The INDEX function returns a value or the reference to a value from within a table or range.
There are two ways to use the INDEX function:
-
If you want to return the value of a specified cell or array of cells, see Array form.
-
If you want to return a reference to specified cells, see Reference form.
Array form
Description
Returns the value of an element in a table or an array, selected by the row and column number indexes.
Use the array form if the first argument to INDEX is an array constant.
Syntax
INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num])
The array form of the INDEX function has the following arguments:
-
array Required. A range of cells or an array constant.
-
If array contains only one row or column, the corresponding row_num or column_num argument is optional.
-
If array has more than one row and more than one column, and only row_num or column_num is used, INDEX returns an array of the entire row or column in array.
-
-
row_num Required, unless column_num is present. Selects the row in array from which to return a value. If row_num is omitted, column_num is required.
-
column_num Optional. Selects the column in array from which to return a value. If column_num is omitted, row_num is required.
Remarks
-
If both the row_num and column_num arguments are used, INDEX returns the value in the cell at the intersection of row_num and column_num.
-
row_num and column_num must point to a cell within array; otherwise, INDEX returns a #REF! error.
-
If you set row_num or column_num to 0 (zero), INDEX returns the array of values for the entire column or row, respectively. To use values returned as an array, enter the INDEX function as an array formula.
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
Examples
Example 1
These examples use the INDEX function to find the value in the intersecting cell where a row and a column meet.
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter.
|
Data |
Data |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Apples |
Lemons |
|
|
Bananas |
Pears |
|
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=INDEX(A2:B3,2,2) |
Value at the intersection of the second row and second column in the range A2:B3. |
Pears |
|
=INDEX(A2:B3,2,1) |
Value at the intersection of the second row and first column in the range A2:B3. |
Bananas |
Example 2
This example uses the INDEX function in an array formula to find the values in two cells specified in a 2×2 array.
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting two blank cells, input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
=INDEX({1,2;3,4},0,2) |
Value found in the first row, second column in the array. The array contains 1 and 2 in the first row and 3 and 4 in the second row. |
2 |
|
Value found in the second row, second column in the array (same array as above). |
4 |
|
Top of Page
Reference form
Description
Returns the reference of the cell at the intersection of a particular row and column. If the reference is made up of non-adjacent selections, you can pick the selection to look in.
Syntax
INDEX(reference, row_num, [column_num], [area_num])
The reference form of the INDEX function has the following arguments:
-
reference Required. A reference to one or more cell ranges.
-
If you are entering a non-adjacent range for the reference, enclose reference in parentheses.
-
If each area in reference contains only one row or column, the row_num or column_num argument, respectively, is optional. For example, for a single row reference, use INDEX(reference,,column_num).
-
-
row_num Required. The number of the row in reference from which to return a reference.
-
column_num Optional. The number of the column in reference from which to return a reference.
-
area_num Optional. Selects a range in reference from which to return the intersection of row_num and column_num. The first area selected or entered is numbered 1, the second is 2, and so on. If area_num is omitted, INDEX uses area 1. The areas listed here must all be located on one sheet. If you specify areas that are not on the same sheet as each other, it will cause a #VALUE! error. If you need to use ranges that are located on different sheets from each other, it is recommended that you use the array form of the INDEX function, and use another function to calculate the range that makes up the array. For example, you could use the CHOOSE function to calculate which range will be used.
For example, if Reference describes the cells (A1:B4,D1:E4,G1:H4), area_num 1 is the range A1:B4, area_num 2 is the range D1:E4, and area_num 3 is the range G1:H4.
Remarks
-
After reference and area_num have selected a particular range, row_num and column_num select a particular cell: row_num 1 is the first row in the range, column_num 1 is the first column, and so on. The reference returned by INDEX is the intersection of row_num and column_num.
-
If you set row_num or column_num to 0 (zero), INDEX returns the reference for the entire column or row, respectively.
-
row_num, column_num, and area_num must point to a cell within reference; otherwise, INDEX returns a #REF! error. If row_num and column_num are omitted, INDEX returns the area in reference specified by area_num.
-
The result of the INDEX function is a reference and is interpreted as such by other formulas. Depending on the formula, the return value of INDEX may be used as a reference or as a value. For example, the formula CELL(«width»,INDEX(A1:B2,1,2)) is equivalent to CELL(«width»,B1). The CELL function uses the return value of INDEX as a cell reference. On the other hand, a formula such as 2*INDEX(A1:B2,1,2) translates the return value of INDEX into the number in cell B1.
Examples
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter.
|
Fruit |
Price |
Count |
|---|---|---|
|
Apples |
$0.69 |
40 |
|
Bananas |
$0.34 |
38 |
|
Lemons |
$0.55 |
15 |
|
Oranges |
$0.25 |
25 |
|
Pears |
$0.59 |
40 |
|
Almonds |
$2.80 |
10 |
|
Cashews |
$3.55 |
16 |
|
Peanuts |
$1.25 |
20 |
|
Walnuts |
$1.75 |
12 |
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=INDEX(A2:C6, 2, 3) |
The intersection of the second row and third column in the range A2:C6, which is the contents of cell C3. |
38 |
|
=INDEX((A1:C6, A8:C11), 2, 2, 2) |
The intersection of the second row and second column in the second area of A8:C11, which is the contents of cell B9. |
1.25 |
|
=SUM(INDEX(A1:C11, 0, 3, 1)) |
The sum of the third column in the first area of the range A1:C11, which is the sum of C1:C11. |
216 |
|
=SUM(B2:INDEX(A2:C6, 5, 2)) |
The sum of the range starting at B2, and ending at the intersection of the fifth row and the second column of the range A2:A6, which is the sum of B2:B6. |
2.42 |
Top of Page
See Also
VLOOKUP function
MATCH function
INDIRECT function
Guidelines and examples of array formulas
Lookup and reference functions (reference)
Функция INDEX (ИНДЕКС) в Excel используется для получения данных из таблицы, при условии что вы знаете номер строки и столбца, в котором эти данные находятся.
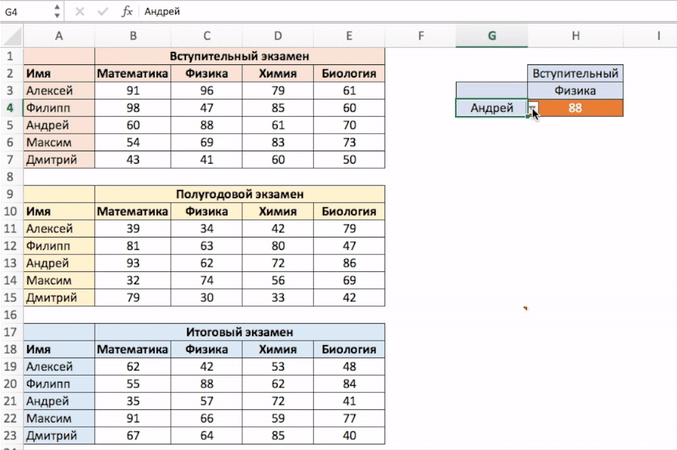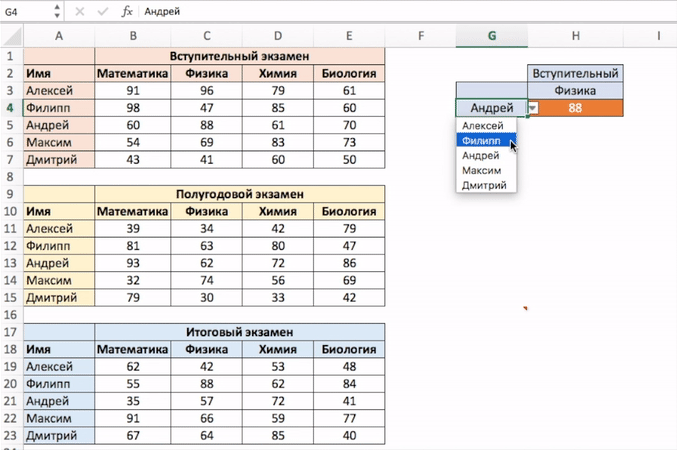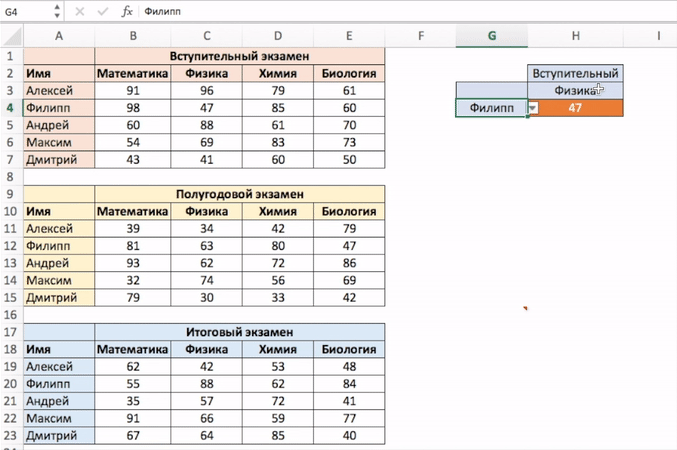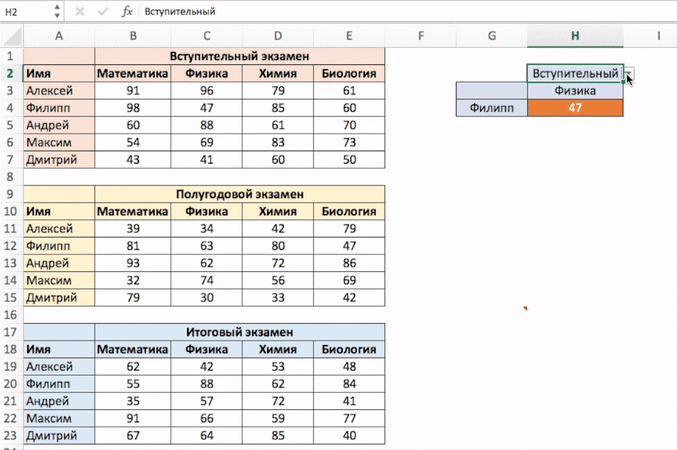
Например, в таблице ниже, вы можете использовать эту функцию для того, чтобы получить результаты экзамена по Физике у Андрея, зная номер строки и столбца, в которых эти данные находятся.
Содержание
- Что возвращает функция
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции
- Дополнительная информация
- Примеры использования функции ИНДЕКС в Excel
- Пример 1. Ищем результаты экзамена по физике для Алексея
- Пример 2. Создаем динамический поиск значений с использованием функций ИНДЕКС и ПОИСКПОЗ
- Пример 3. Создаем динамический поиск значений с использованием функций INDEX (ИНДЕКС) и MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ) и выпадающего списка
- Пример 4. Использование трехстороннего поиска с помощью INDEX (ИНДЕКС) / MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ)
Что возвращает функция
Возвращает данные из конкретной строки и столбца табличных данных.
Синтаксис
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num]) — английская версия
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num], [area_num]) — английская версия
=ИНДЕКС(массив; номер_строки; [номер_столбца]) — русская версия
=ИНДЕКС(ссылка; номер_строки; [номер_столбца]; [номер_области]) — русская версия
Аргументы функции
- array (массив) — диапазон ячеек или массив данных для поиска;
- row_num (номер_строки) — номер строки, в которой находятся искомые данные;
- [col_num] ([номер_столбца]) (необязательный аргумент) — номер колонки, в которой находятся искомые данные. Этот аргумент необязательный. Но если в аргументах функции не указаны критерии для row_num (номер_строки), необходимо указать аргумент col_num (номер_столбца);
- [area_num] ([номер_области]) — (необязательный аргумент) — если аргумент массива состоит из нескольких диапазонов, то это число будет использоваться для выбора всех диапазонов.
Дополнительная информация
- Если номер строки или колонки равен “0”, то функция возвращает данные всей строки или колонки;
- Если функция используется перед ссылкой на ячейку (например, A1), она возвращает ссылку на ячейку вместо значения (см. примеры ниже);
- Чаще всего INDEX (ИНДЕКС) используется совместно с функцией MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ);
- В отличие от функции VLOOKUP (ВПР), функция INDEX (ИНДЕКС) может возвращать данные как справа от искомого значения, так и слева;
- Функция используется в двух формах — Массива данных и Формы ссылки на данные:
— Форма «Массива» используется когда вы хотите найти значения, основанные на конкретных номерах строк и столбцов таблицы;
— Форма «Ссылок на данные» используется при поиске значений в нескольких таблицах (используете аргумент [area_num] ([номер_области]) для выбора таблицы и только потом сориентируете функцию по номеру строки и столбца.
Примеры использования функции ИНДЕКС в Excel
Пример 1. Ищем результаты экзамена по физике для Алексея
Предположим, у вас есть результаты экзаменов в табличном виде по нескольким студентам:
Для того, чтобы найти результаты экзамена по физике для Андрея нам нужна формула:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$9,3,2) — английская версия
=ИНДЕКС($B$3:$E$9;3;2) — русская версия
В формуле мы определили аргумент диапазона данных, где мы будем искать данные $B$3:$E$9. Затем, указали номер строки “3”, в которой находятся результаты экзамена для Андрея, и номер колонки “2”, где находятся результаты экзамена именно по физике.
Пример 2. Создаем динамический поиск значений с использованием функций ИНДЕКС и ПОИСКПОЗ
Не всегда есть возможность указать номера строки и столбца вручную. У вас может быть огромная таблица данных, отображение данных которой вы можете сделать динамическим, чтобы функция автоматически идентифицировала имя или экзамен, указанные в ячейках, и дала правильный результат.
Пример динамического отображения данных ниже:
Для динамического отображения данных мы используем комбинацию функций INDEX (ИНДЕКС) и MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ).
Вот такая формула поможет нам добиться результата:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$9,MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$9,0),MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0)) — английская версия
=ИНДЕКС($B$3:$E$9;ПОИСКПОЗ($G$4;$A$3:$A$9;0);ПОИСКПОЗ($H$3;$B$2:$E$2;0)) — русская версия
В формуле выше, не используя сложного программирования, мы с помощью функции MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ) сделали отображение данных динамическим.
Динамический отображение строки задается следующей частью формулы —
MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$9,0) — английская версия
ПОИСКПОЗ($G$4;$A$3:$A$9;0) — русская версия
Она сканирует имена студентов и определяет значение поиска ($G$4 в нашем случае). Затем она возвращает номер строки для поиска в наборе данных. Например, если значение поиска равно Алексей, функция вернет “1”, если это Максим, оно вернет “4” и так далее.
Динамическое отображение данных столбца задается следующей частью формулы —
MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0) — английская версия
ПОИСКПОЗ($H$3;$B$2:$E$2;0) — русская версия
Она сканирует имена объектов и определяет значение поиска ($H$3 в нашем случае). Затем она возвращает номер столбца для поиска в наборе данных. Например, если значение поиска Математика, функция вернет “1”, если это Физика, функция вернет “2” и так далее.

Пример 3. Создаем динамический поиск значений с использованием функций INDEX (ИНДЕКС) и MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ) и выпадающего списка
На примере выше мы вручную вводили имена студентов и названия предметов. Вы можете сэкономить время на вводе данных, используя выпадающие списки. Это актуально, когда количество данных огромное.
Используя выпадающие списки, вам нужно просто выбрать из списка имя студента и функция автоматически найдет и подставит необходимые данные.
Пример ниже:
Используя такой подход, вы можете создать удобный дашборд, например для учителя. Ему не придется заниматься фильтрацией данных или прокруткой листа со студентами, для того чтобы найти результаты экзамена конкретного студента, достаточно просто выбрать имя и результаты динамически отразятся в лаконичной и удобной форме.
Для того, чтобы осуществить динамическую подстановку данных с использованием функций INDEX (ИНДЕКС) и MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ) и выпадающего списка, мы используем ту же формулу, что в Примере 2:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$9,MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$9,0),MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0)) — английская версия
=ИНДЕКС($B$3:$E$9;ПОИСКПОЗ($G$4;$A$3:$A$9;0);ПОИСКПОЗ($H$3;$B$2:$E$2;0)) — русская версия
Единственное отличие, от Примера 2, мы на месте ввода имени и предмета создадим выпадающие списки:
- Выбираем ячейку, в которой мы хотим отобразить выпадающий список с именами студентов;
- Кликаем на вкладку “Data” => Data Tools => Data Validation;
- В окне Data Validation на вкладке “Settings” в подразделе Allow выбираем “List”;
- В качестве Source нам нужно выбрать диапазон ячеек, в котором указаны имена студентов;
- Кликаем ОК
Теперь у вас есть выпадающий список с именами студентов в ячейке G5. Таким же образом вы можете создать выпадающий список с предметами.
Пример 4. Использование трехстороннего поиска с помощью INDEX (ИНДЕКС) / MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ)
Функция INDEX (ИНДЕКС) может быть использована для обработки трехсторонних запросов.
Что такое трехсторонний поиск?
В приведенных выше примерах мы использовали одну таблицу с оценками для студентов по разным предметам. Это пример двунаправленного поиска, поскольку мы используем две переменные для получения оценки (имя студента и предмет).
Теперь предположим, что к концу года студент прошел три уровня экзаменов: «Вступительный», «Полугодовой» и «Итоговый экзамен».
Трехсторонний поиск — это возможность получить отметки студента по заданному предмету с указанным уровнем экзамена.
Вот пример трехстороннего поиска:
В приведенном выше примере, кроме выбора имени студента и названия предмета, вы также можете выбрать уровень экзамена. Основываясь на уровне экзамена, формула возвращает соответствующее значение из одной из трех таблиц.
Для таких расчетов нам поможет формула:
=INDEX(($B$3:$E$7,$B$11:$E$15,$B$19:$E$23),MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$7,0),MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0),IF($H$2=»Вступительный»,1,IF($H$2=»Полугодовой»,2,3))) — английская версия
=ИНДЕКС(($B$3:$E$7;$B$11:$E$15;$B$19:$E$23);ПОИСКПОЗ($G$4;$A$3:$A$7;0);ПОИСКПОЗ($H$3;$B$2:$E$2;0); ЕСЛИ($H$2=»Вступительный»;1;ЕСЛИ($H$2=»Полугодовой»;2;3))) — русская версия
Давайте разберем эту формулу, чтобы понять, как она работает.
Эта формула принимает четыре аргумента. Функция INDEX (ИНДЕКС) — одна из тех функций в Excel, которая имеет более одного синтаксиса.
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num]) — английская версия
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num], [area_num]) — английская версия
=ИНДЕКС(массив; номер_строки; [номер_столбца]) — русская версия
=ИНДЕКС(ссылка; номер_строки; [номер_столбца]; [номер_области]) — русская версия
По всем вышеприведенным примерам мы использовали первый синтаксис, но для трехстороннего поиска нам нужно использовать второй синтаксис.
Рассмотрим каждую часть формулы на основе второго синтаксиса.
- array (массив) – ($B$3:$E$7,$B$11:$E$15,$B$19:$E$23):Вместо использования одного массива, в данном случае мы использовали три массива в круглых скобках.
- row_num (номер_строки) – MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$7,0): функция MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ) используется для поиска имени студента для ячейки $G$4 из списка всех студентов.
- col_num (номер_столбца) – MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0): функция MATCH (ПОИСКПОЗ) используется для поиска названия предмета для ячейки $H$3 из списка всех предметов.
- [area_num] ([номер_области]) – IF($H$2=”Вступительный”,1,IF($H$2=”Полугодовой”,2,3)): Значение номера области сообщает функции INDEX (ИНДЕКС), какой массив с данными выбрать. В этом примере у нас есть три массива в первом аргументе. Если вы выберете «Вступительный» из раскрывающегося меню, функция IF (ЕСЛИ) вернет значение “1”, а функция INDEX (ИНДЕКС) выберут 1-й массив из трех массивов ($B$3:$E$7).
Уверен, что теперь вы подробно изучили работу функции INDEX (ИНДЕКС) в Excel!
The INDEX function in Excel helps extract the value of a cell, which is within a specified array (range) and, at the intersection of the stated row and column numbers. In other words, the function goes to the cell (within a particular range) whose position is specified, picks its value, and returns it as the output. The INDEX function can also extract an array of values from a dataset.
For example, a worksheet contains the names of continents and the corresponding countries. The entries, typed in Excel (without the double quotation marks), are listed as follows:
Column A
- Cell A1 contains “Asia.”
- Cell A2 contains “Africa.”
- Cell A3 contains “Europe.”
- Cell A4 contains “North America.”
Column B
- Cell B1 contains “India.”
- Cell B2 contains “Nigeria.”
- Cell B3 contains “France.”
- Cell B4 contains “Canada.”
Enter the formula “=INDEX(A1:B4,3,2)” in cell C1. Press the “Enter” key and the output is “France” (without the double quotation marks).
First, the INDEX excel function goes to the range A1:B4. From this range, it fetches the value of the cell, which is at the intersection of the third row (row 3) and the second column (column B). This cell is B3 and its value is “France.”
The INDEX function can return the following values:
- The value at the intersection of the specified row and column numbers
- The value within a table or a named range whose row and column numbers are specified
- The value within non-adjacent ranges whose row and column numbers are specified
The INDEX function in Excel is useful when the dataset is large and one knows the position of the cell from which the value needs to be extracted.
The INDEX function is categorized under the Lookup and Reference functions of Excel.
Table of contents
- Index Function in Excel
- Syntax of the INDEX Function in Excel
- How to use the INDEX Function in Excel?
- Example #1–Array Form With a One-Dimensional Array
- Example #2–Array Form With a Two-Dimensional Array
- Example #3–Array Form With Row and/or Column Numbers as Zeros
- Example #4–Reference Form With Multiple Two-Dimensional Arrays
- The Properties Applicable to Both Forms of the INDEX Function
- The INDEX With Other Functions of Excel
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
Syntax of the INDEX Function in Excel
There are two forms of the INDEX function in excel, the array and the reference. The syntax of both forms is shown in the following image.
Let us discuss both forms of the Excel INDEX function one by one.
The Array Form of the INDEX Excel Function
In the array form, the INDEX function fetches the value of a cell within an array or a table. An array can be either a single range of cells (horizontal or vertical) or multiple adjacent ranges. The value of the cell, which is at the intersection of the supplied row and column numbers, is returned.
The INDEX function accepts the following arguments in the array form:
- Array: This can be a range of cells, table, array constant or named rangeName range in Excel is a name given to a range for the future reference. To name a range, first select the range of data and then insert a table to the range, then put a name to the range from the name box on the left-hand side of the window.read more. The cell whose value is to be returned must necessarily be within this array.
- Row_num: This is the row number of the array from which the value is to be returned.
- Column_num: This is the column number of the array from which the value is to be returned.
The arguments “array” and “row_num” are mandatory, while the argument “column_num” is optional.
It is essential to specify either the “row_num” or the “column_num” to extract a value from a one-dimensional array. To extract a value from a two-dimensional array, one needs to specify both, the “row_num” and the “column_num.”
Note 1: A one-dimensional array consists of a single row or a single column. A two-dimensional array consists of multiple rows and columns.
Note 2: If both “row_num” and “column_num” are entered as zeros (or blanks), the “#VALUE!” error is returned. For instance, the formulas “=INDEX(A1:A4,0,0)” and “=INDEX(A1:A4,,)” return the “#VALUE!” error.
Note 3: If the “array” argument consists of a single column, the “column_num” argument can be omitted, but the “row_num” must be supplied to fetch the value. Likewise, if the “array” argument consists of a single row, the “row_num” argument can be omitted, but the “column_num” must be specified to fetch the value.
For instance, in case of a single column, use the formula “=INDEX(array,row_num)” to fetch a value. In case of a single row, use the formula “=INDEX(array,,column_num)” to fetch a value.
The Reference Form of the INDEX Excel Function
In the reference form, the INDEX function fetches the value of a cell within a defined area (array or range). There can be multiple non-adjacent areas in the reference form. In such cases, the particular area, within which the INDEX function should look for the value, can be specified.
The INDEX function in Excel accepts the following arguments in the reference form:
- Reference: This is the area which can either be a single range or multiple non-adjacent ranges. In the case of multiple non-adjacent ranges, use commas to separate the ranges. In addition, all the ranges must be enclosed within parentheses. For instance, the “reference” argument, (A1:C2, C4:D7) implies two areas (arrays or ranges), A1:C2 and C4:D7.
- Row_num: This is the row number of the area from which the value is to be returned.
- Column_num: This is the column number of the area from which the value is to be returned.
- Area_num: This number indicates the area (of the “reference” argument) in which the INDEX function will look for a value. The first area of the “reference” argument is assigned the number 1. The second area is numbered 2 and so on. For instance, if the “reference” argument is (A1:C2, C4:D7, F4:H8) and the “area_num” is 3, the INDEX function looks for the value in the third area of the “reference” argument, i.e., F4:H8.
The arguments “reference” and “row_num” are required, while the arguments “column_num” and “area_num” are optional.
In the following image, the grey box (pointed by the red arrow) shows the different areas (arrays or ranges) of the reference argument. Further, the area numbers of each range are also given.
Note 1: If the “area_num” argument is omitted, the INDEX excel function looks for the value in the first area of the “reference” argument.
Note 2: All the areas stated in the “reference” argument should be located on one worksheet. If the first area is in one worksheet and the second is in another, the INDEX function returns the “#VALUE!” error.
Note 3: The difference between the array and reference forms is that in the former, adjacent ranges are used, while in the latter, non-adjacent ranges are used.
How to use the INDEX Function in Excel?
Let us consider a few examples to understand the working of the INDEX function in Excel.
You can download this INDEX Function Excel Template here – INDEX Function Excel Template
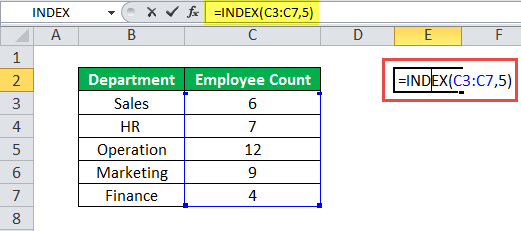
Example #1–Array Form With a One-Dimensional Array
The following image shows the number of employees (column C) working in the different departments (column B) of an organization.
We want to extract the value of cell C7 with the help of the INDEX function. Use the array form with column C as the single array.
The steps to perform the given task are listed as follows:
Step 1: Enter the following formula in cell E2.
“=INDEX(C3:C7,5)”
Step 2: Press the “Enter” key. The output in cell E2 is 4.
Explanation: In the formula entered in step 1, we omitted the “column_num” argument since the array (C3:C7) is a single column. Cell C7 is in the fifth row of the array C3:C7. So, the “row_num” argument is entered as 5.
Hence, the given INDEX formula returns 4, which is the value of row 5 of the range C3:C7.
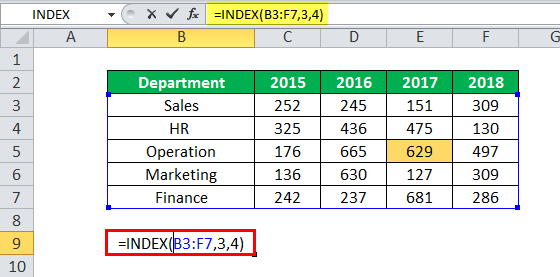
Example #2–Array Form With a Two-Dimensional Array
The following image shows the total number of employees working in five departments of a multinational corporationA multinational company (MNC) is defined as a business entity that operates in its country of origin and also has a branch abroad. The headquarter usually remains in one country, controlling and coordinating all the international branches.
read more (MNC). The numbers pertain to four years, namely, 2015-2018.
We want to extract the value of cell E5 with the help of the INDEX excel function. Use the array form with the entire dataset (except the headings in row 2) as the array.
The steps to perform the given task are listed as follows:
Step 1: Enter the following formula in cell B9.
“=INDEX(B3:F7,3,4)”
Step 2: Press the “Enter” key. The output in cell B9 is 629.
Explanation: In the preceding formula (entered in step 1), the multiple rows and columns of the dataset are entered as a single array (B3:F7). The INDEX formula returns the value of the cell, which is at the intersection of row 3 and column 4 of the range B3:F7. The cell at this position is cell E5 and its value is 629.
Hence, the output, 629, corresponds to the third row and fourth column of the range B3:F7.
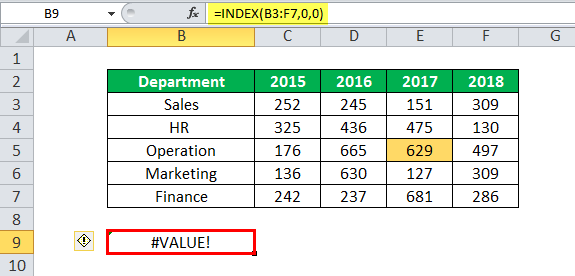
Example #3–Array Form With Row and/or Column Numbers as Zeros
Working on the data of example #2, we want to apply the INDEX function to the entire dataset (B3:F7). Further, observe the output in the following cases:
Case 1: When both arguments “row_num” and “column_num” are zeros
Case 2: When either the “row_num” or the “column_num” is zero
The two cases are discussed as follows:
Case 1: When both row and column numbers are entered as zeros, the INDEX function returns the “#VALUE” error.
Steps to be followed: Enter the formula “=INDEX(B3:F7,0,0)” in cell B9. Press the “Enter” key and the output is the “#VALUE” error. This is shown in the following image.
Conclusion: When multiple rows and columns are used as an array, it is necessary to specify both the row and column numbers to extract a particular cell value. In case, both row and column numbers are entered as zeros, the output is the “#VALUE” error.
Case 2: When either the row or the column number is zero, and the INDEX formula is entered as an array formula, the output is an array of values.
Steps to be followed: Select the blank range B11:B15. Enter the formula “=INDEX(B3:F7,0,1)” in the first cell selected (cell B11). Press the keys “Ctrl+Shift+Enter” together.
The outputs in cells B11, B12, B13, B14, and B15 are “Sales,” “HR,” “Operation,” “Marketing,” and “Finance” respectively. All outputs are obtained (without the double quotation marks) the way they are displayed in the range B3:B7.
Alternatively, select the blank row D11:H11. Enter the formula “=INDEX(B3:F7,3,0)” as an array formula. The output is the array of values of row 5 (of the preceding image). So, the output is “Operation,” “176,” “665,” “629,” and “497” without the double quotation marks.
Conclusion: When either the row or column number is specified while the other is set at zero, the INDEX function returns an array of values. However, in such cases, the INDEX formula must be entered as an array formula.
Moreover, it is essential to select a blank output range prior to entering the INDEX formula. This output range should have as many blank cells as the array of the source dataset.
Note: An array formula is usually completed by pressing the CSE keys (Ctrl+Shift+Enter).
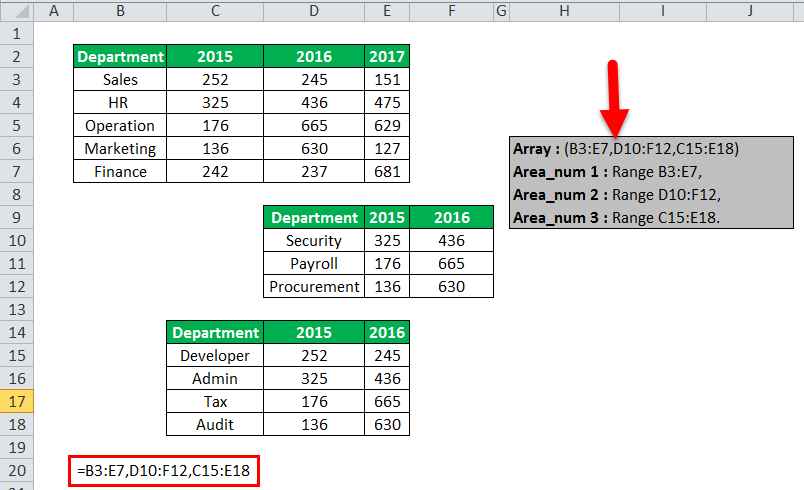
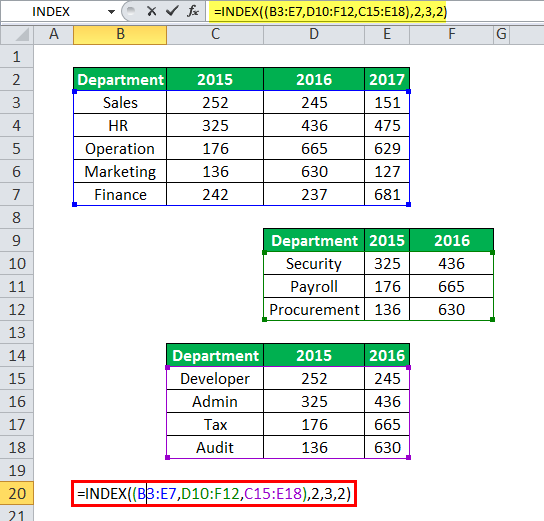
Example #4–Reference Form With Multiple Two-Dimensional Arrays
The following image contains three datasets which display the number of employees working in the different departments of an MNC. The first dataset (B2:E7) shows the figures for the years 2015-2017. The second (D9:F12) and third datasets (C14:E18) show the figures for the years 2015 and 2016.
Use the reference form of the INDEX excel function to extract the value of cell F11. Further, categorize the three datasets into three areas which exclude the top row containing the headings.
The steps to perform the preceding tasks are listed as follows:
Step 1: Enter the following formula in cell B20.
“=INDEX((B3:E7,D10:F12,C15:E18),2,3,2)”
Step 2: Press the “Enter” key. The output is 665, as shown in the following image.
Explanation: In the preceding formula (entered in step 1), the three datasets (given in the question of this example) have been categorized into three areas of the “reference” argument. These areas are B3:E7, D10:F12, and C15:E18. The headings have been excluded from these areas.
Further, the INDEX function looks for a value in the second area (D10:F12). This is because the “area_num” argument is 2. The arguments “row_num” and “column_num” are 2 and 3 respectively. So, the INDEX function returns the value of the cell, which is at the intersection of the second row and the third column in the area D10:F12. This is cell F11.
Hence, the output of the INDEX formula is 665.
The Properties Applicable to Both Forms of the INDEX Function
The properties applicable to both the array and reference forms are listed as follows:
a. If both the arguments “row_num” and “column_num” are entered as zeros, the INDEX excel function returns the “#VALUE!” error.
b. To fetch a value from a single column array, use the following formulas:
- “=INDEX(array,row_num)” in the array form
- “=INDEX((reference),row_num,,area_num)” in the reference form
To fetch a value from a single row array, use the following formulas:
- “=INDEX(array,,column_num)” in the array form
- “=INDEX((reference),,col_num,area_num)” in the reference form
c. If all the column values of an array are required vertically, specify the “column_num” and set the “row_num” at zero. Likewise, if all the row values of an array are required horizontally, specify the “row_num” and set the “column_num” at zero. In both cases, select a blank output range prior to entering the INDEX formula. Moreover, press the keys “Ctrl+Shift+Enter” to complete the formula.
d. The arguments “row_num,” “column_num,” and “area_num” should refer to a cell within the defined array or reference. If not, the INDEX function returns the “#REF!” error.
Note: In pointer “c,” the blank output range can be selected vertically or horizontally depending on whether a vertical or a horizontal array is required.
Further, the number of blank cells (of the output range) must be equal to the cells of the particular row or column array (which is being copied) of the source dataset.
The INDEX With Other Functions of Excel
The INDEX function in excel can be used with several other functions of Excel in the following ways:
a. The INDEX function is used in combination with functions like SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, and MAX to create dynamic ranges. For instance, the formula “AVERAGE(C3:INDEX(C3:C7,3))” returns the average of cells C3, C4, and C5. This is because the formula “INDEX(C3:C7,3)” returns a reference to cell C5. So, the resulting formula becomes “AVERAGE(C3:C5).” Moreover, with a change in the “row_num” argument of the INDEX function, the range of the AVERAGE function changes. This results in a change in the output obtained.
b. The INDEX and MATCH The MATCH function looks for a specific value and returns its relative position in a given range of cells. The output is the first position found for the given value. Being a lookup and reference function, it works for both an exact and approximate match. For example, if the range A11:A15 consists of the numbers 2, 9, 8, 14, 32, the formula “MATCH(8,A11:A15,0)” returns 3. This is because the number 8 is at the third position.
read more functions are used together to perform left lookups. This combination of the INDEX and MATCH functions overcomes the limitations of the VLOOKUP function of Excel. For instance, limitations like compulsory sorting of data, restricted size of the lookup value, decreased speed of Excel, and so on are eliminated.
c. The INDEX function can be used with the COUNTA functionThe COUNTA function is an inbuilt statistical excel function that counts the number of non-blank cells (not empty) in a cell range or the cell reference. For example, cells A1 and A3 contain values but, cell A2 is empty. The formula “=COUNTA(A1,A2,A3)” returns 2.
read more to extract the value of the last used cell of a dataset. With a change in the value of the last used cell, the output updates on its own.
Note 1: Dynamic ranges automatically update with the addition or deletion of data.
Note 2: Usually, the INDEX function returns the value of a cell. However, when a cell referenceCell reference in excel is referring the other cells to a cell to use its values or properties. For instance, if we have data in cell A2 and want to use that in cell A1, use =A2 in cell A1, and this will copy the A2 value in A1.read more and colon (:) precede the INDEX function, it returns a cell reference. This can be observed in the AVERAGE and INDEX formula of pointer “a.”
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Define the INDEX function in Excel.
The INDEX function in Excel returns the value of a cell whose array has been defined. In addition, the row and column numbers of this cell are also specified in the arguments of the INDEX formula.
The INDEX function can also retrieve the values of the entire row or column of a range. The INDEX function has two versions, the array and the reference. Both versions have their own set of arguments.
Note: For details related to the arguments of the INDEX function, refer to the heading “the syntax of the INDEX function in Excel” of this article.
2. How to use the INDEX function in Excel?
The steps for using the INDEX function in Excel are listed as follows:
a. Select the relevant form (array or reference) of the INDEX function to be applied. For this, take into consideration the kind of data.
b. Supply the arguments to the INDEX function. If an array of values is required, select a blank output range prior to entering the arguments.
c. Press either the “Enter” key or the CSE (Ctrl+Shift+Enter) keys, depending on the kind of output required.
The INDEX function processes the arguments. Next, it returns either a single value or an array of values based on the way it has been used.
3. How to use the INDEX MATCH function in place of the VLOOKUP function in Excel?
The INDEX MATCH functions are a versatile combination. This is because these functions can easily lookup a value, regardless of the location of the lookup and the return columns.
The formula to perform a lookup (in rows and columns) by using the INDEX MATCH functions is stated as follows:
“=INDEX(column to return a value from,MATCH(vlookup value,column to be looked up,0),MATCH(hlookup value,row to be looked up,0))”
The working of this formula is explained as follows:
a. The formula “MATCH(vlookup value,column to be looked up,0)” looks for the vlookup value in the column to be looked up (or lookup column). This formula looks for the exact match and returns the row number.
b. The formula “MATCH(hlookup value,row to be looked up,0)” looks for the hlookup value in the row to be looked up (or lookup row). This formula looks for the exact match and returns the column number.
c. The INDEX function uses the row and column numbers returned by the MATCH function. The INDEX function returns a corresponding value from the “column to return a value from” (or return column).
Hence, the INDEX and MATCH formula returns a value at the intersection of certain row and column numbers.
Note 1: It is also possible to supply only the row number or only the column number to the INDEX function. For supplying only the row number, use the first MATCH formula (given in pointer “a”) with the INDEX function. Likewise, to supply only the column number, use the second MATCH formula (given in pointer “b”) with the INDEX function.
Note 2: Looking for a value at the intersection of a row and column is called a 2-way lookup (or 2-dimensional lookup or matrix lookup).
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the INDEX function in Excel. Here we discuss the working of the INDEX formula in Excel along with examples and a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel–
- VLOOKUP
- INDIRECT in Excel
- POWER Function in excel
- Hyperlink Excel | Examples
In this article, we will learn How to use the INDEX function in Excel.
Why do we use the INDEX function ?
Given a table of 500 rows and 50 columns and we need to get a value at 455th row and 26th column. For this either we can scroll down to the 455th row and traverse to the 26th column and copy the value. But we can’t treat Excel like hard copies. Index function returns the value at a given row and column index in a table array. Let’s learn the INDEX function Syntax and illustrate how to use the function in Excel below.
INDEX Function in Excel
Index function returns the cell value at matching row and column index in array.
Syntax:
=INDEX(array, row number, [optional column number])
array : It is the range or an array.
row number : Ther row number in your array from which you want to get your value.
column number : [optional] This column number in array. It is optional. If omitted INDEX formula automatically takes 1 as default.
Excel’s INDEX function has two forms known as:
- Array Form INDEX Function
- Reference Form INDEX Function
Example :
All of these might be confusing to understand. Let’s understand how to use the function using an example. Here we have this data.
I want to retrieve data at the intersection of 3rd Row and 2nd Column. I write this INDEX formula in cell H2:
The result is Gill:
Reference Form INDEX Function
It is much like a multidimensional array index function. Actually in this form of INDEX function, we can give multiple arrays and then in the end we can tell the index from which array to pull data.
Excel INDEX Function Reference Form Syntax
=INDEX( (array1, array2,…), row number, [optional column number], [optional array number] )
(array1, array2,…) : This parenthesis contains a list of arrays. For example (A1:A10,D1:R100,…).
Row number : Ther row number in your array from which you want to get your value.
[optional column number] : This column number in array. It is optional. If omitted, the INDEX formula automatically takes 1 for it.
[optional array number] : The area number from which you want to pull data. In excel it is shown as area_num
Come, let’s have an example.
I have these 3 tables in Excel Worksheet.
Area 1, Area 2 and Area 3 are my ranges as shown in the above image. I need to retrieve data according to values in cell L2, L3 and L4. So, I write this INDEX formula in cell M1.
=INDEX(($B$3:$C$7,$E$3:$F$7,$H$3:$I$7),L2,L3,L4)
Here L2 is 1, L3 is 2 and L4 is 1. Hence the INDEX function will return the value from the 1st row of the second column from the 1st array. And that is East.
Now change L2 to 2 and L4 to 2. You will have West in M2, as shown in below image.
And so on.
The INDEX function in Excel is mostly used with MATCH Function. The INDEX MATCH function is so famous that it is sometimes thought of as one single function. Here I have explained the INDEX MATCH function with multiple criteria in detail. Go check it out. How to lookup values using the INDEX and MATCH function
Hope this article about How to use the INDEX function in Excel is explanatory. Find more articles on calculating values and related Excel formulas here. If you liked our blogs, share it with your friends on Facebook. And also you can follow us on Twitter and Facebook. We would love to hear from you, do let us know how we can improve, complement or innovate our work and make it better for you. Write to us at info@exceltip.com.
Related Articles :
Use INDEX and MATCH to Lookup Value : The INDEX & MATCH formula is used to lookup dynamically and precisely a value in a given table. This is an alternative to the VLOOKUP function and it overcomes the shortcomings of the VLOOKUP function.
Use VLOOKUP from Two or More Lookup Tables : To lookup from multiple tables we can take an IFERROR approach. To lookup from multiple tables, it takes the error as a switch for the next table. Another method can be an If approach.
How to do Case Sensitive Lookup in Excel : The excel’s VLOOKUP function isn’t case sensitive and it will return the first matched value from the list. INDEX-MATCH is no exception but it can be modified to make it case sensitive.
Lookup Frequently Appearing Text with Criteria in Excel : The lookup most frequently appears in text in a range we use the INDEX-MATCH with MODE function.
Popular Articles :
How to use the IF Function in Excel : The IF statement in Excel checks the condition and returns a specific value if the condition is TRUE or returns another specific value if FALSE.
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel : This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel : This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
How to use the COUNTIF Function in Excel : Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
The INDEX function returns the value at a given location in a range or array. INDEX is a powerful and versatile function. You can use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns. INDEX is frequently used together with the MATCH function. In this scenario, the MATCH function locates and feeds a position to the INDEX function, and INDEX returns the value at that position.
In the most common usage, INDEX takes three arguments: array, row_num, and col_num. Array is the range or array from which to retrieve values. Row_num is the row number from which to retrieve a value, and col_num is the column number at which to retrieve a value. Col_num is optional and not needed when array is one-dimensional.
In the example shown above, the goal is to get the diameter of the planet Jupiter. Because Jupiter is the fifth planet in the list, and Diameter is the third column, the formula in G7 is:
=INDEX(B5:E13,5,3) // diameter of Jupiter
The formula above is of limited value because the row number and column number have been hard-coded. Typically, the MATCH function would be used inside INDEX to provide these numbers. For a detailed explanation with many examples, see: How to use INDEX and MATCH.
Basic usage
INDEX gets a value at a given location in a range of cells based on numeric position. When the range is one-dimensional, you only need to supply a row number. When the range is two-dimensional, you’ll need to supply both the row and column number. For example, to get the third item from the one-dimensional range A1:A5:
=INDEX(A1:A5,3) // returns value in A3
The formulas below show how INDEX can be used to get a value from a two-dimensional range:
=INDEX(A1:B5,2,2) // returns value in B2
=INDEX(A1:B5,3,1) // returns value in A3
INDEX and MATCH
In the examples above, the position is «hardcoded». Typically, the MATCH function is used to find positions for INDEX. For example, in the screen below, the MATCH function is used to locate «Mars» (G6) in row 3 and feed that position to INDEX. The formula in G7 is:
=INDEX(B5:E13,MATCH(G6,B5:B13,0),3)
MATCH provides the row number (4) to INDEX. The column number is still hardcoded as 3.
INDEX and MATCH with horizontal table
In the screen below, the table above has been transposed horizontally. The MATCH function returns the column number (4) and the row number is hardcoded as 2. The formula in C10 is:
=INDEX(C4:K6,2,MATCH(C9,C4:K4,0))
For a detailed explanation with many examples, see: How to use INDEX and MATCH
Entire row / column
INDEX can be used to return entire columns or rows like this:
=INDEX(range,0,n) // entire column
=INDEX(range,n,0) // entire row
where n represents the number of the column or row to return. This example shows a practical application of this idea.
Reference as result
It’s important to note that the INDEX function returns a reference as a result. For example, in the following formula, INDEX returns A2:
=INDEX(A1:A5,2) // returns A2
In a typical formula, you’ll see the value in cell A2 as the result, so it’s not obvious that INDEX is returning a reference. However, this is a useful feature in formulas like this one, which uses INDEX to create a dynamic named range. You can use the CELL function to report the reference returned by INDEX.
Two forms
The INDEX function has two forms: array and reference. Both forms have the same behavior – INDEX returns a reference in an array based on a given row and column location. The difference is that the reference form of INDEX allows more than one array, along with an optional argument to select which array should be used. Most formulas use the array form of INDEX, but both forms are discussed below.
Array form
In the array form of INDEX, the first parameter is an array, which is supplied as a range of cells or an array constant. The syntax for the array form of INDEX is:
INDEX(array,row_num,[col_num])
- If both row_num and col_num are supplied, INDEX returns the value in the cell at the intersection of row_num and col_num.
- If row_num is set to zero, INDEX returns an array of values for an entire column. To use these array values, you can enter the INDEX function as an array formula in horizontal range, or feed the array into another function.
- If col_num is set to zero, INDEX returns an array of values for an entire row. To use these array values, you can enter the INDEX function as an array formula in vertical range, or feed the array into another function.
Reference form
In the reference form of INDEX, the first parameter is a reference to one or more ranges, and a fourth optional argument, area_num, is provided to select the appropriate range. The syntax for the reference form of INDEX is:
INDEX(reference,row_num,[col_num],[area_num])
Just like the array form of INDEX, the reference form of INDEX returns the reference of the cell at the intersection row_num and col_num. The difference is that the reference argument contains more than one range, and area_num selects which range should be used. The area_num is argument is supplied as a number that acts like a numeric index. The first array inside reference is 1, the second array is 2, and so on.
For example, in the formula below, area_num is supplied as 2, which refers to the range A7:C10:
=INDEX((A1:C5,A7:C10),1,3,2)
In the above formula, INDEX will return the value at row 1 and column 3 of A7:C10.
- Multiple ranges in reference are separated by commas and enclosed in parentheses.
- All ranges must on one sheet or INDEX will return a #VALUE error. Use the CHOOSE function as a workaround.
Содержание
- Использование функции ИНДЕКС
- Способ 1: использование оператора ИНДЕКС для массивов
- Способ 2: применение в комплексе с оператором ПОИСКПОЗ
- Способ 3: обработка нескольких таблиц
- Способ 4: вычисление суммы
- Вопросы и ответы
Одной из самых полезных функций программы Эксель является оператор ИНДЕКС. Он производит поиск данных в диапазоне на пересечении указанных строки и столбца, возвращая результат в заранее обозначенную ячейку. Но полностью возможности этой функции раскрываются при использовании её в сложных формулах в комбинации с другими операторами. Давайте рассмотрим различные варианты её применения.
Использование функции ИНДЕКС
Оператор ИНДЕКС относится к группе функций из категории «Ссылки и массивы». Он имеет две разновидности: для массивов и для ссылок.
Вариант для массивов имеет следующий синтаксис:
=ИНДЕКС(массив;номер_строки;номер_столбца)
При этом два последних аргумента в формуле можно использовать, как вместе, так и любой один из них, если массив одномерный. При многомерном диапазоне следует применять оба значения. Нужно также учесть, что под номером строки и столбца понимается не номер на координатах листа, а порядок внутри самого указанного массива.
Синтаксис для ссылочного варианта выглядит так:
=ИНДЕКС(ссылка;номер_строки;номер_столбца;[номер_области])
Тут точно так же можно использовать только один аргумент из двух: «Номер строки» или «Номер столбца». Аргумент «Номер области» вообще является необязательным и он применяется только тогда, когда в операции участвуют несколько диапазонов.
Таким образом, оператор ищет данные в установленном диапазоне при указании строки или столбца. Данная функция своими возможностями очень похожа на оператора ВПР, но в отличие от него может производить поиск практически везде, а не только в крайнем левом столбце таблицы.
Способ 1: использование оператора ИНДЕКС для массивов
Давайте, прежде всего, разберем на простейшем примере алгоритм использования оператора ИНДЕКС для массивов.
Имеем таблицу зарплат. В первом её столбце отображены фамилии работников, во втором – дата выплаты, а в третьем – величина суммы заработка. Нам нужно вывести имя работника в третьей строке.
- Выделяем ячейку, в которой будет выводиться результат обработки. Кликаем по значку «Вставить функцию», который размещен сразу слева от строки формул.
- Происходит процедура активации Мастера функций. В категории «Ссылки и массивы» данного инструмента или «Полный алфавитный перечень» ищем наименование «ИНДЕКС». После того, как нашли этого оператора, выделяем его и щелкаем по кнопке «OK», которая размещается в нижней части окна.
- Открывается небольшое окошко, в котором нужно выбрать один из типов функции: «Массив» или «Ссылка». Нужный нам вариант «Массив». Он расположен первым и по умолчанию выделен. Поэтому нам остается просто нажать на кнопку «OK».
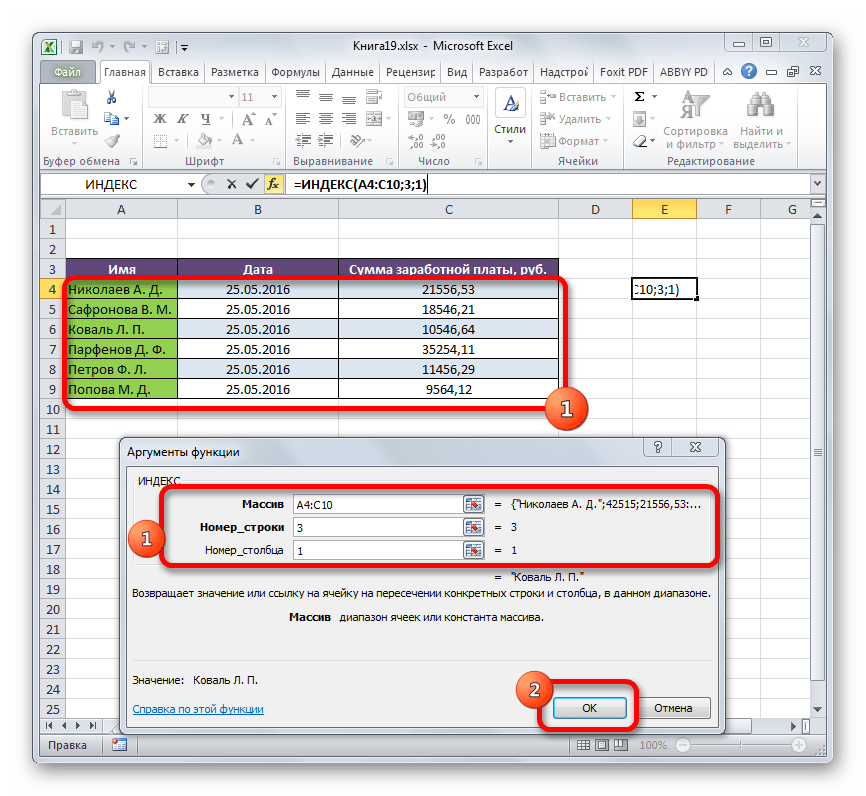
- Открывается окно аргументов функции ИНДЕКС. Как выше говорилось, у неё имеется три аргумента, а соответственно и три поля для заполнения.
В поле «Массив» нужно указать адрес обрабатываемого диапазона данных. Его можно вбить вручную. Но для облегчения задачи мы поступим иначе. Ставим курсор в соответствующее поле, а затем обводим весь диапазон табличных данных на листе. После этого адрес диапазона тут же отобразится в поле.
В поле «Номер строки» ставим цифру «3», так как по условию нам нужно определить третье имя в списке. В поле «Номер столбца» устанавливаем число «1», так как колонка с именами является первой в выделенном диапазоне.
После того, как все указанные настройки совершены, щелкаем по кнопке «OK».
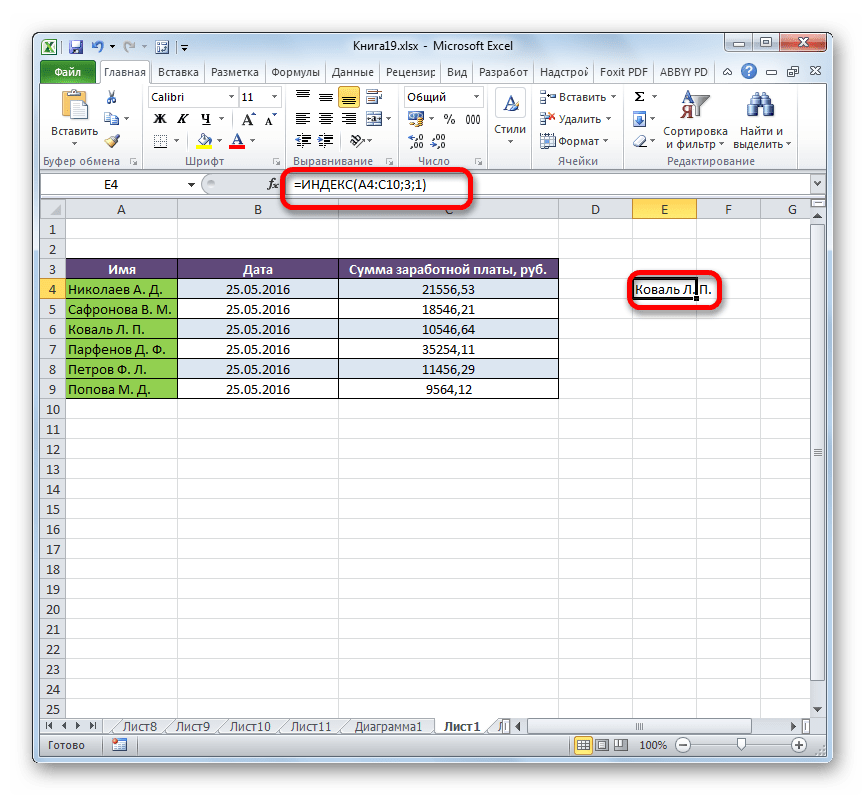
- Результат обработки выводится в ячейку, которая была указана в первом пункте данной инструкции. Именно выведенная фамилия является третьей в списке в выделенном диапазоне данных.
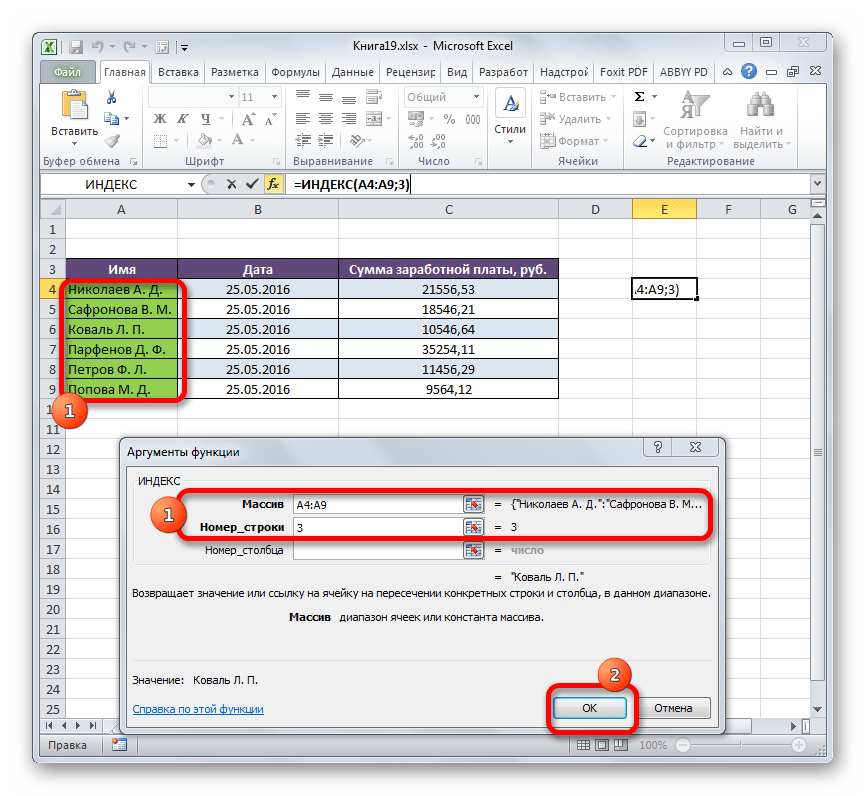
Мы разобрали применение функции ИНДЕКС в многомерном массиве (несколько столбцов и строк). Если бы диапазон был одномерным, то заполнение данных в окне аргументов было бы ещё проще. В поле «Массив» тем же методом, что и выше, мы указываем его адрес. В данном случае диапазон данных состоит только из значений в одной колонке «Имя». В поле «Номер строки» указываем значение «3», так как нужно узнать данные из третьей строки. Поле «Номер столбца» вообще можно оставить пустым, так как у нас одномерный диапазон, в котором используется только один столбец. Жмем на кнопку «OK».
Результат будет точно такой же, что и выше.
Это был простейший пример, чтобы вы увидели, как работает данная функция, но на практике подобный вариант её использования применяется все-таки редко.
Урок: Мастер функций в Экселе
Способ 2: применение в комплексе с оператором ПОИСКПОЗ
На практике функция ИНДЕКС чаще всего применяется вместе с аргументом ПОИСКПОЗ. Связка ИНДЕКС – ПОИСКПОЗ является мощнейшим инструментом при работе в Эксель, который по своему функционалу более гибок, чем его ближайший аналог – оператор ВПР.
Основной задачей функции ПОИСКПОЗ является указание номера по порядку определенного значения в выделенном диапазоне.
Синтаксис оператора ПОИСКПОЗ такой:
=ПОИСКПОЗ(искомое_значение, просматриваемый_массив, [тип_сопоставления])
- Искомое значение – это значение, позицию которого в диапазоне мы ищем;
- Просматриваемый массив – это диапазон, в котором находится это значение;
- Тип сопоставления – это необязательный параметр, который определяет, точно или приблизительно искать значения. Мы будем искать точные значения, поэтому данный аргумент не используется.
С помощью этого инструмента можно автоматизировать введение аргументов «Номер строки» и «Номер столбца» в функцию ИНДЕКС.
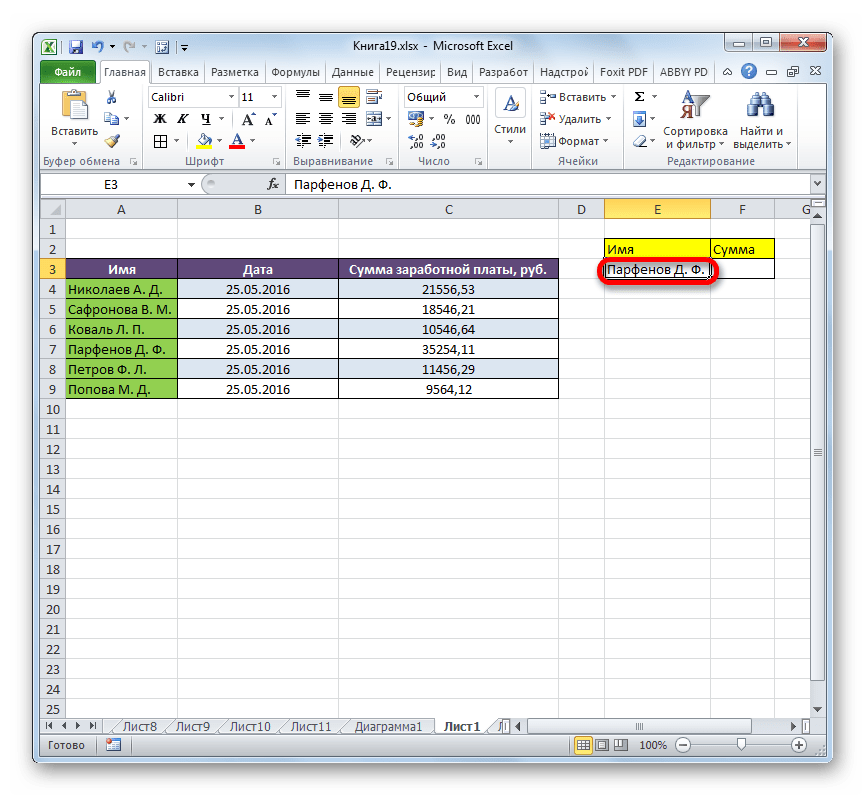
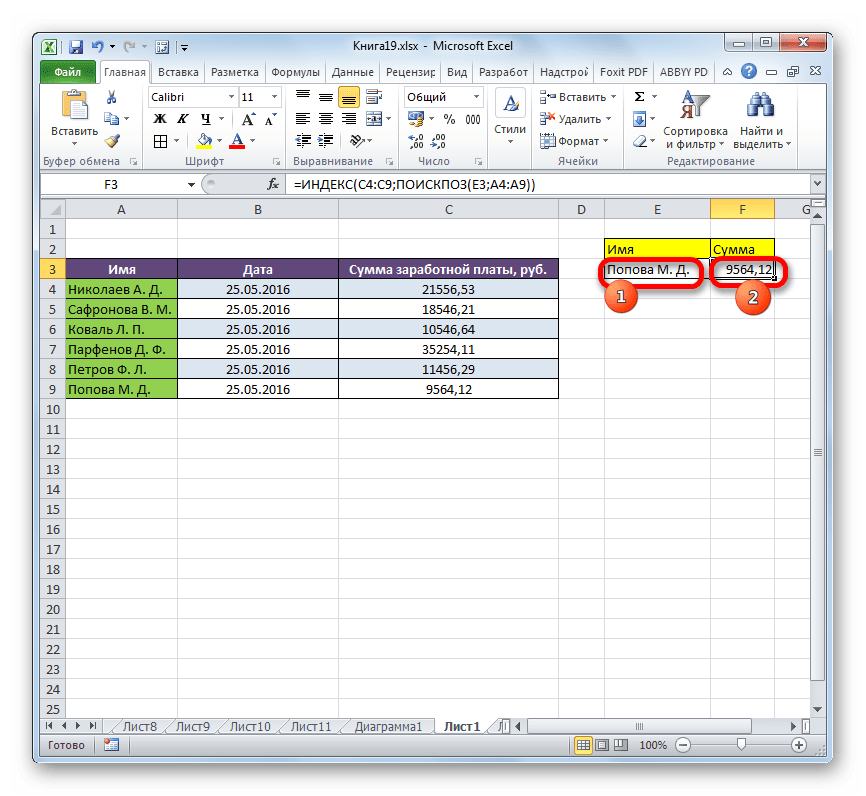
Посмотрим, как это можно сделать на конкретном примере. Работаем все с той же таблицей, о которой шла речь выше. Отдельно у нас имеется два дополнительных поля – «Имя» и «Сумма». Нужно сделать так, что при введении имени работника автоматически отображалась сумма заработанных им денег. Посмотрим, как это можно воплотить на практике, применив функции ИНДЕКС и ПОИСКПОЗ.
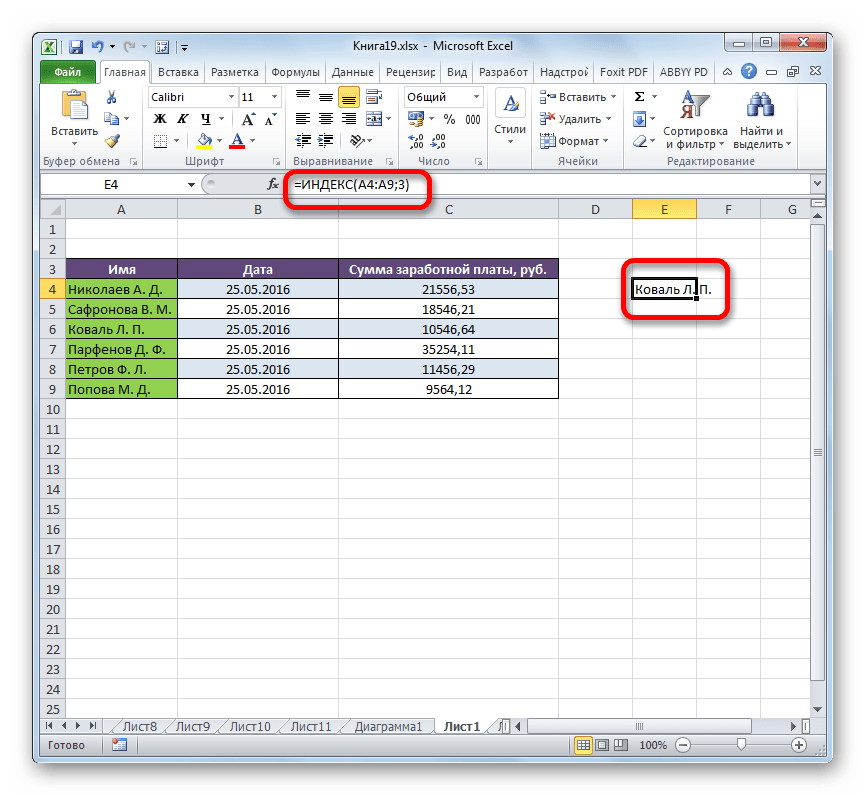
- Прежде всего, узнаем, какую заработную плату получает работник Парфенов Д. Ф. Вписываем его имя в соответствующее поле.
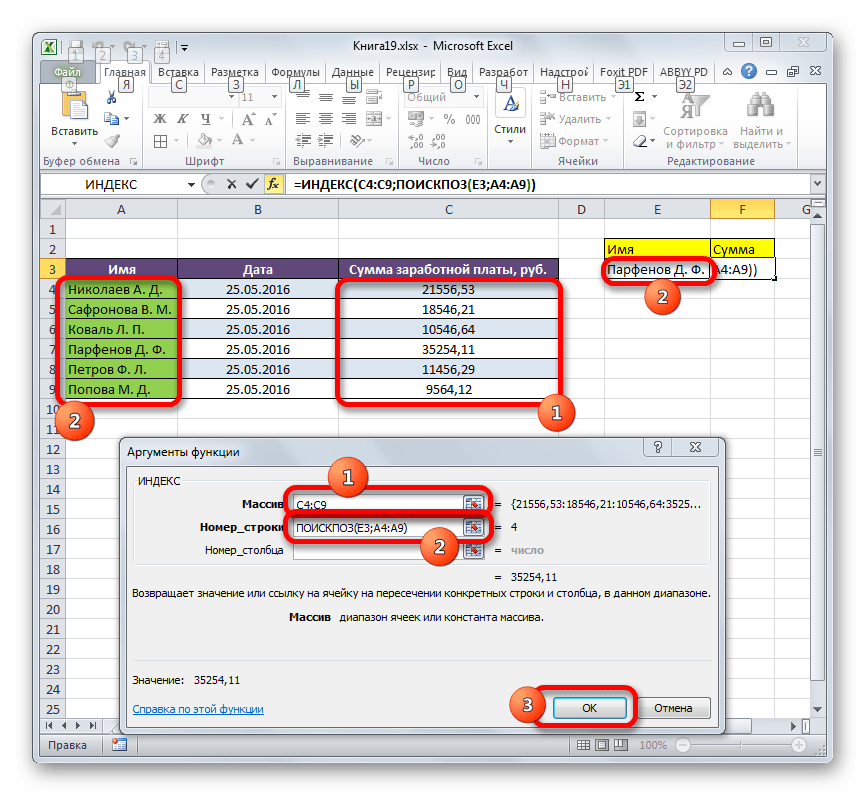
- Выделяем ячейку в поле «Сумма», в которой будет выводиться итоговый результат. Запускаем окно аргументов функции ИНДЕКС для массивов.
В поле «Массив» вносим координаты столбца, в котором находятся суммы заработных плат работников.
Поле «Номер столбца» оставляем пустым, так как мы используем для примера одномерный диапазон.
А вот в поле «Номер строки» нам как раз нужно будет записать функцию ПОИСКПОЗ. Для её записи придерживаемся того синтаксиса, о котором шла речь выше. Сразу в поле вписываем наименование самого оператора «ПОИСКПОЗ» без кавычек. Затем сразу же открываем скобку и указываем координаты искомого значения. Это координаты той ячейки, в которую мы отдельно записали фамилию работника Парфенова. Ставим точку с запятой и указываем координаты просматриваемого диапазона. В нашем случае это адрес столбца с именами сотрудников. После этого закрываем скобку.
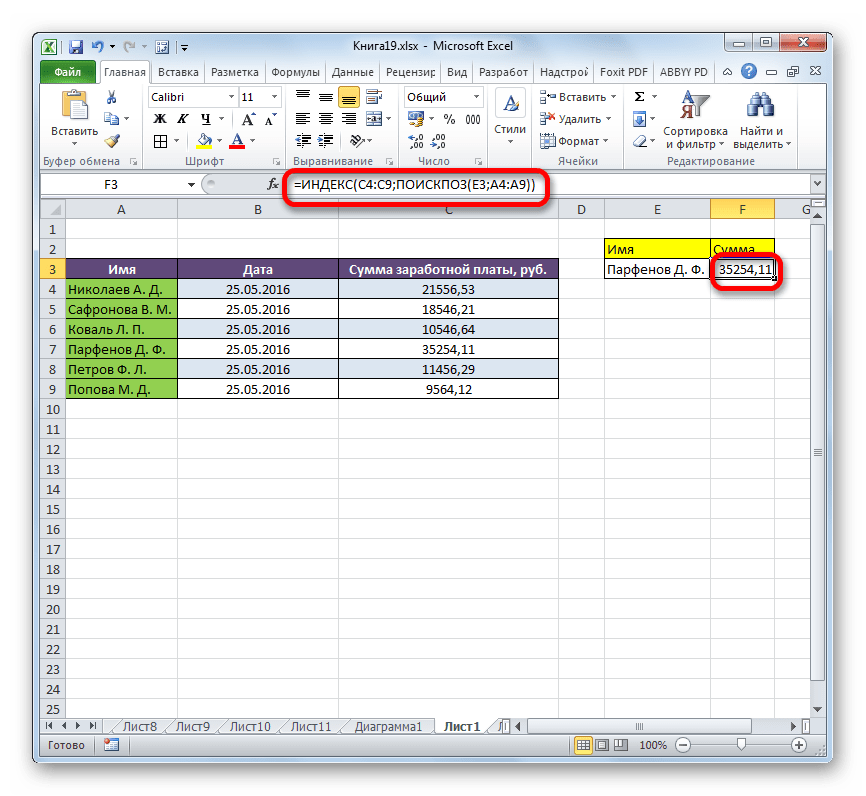
После того, как все значения внесены, жмем на кнопку «OK».
- Результат количества заработка Парфенова Д. Ф. после обработки выводится в поле «Сумма».
- Теперь, если в поле «Имя» мы изменим содержимое с «Парфенов Д.Ф.», на, например, «Попова М. Д.», то автоматически изменится и значение заработной платы в поле «Сумма».
Способ 3: обработка нескольких таблиц
Теперь посмотрим, как с помощью оператора ИНДЕКС можно обработать несколько таблиц. Для этих целей будет применяться дополнительный аргумент «Номер области».
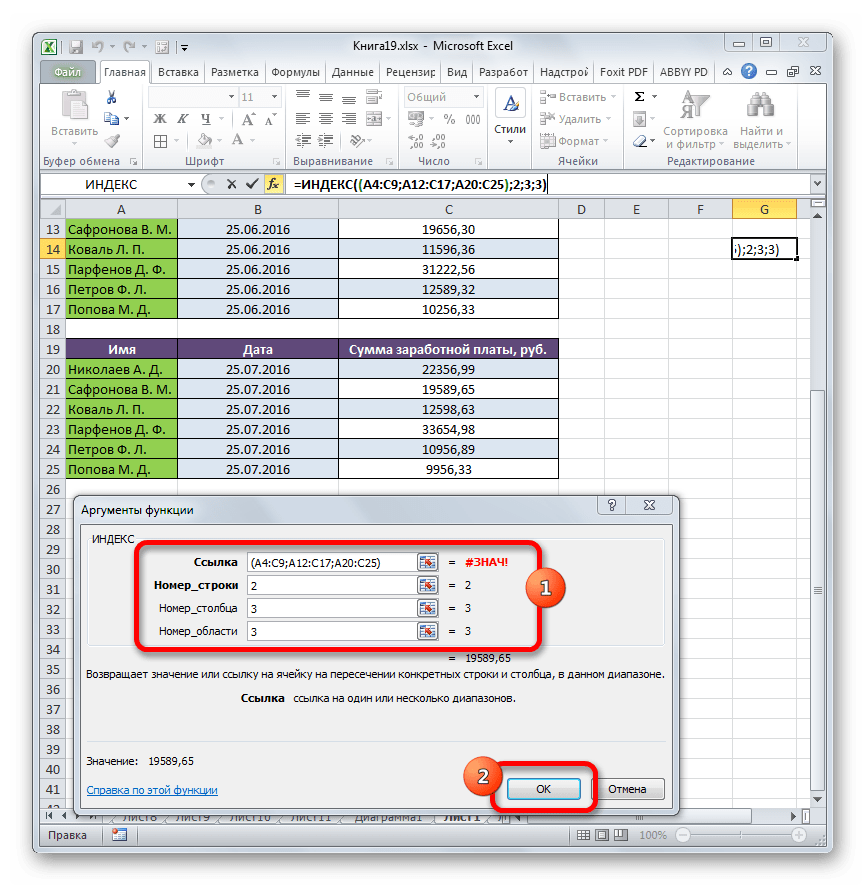
Имеем три таблицы. В каждой таблице отображена заработная плата работников за отдельный месяц. Нашей задачей является узнать заработную плату (третий столбец) второго работника (вторая строка) за третий месяц (третья область).
- Выделяем ячейку, в которой будет производиться вывод результата и обычным способом открываем Мастер функций, но при выборе типа оператора выбираем ссылочный вид. Это нам нужно потому, что именно этот тип поддерживает работу с аргументом «Номер области».
- Открывается окно аргументов. В поле «Ссылка» нам нужно указать адреса всех трех диапазонов. Для этого устанавливаем курсор в поле и выделяем первый диапазон с зажатой левой кнопкой мыши. Затем ставим точку с запятой. Это очень важно, так как если вы сразу перейдете к выделению следующего массива, то его адрес просто заменит координаты предыдущего. Итак, после введения точки с запятой выделяем следующий диапазон. Затем опять ставим точку с запятой и выделяем последний массив. Все выражение, которое находится в поле «Ссылка» берем в скобки.
В поле «Номер строки» указываем цифру «2», так как ищем вторую фамилию в списке.
В поле «Номер столбца» указываем цифру «3», так как колонка с зарплатой является третьей по счету в каждой таблице.
В поле «Номер области» ставим цифру «3», так как нам нужно найти данные в третьей таблице, в которой содержится информация о заработной плате за третий месяц.
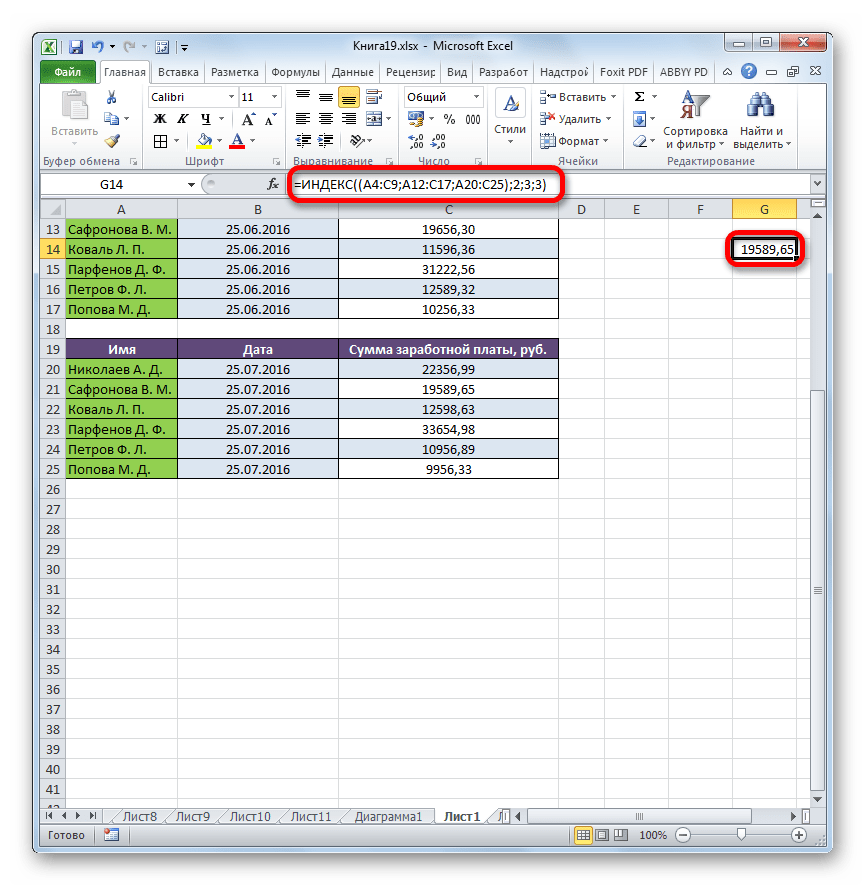
После того, как все данные введены, щелкаем по кнопке «OK».
- После этого в предварительно выделенную ячейку выводятся результаты вычисления. Там отображается сумма заработной платы второго по счету работника (Сафронова В. М.) за третий месяц.
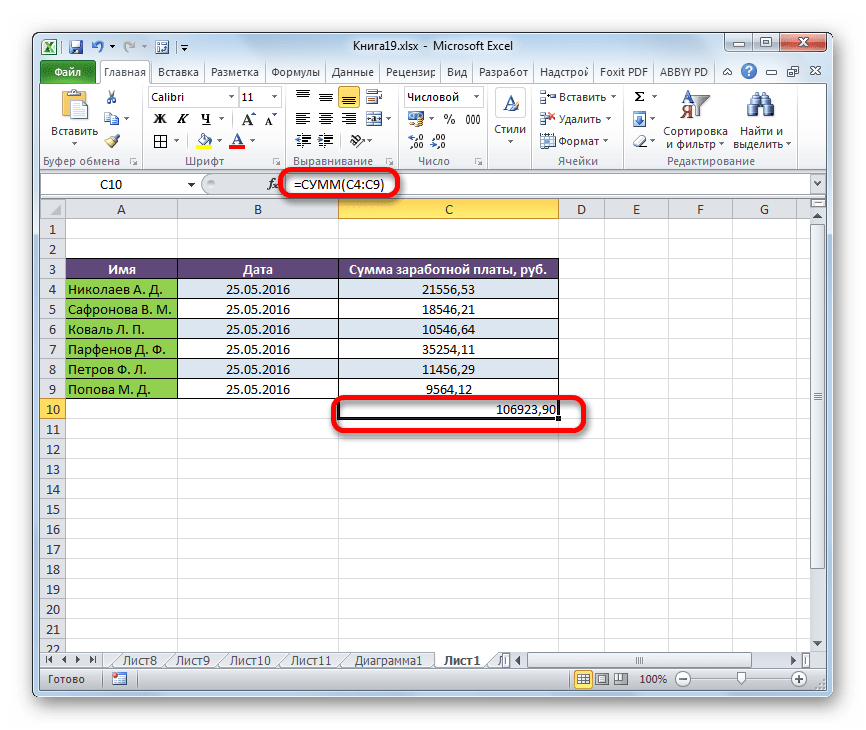
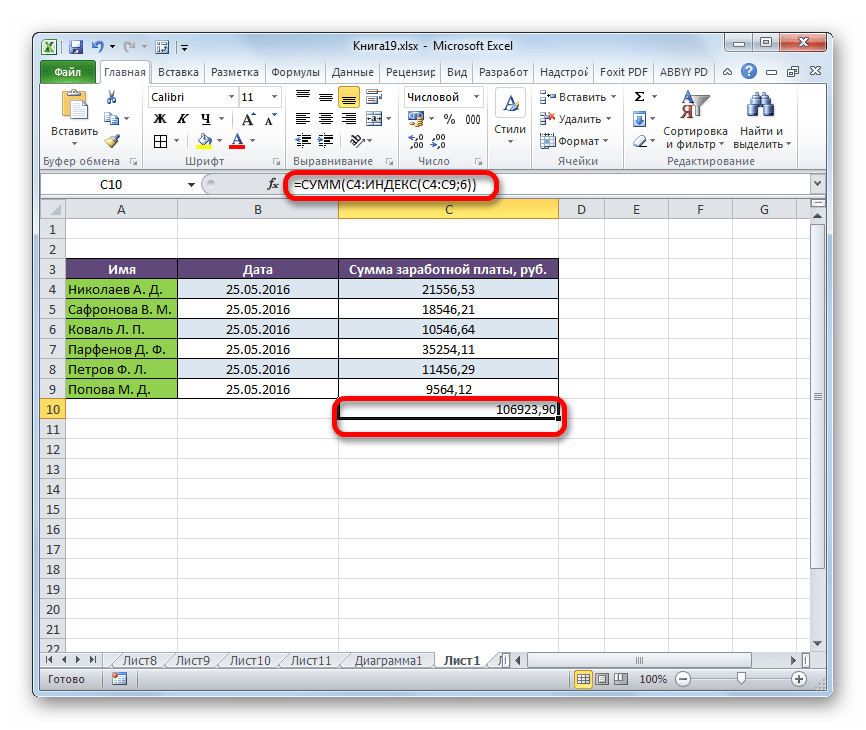
Способ 4: вычисление суммы
Ссылочная форма не так часто применяется, как форма массива, но её можно использовать не только при работе с несколькими диапазонами, но и для других нужд. Например, её можно применять для расчета суммы в комбинации с оператором СУММ.
При сложении суммы СУММ имеет следующий синтаксис:
=СУММ(адрес_массива)
В нашем конкретном случае сумму заработка всех работников за месяц можно вычислить при помощи следующей формулы:
=СУММ(C4:C9)
Но можно её немного модифицировать, использовав функцию ИНДЕКС. Тогда она будет иметь следующий вид:
=СУММ(C4:ИНДЕКС(C4:C9;6))
В этом случае в координатах начала массива указывается ячейка, с которой он начинается. А вот в координатах указания окончания массива используется оператор ИНДЕКС. В данном случае первый аргумент оператора ИНДЕКС указывает на диапазон, а второй – на последнюю его ячейку – шестую.
Урок: Полезные функции Excel
Как видим, функцию ИНДЕКС можно использовать в Экселе для решения довольно разноплановых задач. Хотя мы рассмотрели далеко не все возможные варианты её применения, а только самые востребованные. Существует два типа этой функции: ссылочный и для массивов. Наиболее эффективно её можно применять в комбинации с другими операторами. Созданные таким способом формулы смогут решать самые сложные задачи.
Download Article
Download Article
If your Excel workbook contains numerous worksheets, you can add a table of contents that indexes all of your sheets with clickable hyperlinks. This tutorial will teach you how to make an index of sheet names with page numbers in your Excel workbook without complicated VBA scripting, and how to add helpful «back to index» buttons to each sheet to improve navigation.
-
1
Create an index sheet in your workbook. This sheet can be anywhere in your workbook, but you’ll usually want to place the tab at the beginning like a traditional table of contents.
- To create a new sheet, click the + at the bottom of the active worksheet. Then, right-click the new tab, select Rename, and type a name for your sheet like Index or Worksheets.
- You can rearrange sheets by dragging their tabs left or right at the bottom of your workbook.
-
2
Type Page Number into cell A1 of your index sheet. Column A is where you’ll be placing the page numbers for each sheet.
Advertisement
-
3
Type Sheet Name into cell B1 of your index sheet. This will be the column header above your list of worksheets.
-
4
Type Link into cell C1 of your index sheet. This is the column header that will appear above hyperlinks to each worksheet.
-
5
Click the Formulas tab. It’s at the top of Excel.
-
6
Click Define Name. It’s on the «Defined Names» tab at the top of Excel.
-
7
Type SheetList into the «Name» field. This names the formula you’ll be using with the INDEX function.[1]
-
8
Type the formula into the «Refers to» field and click OK. The formula is =REPLACE(GET.WORKBOOK(1),1,FIND("]",GET.WORKBOOK(1)),"").
-
9
Enter page numbers in column A. This is the only part you’ll have to do manually. For example, if your workbook has 20 pages, you’ll type 1 into A2, 2 into A3, etc., and continue numbering down until you’ve entered all 20 page numbers.
- To quickly populate the page numbers, type the first two page numbers into A2 and A3, click A3 to select it, and then drag the square at A3’s bottom-right corner down until you’ve reached the number of pages in your workbook. Then, click the small icon with a + that appears at the bottom-right corner of the column and select Fill Series.
-
10
Type this formula into cell B2 of your index sheet. The formula is =INDEX(SheetList,A2). When you press Enter or Return, you’ll see the name of the first sheet in your workbook.
-
11
Fill the rest of column B with the formula. To do this, just click B2 to select it, and then double-click the square at its bottom-right corner. This adds the name of each worksheet corresponding to the page numbers you typed into column A.
-
12
Type this formula into C2 of your worksheet. The formula is =HYPERLINK("#'"&B2&"'!A1","Go to Sheet"). When you press Enter or Return, you’ll see a hyperlink to the first page in your index called «Go to Sheet.»
-
13
Fill the rest of column C with the formula. To do this, click C2 to select it, and then double-click the square at its bottom-right corner. Now each sheet in your workbook has a clickable hyperlink that takes you right to that page.
-
14
Save your workbook in the macro-enabled format. Because you created a named range, you’ll need to save your workbook in this format.[2]
Here’s how:- Go to File > Save.
- On the pop-up message that warns you about saving a macro-free workbook, click No.
- In the «Save as type» or file format menu, select Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (*.xlsm) and click Save.
Advertisement
-
1
Click your index or table of contents sheet. If you have a lot of pages in your workbook, it’ll be helpful to readers to add quick «Back to Index» or «Back to Table of Contents» links to each sheet so they don’t have to scroll through lots of worksheet tabs after clicking to that page. Start by opening your index sheet.
-
2
Name the index. To do this, just click the field directly above cell A1, type Index, and then press Enter or Return.
- Don’t worry if the field already contains a cell address.
-
3
Click any of the sheets in your workbook. Now you’ll create your back button. Once you create a back button on one sheet, you can just copy and paste it onto other sheets.
-
4
Click the Insert tab. It’s at the top of the screen.
-
5
Click the Illustrations menu and select Shapes. This option will be in the upper-left area of Excel.
-
6
Click a shape for your button. For example, if you want to create a back-arrow icon sort of like your web browser’s back button, you can click the left-pointing arrow under the «Block Arrows» header.
-
7
Click the location where you want to place the button. Once you click, the shape will appear. If you want, you can change the color and look using the options at the top, and/or resize the shape by dragging any of its corners.
-
8
Type some text onto the shape. The text you type should be something like «Back to Index.» You can double-click the shape to place the cursor and start typing right onto the actual shape
- You might need to drag the corner of the shape to resize it so the text fits.
- To place a text box on or near the shape before typing, just click the Shape Format menu at the top (while the shape is selected), click Text Box in the toolbar, and then click and drag a text box.
- You can stylize the text using the options in Text on the toolbar while the shape is selected.
-
9
Right-click the shape and select Link. This opens the Insert Hyperlink dialog.[3]
-
10
Click the Place in This Document icon. It’s in the left panel.
-
11
Select your index under «Defined Names» and click OK. You might have to click the + next to the column header to see the Index option. This makes the text in the shape a clickable hyperlink that takes you right to the index.
-
12
Copy and paste the hyperlink to other sheets. To do this, just right-click the shape and select Copy. Then, you can paste it onto any other page by right-clicking the desired location and selecting the first icon under «Paste Options» (the one that says «Use Destination Theme» when you hover the mouse over it).
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To create a table of contents in Excel, you can use the «Defined Name» option to create a formula that indexes all sheet names on a single page. Then, you can use the INDEX function to list the sheet names, as well as the HYPERLINK function to create quick links to each sheet.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 55,649 times.
Is this article up to date?
Excel INDEX Function (Examples + Video)
When to use Excel INDEX Function
Excel INDEX function can be used when you want to fetch the value from a tabular data and you have the row number and column number of the data point. For example, in the example below, you can use the INDEX function to get the marks of ‘Tom’ in Physics when you know the row number and the column number in the data set.
What it Returns
It returns the value from a table for the specified row number and column number.
Syntax
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num])
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num], [area_num])
INDEX function has 2 syntax. The first one is used in most cases, however, in case of three-way lookups, the second one is used (covered in Example 5).
Input Arguments
- array – a range of cells or an array constant.
- row_num – the row number from which the value is to be fetched.
- [col_num] – the column number from which the value is to be fetched. Although this is an optional argument, but if row_num is not provided, it needs to be given.
- [area_num] – (Optional) If array argument is made up of multiple ranges, this number would be used to select the reference from all the ranges.
Additional Notes (Boring Stuff.. But Important to Know)
- If the row number or the column number is 0, it returns the values of the entire row or column respectively.
- If INDEX function is used in front of a cell reference (such as A1:) it returns a cell reference instead of a value (see examples below).
- Most widely used along with the MATCH function.
- Unlike VLOOKUP, INDEX function can return a value from the left of the lookup value.
- INDEX function have two forms – Array form and the Reference form
- ‘Array form’ is where you fetch a value based on row and column number from a given table.
- ‘Reference form’ is where there are multiple tables, and you use the area_num argument to select the table and then fetch a value within it using the row and column number (see live example below).
Excel INDEX Function – Examples
Here are six examples of using Excel INDEX Function.
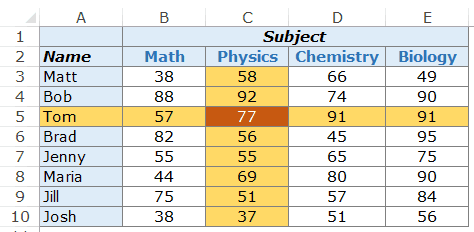
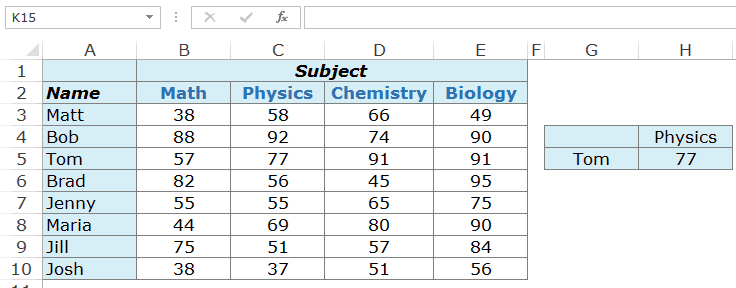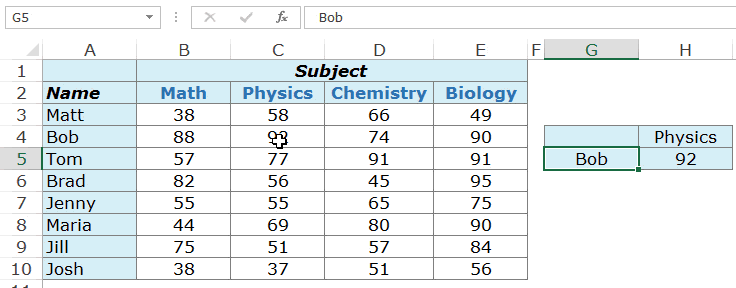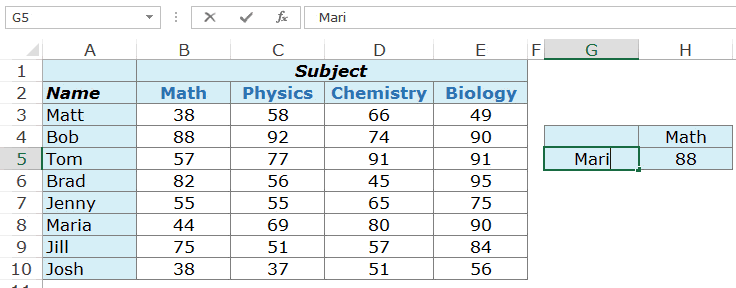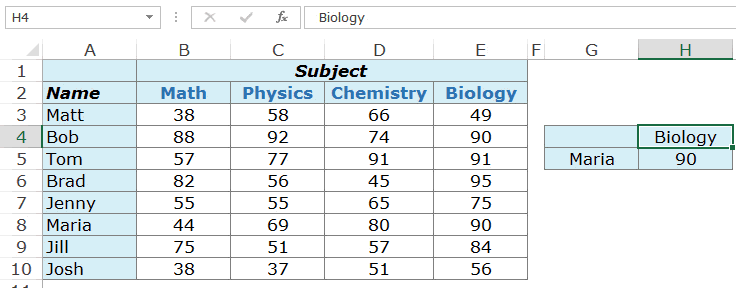
Example 1 – Finding Tom’s Marks in Physics (a two-way lookup)
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
To find Tom’s marks in Physics, use the below formula:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$10,3,2)
This INDEX formula specifies the array as $B$3:$E$10 which has the marks for all the subjects. Then it uses the row number (3) and column number (2) to fetch Tom’s marks in Physics.
Example 2 – Making the LOOKUP Value Dynamic using MATCH Function
It may not always be possible to specify the row number and the column number manually. You may have a huge data set, or you may want to make it dynamic so that it automatically identifies the name and/or subject specified in cells and give the correct result.
Something as shown below:
This can be done using a combination of the INDEX and the MATCH function.
Here is the formula that will make the lookup values dynamic:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$10,MATCH($G$5,$A$3:$A$10,0),MATCH($H$4,$B$2:$E$2,0))
In the above formula, instead of hard-coding the row number and the column number, MATCH function is used to make it dynamic.
- Dynamic Row Number is given by the following part of the formula – MATCH($G$5,$A$3:$A$10,0). It scans the name of students and identifies the lookup value ($G$5 in this case). It then returns the row number of the lookup value in the dataset. For example, if the lookup value is Matt, it’ll return 1, if it is Bob, it’ll return 2 and so on.
- Dynamic Column Number is given by the following part of the formula – MATCH($H$4,$B$2:$E$2,0). It scans the subject names and identifies the lookup value ($H$4 in this case). It then returns the column number of the lookup value in the dataset. For example, if the lookup value is Math, it’ll return 1, if it is Physics, it’ll return 2 and so on.
Example 3 – Using Drop Down Lists as Lookup Values
In the above example, we have to manually enter the data. That could be time-consuming and error-prone, especially if you have a huge list of lookup values.
A good idea in such cases is to create a drop down list of the lookup values (in this case, it could be student names and subjects) and then simply choose from the list. Based on the selection, the formula would automatically update the result.
Something as shown below:
This makes a good dashboard component as you can have a huge data set with hundreds of students at the back end, but the end user (let’s say a teacher) can quickly get the marks of a student in a subject by simply making the selections from the drop down.
How to make this:
The formula used in this case is the same used in Example 2.
=INDEX($B$3:$E$10,MATCH($G$5,$A$3:$A$10,0),MATCH($H$4,$B$2:$E$2,0))
The lookup values have been converted into drop-down lists.
Here are the steps to create the Excel drop down list:
- Select the cell in which you want the drop-down list. In this example, in G4, we want the student names.
- Go to Data –> Data Tools –> Data Validation.
- In the Data Validation Dialogue box, within the settings tab, select List from the Allow drop-down.
- In the source, select $A$3:$A$10
- Click OK.
Now you’ll have the drop-down list in cell G5. Similarly, you can create one in H4 for the subjects.
Example 4 – Return Values from an Entire Row/Column
In the above examples, we’ve used Excel INDEX function to do a 2-way lookup and get a single value.
Now, what if you want to get all the marks of a student. This can enable you to find the maximum/minimum score of that student, or the total marks scored in all subjects.
In simple English, you want to first get the entire row of scores for a student (let’s say Bob) and then within those values identify the highest score or the total of all the scores.
Here is the trick.
In Excel INDEX Function, when you enter the column number as 0, it will return the values of that entire row.
So the formula for this would be:
=INDEX($B$3:$E$10,MATCH($G$5,$A$3:$A$10,0),0)
Now this formula. if used as is, would return the #VALUE! error. While it displays the error, in the backend, it returns an array that has all the scores for Tom – {57,77,91,91}.
If you select the formula in the edit mode and press F9, you’ll be able to see the array it returns (as shown below):
Similarly, based on what the lookup value is, when the column number is specified as 0 (or is left blank), it returns all the values in the row for the lookup value
Now to calculate the total score obtained by Tom, we can simply use the above formula within the SUM function.
=SUM(INDEX($B$3:$E$10,MATCH($G$5,$A$3:$A$10,0),0))
On similar lines, to calculate the highest score, we can use MAX/LARGE and to calculate minimum, we can use MIN/SMALL.
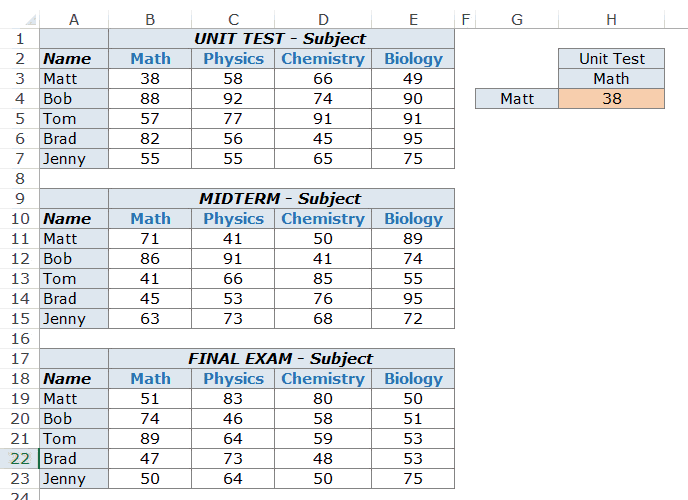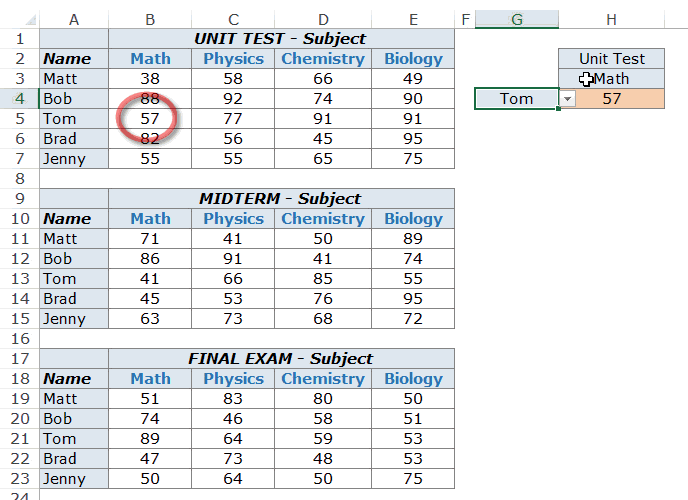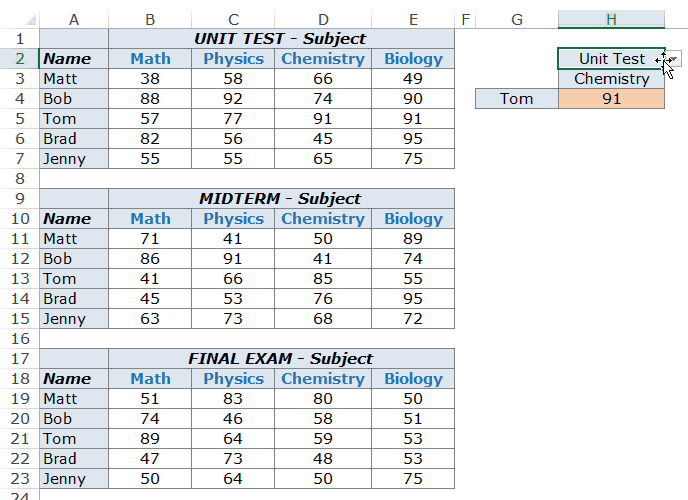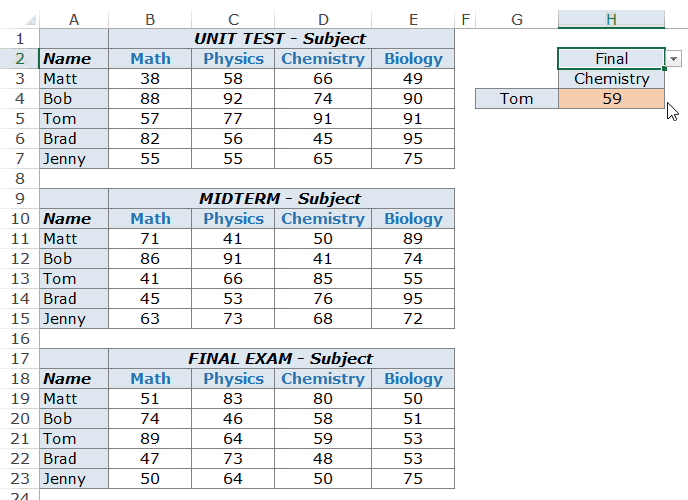
Example 5 – Three Way Lookup Using INDEX/MATCH
Excel INDEX function is built to handle three-way lookups.
What is a three-way lookup?
In the above examples, we’ve used one table with scores for students in different subjects. This is an example of a two-way lookup as we use two variables to fetch the score (student’s name and the subject).
Now, suppose in a year, a student has three different levels of exams, Unit Test, Midterm, and Final Examination (that’s what I had when I was a student).
A three-way lookup would be the ability to get a student’s marks for a specified subject from the specified level of exam. This would make it a three-way lookup as there are three variables (student’s name, subject’s name, and the level of examination).
Here is an example of a three-way lookup:
In the example above, apart from selecting the student’s name and subject name, you can also select the level of exam. Based on the level of exam, it returns the matching value from one of the three tables.
Here is the formula used in cell H4:
=INDEX(($B$3:$E$7,$B$11:$E$15,$B$19:$E$23),MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$7,0),MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0),IF($H$2="Unit Test",1,IF($H$2="Midterm",2,3)))
Let’s break down this formula to understand how it works.
This formula takes four arguments. INDEX is one of those functions in Excel that has more than one syntax.
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num])
=INDEX (array, row_num, [col_num], [area_num])
So far in all the example above, we have used the first syntax, but to do a three-way lookup, we need to use the second syntax.
Now let’s see each part of the formula based on the second syntax.
- array – ($B$3:$E$7,$B$11:$E$15,$B$19:$E$23): Instead of using a single array, in this case, we have used three arrays within parenthesis.
- row_num – MATCH($G$4,$A$3:$A$7,0): MATCH function is used to find the position of the student’s name in cell $G$4 in the list of student’s name.
- col_num – MATCH($H$3,$B$2:$E$2,0): MATCH function is used to find the position of the subject name in cell $H$3 in the list of subject’s name.
- [area_num] – IF($H$2=”Unit Test”,1,IF($H$2=”Midterm”,2,3)): The area number value tells the INDEX function which array to select. In this example, we have three arrays in the first argument. If you select Unit Test from the drop-down, the IF function returns 1 and the INDEX functions select 1st array from the three arrays (which is $B$3:$E$7).
Example 6 – Creating a Reference Using the INDEX Function (Dynamic Named Ranges)
This is one wild use of the Excel INDEX function.
Let’s take a simple example.
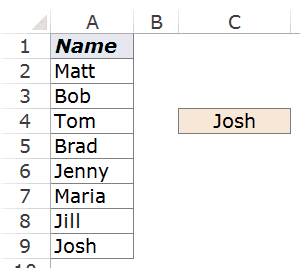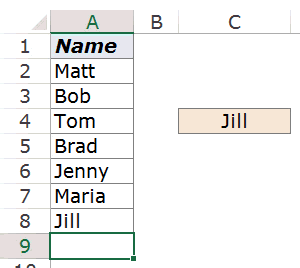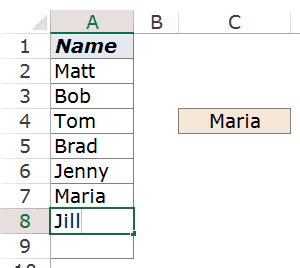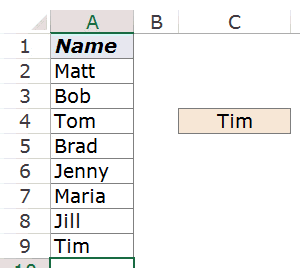
I have a list of names as shown below:
Now I can use a simple INDEX function to get the last name on the list.
Here is the formula:
=INDEX($A$2:$A$9,COUNTA($A$2:$A$9))
This function simply counts the number of cells that are not empty and returns the last item from this list (it works only when there are no blanks in the list).
Now, what here comes the magic.
If you put the formula in front of a cell reference, the formula would return a cell reference of the matching value (instead of the value itself).
=A2:INDEX($A$2:$A$9,COUNTA($A$2:$A$9))
You would expect the above formula to return =A2:”Josh” (where Josh is the last value in the list). However, it returns =A2:A9 and hence you get an array of names as shown below:
One practical example where this technique can be helpful is in creating dynamic named ranges.
That’s it in this tutorial. I’ve tried to cover major examples of using the Excel INDEX function. If you would like to see more examples added to this list, let me know in the comments section.
Note: I’ve tried my best to proof read this tutorial, but in case you find any errors or spelling mistakes, please let me know 🙂
Excel INDEX Function – Video Tutorial
Related Excel Functions:
- Excel VLOOKUP Function.
- Excel HLOOKUP Function.
- Excel INDIRECT Function.
- Excel MATCH Function.
- Excel OFFSET Function.
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- VLOOKUP Vs. INDEX/MATCH
- Excel Index Match
- Lookup and Return Values in an Entire Row/Column.
Бывает у вас такое: смотришь на человека и думаешь «что за @#$%)(*?» А потом при близком знакомстве оказывается, что он знает пять языков, прыгает с парашютом, имеет семеро детей и черный пояс в шахматах, да и, вообще, добрейшей души человек и умница?
Так и в Microsoft Excel: есть несколько похожих функций, про которых фраза «внешность обманчива» работает на 100%. Одна из наиболее многогранных и полезных — функция ИНДЕКС (INDEX). Далеко не все пользователи Excel про нее знают, и еще меньше используют все её возможности. Давайте разберем варианты ее применения, ибо их аж целых пять.
Вариант 1. Извлечение данных из столбца по номеру ячейки
Самый простой случай использования функции ИНДЕКС – это ситуация, когда нам нужно извлечь данные из одномерного диапазона-столбца, если мы знаем порядковый номер ячейки. Синтаксис в этом случае будет:
=ИНДЕКС(Диапазон_столбец; Порядковый_номер_ячейки)
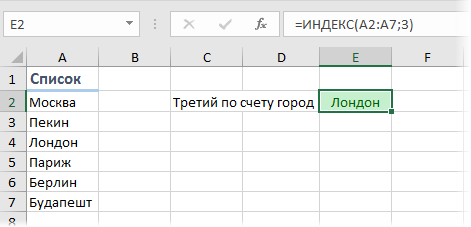
Этот вариант известен большинству продвинутых пользователей Excel. В таком виде функция ИНДЕКС часто используется в связке с функцией ПОИСКПОЗ (MATCH), которая выдает номер искомого значения в диапазоне. Таким образом, эта пара заменяет легендарную ВПР (VLOOKUP):
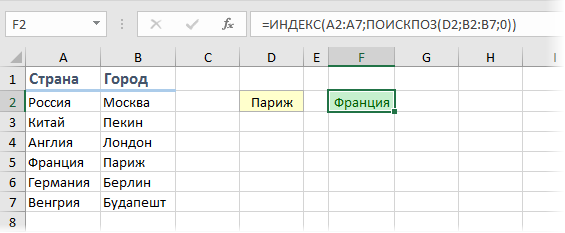
… но, в отличие от ВПР, могут извлекать значения левее поискового столбца и номер столбца-результата высчитывать не нужно.
Вариант 2. Извлечение данных из двумерного диапазона
Если диапазон двумерный, т.е. состоит из нескольких строк и столбцов, то наша функция будет использоваться немного в другом формате:
=ИНДЕКС(Диапазон; Номер_строки; Номер_столбца)
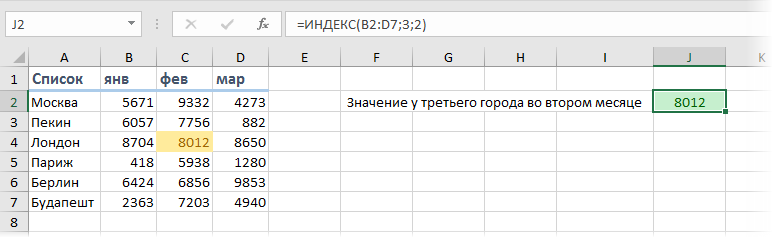
Т.е. функция извлекает значение из ячейки диапазона с пересечения строки и столбца с заданными номерами.
Легко сообразить, что с помощью такой вариации ИНДЕКС и двух функций ПОИСКПОЗ можно легко реализовать двумерный поиск:
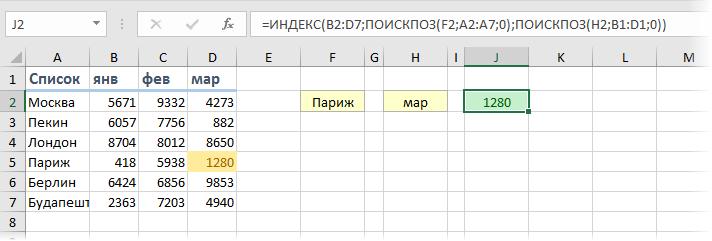
Вариант 3. Несколько таблиц
Если таблица не одна, а их несколько, то функция ИНДЕКС может извлечь данные из нужной строки и столбца именно заданной таблицы. В этом случае используется следующий синтаксис:
=ИНДЕКС((Диапазон1;Диапазон2;Диапазон3); Номер_строки; Номер_столбца; Номер_диапазона)
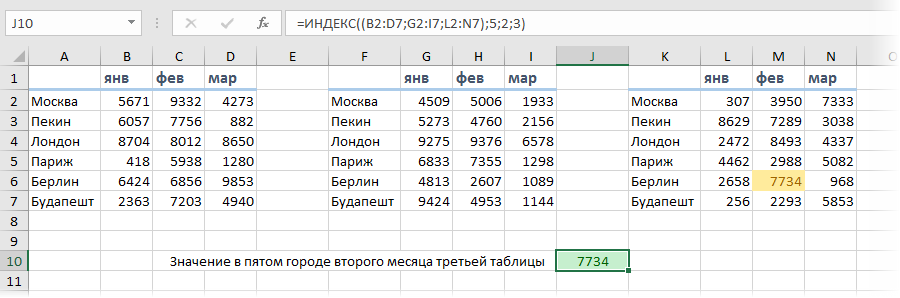
Обратите особое внимание, что в этом случае первый аргумент – список диапазонов — заключается в скобки, а сами диапазоны перечисляются через точку с запятой.
Вариант 4. Ссылка на столбец / строку
Если во втором варианте использования функции ИНДЕКС номер строки или столбца задать равным нулю (или просто не указать), то функция будет выдавать уже не значение, а ссылку на диапазон-столбец или диапазон-строку соответственно:
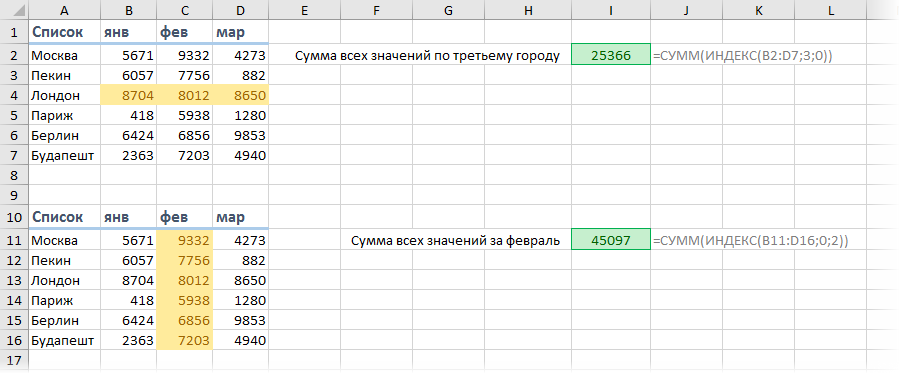
Обратите внимание, что поскольку ИНДЕКС выдает в этом варианте не конкретное значение ячейки, а ссылку на диапазон, то для подсчета потребуется заключить ее в дополнительную функцию, например СУММ (SUM), СРЗНАЧ (AVERAGE) и т.п.
Вариант 5. Ссылка на ячейку
Общеизвестно, что стандартная ссылка на любой диапазон ячеек в Excel выглядит как Начало-Двоеточие-Конец, например A2:B5. Хитрость в том, что если взять функцию ИНДЕКС в первом или втором варианте и подставить ее после двоеточия, то наша функция будет выдавать уже не значение, а адрес, и на выходе мы получим полноценную ссылку на диапазон от начальной ячейки до той, которую нашла ИНДЕКС:
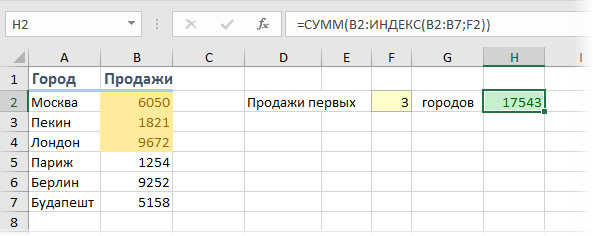
Нечто похожее можно реализовать функцией СМЕЩ (OFFSET), но она, в отличие от ИНДЕКС, является волатильной, т.е. пересчитывается каждый раз при изменении любой ячейки листа. ИНДЕКС же работает более тонко и запускает пересчет только при изменении своих аргументов, что ощутимо ускоряет расчет в тяжелых книгах по сравнению со СМЕЩ.
Один из весьма распространенных на практике сценариев применения ИНДЕКС в таком варианте — это сочетание с функцией СЧЁТЗ (COUNTA), чтобы получить автоматически растягивающиеся диапазоны для выпадающих списков, сводных таблиц и т.д.
Ссылки по теме
- Трехмерный поиск данных по нескольким листам (ВПР 3D)
- Поиск и подстановка по нескольким условиям (ВПР по нескольким столбцам)
- Подстановка данных из одной таблицы в другую с помощью функции ВПР (VLOOKUP)