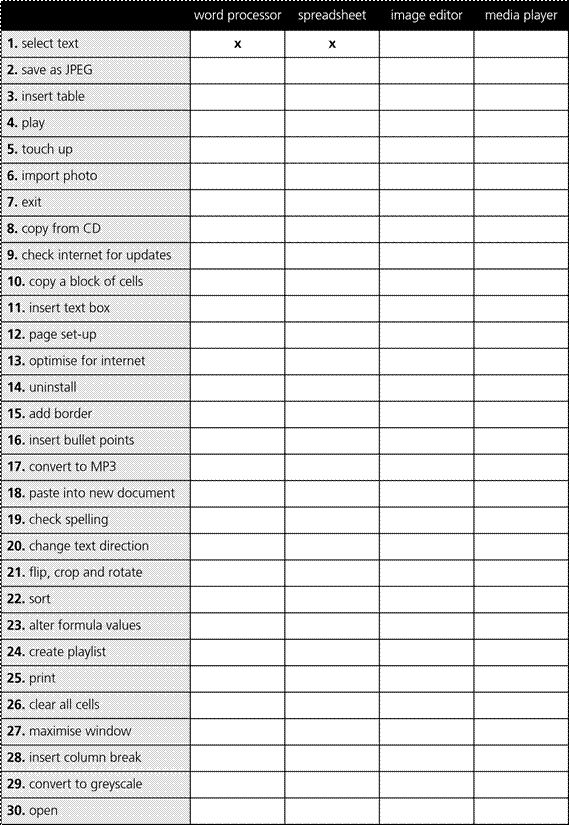
CHECK YOUR ENGLISH VOCABULARY
FOR COMPUTER AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
SECTION 2: SOFTWARE
2.8 Word processing 3
A. Match the word processing tool with
the task.
|
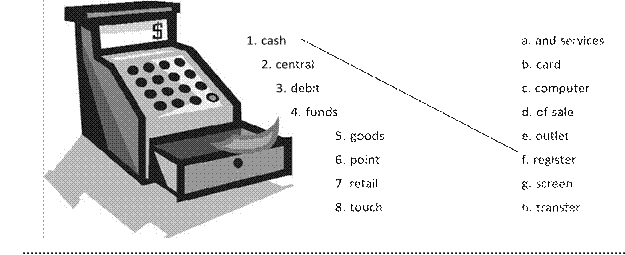
1 |
word count spell checker auto format template find replace print preview track changes mail merge macro |
a |
produces form letters and counts the number of words, finds all instances of a word checks the text for spelling automatically changes the shows how a document has been records a sequence of a pre-formatted blank document shows how the document will replaces words or phrases in a |
|
|
2 |
b |
|||
|
3 |
c |
|||
|
4 |
d |
|||
|
5 |
e |
|||
|
6 |
f |
|||
|
7 |
g |
|||
|
8 |
h |
|||
|
9 |
i |
|||
|
10 |
j |
B. Match the words with the examples.
|
1 |
Times 10 point |
|
|
2 |
Times 24 point |
|
|
3 |
bullet points |
|
|
4 |
superscript |
|
|
5 |
subscript |
|
|
6 |
justified text |
|
|
7 |
highlighted text |
|
|
8 |
text wrap |
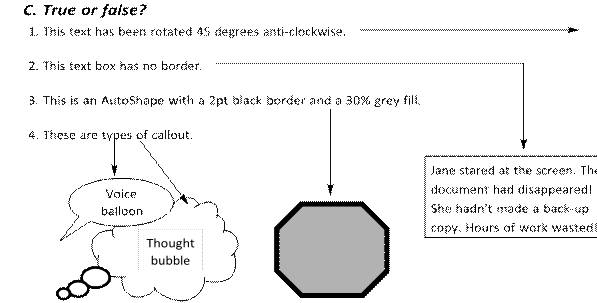
C. True or false?
D. Choose the best words.
|
1 |
Making changes to a text is |
||||
|
A |
altering |
B |
renewing |
C |
editing |
|
2 |
To change normal text to |
||||
|
A |
choose |
B |
take |
C |
select |
|
3 |
A very pale image behind the |
||||
|
A |
an ink mark |
B |
a watermark |
C |
a grey mark |
|
4 |
To divide the text into two |
||||
|
A |
page break |
B |
page stop |
C |
page change |
|
5 |
The numbers at the bottom of |
||||
|
A |
page numbers |
B |
sheet numbers |
C |
paper numbers |
|
6 |
An extra note at the bottom of |
||||
|
A |
bottom note |
B |
foot |
C |
footnote |
|
7 |
In word processing, to put |
||||
|
A |
sort |
B |
organise |
C |
order |
|
8 |
A list of contacts, addresses |
||||
|
A |
an archive |
B |
a list |
C |
a database |
|
9 |
Producing a document on your |
||||
|
A |
computer publishing |
B |
desktop publishing |
C |
electronic publishing |
|
10 |
Cut or copied text is |
||||
|
A |
clipboard |
B |
clip |
C |
clipart |
ANSWER
KEY
A: 1 b, 2 d, 3 e, 4 h, 5 c, 6 j, 7 i, 8
f, 9 a, 10 g
B: 1 e, 2 a, 3 c, 4 f, 5 g, 6 h, 7 d, 8
b
C: 1 false (it’s been rotated 90
degrees anti-clockwise), 2 false, 3 true, 4 true
D: 1 c, 2 c, 3 b, 4 a, 5 a, 6 c, 7 a, 8
c, 9 b, 10 a
Добавил:
Upload
Опубликованный материал нарушает ваши авторские права? Сообщите нам.
Вуз:
Предмет:
Файл:
Check Your English Vocabulary for Computing.docx
Скачиваний:
741
Добавлен:
21.03.2016
Размер:
2.79 Mб
Скачать
-
Match
the words with the punctuation marks and symbols.-
full stop
-
comma
-
exclamation mark
-
question mark5. single quotes
-
double quotes
-
dollar sign
-
percentage sign
-
ampersand
-
asterisk
-
hash
-
brackets
-
left bracket
-
square brackets
-
underscore
-
hyphen
-
plus sign
-
equals sign
-
colon
-
semicolon
-
«at» sign
-
forward slash
-
backward slash
-
arrow
-
!
-
@
-
,
-
&
-
.
-
=
-
‘Hello’
-
*
-
“Hello”
-
_
-
—
-
?
-
/
-
(
) -
$
-
[
] -
%
-
(
-
#
-
:
-
+
-
;
-
-
Look
at this table, and answer true or false.-
All the cells are the same size.
-
Departure
times
|
Bristol |
London |
Dover |
|
8.15 |
10.30 |
12.45 |
|
14.00 |
16.15 |
18.30 |
|
17.45 |
19.00 |
21.15 |
-
There are four columns and three rows.
-
The text in the top bar is reversed-out.
-
The middle column has a lighter flood fill.
-
The text is centred within its cells.
-
The table gridlines are grey.
2.8 Word processing 3
-
Match
the word processing tool with the task.-
word count
-
spell checker
-
auto format
-
template
-
find
-
replace
-
print preview
-
track changes
-
mail merge
-
macro
-
produces form letters and address labels
-
counts the number of words, lines and
paragraphs -
finds all instances of a word or phrases in
a document -
checks the text for spelling errors
-
automatically changes the styles of
headings, lists etc. -
shows how a document has been altered
-
records a sequence of commands, and applies
them when required -
a pre-formatted blank document – just type
your text into the fields -
shows how the document will look in print
-
replaces
words or phrases in a document with new text
-
-
Match
the words with the examples.
-
Times 10 point
-
Times 24 point
-
bullet points
-
superscript
-
subscript
-
justified text
-
highlighted text
-
text wrap
A. Jane stared at the screen
-
Jane stared at the screen. The document had
disappeared! She hadn’t made a back-up copy. Hours of work
wasted! -
Possible courses of action:
Re-type the entire document.
Get a computer engineer to find if the text
could be retrieved.
Resign, and get another job.
-
Jane stared at
the screen. -
Jane stared
at the screen. -
Jan. 24th
-
A2
-
Jane stared at the screen. The document had
disappeared! She hadn’t made a back-up copy. Hours of work
wasted!
D.
Choose the best words.
-
Making changes to a text is called _________.
a.
altering b.
renewing c.
editing
-
To change normal text to italic, first you must
_________ the text you want to format.
|
a. 3. |
c. |
|
a. 4. |
c. |
|
a. 5. |
c. |
|
a. |
c. paper numbers |
-
An extra note at the bottom of the page (usually
in a smaller font size) is called a ________.-
bottom note b.
foot c.
footnote
-
-
In word processing, to put things into
alphabetical order is to ________.-
sort b. organisec. order
-
-
A list of contacts, addresses etc. is called
_________.-
an archive b. a
list c. a
database
-
-
Producing a document on your computer and
sending it direct to a printing press is __________.
|
a. 10. |
c. electronic publishing |
|
a. |
c. |
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
CHECK YOUR ENGLISH VOCABULARY FOR
COMPUTERS
AND
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Jon Marks
A & C Black London
www.acblack.com
First
edition published 1995
Second
edition published 1999
This
third edition published in Great Britain 2007
A
& C Black Publishers Ltd
38
Soho Square, London W1D 3HB
©
Jonathan Marks 2007
All
rights reserved.
No
part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the permission
of the publishers.
A
CIP entry for this book is available from the British Library.
ISBN-10:
0 7136 7917 4 ISBN-13: 978 0 7136 7917 5
eISBN-13: 978-1-4081-0246-6
Text
typeset by A & C Black
Printed
in Great Britain at Caligraving Ltd, Thetford, Norfolk
This book is produced using paper that is made from wood grown in
managed, sustainable forests. It is natural, renewable and recyclable. The
logging and manufacturing processes conform to the environmental regulations of
the country of origin.
Contents
Page
Introduction 4
Section 1: Hardware
1.1 Hardware 6
1.2 Some
useful verbs 7
1.3 The
workstation 8
1.4 The
keyboard 10
1.5 The
mouse 11
1.6 Scanning 12
1.7 Some
useful adjectives 13
1.8 Printing 14
1.9 Mobile
phones 16
1.10 Other
devices 18
1.11 Inside
a computer 19
1.12 Data
storage 20
1.13 Connectivity 21
1.14 Networks 22
1.15 Electronic
payments 23
1.16 Review
crossword 24
1.17 Your
computer 26
Section 2: Software
2.1 Software:
the basics 28
2.2 Using
software: useful verbs 30
2.3 The
control panel 31
2.4 Applications 32
2.5 Some
useful adjectives 33
2.6 Word
processing 1 34
2.7 Word
processing 2 36
2.8 Word
processing 3 38
2.9 Image
editing 40
2.10 Graphic
design 41
2.11 Spreadsheets 42
2.12 Presentation
software 44
2.13 Problems
with software 45
2.14 Which
program? 46
2.15 Review
quiz 47
2.16 Your
software 48
Section 3: The internet
3.1 The
internet: the basics 50
3.2 Internet
browsers 52
3.3 Search
engines 53
3.4 Things
on the net 54
3.5 Internet
terms 55
3.6 E-commerce 56
3.7 Internet
security 58
3.8 Email 59
3.9 Email
comprehension 1 60
3.10 Email
comprehension 2 61
3.11 Useful
verbs crossword 62
3.12 Revision
wordsearch 63
3.13 Your
internet 64
Answer
key 65
Index 75
Introduction
Who is the book for?
This book has been
written for people whose first language is not English, and who use or are
going to use computers and other information technology in an English-speaking
environment. It covers the language needed to use information technology
equipment, work with computer programs, discuss problems and plan projects. It
does not cover advanced technical vocabulary for computer programmers or
electronic engineers. All the language in the book is intended to be accessible
to intermediate level students and above.
How can the book be used?
The vocabulary is
arranged by topic. Choose the topics that interest you. The pages do not have
to be completed in any particular order, and there is no need to complete all
the pages if some are on topics which are not useful to you. It is better to
complete one or two pages in a day, and remember the vocabulary, rather than
completing as many pages as possible. The answers to the exercises can be found
at the back of the book. There is also an index to help you find the pages
which are most useful to you.
Write new words and
phrases you learn in a notebook or file. Review this language regularly so that
it becomes part of your active vocabulary.
A good general dictionary
will be very helpful, providing pronunciation guides and more contexts. For
vocabulary relating specifically to computers, Dictionary of Computing (A&C
Black, ISBN 978 07475 6622 9) will be a useful reference source.
Section 1: Hardware
A.
Match
the verbs with the nouns.
1.
recharge
2.
click on
3.
dial
4.
give
5.
move
6.
print out
7.
send and receive
8.
take some
B.
Choose
the best verb.
1.2 Some useful verbs
a.
digital photos
b.
faxes
c.
a number on your mobile phone
d.
a presentation
e.
something with the mouse
f.
the battery
g.
the mouse
h.
twenty pages
9. To turn on the computer,
__________ the «Start» button.
|
a. touch b. 10. The printer has __________ of ink. |
c. switch |
|
a. |
c. run |
11. Unfortunately, my scanner
isn’t __________ at the moment.
|
a. working b. 12. Please __________ the CD ROM. |
c. doing |
|
a. |
c. inject |
13. The projector
isn’t working because it isn’t __________.
a. plugged b.
plugged in c. plugged into
14. The batteries
in my digital camera are nearly dead. They need __________.
a. to change b.
exchanging c. changing
15. I have to
__________ a computer screen for eight hours a day.
a. see b.
look at c. watch
16. Switch off your
computer, and __________ it from the wall socket.
a. de-plug b.
unplug c. non-plug
17. I turned off
the photocopier and ___________ the plug.
a. pulled out b.
extracted c. took away
18. __________ any
key to continue.
a.
Kick b. Smash c. Hit
1.3 The workstation
Rearrange the letters to make things which can be part of a
workstation.
tucmepor ___computer____
13. trirpen _______________
14. nasecnr
_______________
15. kesd
_______________
16. hacir
_______________
17. nopelethe
_______________
Choose the best word.
18.
The mouse moves on a __________.
|
a. mouse mat b. 19. TV and computer screens are usually measured in |
c. mouse |
|
a. feet b. 20. Before you start work, __________ the height of your |
c. inches |
|
a. adjust b. 21. To get sound from your computer, plug in a pair of |
c. rearrange |
|
a. loudhailers b. 22. The computer is connected to the telephone line via a |
c. loud voices |
|
a. |
c. mod |
23. You can
increase the functions or performance of a computer with an __________.
a. extension card b.
exploding card c. expansion card
24.
Mobile phones and PDAs can communicate with computers via
__________.
|
a. Bluebeard ® b. 25. There’s a spare __________ in the workstation… |
c. Bluetooth ® |
|
a. electric hole b. 26. …so you can plug in your mobile phone __________. |
c. electrical |
|
a. charger b. 27. SD cards can be read in a computer’s __________. |
c. electrification |
|
a. |
c. card reader |
1.4 The keyboard
space
bar alphabet keys calculator keys
function
keys return key (or enter key) indicator
lights
shift
key alt key control key escape key delete
key tab key caps lock key backspace key
1. To go back one space, hit the _______________. 2.
To change to capital letters, press the _______________.
You can
3.
To change the capital letters permanently, hit the
_______________.
4.

insert a tabulation, press the _______________. say «key» or
5.
To activate the «Ctrl» functions, press the
_______________. «button»
6.
To activate the «alt» functions, hit the
_______________.
7.
To stop the computer doing something, you can press
the_______________.
8.
Select the text you want to remove, and hit the _______________.
standard
keyboard ergonomic keyboard key in (or type in)
enter data input
9.

10.
It took me two hours to _______________ all that text.
11.
A keyboard is a _______________ device.
12.
Do you have a _______________?
No. I have a special _______________. It’s better for my
arms and back.
1.5 The mouse
|
pointer |
on |
optical |
roll |
|
scroll up |
scroll down |
touchpad |
left button |
|
right button |
joystick |
single |
double |
|
scroll wheel |
hold |
repetitive strain injury |
1.
______________ to see pages above.
2.
______________ to see pages below.
3.
To select text, ______________ the left button, and move the
mouse pointer.
4.
If you use a mouse for many hours every day, you can get
______________ in your fingers.
5.
With a laptop computer, plug in a mouse, or use the ______________
in front of the keyboard.
6.
To play some games, you need to use a ______________ instead of a
mouse.
7.
To move up and down a page, you can ______________ the mouse
wheel.
8.
This mouse doesn’t have a ball. It’s an ______________ mouse.
9.
One click of a mouse button is called a ______________ click.
10.
Two clicks of a mouse button are called a ______________ click.
11.
Click ______________ the folder to open it.
12.
___________________
13.

14.
___________________
15.
___________________
A
wheel mouse
1.6 Scanning
|
adjust |
all-in-one |
at |
preview (or |
|
brightness |
connected |
contrast |
file format |
|
flatbed |
handheld |
high |
image editing |
|
low |
OCR software |
original |
click |
|
text |
dpi |
How to scan an image
1.
Make sure the scanner is _____________ to the computer.
2.
Lift the lid and put the _____________ on the scanner glass.
3.
For high image quality, scan _____________ 300 _____________ or
higher.
4.
The scanning software will automatically do a _____________.
5.
If the image is too dark or too light, you can __________ the
_____________ and _____________.
6.
_____________ «scan». A
7.

by _____________.
8.
If you want to save the image, choose a _____________. JPEG is a
good choice for photos.
9.
The scanned image can be manipulated using _____________
software.
10.
An _____________ printer/scanner can print, scan and copy. B
11.
12.
Picture B is a _____________ scanner.
13.
Picture C is a _____________ resolution photograph.
14.
Picture D is a _____________ resolution photograph.
C  D
D 
1.7 Some useful adjectives
Choose the best adjective.
|
1. Oh dear. I pressed the __________ button. |
|
|
a. incorrect b. 2. I can’t use my mobile phone. The battery’s __________. |
c. false |
|
a. over b. 3. The battery isn’t completely flat, but its very |
c. exhausted |
|
a. down b. 4. My video camera is very __________. |
c. low |
|
a. easy to use b. 5. My new computer has a very __________ processor. |
c. obvious |
|
a. quick b. 6. The X19 notebook computer features a very __________ |
c. fast |
|
a. compact b. 7. Keeping files on paper is __________ solution. |
c. small |
|
a. an old-tech b. 8. Keeping files on a computer database is a __________ |
c. a low-tech |
|
a. new-tech b. 9. My new PDA is the __________ model. |
c. high-tech |
|
a. latest b. 10. In our office, we’ve set up a __________ network. |
c. most |
|
a. wire-free b. 11. A call from New York to Toyko is __________ distance. |
c. wireless |
|
a. far b. 12. I don’t think this printer is __________ with my |
c. faraway |
|
a. compatible b. 13. My laptop is only 3 centimetres ___________. |
c. suitable |
|
a. thick b. 14. The screen on my laptop isn’t very __________. |
c. wide |
|
a. light b. 15. In three or four years, my new computer will probably |
c. bright |
|
a. |
c. obsolete |
16. When you connect this to your
computer, it will work immediately. It’s __________.
a. plug
and go b. plug and play c.
plug and use
1.8 Printing
A. Put the words in the spaces.
|
cartridge |
collate |
cover |
feed |
|
double-sided |
landscape |
mono |
out |
|
out of |
portrait |
jammed |
print-heads |
|
reload |
replacement |
via |
1.
When the ink runs out, you have to change the ____________.
2.
____________ cartridges can be ordered online.
3.
To change the cartridge, you have to lift the ____________.
4.
The printer is connected to the computer ____________ a USB
cable.
5.
The printer is ____________ paper. ____________ the paper tray.
6.
I think some paper is ____________ inside the printer.
7.
My printer keeps getting jammed. I think there’s a problem with
the paper ____________.
8.
Shall I print this ____________ in colour or black and white?
9.
«Black and white» is also known as ____________.
10.
If there’s a problem with the print quality, perhaps the
____________ need cleaning.
11.
Can your printer do ____________ printing?
12.
To ____________ means to put all the pages into the correct
order.
|
13. This page is in ____________ orientation. |
14. This page is in ____________ |
B.
Which
type of printer 

inkjet
printer laser printer
1. cheaper to buy x
2. cheaper to run
3. faster printing
speed
4. takes up more
space
5. uses liquid ink
6. uses toner
7. more reliable
8. cartridges need
changing more often
C.
True
or false?
|
1. |
Inkjet cartridges can be refilled up to three times. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
2. |
Colour images are printed by mixing red, green and yellow |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
3. |
«ppm» stands for pages per minute. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
4. |
Most inkjet printers can print out at 100 ppm or more. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
5. |
Inkjet cartridges are very difficult to change. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
6. |
Photo-paper is a lot more expensive than plain paper. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
7. |
Recycled paper is made out of old bottles. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
8. |
Some Inkjet printers have three print qualities: draft, |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
9. |
Before you can use a new printer, you have to install the |
|
|
a CD-ROM. |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
|
10. |
When a print job has started, it can’t be cancelled. |
TRUE / FALSE |
1.9 Mobile Phones
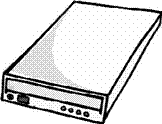
Mobile Phone networks
|
contract |
installed |
networks |
operators |
|
pay-as-you-go |
SIM card |
roaming |
tariffs |
|
top up |
users |
In Britain there are several mobile phone 1_______________
including Vodaphone, O2, T-mobile and Orange. There are also 2_______________
like Virgin Mobile who use the network of another company.
When you buy a cell phone, you have a
choice of 3_______________. The most popular is «4_______________»,
with customers paying for their calls in advance. They can 5_______________
their accounts in shops, over the internet, and at cash machines. Heavy 6_______________
may prefer a 7_______________. They pay a fixed amount every month,
but the calls are much cheaper than they are for pay-as-you-go customers.
Mobile phones usually come with a 8_______________
already 9_______________. If you take the phone abroad, you may be
able to use it on a local network. This is called «10_______________».
It can be expensive, and it may be cheaper to buy a foreign SIM card.
Choose the best word.
1.
After 6pm, calls cost 20p __________ minute
a. for one b.
per c. each
2.
You can’t use a mobile in a cave because there’s no __________.
a. network b.
connection c. power
3.
I need to charge up my mobile phone battery. Have you seen my
__________?
a. charger b.
recharger c. charging machine
4.
When you send a text message, the __________ function can help
your write it more quickly.
a. predicting
text b. predictive text c. text predictor
5.
In the car, it’s safer to use a __________ phone.
a. handless b.
no hands c. hands-free
|
6. |
||
|
a. keypad locker b. 7. a. 8. a. 9. a. 10. a. 11. a. Which is not possible? 12. |
c. locker of keypad c. call expenses c. amount c. duration c. transmitter c. |
|
|
a. mobile phone b. 13. |
c. moving phone |
d. cellular phone |
|
a. SIM card b. 14. |
c. sim chip |
d. |
|
a. a text message b. 15. |
c. |
d. a phone message |
|
a. |
c. |
d. |
1.10 Other devices
A. Match the devices with the places you would find them.
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. |
cash |
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. |
at a supermarket checkout connected to a pair of headphones |
|
B. |
|||
|
9. |
|||
|
a. |
c. swapped |
10. A laptop
computer with a screen you can write on is called a __________.
a. tablet PC b.
table PC c. flat screen PC
11. An image on TV
or computer screen is made up of thousands of __________.
a. points b.
pixels c. bits
12. You can draw
directly onto a computer screen with a __________.
a. bright pen b.
light pen c. pixel pen
13.

a.
an internet camera b. a web watcher
c.
a webcam
14.
The woman in the photo is wearing a __________.
a.
headpiece b. headphone
c.
headset
15.
She talks to customers on the telephone all day. Sheworks in a
__________.
a.
telephone centre b. call centre
c.
talking centre
1.11 Inside a computer
|
A. |
||
|
chips dual |
megabytes |
megahertz |
|
motherboard processor |
speed |
upgraded |
Most of these are made by Intel and AMD, and are sometimes referred to as
«[2]_______________». The fastest
processors are [3]_______________, which means that there
are two processors working together. The [4] _______________
of a processor is measured in [5]_______________, which is usually
written as MHz.
A computer’s memory is measured in 6_______________.
If a computer has 1,024 megabytes of memory, and the memory type is SDRAM, this
is written as 1,024 MB SDRAM, and is pronounced «a thousand and
twenty-four megabytes ess-dee-dram».
The processor and
memory modules are located on the 7_______________. Changing a
computer’s processor is not generally practical, but the memory can usually be 8_______________.
B. Power
|
disconnect |
fan |
mains |
|
overheating |
shock |
spikes |
|
supply |
surge protector |
transformer |
1.12 Data storage
|
burn |
capacity |
card |
drawer |
|
eject |
free space |
hard drive |
stick |
1.
The data and applications on your computer are stored on the
_______________.
2.
To run this application you need at least 50MB of _______________
on your hard drive.
3.
My computer’s hard drive has a _______________ of 120GB.
4.
you want.
5.
The opposite of «Insert the DVD» is
«_______________ the DVD».
6.
I can’t eject the CD. I think the _______________’s stuck.
7.
Digital cameras usually store pictures on a memory
_______________ or a memory _______________.
Which do you think is the best solution for each
problem? (More than one solution
1.13 Connectivity
|
1. Scanners, printers and webcams are __________. |
|
|
a. extras b. 2. Add extra USB __________ to your computer…. |
c. |
|
a. ports b. 3. … with a USB __________. |
c. |
|
a. centre b. 4. ADSL is also known as __________. |
c. hub |
|
a. wideband b. 5. I want to get a __________ ADSL modem. |
c. |
|
a. |
c. high-speed |
6. The internet is
much faster with a broadband connection than with __________.
a. dial-up b.
phone-up c. call-up
7. With a wireless
router, you can __________ your broadband connection with other users.
a. divide b.
combine c. share
8. This wire’s too
short. I need an __________ cable.
a. extended b.
extension c. extender
9. You can connect
a USB plug to a PS/2 port by using __________.
a. an adaptor b.
a bridge c. a connector
1.14 Networks
LAN
|
intranet |
Local |
log onto |
network card |
|
satellite |
server |
terminals |
WAN (Wide |
LAN is pronounced «lan», and stands for 1_________________
Area Network. In a typical LAN, there is a central network 2_________________
which supports a number of 3_________________. Users have to 4_________________
the network server. Pages of information that can be viewed within a LAN are
called an 5_______________ . A number of LANs connected to each
other via 6_________________ or other form of __communication are
called a 7_________________. To be used as network terminals, each
computer needs to have a 8_________________ installed.
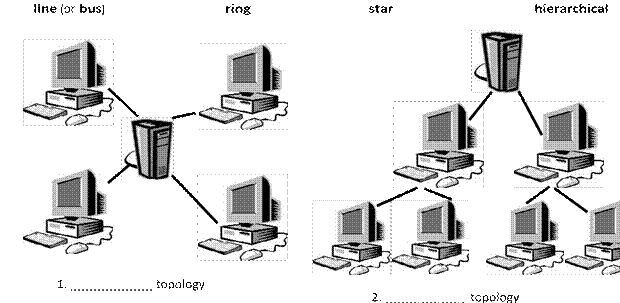
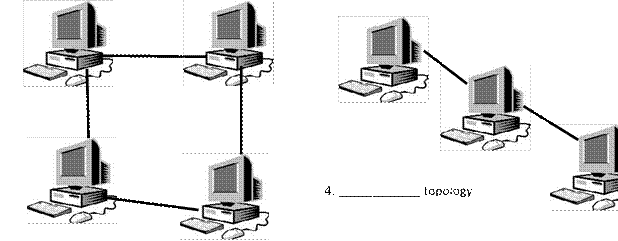
Network topologies
3. ____________ topology
1.15 Electronic payments
A.
EPOS and EFTPOS
Cross out the incorrect word

sale) terminals are cash / money registers found in retail openings
/ outlets such as shops and restaurants. They are connected to a central
/ centre computer, and data about objects / goods and
services sold is entered into the terminals via keyboards, barcode readers, touch
/ finger screens etc. They are useful for stock management, and can
produce itemised bills and receipts / recipes.
EFTPOS
(electronic funds transfer point of sale) can also transfer cash / funds
directly from the customer’s bank account via a debit / paying card.
They are now more
common than EPOS terminals.
B.
Word
partnershipsMatch
the words.
C. Plastic
Match the cards with the phrases.
1. credit card a.
Buy now, pay now.
2. debit card b.
Buy now, pay the bank later.
3. cash card c.
Buy now, pay the shop later.
4. loyalty card d.
Spend, and get some money or goods back from the shop.
5.
store card e. Take money out of a cash machine.
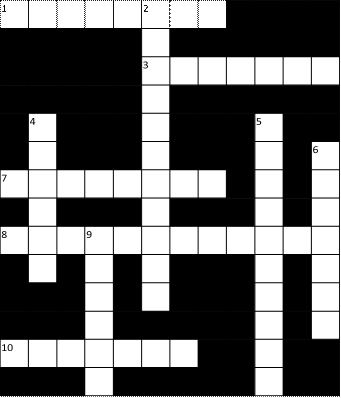
1.16 Review crossword
All the words can be found in Units 1.1 to 1.15
Across
1. A camera connected to the internet. (6 letters)
6. To send an SMS message. (4)
9. The
most common page orientation. (8)
10. A computer’s
«brain». (9)
11. It prevents a
computer from overheating. (3)
14. A connection
without wires. (7)
15. The place where
you put a plug. (6)
20. Processor
speeds are measured in these. (9)
21. The cheapest
type of printer. (6)
22. Lift this
before you use your scanner. (3)
24. The shop assistant does this to your credit card. (5)
26. The strip on the back of a credit or debit card. (8)
Down
2. When it’s dead,
recharge it or replace it. (7)
3. You speak into
this. (10)
4. The mouse moves
on this. (3)
5. A computer,
printer and scanner on a desk with a chair. (11)
7. Laser printers
use this instead of ink. (5)
8. A design (for
example, a type of keyboard) which is better for your body. (9)
12. An image on a
screen is made up of thousands of these. (6)
13. Printers,
scanners, webcams etc. (10)
16. A very large
computer which never moves. (9)
17. A photo or
drawing. (5)
18. You need to
change or refill this when your printer runs out of ink. (9)
19. Two or more
computers connected together. (7)
23. The slowest form of internet connection. (4, 2)
26. Image resolution is usually
measured in this. (3)
|
1 |
2 |
||||||||||||||
|
3 |
4 |
||||||||||||||
|
5 |
6 |
7 |
|||||||||||||
|
8 |
9 |
||||||||||||||
|
10 |
|||||||||||||||
|
11 |
12 |
13 |
|||||||||||||
|
14 |
|||||||||||||||
|
15 |
|||||||||||||||
|
16 |
17 |
18 |
|||||||||||||
|
19 |
20 |
||||||||||||||
|
21 |
|||||||||||||||
|
22 |
23 |
||||||||||||||
|
24 |
|||||||||||||||
|
25 |
|||||||||||||||
|
26 |
1.17 Your computer
Can you answer these questions in English?
1. What kind of
computer do you have?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Do you know the
technical specifications of you computer?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Would you like
to upgrade your computer? If so, what kind of computer would you like to get?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
4. Which
peripherals do you use most often? Why?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
5. Do you use
computer networks? If so, how do you connect to the networks you use?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Section 2:
Software
2.1 Software: the basics
A. Choose the correct word to fill the spaces.
1. Turn on your computer. It
will usually take a few minutes to __________.
|
a. boot itself b. 2. Windows XP, Macintosh OSX and Linux are __________. |
c. get booted |
|
a. operating systems b. 3. On my computer, I have a picture of my cat as the |
c. operators |
|
a. desktop background b. 4. Microsoft Word, Adobe Acrobat and CorelDraw are programs |
c. desktop |
|
a. applicators b. 5. To open Microsoft Word, click on the __________. |
c. applications |
|
a. picture b. 6. I keep all my digital photos in a __________ called |
c. icon |
|
a. folder b. 7. Is it possible to open Microsoft Excel __________ in |
c. box |
|
a. texts b. 8. In Microsoft Word, to start typing a new letter, open a |
c. pages |
|
a. document b. 9. When you __________ a document, it’s sent to the recycle |
c. paper |
|
a. destroy b. 10. Deleted documents stay in the recycle bin until you |
c. delete |
|
a. |
c. clean |
11. In Windows, the icon is just a __________ to the
application. If you delete the icon, the application will
still be on your computer.
|
a. connector b. 12. If the computer crashes, you can try pressing the |
c. link |
|
a. restart b. 13. When I’ve finished using my computer, I always |
c. replay |
|
a. |
c. shut |
14. If I leave my computer on without using it, after a
while it goes into __________ mode.
a. stand
down b. waiting c.
standby
B. Insert the missing words.

installed launch
2.2 Using software: useful verbs
Match the words on the left with the words on the right.
Set 1
1.
arrange the
2.
cut and paste
3.
install
4.
open the document in
5.
resize the
6.
save it as
Set 2
1.
copy the
2.
customize your
3.
launch
4.
search
5.
send the file
6.
use the
Set 3
1. accidentally deleted
an
2.
exit
3.
click on that button 4. pull down a
5. replace the
existing
6.
view
Set 4
1.
close down an
2.
log off
3.
look in
4. put the
file
5. run a
6. wipe the
a.
a Microsoft Word
file
b.
a new window
c.
photo. It’s too
big.
d.
an application
e.
some text
f.
icons on the
desktop
a.
for a lost file
b.
a program
c.
«search»
function
d.
text into a new
document
e.
to a different
folder
f.
desktop
a.
menu
b.
important file
c.
an application
d.
as a web page
e.
on the task bar
f.
file
a.
after a session
b.
all folders
c.
application
d.
hard drive
e.
on a USB memory
key
f.
program
2.3 The control panel
2.4 Applications
A.
Match
the descriptions on the left with these famous applications.
1. word
processor a. Adobe Photoshop
2. spreadsheet b.
Internet Explorer
3. virus
protection c. Microsoft Word
4. browser d.
Microsoft Excel
5. image
editor e. Microsoft PowerPoint
6. media
player f. Norton AntiVirus
7. email
software g. Outlook Express
8. presentation
software h. Adobe PageMaker
9. graphic
design software i. RealPlayer
B.
Crossword
1. programs
which tell the computer whatto do (8)
2. 
piece of software which makes acomputer do a task (for example, edit an image)
(11)
3. any
set of instructions for a computer (7)
4. software
which operates a peripheral,such as a scanner or printer (6)
5. application
which stores and displaysdigital photos (5,5)
6. you
enter a security code to prove thatyou have a _______ to use the software (7)
7. software
which prevents unauthorisedaccess to your computer over the internet
(8)
8. a
series of letters and numbers whichyou have to enter before installing some
programs (8,4)
9. download
new features for anapplication (6)
10.
an unauthorised copy of a program (7)
2.5 Some useful adjectives
A. Choose the best words.
1. Software which is easy to use
is…
|
a. user-easy b. 2. Software which is obvious to use is… |
c. usable |
|
a. intuitive b. 3. Software which is not obvious to use is… |
c. comprehensible |
|
a. counter-intuitive b. 4. Software for use by children and schools is… |
c. non-intuitive |
|
a. learning b. 5. Software for use by businesses is… |
c. educational |
|
a. commercial b. 6. Software made specially for one company is… |
c. busy |
|
a. one-off b. 7. Software for use at home is… |
c. tailor-made |
|
a. for home use b. 8. Software which has been illegally copied is… |
c. for |
|
a. |
c. fake |
9. Software which has been bought from the company that
produced it is…
a. real b.
justified c. licensed
Types of software
B. Match the type of software with the definition.
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
a. b. c. d. |
e. You
can use it for free for a while (often a month). When the trial period finishes,
you have to pay, or the program will de-activate.
2.6 Word processing 1
A. Write the numbers next to
the words. B. Match the words with the
types of lettering
top margin
bold
bold italic italic
bottom margin lower
case (or small letters)
outline plain text shadow
left-hand margin
strikethrough
underline
case (or capital letters) heading (or title) 1. ____________ ABCDEFG body text 2.
____________ abcdefg
3.
____________ Typewriters
paragraph break
4.
____________ Typewriters
indent
5. ____________
Typewriters
illustration
6. ____________ Typewriters border (or frame) 7. ____________
Typewriters
page number 8.
____________ Typewriters
9. ____________
Typewriters
page border (or edge of the page)
10. ___________
Typewriters
C. Choose the
best words.
1. The text about typewriters is
divided into three __________.
|
a. sections b. 2. Times, Arial and Courier are types of __________. |
c. chunks |
|
a. lettering b. 3. The text about typewriters is __________. |
c. font |
|
a. single spaced b. 4. «Inventions that Changed the World» is the |
c. one-and-half |
|
a. header b. 5. Do you think the margins are too __________ or |
c. footnote |
|
a. big / small b. 6. Do you like the page _________? |
c. long / short |
|
a. |
c. pattern |
2.7 Word processing 2
Sunnydays Coach Tours
Winter /
Spring Tours
Dec
1st: Paris March
20th / March 27th: Berlin
Five
nights in a four star hotel just 200 metres from the Eiffel Five
nights full board in a two star Towers. All meals included. Depart London 10
am. hotel conveniently located a short metro ride from the city
centre. Price includes a three-day travel
Dec 7th: Amsterdam pass.
Depart 8.00 am Bristol,
Three
nights in simple guest house overlooking a canal in 10.15 am
London the heart of Amsterdam. Breakfast and a canal tour included in the
price. Depart 8.00 am Bristol, 10.15 am London.
April 4th: Easter in San Sebastian
Enjoy the traditional Easter celebrations in one of
northern
Dec 11th / Dec 16th: Christmas Markets in
Vienna Spain’s most elegant and
Discover the magic of Austria’s Christmas markets. Five atmospheric
cities. 6 nights half board in a three star seanights half-board. Optional
extra trip to Innsbruck. Depart front
hotel.
Cardiff 8 am Dec 11th,
and London 9 am Dec 16th. Depart
London 8.30 am.
April 11th / April 17th : The Tulip Fields
of Holland
Dec 29th: New Year in Verona Experience
the beauty of rural Holland in spring, based in a
Three
nights half board in one of northern Italy’s most comfortable
guesthouse in the historic city of Delft. Five beautiful cities. On the
evening of Dec 31st enjoy a five nights half board. Depart
Cardiff 8 am April 11th, and course gourmet meal in one of Verona’s finest
restaurants, London 9 am April 17th. followed by the traditional
firework display in Piazza Bra.
April 24th: Barcelona
January 13th to March
10th: Skiing in the French Alps Five
nights in a centrally-located one-star hotel on a bed-
Avoid the airport
crowds – go by coach! Departures and-breakfast basis.
Price includes a three-day city
Saturdays 9am London.
Drop-off points throughout SW transport card. Optional
extra excursion to the Salvador Dali
France. Wide range of accommodation packages available. museum
in Figueres. Depart London 8 am
A. Choose the best words.
1. «Winter / Spring
Tours» is the __________.
|
a. under-heading b. 2. The body text is divided into two __________. |
c. below-heading |
|
a. columns b. 3. The body text is __________. |
c. strips |
|
a. left-aligned b. 4. The illustration isn’t original artwork. It’s |
c. justified |
|
a. screen art b. 5. The clipart has been given _________. |
c. clipart |
|
a. an under shadow b. 6. This poster has been given a 10% grey background |
c. a sub-shadow |
|
a. wash b. 7. The design of this poster is __________. |
c. colour |
|
a. |
c. state-of-the-art |
Punctuation and symbols
B.
Match
the words with the punctuation marks and symbols.
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. |
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. v. w. x. |
C.
Look
at this table, and answer true or false.
1.
All the cells are the same size.
Departure times
|
Bristol |
London |
Dover |
|
8.15 |
10.30 |
12.45 |
|
14.00 |
16.15 |
18.30 |
|
17.45 |
19.00 |
21.15 |
2. There are four
columns and three rows.
3. The text in the
top bar is reversed-out.
4. The middle
column has a lighter flood fill.
5. The text is
centred within its cells.
6.
The table gridlines are grey.
2.8 Word processing 3
A.
Match
the word processing tool with the task.
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. |
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. |
B.
Match
the words with the examples.
1. Times 10
point
2. Times 24
point
3. bullet
points
4. superscript
5. subscript
6. justified
text
7. highlighted
text
8.
text wrap
a. Jane stared at the
screen
b.
Jane stared at the screen. The document had disappeared!
She hadn’t made a back-up copy. Hours of work wasted!
c.
Possible courses of action:
Re-type the entire document.
Get a computer engineer to find if the
text could be retrieved.
Resign, and get another job.
d.
Jane stared at the screen.
e.
Jane stared
at the screen.
f.
Jan. 24th
g.
A2
h.
Jane stared at the screen. The document had disappeared! She
hadn’t made a back-up copy. Hours of work wasted!
D. Choose the best words.
1.
Making changes to a text is called _________.
a. altering b.
renewing c. editing
2.
To change normal text to italic, first you must _________ the
text you want to format.
|
a. choose b. 3. A very pale image behind the text is called ________. |
c. select |
|
a. an ink mark b. 4. To divide the text into two pages, insert a ________. |
c. a grey mark |
|
a. page break b. 5. The numbers at the bottom of the page are ________. |
c. page change |
|
a. |
c. paper |
6.
An extra note at the bottom of the page (usually in a smaller
font size) is called a ________.
a. bottom note b.
foot c. footnote
7.
In word processing, to put things into alphabetical order is to
________.
a. sort b.
organise c. order
8.
A list of contacts, addresses etc. is called _________.
a.
an archive b. a list c. a database
9.
Producing a document on your computer and sending it direct to a
printing press is __________.
|
a. computer 10. Cut or copied text is temporarily stored in the |
c. electronic |
|
a. |
c. clipart |
2.9 Image editing
A. Match the word with the
definition.
1. crop a.
turn an image
2. sharpen b. reverse
an image
c. improve the appearance
of an
3.
soften image
4. zoom
in
d. remove part of an image
5. zoom out e. copy
part of an image to
6. flip another
point in that image
f.
view part of the image in more detail
7. rotate
g.
view more of the image in less detail
8. touch
up
h. convert
a vector image to a bitmap image (see B5 below)
9. clone i. make
the image less blurred 10. rasterize j. make the image more
blurred
B. True or false?
1. Greyscale images
take up more disk space than colour images.
2. It’s often
preferable to scan line drawings as black and white images rather
than greyscale images. This takes up less disk space, and produces sharper
lines. This type of image is also known as lineart.
3. On most
computers, you can view photos as a slideshow – each photo is shown for
a few seconds.
4. You can also view
photos as fingernails – small versions of the photos, with lots shown on
the screen at the same time.
5. A vector image
(for example, a clipart image) can be expanded to any size without
loss of resolution. A bitmap image (for example, a photo) is made
of pixels, so it loses resolution when it is expanded.

contrast
greyscale black
and white high
brightness
2.10 Graphic design
Choose the best words
from each pair in bold.
1.
It’s usually possible to 1 import / introduce
Adobe PageMaker files into Adobe InDesign. The majority of graphic design
applications can 2 export / send off documents as PDF
files, or as HTML web pages.
2.
This box has a black 3 frame / outside,
also known as a «stroke». Inside the frame, the fill is a 4 fade
/ gradient from dark grey to light grey.
The difference
between the two versions of «wave», is that 5 curling /
kerning has been applied to the top version.
3.
A frame, graphic or block of text is known as 6 an
object / a thing. These are arranged in 7 levels /
layers – the top layer 8 overlaps / overruns the
layer below.
4. This image is 9
blurred / soft at the edges (see unit 1.6 for the
original).
This 10 result / effect
is also known as 11 feathering / birding.
5.
12 Full bleed / total bleed means that
the page is printed right up to the edges – there are no white margins. The 13
snail / slug area is the area outside the area to be
printed where instructions for the printer are written.
6.
This image has been 14 pulled / stretched
(see unit 2.8 for the original).
7.
Before a document goes 15 to press / for
printing, it’s essential to check the 16 examples / proofs
for errors.
8.
Like desktop printers, most colour printing 17 machines
/ presses print in four colours: cyan (light blue), magenta (dark
pink), yellow and black. Before printing, a document must be divided into the
four colours. this process is called colour 18 separation / division.
These separations are then turned into 19 plates / stamps –
one for each of the inks that will be used.
9.
Prior to colour separation, coloured images, graphics and text
have to be 20 transformed / converted from RGB (Red
Green Blue), the colour format of computer displays, to CMYK (Cyan Magenta
Yellow Black) the colour format of printing presses.
10.
The process of preparing documents from a graphic designer for
the printing press is called 21 reprographics / reproduction.
2.11 Spreadsheets
A.
Choose
the best word.
|
1. A basic spreadsheet is a __________ of spaces for data. |
|
|
a. grid b. 2. A spreadsheet consists of columns and __________. |
c. ladder |
|
a. |
c. rows |
3. A
spreadsheet grid is called a worksheet. A file containing one or more
worksheets is called a __________.
|
a. workout b. 4. In the worksheet above, the __________ cell is in column |
c. workbook |
|
a. important b. 5. Use the mouse pointer to select a single cell or |
c. focus |
|
a. bunch b. 6. It’s easy to adjust the column __________. |
c. block |
|
a. size b. 7. Spreadsheets can perform mathematical __________. |
c. space |
|
a. |
c. jobs |
8. To get a
worksheet to perform a mathematical calculation, you have to enter a
___________.a format b. form c. formula
9. A number in a
spreadsheet cell is often called a __________.
a. digit b.
numeral c. value
10. To remove the contents of a cell is to __________ that
cell.
a. clean b.
wash c. clear
11. To remove a complete row is to __________ that row.
a. wipe b.
delete c. erase
12. Changing the fonts, colours etc. of a spreadsheet is
called __________.
a.
formatting b. forming c.
reforming
B.
Add
the arithmetic operator symbols to the table below.* / ^ — +
|
symbol |
verb |
noun |
everyday |
|
add |
addition |
«five |
|
|
subtract |
subtraction |
«five |
|
|
multiply |
multiplication |
«five «five |
|
|
divide |
division |
«fifteen |
|
|
raise |
«ten |
C.
Answer
true or false.
0.75
7.5
|
1. The decimal point has been shifted one place to the |
TRUE / FALSE |
|
188 102 65 12 2. 0.005 0.05 5,000 5,055.5 3. apples bananas pears pineapples 4. |
TRUE / FALSE TRUE / FALSE TRUE / FALSE |
D.
Choose
the best words from each pair in grey type.
Three useful features in Microsoft Excel:
Cells can contain 1
text / language, numerical 2 values / details
and formulas. It’s also possible to add pop-up comment 3 boxes / squares
containing additional information (choose Comment from the Insert
menu).
The Fill
and Autofill commands can be used for making multiple copies of the
contents of a cell. Autofill can also be used to automatically create a 4 list / series of
months, numbers etc.
You
can improve the 5 looks / appearance of a spreadsheet very quickly by
using the AutoFormat feature.
2.12 Presentation software
1. In Microsoft PowerPoint, when
creating a new presentation, you can choose between a blank presentation, a
design template and the AutoContent __________.
|
a. witch b. 2. PowerPoint can be used to create presentation |
c. bogeyman |
|
a. slideshows b. 3. You can choose a _________ to move from one slide to |
c. exhibitions |
|
a. |
c. transition |
4. You can include moving
pictures in your presentation. These are called __________.
|
a. films b. 5. You can choose a __________ for your presentation. |
c. animations |
|
a. colour pattern b. 6. You can give your presentation over the internet as an |
c. colour scheme |
|
a. |
c. online |
7. It’s
usually clearer to present statistics in the form of a table or __________.
a. chart b.
figure c. track
8. If
you wish, the software will help you __________ of your presentation.
a. practice the
times b. rehearse the timing c. try out the times
9. You
can choose to record the __________ on your computer…
a. narration b.
speaking c. voice
10. …rather than
giving it __________.
a. in real life b.
for real c. live
2.13 Problems with software
Choose the correct preposition. Then match the problem with
the solution.
|
1. ____ |
2. ____ |
3. ____ |
4. ____ |
5. ____ |
6. ____ |
7. ____ |
8. ____ |
9. ____ |
2.14 Which program?
Match the operations with the application types.
2.15 Revision Quiz
2.16 Your software
Can you answer these questions in English?
1. Which application do you use most often? Why?
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
2. How does it help you in your work?
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Which features do you find most useful?
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
4. Does it have any limitations which annoy you? What are they?
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
5. Is there an application you’d like to learn to use? What would you
use it for?
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
Section 3: The Internet
3.1 The internet: the basics
A. Choose the best word from each
pair in grey type.
What’s the difference between the Web
and the internet?
Some people think that the internet and the Web are the same
thing, but in fact they are different. The internet (often called simply
«the net») is a global 1 network
/ net of interconnected
computers. These computers communicate with each other 2 over / through existing
telecommunications networks – principally, the telephone system. The Word Wide
Web (usually known as just «the Web») is the billions of web pages
that are stored on large computers called web 3 servers / services.
To 4 see / access the
web, you need a computer and a modem. You then connect over your telephone line
to an internet service 5 port /
provider (ISP), which sends your
request to view a particular web page to the correct web server.
Websites are not the only service
available on the internet. It is also used for many other functions, including
sending and receiving email, and connecting to newsgroups and 6 discussion / talking
groups.
You could say
that the internet is a system of roads, and web pages and emails are types of
traffic that travel on those roads.
B.
Put
these operations in the order that you do them (variations are possible).
close down your browser connect to your
ISP disconnect from the internet enter a web address (also known as a URL*)
into the address field launch your browser (for example, Internet Explorer,
Netscape Navigator or Mozilla Firefox) perhaps wait for a few seconds while the
web-page downloads view the page
* URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, but the full term
is almost never used
C.
Choose
the best words.
|
1. ADSL* is more commonly known as __________. |
|
|
a. longband b. 2. Broadband internet connection is much faster than |
c. wideband |
|
a. |
c. dial-up |
3. Before you can connect to the
internet for the first time, you have to __________ an account with an ISP.
a. set b.
set up c. set in
4. Each time you want to connect to
your ISP’s system, you have to enter a log-in name and a __________.
a. security word b.
safe word c. password
5. You can set your computer to
__________ your log-in details, so you don’t have to type them in each time.
|
a. store b. 6. With a broadband connection, you usually have to pay a |
c. recall |
|
a. fixed monthly 7. With dial-up, you can usually choose a ________ tariff. |
c. fixed monthly cost |
|
a. |
c. pay-if-you-like |
8.
Some broadband contracts limit the amount of _________ you can
have each month.
a. pages b.
traffic c. use
9.
Looking at web pages can be called «navigating the Web»
but is more commonly called ________.
a. «surfing the net» b.
«skiing the net» c. «swimming
the net»
10.
You can often find the answer to a question by ________ on the
internet.
a. looking at it b.
looking for it c. looking it up
11.
When your computer is not connected to the internet, it is
________.
a. out of line b.
offline c. off the
line
12.
Internet banking is also called ________.
a. online banking b.
on the line banking c. inline banking
13.
An unexpected disconnection from the internet is called a
__________.
a. lost connection b.
missed connection c. dropped connection
14.
A file which is copied from the internet onto your computer is
called _________
a. an upload b.
a download c. a load
15.
Downloading files from the internet can ________ your computer
with a virus.
a. infect b.
contaminate c. dirty
*ADSL stands for asymmetric digital subscriber line, but the
full term is almost never used.
3.2 Internet browsers
A. Match the browser toolbar button with the function.
1. Back a.
Shows a list of the websites you have visited recently.
2. Forward b.
Opens the media bar, accessing internet radio, music, video etc.
3. Stop c.
Displays the page you were on before.
4. Refresh[6] / Reload2 d. Shows the
latest version of the page.
5. Home e.
Opens the search panel.
6. Search f.
Displays the page you were on before using the Back button.
7. Favourites1 / Bookmarks2 g. Displays
the page you have set as your home page.
8. Media h.
Prints the current page.
9. History i.
Stops a page from downloading.
10. Mail j. Displays
the web addresses you have chosen as your favourites.
11. Print k.
Shows email options.
3.3 Search engines
What’s
the difference between a web directory and a search engine?
Web directories
(for example, Excite, Lycos) list categories and sub-categories with links to
websites. Search engines (for example, Google, Altavista) search the Web for
web pages according to the instructions that you give them.
A.
Using
a search engine
Put the words into the spaces.
|
click on |
criteria |
database |
hyperlinks |
|
keywords |
matches |
media |
refine |
|
returns |
sponsored |
view |
Stage 1: Enter one or more _____________.
Stage 2: The search engine looks for _____________ in
all the web pages on their _____________.
Stage 3: The search engine ____________ the
matches (or «hits») with _____________ to the web pages.
Stage 4: The search engine may also return
«_____________ links». These are links to the websites of companies
who have paid the search engine company.
Stage 5: You _____________ the hyperlink to
____________ the web page.
Stage 6: If necessary, you can _____________
your search by using advanced search _____________ such as language, country or
the type of _____________ you are looking for.
B.
Logical
operators
You can refine your search by using logical operators. Match
the search engine instructions with the matches.
|
1. «English vocabulary» |
a. Pages where both words appear. |
|
2. English + vocabulary |
b. Pages containing the phrase English vocabulary. |
|
3. English NEAR vocabulary |
c. Pages containing one of the words, but not both. |
|
4. English OR vocabulary |
d. Pages where the two words appear close together. |
|
5. English NOT vocabulary |
e. All pages that contain English except the |
3.4 Things on the net
A. Match the activities with the internet features.
1. Keep
a public diary of your journey through South America
2. Lose
lots of money
3. Find
out about the First World War
4. Download
songs
5. Listen
to music in real time
6. Check
your email from any computer
7. Find
links to other websites
8. Exchange
messages in real time with friends or colleagues
9. Check
the latest exchange rates
10.
Read new articles about a subject that interests you
a. webmail
b. online
music store
c. instant
messaging
d. online
radio
e. portal
f. blog
g. online
encyclopedia
h. currency
converter
i. e-zine
j.
online casino
B. Can you match these activities with the internet features?
(It’s not easy – the terms are sometimes confused with each other.)
|
1. Exchange messages in real time about anything you |
a. newsgroup |
|
|
2. Post messages about your favourite pop group, and |
b. forum |
|
|
3. Exchange information and messages about saving a |
c. discussion group |
|
|
4. Exchange information and views about the economy |
d. bulletin board / noticeboard |
|
|
5. Post / download photos, video clips and messages |
e. chatroom |
3.5 Internet terms
Choose the best words to complete the sentences.
1. «The
website gets a thousand hits a week» means the website has a thousand
_________ a week.
a. sales b.
visits c. search
engine matches
2.
The words, images and other material that make up a website are
called __________.
|
a. the contents b. 3. Designs and drawings in websites are usually called |
c. the filling |
|
a. web pictures b. 4. Moving pictures in websites are usually called |
c. web |
|
a. |
c. animations |
5. Websites with
sounds and/or video clips and/or animations have __________ content.
a. multimedia b.
many-media c. mixed-media
6.
A space in a website where you enter information (address,
password etc.) is called a __________.
|
a. box b. 7. A hyperlink (see 3.3) is often called just __________. |
c. field |
|
a. a link b. 8. In real time (see 3.4) means __________. |
c. an HL |
|
a. |
c. in |
9. A place with computers for public internet use is
usually called an internet café or __________. even if they don’t serve
coffee.
|
a. web café b. 10. Internet cafés offer internet __________. |
c. cyber |
|
a. |
c. access |
11. A program that adds functions
to a browser (eg Shockwave) is called a __________.
|
a. plug b. 12. Temporary internet files are stored in the __________. |
c. plug-in |
|
a. |
c. cashe |
13. Colours which all browsers can display without problems
are called __________ colours.
a. browser
safe b. browser acceptable c.
browser easy
3.6 E-commerce
Shopping on the net
A. Fill the gaps, then put these stages in order (number them
1 to 8).
account
add browse checkout
confirm delivery
details invoice
shopping
basket sign in
You usually have to allow at least two working days for 1______________.
Choose an item, and 2______________ it to your 3______________.
Click 4 «______________». Now it’s too
late to change your mind!
When you have finished shopping, click «proceed to 5______________».
Usually, you will receive an 6______________ by
email.
Enter your name, address and card 7______________.
Before you can start shopping, you
usually have to 8______________ to the site. (If you don’t already
have an 9______________, you have to create one.) 10____________
the website, and decide what you want to buy.
B. Put the words into the spaces.
bid
down encrypted online outbid
padlock secure server system
1.
Sites that ask for your credit card number or other personal
information should use a _________________, so the data you send is
_________________.
2.
A: «Have you ever bought anything on an auction site like
eBay?»
B: «No. Once I made a
_________________ on something, but I was _________________ a few seconds
before the auction closed.»
3.
The _________________ symbol means that a web-page is secure.
4: I couldn’t book my flight _________________ because
the airline’s ________________ was _________________.
Booking a hotel online
C.
Choose the best words.
You can often make a hotel reservation [7]
by /over
the internet, but you may have to pay a deposit. The deposit will
usually be returned 2 to /
for you if you cancel your
reservation a week or more 3 in /
with advance.
You will usually receive
notification 4 about / of the booking 5 by / from email.
When you check 6 in / into the hotel, your details will probably
already be 7 on / inside the hotel system. When you check 8
out / out of, you will usually be given a receipt.
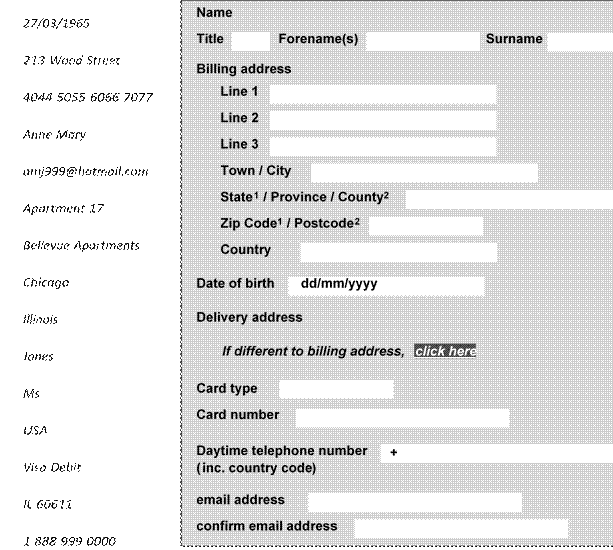
Filling in an e-form
D. Write the information into the fields.
3. 7 internet security
A.
Choose
the best words to go into each of the spaces.
1.
A person who illegally accesses somebody else’s computer over the
internet is called a
__________.
a. pirate b.
hack c. hacker
2.
A website which (in theory) cannot be accessed by a hacker is
__________.
a. strong b.
secure c. clean
3.
A website which can only be viewed by authorised people has
__________ access.
a. reduced b.
small c. restricted
4.
Unwanted advertising emails are popularly known as __________.
a. meatloaf b.
spam c. sausages
5.
Software which blocks attempts by others to access your computer
over the internet is called a__________.
|
a. firewall b. 6. It’s essential to __________ your anti-virus protection |
c. fire |
|
a. up-to-date b. 7. Anti-virus software can __________ your computer for |
c. update |
|
a. |
c. scan |
8. Anti-virus software can also
____________ viruses on removable media, such as floppy disks.
|
a. detect b. 9. When your anti-virus software subscription __________… |
c. see |
|
a. ends b. 10. … it’s a good idea to __________ it immediately. |
c. expires |
|
a. |
c. replace |
B.
Match
the malware with the damage. (It’s not easy, and the terms aresometimes
confused with each other.)
1.
virus a. collects and sends private
information from the infected
computer
to a third party
2.
spyware b. an undesirable program which can
replicate itself across a network
3.
trojan horse c. allows a hacker to access
private information when he/she wishes
4.
keystroke logger or keylogger d. a
program which adds itself to an executable file, and can
cause
considerable damage to the data on the infected computer
5.
worm e. records characters that are typed into a
computer
3.8 Email
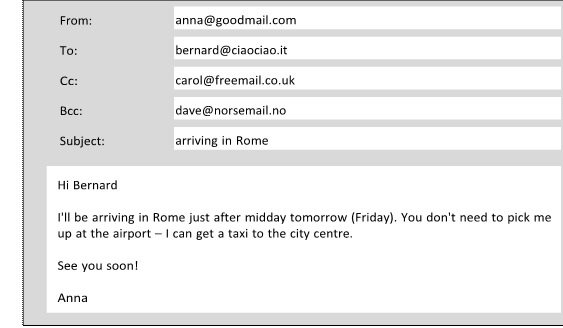
A. Look at the email and answer the questions true or false.
1. The
recipient is Anna.
2. The
sender is Anna.
3. Bernard
knows that Carol knows when Anna will be arriving in Rome.
4. Bernard
knows that Dave knows when Anna will be arriving in Rome.
5. You
can say that Anna Cc-ed her email to Carol.
6. You
can say that Anna Bcc-ed her email to Dave.
7. The
subject line is empty.
8. The
style of the email is formal.
9.
Cc stands for carbon copy and Bcc stands for blind carbon copy,
but the full terms are almost never used.
10. Carbon copies
were a method of making copies of documents typed on typewriters.
Sending an attachment
B. Put the words in the spaces.
attach
browse field inboxes
open
send size
You can send almost any file as an attachment. 1_______________
through the folders on your computer until you find the file you want to
attach. Click on «2_______________». The file will appear
in the attachments 3_______________. Then click «4_______________»,
and wait while the file uploads. Add more files if you wish. When you have
finished adding files, click «5_______________».
Some email 6_______________
will only receive attachments up to a certain 7_______________ with
one email, for example 10MB. If you need to send a lot of very big attachments,
it’s sometimes necessary to spread them over a number of separate emails.
3.9 Email comprehension 1
Hi Tony
Thanks for sending through that a/w so quickly. Just one
problem – I couldn’t open the attachment. I’m not sure why. My inbox is
virtually empty, so there’s plenty of room, and the attachment limit is 20MB,
so there’s no problem there. Perhaps there was a glitch somewhere. Anyway,
rather than trying to figure out what went wrong, could you just send it again?
Did we discuss file format? I don’t know much about TIFFs,
JPEGs etc, but I meant to tell you that if you have any queries on this, you
could get in touch with Steve, our designer. His email address is
steve@stevegreendesign.co.uk.
One other thing. When you resend me the a/w, could you cc it
to Angela? I’ve asked her to have a quick look at it before we put it in the
brochure.
I’m looking forward very much to seeing those pics – fingers
crossed that they’ll come through OK this time. However, if I still can’t
download them, I’ll ask you to put them on a disk and mail them. All the best
Jenny
A.
Are
these statements true or false?
1. Jenny didn’t
receive the a/w because her inbox is too small.
2. The attached
files came to less than 20MB in total.
3.
Jenny has resolved a technical problem, and the attachment will
come through without any problems next time.
4. Tony will have
to resend the a/w.
5. Jenny is a
graphic design expert
6. Tony is also
going to put the files onto a disk and mail them.
7. Angela has
already seen the a/w.
8. The style is
too informal – business emails should always be more formal than this.
B.
Find
words or expressions in the email which mean the same as the phrasesbelow.
|
1. artwork |
_____________________________________ |
|
2. a small technical problem |
_____________________________________ |
|
3. type of file |
_____________________________________ |
|
4. questions about this |
_____________________________________ |
|
5. send again |
_____________________________________ |
|
6. email a copy to |
_____________________________________ |
|
7. communicate with |
_____________________________________ |
|
8. with luck… |
_____________________________________ |
3.10 Email comprehension 2
A.
Are
these statements true or false?
1. Tony thinks
Jenny should change her email provider.
2. The designer
will need to reformat the files.
3. Angela doesn’t
have broadband.
4. Tony is sending
resized versions of the a/w files to Angela.
5. These versions
will look the same as the original versions.
6. Tony is going
on holiday on Friday morning.
7. Trevor may be
able to help with any problems that come up while Tony is away.
8. The style is
neutral – neither formal nor informal.
B.
Find
words or expressions in the email which mean the same as the phrasesbelow.
|
1. as you asked |
_____________________________________ |
|
2. famous companies |
_____________________________________ |
|
3. change the type of file |
_____________________________________ |
|
4. I think, but I may be wrong… |
_____________________________________ |
|
5. Low image resolution (see 1.6) |
_____________________________________ |
|
6. on Friday afternoon or before |
_____________________________________ |
|
7. comes up |
_____________________________________ |
|
8. that’s urgent |
_____________________________________ |
3.11 Useful verbs crossword
Complete the sentences with the missing verbs, and write them
into the crossword puzzle. Words in brackets mean the same as the missing
verbs.
1.
__________ your holiday photos on theweb (display)
2.
__________ the attachment in a newwindow
3. __________
pop-ups (stop)
4. __________ to
the internet
5 . __________ your wireless connection
(turn on)
5 . __________ your credit card details
(type in)
6. __________
your anti-virus protection
7. __________
the photo as a JPEG
8. __________
a technical problem (sort
out)
9. __________
on your firewall (enable)
10. __________
your wireless connection
(turn off)
11.
__________ your webpage to a webserver
12.
__________ some clipart from theinternet
13. __________ an
attachment with an email
14. __________ for
something on eBay
15 . __________ pop-ups (permit)
15. __________
the internet (use)
16. __________ the
email to everybody else onthe team (send a copy of )
17. __________ a
bid for something on eBay
18.
__________ to a different ISP (change)
3.12 Revision wordsearch
There are 33 words connected with internet in this grid. Can
you find them all?
(Look down and across.)
|
_______email____________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ |
_______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ |
_______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ |
3.13 Your internet
1.
Who is your current ISP?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
2.
Have you had any problems with them? If so, what?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
3.
What type of internet connection do you have?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
4. Is it fast
enough for your requirements? If not, how would a faster connection be useful
to you?___________________________________________________________________________________________
5.
From where do you usually access the internet?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
6.
On average, how many hours a week do you spend online?
___________________________________________________________________________________________
7.
Have you ever done these things?
a.
sent and received emails
b.
chatted in real time
c.
booked a flight online
d.
used your credit or debit card to pay for something over the
internet
e.
had a virus on your computer
f.
had a problem with identity theft
g.
downloaded a photo from a bulletin board
h.
connected to the internet over a wireless connection
i. set
up a wireless network in your own home or office
Answer keyUnit 0000
1.1 Hardware
From left to right:
laptop computer / desktop computer
mouse / printer / scanner digital camera / fax machine / mobile phone PDA /
projector
docking station / battery / cable / socket / plug
1.2 Some useful verbs
1 f, 2 e, 3 c, 4 d, 5 g, 6 h, 7 b, 8 a, 9 b, 10 c, 11 a, 12
a, 13 b, 14 c, 15 b, 16 b, 17 a, 18 c
1.3 The workstation
1 tower, 2 power button, 3 floppy disk drive, 4 CD / DVD
drive, 5 screen, 6 wire / cable, 7 keyboard, 8 mouse, 9 key, 10 flat panel
monitor, 11 CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitor, 12, stand, 13 printer, 14 scanner,
15 desk, 16 chair, 17 telephone, 18 a, 19 c, 20 a, 21 b, 22 b, 23 c, 24 c, 25
b, 26 a, 27 c.
1.4 The keyboard
Part 1: (clockwise from top left)
function keys / indicator lights / calculator keys / return key / alphabet keys
/ space bar
Part 2: 1 backspace key, 2 shift key,
3 caps lock key, 4 tab key, 5 control key, 6 alt key, 7 escape key, 8 delete
key, 9 enter, 10, key in, 11 data input, 12 standard keyboard / ergonomic
keyboard
1.5 The mouse
1 scroll up, 2 scroll down, 3 hold down, 4 repetitive strain
injury, 5 touchpad (or mouse pad), 6 joystick, 7 roll, 8 optical, 9 single, 10
double, 11 on, 12 left button, 13 right button, 14 scroll wheel (or mouse
wheel), 15 pointer
1.6 Scanning
1
connected, 2 original, 3 at / dpi, 4 preview, 5 adjust /
brightness / contrast, 6 click, 7 text / OCR software,8 file format, 9 image
editing software, 10 all-in-one, 11 handheld, 12 flatbed, 13 high, 14 low
1.7 Some useful adjectives
1 b, 2 b, 3 c, 4 a, 5 c, 6 a, 7 c,
8 c, 9 a, 10 c, 11 b, 12 a, 13 a, 14 c, 15 c, 16 b
1.8 Printing
A: 1 cartridge, 2 replacement, 3 cover, 4 via, 5 out
of / reload, 6 jammed, 7 feed, 8 out, 9 mono, 10 printheads (or print nozzles),
11 double-sided (or two-sided), 12 collate, 13 portrait, 14 landscape
B: 2 laser, 3 laser, 4 laser, 5 inkjet, 6 laser, 7
laser, 8 inkjet
C: 1 T, 2 F (the colours are
cyan, magenta, yellow and black), 3 T, 4 F (they’re much slower than that), 5
F,
6 T, 7 F, 8 T, 9 T, 10 F
1.9 Mobile phones
Part 1: (from the top) earpiece / screen / keypad /
star key / hash key / microphone
Part 2: 1 networks, 2 operators, 3 tariffs, 4
pay-as-you-go, 5 top up, 6 users, 7 contract, 8 SIM card, 9 installed, 10
roaming.
Part 3: 1 b, 2 a, 3 a, 4 b, 5 c, 6 b, 7 a, 8 a, 9 c,
10 c, 11 b, 12 c, 13 d, 14 d, 15 b
1.10 Other devices
1 h, 2 a, 3 g, 4 b, 5 d, 6 c, 7 e, 8 f, 9 b, 10 a, 11 b, 12
b, 13 c, 14 c, 15 b
1.11 Inside a computer
A: 1 processor, 2 chips, 3 dual core, 4 speed, 5
megahertz, 6 megabytes, 7 motherboard, 8 upgraded
B: 1 mains electricity, 2 transformer, 3 surge
protector / spikes, 4 disconnect / supply / shock, 5 fan / overheating
1.12 Data storage
Part 1: 1 hard drive, 2 free space, 3 capacity, 4
burn, 5 eject, 6 drawer, 7 card / stick
Part 2: 2 e, 3 c, 4 d, 5 a, 6 g, 7 f
1.13 Connectivity
Part 1: 1 b, 2 a, 3 c, 4 b, 5 c, 6 a, 7 c, 8 b, 9 a
Part 2: 1 wireless, 2 devices, 3 enabled, 4 signals, 5
data, 6 developed, 7 telecommunications
1.14 Networks
LAN: 1 Local, 2 server, 3 terminals, 4 log onto, 5
intranet, 6 satellite, 7 WAN, 8 network card
Network topologies: 1 star, 2 hierarchical, 3 ring, 4
line or bus
1.15 Electronic payments
A: cash / outlets / central / goods / touch / receipts
/ funds / debit
B: 1 f, 2 c, 3 b, 4 h, 5 a, 6 d, 7 e, 8 g
C: 1 b, 2 a, 3 e, 4 d, 5 c
1.16 Review crossword
|
W |
E |
B |
C |
A |
M |
||||||||||
|
M |
M |
A |
|||||||||||||
|
I |
W |
A |
T |
E |
X |
T |
|||||||||
|
C |
E |
P |
O |
R |
T |
R |
A |
I |
T |
O |
|||||
|
R |
R |
R |
E |
N |
|||||||||||
|
O |
G |
K |
R |
E |
|||||||||||
|
P |
R |
O |
C |
E |
S |
S |
O |
R |
Y |
R |
|||||
|
H |
N |
T |
|||||||||||||
|
O |
O |
F |
A |
N |
P |
P |
|||||||||
|
N |
M |
T |
W |
I |
R |
E |
L |
E |
S |
S |
|||||
|
E |
I |
I |
X |
R |
|||||||||||
|
C |
S |
O |
C |
K |
E |
T |
I |
||||||||
|
N |
L |
P |
|||||||||||||
|
S |
H |
||||||||||||||
|
M |
I |
C |
E |
||||||||||||
|
A |
N |
M |
E |
G |
A |
H |
E |
R |
T |
Z |
|||||
|
I |
N |
K |
J |
E |
T |
A |
R |
A |
|||||||
|
N |
T |
G |
T |
L |
I |
D |
|||||||||
|
F |
S |
W |
I |
P |
E |
R |
S |
I |
|||||||
|
R |
O |
I |
A |
||||||||||||
|
A |
R |
D |
D |
L |
|||||||||||
|
M |
K |
G |
P |
U |
|||||||||||
|
E |
M |
A |
G |
N |
E |
T |
I |
C |
P |
2.1 Software: the basics
A: 1 b, 2 a, 3 a, 4 c, 5 c, 6 a, 7 b, 8 a, 9 c, 10 b,
11 b, 12 a, 13 b, 14 c
B: 1 installed, 2 launch, 3 renamed, 4 running /
close, 5 start menu, 6 window, 7 drag and drop, 8 search / find, 9 user /
password, 10 free up / uninstalling, 11 save
2.2 Using software: useful verbs
Set 1: 1 f, 2 e, 3 d, 4 b, 5 c, 6 a
Set 2: 1 d, 2 f, 3 b, 4 a, 5e, 6 c
Set 3: 1 b, 2 c, 3 e, 4 a, 5 f, 6 d
Set 4: 1 c, 2 a, 3 b, 4 e, 5 f, 6 d
2.3 The control panel
2 adding, 3 setting up, 4 format, 5 displayed, 6 background,
7 digital, 8 wallpaper, 9 image, 10 screen saver,
11 wireless, 12 performance, 13
properties, 14 tasks, 15 default
2.4 Applications
A: 1 c, 2 d, 3 f, 4 b, 5 a, 6 i, 7 g, 8 e, 9 h B:
|
S |
O |
F |
T |
W |
A |
R |
E |
||||
|
P |
|||||||||||
|
P |
R |
O |
G |
R |
A |
M |
|||||
|
L |
|||||||||||
|
D |
I |
P |
|||||||||
|
R |
C |
H |
L |
||||||||
|
F |
I |
R |
E |
W |
A |
L |
L |
O |
I |
||
|
V |
T |
T |
C |
||||||||
|
S |
E |
C |
U |
R |
I |
T |
Y |
C |
O |
D |
E |
|
R |
P |
O |
A |
N |
|||||||
|
D |
N |
L |
C |
||||||||
|
A |
B |
E |
|||||||||
|
B |
O |
O |
T |
L |
E |
G |
U |
||||
|
E |
M |
NOTES
A security code (no. 
product registration code or product licence code. A bootleg (no.
10) can also be called a pirate copy.
2.5 Some useful adjectives
A: 1 b, 2 a, 3 a, 4 c, 5 a, 6 c, 7 a, 8 b, 9 c
B: 1 e, 2 d, 3 b, 4 a, 5 c
2.6 Word processing 1
|
2 |
|
11 |
|
1 |
|
12 |
|
3 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
4 |
A:top margin
bottom margin left-hand margin right-hand margin
heading (or title) body text paragraph break indent
illustration illustration border (or frame) page
number
page border (or edge of the page)
B: 1 upper case (or capital
letters), 2 lower case (or small letters), 3 plain text, 4 bold, 5 italic, 6
bold italic,
7 underline, 8 strikethrough, 9 outline, 12 shadow
C: 1 b, 2 c, 3 b, 4 a, 5 b,
6 a
2.7 Word processing 2
A: 1 b, 2 a, 3 a, 4 c, 5 b, 6 b, 7 a
B: 1 e, 2 c, 3 a, 4 m, 5 g, 6 j, 7 p, 8 s, 9 d, 10 i,
11 u, 12 o, 13 t, 14 r, 15 k, 16 l, 17 w, 18 f, 19 v, 20 x, 21 b, 22 n, 23 q,
24 h
C: 1 true, 2 false (three columns and four rows), 3
true (also known as «white on black» or «WoB»), 4 false
(it’s the other way round), 5 true, 6 false (they’re black).
2.8 Word processing 3
A: 1 b, 2 d, 3 e, 4 h, 5 c, 6 j, 7 i, 8 f, 9 a, 10 g
B: 1 e, 2 a, 3 c, 4 f, 5 g, 6 h, 7 d, 8 b
C: 1 false (it’s been rotated 90 degrees
anti-clockwise), 2 false, 3 true, 4 true
D: 1 c, 2 c, 3 b, 4 a, 5 a, 6 c, 7 a, 8 c, 9 b, 10 a
2.9 Image editing
A: 1 d, 2 i, 3 j, 4 f, 5 g, 6 b, 7 a, 8 c, 9 e, 10 h
B: 1 false, 2 true, 3 true, 4 false (the word is thumbnails),
5 true
2.10 Graphic design
1 import, 2 export, 3 frame, 4 gradient, 5 kerning, 6 object,
7 layers, 8 overlaps, 9 blurred, 10, effect, 11 feathering, 12 full bleed, 13
slug, 14 stretched, 15 to press, 16 proofs, 17 presses, 18 separation, 19
plates, 20 converted, 21 reprographics
2.11 Spreadsheets
|
symbol |
verb |
noun |
everyday |
|
+ |
add |
addition |
«five |
|
— |
subtract |
subtraction |
«five |
|
* |
multiply |
multiplication |
«five «five |
|
/ |
divide |
division |
«fifteen |
|
^ |
raise |
«ten |
A: 1 a, 2 c, 3 c, 4 b, 5 c,
6 b, 7 a, 8 c, 9 c, 10 c, 11 b, 12 a B:
C: 1 true, 2 false (descending), 3 false (ascending),
4 true
D: 1 text, 2 values, 3
boxes, 4 series, 5 appearance
2.12 Presentation software
1 b, 2 a, 3 c, 4 c, 5 c, 6 a, 7 a, 8 b, 9 a, 10 c
2.13 Problems with software
Prepositions: 1 on / of, 3 to, 5 in, 6 on, 7 in, 8 to,
9 on, a from, d on, e down, g with, h to / on Matching: 1 b, 2 g, 3 e, 4
f, 5 d, 6 h, 7 i, 8 c, 9 a
2.14 Which program?
(Features generally associated with
application types – some versions may have different features.)
word processor spreadsheet image
editor media player
1.
select text x x
2.
save as JPEG x
3.
insert table x
|
4. play |
x |
|||
|
5. touch up |
x |
|||
|
6. import |
x |
x |
||
|
7. exit |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
8. copy from |
x |
|||
|
9. check |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
10. copy |
x |
x |
||
|
11. insert |
x |
|||
|
12. page |
x |
x |
||
|
13. optimise |
x |
|||
|
14. |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
15. add |
x |
x |
||
|
16. insert |
x |
|||
|
17. convert |
x |
|||
|
18. paste |
x |
x |
||
|
19. check |
x |
x |
||
|
20. change |
x |
|||
|
21. flip, |
x |
|||
|
22. sort |
x |
x |
||
|
23. alter |
x |
|||
|
24. create |
x |
|||
|
25. print |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
26. clear |
x |
|||
|
27. maximise |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
28. insert |
x |
|||
|
29. convert |
x |
|||
|
30. open |
x |
x |
x |
x |
2.15 Revision quiz
1. Windows (95/98/2000/ME/XP), Mac (OS9, OSX etc), Linux, 2.
The recycle bin, 3. Wallpaper, 4. The control panel, 5. An image editor, 6. A
media player, 7. Freeware, 8. Capital letters in highlighted bold italic
underline, 9. Arial 9 point double spaced, 10. A template, 11. The clipboard,
12. It’s a mirror image of the original, 13. Softening an image, 14.
Thumbnails, 15. To sort, 16. A cell, 17 A slideshow, 18. A bug, 19. It
compresses files, 20. Drivers, 21. Columns and rows, 22. Dollar sign, 23. ampersand,
24. asterisk (or multiply sign), 25. hash, 26. brackets, 27. forward slash (or
divide sign), 28. backward slash, 29. question mark, 30. plus sign
3.1 The internet: the basics
A: 1 network, 2 over, 3 servers, 4 access, 5 provider,
6 discussion
B: close
down your browser connect to your ISP disconnect from the internet enter a web
address (also known as a URL)
launch your browser (for example,
Internet Explorer, Netscape Navigator or Mozilla Firefox) perhaps wait for a
few seconds while the web-page downloads view the page
C: 1 b, 2 c, 3 b, 4 c, 5 b, 6 b, 7 a, 8 b, 9 a, 10 c,
11 b, 12 a, 13 c, 14 b, 15 a
3.2 Internet browsers
A: 1 c, 2 f, 3 i, 4 d, 5 g, 6 e, 7 j, 8 b, 9 a, 10 k,
11 h
B:
1. False. They
are similar, but there are some minor differences.
2. True
3. True
4. False –
they can be deleted (in Internet Explorer, go to Tools / Internet
Options / Delete Files)
5. True
6. True
7. False. Many
are advertisements, but information about program updates etc. is also
sometimes displayed as pop-ups.
8. True
3.3 Search engines
A: 1 keywords, 2 matches / database, 3 returns /
hyperlinks, 4 sponsored, 5 click on / view, 6 refine / criteria
/ media
B: 1 b, 2 a, 3 d, 4 c, 5 e
3.4 Things on the net
A: 1 f, 2 j, 3 g, 4 b, 5 d, 6 a, 7 e, 8 c, 9 h, 10 i
B: 1 e, 2 c, 3 a, 4 b, 5 d (but
note that a, b and c are sometimes confused with each other)
3.5 Internet terms
1 b, 2 b, 3 b, 4 c, 5 a, 6 c, 7 a,
8 b, 9 c, 10 c, 11c, 12 b, 13 a
3.6 E-commerce
A:
You usually have to allow at least two working days for 1 delivery.
Choose an item, and 2 add it to your 3 shopping
basket.
Click 4 «confirm«. Now it’s too late to
change your mind!
When you have finished shopping, click «proceed to 5 checkout«.
Usually, you will receive an 6 invoice by email.
Enter your name, address and card 7 details.
Before you can start shopping, you usually have to 8 sign
in to the site. (If you don’t already have an 9 account,
you have to create one.)
10 Browse the
website, and decide what you want to buy.
B: 1 secure server / encrypted,
2 bid / outbid, 3 padlock, 4 online / system / down C: 1 over, 2 to, 3
in, 4 of, 5 by, 6 into, 7 on, 8 out
D:
Name
Title: Ms
Forename(s): Anne Mary
Surname: Jones
Billing address
Line 1: Apartment 17
Line 2: Bellevue Apartments
Line 3: 213 Wood Street
Town / City: Chicago
State1 / Province /
County2: Illinois
Zip Code1 / Postcode2:
IL 60611
Country:
USA
Date of birth: 27/03/1965
Card type: Visa debit
Card number: 4044 5055 6066
7077
Daytime telephone number (inc.
country code) +1 888 999 0000 email address: amj999@hotmail.com confirm
email address: amj999@hotmail.com
E: When you pay by debit card, the money is taken
almost immediately from your bank account. When you pay by credit card, you
don’t have to pay anything until you receive a bill from the credit card
company.
3.7 Internet security
A: 1 c, 2 b, 3 c, 4 b, 5 a, 6 c, 7 c, 8 a, 9 c, 10 a
B: 1 d, 2 a, 3 c, 4 e, 5 b
3.8 Email
A: 1 false (the recipient is
Bernard), 2 true, 3 true, 4 false, 5 true, 6 true, 7 false, 8 false, 9 true,
10, true B: 1 browse, 2 open, 3 field, 4 attach, 5 send, 6 inboxes, 7
size
3.9 Email comprehension 1
A: 1 false, 2 true, 3 false, 4 true, 5 false, 6 false,
7 false, 8 false – some business emails are very informal, other are very
formal. It depends on the situation.
B: 1 a/w, 2 glitch (informal word), 3 file format, 4
queries on this, 5 resend, 6 cc, 7 get in touch with, 8 fingers crossed
3.10 Email comprehension 2
A: 1 true, 2 false, 3 true, 4 true, 5 false, 6 false,
7 true, 8 true. Some of the language is quite informal, but the email begins
and ends with Dear… and Best regards, and the tone is not particularly
friendly.
B: as requested, 2 big names, 3 reformat, 4 I
understand that…, 5 low-res, 6 by Friday afternoon, 7 arises, 8 that won’t keep
3.11 Useful verbs crossword
|
P |
O |
S |
T |
||||||
|
P |
B |
L |
O |
C |
K |
||||
|
E |
O |
||||||||
|
E |
N |
A |
B |
L |
E |
N |
|||
|
N |
N |
||||||||
|
T |
U |
P |
D |
A |
T |
E |
|||
|
E |
C |
||||||||
|
R |
E |
F |
O |
R |
M |
A |
T |
||
|
E |
|||||||||
|
T |
S |
||||||||
|
D |
U |
P |
L |
O |
A |
D |
|||
|
I |
R |
L |
O |
||||||
|
S |
E |
N |
D |
V |
W |
||||
|
A |
E |
N |
|||||||
|
B |
I |
D |
L |
||||||
|
L |
A |
L |
L |
O |
W |
||||
|
E |
C |
C |
A |
||||||
|
C |
D |
||||||||
|
M |
A |
K |
E |
||||||
|
S |
|||||||||
|
S |
W |
I |
T |
C |
H |
1
post
2
open
3
block
4
connect
5 across
– enable, 5 down – enter
6
update
7 reformat8
resolve
9
turn (on)
10
disable11 upload
12
download
13
send
14
bid
15
across – allow, 15 down – access
16
cc (used as a verb)
17
make
18
switch
3.12 Revision wordsearch
|
b |
s |
b |
d |
o |
m |
a |
i |
n |
n |
||||||||||||
|
r |
v |
i |
r |
u |
s |
l |
i |
s |
e |
c |
u |
r |
e |
h |
|||||||
|
o |
r |
o |
s |
t |
e |
w |
y |
||||||||||||||
|
w |
f |
g |
c |
o |
m |
c |
s |
p |
|||||||||||||
|
s |
b |
o |
o |
a |
h |
g |
f |
e |
|||||||||||||
|
e |
n |
c |
r |
y |
p |
t |
i |
o |
n |
l |
i |
a |
r |
i |
r |
||||||
|
r |
o |
n |
b |
l |
t |
o |
r |
l |
|||||||||||||
|
a |
h |
a |
c |
k |
e |
r |
a |
r |
u |
e |
i |
||||||||||
|
m |
u |
p |
d |
a |
t |
e |
c |
r |
o |
p |
w |
n |
|||||||||
|
u |
b |
h |
i |
t |
s |
o |
a |
k |
|||||||||||||
|
l |
p |
a |
s |
s |
w |
o |
r |
d |
w |
e |
b |
m |
a |
i |
l |
l |
|||||
|
t |
n |
l |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
i |
c |
d |
s |
p |
y |
w |
a |
r |
e |
||||||||||||
|
m |
o |
o |
p |
a |
d |
l |
o |
c |
k |
||||||||||||
|
e |
o |
i |
n |
b |
o |
x |
r |
||||||||||||||
|
d |
k |
a |
t |
t |
a |
c |
h |
m |
e |
n |
t |
||||||||||
|
i |
i |
r |
e |
l |
o |
a |
d |
||||||||||||||
|
a |
e |
l |
w |
e |
b |
s |
i |
t |
e |
||||||||||||
|
s |
k |
e |
y |
w |
o |
r |
d |
||||||||||||||
|
s |
p |
a |
m |
l |
a |
u |
n |
c |
h |
||||||||||||
|
email |
hacker offline |
portal virus webmail |
|||||||||||||||||||
Index
References refer to the unit number
a/w 3.9, 3.10
access 2.1, 3.1, 3.2, 3.7,
3.11, 3.13 account 1.9, 3.1, 3.6 Acrobat 2.1 active 2.11 adaptor 1.13 add
2.3, 2.11, 2.14, 3.6, 3.8 addition 2.11 address 3.5, 3.6 address label 2.8
adjust 1.6 Adobe 2.4
Adobe Acrobat 2.1
Adobe InDesign 2.10
Adobe PageMaker 2.4
Adobe Photoshop 2.4
ADSL 1.13, 3.1
advanced search 3.3 advertisement 3.2 airline 3.6 align 2.7
All Programs
2.13 alphabet key 1.4 alphabetical 2.11, 2.15
alt 1.4 alt key 1.4 Altavista 3.3
alter 2.14 AMD 1.11
ampersand 2.7,
2.15 animation 2.12, 3.5 Antivirus 2.4 anti-virus 3.7, 3.11 appearance 2.15
application 1.12, 2.1, 2.2, 2.4, 2.10,
2.13, 2.14, 2.15, 2.16
area 2.10 Arial 2.6 arrange 2.2
arrow 2.7 article 3.4 artwork 2.7,
3.9
ascending 2.11 asterisk 2.7, 2.15
asymmetric digital subscriber line 3.1 at sign 2.7
ATM 1.10
attach 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 attachment 3.8, 3.9, 3.11, 3.12
auction 3.6 auction site 3.6 auto format 2.8 AutoContent
2.12 Autofill 2.11
AutoFormat 2.11 AutoShape 2.8 back 3.2 back
up 1.12 background 2.3, 2.7 backspace key 1.4 back-up copy 2.8 backward
slash 2.7, 2.15 balance 1.9 ball 1.5
bank account 1.15 bar 2.7, 3.2 barcode 1.10
barcode reader 1.10, 1.14
|
battery 1.16 |
1.1, 1.2, 1.7, 1.9, 1.11, |
|
bcc |
3.8 |
|
bid |
3.6, 3.11 |
|
bill |
1.15 |
billing address 3.6
bitmap 2.9 black 2.10
black and white 1.8, 2.9 blank 2.8, 2.12, 2.15
blind carbon copy 3.8 block 2.11, 2.14, 3.7, 3.11
blog 3.4, 3.12
Bluetooth 1.3, 1.13
blur 2.10
body text 2.6, 2.7
bold 2.6 bold italic 2.6
book 3.6, 3.13 booking 3.6
bookmarks 3.2 boot up 2.1 bootleg 2.4 border 2.6, 2.8, 2.14 bracket 2.7,
2.15 brightness 1.6, 2.9 broadband 1.13, 3.1, 3.10, 3.12 broadcast 2.12
browse 3.6, 3.8 browser 2.4, 3.1, 3.2, 3.5, 3.12 browser safe colours 3.5
bug 2.13, 2.15 bullet point 2.8, 2.14 bulletin board 3.4, 3.13 burn 1.12
bus topology 1.14 button 1.2, 1.4, 1.5, 1.7, 2.1, 2.2
buy 3.6
cable 1.1, 1.3, 1.8, 1.13
cache 3.5
calculator key 1.4 call centre 1.10 call
charge 1.9 callout 2.8 camera 1.10, 1.16 cancel
1.8 cancel 3.6 capacity 1.12 capital letters 1.4 caps lock key 1.4
car 1.9
carbon copy 3.8
card details 3.6 card number 3.6 card type 3.6 cartridge 1.8, 1.16, 2.6
cash card 1.15
cash dispenser
1.10 cash machine 1.9, 1.10, 1.15 cash register 1.15 casino 3.4 cc 3.8,
3.9, 3.11 CD 1.12, 2.14
CD drive 1.3, 1.12
CD
ROM 1.2, 1.8
CD-R 1.12 CD-RW 1.12 cell 2.7, 2.11, 2.14
cell phone 1.9 cellular phone 1.9 centred 2.7
character 3.7 charger 1.3, 1.9 chart 2.12 chat 3.13
chatroom 3.4, 3.12 check 3.10
checkout 3.6 chip 1.9, 1.11 clear 2.11, 2.14 click 1.2,
1.5, 1.6, 2.1, 2.2,
2.13, 3.3, 3.6, 3.8 clipart 2.7, 3.11 clipboard 2.8,
2.15
clone 2.9 close 2.1
close down 2.1, 2.2, 2.13, 3.1
CMYK 2.10
collate 1.8 colon 2.7
colour 1.8, 3.5 colour scheme 2.12 colour separation 2.10 column 2.7,
2.11, 2.15 column break 2.14 comma 2.7 command 2.8 comment box
2.11 commercial 2.5 communication 1.14 compact 1.7 compatible 1.7
compress 2.13, 2.15 computer 1.7, 1.8, 1.10, 1.11, 1.12,
1.13, 1.14, 1.16, 1.17, 2.1, 2.3, 2.4,
2.12, 2.13, 3.1, 3.4, 3.5,
3.7, 3.8, 3.13 confirm 3.6 connect 1.7, 1.8, 1.13, 1.14, 1.15, 1.16, 1.17,
3.1, 3.11, 3.13 connection 1.13, 2.3, 3.1, 3.10, 3.11, 3.13
connectivity 1.13 content
3.5 contract 1.9, 3.1 contrast 1.6, 2.9
Index
(cont.)
control key 1.4 control panel 2.3, 2.15
convert 2.9, 2.10, 2.14 cookie 3.2, 3.12 cool 1.11
copy 1.12, 2.2, 2.6, 2.8, 2.14,
2.15, 3.1, 3.9, 3.11
CorelDraw 2.1
counter-intuitive 2.5 country code 3.1 country code 3.6
Courier 2.6 cover 1.8, 1.11 crash 2.1
credit card 1.10, 1.15, 1.16, 3.6, 3.11, 3.13 criteria 3.3
crop 2.9, 2.14
CRT monitor 1.3
Ctrl 1.4 currency converter 3.4
customise 2.2, 2.3, 2.15 cut 2.2, 2.6, 2.15
cut and paste 2.2
cyan 2.10
cyan magenta yellow black 2.10 cyber café 3.5 data 1.12,
1.13, 1.15, 2.11,
3.6, 3.7
data input 1.4 data storage 1.12 database
1.7, 2.8, 3.3
date 2.3
date of birth 3.6 daytime telephone number 3.6
deactivate 2.5
debit card 1.15, 1.16, 3.6, 3.13 decimal point 2.11 default 2.3
defragment 1.12 delete 2.1, 2.2, 2.6, 2.11, 2.15,
3.2 delete key
1.4 delivery 3.6 delivery address 3.6 deposit 3.6 descending 2.11 design
2.7 design template 2.12 designer 3.9, 3.10 desktop 2.1, 2.2, 2.13
desktop background 2.1, 2.3,
2.15
desktop computer 1.1
desktop printer 2.10
desktop publishing 2.8
details 3.6
detect 3.7
device 1.4, 1.10, 1.13
dial 1.2
dial-up 1.13, 1.16, 3.1, 3.10
digital 2.3
digital camera 1.1, 1.2, 1.12, 2.3 digital photo 1.2, 2.1, 2.4
disable 3.11 disconnect 1.11, 3.1, 3.12 discussion
group 3.1, 3.4
disk 3.9
display 2.3, 2.4, 2.10,
3.2, 3.5, 3.11
divide 2.11 division 2.11
docking station 1.1 document 2.1, 2.2, 2.8, 2.10, 3.8 dollar sign 2.7, 2.15
domain 3.1, 3.12 domain name 3.1 dots per inch 1.6 double click 1.5 double
quotes 2.7 double spaced 2.6, 2.15
double-sided 1.8
down 3.6
download 2.4, 2.13, 3.1, 3.2, 3.4,
3.9, 3.11, 3.13
dpi 1.6, 1.16 draft 1.8
drag and drop 2.1 drawer 1.12 driver 1.8,
2.4, 2.13 drop shadow 2.7 dropped connection 3.1
dual core 1.11 duration 1.9
DVD 1.12
DVD drive 1.3 earpiece 1.9 eBay 3.6,
3.11 e-commerce 3.6 edit 2.4, 2.8 educational 2.5
e-form 3.6 EFTPOS 1.15 eject 1.12
electric shock 1.11
electricity 1.11 electronic funds transfer at point of
sale 1.15 electronic payment 1.15 electronic point of
sale 1.15 email 2.1, 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9, 3.10,
3.11, 3.12 email address 3.6 email provider 3.10
email software 2.4
empty 2.1 enable 1.13, 3.11 encrypt 3.6 encryption 3.12
encyclopaedia 3.4 enter 1.4, 2.11, 3.1, 3.3, 3.6, 3.11
enter key 1.4
EPOS 1.15
equals sign 2.7 ergonomic 1.4, 1.16 escape key
1.4 Excel 2.1, 2.11 Excite 3.3 exclamation mark 2.7
executable file 3.7 exit 2.2, 2.14 expand 2.9
expansion card 1.3 expire 3.7 export 2.10
extension cable 1.13 external 1.12 external hard drive 1.12 e-zine
3.4 fan 1.11, 1.16
|
feature |
2.4, 2.5, |
|
fee |
2.5, 3.1 |
|
feed |
1.8 |
|
field |
2.8, 3.1, |
|
file |
1.7, 1.12, 2.1, 2.2, 2.13, |
favourites 3.2 fax machine 1.1 faxes 1.2 feathering 2.10
3.1, 3.8, 3.9, 3.10
file 1.6, 3.9, 3.10
file size 3.10
fill 2.7, 2.8, 2.10
Fill 2.11
fill in 3.6
find 2.1, 3.4
firewall 2.4, 3.7, 3.11, 3.12
flash drive 1.12 flat panel monitor 1.3
flatbed scanner 1.6 flight 3.6, 3.13 flip 2.9,
2.14, 2.15
flood fill 2.7 floppy disk 1.12, 3.7 floppy disk drive 1.3
folder 1.5, 2.1, 2.2, 3.8
font 2.6 font size 2.8 footer 2.6 footnote
2.8 forename 3.6 form letter 2.8 format 2.3, 2.8, 2.10,
2.11
formula 2.11, 2.14 forum 3.4 forward 3.2 forward
slash 2.7, 2.15 four colour 2.10 frame 2.6, 2.10 free
space 1.12 free up 2.1 freeware 2.5, 2.15
from 3.8
full bleed 2.10 full stop 2.7 full version 2.5
function 2.2, 3.2, 3.5 function key 1.4 funds transfer 1.15
game 1.5
GB 1.12
glitch 3.9
Gmail 3.10
go to 2.13
Google 3.2, 3.3
Index (cont.)
gradient 2.10 graphic design 2.4, 2.10, 3.9
graphic design software 2.4
graphic designer 2.10
graphics 2.10, 3.5
greyscale 2.9, 2.14
grid 2.11, 2.15
gridline 2.7
hacker 3.7, 3.12
handheld scanner 1.6
hands-free 1.9
hard drive 1.12, 2.1, 2.2
hardware 1.1
hash 2.7, 2.15
hash key 1.9
header 2.6
heading 2.6, 2.8
headset 1.10
hierarchical topology 1.14
high resolution 1.6 highlighted 2.8 high-tech
1.7 history 3.2 hit 3.3, 3.5, 3.12 home 3.2 home
page 3.2 home-use 2.5 host 3.1 hotel 3.6
html 2.10 hub 1.13
hyperlink 3.3, 3.5, 3.12 hyphen 2.7 icon 2.1,
2.2, 2.13
identity theft 3.13 illustration 2.6, 2.7 image 1.6, 1.8, 1.10,
1.16, 2.3, 2.4, 2.9, 2.10, 2.15, 3.5, 3.10 image editing 1.6, 2.9 image
editor 2.4, 2.14, 2.15 import 2.10, 2.14 impression 2.3
in real time 3.4, 3.5, 3.13 inbox 3.8, 3.9, 3.12
indent 2.6 InDesign 2.10
indicator lights 1.4 infect 3.1 infect 3.7
information 1.14, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7 ink 1.2, 1.8, 1.16,
2.10
inkjet printer 1.8, 1.16
insert 1.4, 1.12, 2.8, 2.14
install 1.8, 1.9, 1.14,
2.1, 2.2, 2.4
instant messaging 3.4 instruction 2.4 Intel 1.11 internal 1.12
internet 1.9, 1.10, 1.13, 1.16, 2.3,
2.4, 2.12, 2.13, 2.14, 3.1, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7, 3.11, 3.12, 3.13
internet access 3.5 Internet Explorer 2.1, 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 internet service
provider 3.1 intranet 1.14 intuitive 2.5
invoice 3.6 ISP 3.1, 3.11, 3.13
italic 2.6, 2.8 itemised 1.15 jammed 1.8
job 1.8
joystick 1.5
JPEG 1.6, 2.1, 2.14, 3.9, 3.11
justified 2.7
kerning 2.10
key 1.2, 1.3, 1.4
key in 1.4
keyboard 1.3, 1.4, 1.15 keylogger 3.7 keypad 1.9
keystroke logger 3.7 keyword 3.3, 3.12
LAN 1.14
landscape 1.8
language setting 2.13 laptop
1.7, 1.11 laptop computer 1.1, 1.5, 1.13 laser printer 1.8, 1.16
launch 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, 3.12
layer 2.10 layout 2.6 left button 1.5 left-align 2.7 lettering 2.6
licence 2.4 licensed 2.5 lid 1.16 light pen 1.10
line 2.8
line drawing 2.9 line topology 1.14
lineart 2.9
link 3.3, 3.4, 3.5
Linux 2.1
list 2.8, 3.2
live 2.12
local area network 1.14 lock 1.9
log off 2.2 log onto 1.14 logical operator 3.3
log-in 3.1 log-in name 3.1 loudspeaker 1.3 low
resolution 1.6 lower case 2.6 low-res 3.10 low-tech
1.7 loyalty card 1.15
Lycos 3.3
Macintosh 2.1 Macintosh OSX 2.1 macro 2.8
magenta 2.10 magnetic strip 1.10, 1.16
mail 3.2 mail 3.9
mail merge 2.8 mainframe 1.10, 1.16 mains
electricity 1.11 malware 3.7 manipulate 1.6 manual 2.13 margin 2.6 match
3.3
mathematical calculation 2.11 maximise 2.14 MB 1.11,
1.12, 3.8, 3.9 media 3.2, 3.3
media player 2.4, 2.13, 2.14
megabyte 1.11
megahertz 1.11, 1.16 memory 1.11, 2.1, 2.13 memory card
1.12 memory key 2.2 memory stick 1.12
menu 2.2 message 3.4
MHz 1.11
microphone 1.9, 1.16 Microsoft 2.1, 2.4, 3.2
Microsoft Excel 2.1, 2.4, 2.11
Microsoft PowerPoint 2.4, 2.12 Microsoft Word 2.1, 2.2, 2.4
mobile 1.9
mobile phone 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.7, 1.9, 1.13 modem 1.3,
1.13, 2.3, 3.1 module 1.11 monitor 1.3 mono 1.8
motherboard
1.11 mouse 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.5, 1.16
mouse mat 1.3,
1.16 mouthpiece 1.9, 1.16
move 2.1
Mozilla Firefox 3.1, 3.2
MP3 2.14
MP3 player 1.10 multimedia 3.5, 3.12
multiplication 2.11 multiply 2.11 music 2.15, 3.2, 3.4 name 3.6
narration 2.12 navigate 3.1
NEAR 3.3 net 3.1, 3.4 Netscape Navigator 3.1, 3.2
network 1.7, 1.9, 1.14,
1.16, 1.17, 2.3, 3.1, 3.7, 3.13 network card 1.14
network connection 2.3
network server 1.14
new document 2.14 newsgroup 3.1, 3.4, 3.12 normal 2.8
Norton Antivirus 2.4
NOT 3.3
notebook 1.1, 1.7 noticeboard 3.4 notification 3.6
numerical order 2.15 numerical value 2.11 object 2.10 obsolete 1.7
OCR 1.6
Index (cont.)
offline 3.1,
3.12 online 1.8, 3.4, 3.6, 3.13 online banking 3.1 open 1.5, 2.1, 2.2, 2.13,
2.14, 3.8, 3.9, 3.11 operate 2.4 operating system 2.1, 2.13, 2.15 operation
2.14 operator 1.9 optical 1.5
optical character recognition 1.6 optimise 2.14
OR 3.3
original 2.10
OSX 2.1 outbid 3.6 outline 2.6
Outlook Express 2.4 overheat 1.11, 1.16 overlap 2.10 padlock 3.6,
3.12 page 1.5, 1.8, 1.14, 2.8, 2.10,
3.1, 3.2
page break 2.8 page layout 2.6 page
number 2.6, 2.8 page orientation 1.8, 1.15 page set-up 2.14
PageMaker 2.4 paper 1.8 paper
tray 1.8 paragraph 2.6, 2.8 paragraph break 2.6 password 1.4, 2.1,
3.1, 3.5, 3.12 paste 2.2, 2.6, 2.14 pay-as-you-go 1.9, 3.1 PDA 1.1,
1.7, 1.13
pdf 2.10
percentage sign 2.7 performance 2.3 peripheral 1.13, 1.16,
1.17, 2.4 personal digital assistant 1.1 personal information 3.6 photo
album 2.4 photocopier 1.10 photograph 1.6
pirated 2.5
pixel 1.10, 1.16, 2.9
plastic 1.15
plate 2.10
play 2.14
playlist 2.14
plug 1.1, 1.2, 1.13, 1.16
plug and play 1.7 plug-in 3.5 plus sign 2.7, 2.15
point 2.8
point of sale 1.15
pointer 1.5, 2.11
pop-up 2.11, 3.2, 3.11
port 1.13
portal 3.4, 3.12
portrait 1.8, 1.16
post 3.4, 3.11
postcode 3.6
poster 2.7 power 1.11
power button
1.3 power spike 1.11 power supply 1.11 PowerPoint 2.4, 2.12
ppm 1.8
predictive text 1.9 pre-formatted 2.8, 2.15 prescan 1.6
presentation 1.2, 2.12,
2.15 presentation software 2.4, 2.12 preview 1.6 print 1.8, 2.8, 2.14, 3.2
print job 1.8 print out 1.2 print preview 2.8 print quality 1.8 printer
1.1, 1.2, 1.7, 1.8, 1.13, 1.16, 2.4, 2.13, 2.15
print-head 1.8
printing press 2.10
problem 2.13
proceed to checkout 3.6
processor 1.7, 1.11, 1.16 professional version 2.5 program 2.1,
2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.13, 3.5, 3.7 projector 1.1, 1.2
proof 2.10 properties 2.3
protocol 3.1
PS/2 1.13 pt 2.8
public domain 2.5 pull down 2.2 punctuation
2.7 question mark 2.7, 2.15 radio 3.2, 3.4 rasterise 2.9 read 1.12
RealPlayer 2.4 receipt 1.15
receive 3.1, 3.6, 3.13 recharge 1.2, 1.16 recipient 3.8 record 2.12,
3.7
recycle bin 2.1, 2.15
red green blue 2.10 refine 3.3
reformat 3.10, 3.11 refresh 3.2 reload 1.8,
3.2, 3.12 removable media 3.7 remove 2.3, 2.11 rename 2.1 renew 3.7
repetitive strain injury 1.5 replace 2.2,
2.8 replicate 3.7 reprographics 2.10 request 3.1 reservation 3.6
resize 2.2, 3.10
resolution 1.6, 1.16, 2.9, 3.10 resolve 3.11
restart 2.1
restricted access 3.7 retail outlet 1.15 return 3.3 return key 1.4 reverse
2.9 reversed-out 2.7
RGB 2.10
right button
1.5 ring topology 1.14 roaming 1.9
roll 1.5
rotate 2.8, 2.9, 2.14
router 1.13
row 2.7, 2.11, 2.15
run 1.12, 2.1, 2.2
satellite 1.14
save 2.1, 2.2
save as 2.2, 2.14
scan 3.7
scanner 1.1, 1.2, 1.6, 1.13, 1.16,
2.4, 2.15
scanning software 1.6
scheduled tasks 2.3 screen
1.2, 1.3, 1.7, 1.9, 1.10, 1.16, 2.1, 2.3, 2.9 screen saver 2.3 scroll down
1.5 scroll up 1.5 scroll wheel 1.5 SD card 1.3 SDRAM 1.11
search 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 search
engine 3.3 secure 3.6, 3.7, 3.12 secure server 3.6 security 3.7 security
code 2.4 select 1.4, 1.5, 2.8, 2.14
semicolon 2.7 send 1.12,
1.16, 2.2, 3.1, 3.8, 3.9, 3.11, 3.13 sender 3.8 separation 2.10 series 2.11
server 1.14, 3.1, 3.2 session 2.2
set up 2.3, 3.1, 3.13
settings 2.3, 2.15 shadow 2.6 share 1.13 shareware 2.5
sharpen 2.9, 2.15 shift key 1.4 Shockwave 3.5 shopping 3.6 shopping
basket 3.6 shortcut 2.1 short-range radio 1.13 sign in 3.6 signal 1.9,
1.13 SIM card 1.9 single click 1.5 single quotes 2.7 single spaced
2.6, 2.15
site 3.6
Index (cont.)
size 3.8, 3.10 slide 2.12
slideshow 2.9, 2.12, 2.15
slug 2.10
small letters 2.6
SMS 1.9, 1.16
socket 1.1, 1.2, 1.16 soften 2.9, 2.15 software 1.6,
2.1, 2.4, 2.12, 2.13,
2.15, 2.16, 3.7 sort 2.8, 2.14, 2.15 sound 3.5
space 2.1 space bar 1.4
spam 3.7, 3.12 speed 1.11
spell checker 2.8 spelling 2.14 sponsored links 3.3
spreadsheet 2.4, 2.11, 2.14, 2.15 spyware 3.7, 3.12 square bracket 2.7
stand 1.3 standby 2.1 star key 1.9
star topology 1.14 start menu 2.1
statistics 2.12
stock
management 1.15 stop 3.2 storage 1.12 store 1.12, 2.4, 3.1 store card 1.15
stretch 2.10 strikethrough 2.6 stroke 2.10 style 2.8
sub-heading 2.7 subject 3.8 subject line 3.8
subscript 2.8 subscription 3.7 subtract 2.11 subtraction 2.11
superscript 2.8 surf 3.1, 3.12 surge protector 1.11 surname 3.6
swipe 1.10, 1.16
switch 3.11
symbol 2.7, 3.6
system 3.6
tab key 1.4
table 2.7, 2.12, 2.14, 2.15
tablet PC 1.10 tabulation 1.4 tailor-made 2.5
tariff 1.9, 3.1
task 2.3, 2.4
task bar 2.2
technical specifications 1.17
technology 1.13
telecommunications 1.13, 3.1
telephone 1.10
telephone line 3.1
telephone system 3.1
telex 1.10
template 2.8, 2.15
temporary internet files 3.2, 3.5
terminal 1.14, 1.15
text 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.9, 1.15,
2.2, 2.8, 2.10,
2.11, 2.14, 2.15
text box 2.8,
2.14 text direction 2.14 text message 1.9 text wrap 2.8 thinks bubble 2.8
thumbnail 2.9, 2.15
TIFF 2.1, 3.9, 3.10
time 2.3
Times 2.6
title 2.6, 3.6
to 3.8
to press 2.10
toner 1.8, 1.16
tool 2.8
toolbar 3.2, 3.12
Tools 3.2
top up 1.9
topology 1.14 touch screen
1.15 touch up 2.9, 2.14, 2.15 touchpad 1.5 tower 1.3
track changes
2.8 transformer 1.11 transition effect 2.12 transmitter 1.9 trial period
2.5 trial version 2.5 trojan horse 3.7
TV 1.10
type 2.1, 3.7, 3.8, 3.11
typewriter 2.6, 3.8 unauthorised access 2.4 underscore 2.7 uniform resource
locator 3.1 uninstall 2.1, 2.13, 2.14 update 1.12, 2.4, 2.13, 2.14, 3.7,
3.11, 3.12 upgrade 1.11, 1.17 upload 3.8, 3.11 upper case 2.6
URL 3.1
USB 1.8, 1.12, 1.13, 2.2
USB cable 1.8
USB hub 1.13
USB port 1.13
use 2.2
user 1.9, 1.14, 2.1, 2.3, 3.2 user-friendly 2.5
value 2.11
vector image 2.9 version 2.13 video 3.2,
3.4, 3.5 video camera 1.7, 1.10 view 2.1, 2.2, 2.9, 3.1, 3.3 virus
3.1, 3.7, 3.12, 3.13
virus protection 2.4
visit 3.5
voice balloon 2.8 voltage 1.11 wallpaper 2.3, 2.15
WAN 1.14
watermark 2.8 Web 3.1, 3.3
web address 3.1, 3.2 web
directory 3.3 web page 2.2, 2.10, 3.1, 3.3, 3.6, 3.11 web server 3.1, 3.11
webcam 1.10, 1.13, 1.16
webmail 3.4, 3.12 website
3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7, 3.12 wheel mouse 1.5
wide area network 1.14
width 2.11
window 2.1, 2.2, 2.14, 3.2, 3.11 Windows 2.1 Windows XP
2.1
WinZip 2.13, 2.15
wipe 2.2
wire 1.3, 1.13, 1.16
wireless 1.7, 1.13, 1.16, 2.3, 3.11,
3.13
wizard 2.12
Word 2.1, 2.2
word count 2.8 word processing 2.6, 2.7, 2.8
word processor 2.4, 2.14
workbook 2.11 worksheet 2.11
workstation 1.3, 1.16 World Wide Web 3.1
worm 3.7
write 1.12
XP 2.1
Yahoo 3.10
yellow 2.10
zip code 3.6
zoom in 2.9 zoom out 2.9
Acknowledgements
Adobe®, PageMaker®,
Photoshop®and InDesign® are trademarks of Adobe Systems Inc.
Microsoft®, Windows® and PowerPoint®
are trademarks of
the Microsoft corporation.
Mozilla FirefoxTM is
a trademark of the Mozilla Foundation.
Netscape® is a trademark of Netscape
Communication Corps.
Norton AntiVirus® is a trademark of Symantec
Corporation.
RealPlayerTM is
a trademark of RealNetworks Inc.
WinZipTM is a
registered trademark of WinZip Computing Inc.
[1] . Laptops are
powered by batteries or _______________.
[2] . Mains
electricity is converted to lower voltage by a
_______________.
[3]
. A _______________ protects electronic equipment from damage caused
by power _______________.
[4]
. If you remove the cover from a computer, make sure you
_______________ the electricity _______________. Otherwise, you may get an
electric _______________.
[5] . The computer is
cooled by a _______________. This prevents the processor from _______________.
[6] Microsoft Internet Explorer; 2 Netscape
Navigator / Mozilla Firefox
[7] USA 2 United Kingdom
E. How is a credit card different to a debit card? Do
you have one or both or neither?
Recommended textbook solutions
The Language of Composition: Reading, Writing, Rhetoric
2nd Edition•ISBN: 9780312676506Lawrence Scanlon, Renee H. Shea, Robin Dissin Aufses
661 solutions
Technical Writing for Success
3rd Edition•ISBN: 9781111260804Darlene Smith-Worthington, Sue Jefferson
468 solutions
Technical Writing for Success
3rd Edition•ISBN: 9781111445072Darlene Smith-Worthington, Sue Jefferson
468 solutions
Edge Reading, Writing and Language: Level C
ISBN: 9781285439594David W. Moore, Deborah Short, Michael W. Smith
304 solutions
Goals
- Students will recognize the major types of word processing programs.
- Students will discriminate the types of problems that are best solved
with various types of word processors. - Students will recognize the major tools that are available in word
processor application programs. - Students will use a text editor to create and modify a simple ASCII
text file. - Students will use a high end word processing program to practice
common text formatting problems.
Prereqs
- Comfort with the keyboard and mouse
- Experience with the STAIR process for solving problems
- Familiarity with principles of data encoding
- Familiarity with differences between hardware and software
- Understanding of the attributes of RAM
- Familiarity with operating systems, file names and directories
Discussion
Word processing is one of the most common applications for computers
today. It would be difficult to spend a day in a modern office or
university without coming into contact with a word processing program.
Most people have had some contact with word processing. We shall
examine the concept in some detail, so you will be familiar with a
number of levels of word processing software applications, the types
of tools such programs make available to you, and so you will know
what kinds of problems are best solved with this type of program.
How Word Processors Work
The advantages of word processing programs can best be illustrated by
thinking of some of the disadvantages of typewriters. When we use a
typewriter to create a document, there is a direct connection between
the keys and the paper. As soon as you press a key on the keyboard,
there is an impact on the paper, and the document has been modified.
If you catch a mistake quickly, you can fix it with correction tape or
white-out. If your mistake is more than one character long, it is
much harder to fix. If you want to add a word, move a
paragraph, or change the margins, you have to completely retype the
page. Sometimes this necessitates changes on other pages as well. A
one word change could lead to retyping an entire document.
Word processing is a type of software that focuses on the ability to
handle text. The computer does this by assigning each letter of the
alphabet and each other character on the keyboard a specific numeric
code. These numeric codes are translated into computer machine language,
and stored in the computer’s memory. Because the information is in memory,
it is very easy to change and manipulate. This is the key to the
success of word processing.
Example
Information in memory can be moved very quickly and easily. If we
want to change a word in a document, what happens in the computer is
something like this:
Imagine Darlene has started out her resume with the following word:
REUME
Obviously she has forgotten a letter. If she were using a typewriter,
the page would be trashed, and she would have to start over. Since
this is a word processor, Darlene can manipulate the memory containing
codes for the word «REUME» and add the «S» to it. When she tries, the
following things happen:
She moves her cursor to the spot in the text where she wants the S to
show up. The «cursor» is a special mark on the screen that indicates
at which place in the document the computer is currently focused. In this
case, Darlene wants to put an S between the E and the U. Her word
processor won’t let her put the cursor between two letters (although
some will), so she puts it on the U.
By moving the cursor, Darlene is telling the program to move around in
memory as well. When she place her cursor on the U on the screen, she
is telling the program to point to the corresponding spot in the
computer’s memory. The computer is now concentrating on the memory
cell that contains the code for the character «U».
She checks to be sure she is in insert mode (more on that later),
and she types the letter «S».
When Darlene does this, the computer shifts all the letters one memory
cell to the right, and inserts the code for the S in its proper
place.
Word processors and RAM
It sounds like a lot is happening. That’s true, but computers do all
these things so quickly that it seems instantaneous to us. You don’t
really have to know exactly where the stuff is in memory, or how it
gets moved around. The important thing to understand is that all the
information in your document is stored in some kind of digital
format in the computer’s memory. When you modify a document, you are really
modifying the computer’s memory. A word processing program handles
all the messy memory manipulation, so all you have to do is concentrate
on writing your paper.
RAM (Random Access Memory), where all the action is happening, has
one serious drawback. It only lasts as long as the computer is receiving
electrical power. Obviously this will cause some problems, because you
can’t just carry a computer around to show people your documents.
(Imagine the extension cord!) You also might run into some serious
problems if your computer were suddenly hit by a monsoon or something,
and you lost electrical power. In short, you cannot count on RAM memory
alone.
Word processing programs (as well as almost every type of program) are
designed to allow you to copy your information. Computer scientists
refer to the information your program is using as data. The data in
RAM can easily be duplicated to floppy disks or a hard drive. This is
called saving. Copying the data from RAM to a printer is called
printing. You can also copy data from other places to RAM. Copying the data
from the disk is referred to as loading the data. You might already
know what saving and printing are. We don’t mean to insult you by
telling you again. We just want to illustrate that it all boils down
to copying binary information to and from RAM.
Types of Word Processing Programs
There are many flavors of word processing programs. Different
programs are better for different types of jobs. One common problem
is deciding which program you will use to do a certain type of job.
It is important to know your options.
Text Editors
The simplest programs that do word processing are known as text
editors. These programs are designed to be small, simple, and cheap.
Almost every operating system made has at least one built in text
editor. Most text editors save files in a special format called
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange — Whew!)
ASCII is a coding convention that almost all computers understand.
Each letter is assigned a numeric value that will fit in eight digits
of binary notation. «a» is 97 in ASCII, and «A» is 65. All the
numeric digits, and most punctuation marks also have numeric values in
ASCII. You certainly don’t need to memorize all the codes, (That’s
the text editor’s job.) but you should recognize the word « ASCII».
The biggest advantage of this scheme is that almost any program
can read and write ASCII text.
Text editors can be wonderful programs. The biggest advantage is the
price. There is probably already one or more installed on your
computer. You can find a number of text editors for free on the
Internet. Text editors are generally very easy to learn. Since they don’t
do a lot of fancy things, they are generally less intimidating than
full fledged word processor packages with all kinds of features.
Finally, text editors are pretty universal. Since they almost all use
the ASCII standard, you can read a text file written on any text
editor with just about any text editor. This is often not the case
when using fancier programs.
The ability to write ASCII text is the biggest benefit of text
editors. ASCII is also the biggest disadvantage of most text editors.
It is a very good way of storing text information, but it has no way
of handling more involved formatting. Text editors generally do not
allow you to do things like change font sizes or styles, spell
checking, or columns. (If you don’t know what those things are, stay
tuned. We will talk about them later in this chapter.)
Text editors aren’t all simple, though. Text editors are actually the
workhorses of the computing world. Most computer programs and web
pages are written with specialized text editors, and these programs
can be quite involved. You won’t need to learn any hard-core text editors
for this class, but you may end up learning one down the road.
If all you want to do is get text written, and you aren’t too
concerned about how fancy it looks, text editors are fine. (In fact,
this book was written entirely in emacs, a unix-based text editor.)
Common text editor programs:
- Windows: Notepad
- Macintosh: SimpleText
- Linux: vi, emacs
- Multi-platform: notepad++, jedit, synedit, many more
Integrated Packages
Frequently these software packages are included when a person buys a
new computer system. An integrated package is a huge program that
contains a word processor, a spreadsheet, a database tool, and other
software applications in the same program. (Don’t worry if you don’t
know what a spreadsheet or a database is. We’ll get there soon
enough!) An integrated application package is kind of like a «Swiss
army knife» of software.
The advantages of an integrated package derive from the fact that all
the applications are part of the same program, and were written by the
same company. It should be relatively easy to use the parts of an
integrated package together. These programs tend to be smaller, older
versions of larger programs, so they might be less complicated to use.
Since they were presumably written together, they should all have the
same general menu structure, and similar commands. (The command to
save a file would be the same set of keystrokes in all the programs,
for example.) Integrated packages are often designed with casual
users in mind. This might make them easier to use than more robust
programs. The word processor built into an integrated package is
probably more powerful than a typical text editor. Integrated
packages are often already installed on new computers, so they might
not cost you any more than the original purchase price of the
computer. The word processor on an integrated package will almost
certainly give you some features you would not expect to find on plain
text editors.
Integrated packages have some disadvantages. With the advent of
graphic user interfaces and modern operating systems, programs have
become more and more standard even if they were written by completely
different companies. Almost every program for Windows uses Alt-F-S to
save, for example. Also, as in the Swiss army knife analogy, the
programmers had to make some compromises in order to make all the
applications fit in one program. A Swiss army knife does contain a
saw, but if you had to cut down a tree, wouldn’t you rather use a real
saw? The programs in an integrated package are usually stripped down
or older versions of the company’s high end software. They certainly
have fewer features, and might be less friendly. Word processing
programs that are part of integrated packages generally have their own
special code for storing text information, although they can usually
read and write ASCII as well. (However, if you choose to save in
ASCII, you cannot save all the special formatting commands).
Common Integrated Packages:
- Microsoft Works
- Lotus Works
- Claris Works
Today the trend is to package all the high-level programs together, so
MS-Office and OpenOffice.org both contain fully-featured Word
Processors, Databases, Spreadsheets, and more.
High-End Word Processors
Word processing programs have evolved a great deal from the early
days of computing. A modern word processing program can do many
things besides simply handling text.
Since the early ’90s, most word processors feature a WYSIWYG
interface. WYSIWYG (pronounced «whizeewig») stands for «What You See
Is What You Get.» This means that the screen will look reasonably
like the printed document. This feature is important because the
real strength of word processors is in the formatting they allow.
Formatting is the manipulation of characters, paragraphs, pages, and
documents. Most of the word processor features we will discuss below
are various ways of formatting the text, or changing the way it looks
on the page. Formatting was possible before WYSIWYG, but it required
more imagination from the writer, because you couldn’t see the effects
of the formatting until you printed out the document.
Modern word processors also are designed to have numerous features for
advanced users. Since a large portion of most people’s computer time
is spent with a word processing program, it is important that these
programs have features to make editing documents easier. Some of the
additional features that one can expect to find on a modern word
processor are spelling and grammar checkers, ability to handle
graphics, tables, and mathematical formulas, and outline editors. The
word processing market is a very competitive one, and the major
software companies are always competing to have the word processor
with the most advanced features available.
Software companies are also interested in making their programs as
easy to learn as possible. With this goal in mind, most word
processors come with tutorial programs, extensive on-line help, and
clear menus.
These full featured word processors sound wonderful, and they are.
You might wonder if they have any drawbacks. Of course they do.
Word processing programs as have been described often cost hundreds of
dollars. The cost seems prohibitive for something that doesn’t even
have a physical presence! Many of the features of full-fledged
word processors are not needed by casual users. Sometimes the sheer
number of unneeded features can be intimidating. Using a full-power
word processor just to write a couple of letters a week is like
killing flies with a chain saw. You simply might not need that much
power to do the job properly. High end word processing programs
almost always save documents in special proprietary codes rather than
as ASCII code. This means the programs can save all the special
formatting that ASCII cannot handle (like font sizes, columns,
graphics, and so on.) It also means that if you write a document in
WordPerfect, you may not be able to read it in Word. Even
different versions of the same program might not be able to read each
other’s documents directly. There are ways you can work around this
problem, but you should know it exists.
High-end Word Processing Packages:
- WordPerfect
- Microsoft Word
- OpenOffice.org Write
Ironically, there is now a trend away from WYSIWYG towards
«semantic markup.» The idea is not to put all the formatting details
in place, but to explain the meaning of the text in the document. The
actual markup of each meaning is defined in a separate document. For
example, here’s the semantic markup of this paragraph:
<p class = "update"> Ironically, there is now a trend away from WYSIWYG towards "semantic markup." The idea is not to put all the formatting details in place, but to explain the meaning of the text in the document. The actual markup of each meaning is defined in a separate document. For example, here's the semantic markup of this paragraph: </p>
In another part of the document I describe how to format «updates»:
.update {
border: 1px black solid;
background-color: #FFFFCC;
padding-left: .5em;
}
It’s completely OK if you don’t understand any of the code. The
important idea is how markup can be separated from meaning.
Desktop Publishing
Another classification of programs you should know about has an
uncertain future. These programs are called desktop publishing
applications. Desktop publishing takes text that has already been
created, and applies powerful formatting features to that text.
Traditionally, applications that allowed the integration of text and
graphics, and allowed the development of style sheets were thought of
as desktop publishing. Such a program makes it easy to create other
kinds of documents rather than just plain pages. With a desktop
publisher, there are already style sheets developed to help you create
pamphlets, cards, signs, and other types of documents that you wouldn’t
be able to create on a typewriter.
The higher end word processing programs give you most of the features
you could want in a desktop publishing program. It is possible to do
many of the same things. Desktop Publishers are still very popular in
certain specialty fields (graphic arts, printing, and publishing,) but
the effects can be duplicated with skillful use of a word processing
program.
Common Desktop Publishing programs:
- Pagemaker
- Microsoft Publisher
Sign / Banner Programs
Another level of desktop publishing that has become very popular is
the advent of specialty printing programs such as «The Print Shop» or
«Print Master +». These programs are designed specifically to help the
user create signs, banners, and greeting cards. They are very easy to
use, and much less expensive than full-feature desktop publishing
applications, but again the effects can be duplicated with a higher
end word processor.
How Do You Choose Which Word Processor You Use?
As always, the critical question is: «What kinds of problems are you
trying to solve?» For most beginners, the lower end word processor
that came with their computer is a fine start. If it does what you
need, and you are happy with it, don’t spend money unnecessarily.
Many people find that if they do a lot of writing, they begin to yearn
for the features of a more powerful word processing program. As you
gain experience, you will find a favorite program and learn its
commands and idiosyncrasies well. You will find if you concentrate on
the concepts, that all word processors of a certain level are pretty
much the same, although the exact layout and command structure may
differ. You will also probably discover if you do a lot of writing
with the computer that you have several programs you use
interchangeably. A skilled computer user often chooses the program to
solve a specific problem much like a golfer chooses a different club
for each type of shot. Sometimes a text editor is sufficient, and
sometimes only the best, most powerful, and most expensive program
will do the job properly. Learning what is best for you is part of
the process.
Layout of Word Processors
Word processing programs of any type usually share the most basic
features. They universally reserve most of the screen for the text
being edited. Most word processing programs also contain a
menu structure with most of the programs commands available in a
hierarchical organization scheme. Many word processors have graphic
toolbars with icons representing the most critical commands. Almost
all such programs have scroll bars or some other mechanism for
allowing the user to move around in large documents. All word
processors also have a cursor, which is usually a small box or line,
which shows the user where in the document she is currently typing.
Commands Available In Most Word Processing Programs:
Different types of word processing programs will have different
commands available. Generally, text editors have the fewest commands.
More complex programs often start with the same types of commands and
add to them. Commands may be available in a number of ways; by
locating them on the menu system, by looking up shortcut keys, or by
pressing an icon on a graphic tool bar. If in doubt, utilize the
on-line help to locate the command you want.
File Handling Commands
Any level of text editor or word processor will have commands to save,
load, and print your text. These commands are so frequent that you
will usually see many ways to invoke them.
- Save Document
-
Allows you to save your document onto some kind of disk.
If you have already saved this document at least once, it will save
the document to the same drive, directory, and file name you used last
time. Saving a document really means making a copy of the codes in
memory that represent the document, and copying those codes onto a
disk file. If you have never given this document a name, a Save
command often acts like a Save As. (see below) You might also look for
a Write command, a picture of a disk, or a Save As command. - Save As…
-
Often you will see this command in addition to a save command. There
is a subtle difference between the two commands. Save As {it always}
asks you for the name and location of your file. Most of the time,
the Save command does not ask for this information. If the Save
command does not know what to call the file (because you have never
saved it before) it will automatically invoke a Save As. The only
time you absolutely must use a Save As is when you want to load a
file, make some changes to it, and save it as a NEW file with a
DIFFERENT name. If you use the Save command, the new changes will be
written on top of the old document. With Save As, you can force the
changed document to be in a new file. This really doesn’t happen very
much. Many people spend their whole lives using nothing but Save. - Load or Open
-
You will almost always see a command that allows you to open or load a
document. These terms usually mean the same thing. You will usually
get some sort of a dialog box asking you for the directory and file
name of a text document, and the program goes to the disk, grabs the
file, and loads it into the editing area of the screen. (Actually, it
loads the file into memory, and then shows a copy of the memory onto
the screen.) -
A print command takes the document and copies it to the printer.
Obviously, for this to work, you must have a printer attached to your
machine. There are occasional variations to this command. You might
get a dialog box that asks you which pages to print, how many copies you
want, which printer you want to use (if more than one is set up on
your computer), and so on. You might also see a Print Preview command
that shows a picture of what the page will look like when printed.
This is especially useful when you are using a program that does not
support WYSIWYG.
Editing Commands and Block Manipulation
There are a number of commands you will find on nearly any word
processor that enable you to manipulate text in special ways.
Frequently you will find these commands on an Edit menu. The editing
commands are based on a concept called block manipulation.
Block manipulation simply means taking a «chunk» of text and marking
it in some way so it can be treated as one unit. Once a block of text
is marked as such, it can be deleted or manipulated easily.
- Marking a Block
-
Many modern programs allow you to mark a block of text with the mouse.
Simply point the mouse at the beginning of the text you want to mark,
hold down the mouse button, and drag to the end of the block. You
will probably see the text you have dragged over change color. Some
programs put highlighted text in inverse video. Many programs also
allow you to select text with the Shift key and the arrow keys in
combination. This is sometimes more precise than the mouse
techniques. Some older programs require you to move the cursor to the
beginning of the text, mark it as the beginning of a block, move to
the end of the text you want to manipulate, and mark it as the end of
the block. Learn how your program does it. It is worth the effort. - Copying a Block
-
You will usually find some kind of command called Copy. It only works
after you have marked a block of text. Copy by itself doesn’t do
anything on the screen, but it is still a very important command.
What it does is to take the block of text and make a copy of it in a
special part of memory called the clipboard (or sometimes the buffer).
The copy command does not change the original text; it just places a
copy of the text in the clipboard. - Cutting a Block
-
Cutting is very similar to copying. You must start by marking a block
of text. When you activate a cut command, the original block will
disappear. It isn’t gone forever, though. A copy of it has been made
in the clipboard. - Pasting a Block
-
The paste command doesn’t make much sense until you have cut or copied
a block of text into the clipboard. The paste command copies the
contents of the clipboard into the document at whatever point the
cursor was sitting when the paste command was activated. - How Block Manipulation Works
-
These commands really need to be used together to be useful. Which
ones you use depend on the kind of problem you are trying to solve.
If you had to write «I will not talk out in class» 100 times, you
might write the phrase once, mark it as a block, copy it, and then
paste it 99 times.
If you have written a document and realize that the last line really
belongs at the beginning of the document, you might mark the line you
want to move as a block, cut the block move the cursor to the
beginning of the document, and activate the paste command.
Formatting Commands
Another set of commands are found less frequently on text editors, but
are common on higher-level word processors. These commands are for
formatting various elements of a document. You may find a format
menu. Many of these commands also are available on toolbars.
Formatting a Character
A character is one letter or other symbol. There are many ways to
format characters in word processing programs. It is possible to make
characters bold, italic, underlined, or perhaps some other attribute.
Not all word processors will do all these things, but most will do
bold, italic, and underline. Often you activate the command by
choosing it from a menu, clicking on a toolbar icon, or activating a
key sequence. Once you have started the command, anything you type
will be typed in that style. When you want to go back to standard
letters, you activate the same command again. Commands that turn off
and on like this are called toggles, because they are reminiscent of
toggle switches. Many word processors allow you to enter the text
without any format, then to select a set of characters as a block
(like you did to copy and paste), then to activate the command.
Experiment with your word processor to see how it works.
Word processors that feature WYSIWYG frequently support the use of
fonts. A font is defined in computing as a combination of a special
character set and type size. In the typewriter world, you were pretty
much stuck with the size and style of letters the typewriter came
with. Some of the later typewriters had the characters on a ball you
could change, but you still had very little control of exactly how the
letters looked. In a modern word processing application, you have a
great deal of control. You can choose different type faces that look
like script, handwriting, Old English, or whatever. After you have
chosen a basic look for your letters, you can choose what size the
letters are.
Fonts are measured by typesetters in points. 72.25 points is
equivalent to an inch. Most standard text is 10 points. A newspaper
headline might be 200 points. You may be able to control other
attributes of each letter, such as its color, a shadow, and other advanced
features.
Formatting Paragraphs}
Most writing is organized into paragraphs. These divisions make a
document easier to read. There are ways you can control how
paragraphs look on the screen. You can control how your program
handles indention. You can often force the computer to indent the
first line of every paragraph automatically. You can also frequently
control the line spacing inside the paragraph, the amount of spacing
between paragraphs, and the justification.
Justification refers to how the text is lined up between the margins.
Most documents created with a typewriter or word processor are
left-justified. That means that the left margin is lined up perfectly, but
the right margin is a little ragged. The computer keeps track of the
right margin for you when you use a word processor, so you don’t have
to press the «Enter» key at the end of every line (in fact you
shouldn’t press «Enter» at the end of every line. The only time you
should press «Enter» is when you want to end a paragraph!) The
automatic process the computer uses to send text to the next line is
called word wrap. If you want to have the right margin line up
cleanly, but let the left one be a little ragged (Maybe as you type
the return address and date of a business letter) you can choose a
right justify command. If you look at books and magazines, you will
see that both the right and left columns are justified. Many word
processors will allow you to justify both margins. This works by
adjusting the amount of space between letters and words so the margins
work out perfectly. The computer does it automatically when you ask
it to do so. Another form of justification is centering. When you
center a line, you tell the program to give it equal left and right
margins, regardless of the length of the line. Centering is useful
for headlines, but is often distracting when used for body text.
The other major element of a document is the page. There are some
page formatting commands you should be able to find in any word
processor as well. You will probably have some way to adjust the
margins of the page. Note that there are top and bottom margins, as
well as left and right margins.
You can also frequently find some kind of header/footer command.
Headers and footers are special areas at the top and bottom,
respectively, of the page. These areas are not used for regular text,
but reserved for special things like a title at the top of every page,
page numbers, and footnotes. You will have to experiment a little
to see how your word processor handles these features, but they are
well worth learning. You will never go back to the old way of writing
footnotes once you have mastered using footers to automate the
process.
One more page formatting command you might find useful is page
orientation. Many word processors allow you to choose how information
is printed on the page. The «up and down» orientation we are used to
seeing on typewritten documents is called portrait mode. (If you
think about painted portraits, they are usually up-and-down rectangles.)
When your document is printed «sideways» it is referred to as landscape
mode. (Landscape paintings are often oriented in this way.)
__________
| ___ | ________________
| /o o | | |
|| L | | | /WWW |
||___/| | | / |
| / | |/ |
|_/_____| |______________|
Portrait Landscape
mode mode
Most of the time you should use portrait mode, but sometimes landscape
mode is appropriate, especially when you are doing something special
like tables, graphics, or fancy desktop publishing.
Commands Found in More Advanced Programs
High-End Formatting Tools
There are a few more elaborate formatting tools generally found
only in the higher end word processors. These tools border on desktop
publishing, and allow you better control of your document. You
probably won’t use them every day, but they are wonderful when you
need them.
- Tables
-
On a typewriter, creating a table required judicious use of the TAB
key and very careful planning. Most advanced word processors allow
you to create tables very easily. You can usually select the number
of rows and columns, change the size and format of rows and columns,
and easily copy and paste specific cells. The table tool is worth
learning. - Columns
-
Sometimes you will want to have a page formatted into two or more
vertical columns. This was quite tedious on a typewriter, but there
is usually some kind of tool to make column creation easier on a
modern word processor. - Lists
-
You will frequently find tools for making lists. Lists can have
automatic numbering (like an outline) or each list item might have a
small icon marking, called a bullet. Most modern word processing
programs have some kind of tool to make list management easier. - Graphics
-
Most high-end word processing programs enable you to incorporate
graphics into text documents with relative ease. Often they
incorporate small painting programs so you can generate your own
graphics as well. To make graphics and text easier to work with, many
word processing programs include frames, which are boxes on the screen
that can hold text and graphics. When you mix text and graphics on a
page, you may want to investigate frames in the on-line help so you can
have more control over how the text and graphics interact.
Composition Tools
Many word processors have other advanced features that help a writer
with the mechanics of writing properly. These tools can be
instrumental in avoiding common writing mistakes.
- Spell Checking
-
A spell checker is a program that looks at a document and compares
each word in the document to an electronic dictionary. If it finds
the word in the dictionary, it moves on to the next word. If it does
not find the word, it stops and asks the user for guidance. Good
spell checkers try to guess what word the user was trying to type and
make suggestions. Even if you are a very good speller, you should get
in the habit of running your materials through a spell checker. It is
a quick and relatively painless way to keep typos from marring your
paper.Keep in mind that spelling checkers are not perfect, and they cannot
catch every mistake. The following poem excerpt points out the
problem:Ode To The Spell Checker I have a spelling checker. It came with my PC. It plane lee marks four my revue, Miss steaks aye can know sea. Eye ran this poem threw it, Your sure reel glad two no. Its vary polished in it's weigh, My checker tooled me sew.(This poem can be found in its entirety at:
http://selma.ucd.ie/~pdurkin/Jokes/spellcheck.html It is attributed
to Jerry Zar, the Dean of the Graduate School, NW Ill. U) - Grammar Checkers
-
There are also tools available on most high end word processors that
will check your grammar for common mistakes. Grammar checkers are
wonderful at catching mechanical problems like incomplete sentences
and subject-verb agreement. Grammar tends to be more subjective
than spelling, so the advice of a grammar checker might or might not
be useful to you. It is worth running to check your mistakes, but it
will never replace the lessons you learned from your English teachers
or a skilled editor. When grammar checkers first came on the market,
a reporter tried testing the Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln.
The program gave the speech extremely poor marks. Many people
consider it to be one of the most beautiful passages of American
English ever. Use a grammar checker if you have one, but also use
your judgment. - Outline Editors
-
These features allow you to organize your thoughts in outline format.
The advantage is that you can choose to see only your main ideas or
headings, and have all the text hidden. This feature allows you to
move the main headings around and all the text associated with the
headings will automatically move appropriately. If you are going to
do term papers or other serious writing, you should investigate this
feature.
Vocabulary/Important Ideas
- Word Processing
-
A type of software that specializes in handling text. Word processing
programs typically contain commands for handling and formatting text
documents. - Insert/Overwrite Modes
-
Most word processors allow you to choose one of these modes. When you
are in {bf insert} mode, any text you type is inserted into the
document at the cursor position. {it Overwrite} mode also types text
at the cursor position, but it writes over the top of existing text,
much like a typewriter with correcting tape. Most experienced word
processor users prefer insert mode for most of their work. - Text Editors
-
A classification of word processing software characterized by its low
cost, ready availability, tendency to work only in ASCII format, and
inability to do high-powered formatting. - ASCII
-
American Standard C}ode for Information
Interchange. A standard convention used to encode text, numbers, and
common punctuation in numeric format so they can be stored in a
computer’s memory. Nearly all computers and programs can work with
some form of ASCII. Text editors are designed especially to work with
ASCII-based documents. - Integrated Packages
-
Programs that contain all the major applications within one «super
application». These programs are useful, but often lack some of the
more advanced features of full-fledged application packages. - WYSIWYG
-
What You See is What You Get.
A capability often found on higher-level word processing
programs. The screen mimics the output of the printer, so the typist
can see pretty much what the final output of the document will be. - Proprietary
-
The term {it proprietary} is frequently used when discussing software to
denote a certain idea that is particular to a specific brand of
software. When a program uses a proprietary scheme to save word
processing documents, for example, other programs may not be able to
read these documents without some kind of translation. - Desktop Publishing
-
A classification of word processing software that concentrates on
incorporation of graphics, powerful formatting, and development of
complex styles including newsletters, signs, and pamphlets. - Style Sheet
-
In desktop publishing, a template that specifies how a certain type of
document will be created. Style sheets are used to define a uniform
look and feel for documents of the same general type. For example, a
company might issue a standard style sheet for intra-corporation
memoranda. Many high-end word processors incorporate this feature.
Sometimes style sheets are referred to as templates. - Scroll Bars
-
Horizontal or vertical bars which indicate the cursor position in a
document. Usually scroll bars can be used with the mouse to
facilitate moving through the document. - Cursor
-
A small mark on the screen, usually a rectangle, underline, or
I-shaped design. The cursor indicates the exact position within the document
(and memory) where any commands and typing will be executed. - Save
-
The Save command saves a document without prompting for the file
name, unless the file has never been saved before. If this is the
case, it invokes a Save As command instead. - Save As
-
This command always prompts for a file name. It is used when
you want to save the changes to file without changing the file already
saved on the disk. - Load (or Open)
-
This command prompts the user for a file name, then loads the document
into the application. -
A print command is used to send a copy of the document to the
printer. - Print Preview
-
This command is especially useful in non-WYSIWYG environments. It
allows you to see a preview of the document exactly as it will be
printed. It is often a good idea to invoke this command before you
print a document, to be sure it will turn out exactly as you plan. - Block Manipulation
-
The process of defining a section of text so it can be copied, pasted,
or otherwise manipulated as one unit. - Copy
-
A copy command takes a block of text and copies it to a memory
buffer without removing the original text. Used to it
duplicate sections of a document. - Cut
-
This command copies a block of text to a memory buffer, and removes
the original text from the document. Used to {it move} sections of a
document. - Paste
-
This command takes the block of text last placed in the buffer by a
cut or copy command, and inserts it into the document at the current
cursor position. - Formatting
-
The process of defining how a document will look. Formatting can
occur at the character level, as well as at the paragraph and page
level. - Character Attributes
-
The special modifications to letters, such as {bf boldface} and {it
italic} - Font
-
The combination of character set and size that defines how an
individual character looks. Most word processing packages allow the
user to choose from many fonts. - Toggle
-
A command is referred to as a {it toggle} if repeated execution of
the command causes something to switch between two modes. Insert
and Overwrite modes are good examples of toggles. Often character
attributes are also considered toggles. - Point
-
A point is a type setter’s measurement of character size. Officially,
there are 72.25 points to an inch. - Justification
-
The way the lines of text are arranged on the page. The usual options
are left-justified, right-justified, centered, and both-justified. - Left-Justified
-
The text is lined up so that the left margin is even. The right
margin will not be even in left-justified text. - Right-Justified
-
The text is lined up so that the left margin is ragged, but the right
margin is even. Often used to line up dates and return addresses on
business letters. - Both-Justified
-
The text is lined up so that both the left and right margins are lined
up, as in a newspaper or magazine. - Centered
-
The text is lined up with an equal distance from the left and right
margins. Usually used in headlines. - Word Wrap
-
A behavior of word processing programs which automatically moves words
too large to fit the current line onto a new line. Eliminates the
need to press «return» at the end of each line. - Headers, Footers
-
Special areas at the top and bottom of word processing documents.
These sections are reserved for information that will appear on {it
each page} of the document. Usually page numbers, document name, or
document author will be in the header/footer area. The footer is
also useful for holding footnotes. - Landscape Mode
-
Documents in this mode print the long part of the page horizontally, as
in a landscape painting. - Portrait Mode
-
Documents in this mode print the long part of the page vertically,
as in a portrait painting. - Table
-
A section of a document organized into rows and columns. Higher-end
word processors often have a number of tools to help make tables
easier to create and manage. - Column
-
Vertical separation of text into two or more sections. Newspapers and
newsletters are often arranged in columns. High-end word processing
programs and desktop publishing programs usually include some tools to
make column manipulation easier. - Spell Checker
-
A feature of higher-end word processing programs that compares each
word in a document to a dictionary of proper spellings. Most spell
checkers «guess» which word the user was trying to type and give the
user some guesses to choose from. - Grammar Checker
-
A feature in word processing programs that checks a document for
common grammatical errors. Grammar checkers can also grade documents
for readability and complexity. Sometimes grammar checkers are
separate programs. - Outline Editors
-
A feature or program that easily enables the user to create and
manipulate outlines. Most of these programs allow you to hide the
body text so you can see and modify the subject headings. The
associated body text is automatically moved with the appropriate heading.
Summary
Word processing programs are a type of software that make
it easier to create and modify text documents. Word Processing
applications are organized into a number of categories according to
their complexity: Simple programs that manipulate ASCII are called
Text Editors. More complex programs that feature formatting commands
are called Word Processors. Some word processors are included in
integrated application packages, which also feature other application
programs. Such packages are convenient, but may not have all the
features of larger programs. Full-featured word processing programs
contain many options for formatting text and documents. They also
might contain special utilities for more complex formatting and
composition. Desktop publishing programs are designed for more
complex formatting, especially the integration of text and graphics.
Most word processing programs contain the same types of commands,
although the exact ways to access these commands may vary. You will
almost always see file handling commands, including commands to Load,
Save, Save As, and Print. Frequently, you will also see commands for block
manipulation, including Copy, Cut, and Paste. More advanced programs
may contain special commands for formatting characters and paragraphs,
as well as other commands to deal with tables, columns, and lists.
The fanciest word processing programs may also contain commands to
assist with composition, such as spelling and grammar checkers and
outline editors.

Ash Manor School
Computing Department
Word processing
Word processing is the creation, editing and publication of digital artefacts which are based on formatted text. We use a word porcessor in school to write up assignments, essays, magazine articles, letters, plays and many other uses. In this unit we will also introduce you to the file system, and how to use this to your advantage.
Aims
This is an introduction to Word processing, and file operations. We will be focusing on the theme «Employment»
By the end of this unit you will learn:
- Level 3
- (IT) Organises files in a folder structure
- (IT) creates digital content to achieve a goal
- (IT) Combines digital packages (imports pictures, and spreadsheets into a word document)
- (IT) Makes appropriate improvements to digital content based on feedback
- Level 4
- (IT) Makes judgements about digital artefacts produced.
- (IT) Recognises audience when producing digital artefacts.
- (IT) Uses criteria provided to evaluate the quality of digital artefacts
- (IT) independantly identifies improvements to digital content, and makes appropriate improvements
- Level 5
- (IT) Designs criteria to evaluate the quality of digital artefacts
- (IT) Uses criteria to identify appropriate improvements to digital content, and carries out these improvements
- (IT) Uses styles appropriately.
- Level 6
- (IT) Justifies choice of software and independantly combines resources to produce a digital artefact.
- (IT) Designs digital artefacts for wider, or remote audience.
- (IT) Designs criteria for users to evaluate the quality of digital artefacts
- (IT) Uses feedback from users to refine solution, or make recommendations for refinements.
Activity 1
Learning aims:
- Creates digital content to achieve a goal — L3
- Combines digital packages (import pictures into a word document) L3
- Uses styles appropriately
Starter
A newspaper classified sales clerk notes down this advertisement over the phone:
Laptop for sale, Intel Pentium M 760 Processor 2.0 GHz, 512MB memory, 80GB hard disk. £225. Excellent condition. Phone John Smith 417639.
Describe five different features of a Word Processing package you could use to improve this advert.
Save your answer in a word document as «Starter» and upload to here.
Task 1
HOW DO YOU COMMUNICATE WITH THE COMPUTER?
In the windows environment you can communicate with the computer using a Graphical User Interface (GUI -pronounced Gooey). This means you give instructions to the computer by using a mouse to click on icons, tabs and buttons. In Microsoft Word there is a ribbon which goes across the window. This is where you can find a set of tabs, a series of buttons, icons and controls called commands.

Do you know your icons?
An icon is a small symbol or picture that represents a series of instructions or programs.
Complete the table
and upload your saved document here
Activity 2
Applying for a Job!
You have been asked to research and apply for a job. In order to apply, you need to produce a CV and covering letter. Job can be any choice of yours.
Learning aims:
- Uses styles appropriately — L5
Task 1 — Writing your CV
Here are a few simple guidelines:
- keep it short (1-4 pages)
- put your best skills first
- use simple language and short sentences
- be positive and enthusiastic
- don’t staple lots of things to it
- make it look good – and always type it
- check your spelling and grammar (get someone else to check it too)
What should my CV say?
Here are the main things you need to include:
Personal details.
Give your full name, and an address and phone number where the employer can contact you. Age and family details are optional.
Career or personal objective.
Say what you want to achieve in your working future. This helps the employer relate your skills to the job.
Work experience.
List the jobs you’ve had, starting with the most recent and working backwards. Give the job title, the employer’s name, the date you started and finished, and a brief description.
Skills and abilities.
List your work-related skills and abilities. Some of these might be skills you learnt outside work. So include unpaid, community or family work and say how these skills might suit the job you are applying for.
Education and training.
Include your schooling and other training. Give details of technical and trade certificates, and any study or courses you’ve done (even if you haven’t completed them).
Other things.
Give brief details of your hobbies and interests. Include anything else you think is important such as driver’s licence or your state of health.
Referees.
Include at least 2 people who can talk about how well you’ve worked in the past. Give their name, position, and phone number. But check with them first. Let them know they may be contacted and ask what they will say about you.
Create your CV using a word processor and click here to upload your CV
You can use the CV Template
Task 2 — Writting a covering letter for a Job
Cover Letter Tips:
The basics
Always send a cover letter as part of any job application.
Be neat and tidy: type your letter on unmarked, white A4 paper.
Keep it concise: ideally just one page.
Attention to detail: ensure there are no spelling or grammatical mistakes (especially the correct job title and name of who you are writing to).
Make sure you include your contact phone and address details.
Be professional, positive and confident.
Bullet points are great to describe your key skills / achievements but remember you are writing a formal letter. Most of your letter should be written in full sentences and split into relevant paragraphs.
What to say
- Include where you saw the job advertised and the vacancy reference number if applicable.
- Describe why you are interested in this job.
- Include highlights or key achievements from your background but remember you don’t need to repeat lists of responsibilities from your CV.
- Make it relevant to the job you’re applying for: you need to show how your skills, experience, and qualifications match what they are looking for. (Refer back to their job advertisement or job description).
- Don’t forget that any skills gained through education, training, work experience, voluntary work and/or community activities might also be relevant.
- Cover off any other details as applicable: for example, your willingness to relocate if you live in a different town from where the job is based.
- Confirm you would appreciate the opportunity to be interviewed. Say if you are going to be unavailable during the likely interview process timeframe.
Click here for a formal letter template.
Use the template to complete your covering letter. Click here to send your letter.
Activity 3
«Congratulation, you are through to next level»
Once again Congratulations! Tou have been short listed for an interview.
Part of the process is to produce a company logo. You may use other software to produce your design. However you need to justify the choice of software and combined resources to produce a logo. You must import your logo into word document as we might not support other software.
We expect to see progression as to how you deliver your final product.
We expect the following from you:
- Logo (import to word processing) – Your first attempt
- Logo (import to word processing) –Your second attempt showing improvements
- Logo (import to word processing) – Your final design, following feedback
- Report – Word document explaining/justifying your decisions step by step.
Learning aims:
- Creates digital content to achieve a goal — L3
- Recognises audience when producing digital artefacts. L4
Task 1 — Logo for the Company (Create a Logo)
Import your logo into a word documents and save as «Logo_YOURNAME»
Click here to upload your Logo version 1
Activity 4
Visual Literacy exercise.
Learning aims:
- Makes judgements about digital artefacts produced. L4
- Designs criteria to evaluate the quality of digital artefacts — L5
- Independantly identifies improvements to digital content, and makes appropriate improvements — L4
Task 2 — Develop your Logo
Self Mark your design — Independently identified improvement to your logo, and make appropriate improvements.
Import your logo into a word documents and save as «Logo1.YOUERNAME»
Click here to upload your Logo version 2
Activity 5
Visual Literacy exercise.
Learning aims:
- Makes appropriate improvements to digital content based on feedback — L3
- Uses feedback from users to refine solution, or make recommendations for refinements.L6
Task 3 — Review your Design
Peer Mark — Make appropriate improvements to your desgin based on feedback.
Import your logo into a word documents and save as «Logo_Final.YOUERNAME»
Click here to upload your final Logo
Activity 6
Visual Literacy exercise.
Learning aims:
- Justifies choice of software and independantly combines resources to produce a digital artefact. L6
- Organises files in a folder structure — L3 — Task 2
Task 1 — Justify your design
Produce a report using word document explaining/justifying your decisions step by step.
Save your report as «Report_YOURNAME»
Click here to upload your report
Task 2 — Organisation Skill
Produce a word document showing screen shots of your files in a folder structure.
Save your document as «Folder_YOURNAME» and upload it here
Word processing is the process of adding text to a word processing unit such as a computer or typewriter. The typed words are stored in the computer or word processor temporarily to allow for editing before a hard copy of the document. The term «word processing» is a fairly general term, so it may refer to several types of writing without the use of pen and paper. Typewriters, for example, process words directly onto a paper without storing the data, while computers use specific programs to store the typed data before printing.
Modified typewriters have been commonly used in the past for word processing. The typewriter would store the data — usually with the use of a computer chip — before printing the words onto a page. The person using the word processor could then check the writing for errors before printing the final draft. When computers became common in the workplace and at home, word processors became mostly obsolete, though some models are still used for a wide range of purposes, including as educational devices for students with special needs.
Computers have generally taken over word processing duties. The computers feature specific programs in which a person can type manuscripts of any length. The data is stored as an electronic document that can be opened, closed, saved, and edited at any time. This allows the user to make corrections or changes to a document multiple times before printing out a hard copy of the document. In many cases, the document is not printed out onto hard copy paper at all; instead, it can be used on the internet, in e-mails, or for other digital purposes.
Simpler programs, such as text editors or notepads, can be used to record text quickly without excess formatting options, such as multiple fonts or font sizes. Such programs are easy to use and do not come loaded with formatting features, such as color, multiple fonts, line spacing options, and so on. They are meant to be used for quick word processing that will not need to be formatted for presentation.
Word processing software often includes several features unavailable on typewriters or older word processors. Such features may include the ability to manipulate the layout of the text, the size and color of the font, the type of font used, line spacing, margin adjustments, and the ability to insert photos, web links, graphs, charts, and other objects directly into the document.
A word processor enables you to create a document, store it electronically on a disk, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it on a printer.
Word processors usually support these features (and a few others).
Cut and paste: Allows you to remove (cut) a section of text and insert (paste) it somewhere else.
Find and replace: Allows you to direct the word processor to search for a particular word or phrase. You can also direct the word processor to replace one group of characters with another everywhere that the first group appears.
Word wrap: The word processor automatically moves to the next line when you have filled one line with text, and it will readjust text if you change the margins.
Print: Allows you to send a document to a printer to get hard copy.
Font specifications: Allows you to change fonts within a document. For example, you can specify bold, italics, and underlining. Most word processors also let you change the font size and the typeface.
Graphics: Allows you to include illustrations and graphs in a document.
Headers, footers and page numbering: Allows you to specify customized headers and footers that the word processor will put at the top and bottom of every page. The word processor automatically keeps track of page numbers so that the correct number appears on each page.
Layout: Allows you to specify different margins within a single document and to specify various methods for indenting paragraphs — how much space you leave between the margins and the paragraphs.
Merge: Allows you to merge text from one file into another file. This is particularly useful for generating many files that have the same format but different data.
Spell checker: A utility that allows you to check the spelling of words. Ir will highlight any words that it does not recognize.
Thesaurus: Allows you to search for synonyms without leaving the word processor.
(from Professional English in use)
6. Find English equivalents in the text:
Вирізати і вставити, знайти й замінити, вирівнювання тексту, скорегувати текст, поля, щоб отримати інформацію у друкованому вигляді, характеристики шрифтів, задати напівжирний шрифт, курсив, підкреслення, розмір шрифту та накреслення символу, верхні і нижні колонтитули, об’єднати текст, створення файлів, програма перевірки орфографії, виділити, шукати синоніми.
7. Make up word combinations:
| 1. to display a document | a) with another |
| 2. to store a document | b) for a particular word |
| 3. to modify a document | c) hard copy |
| 4. to print a document | d) by entering commands |
| 5. to support | e) fonts |
| 6. to search | f) on a screen |
| 7. to replace one group of characters | g) of page numbers |
| 8. to get | h) electronically on a disk |
| 9. to change | i) on a printer |
| 10. keeps track | j) the features |
|
Важнейшие способы обработки и анализа рядов динамики Не во всех случаях эмпирические данные рядов динамики позволяют определить тенденцию изменения явления во времени… |
ТЕОРЕТИЧЕСКАЯ МЕХАНИКА Статика является частью теоретической механики, изучающей условия, при которых тело находится под действием заданной системы сил… |
Теория усилителей. Схема Основная масса современных аналоговых и аналого-цифровых электронных устройств выполняется на специализированных микросхемах… |
Логические цифровые микросхемы Более сложные элементы цифровой схемотехники (триггеры, мультиплексоры, декодеры и т.д.) не имеют… |
|
Огоньки» в основной период В основной период смены могут проводиться три вида «огоньков»: «огонек-анализ», тематический «огонек» и «конфликтный» огонек… Упражнение Джеффа. Это список вопросов или утверждений, отвечая на которые участник может раскрыть свой внутренний мир перед другими участниками и узнать о других участниках больше… Влияние первой русской революции 1905-1907 гг. на Казахстан. Революция в России (1905-1907 гг.), дала первый толчок политическому пробуждению трудящихся Казахстана, развитию национально-освободительного рабочего движения против гнета. В Казахстане, находившемся далеко от политических центров Российской империи… |




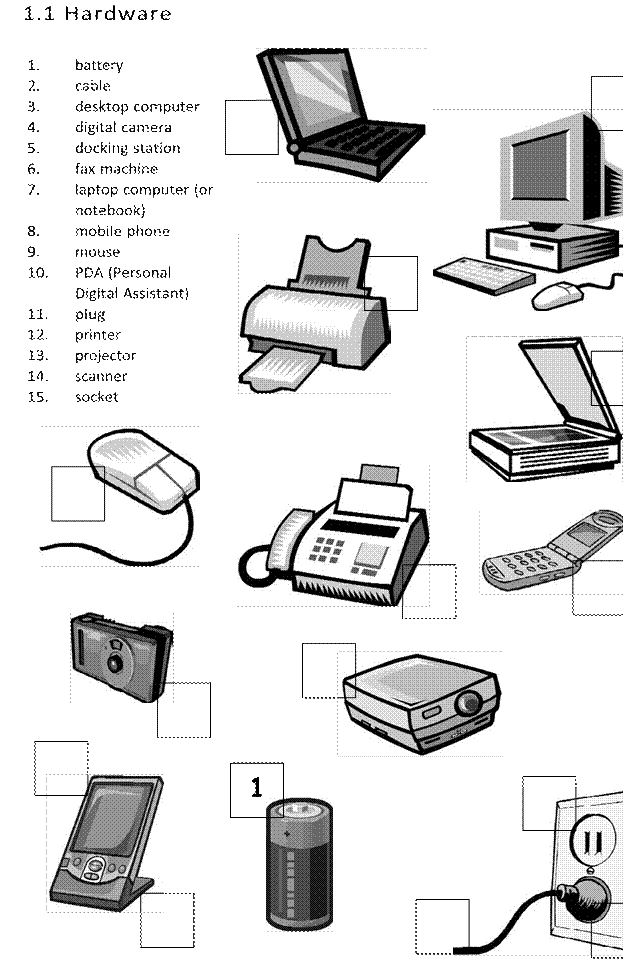
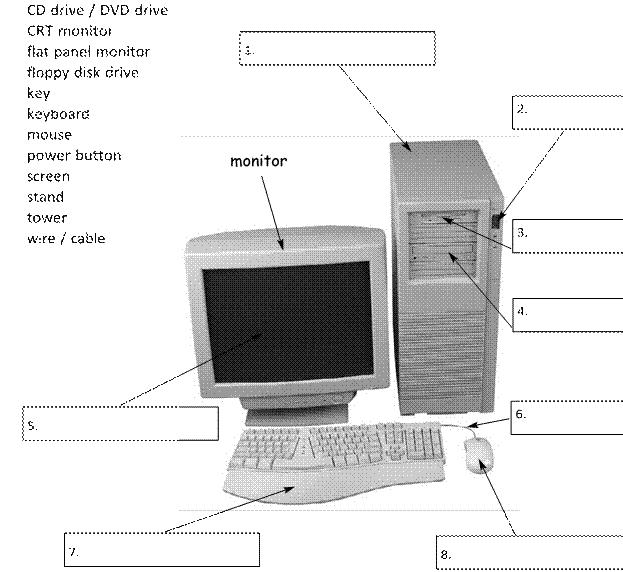


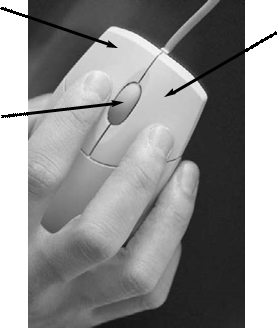
 D
D