» or bare infinitive, and example sentences.
| To particles do not require: | Example: | Translation: |
| Modal ch .: can (could) — to be able, to be able, must — should, may (might) — you can, shall (should) — should, will (would) — should | My mother can sing as a singer. stay inbed. | My mom can sing as a singer. you should to park in bed. |
| Make — force, let — allow | She makes me tidy my room. Let me see. | She makes me remove your room. take a look. |
| Perceptual words, for example see, feel in the Complex object, so the translation of sentences is somewhat different from the rest of the examples. | She saw him knock the door. I felt it cool at me. | She saw him knocked at the door. I felt that he looks on me. |
| Help, dare | Children always help their mother clean the house. | Children always help mom remove house. |
It’s simple, isn’t it? Then let’s go a little deeper into the grammatical varieties of infinitive.
Modified undefined?
Unlike Russian in British, the initial form of the verb has several varieties. Their number for each separate word depends on whether it can have a passive voice, whether it can be continued. Their maximum number is six. A table of infinitive varieties will help you understand them.
As you can see from the diagram, there are only two varieties of the indefinite verb in the passive voice.
I hope my story helped you understand what the indefinite form of the verb is in English.
Practice English with your friends and you can use any kind of infinitive in your speech easily and naturally.
You can read even more interesting and useful information about foreign languages in our blog, subscribe and learn a foreign language playfully.
By subscribing, you will receive, completely free of charge, an excellent basic phrasebook in three languages, English, German and French. Its main plus is that there is Russian transcription, therefore, even without knowing the language, you can easily master colloquial phrases.
I was with you, Natalya Glukhova, I wish you a good day!
Don’t forget to tell your friends what you learned today.
(2 5,00 of 5)
- Payments in Germany in connection with the coronavirus for pensioners
Source: https://vivaeurope.ru/languages/english/gramatika/glagol
Infinitive. Infinitive in Russian
An infinitive is an indefinite form of a verb. Answers the questions what to do? what to do? Examples of verbs in the indefinite form: live, speak, think, love, work, say, leave.
The infinitive is the impersonal, initial form of the verb. She has no face, gender, number and time.
Move, release, recover, refuse.
There are no forms of any 1st, 2nd or 3rd person, no plural or singular, no present, past or future tense, no masculine, feminine, or neuter.
The term comes from the Latin word infinitivus — indefinite. It is in this form that verbs are indicated in dictionaries.
«Indicate / write out verbs in an indefinite form.» How to find out the infinitive
The infinitive — an indefinite form of the verb — can be recognized by the suffixes -ty or -ty. For reflexive verbs, the postfix -sya or -s is added.
What to do? Walk, sing, play, carry, graze, wash.
What to do? Shout, jump, bend, bring the ride.
The ending -т is usually written after a vowel sound: think, love, interfere, chop, give birth, blow.
The ending -ti, as a rule, appears after a consonant sound: weight-ti, go-ti, revenge, graze, shake, grow. However, in the case of an unstressed suffix, it is also in this case reduced to -ty: to climb.
Some verbs in an indefinite form end in -ch. Cut, bake, distract, warn, burn, etc. In this case, -ch is no longer an ending, but a part of the root.
Write out the verbs in indefinite form. Example task
We went over to see and figure out if something had happened.
There are four verbs in this sentence — come up, look, figure it out, it happened.
Two of them answer the questions what to do? what to do? — look and understand verbs. These are the infinitives — we need to write them out.
Example. The indefinite form of the verb «read»
Let’s say we need to form an indefinite form from the verb read (Vasya will read this book tomorrow).
What will it do? Will read it.
What to do? Read it.
The indefinite form of the verb is to read.
Example. The indefinite form of the verb «will be»
Another task — you need to form an indefinite form from the verb will (will you be at home tomorrow?)
What will you do? You will.
What to do? To be.
How to write indefinite verbs? How to put these verbs in an indefinite form?
«Form verbs of an indefinite form from these verbs» is a popular task from school textbooks. How to do it: how to put these verbs in an indefinite form?
Indefinite verbs answer the questions what to do? what to do?
- Ask the question: what to do? what to do? The answer is an undefined form.
For example, the personal forms of the verbs are given: the girl was walking, dad works, they came up with.
What to do / do? Walk, work, come up with. These are indefinite forms — infinitives.
Morphological analysis of the verb in an indefinite form. Grammatical signs of the infinitive
The infinitive has only constant verbal features in morphological analysis:
Morphological analysis of the indefinite form of the verb. Examples of
I went for a walk in the yard.
(What to do?) To walk — a verb, denotes an action; indefinite form; imperfect form; intransitive; irreversible; I conjugation.
The syntactic role is the circumstance of the goal.
The teacher wanted to understand why we are silent. (What to do?) To understand — a verb, means a state; indefinite form; perfect form; transitional; irreversible; I conjugation.
The syntactic role is part of the compound verbal predicate (I wanted to understand).
The infinitive in a sentence: the syntactic role of the infinitive
The infinitive can play the role of any member of the sentence.
-
Subject. There is no point in discussing this issue.
-
Part of the predicate. I really want to see you.
-
Addition. Dad asked me to think about my plans for the summer.
-
Inconsistent definition. He had a habit of talking very loudly.
-
The circumstance of the goal. We went to the forest to pick mushrooms.
Read more about the members of the proposal: Common proposal — what is it? How to write it and how to distribute the proposal
Sentences with an indefinite verb. Examples of
And even you cannot imagine how unhappy I am! (A.P. Chekhov)
I went out to smoke in the buffet (M.A.Bulgakov)
We need to come to an agreement with you on the terms of the delivery of the regiment. (M.A.Sholokhov)
Of course, he had to see the picture more than once. (Yu. Trifonov)
I often try to understand why my grandfather was so gloomy? (S. Dovlatov)
Just think that I myself once dreamed about it! (D. Granin)
It’s fun to walk across the open spaces together. (M. Matusovsky)
Ah, if only there was someone to talk to. (T. and S. Nikitin)
Source: https://www.anews.com/p/110739141-neopredelennaya-forma-glagola-infinitiv-v-russkom-yazyke/
What is the initial form of a verb? How to define it?
Initial, original form of the verb — this is an indefinite form, or an infinitive, which, depending on the grammatical category of the type of the verb, answers the question: what to do? or what to do?
Let’s repeat what words in Russian are called verbs.
In determining the words of the part of speech under consideration, the following questions were asked:
We will ask these questions for any form of the verb, if we want to establish its initial form, which is called the indefinite form, or the Latin term — «infinitive».
The verb changes in persons and numbers (conjugated), in tenses and moods.
The initial form is called indefinite, because for words in this form it is impossible to determine many grammatical categories of the verb: person, number, mood, tense, gender.
How to determine the initial form of a verb?
Every verb that denotes an action or state has an initial form, for example:
- (what does he do?) walks — (what to do?) walk,
- (what are you doing?) you write — (what to do?) write,
- (what will I do?) get ready — (what can I do?) get ready
- (what shall we do?) let’s go — (what shall we do?) go.
You can «find out» the initial form of the verb by asking the questions already asked to the words of this part of speech, and by the endings -ty, -ty, for example:
- to ask
- overtake
- twirl
- breathe
- bear
- crawl away.
Some verbs ending in -ch do not have this ending, for example:
- keep — root / zero ending,
- neglect — root / zero ending,
- draw — prefix / root / null ending,
- bake — prefix / root / zero ending / postfix.
Let’s remember the spelling of the indefinite form of the verb «come» with the letter «y» in its root. Let’s compare:
- get around
- come in
- go over
- log off.
What is the indefinite form of the verb used for?
First, for many word forms of verbs, personal endings are unstressed. For example, there are doubts about the spelling of the letters «e» or «and» in the forms of words:
- build or build
- glues or glues,
- get well or get well.
To correctly spell words in a similar situation, it is necessary to establish the conjugation of the verb by its indefinite form. The algorithm for this is explained in detail in this article.
Secondly, the past tense of many verbs is an unstressed suffix, for example:
- glue — glue-l,
- sow-th — sow-l,
- hate — hate
Many verb forms are formed from the stem of the indefinite form, for example:
sow-sow-sow-l, sow-lice, sow-i-nn-th, sow-in, sow-lice.
Therefore, it is important to correctly determine the indefinite form, and in it the unstressed verb suffix, the knowledge of which will help in writing the verb forms of the past tense, the real and passive participles of the past tense, forms of adverbial participles.
Morphological signs of the indefinite form of the verb
The initial form of the verb denotes the action or state of the object, but at the same time it does not have fickle verbal signs of a person, number, mood, tense and gender. The infinitive has only constant morphological features:
- view
- transitivity
- recurrence
- conjugation.
The stars began to fade slowly.
Let us indicate the morphological features of the word «go out».
I. Go out (what to do?)
- verb, denotes an action;
- indefinite form
- imperfect species
- intransitive
- irrevocable
- I conjugation.
II. The syntactic role is part of the compound verbal predicate «began to fade.»
The dream of breaking free from household chores was strong in her.
I. Break out (what to do?)
- verb, denotes an action;
- indefinite form
- perfect view
- intransitive,
- returnable
- I conjugation.
II. The syntactic role is an inconsistent definition.
lesson «The indefinite form of the verb»
Source: https://russkiiyazyk.ru/chasti-rechi/glagol/chto-takoe-nachalnaya-forma-glagola.html
I want to get initial form of natural English words, e.g.:
'words' -> 'word'
'Jhon' -> 'John'
'openning' -> 'open'
I have tried python Stemer lib:
st=Stemer.Stemer()
for w in ('very', 'words', 'openning'):
print st.stemWord(w),
>>>veri word open
i expect ‘very’ but instead got ‘veri’
then nltk.corpus.wordnet lib:
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
wordnet.synsets( 'beans' )
[Synset('bean.n.01'),
>>>Synset('bean.n.02'),
>>>Synset('bean.n.03'),
>>>Synset('attic.n.03'),
>>>Synset('bean.v.01')]
it give more info but not a quick dictionary.
LancasterStemmer can not get ‘english’ as ‘english’:
from nltk.stem.lancaster import LancasterStemmer
st = LancasterStemmer()
st.stem('english')
>>>>'engl'
enchant lib method check() and sugguest() is not suitable:
>>> import enchant
>>> d = enchant.Dict("en_US")
>>> d.check("Hello")
Any method to get quick original form, for a document text?
continuing
weakness maintenance unscrupulous
existence
smugglers undertake uncovered
10.3.2.
Give English equivalents of the following words and collocations:
платить
налоги,
неудачник,
генерал-губернатор,
проложить
тропу, огром-ные прибыли, эффективность,
запрет, обойти систему, голод (истощение),
взя-точничество, малая часть.
10.3.3.
Say whether the following statements are true or false:
-
Corruption
has been the major problem for the U.S. Service. -
Everybody
likes to pay taxes. -
The
reality is that the Customs Service has always been something of an
undercat. -
If
it had been not for the supplies, the American force in Canada would
have suffered from famine. -
The
White House Office of National Drug Control Policy estimates that
federal agents in 1998 seized 120 metric tons of cocaine and 1,580
kilograms of heroin.
10.3.4. Write an abstract
of the text.
Unit
11. Customs Tariffs and International Trade
11.1.
Pre-text Assignments.
11.1.1. Practice
the reading of the following words and guess their meaning:
tariff
barter record exchange preferentially procedure
area
general
duty result transit licence
quota
domestic
11.1.2. Give
the initial forms of the following words and state what parts
of
speech they belong to:
permissible
equipment
completely valuation account protection
arrangement comparative differentiate restrictive
11.1.3.
Read the following words and their translation. Try to memorize the
vocabulary:
|
trace |
проследить |
|
interfere |
вмешиваться |
|
costly |
дорогой |
|
permissible |
допустимый |
|
restrain |
сдерживать; |
|
удерживать |
|
|
consequence |
следствие |
|
impel |
побуждать, |
|
подталкивать |
|
|
mercantilist |
расчетливый |
|
dictum |
афоризм, |
|
максима, |
|
|
discourage |
не |
|
осуществлению, |
|
|
препятствовать, |
|
|
отговаривать |
|
|
encourage |
ободрять; |
|
поддерживать |
|
|
revenue |
фискальный |
|
фискальные |
|
|
yield |
приносить |
|
плоды; |
|
|
результат, |
|
|
en |
по |
|
quantitative |
количественный |
|
commodity |
товар |
|
windfall |
неожиданная |
|
ad |
тарифы, |
|
trade |
предпочтения |
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
People in general have no difficulty coping the new words. We can very quickly understand a new word in our language (a neologism) and accept the use of different forms of that new word. This ability must derive in part from the fact that there is a lot of regularity in the word-formation process in our language.
In some aspects the study of the processes whereby new words come into being language like English seems relatively straightforward. This apparent simplicity however masks a number of controversial issues. Despite the disagreement of scholars in the area, there don´t seem to be a regular process involved.
These processes have been at work in the language for some time and many words in daily use today were, at one time, considered barbaric misuses of the language.
What is Coinage?
Coinage is a common process of word-formation in English and it is the invention of totally new terms. The most typical sources are invented trade names for one company´s product which become general terms (without initial capital letters) for any version of that product.
For example: aspirin, nylon, zipper and the more recent examples kleenex, teflon.
This words tend to become everyday words in our language.
What is Borrowing?
Borrowing is one of the most common sources of getting new words in English. That is the taking over of words from other languages. Throughout history the English language has adopted a vast number of loan words from other languages. For example:
- Alcohol (Arabic)
- Boss (Dutch)
- Croissant (French)
- Piano (Italian)
- Pretzel (German)
- Robot (Czech)
- Zebra (Bantu)
Etc…
A special type of borrowing is the loan translation or calque. In this process, there is a direct translation of the elements of a word into the borrowing language. For example: Superman, Loan Translation of Übermensch, German.
What is Compounding?
The combining process of words is technically known as compounding, which is very common in English and German. Obvious English examples would be:
- Bookcase
- Fingerprint
- Sunburn
- Wallpaper
- Textbook
- Wastebasket
- Waterbed
What is Blending?
The combining separate forms to produce a single new term, is also present in the process of blending. Blending, takes only the beginning of one word and joining it to the end of the other word. For instance, if you wish to refer to the combined effects of smoke and fog, there´s the term smog. The recent phenomenon of fund rising on television that feels like a marathon, is typically called a telethon, and if you´re extremely crazy about video, you may be called a videot.
What is Clipping?
Clipping is the process in which the element of reduction which is noticeable in blending is even more apparent. This occurs when a word of more than one syllable is reduced to a shorter form, often in casual speech. For example, the term gasoline is still in use but the term gas, the clipped form is used more frequently. Examples
- Chem.
- Gym
- Math
- Prof
- Typo
What is Backformation?
Backformation is a very specialized type of reduction process. Typically a word of one type, usually noun, is reduced to form another word of a different type, usually verb. A good example of backformation is the process whereby the noun television first came into ude and then the term televise is created form it.
More examples:
- Donation – Donate
- Option – Opt
- Emotion – Emote
- Enthusiasm – Enthuse
- Babysit – Babysitter
What is Conversion?
Conversion is a change in the function of a word, as for example, when a noun comes to be used as a verb without any reduction. Other labels of this very common process are “category change” and “functional shift”. A number of nouns such as paper, butter, bottle, vacation and so on, can via the process of conversion come to be used as verbs as in the following examples:
- My brother is papering my bedroom.
- Did you buttered this toast?
- We bottled the home brew last night.
What is an Acronym?
Some new words known as acronyms are formed with the initial letters of a set of other words. Examples:
- Compact Disk – CD
- Video Cassette Recorder – VCR
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration – NASA
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization – UNESCO
- Personal Identification Number –PIN
- Women against rape – WAR
What is Derivation?
Derivation is the most common word formation process and it accomplished by means of a large number of small bits of the English language which are not usually given separate listings in dictionaries. These small bits are called affixes. Examples:
- Unhappy
- Misrepresent
- Prejudge
- Joyful
- Careless
- Happiness
Prefixes and Suffixes
In the preceding group of words, it should be obvious that some affixes have to be added to the beginning of a word. These are called prefixes: unreliable. The other affix forms are called suffixes and are added at the end of the word: foolishness.
Infixes
One of the characteristics of English words is that any modifications to them occur at the beginning or the end; mix can have something added at the beginning re-mix or at the end, mixes, mixer, but never in the middle, called infixes.
Activities – WORDS AND WORD FORMATION PROCESSES
Activity 1
Identify the word formation process involved in the following sentences:
- My little cousin wants to be a footballer
- Rebecca parties every weekend
- I will have a croissant for breakfast.
- Does somebody know where is my bra?
- My family is vacationing in New Zealand
- I will babysit my little sister this weekend
- Would you give me your blackberry PIN?
- She seems really unhappy about her parents’ decision.
- I always have kleenex in my car.
10. A carjacking was reported this evening.
(To check your answers, please go to home and check the link: Activities Keyword)
*You may require checking other sources
Because the form of a word can change, that is, a certain point of reference, a form that is considered to be the starting point. For each part of speech the way of determining the initial form of a word is different. Here, for example, what is the initial form of the noun:
But how to find the initial form of adjectives:
And the initial form of the verbs:
In order for this form to be, in Russian, it is necessary that this word should change in its forms, after it was declined by the rules of the Russian language.
If such changes are observed, then the verb, such a form is uncertain and ends in — Th. For example — to escape.
If we deal with a noun, then the word must necessarily stand in the Nominative case and singular, since from such its characteristics, proceed from the beginning, inclined it.
As for the adjective, then the main thing is the gender and the word, it must necessarily be in the form of a masculine gender and nothing else.
Each variable part of the word has its own definite initial form, which is determined according to the rules of the Russian language.
So:
the noun is considered to be the initial form of the nominative case and the only number, of course, except those words that are used exclusively in the plural (pants, scales, etc.)
The adjectives have a masculine gender and also a single number;
Verbs are an undefined form of a word that answers such vague questions as «what to do?», «What should I do?».
Pronouns have a masculine gender and a single number.
Term Initial form words is meaningful only for the variable parts of speech, since in the immutable parts of speech the form is only one. Therefore, we find the initial form for nouns, adjectives, verbs, pronouns, participles, numerals, that is, parts of speech in which a change in case, gender, number, and time is possible.
For nouns, the initial form consider the nominative case of the singular. For example, when performing the morphological analysis of the word Valley, we find its initial form — the noun VALLEY.
For verbs, the initial form is an infinitive, an undefined form. For example, if you want to perform a morphological analysis of the word Runs, we find its infinitive BEAT which answers the question What should I do?
For adjectives, the initial form will be form of the masculine gender and nominative case, and this applies to the short adjectives and adjectives in a comparative degree. For example, you need to perform a morphological analysis of the adjective Transparent. We put it in its full form and get a TRANSPARENT.
Similarly we do with the sacraments, even though they are the verb form. Example of the morphological analysis of the sacrament. Expanded. The initial form is the word Expanded, the masculine gender and the full form.
For numerals, the initial form will be the nominative. For example, for the word Eight, this word is EIGHT.
For pronouns, the initial form it is again the nominative case of the masculine gender, or simply the masculine gender. For example, when morphologic analysis of the pronoun Eu, we single out the initial form of SHE.
Each changeable parts of speech have their own initial form. For example, a noun is a nominative singular case, except for words that are used only in the plural: apple trees — apple trees, boots — boots, but scales, rakes, trousers, inks, rails.
In adjectives, the initial form is the masculine word of the singular: blue, beautiful, and without malice.
In verbs, the initial form is an undefined verb form, or an infinitive: ask, distract, bring.
У mutable pronouns the initial form will be the nominative singular of the masculine gender (if there is a genus): mine, yours, which.
Pronouns what is it do not change by case, so they have the initial form — the masculine gender of the singular.
Forms of words there are only variable words, and for the initial form of the word it is customary to take exactly that variant of the use of the word, which is written in dictionaries.
Forms of words are called variants of using the same word, which have different values of number and case, time, face, etc., etc.
Forms of words are formed using different endings:
У what parts of speech is the initial form of the word?
Initial form:
- noun nouns;
- adjectives;
- the number of numerals;
- pronouns;
- verbs.
The initial form of the word is the very form in which the word is given to us in dictionaries. If a word can change, it can acquire other forms (by gender and number). For example: I jump, you jump, we jump, cat, cat, cat, etc.
The form of the word is known in the Russian language is morphology, forms are only for mutable words and one of the forms is usually called initial, the initial one is the very form in which the word is given in dictionaries, below are the initial forms of different parts of speech.
First, let’s see what a word form is.
Form of the word is a word that has several variants and they express several grammatical meanings (time, number, face, etc.)
What is the initial form of the word?
The initial form of a word is a word that has the ability to change (noun, verb, pronoun, adjective and numeral). If you need to find the initial form of a word, you can find it simply in the dictionary.