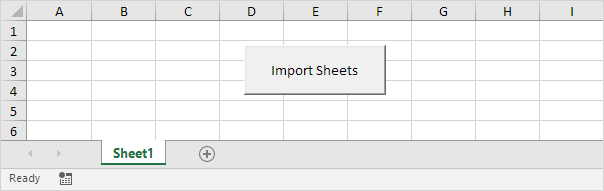
We need to write an Excel spreadsheet with VBA code in it; the code reads and performs operations on the data in the first worksheet.
The user will be receiving spreadsheets containing data but that do not contain the VBA code. We need to be able to import the data from the spreadsheets containing the data into the spreadsheet containing the VBA code automatically. The worksheets containing the data have the same column format and datatypes as the worksheet of the spreadsheet containing the data.
Ideally, you would open the spreadsheet containing the VBA code, be presented with a UI allowing the user to navigate to the spreadsheet containing the data, click OK and the data will be imported.
How would you go about doing this? It has to be done using VBA in Excel spreadsheets.
Many thanks.
asked Oct 24, 2011 at 13:14
0
This should get you started:
Using VBA in your own Excel workbook, have it prompt the user for the filename of their data file,
then just copy that fixed range into your target workbook (that could be either the same workbook as your macro enabled one, or a third workbook).
Here’s a quick vba example of how that works:
' Get customer workbook...
Dim customerBook As Workbook
Dim filter As String
Dim caption As String
Dim customerFilename As String
Dim customerWorkbook As Workbook
Dim targetWorkbook As Workbook
' make weak assumption that active workbook is the target
Set targetWorkbook = Application.ActiveWorkbook
' get the customer workbook
filter = "Text files (*.xlsx),*.xlsx"
caption = "Please Select an input file "
customerFilename = Application.GetOpenFilename(filter, , caption)
Set customerWorkbook = Application.Workbooks.Open(customerFilename)
' assume range is A1 - C10 in sheet1
' copy data from customer to target workbook
Dim targetSheet As Worksheet
Set targetSheet = targetWorkbook.Worksheets(1)
Dim sourceSheet As Worksheet
Set sourceSheet = customerWorkbook.Worksheets(1)
targetSheet.Range("A1", "C10").Value = sourceSheet.Range("A1", "C10").Value
' Close customer workbook
customerWorkbook.Close
answered Oct 24, 2011 at 15:30
jdhjdh
1,62714 silver badges12 bronze badges
1
Data can be pulled into an excel from another excel through Workbook method or External reference or through Data Import facility.
If you want to read or even if you want to update another excel workbook, these methods can be used. We may not depend only on VBA for this.
For more info on these techniques, please click here to refer the article
answered Apr 26, 2014 at 11:57
Excel Import Data From Another Workbook – VBA Codes
To pull data from an external Excel file, use on of these scenarios.
- Closed Excel file: Using VBA Import data with Workbook object
- Opened Workbook: Using VBA Read Excel file.
- External Reference within Worksheets.
- ODBC Data Import from another workbook.
Excel – Pull data from another Workbook using VBA
To understand how to get data from another Excel file, lets assume these 2 workbook names.
- Source: In this workbook, VBA code will be executed to write or import data from/to Target file.
- Target: This workbook has the data that the Source Workbook will read or modify through VBA.
1. VBA To Update Closed Workbook
This Excel vba import data from another workbook without opening the file manually.
First we will create an Workbook object to refer the external Excel file. And use that object to import data into our Active workbook or Source Workbook.
Let’s see the actual VBA code for this purpose. Copy paste the below code to VB Editor and execute the code by pressing F5. Make sure that the Target file exists in correct path as mentioned in Target_Path in the code, before executing the code.
Sub VBA_Read_Data_Another_External_Workbook()
'''''Define Object for Target Workbook
Dim Target_Workbook As Workbook
Dim Source_Workbook As Workbook
Dim Target_Path As String
'''''Assign the Workbook File Name along with its Path
'''''Change path of the Target File name
Target_Path = "D:Sample.xlsx"
Set Target_Workbook = Workbooks.Open(Target_Path)
Set Source_Workbook = ThisWorkbook
'''''With Target_Workbook object now, it is possible to pull any data from it
'''''Read Data from Target File
Target_Data = Target_Workbook.Sheets(1).Cells(1, 1)
Source_Workbook.Sheets(1).Cells(1, 1) = Target_Data
'''''Update Target File
Source_data = Source_Workbook.Sheets(1).Cells(3, 1)
Target_Workbook.Sheets(1).Cells(2, 1) = Source_data
'''''Close Target Workbook
Source_Workbook.Save
Target_Workbook.Save
Target_Workbook.Close False
'''''Process Completed
MsgBox "Task Completed"
End Sub
2. VBA Read Excel file or Write To Open Workbook?
If a workbook is already in opened and executing, then you can reference that Excel with its name through ‘Workbooks’ collection. You have to use the workbook name itself inside the code to read or write content as mentioned in this sample code.
Sub Write_To_Open_Excel()
Dim wb As Workbook
'Reference Workbook with its name
Workbooks("Book2").Worksheets("Sheet2").Activate
Workbooks("Book3.xls").Worksheets("Sheet2").Activate
'Search for Each Opened Workbook
For Each wb In Workbooks
If wb.Name = "Book2" Then
wb.Sheets(1).Cells(1, 1) = "Writing To Open Excel Worksheet - Testing"
End If
Next
End Sub
3. External Reference to Import Data from another Workbook
With this technique, in the Excel we pull data from another cell by using references. For example, in Cell A1 if we need to get date from Cell B1, we enter “=B1” in cell A1. This is a reference that is made within the scope of current workbook.
In our example if we need to refer the Target sheet, use the command as below.
=’D:[sample.xlsx]Sheet1′!A2
This will fetch the data from the external workbook.
Reference from Microsoft: How to create External reference and pull data from another excel?
4. Data Import Option or ODBC in Excel VBA
This is similar to Data Import facility available in Excel. To do this, the Target workbook should be having some table defined in it.
To import the data from Target, Go to Source Workbook, Data->From Other Sources ->From Microsoft Query and Give the path of the Target Workbook or use the below code by modifying the File path and Column Header Details.
Sub Data_Import_Recorded_Macro()
'''''Change File path and Column Headers to Use this code
With ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(SourceType:=0, Source:= _
"ODBC;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=D:Sample.xlsx;DefaultDir=D:;DriverId=1046;MaxBufferSize=2048;PageTimeout=5;" _
, Destination:=Range("$A$1")).QueryTable
.CommandText = Array( _
"SELECT `Sheet1$`.Column1, `Sheet1$`.Column2, `Sheet1$`.Column3" & Chr(13) & "" & Chr(10) & "FROM `D:Sample.xlsx`.`Sheet1$` `Sheet1$`" _
)
.RowNumbers = False
.FillAdjacentFormulas = False
.PreserveFormatting = True
.RefreshOnFileOpen = False
.BackgroundQuery = True
.RefreshStyle = xlInsertDeleteCells
.SavePassword = False
.SaveData = True
.AdjustColumnWidth = True
.RefreshPeriod = 0
.PreserveColumnInfo = True
.ListObject.DisplayName = "Table_Query_from_Excel_Files"
.Refresh BackgroundQuery:=False
End With
End Sub
These are some of the methods that are available to import from an external workbook to current active workbook. But still, this is not the limit.
Note: To read a Plain Text file or binary file, use VBA File Handling commands as in this link. How to Read contents from a Text File using VBA?
There might be other feasible methods known to others. If there is any, please post a reference as you find.
Below we will look at a program in Excel VBA that imports sheets from other Excel files into one Excel file.
Download Book4.xlsx, Book5.xlsx and add them to «C:test»
Situation:
Add the following code lines to the command button:
1. First, we declare two variables of type String, a Worksheet object and one variable of type Integer.
Dim directory As String, fileName As String, sheet As Worksheet, total As Integer
2. Turn off screen updating and displaying alerts.
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
3. Initialize the variable directory. We use the Dir function to find the first *.xl?? file stored in this directory.
directory = «c:test»
fileName = Dir(directory & «*.xl??»)
Note: The Dir function supports the use of multiple character (*) and single character (?) wildcards to search for all different type of Excel files.
4. The variable fileName now holds the name of the first Excel file found in the directory. Add a Do While Loop.
Do While fileName <> «»
Loop
Add the following code lines (at 5, 6, 7 and 
5. There is no simple way to copy worksheets from closed Excel files. Therefore we open the Excel file.
Workbooks.Open (directory & fileName)
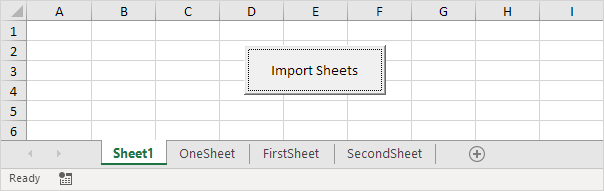
6. Import the sheets from the Excel file into import-sheet.xlsm.
For Each sheet In Workbooks(fileName).Worksheets
total = Workbooks(«import-sheets.xlsm»).Worksheets.count
Workbooks(fileName).Worksheets(sheet.Name).Copy _
after:=Workbooks(«import-sheets.xlsm»).Worksheets(total)
Next sheet
Explanation: the variable total holds track of the total number of worksheets of import-sheet.xlsm. We use the Copy method of the Worksheet object to copy each worksheet and paste it after the last worksheet of import-sheets.xlsm.
7. Close the Excel file.
Workbooks(fileName).Close
8. The Dir function is a special function. To get the other Excel files, you can use the Dir function again with no arguments.
fileName = Dir()
Note: When no more file names match, the Dir function returns a zero-length string («»). As a result, Excel VBA will leave the Do While loop.
9. Turn on screen updating and displaying alerts again (outside the loop).
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
10. Test the program.
Result:
This tutorial will cover the ways to import data from Excel into an Access Table and ways to export Access objects (Queries, Reports, Tables, or Forms) to Excel.
Import Excel File Into Access
To import an Excel file to Access, use the acImport option of DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet :
DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acImport, acSpreadsheetTypeExcel12, "Table1", "C:TempBook1.xlsx", TrueOr you can use DoCmd.TransferText to import a CSV file:
DoCmd.TransferText acLinkDelim, , "Table1", "C:TempBook1.xlsx", TrueImport Excel to Access Function
This function can be used to import an Excel file or CSV file into an Access Table:
Public Function ImportFile(Filename As String, HasFieldNames As Boolean, TableName As String) As Boolean
' Example usage: call ImportFile ("Select an Excel File", "Excel Files", "*.xlsx", "C:" , True,True, "ExcelImportTest", True, True,false,True)
On Error GoTo err_handler
If (Right(Filename, 3) = "xls") Or ((Right(Filename, 4) = "xlsx")) Then
DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acImport, acSpreadsheetTypeExcel12, TableName, Filename, blnHasFieldNames
End If
If (Right(Filename, 3) = "csv") Then
DoCmd.TransferText acLinkDelim, , TableName, Filename, True
End If
Exit_Thing:
'Clean up
'Check if our linked in Excel table already exists... and delete it if so
If ObjectExists("Table", TableName) = True Then DropTable (TableName)
Set colWorksheets = Nothing
Exit Function
err_handler:
If (Err.Number = 3086 Or Err.Number = 3274 Or Err.Number = 3073) And errCount < 3 Then
errCount = errCount + 1
ElseIf Err.Number = 3127 Then
MsgBox "The fields in all the tabs are the same. Please make sure that each sheet has the exact column names if you wish to import mulitple", vbCritical, "MultiSheets not identical"
ImportFile = False
GoTo Exit_Thing
Else
MsgBox Err.Number & " - " & Err.Description
ImportFile = False
GoTo Exit_Thing
Resume
End If
End FunctionYou can call the function like this:
Private Sub ImportFile_Example()
Call VBA_Access_ImportExport.ImportFile("C:TempBook1.xlsx", True, "Imported_Table_1")
End SubAccess VBA Export to New Excel File
To export an Access object to a new Excel file, use the DoCmd.OutputTo method or the DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet method:
Export Query to Excel
This line of VBA code will export a Query to Excel using DoCmd.OutputTo:
DoCmd.OutputTo acOutputQuery, "Query1", acFormatXLSX, "c:tempExportedQuery.xls"Or you can use the DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet method instead:
DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acExport, acSpreadsheetTypeExcel8, "Query1", "c:tempExportedQuery.xls", TrueNote: This code exports to XLSX format. Instead you can update the arguments to export to a CSV or XLS file format instead (ex. acFormatXLSX to acFormatXLS).
Export Report to Excel
This line of code will export a Report to Excel using DoCmd.OutputTo:
DoCmd.OutputTo acOutputReport, "Report1", acFormatXLSX, "c:tempExportedReport.xls"Or you can use the DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet method instead:
DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acExport, acSpreadsheetTypeExcel8, "Report1", "c:tempExportedReport.xls", TrueExport Table to Excel
This line of code will export a Table to Excel using DoCmd.OutputTo:
DoCmd.OutputTo acOutputTable, "Table1", acFormatXLSX, "c:tempExportedTable.xls"Or you can use the DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet method instead:
DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acExport, acSpreadsheetTypeExcel8, "Table1", "c:tempExportedTable.xls", TrueVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Export Form to Excel
This line of code will export a Form to Excel using DoCmd.OutputTo:
DoCmd.OutputTo acOutputForm, "Form1", acFormatXLSX, "c:tempExportedForm.xls"Or you can use the DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet method instead:
DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acExport, acSpreadsheetTypeExcel8, "Form1", "c:tempExportedForm.xls", TrueExport to Excel Functions
These one line commands work great to export to a new Excel file. However, they will not be able to export into an existing workbook. In the section below we introduce functions that allow you to append your export to an existing Excel file.
Below that, we’ve included some additional functions to export to new Excel files, including error handling and more.
Export to Existing Excel File
The above code examples work great to export Access objects to a new Excel file. However, they will not be able to export into an existing workbook.
To export Access objects to an existing Excel workbook we’ve created the following function:
Public Function AppendToExcel(strObjectType As String, strObjectName As String, strSheetName As String, strFileName As String)
Dim rst As DAO.Recordset
Dim ApXL As Excel.Application
Dim xlWBk As Excel.Workbook
Dim xlWSh As Excel.Worksheet
Dim intCount As Integer
Const xlToRight As Long = -4161
Const xlCenter As Long = -4108
Const xlBottom As Long = -4107
Const xlContinuous As Long = 1
Select Case strObjectType
Case "Table", "Query"
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(strObjectName, dbOpenDynaset, dbSeeChanges)
Case "Form"
Set rst = Forms(strObjectName).RecordsetClone
Case "Report"
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(Reports(strObjectName).RecordSource, dbOpenDynaset, dbSeeChanges)
End Select
If rst.RecordCount = 0 Then
MsgBox "No records to be exported.", vbInformation, GetDBTitle
Else
On Error Resume Next
Set ApXL = GetObject(, "Excel.Application")
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Set ApXL = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
End If
Err.Clear
ApXL.Visible = False
Set xlWBk = ApXL.Workbooks.Open(strFileName)
Set xlWSh = xlWBk.Sheets.Add
xlWSh.Name = Left(strSheetName, 31)
xlWSh.Range("A1").Select
Do Until intCount = rst.fields.Count
ApXL.ActiveCell = rst.fields(intCount).Name
ApXL.ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select
intCount = intCount + 1
Loop
rst.MoveFirst
xlWSh.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset rst
With ApXL
.Range("A1").Select
.Range(.Selection, .Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select
.Selection.Interior.Pattern = xlSolid
.Selection.Interior.PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic
.Selection.Interior.TintAndShade = -0.25
.Selection.Interior.PatternTintAndShade = 0
.Selection.Borders.LineStyle = xlNone
.Selection.AutoFilter
.Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
.Cells.EntireRow.AutoFit
.Range("B2").Select
.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = True
.ActiveSheet.Cells.Select
.ActiveSheet.Cells.WrapText = False
.ActiveSheet.Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
xlWSh.Range("A1").Select
.Visible = True
End With
'xlWB.Close True
'Set xlWB = Nothing
'ApXL.Quit
'Set ApXL = Nothing
End If
End FunctionYou can use the function like this:
Private Sub AppendToExcel_Example()
Call VBA_Access_ImportExport.ExportToExcel("Table", "Table1", "VBASheet", "C:TempTest.xlsx")
End SubNotice you are asked to define:
- What to Output? Table, Report, Query, or Form
- Object Name
- Output Sheet Name
- Output File Path and Name.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Export SQL Query to Excel
Instead you can export an SQL query to Excel using a similar function:
Public Function AppendToExcelSQLStatemet(strsql As String, strSheetName As String, strFileName As String)
Dim strQueryName As String
Dim ApXL As Excel.Application
Dim xlWBk As Excel.Workbook
Dim xlWSh As Excel.Worksheet
Dim intCount As Integer
Const xlCenter As Long = -4108
Const xlBottom As Long = -4107
Const xlVAlignCenter = -4108
Const xlContinuous As Long = 1
Dim qdf As DAO.QueryDef
Dim rst As DAO.Recordset
strQueryName = "tmpQueryToExportToExcel"
If ObjectExists("Query", strQueryName) Then
CurrentDb.QueryDefs.Delete strQueryName
End If
Set qdf = CurrentDb.CreateQueryDef(strQueryName, strsql)
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(strQueryName, dbOpenDynaset)
If rst.RecordCount = 0 Then
MsgBox "No records to be exported.", vbInformation, GetDBTitle
Else
On Error Resume Next
Set ApXL = GetObject(, "Excel.Application")
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Set ApXL = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
End If
Err.Clear
ApXL.Visible = False
Set xlWBk = ApXL.Workbooks.Open(strFileName)
Set xlWSh = xlWBk.Sheets.Add
xlWSh.Name = Left(strSheetName, 31)
xlWSh.Range("A1").Select
Do Until intCount = rst.fields.Count
ApXL.ActiveCell = rst.fields(intCount).Name
ApXL.ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select
intCount = intCount + 1
Loop
rst.MoveFirst
xlWSh.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset rst
With ApXL
.Range("A1").Select
.Range(.Selection, .Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select
.Selection.Interior.Pattern = xlSolid
.Selection.Interior.PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic
.Selection.Interior.TintAndShade = -0.25
.Selection.Interior.PatternTintAndShade = 0
.Selection.Borders.LineStyle = xlNone
.Selection.AutoFilter
.Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
.Cells.EntireRow.AutoFit
.Range("B2").Select
.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = True
.ActiveSheet.Cells.Select
.ActiveSheet.Cells.WrapText = False
.ActiveSheet.Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
xlWSh.Range("A1").Select
.Visible = True
End With
'xlWB.Close True
'Set xlWB = Nothing
'ApXL.Quit
'Set ApXL = Nothing
End If
End FunctionCalled like this:
Private Sub AppendToExcelSQLStatemet_Example()
Call VBA_Access_ImportExport.ExportToExcel("SELECT * FROM Table1", "VBASheet", "C:TempTest.xlsx")
End SubWhere you are asked to input:
- SQL Query
- Output Sheet Name
- Output File Path and Name.
Function to Export to New Excel File
These functions allow you to export Access objects to a new Excel workbook. You might find them more useful than the simple single lines at the top of the document.
Public Function ExportToExcel(strObjectType As String, strObjectName As String, Optional strSheetName As String, Optional strFileName As String)
Dim rst As DAO.Recordset
Dim ApXL As Object
Dim xlWBk As Object
Dim xlWSh As Object
Dim intCount As Integer
Const xlToRight As Long = -4161
Const xlCenter As Long = -4108
Const xlBottom As Long = -4107
Const xlContinuous As Long = 1
On Error GoTo ExportToExcel_Err
DoCmd.Hourglass True
Select Case strObjectType
Case "Table", "Query"
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(strObjectName, dbOpenDynaset, dbSeeChanges)
Case "Form"
Set rst = Forms(strObjectName).RecordsetClone
Case "Report"
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(Reports(strObjectName).RecordSource, dbOpenDynaset, dbSeeChanges)
End Select
If rst.RecordCount = 0 Then
MsgBox "No records to be exported.", vbInformation, GetDBTitle
DoCmd.Hourglass False
Else
On Error Resume Next
Set ApXL = GetObject(, "Excel.Application")
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Set ApXL = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
End If
Err.Clear
On Error GoTo ExportToExcel_Err
Set xlWBk = ApXL.Workbooks.Add
ApXL.Visible = False
Set xlWSh = xlWBk.Worksheets("Sheet1")
If Len(strSheetName) > 0 Then
xlWSh.Name = Left(strSheetName, 31)
End If
xlWSh.Range("A1").Select
Do Until intCount = rst.fields.Count
ApXL.ActiveCell = rst.fields(intCount).Name
ApXL.ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select
intCount = intCount + 1
Loop
rst.MoveFirst
xlWSh.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset rst
With ApXL
.Range("A1").Select
.Range(.Selection, .Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select
.Selection.Interior.Pattern = xlSolid
.Selection.Interior.PatternColorIndex = xlAutomatic
.Selection.Interior.TintAndShade = -0.25
.Selection.Interior.PatternTintAndShade = 0
.Selection.Borders.LineStyle = xlNone
.Selection.AutoFilter
.Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
.Cells.EntireRow.AutoFit
.Range("B2").Select
.ActiveWindow.FreezePanes = True
.ActiveSheet.Cells.Select
.ActiveSheet.Cells.WrapText = False
.ActiveSheet.Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit
xlWSh.Range("A1").Select
.Visible = True
End With
retry:
If FileExists(strFileName) Then
Kill strFileName
End If
If strFileName <> "" Then
xlWBk.SaveAs strFileName, FileFormat:=56
End If
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
DoCmd.Hourglass False
End If
ExportToExcel_Exit:
DoCmd.Hourglass False
Exit Function
ExportToExcel_Err:
DoCmd.SetWarnings True
MsgBox Err.Description, vbExclamation, Err.Number
DoCmd.Hourglass False
Resume ExportToExcel_Exit
End FunctionThe function can be called like this:
Private Sub ExportToExcel_Example()
Call VBA_Access_ImportExport.ExportToExcel("Table", "Table1", "VBASheet")
End Sub
-
#2
Does anyone by any chance know of a VBA (or maybe help me start out to build one
)
By «chance» there are probably hundreds of members here who could bang out the entire thing for you within minutes (and maybe someone actually will).
But in the meantime, I’ll help you «start», since you really should use Google (or this site!) to gather information on how to construct the different elements of the process that you wish to create.
-The user should be able to specify which document should be copied from. So a pop up appears in which the user selects the document to copy from.
specifyFile = Application.GetOpenFilename _
(Title:=»Specify the file to open», FileFilter:=»Excel Files *.xls (*.xls),»)
Workbooks.Open Filename:=specifyFile
Do you know how to implement that?
-
#3
specifyFile = Application.GetOpenFilename _
(Title:=»Specify the file to open», FileFilter:=»Excel Files *.xls (*.xls),»)
Workbooks.Open Filename:=specifyFile
Do you know how to implement that?
Thanks for your help! I’m very new to this and am not that bright.
I’ve managed to run it by adding a new module and inserting your code between sub and end sub. It opens the selection screen but when you open a file it opens a new file.
-
#4
That piece of code opens a file that exists on your computer.
Try this…
specifyFile = Application.GetOpenFilename _
(Title:=»Specify the file to open», FileFilter:=»Excel Files *.xls (*.xls),»)
Workbooks.Open Filename:=specifyFile
MsgBox (ActiveWorkbook.Name)
The message box should reveal the name of the file that you just selected to open.
Same, yes?
-
#5
Yea it shows the message. What I was looking for was something like this code I found online. When I import a sheet it does everything perfectly but for some reason it skips D1:AG1??? Can anyone tell me how to solve this?
Code:
Public Sub GetData(SourceFile As Variant, SourceSheet As String, _
SourceRange As String, TargetRange As Range, Header As Boolean, UseHeaderRow As Boolean)
' 30-Dec-2007, working in Excel 2000-2007
Dim rsCon As Object
Dim rsData As Object
Dim szConnect As String
Dim szSQL As String
Dim lCount As Long
' Create the connection string.
If Header = False Then
If Val(Application.Version) < 12 Then
szConnect = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & SourceFile & ";" & _
"Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=No"";"
Else
szConnect = "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & SourceFile & ";" & _
"Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0;HDR=No"";"
End If
Else
If Val(Application.Version) < 12 Then
szConnect = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & SourceFile & ";" & _
"Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes"";"
Else
szConnect = "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;" & _
"Data Source=" & SourceFile & ";" & _
"Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0;HDR=Yes"";"
End If
End If
If SourceSheet = "" Then
' workbook level name
szSQL = "SELECT * FROM " & SourceRange$ & ";"
Else
' worksheet level name or range
szSQL = "SELECT * FROM [" & SourceSheet$ & "$" & SourceRange$ & "];"
End If
On Error GoTo SomethingWrong
Set rsCon = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
Set rsData = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
rsCon.Open szConnect
rsData.Open szSQL, rsCon, 0, 1, 1
' Check to make sure we received data and copy the data
If Not rsData.EOF Then
If Header = False Then
TargetRange.Cells(1, 1).CopyFromRecordset rsData
End If
Else
MsgBox "No records returned from : " & SourceFile, vbCritical
End If
' Clean up our Recordset object.
rsData.Close
Set rsData = Nothing
rsCon.Close
Set rsCon = Nothing
Exit Sub
SomethingWrong:
MsgBox "The file name, Sheet name or Range is invalid of : " & SourceFile, _
vbExclamation, "Error"
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
' With the example below you can select one file with GetOpenFilenamewhere
Sub GetData_Example4()
SaveDriveDir = CurDir
MyPath = "C:" 'or use "C:Data"
ChDrive MyPath
ChDir MyPath
FName = Application.GetOpenFilename(FileFilter:="Excel Files, *.xl*")
If FName = False Then
'do nothing
Else
GetData FName, "Sheet1", "A1:ZZ100", Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1"), False, False
End If
ChDrive SaveDriveDir
ChDir SaveDriveDir
End Sub
-
#6
Got this code from someone in another forum and it works!
Code:
<code>Sub tgr() Dim wsDest As Worksheet Set wsDest = ActiveWorkbook.Sheets(2) Application.ScreenUpdating = False On Error Resume Next With Workbooks.Open(Application.GetOpenFilename("Excel Files, *.xls*")) .Sheets(1).Range("A1:Z100").Copy wsDest.Range("A1") .Close False End With On Error GoTo 0 Application.ScreenUpdating = True Set wsDest = Nothing End Sub</code>
-
#7
You’re posting SQL code, which seems to have no bearing whatsoever on your original request.
(and overkill, to say the least)
btw….
I know it shows the message. That wasn’t the point.
Good luck with your project.
-
#8
……….»…………..since you really should use Google (or this site!) to gather information on how to construct the different elements of the process that you wish to create………….»
Google for this site is very good… see my signiture below
Alan
Last edited: Jul 6, 2014
-
#9
what if I need to put a list of drop down menu inside the VBA code to select the worksheet?
How to do that?
-
#10
what if I need to put a list of drop down menu inside the VBA code to select the worksheet?
How to do that?
Hi
. I am not quite sure wot you are doing on this old (mostly dead!) thread.
As a new member I suggest you start a new thread or at least give a lot more detail about exactly wot you want, assuming your requirement is similar to that originally in this thread