The IF function allows you to make a logical comparison between a value and what you expect by testing for a condition and returning a result if that condition is True or False.
-
=IF(Something is True, then do something, otherwise do something else)
But what if you need to test multiple conditions, where let’s say all conditions need to be True or False (AND), or only one condition needs to be True or False (OR), or if you want to check if a condition does NOT meet your criteria? All 3 functions can be used on their own, but it’s much more common to see them paired with IF functions.
Use the IF function along with AND, OR and NOT to perform multiple evaluations if conditions are True or False.
Syntax
-
IF(AND()) — IF(AND(logical1, [logical2], …), value_if_true, [value_if_false]))
-
IF(OR()) — IF(OR(logical1, [logical2], …), value_if_true, [value_if_false]))
-
IF(NOT()) — IF(NOT(logical1), value_if_true, [value_if_false]))
|
Argument name |
Description |
|
|
logical_test (required) |
The condition you want to test. |
|
|
value_if_true (required) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is TRUE. |
|
|
value_if_false (optional) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is FALSE. |
|
Here are overviews of how to structure AND, OR and NOT functions individually. When you combine each one of them with an IF statement, they read like this:
-
AND – =IF(AND(Something is True, Something else is True), Value if True, Value if False)
-
OR – =IF(OR(Something is True, Something else is True), Value if True, Value if False)
-
NOT – =IF(NOT(Something is True), Value if True, Value if False)
Examples
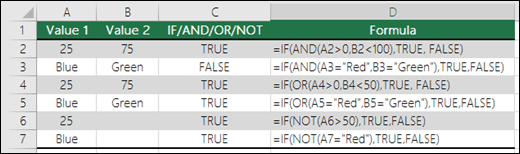
Following are examples of some common nested IF(AND()), IF(OR()) and IF(NOT()) statements. The AND and OR functions can support up to 255 individual conditions, but it’s not good practice to use more than a few because complex, nested formulas can get very difficult to build, test and maintain. The NOT function only takes one condition.
Here are the formulas spelled out according to their logic:
|
Formula |
Description |
|---|---|
|
=IF(AND(A2>0,B2<100),TRUE, FALSE) |
IF A2 (25) is greater than 0, AND B2 (75) is less than 100, then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case both conditions are true, so TRUE is returned. |
|
=IF(AND(A3=»Red»,B3=»Green»),TRUE,FALSE) |
If A3 (“Blue”) = “Red”, AND B3 (“Green”) equals “Green” then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case only the first condition is true, so FALSE is returned. |
|
=IF(OR(A4>0,B4<50),TRUE, FALSE) |
IF A4 (25) is greater than 0, OR B4 (75) is less than 50, then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case, only the first condition is TRUE, but since OR only requires one argument to be true the formula returns TRUE. |
|
=IF(OR(A5=»Red»,B5=»Green»),TRUE,FALSE) |
IF A5 (“Blue”) equals “Red”, OR B5 (“Green”) equals “Green” then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case, the second argument is True, so the formula returns TRUE. |
|
=IF(NOT(A6>50),TRUE,FALSE) |
IF A6 (25) is NOT greater than 50, then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case 25 is not greater than 50, so the formula returns TRUE. |
|
=IF(NOT(A7=»Red»),TRUE,FALSE) |
IF A7 (“Blue”) is NOT equal to “Red”, then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. |
Note that all of the examples have a closing parenthesis after their respective conditions are entered. The remaining True/False arguments are then left as part of the outer IF statement. You can also substitute Text or Numeric values for the TRUE/FALSE values to be returned in the examples.
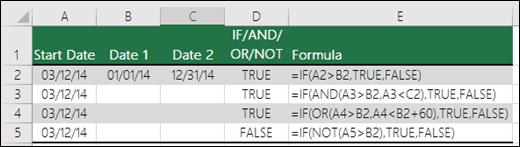
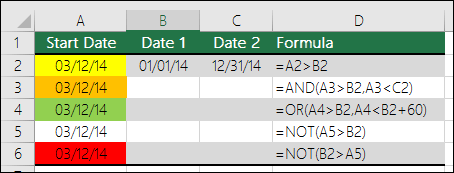
Here are some examples of using AND, OR and NOT to evaluate dates.
Here are the formulas spelled out according to their logic:
|
Formula |
Description |
|---|---|
|
=IF(A2>B2,TRUE,FALSE) |
IF A2 is greater than B2, return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. 03/12/14 is greater than 01/01/14, so the formula returns TRUE. |
|
=IF(AND(A3>B2,A3<C2),TRUE,FALSE) |
IF A3 is greater than B2 AND A3 is less than C2, return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case both arguments are true, so the formula returns TRUE. |
|
=IF(OR(A4>B2,A4<B2+60),TRUE,FALSE) |
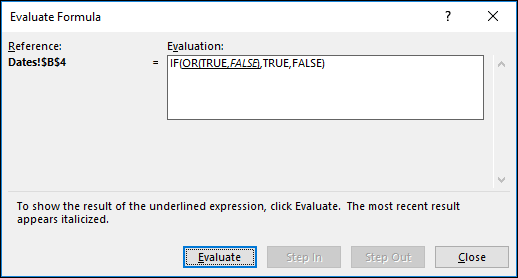
IF A4 is greater than B2 OR A4 is less than B2 + 60, return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case the first argument is true, but the second is false. Since OR only needs one of the arguments to be true, the formula returns TRUE. If you use the Evaluate Formula Wizard from the Formula tab you’ll see how Excel evaluates the formula. |
|
=IF(NOT(A5>B2),TRUE,FALSE) |
IF A5 is not greater than B2, then return TRUE, otherwise return FALSE. In this case, A5 is greater than B2, so the formula returns FALSE. |
Using AND, OR and NOT with Conditional Formatting
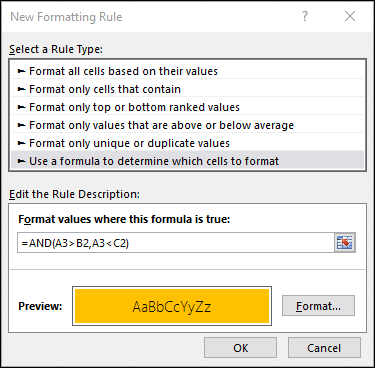
You can also use AND, OR and NOT to set Conditional Formatting criteria with the formula option. When you do this you can omit the IF function and use AND, OR and NOT on their own.
From the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting > New Rule. Next, select the “Use a formula to determine which cells to format” option, enter your formula and apply the format of your choice.
Using the earlier Dates example, here is what the formulas would be.
|
Formula |
Description |
|---|---|
|
=A2>B2 |
If A2 is greater than B2, format the cell, otherwise do nothing. |
|
=AND(A3>B2,A3<C2) |
If A3 is greater than B2 AND A3 is less than C2, format the cell, otherwise do nothing. |
|
=OR(A4>B2,A4<B2+60) |
If A4 is greater than B2 OR A4 is less than B2 plus 60 (days), then format the cell, otherwise do nothing. |
|
=NOT(A5>B2) |
If A5 is NOT greater than B2, format the cell, otherwise do nothing. In this case A5 is greater than B2, so the result will return FALSE. If you were to change the formula to =NOT(B2>A5) it would return TRUE and the cell would be formatted. |
Note: A common error is to enter your formula into Conditional Formatting without the equals sign (=). If you do this you’ll see that the Conditional Formatting dialog will add the equals sign and quotes to the formula — =»OR(A4>B2,A4<B2+60)», so you’ll need to remove the quotes before the formula will respond properly.
Need more help?

See also
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Learn how to use nested functions in a formula
IF function
AND function
OR function
NOT function
Overview of formulas in Excel
How to avoid broken formulas
Detect errors in formulas
Keyboard shortcuts in Excel
Logical functions (reference)
Excel functions (alphabetical)
Excel functions (by category)
In this article, we will learn to apply multiple conditions in a single formula using OR and AND function with the IF function.
IF function in Excel is used to check the condition and returns value on the basis of it.
Syntax:
=IF(Logic_test, [Value_if True], [Value_if_False])
OR function works on logic_test. It helps you run multiple conditions in Excel. If any one of them is True, OR function returns True else False.
Syntax:
=OR( Logic_test 1, [logic_test 2], ..)
AND function works on logic_test. It helps you run multiple conditions in Excel. If every one of them is True, then only AND function returns True else False.
Syntax:
=AND( Logic_test 1, [logic_test 2], ..)
First we will use IF with OR function.
Let’s get this by an example here.
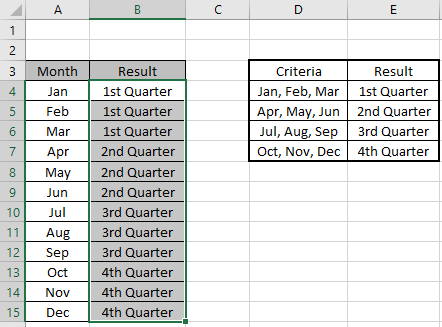
We have a list of months and need to know in which quarter it lay.
Use the formula to match the quarter of the months
Formula:
=IF(OR(A4=”Jan”,A4=”Feb”,A4=”Mar”),”1st
Quarter”,IF(OR(A4=”Apr”,A4=”May”,A4=”Jun”),”2nd
Quarter”,IF(OR(A4=”Jul”,A4=”Aug”,A4=”Sep”),”3rd
Quarter”,IF(OR(A4=”Oct”,A4=”Nov”,A4=”Dec”),”4th Quarter”))))
Copy the formula in other cells, select the cells taking the first cell where the formula is already applied, use shortcut key Ctrl +D
We got the result.
You can use IF and OR function to meet multiple conditions in a single formula.
Now we will use IF with AND function in Excel.
Let’s get this by an example here.
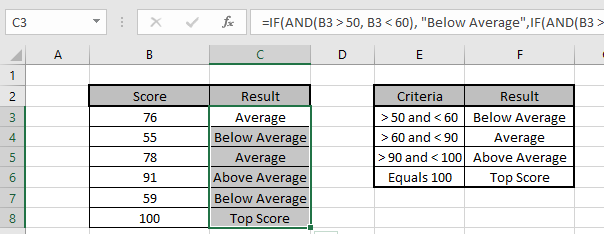
We have a list of Scores and We need to know under which criteria it lay.
Use the formula to match the criteria
Formula:
=IF(AND(B3 > 50, B3 < 60), «Below Average»,IF(AND(B3 > 60, B3 < 90),»Average»,IF(AND(B3 > 90,B3< 100),»Above Average»,»Top Score»)))
Copy the formula in other cells, select the cells taking the first cell where the formula is already applied, use shortcut key Ctrl + D
We got the Results corresponding to the Scores.
You can use IF and AND function to meet multiple conditions in a single formula.
Hope you understood IF, AND and OR function in Excel 2016. Find more articles on Logic_test here. Please share your query below in the comment box. We will assist you.
The IF function helps to determine what will be displayed to those who view your worksheets in Excel. Because of its purpose, it’s one of the most important functions you will learn. IF functions can be used to add comments to your data. They can also be used to hide errors in calculations.
In this article, we will learn about:
-
The IF function
-
The IFNA and IFERROR functions
-
Nesting IF functions
-
The AND operator
-
The OR operator
-
The NOT operator
-
Displaying formulas from one cell in another
The syntax for the IF function is =IF. This lets Excel know that it is an IF function.
Then, we begin the formula that Excel will use to produce the results we want.
We start with an opening bracket:
Next, we add the evaluation criteria. For example, is six greater than three? The evaluation criteria asks a question. The question has two outcomes. If the answer (or outcome) is correct, such as «Yes, six is greater than three,» then the answer is true. If not it is false.
If it’s true, we put what happens when the answer is true.
If it’s false, we put what happens when it’s false.
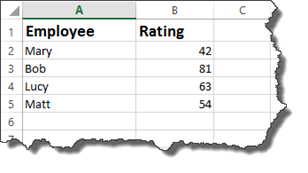
In the worksheet below, we have a list of employees, followed by the rating they received as part of their annual review.
Now, we want to add another column called Comments. In this column, we want to add comments about the scores. This way, when a manager looks at the worksheet, he/she doesn’t need to worry themselves with the actual rating – and what that means. They can simply look in comments.
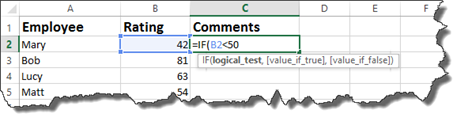
To add a comment based on the rating, we are going to use the IF function.
We have started the formula in the snapshot above.
We have said if the employee’s rating is less than fifty…
Now we enter what happens.
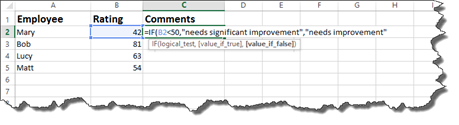
If it is correct that the employee’s rating is less than fifty, the comment should be «needs significant improvement. However, if it’s false and if the rating is not less than fifty, the comment should be needs improvement.
Notice that we use quotation marks to enter the comments into the formula.
Now, add an end bracket, then push Enter.
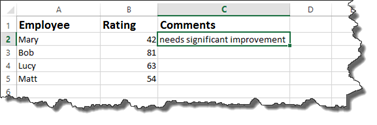
Since this contains a formula where all are cell references are relative, you can use the handle in the lower right corner of the cell, then drag it down to complete the comments for the other employees.
You can also use the IF function to hide Excel error messages.
Let’s show you what we mean by taking a look at the worksheet below.
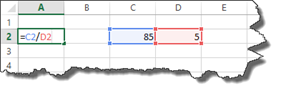
In this worksheet, we have a formula that will divide cell C2 by cell D2.
If we push enter in cell A2, it will give us the answer.
However, let’s say the data in cell D2 is missing.
When we push Enter, we see an error message.
We can use the IF function to hide this error message.
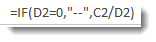
To do this, we write the formula below:
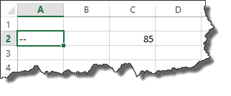
Let’s translate what it says. If D2 equals 0, enter two dashes into cell A2 where we have our formula. If it doesn’t equal zero, then go ahead and divide cell C2 by D2.
If we would put the number five back into cell D2 and leave the IF formula in place, we would see the answer to C2/D2.
Here’s our worksheet below. We have hidden the error message with two dashes.
NOTE: All of the IF functions appear under the Formulas tab and by clicking the Logical button. From there, you can access the Function Arguments dialogue box.
The IFNA and IFERROR Functions
The IFNA function tells Excel what to do if an #NA error is produced, whereas the isna tells Excel what to do if the returned value is #NA.
The #NA error appears in a cell when a value is not available to a formula.
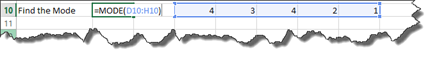
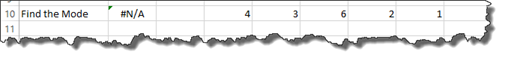
If in our worksheet below, we wanted to find the mode, we would enter this formula:
When we push Enter, the result is displayed.
However, if we went back and changed the second instance of the number four to a six, we would see an #NA error because the value needed is not available to determine the mode.
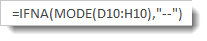
To avoid #NA values from appearing, we could use the new IFNA function.
It would be entered like this:
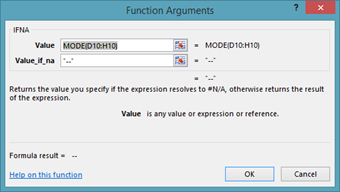
All of the IF functions appear under the Formulas tab and by clicking the Logical button. The easiest way to use the IFNA function is to click the Logical button, then select IFNA.
Below you can see the dialogue box for the IFNA function.
The IFERROR function can be used as a general «cover all» for any errors that might appear in your data. You can use it to specify what will be entered if any error occurs in the calculation of a formula.
It is written the same way as an IF function. However, instead of writing IF, you would write IFERROR. You can access the dialogue box for IFERROR by going to the Logical button under the Formulas tab.
Nesting IF Statements
Just as with VLOOKUPs and HLOOKUPs, you can nest an IF statement within an IF statement.
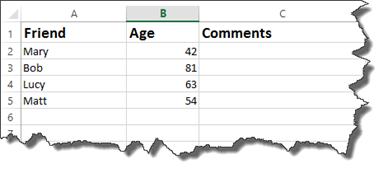
In our worksheet below, we have a list of friends, along with their ages.
We could create a simple IF formula to enter comments.
This says if the age is greater than 50, then the comment is getting older. If it’s less than 50, then they’re still young.
If we nest an IF statement within the current IF statement, we would keep the evaluation criteria, but we would replace one of the outcomes with our new IF statement. However, keep in mind, then when you nest an IF statement, you do not need another equal sign.
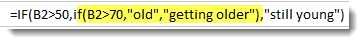
Take a look at our new formula below:
We have our original IF statement intact. We have highlighted the first part of it below.
If the age is greater than 50, followed by the two outcomes.
As you can see in our formula above, the TRUE outcome has another IF statement.
The nested IF statement tells Excel that if the age is greater than 70, enter the comment «old.» If it’s not, enter getting older.
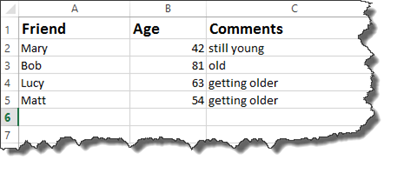
Our worksheet is shown below with the nested IF statements determining what comment is displayed.
Now, let’s break this down into easy to understand terms.
When you enter the formula above with a nested IF statement, Excel reads the first IF statement. It looks at your criteria, then the outcomes for the criteria.
If the outcome for the first IF statement is true, Excel is then going to perform another IF statement to determine what appears in the comments. It will put «old» if the age is greater than 70. It will put getting older if it’s not greater than 70. It’s very important to remember that these two outcomes both serve as your TRUE outcome for the first IF function.
Now, if your original IF statement returns a FALSE outcome, then Excel will enter «still young.»
A nested IF statement gives you a way to enter more than one response for an outcome.
We used a nested if statement for the TRUE outcome. However, you can also use a nested IF statement for a FALSE outcome.
If the nested IF statements are still confusing to you, remember it this way: the nested IF statement provides two additional outcomes for either the TRUE or FALSE outcome of your original IF statement.
Using the AND Operator in an IF Statement
You use the AND operator within an IF statement if you have more than one criteria that needs to be true. Using the AND operator can sometimes be easier to write than multiple nested IF statements.
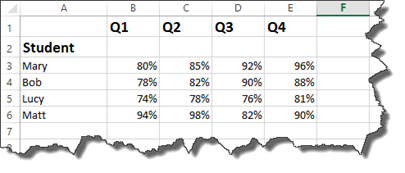
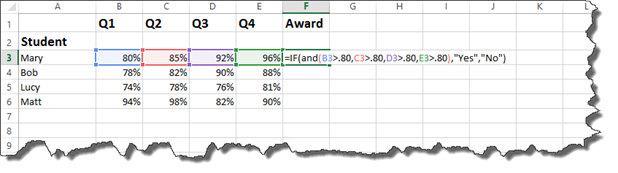
Take a look at the worksheet below.
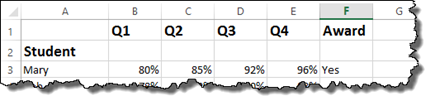
In it, we have a list of students and their grades for the four grading periods.
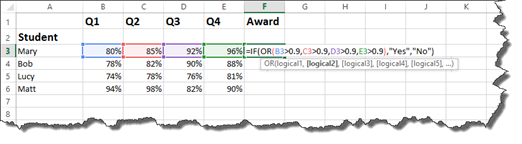
Each student must have earned greater than 80% in each quarter in order to receive an award. We will use the AND operator to set this as criteria.
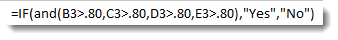
Take a look at how at the formula bar to see how we wrote this.
Now, let’s examine it.
We start out by starting the IF statement with =IF, then the open bracket.
Next, we write AND for the AND operator. The criteria then is placed within brackets. Notice that we have four sets of criteria. The criteria is that each quarter’s grades must be greater than 80%. Also notice that all percentages have been converted to decimals when entered in as criteria.
After you’ve entered the criteria in brackets, you can enter your TRUE and FALSE values. We want the cell to display «Yes» if the criteria is met. We want it do display «No» if it is not met. We then type in an end bracket to close the IF statement.
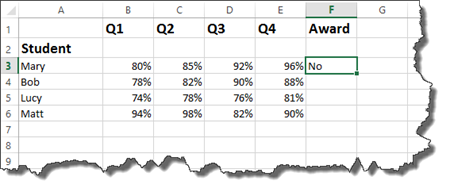
Press Enter.
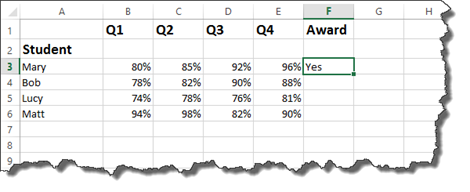
As you can see above, student Mary had one grade that was 80%. All of the grades had to be above 80% to meet our criteria, so a NO was returned.
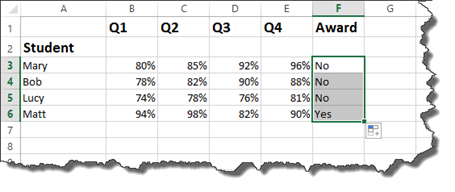
You can now drag the handle in the cell down to complete the worksheet for all students.
Using the OR Operator in an IF Statement
The OR operator works in the same way as the AND, except it says if one of the criteria listed is true, then the outcome for TRUE is what is displayed.
Let’s look at our worksheet.
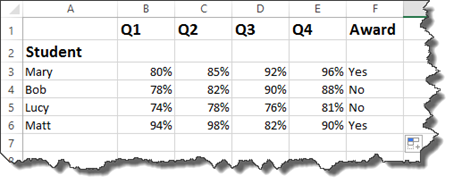
This time, we want to say if the grade for Q1, Q2, Q3, or Q4 is greater than 90%, then the student gets the award.
You enter it in the same way you did with the IF statement and the AND operator, expect you type OR instead of AND.
Press Enter.
You can then complete the worksheet.
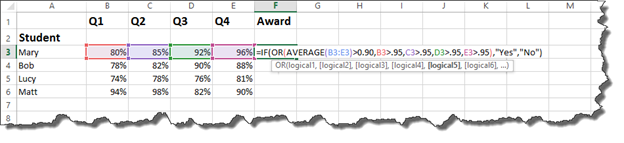
Now let’s make it a bit more complicated.
Now we want to say that in order to get the award, the average of all four quarters must be greater than 90% OR at least one of the quarters must be greater than 95%.
In other words, the average of the quarters must be greater than 90%. Or Q1, Q2, Q3, or Q4 must be higher than 95%.
This is the perfect time for you to test your ability writing formulas by entering the formula into the cell.
Press Enter.
Using the NOT Operator
The NOT operator is used in conjunction with the AND or OR operator.
The best way to explain how the NOT operator works is to show you the NOT operator in action.
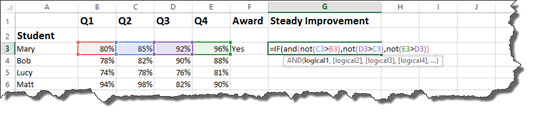
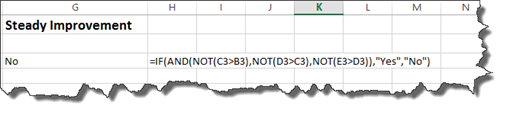
Working with our students and grades again, we want to determine if the grades have improved each quarter.
To do that, we are going to use the IF statement with the AND operator since we are using multiple criteria.
We will use the NOT operator to make sure Q1 is not higher than Q2. Q2 must be greater than Q1.
In addition, Q3 must be greater than Q2, and Q4 must be greater than Q3.
We’ve started the write it below:
Let’s finish.
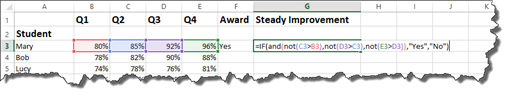
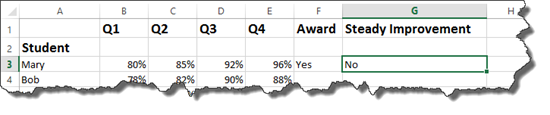
Hit Enter.
We can see there is not steady improvement.
Remember: The NOT Operator is used within AND or IF options. You must use the NOT operator for each piece of criteria. You cannot type in the NOT operator once, then use it for all criteria.
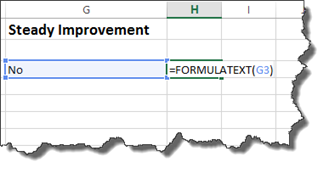
Displaying Cell Formulas In Another Cell
Starting with Excel 2013, you can display the formula from one cell in another. In our worksheets so far, we could view the formula in a cell by double clicking on the cell. However, once we pressed Enter or tabbed out of a cell, we couldn’t see the formula unless we looked in the Formula Bar.
To display a formula from one cell in another cell, go to the cell where you want to formula to appear.
You will use the FORMULATEXT function.
Type the equal sign, followed by formula text.
Enter an open bracket, then click the cell that contains the formula you want to display.
Add the closing bracket.
For our example, we are going to display the formula in cell G3 in sell H3.
Press Enter.
The logical IF statement in Excel is used for the recording of certain conditions. It compares the number and / or text, function, etc. of the formula when the values correspond to the set parameters, and then there is one record, when do not respond — another.
Logic functions — it is a very simple and effective tool that is often used in practice. Let us consider it in details by examples.
The syntax of the function «IF» with one condition
The operation syntax in Excel is the structure of the functions necessary for its operation data.
=IF(boolean;value_if_TRUE;value_if_FALSE)
Let us consider the function syntax:
- Boolean – what the operator checks (text or numeric data cell).
- Value_if_TRUE – what will appear in the cell when the text or numbers correspond to a predetermined condition (true).
- Value_if_FALSE – what appears in the box when the text or the number does not meet the predetermined condition (false).
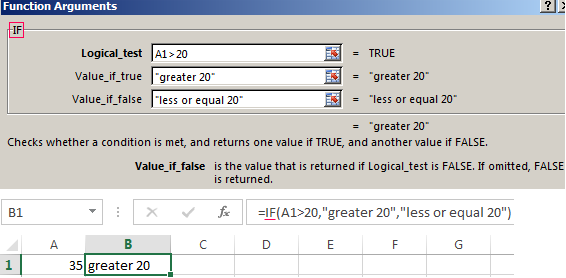
Example:
Logical IF functions.
The operator checks the A1 cell and compares it to 20. This is a «Boolean». When the contents of the column is more than 20, there is a true legend «greater 20». In the other case it’s «less or equal 20».
Attention! The words in the formula need to be quoted. For Excel to understand that you want to display text values.
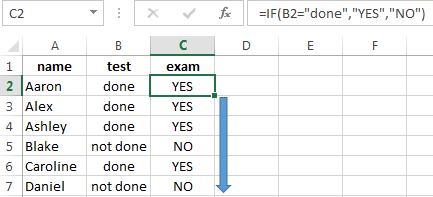
Here is one more example. To gain admission to the exam, a group of students must successfully pass a test. The results are listed in a table with columns: a list of students, a credit, an exam.
The statement IF should check not the digital data type but the text. Therefore, we prescribed in the formula В2= «done» We take the quotes for the program to recognize the text correctly.
The function IF in Excel with multiple conditions
Usually one condition for the logic function is not enough. If you need to consider several options for decision-making, spread operators’ IF into each other. Thus, we get several functions IF in Excel.
The syntax is as follows:
Here the operator checks the two parameters. If the first condition is true, the formula returns the first argument is the truth. False — the operator checks the second condition.
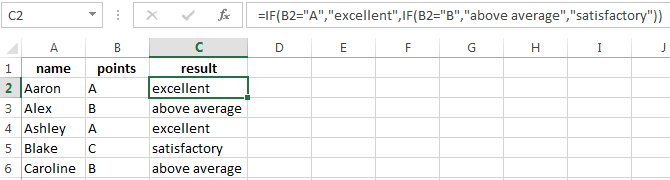
Examples of a few conditions of the function IF in Excel:
It’s a table for the analysis of the progress. The student received 5 points:
- А – excellent;
- В – above average or superior work;
- C – satisfactory;
- D – a passing grade;
- E – completely unsatisfactory.
IF statement checks two conditions: the equality of value in the cells.
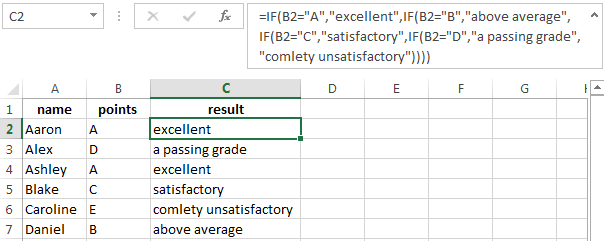
In this example, we have added a third condition, which implies the presence of another report card and «twos». The principle of the operator is the same.
Enhanced functionality with the help of the operators «AND» and «OR»
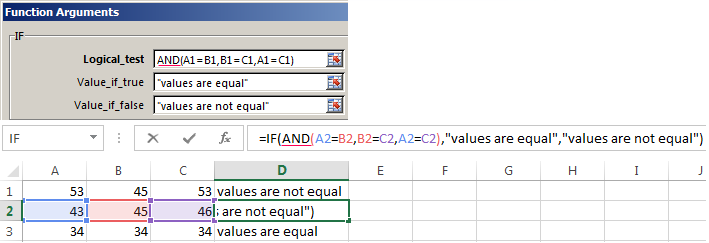
When you need to check out a few of the true conditions you use the function И. The point is: IF A = 1 AND A = 2 THEN meaning в ELSE meaning с.
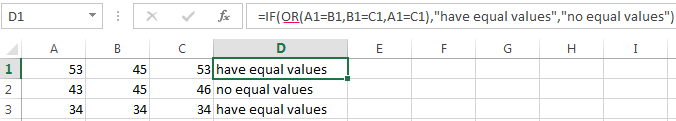
OR function checks the condition 1 or condition 2. As soon as at least one condition is true, the result is true. The point is: IF A = 1 OR A = 2 THEN value B ELSE value C.
Functions AND & OR can check up to 30 conditions.
An example of using the operator AND:
It’s the example of using the logical operator OR.
How to compare data in two tables
Users often need to compare the two spreadsheets in an Excel to match. Examples of the «life»: compare the prices of goods in different bringing, to compare balances (accounting reports) in a few months, the progress of pupils (students) of different classes, in different quarters, etc.
To compare the two tables in Excel, you can use the COUNTIFS statement. Consider the order of application functions.
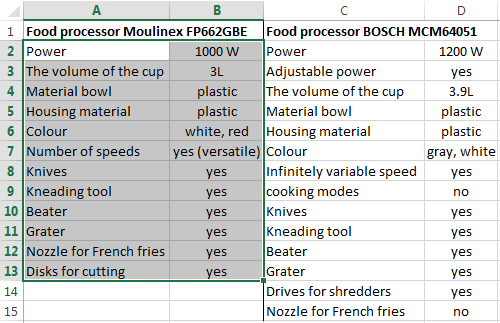
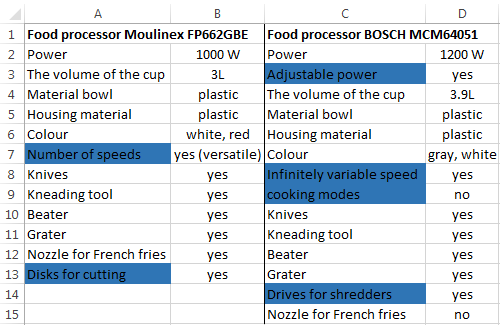
For example, consider the two tables with the specifications of various food processors. We planned allocation of color differences. This problem in Excel solves the conditional formatting.
Baseline data (tables, which will work with):
Select the first table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use a formula to determine the formatted cells:
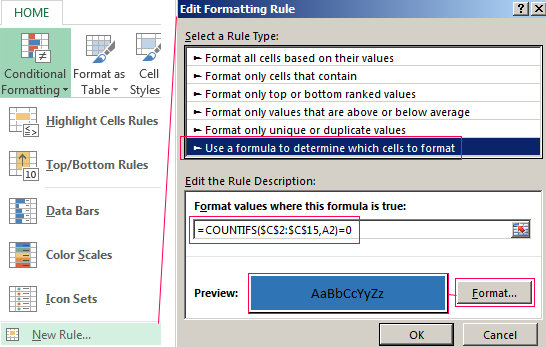
In the formula bar write: = COUNTIFS (comparable range; first cell of first table)=0. Comparing range is in the second table.
To drive the formula into the range, just select it first cell and the last. «= 0» means the search for the exact command (not approximate) values.
Choose the format and establish what changes in the cell formula in compliance. It’s better to do a color fill.
Select the second table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use the formula. Use the same operator (COUNTIFS). For the second table formula:
Download all examples in Excel
Now it is easy to compare the characteristics of the data in the table.
IF AND Excel Formula
The IF AND excel formula is the combination of two different logical functions often nested together that enables the user to evaluate multiple conditions using AND functions. Based on the output of the AND function, the IF function returns either the “true” or “false” value, respectively.
- The IF formula in ExcelIF function in Excel evaluates whether a given condition is met and returns a value depending on whether the result is “true” or “false”. It is a conditional function of Excel, which returns the result based on the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the given criteria.
read more is used to test and compare the conditions expressed with the expected value. It is used to test a single criterion. - The logical AND formula is used to test multiple criteria. It returns “true” if all the conditions mentioned are satisfied, or else returns “false.” It tests more than one criterion and accordingly returns an output. It can also be used along with the IF formula to return the desired result.
Table of contents
- IF AND Excel Formula
- Syntax
- How to Use IF AND Excel Statement?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- The Characteristics of IF AND function
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recommended Articles
Syntax
The IF AND formula can be applied as follows:
“=IF(AND (Condition 1,Condition 2,…),Value _if _True,Value _if _False)”
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: IF AND in Excel (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Use IF AND Excel Statement?
You can download this IF AND Formula Excel Template here – IF AND Formula Excel Template
Let us understand the usage of the IF AND formula with the help of some examples mentioned below:
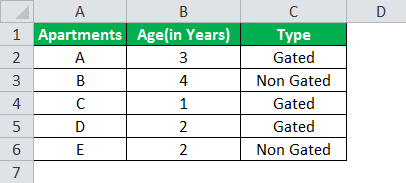
Example #1
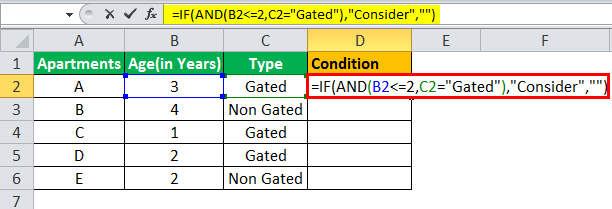
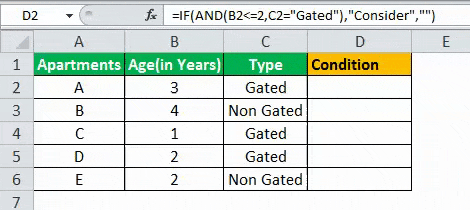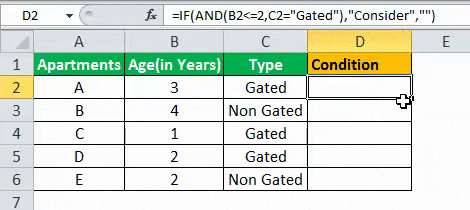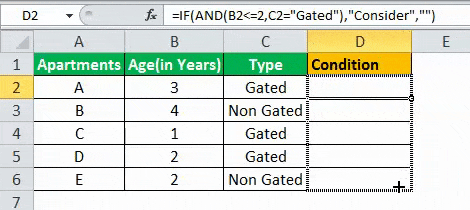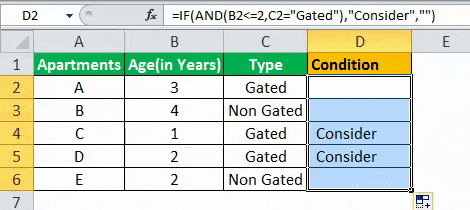
The table given below provides a list of apartments along with their age (in years) and type of society. Now we need to perform a comparative analysis for the apartments based on the age of the building and the type of society.
Here, we use the combination of less than equal (<=) to operator and the equal to (=) text functions in the condition to be demonstrated for IF AND function.
- The IF AND formula used to perform the analysis is stated as follows:
“=IF(AND(B2<=2,C2=“Gated”),“Consider”, “”)”
- The succeeding image shows the IF AND condition applied to perform the evaluation.
- Press “Enter” to get the answer.
- Drag the formula to find the results for all the apartments.
The results in the cell D of the above table shows that the IF AND formula will be performing one among the following:
- If both the arguments entered in the AND function is “true,” then the IF function will return that apartment to be “Consider.”
- If either of the arguments in the AND functionThe AND function in Excel is classified as a logical function; it returns TRUE if the specified conditions are met, otherwise it returns FALSE.read more is “false” or both the arguments entered are “false,” then the IF function will return a blank string.
The IF AND formula can also perform calculations based on whether the AND function returns “true” or “false,” apart from returning only the predefined text strings.
We will understand this concept with the help of the below-mentioned example.
Example #2
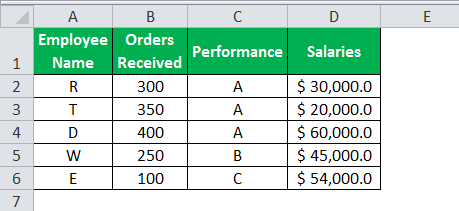
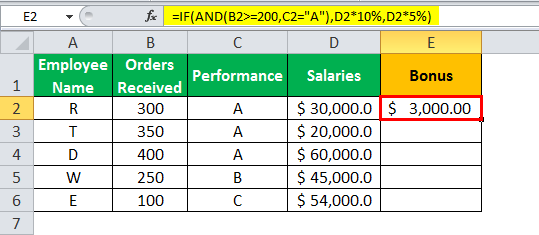
The given data tableA data table in excel is a type of what-if analysis tool that allows you to compare variables and see how they impact the result and overall data. It can be found under the data tab in the what-if analysis section.read more has the list of employee name along with their orders received, performance, and salaries. Calculate the employee hike (or bonus) based on two parameters–the number of orders received and performance.
The criteria to calculate the bonus is as follows.
- The number of orders received is greater than or equal to 200, and the performance is equal to “A.”
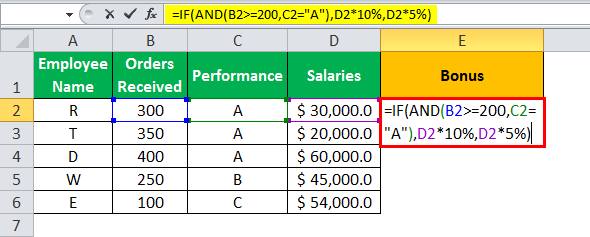
- The IF AND formula will be,
“=IF(AND(B2>=200,C2= “A”),D2*10%,D2*5%)”
- Press “Enter” to get the final output. The bonus appears in cell E2.
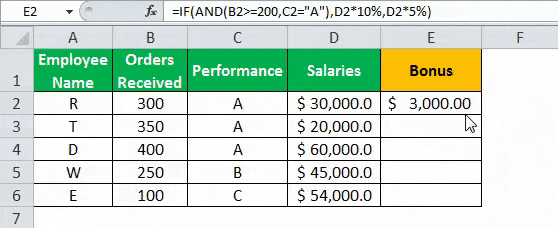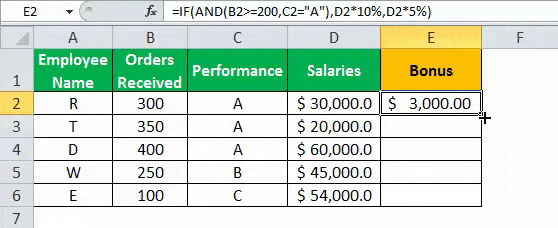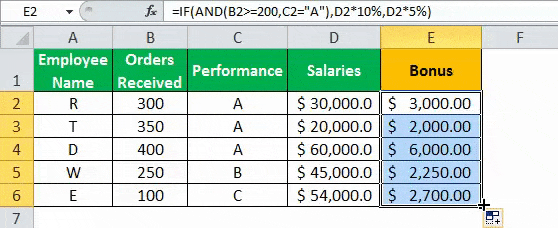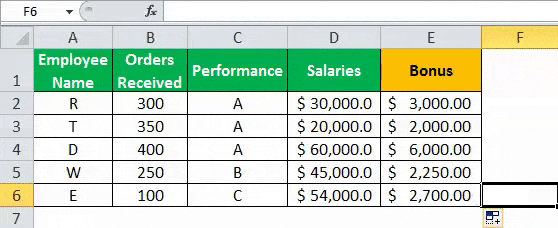
- Drag the formula to find the bonus of all employees.
Based on these results, the IF formula does the following evaluation:
- If both the conditions are satisfied, the AND function returns “true,” then the bonus received is calculated as salary multiplied by 10%.
- If either one or both the conditions are found to be “false” by the AND function, then the bonus is calculated as salary multiplied by 5%.
Examples 1 and 2 have only two criteria to test and evaluate. Using multiple arguments or conditions to test them for “true” or “false” is also allowed.
Example #3
Let us evaluate multiple criteria and use AND function.
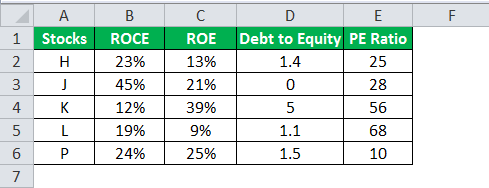
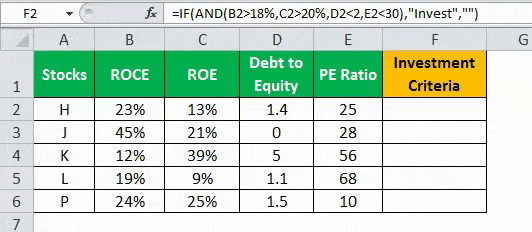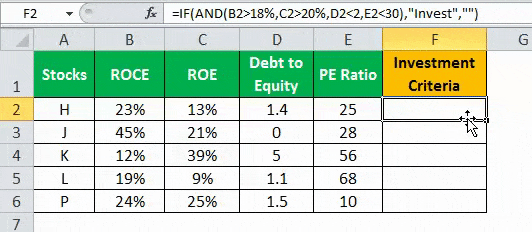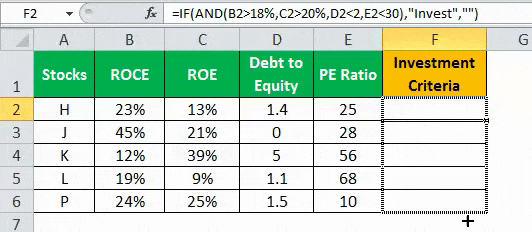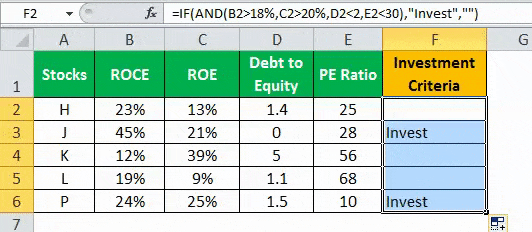
A table with five stocks and their parameter details including financial ratiosFinancial ratios are indications of a company’s financial performance. There are several forms of financial ratios that indicate the company’s results, financial risks, and operational efficiency, such as the liquidity ratio, asset turnover ratio, operating profitability ratios, business risk ratios, financial risk ratio, stability ratios, and so on.read more, such as ROCEReturn on Capital Employed (ROCE) is a metric that analyses how effectively a company uses its capital and, as a result, indicates long-term profitability. ROCE=EBIT/Capital Employed.read more, ROEReturn on Equity (ROE) represents financial performance of a company. It is calculated as the net income divided by the shareholders equity. ROE signifies the efficiency in which the company is using assets to make profit.read more, Debt to equityThe debt to equity ratio is a representation of the company’s capital structure that determines the proportion of external liabilities to the shareholders’ equity. It helps the investors determine the organization’s leverage position and risk level. read more, and PE ratioThe price to earnings (PE) ratio measures the relative value of the corporate stocks, i.e., whether it is undervalued or overvalued. It is calculated as the proportion of the current price per share to the earnings per share. read more is provided (shown in the below table). Using this data lets us test the condition to invest in suitable stocks. That is, using the parameters, let us analyze the stocks to derive the best investment horizonThe term «investment horizon» refers to the amount of time an investor is expected to hold an investment portfolio or a security before selling it. Depending on the need for funds and risk appetite, the investor may invest for a few days or hours to a few years or decades.read more, which is important for growth.
The following syntax is used where the conditions are applied to arrive at the result (shown in the below table).
“=IF(AND(B2>18%,C2>20%,D2<2,E2<30%),“Invest”,“”)”
- Press “Enter” to get the final output (Investment Criteria) of the above formula.
- Drag the formula to find the Investment Criteria.
In the above data table, the AND function tests for the parameters using the operators. The resulting output generated by the IF formula is as follows:
- If all the four criteria mentioned in the AND function are tested and satisfied, then the IF function returns the “Invest” text string.
- If either one or more among the four conditions or all the four conditions fail to satisfy the AND function, then the IF function returns empty strings (“”).
The Characteristics of IF AND function
- The IF AND function does not differentiate between case-insensitive texts.
- The AND function can be used to evaluate up to 255 conditions for “true” or “false,” and the total formula length does not exceed 8192 characters.
- Text values or blank cells are given as an argument to test the conditions in AND function.
- The AND formula will return “#VALUE!” if there is no logical output found while evaluating the conditions.
- IF AND excel statement is a combination of two logical functions that tests and evaluates multiple conditions.
- The output of the AND function is based on, whether the IF function will return the value “true” or “false,” respectively.
- IF function is used to test a single criterion whereas, the AND function is used to test multiple criteria.
- The syntax of the IF AND formula is:
“=IF(AND (Condition 1,Condition 2,…),Value _if _True,Value _if _False)”
- The IF AND formula also performs a calculation based on whether the AND function is “true” or “false” apart from returning only the predefined text strings.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to use IF AND function in Excel?
The IF AND excel statement is the two logical functions often nested together.
Syntax:
“=IF(AND(Condition1,Condition2, value_if_true,vaue_if_false)”
The IF formula is used to test and compare the conditions expressed, along with the expected value. It provides the desired result if the condition is either “true” or “false.”
The AND formula is used to test multiple criteria. It returns “true” if all the given conditions are satisfied, or else returns “false.”
2. What is the IF AND function in Excel?
IF AND formula is applied as the combination of the two logical functions that enable the user to evaluate the multiple conditions. Based on the output of the AND function, the IF function returns the output “true” or “false.”
3. How to combine IF and AND functions in Excel?
To combine IF and AND functions, you need to replace the “condition_test” argument in the IF function with AND function.
“=IF(condition_test, value_if_true,vaue_if_false)”
“=IF(AND(Condition1,Condition2, value_if_true,vaue_if_false)”
In AND function we can use multiple conditions.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to IF AND function in Excel. Here we discuss how to use IF Formula combined with AND function along with examples and downloadable templates. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel –
- IF EXCEL FunctionIF function in Excel evaluates whether a given condition is met and returns a value depending on whether the result is “true” or “false”. It is a conditional function of Excel, which returns the result based on the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the given criteria.
read more - Average IF Function
- SUMIF with Multiple CriteriaThe SUMIF (SUM+IF) with multiple criteria sums the cell values based on the conditions provided. The criteria are based on dates, numbers, and text. The SUMIF function works with a single criterion, while the SUMIFS function works with multiple criteria in excel.read more
- Nested If ConditionIn Excel, nested if function means using another logical or conditional function with the if function to test multiple conditions. For example, if there are two conditions to be tested, we can use the logical functions AND or OR depending on the situation, or we can use the other conditional functions to test even more ifs inside a single if.read more