Однострочная и многострочная конструкции оператора If…Then…Else и функция IIf, используемые в коде VBA Excel — синтаксис, компоненты, примеры.
Оператор If…Then…Else предназначен для передачи управления одному из блоков операторов в зависимости от результатов проверяемых условий.
Однострочная конструкция
Оператор If…Then…Else может использоваться в однострочной конструкции без ключевых слов Else, End If.
Синтаксис однострочной конструкции If…Then…
|
If [условие] Then [операторы] |
Компоненты однострочной конструкции If…Then…
- условие — числовое или строковое выражение, возвращающее логическое значение True или False;
- операторы — блок операторов кода VBA Excel, который выполняется, если компонент условие возвращает значение True.
Если компонент условие возвращает значение False, блок операторов конструкции If…Then… пропускается и управление программой передается следующей строке кода.
Пример 1
|
Sub Primer1() Dim d As Integer, a As String d = InputBox(«Введите число от 1 до 20», «Пример 1», 1) If d > 10 Then a = «Число « & d & » больше 10″ MsgBox a End Sub |
Многострочная конструкция
Синтаксис многострочной конструкции If…Then…Else
|
If [условие] Then [операторы] ElseIf [условие] Then [операторы] ———————— Else [операторы] End If |
Компоненты многострочной конструкции If…Then…Else:
- условие — числовое или строковое выражение, следующее за ключевым словом If или ElseIf и возвращающее логическое значение True или False;
- операторы — блок операторов кода VBA Excel, который выполняется, если компонент условие возвращает значение True;
- пунктирная линия обозначает дополнительные структурные блоки из строки
ElseIf [условие] Thenи строки[операторы].
Если компонент условие возвращает значение False, следующий за ним блок операторов конструкции If…Then…Else пропускается и управление программой передается следующей строке кода.
Самый простой вариант многострочной конструкции If…Then…Else:
|
If [условие] Then [операторы] Else [операторы] End If |
Пример 2
|
Sub Primer2() Dim d As Integer, a As String d = InputBox(«Введите число от 1 до 40», «Пример 2», 1) If d < 11 Then a = «Число « & d & » входит в первую десятку» ElseIf d > 10 And d < 21 Then a = «Число « & d & » входит во вторую десятку» ElseIf d > 20 And d < 31 Then a = «Число « & d & » входит в третью десятку» Else a = «Число « & d & » входит в четвертую десятку» End If MsgBox a End Sub |
Функция IIf
Функция IIf проверяет заданное условие и возвращает значение в зависимости от результата проверки.
Синтаксис функции
|
IIf([условие], [если True], [если False]) |
Компоненты функции IIf
- условие — числовое или строковое выражение, возвращающее логическое значение True или False;
- если True — значение, которое возвращает функция IIf, если условие возвратило значение True;
- если False — значение, которое возвращает функция IIf, если условие возвратило значение False.
Компоненты если True и если False могут быть выражениями, значения которых будут вычислены и возвращены.
Пример 3
|
Sub Primer3() Dim d As Integer, a As String Instr: On Error Resume Next d = InputBox(«Введите число от 1 до 20 и нажмите OK», «Пример 3», 1) If d > 20 Then GoTo Instr a = IIf(d < 10, d & » — число однозначное», d & » — число двузначное») MsgBox a End Sub |
Пример 4
Стоит отметить, что не зависимо от того, выполняется условие или нет, функция IIf вычислит оба выражения в параметрах если True и если False:
|
Sub Primer4() On Error GoTo Instr Dim x, y x = 10 y = 5 MsgBox IIf(x = 10, x + 5, y + 10) MsgBox IIf(x = 10, x + 5, y / 0) Exit Sub Instr: MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End Sub |
При нажатии кнопки «Cancel» или закрытии крестиком диалогового окна InputBox из первых двух примеров, генерируется ошибка, так как в этих случаях функция InputBox возвращает пустую строку. Присвоение пустой строки переменной d типа Integer вызывает ошибку. При нажатии кнопки «OK» диалогового окна, числа, вписанные в поле ввода в текстовом формате, VBA Excel автоматически преобразует в числовой формат переменной d. В третьем примере есть обработчик ошибок.
In this Article
- VBA If Statement
- If Then
- ElseIF – Multiple Conditions
- Else
- If-Else
- Nested IFs
- IF – Or, And, Xor, Not
- If Or
- If And
- If Xor
- If Not
- If Comparisons
- If – Boolean Function
- Comparing Text
- VBA If Like
- If Loops
- If Else Examples
- Check if Cell is Empty
- Check if Cell Contains Specific Text
- Check if cell contains text
- If Goto
- Delete Row if Cell is Blank
- If MessageBox Yes / No
- VBA If, ElseIf, Else in Access VBA
VBA If Statement
If Then
VBA If Statements allow you to test if expressions are TRUE or FALSE, running different code based on the results.
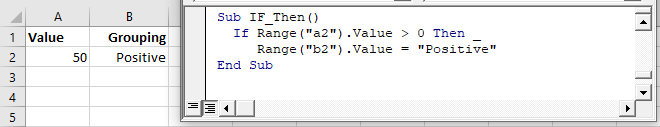
Let’s look at a simple example:
If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then Range("b2").Value = "Positive"This tests if the value in Range A2 is greater than 0. If so, setting Range B2 equal to “Positive”
Note: When testing conditions we will use the =, >, <, <>, <=, >= comparison operators. We will discuss them in more detail later in the article.
Here is the syntax for a simple one-line If statement:
If [test_expression] then [action]To make it easier to read, you can use a Line Continuation character (underscore) to expand the If Statements to two lines (as we did in the above picture):
If [test_expression] then _
[action]If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then _
Range("b2").Value = "Positive"End If
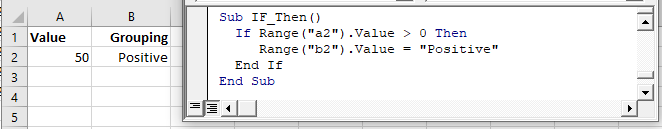
The above “single-line” if statement works well when you are testing one condition. But as your IF Statements become more complicated with multiple conditions, you will need to add an “End If” to the end of the if statement:
If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Positive"
End IfHere the syntax is:
If [test_expression] then
[action]
End IfThe End If signifies the end of the if statement.
Now let’s add in an ElseIF:
ElseIF – Multiple Conditions
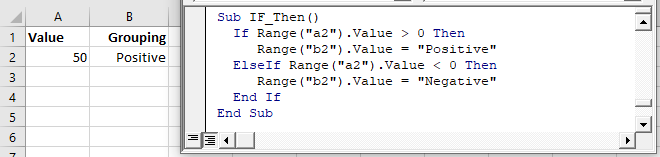
The ElseIf is added to an existing If statement. ElseIf tests if a condition is met ONLY if the previous conditions have not been met.
In the previous example we tested if a cell value is positive. Now we will also test if the cell value is negative with an ElseIf:
If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Positive"
ElseIf Range("a2").Value < 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Negative"
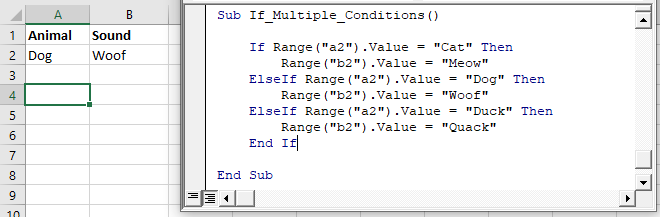
End IfYou can use multiple ElseIfs to test for multiple conditions:
Sub If_Multiple_Conditions()
If Range("a2").Value = "Cat" Then
Range("b2").Value = "Meow"
ElseIf Range("a2").Value = "Dog" Then
Range("b2").Value = "Woof"
ElseIf Range("a2").Value = "Duck" Then
Range("b2").Value = "Quack"
End If
End SubNow we will add an Else:
Else
The Else will run if no other previous conditions have been met.
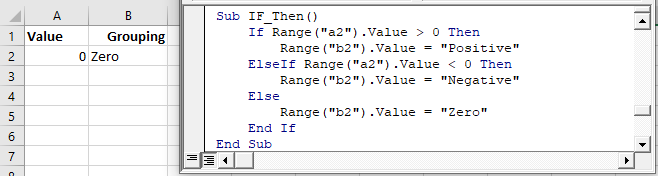
We will finish our example by using an Else to indicate that if the cell value is not positive or negative, then it must be zero:
If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Positive"
ElseIf Range("a2").Value < 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Negative"
Else
Range("b2").Value = "Zero"
End IfIf-Else
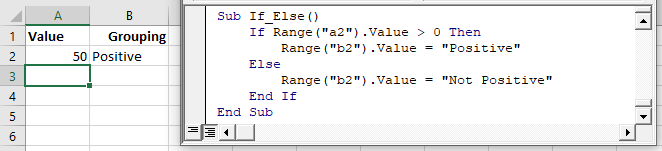
The most common type of If statement is a simple If-Else:
Sub If_Else()
If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Positive"
Else
Range("b2").Value = "Not Positive"
End If
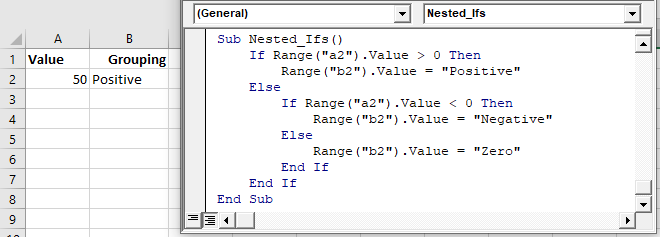
End SubNested IFs
You can also “nest” if statements inside of each other.
Sub Nested_Ifs()
If Range("a2").Value > 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Positive"
Else
If Range("a2").Value < 0 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Negative"
Else
Range("b2").Value = "Zero"
End If
End If
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
IF – Or, And, Xor, Not
Next we will discuss the logical operators: Or, And, Xor, Not.
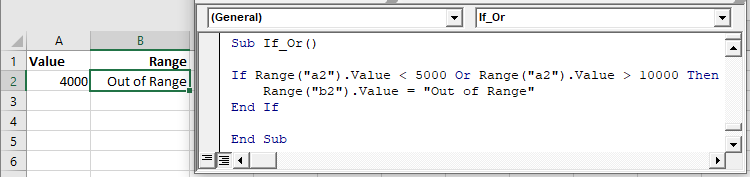
If Or
The Or operator tests if at least one condition is met.
The following code will test if the value in Range A2 is less than 5,000 or greater than 10,000:
If Range("a2").Value < 5000 Or Range("a2").Value > 10000 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Out of Range"
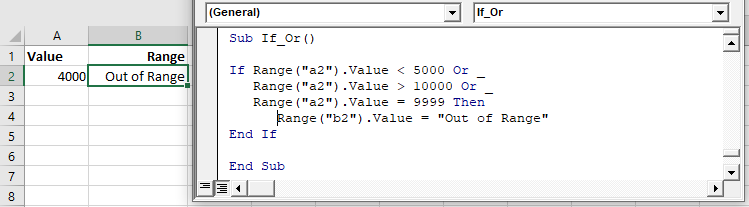
End IfYou can include multiple Ors in one line:
If Range("a2").Value < 5000 Or Range("a2").Value > 10000 Or Range("a2").Value = 9999 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Out of Range"
End IfIf you are going to use multiple Ors, it’s recommended to use a line continuation character to make your code easier to read:
If Range("a2").Value < 5000 Or _
Range("a2").Value > 10000 Or _
Range("a2").Value = 9999 Then
Range("b2").Value = "Out of Range"
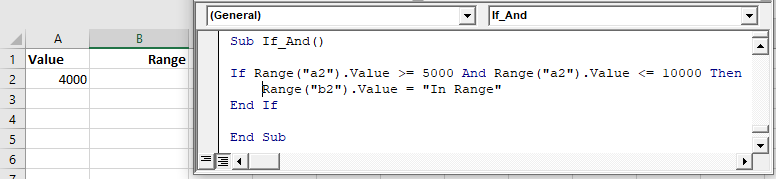
End IfIf And
The And operator allows you to test if ALL conditions are met.
If Range("a2").Value >= 5000 And Range("a2").Value <= 10000 Then
Range("b2").Value = "In Range"
End IfVBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
If Xor
The Xor operator allows you to test if exactly one condition is met. If zero conditions are met Xor will return FALSE, If two or more conditions are met, Xor will also return false.
I’ve rarely seen Xor used in VBA programming.
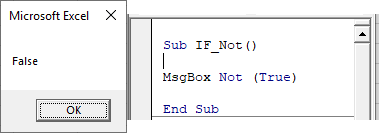
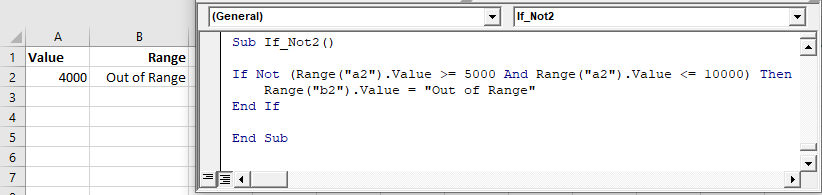
If Not
The Not operator is used to convert FALSE to TRUE or TRUE To FALSE:
Sub IF_Not()
MsgBox Not (True)
End SubNotice that the Not operator requires parenthesis surrounding the expression to switch.
The Not operator can also be applied to If statements:
If Not (Range("a2").Value >= 5000 And Range("a2").Value <= 10000) Then
Range("b2").Value = "Out of Range"
End IfIf Comparisons
When making comparisons, you will usually use one of the comparison operators:
| Comparison Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|
| = | Equal to |
| <> | Not Equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| >= | Greater than or Equal to |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less than or Equal to |
However, you can also use any expression or function that results in TRUE or FALSE
If – Boolean Function
When build expressions for If Statements, you can also use any function that generates TRUE or False. VBA has a few of these functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| IsDate | Returns TRUE if expression is a valid date |
| IsEmpty | Check for blank cells or undefined variables |
| IsError | Check for error values |
| IsNull | Check for NULL Value |
| IsNumeric | Check for numeric value |
They can be called like this:
If IsEmpty(Range("A1").Value) Then MsgBox "Cell Empty"Excel also has many additional functions that can be called using WorksheetFunction. Here’s an example of the Excel IsText Function:
If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Range("a2").Value) Then _
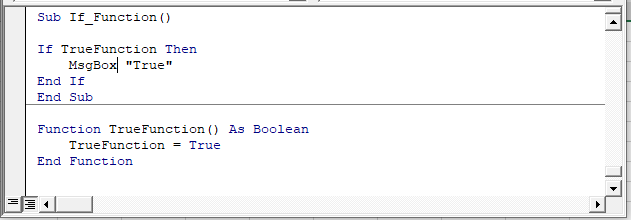
MsgBox "Cell is Text"You can also create your own User Defined Functions (UDFs). Below we will create a simple Boolean function that returns TRUE. Then we will call that function in our If statement:
Sub If_Function()
If TrueFunction Then
MsgBox "True"
End If
End Sub
Function TrueFunction() As Boolean
TrueFunction = True
End FunctionComparing Text
You can also compare text similar to comparing numbers:
Msgbox "a" = "b"Msgbox "a" = "a"When comparing text, you must be mindful of the “Case” (upper or lower). By default, VBA considers letters with different cases as non-matching. In other words, “A” <> “a”.
If you’d like VBA to ignore case, you must add the Option Compare Text declaration to the top of your module:
Option Compare TextAfter making that declaration “A” = “a”:
Option Compare Text
Sub If_Text()
MsgBox "a" = "A"
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
VBA If Like
The VBA Like Operator allows you to make inexact comparisons of text. Click the “Like Operator” link to learn more, but we will show a basic example below:
Dim strName as String
strName = "Mr. Charles"
If strName Like "Mr*" Then
MsgBox "True"
Else
MsgBox "False"
End IfHere we’re using an asterisk “*” wildcard. The * stands for any number of any characters. So the above If statement will return TRUE. The Like operator is an extremely powerful, but often under-used tool for dealing with text.
If Loops
VBA Loops allow you to repeat actions. Combining IF-ELSEs with Loops is a great way to quickly process many calculations.
Continuing with our Positive / Negative example, we will add a For Each Loop to loop through a range of cells:
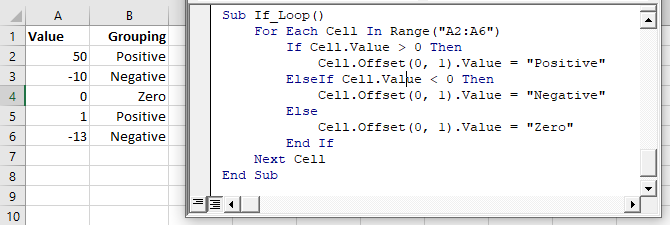
Sub If_Loop()
Dim Cell as Range
For Each Cell In Range("A2:A6")
If Cell.Value > 0 Then
Cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Positive"
ElseIf Cell.Value < 0 Then
Cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Negative"
Else
Cell.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Zero"
End If
Next Cell
End SubIf Else Examples
Now we will go over some more specific examples.
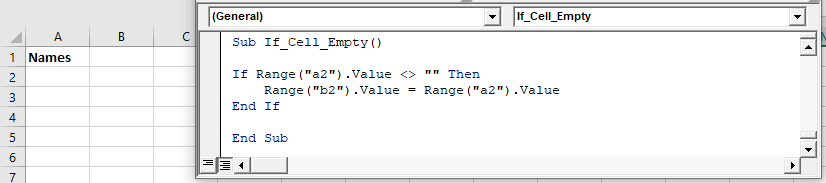
Check if Cell is Empty
This code will check if a cell is empty. If it’s empty it will ignore the cell. If it’s not empty it will output the cell value to the cell to the right:
Sub If_Cell_Empty()
If Range("a2").Value <> "" Then
Range("b2").Value = Range("a2").Value
End If
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Check if Cell Contains Specific Text
The Instr Function tests if a string of text is found in another string. Use it with an If statement to check if a cell contains specific text:
If Instr(Range("A2").value,"text") > 0 Then
Msgbox "Text Found"
End IfCheck if cell contains text
This code will test if a cell is text:
Sub If_Cell_Is_Text()
If Application.WorksheetFunction.IsText(Range("a2").Value) Then
MsgBox "Cell is Text"
End If
End SubIf Goto
You can use the result of an If statement to “Go to” another section of code.
Sub IfGoTo ()
If IsError(Cell.value) Then
Goto Skip
End If
'Some Code
Skip:
End SubDelete Row if Cell is Blank
Using Ifs and loops you can test if a cell is blank and if so delete the entire row.
Sub DeleteRowIfCellBlank()
Dim Cell As Range
For Each Cell In Range("A2:A10")
If Cell.Value = "" Then Cell.EntireRow.Delete
Next Cell
End SubAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
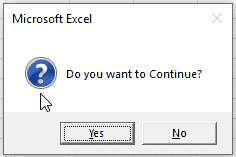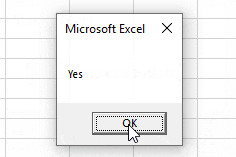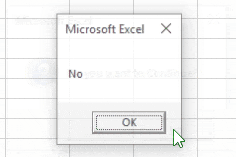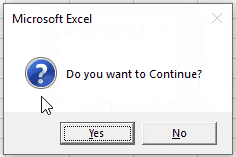
If MessageBox Yes / No
With VBA Message Boxes you’re able to ask the user to select from several options. The Yes/No Message Box asks the user to select Yes or No. You can add a Yes / No Message Box to a procedure to ask the user if they would like to continue running the procedure or not. You handle the user’s input using an If statement.
Here is the Yes/No Message Box in practice:
Sub MsgBoxVariable()
Dim answer As Integer
answer = MsgBox("Do you want to Continue?", vbQuestion + vbYesNo)
If answer = vbYes Then
MsgBox "Yes"
Else
MsgBox "No"
End If
End SubVBA If, ElseIf, Else in Access VBA
The If, ElseIf and Else functions work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA.
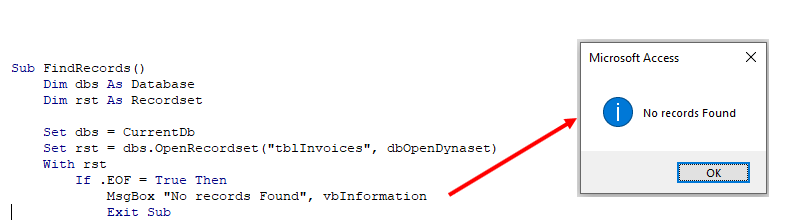
You can use an If statement to check if there are records in a Recordset.
In Excel VBA, IF Then Else statement allows you to check for a condition, and perform an action accordingly.
This is extremely valuable in many situations as we will see in the examples later in this tutorial.
To give you a simple example, suppose you have a list of grades in Excel and you want to highlight all those students who have scored an A. Now, if I ask you to do this manually, you will check each student’s grade and if it’s an A, you’ll highlight it, and if it isn’t, then you’ll leave it as is.
The same logic can be built in VBA using the If Then Else statement as well (and of course do a lot more than just highlighting grades).
In this tutorial, I’ll show you different ways the ‘If Then Else’ construct can be used in Excel VBA, and some practical examples in action.
But before I get into the specifics, let me give you the syntax of the ‘IF Then Else’ statement.
If you’re interested in learning VBA the easy way, check out my Online Excel VBA Training.
Syntax – IF Then Else
Below is the generic syntax of If Then Else construct in VBA
IF condition Then true_code [Else false_code]
Or
IF condition Then true_code Else false_code End IF
Note that the Else part of this statement is optional.
Now if you’re wondering what’s the difference between the two syntaxes, let me clarify.
The first syntax is a simple one-line IF THEN ELSE statement where you don’t need to use the END IF statement.
However, in the second syntax, the true_code part is in the second line. This is helpful when the code that you need to run in case the IF condition is true is long and consists of multiple lines.
When you split the IF statement into multiple lines, you need to tell VBA where the IF Then construct ends.
Hence you need to use the End IF statement.
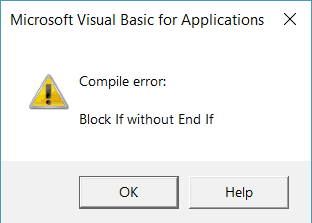
In case you don’t use End IF when required, VBA will show you an error – “Block IF without END IF”
Examples of Using IF Then Statement in VBA
To give you an idea of how the IF-THEN statement works in VBA, let me start with some basic examples (some practical and more useful examples are covered later in this tutorial).
Suppose you have a student’s score in cell A1 and you want to check whether the student passed the exam or not (passing marks threshold being 35).
Then you can use the following code:
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value >=35 Then MsgBox "Pass"
End Sub
The above code has a single line of IF statement that checks the value in cell A1.
If it’s more than 35, it shows the message – “Pass”.
If it’s less than 35, nothing happens.
But what if you want to show a message in both the cases, whether a student passed or failed the exam.
The below code would do this:
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value >= 35 Then
MsgBox "Pass"
Else
MsgBox "Fail"
End If
End Sub
The above code uses the IF as well as the ELSE statement to execute two different conditions. When the score is more than (or equal to) 35, the IF condition is true, and the code right below it gets executed (everything before the Else statement).
But when the IF condition is FALSE, the code jumps to the Else part and executes the code block in it.
Note that when we use a single line of IF Then statement, we don’t need to use End IF. But when we split it into more than one line, we need to use the End If statement.
Nested IF Then (Multiple IF Then statements)
So far we have used a single IF Then statement.
In case you have multiple conditions to check, you can use:
- Multiple IF conditions
- If Then Else statement
- IF Then ElseIf Else construct
Let me show you how these differ and how to use this in Excel VBA.
Multiple IF Then Statements
Let’s take the same example of using a student’s score.
If the student scores less than 35, the message to display is ‘Fail’, if the score is more than or equal to 35, the message to display is ‘Pass’.
We can use the below code to get this done:
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value < 35 Then MsgBox "Fail"
If Range("A1").Value >= 35 Then MsgBox "Pass"
End Sub
You can use multiple IF Then statement as shown above. While this works, it’s not an example of good coding (as you will see the alternatives below).
In case you decide to use this, remember that these statements should either be independent or mutually exclusive. The important thing to know here is that in the above construct, all the IF statements are evaluated and the ones where the condition is true, the code is executed.
So even if the first IF statement is correct, the second would still be evaluated.
IF Then Else Statement
Suppose this time, instead of just displaying the message Pass/Fail, we have one more condition.
If the student scores less than 35, the message to display is ‘Fail’, if the score is more than or equal to 35, the message to display is ‘Pass’, and if the score is more than 80, the message to display is ‘Pass, with Distinction’.
We can use the below code to get this done:
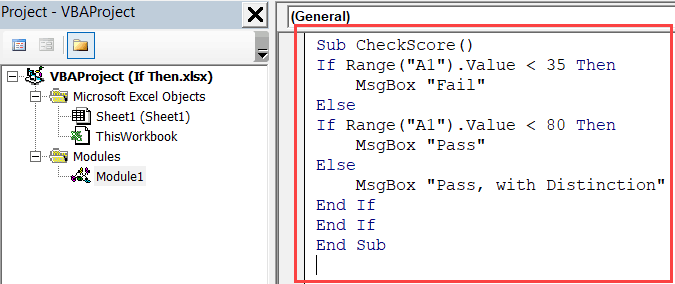
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value < 35 Then
MsgBox "Fail"
Else
If Range("A1").Value < 80 Then
MsgBox "Pass"
Else
MsgBox "Pass, with Distinction"
End If
End If
End Sub
In the above code, we have used multiple IF statements (nested IF Then) with the help of Else.
So there is an ‘IF Then Else’ construct within an ‘IF Then Else’ construct. This type of nesting allows you to check for multiple conditions and run the relevant block of code.
IF Then ElseIf Else Statement
The above code (that we saw in the previous section) can be further optimized by using the ElseIf statement.
Here is what we’re trying to do – If the student scores less than 35, the message to display is ‘Fail’, if the score is more than or equal to 35, the message to display is ‘Pass’, and if the score is more than 80, the message to display is ‘Pass, with Distinction’.
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value < 35 Then
MsgBox "Fail"
ElseIf Range("A1").Value < 80 Then
MsgBox "Pass"
Else
MsgBox "Pass, with Distinction"
End If
End Sub
The above code uses ElseIf, which allows us to keep all the conditions within one single IF Then statement.
Using AND and OR in IF Then Else
So far in this tutorial, we have only checked for a single condition at a time.
However, when you have multiple dependent conditions, you can use the AND or OR statement with the IF conditions.
Below is the syntax of using AND/OR condition with the IF Then statement.
IF Condition1 AND Condition2 Then true_code Else false_code End IF
In the above code, only when both Condition1 and Condition2 are met, the true_code is executed. Even if one of the conditions is false, it will execute the false_code.
With OR, even if one of the conditions are true, it will execute the true_code. Only when all the conditions are false, it executes the false_code.
Now let’s see how AND and OR statement work with the IF Then Else construct.
Suppose you have the scores for two subjects instead of one, and you want to check for the following conditions:
- Fail – When the score is less than 35 in any of the subjects.
- Pass – When the score is more than or equal to 35, but less than 80 in both the subjects.
- Pass, with Distinction – When the score is more than 35 in both the subjects and is more than or equal to 80 in one or both the subjects.
Here is the code that will do this:
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value < 35 Or Range("B1").Value < 35 Then
MsgBox "Fail"
ElseIf Range("A1").Value < 80 And Range("B1").Value < 80 Then
MsgBox "Pass"
Else
MsgBox "Pass, with Distinction"
End If
End Sub
The above code uses both OR and AND statements.
You can also write this same code with a slight change (using OR instead of AND).
Sub CheckScore()
If Range("A1").Value < 35 Or Range("B1").Value < 35 Then
MsgBox "Fail"
ElseIf Range("A1").Value > 80 Or Range("B1").Value > 80 Then
MsgBox "Pass, with Distinction"
Else
MsgBox "Pass"
End If
End Sub
Both the above VBA codes will give you the same result. Personally, I prefer the first one as it has a logical flow of checking the scores (but that’s just me).
Using Not Equal to in If Then
In all the examples above, we have used the conditions that check whether a value equal to a specified value or not.
You can also use similar codes when checking when the value is not equal to a specified value in the VBA code. Not equal to represented by <> the Excel VBA.
To see a practical example of using <>, have a look at Example 1 below.
Using If Then Else with Loops in VBA
So far, we have been going through some examples that are good to understand how the ‘IF-THEN’ statements work in VBA, however, are not useful in the practical world.
If I need to grade students, I can easily do that using Excel functions.
So let’s have a look at some useful and practical examples that can help you automate some stuff and be more efficient.
Example 1 – Save and Close All Workbooks Except The Active Workbook
If you have a lot of workbooks open and you quickly want to close all, except the active workbook, you can use the below code,
Sub SaveCloseAllWorkbooks() Dim wb As Workbook For Each wb In Workbooks On error resume next If wb.Name <> ActiveWorkbook.Name Then wb.Save wb.Close End If Next wb End Sub
The above code would save and close all the workbooks (except the active one).
It uses the For Next loop to go through the collection of all the open workbooks and checks the name using the IF condition.
If the name is not the same as that of the Active workbook, it saves and closes it.
In case there is a VBA code in any of the workbooks and you haven’t saved it as .xls or .xlsm, you will see a warning (as the vba codes are lost when you save it in .xlsx format).
Example 2 – Highlight Cells with Negative Values
Suppose that you have a column full of numbers and you want to quickly highlight all the cells with negative values in red, you can do that using the below code.
Sub HighlightNegativeCells() Dim Cll As Range For Each Cll In Selection If Cll.Value < 0 Then Cll.Interior.Color = vbRed Cll.Font.Color = vbWhite End If Next Cll End Sub
The above code uses the For Each loop and checks each cell in the selection that you have made. If the cell has a value that is negative, it’s highlighted in red with white font color.
Example 3 – Hide All the Worksheet Except the Current Worksheet
In case you want to quickly hide all the worksheets except the active one, you can use the below code:
Sub HideAllExceptActiveSheet() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden Next ws End Sub
The above code uses the For Each loop to go through a collection of worksheets. It checks the name of each worksheet and hides it if it’s not the active worksheet.
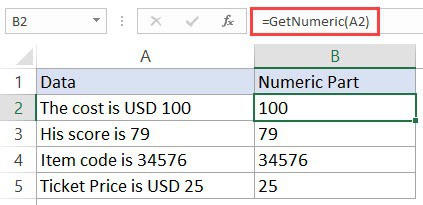
Example 4 – Extract the Numeric Part from an Alphanumeric String
If you have alphanumeric strings in cells and you want to extract the numeric part from it, you can do that using the below code:
Function GetNumeric(CellRef As String) Dim StringLength As Integer StringLength = Len(CellRef) For i = 1 To StringLength If IsNumeric(Mid(CellRef, i, 1)) Then Result = Result & Mid(CellRef, i, 1) Next i GetNumeric = Result End Function
This code will create a custom function in Excel that can use within the worksheet (just like a regular function).
Where to Put the VBA Code?
Wondering where the VBA code goes in your Excel workbook?
Excel has a VBA backend called the VB editor. You need to copy and paste the code in the VB Editor module code window.
Here are the steps to do this:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click on Visual Basic option. This will open the VB editor in the backend.
- In the Project Explorer pane in the VB Editor, right-click on any object for the workbook in which you want to insert the code. If you don’t see the Project Explorer go to the View tab and click on Project Explorer.
- Go to Insert and click on Module. This will insert a module object for your workbook.
- Copy and paste the code in the module window.
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- How to Record a Macro in Excel.
- Working with Cells and Ranges in Excel VBA.
- Working with Worksheets in Excel VBA.
- Working with Workbooks in Excel VBA.
- Creating a Custom Function in Excel Using VBA.
- Excel VBA Events – An Easy (and Complete) Guide.
- Excel VBA MsgBox
- How to Run a Macro in Excel.
- How to Create and Use an Excel Add-in.
- Excel Personal Macro Workbook | Save & Use Macros in All Workbooks.
- Useful Excel Macro Examples for VBA Beginners (Ready-to-use).
- How to Use Excel VBA InStr Function (with practical EXAMPLES).
This post provides a complete guide to the VBA If Statement in VBA. If you are looking for the syntax then check out the quick guide in the first section which includes some examples.
The table of contents below provides an overview of what is included in the post. You use this to navigate to the section you want or you can read the post from start to finish.
“Guess, if you can, and choose, if you dare.” – Pierre Corneille
Quick Guide to the VBA If Statement
| Description | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| If Then | If [condition is true] Then [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» End If |
| If Else | If [condition is true] Then [do something] Else [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» Else Debug.Print «Try again» End If |
| If ElseIf | If [condition 1 is true] Then [do something] ElseIf [condition 2 is true] Then [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» ElseIf score > 50 Then Debug.Print «Passed» ElseIf score <= 50 Then Debug.Print «Try again» End If |
| Else and ElseIf (Else must come after ElseIf’s) |
If [condition 1 is true] Then [do something] ElseIf [condition 2 is true] Then [do something] Else [do something] End If |
If score = 100 Then Debug.Print «Perfect» ElseIf score > 50 Then Debug.Print «Passed» ElseIf score > 30 Then Debug.Print «Try again» Else Debug.Print «Yikes» End If |
| If without Endif (One line only) |
If [condition is true] Then [do something] | If value <= 0 Then value = 0 |
The following code shows a simple example of using the VBA If statement
If Sheet1.Range("A1").Value > 5 Then Debug.Print "Value is greater than five." ElseIf Sheet1.Range("A1").Value < 5 Then Debug.Print "value is less than five." Else Debug.Print "value is equal to five." End If
The Webinar
Members of the Webinar Archives can access the webinar for this article by clicking on the image below.
(Note: Website members have access to the full webinar archive.)
What is the VBA If Statement
The VBA If statement is used to allow your code to make choices when it is running.
You will often want to make choices based on the data your macros reads.
For example, you may want to read only the students who have marks greater than 70. As you read through each student you would use the If Statement to check the marks of each student.
The important word in the last sentence is check. The If statement is used to check a value and then to perform a task based on the results of that check.
The Test Data and Source Code
We’re going to use the following test data for the code examples in this post:
You can download the test data with all the source code for post plus the solution to the exercise at the end:
Format of the VBA If-Then Statement
The format of the If Then statement is as follows
If [condition is true] Then
The If keyword is followed by a Condition and the keyword Then
Every time you use an If Then statement you must use a matching End If statement.
When the condition evaluates to true, all the lines between If Then and End If are processed.
If [condition is true] Then [lines of code] [lines of code] [lines of code] End If
To make your code more readable it is good practice to indent the lines between the If Then and End If statements.
Indenting Between If and End If
Indenting simply means to move a line of code one tab to the right. The rule of thumb is to indent between start and end statements like
Sub … End Sub
If Then … End If
If Then… ElseIf … Else … Endif
For … Next
Do While … Loop
Select Case … End Case
To indent the code you can highlight the lines to indent and press the Tab key. Pressing Shift + Tab will Outdent the code i.e. move it one tab to the left.
You can also use the icons from the Visual Basic Toolbar to indent/outdent the code
Select code and click icons to indent/outdent
If you look at any code examples on this website you will see that the code is indented.
A Simple If Then Example
The following code prints out the names of all students with marks greater than 50 in French.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub ReadMarks() Dim i As Long ' Go through the marks columns For i = 2 To 11 ' Check if marks greater than 50 If Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value > 50 Then ' Print student name to the Immediate Window(Ctrl + G) Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & " " & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value End If Next End Sub
Results
Bryan Snyder
Juanita Moody
Douglas Blair
Leah Frank
Monica Banks
Play around with this example and check the value or the > sign and see how the results change.
Using Conditions with the VBA If Statement
The piece of code between the If and the Then keywords is called the condition. A condition is a statement that evaluates to true or false. They are mostly used with Loops and If statements. When you create a condition you use signs like >,<,<>,>=,<=,=.
The following are examples of conditions
| Condition | This is true when |
|---|---|
| x < 5 | x is less than 5 |
| x <= 5 | x is less than or equal to 5 |
| x > 5 | x is greater than 5 |
| x >= 5 | x is greater than or equal to 5 |
| x = 5 | x is equal to 5 |
| x <> 5 | x does not equal 5 |
| x > 5 And x < 10 | x is greater than 5 AND x is less than 10 |
| x = 2 Or x >10 | x is equal to 2 OR x is greater than 10 |
| Range(«A1») = «John» | Cell A1 contains text «John» |
| Range(«A1») <> «John» | Cell A1 does not contain text «John» |
You may have noticed x=5 as a condition. This should not be confused with x=5 when used as an assignment.
When equals is used in a condition it means “is the left side equal to the right side”.
The following table demonstrates how the equals sign is used in conditions and assignments
| Using Equals | Statement Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Loop Until x = 5 | Condition | Is x equal to 5 |
| Do While x = 5 | Condition | Is x equal to 5 |
| If x = 5 Then | Condition | Is x equal to 5 |
| For x = 1 To 5 | Assignment | Set the value of x to 1, then to 2 etc. |
| x = 5 | Assignment | Set the value of x to 5 |
| b = 6 = 5 | Assignment and Condition | Assign b to the result of condition 6 = 5 |
| x = MyFunc(5,6) | Assignment | Assign x to the value returned from the function |
The last entry in the above table shows a statement with two equals. The first equals sign is the assignment and any following equals signs are conditions.
This might seem confusing at first but think of it like this. Any statement that starts with a variable and an equals is in the following format
[variable] [=] [evaluate this part]
So whatever is on the right of the equals sign is evaluated and the result is placed in the variable. Taking the last three assignments again, you could look at them like this
[x] [=] [5]
[b] [=] [6 = 5]
[x] [=] [MyFunc(5,6)]
Using ElseIf with the VBA If Statement
The ElseIf statement allows you to choose from more than one option. In the following example we print for marks that are in the Distinction or High Distinction range.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseElseIf() If Marks >= 85 Then Debug.Print "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" End If End Sub
The important thing to understand is that order is important. The If condition is checked first.
If it is true then “High Distinction” is printed and the If statement ends.
If it is false then the code moves to the next ElseIf and checks it condition.
Let’s swap around the If and ElseIf from the last example. The code now look like this
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseElseIfWrong() ' This code is incorrect as the ElseIf will never be true If Marks >= 75 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 85 Then ' code will never reach here Debug.Print "High Destinction" End If End Sub
In this case we check for a value being over 75 first. We will never print “High Distinction” because if a value is over 85 is will trigger the first if statement.
To avoid these kind of problems we should use two conditions. These help state exactly what you are looking for a remove any confusion. The example below shows how to use these. We will look at more multiple conditions in the section below.
If marks >= 75 And marks < 85 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" ElseIf marks >= 85 And marks <= 100 Then Debug.Print "High Destinction" End If
Let’s expand the original code. You can use as many ElseIf statements as you like. We will add some more to take into account all our mark classifications.
If you want to try out these examples you can download the code from the top of this post.
Using Else With the VBA If Statement
The VBA Else statement is used as a catch all. It basically means “if no conditions were true” or “everything else”. In the previous code example, we didn’t include a print statement for a fail mark. We can add this using Else.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub UseElse() If Marks >= 85 Then Debug.Print "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then Debug.Print "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then Debug.Print "Credit" ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then Debug.Print "Pass" Else ' For all other marks Debug.Print "Fail" End If End Sub
So if it is not one of the other types then it is a fail.
Let’s write some code to go through our sample data and print the student and their classification:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub AddClass() ' get the last row Dim startRow As Long, lastRow As Long startRow = 2 lastRow = Sheet1.Cells(Sheet1.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Dim i As Long, Marks As Long Dim sClass As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = startRow To lastRow Marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check marks and classify accordingly If Marks >= 85 Then sClass = "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then sClass = "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then sClass = "Credit" ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then sClass = "Pass" Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End If ' Write out the class to column E Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass Next End Sub
The results look like this with column E containing the classification of the marks
Results
Remember that you can try these examples for yourself with the code download from the top of this post.
Using Logical Operators with the VBA If Statement
You can have more than one condition in an If Statement. The VBA keywords And and Or allow use of multiple conditions.
These words work in a similar way to how you would use them in English.
Let’s look at our sample data again. We now want to print all the students that got over between 50 and 80 marks.
We use And to add an extra condition. The code is saying: if the mark is greater than or equal 50 and less than 75 then print the student name.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CheckMarkRange() Dim i As Long, marks As Long For i = 2 To 11 ' Store marks for current student marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check if marks greater than 50 and less than 75 If marks >= 50 And marks < 80 Then ' Print first and last name to Immediate window(Ctrl G) Debug.Print Sheet1.Range("A" & i).Value & Sheet1.Range("B" & i).Value End If Next End Sub
Results
Douglas Blair
Leah Frank
Monica Banks
In our next example we want the students who did History or French. So in this case we are saying if the student did History OR if the student did French:
' Description: Uses OR to check the study took History or French. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub UseOr() ' Get the data range Dim rg As Range Set rg = shMarks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion Dim i As Long, subject As String ' Read through the data For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count ' Get the subject subject = rg.Cells(i, 4).Value ' Check if subject greater than 50 and less than 80 If subject = "History" Or subject = "French" Then ' Print first name and subject to Immediate window(Ctrl G) Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value & " " & rg.Cells(i, 4).Value End If Next End Sub
Results
Bryan History
Bradford French
Douglas History
Ken French
Leah French
Rosalie History
Jackie History
Using Multiple conditions like this is often a source of errors. The rule of thumb to remember is to keep them as simple as possible.
Using If And
The AND works as follows
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
What you will notice is that AND is only true when all conditions are true
Using If Or
The OR keyword works as follows
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | TRUE |
| FALSE | TRUE | TRUE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
What you will notice is that OR is only false when all the conditions are false.
Mixing AND and OR together can make the code difficult to read and lead to errors. Using parenthesis can make the conditions clearer.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub OrWithAnd() Dim subject As String, marks As Long subject = "History" marks = 5 If (subject = "French" Or subject = "History") And marks >= 6 Then Debug.Print "True" Else Debug.Print "False" End If End Sub
Using If Not
There is also a NOT operator. This returns the opposite result of the condition.
| Condition | Result |
| TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE |
The following two lines of code are equivalent.
If marks < 40 Then If Not marks >= 40 Then
as are
If True Then If Not False Then
and
If False Then If Not True Then
Putting the condition in parenthesis makes the code easier to read
If Not (marks >= 40) Then
A common usage of Not when checking if an object has been set. Take a worksheet for example. Here we declare the worksheet
Dim mySheet As Worksheet ' Some code here
We want to check mySheet is valid before we use it. We can check if it is nothing.
If mySheet Is Nothing Then
There is no way to check if it is something as there is many different ways it could be something. Therefore we use Not with Nothing
If Not mySheet Is Nothing Then
If you find this a bit confusing you can use parenthesis like this
If Not (mySheet Is Nothing) Then
The IIF function
Note that you can download the IIF examples below and all source code from the top of this post.
VBA has an fuction similar to the Excel If function. In Excel you will often use the If function as follows:
=IF(F2=””,””,F1/F2)
The format is
=If(condition, action if true, action if false).
VBA has the IIf statement which works the same way. Let’s look at an example. In the following code we use IIf to check the value of the variable val. If the value is greater than 10 we print true otherwise we print false:
' Description: Using the IIF function to check a number. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub CheckNumberIIF() Dim result As Boolean Dim number As Long ' Prints True number = 11 result = IIf(number > 10, True, False) Debug.Print "Number " & number & " greater than 10 is " & result ' Prints false number = 5 result = IIf(number > 10, True, False) Debug.Print "Number " & number & " greater than 10 is " & result End Sub
In our next example we want to print out Pass or Fail beside each student depending on their marks. In the first piece of code we will use the normal VBA If statement to do this:
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CheckMarkRange() Dim i As Long, marks As Long For i = 2 To 11 ' Store marks for current student marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check if student passes or fails If marks >= 40 Then ' Write out names to to Column F Sheet1.Range("E" & i) = "Pass" Else Sheet1.Range("E" & i) = "Fail" End If Next End Sub
In the next piece of code we will use the IIf function. You can see that the code is much neater here:
' Description: Using the IIF function to check marks. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub CheckMarkRange() ' Get the data range Dim rg As Range Set rg = shMarks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion Dim i As Long, marks As Long, result As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count ' Store marks for current student marks = rg.Cells(i, 3).Value ' Check if student passes or fails result = IIf(marks >= 40, "Pass", "Fail") ' Print the name and result Debug.Print rg.Cells(i, 1).Value, result Next End Sub
You can see the IIf function is very useful for simple cases where you are dealing with two possible options.
Using Nested IIf
You can also nest IIf statements like in Excel. This means using the result of one IIf with another. Let’s add another result type to our previous examples. Now we want to print Distinction, Pass or Fail for each student.
Using the normal VBA we would do it like this
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub CheckResultType2() Dim i As Long, marks As Long For i = 2 To 11 ' Store marks for current student marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value If marks >= 75 Then Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Distinction" ElseIf marks >= 40 Then ' Write out names to to Column F Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Pass" Else Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = "Fail" End If Next End Sub
Using nested IIfs we could do it like this:
' Description: Using a nested IIF function to check marks. ' Worksheet: Marks ' Output: Result are printed to the Immediate Windows(Ctrl + G) ' https://excelmacromastery.com/vba-if Sub UsingNestedIIF() ' Get the data range Dim rg As Range Set rg = shMarks.Range("A1").CurrentRegion Dim i As Long, marks As Long, result As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = 2 To rg.Rows.Count marks = rg.Cells(i, 3).Value result = IIf(marks >= 55, "Credit", IIf(marks >= 40, "Pass", "Fail")) Debug.Print marks, result Next i End Sub
Using nested IIf is fine in simple cases like this. The code is simple to read and therefore not likely to have errors.
What to Watch Out For
It is important to understand that the IIf function always evaluates both the True and False parts of the statement regardless of the condition.
In the following example we want to divide by marks when it does not equal zero. If it equals zero we want to return zero.
marks = 0 total = IIf(marks = 0, 0, 60 / marks)
However, when marks is zero the code will give a “Divide by zero” error. This is because it evaluates both the True and False statements. The False statement here i.e. (60 / Marks) evaluates to an error because marks is zero.
If we use a normal IF statement it will only run the appropriate line.
marks = 0 If marks = 0 Then 'Only executes this line when marks is zero total = 0 Else 'Only executes this line when marks is Not zero total = 60 / marks End If
What this also means is that if you have Functions for True and False then both will be executed. So IIF will run both Functions even though it only uses one return value. For example
'Both Functions will be executed every time total = IIf(marks = 0, Func1, Func2)
(Thanks to David for pointing out this behaviour in the comments)
If Versus IIf
So which is better?
You can see for this case that IIf is shorter to write and neater. However if the conditions get complicated you are better off using the normal If statement. A disadvantage of IIf is that it is not well known so other users may not understand it as well as code written with a normal if statement.
Also as we discussed in the last section IIF always evaluates the True and False parts so if you are dealing with a lot of data the IF statement would be faster.
My rule of thumb is to use IIf when it will be simple to read and doesn’t require function calls. For more complex cases use the normal If statement.
Using Select Case
The Select Case statement is an alternative way to write an If statment with lots of ElseIf’s. You will find this type of statement in most popular programming languages where it is called the Switch statement. For example Java, C#, C++ and Javascript all have a switch statement.
The format is
Select Case [variable] Case [condition 1] Case [condition 2] Case [condition n] Case Else End Select
Let’s take our AddClass example from above and rewrite it using a Select Case statement.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub AddClass() ' get the last row Dim startRow As Long, lastRow As Long startRow = 2 lastRow = Sheet1.Cells(Sheet1.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Dim i As Long, Marks As Long Dim sClass As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = startRow To lastRow Marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check marks and classify accordingly If Marks >= 85 Then sClass = "High Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 75 Then sClass = "Destinction" ElseIf Marks >= 55 Then sClass = "Credit" ElseIf Marks >= 40 Then sClass = "Pass" Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End If ' Write out the class to column E Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass Next End Sub
The following is the same code using a Select Case statement. The main thing you will notice is that we use “Case 85 to 100” rather than “marks >=85 And marks <=100”.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub AddClassWithSelect() ' get the first and last row Dim firstRow As Long, lastRow As Long firstRow = 2 lastRow = Cells(Cells.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Dim i As Long, marks As Long Dim sClass As String ' Go through the marks columns For i = firstRow To lastRow marks = Sheet1.Range("C" & i).Value ' Check marks and classify accordingly Select Case marks Case 85 To 100 sClass = "High Destinction" Case 75 To 84 sClass = "Destinction" Case 55 To 74 sClass = "Credit" Case 40 To 54 sClass = "Pass" Case Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End Select ' Write out the class to column E Sheet1.Range("E" & i).Value = sClass Next End Sub
Using Case Is
You could rewrite the select statement in the same format as the original ElseIf. You can use Is with Case.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Select Case marks Case Is >= 85 sClass = "High Destinction" Case Is >= 75 sClass = "Destinction" Case Is >= 55 sClass = "Credit" Case Is >= 40 sClass = "Pass" Case Else ' For all other marks sClass = "Fail" End Select
You can use Is to check for multiple values. In the following code we are checking if marks equals 5, 7 or 9.
' https://excelmacromastery.com/ Sub TestMultiValues() Dim marks As Long marks = 7 Select Case marks Case Is = 5, 7, 9 Debug.Print True Case Else Debug.Print False End Select End Sub
What’s Next?
Free VBA Tutorial If you are new to VBA or you want to sharpen your existing VBA skills then why not try out the The Ultimate VBA Tutorial.
Related Training: Get full access to the Excel VBA training webinars and all the tutorials.
(NOTE: Planning to build or manage a VBA Application? Learn how to build 10 Excel VBA applications from scratch.)
If you want to be an advanced VBA user then an IF statement is a must-learn. And, I believe that you are already familiar with the word IF and you are frequently using it as a worksheet function.
In VBA, IF works just like the same. Its basic idea is to perform a task when a condition is TRUE else do nothing or do something else. You can write simply as well as in complex conditions.
For understanding purposes, I have split it into three different parts.
- A condition to test.
- A task to perform if the condition is TRUE.
- A task to perform if the condition is FALSE.
This is what it looks like in real life:

In the above example, rain is a condition. If this condition is TRUE, the boy will open his umbrella and if the condition is FALSE he will wear his hat. Conditions are everywhere in our day-to-day life. But now, let’s back to our coding world and explore it.
Syntax: VBA IF
We have three different types of IF statements in VBA.
1. IF-Then
IF THEN is the simplest form of an IF statement. All we need to do is specify a condition to check and if that condition is TRUE it will perform a task. But, if that condition is FALSE it will do nothing and skip the line instantly.
Syntax
IF condition Then statement[s]In the above syntax, we have to specify a condition to evaluate and a task to perform if that condition is TRUE.
Example
In the above example, we have used verified that cell A1 has value 10 in it and if it has, the statement will show a message box with the message “Cell A1 has value 10”.
Sub CheckValue()
If Range("A1").Value = 10 Then
MsgBox ("Cell A1 has value 10")
End Sub2. IF-Then-Else
You can use the IF-Then-Else statement where you want to perform a specific task if a condition is TRUE and a different task if a condition is FALSE.
Syntax
IF Condition Then
Statement[s]
Else
Statement[s]
End IfWith the above syntax, we can perform different tasks according to the result of a condition. If the condition is TRUE then it will perform the statement which you have mentioned after “Then” or if the condition is FALSE it will perform the statement which you have mentioned after “Else”.
Example
Sub CheckValue()
If Range("A1").Value = "10" Then
MsgBox ("Cell A1 has value 10")
Else
MsgBox ("Cell A1 has a value other than 10")
End Sub
In the above example, I have used the IF-Then-Else statement to check the value in cell A1.
If cell A1 has a value of 10, you will get a message box showing “Cell A1 has a value of 10” and if there is any other value in cell A1 you get a message box showing “Cell A1 has a value other than 10”. So, here we are able to perform different tasks according to the result of the condition.
3. IF-Then-Elseif-Else
This is the most useful and important type of IF which will help you to write advanced condition statements. In this type, you can specify the second condition after evaluating your first condition.
Syntax
IF Condition Then
Statement[s]
Elseif Condition Then
Statement[s]
Else
Statement[s]
End IfIn the above syntax, we have:
- A condition to evaluate.
- A statement to perform if that condition is TURE.
- If that condition is FALSE then we have the second condition to evaluate.
- And, if the second condition is TRUE we have a statement to perform.
- But, if both conditions, first and second are FALSE then it will perform a statement that you have mentioned after “Else”.
And, the best part is you can use any number of “Elseif” in your code. That means you can specify any number of conditions in your statement.
Example
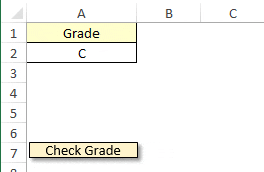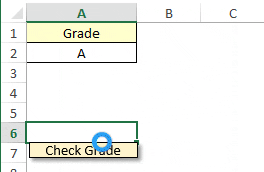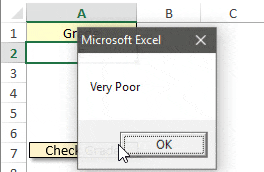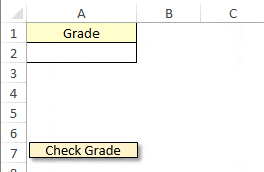
Sub check_grade()
If Range("A2").Value = "A" Then
MsgBox "Very Good"
Else
If Range("A2").Value = "B" Then
MsgBox "Good"
ElseIf Range("A2").Value = "C" Then
MsgBox "Average"
ElseIf Range("A2").Value = "D" Then
MsgBox "Poor"
ElseIf Range("A2").Value = "E" Then
MsgBox "Very Poor"
Else
MsgBox "Enter Correct Grade"
End SubIn the above example, we have written a macro that will first check cell A2 for the value “A” and if the cell has the grade “A”, the statement will return the message “Very Good”.
This statement will first check cell A2 for value “A” and if the cell has the grade “A”, the statement will return the message “Very Good”.
And, if the first condition is FALSE then it will evaluate the second condition and return the message “Good” if the cell has a grade of “B”.
And, if the second condition is false then it will go to the third condition and so on. In the end, if all five conditions are false it will run the code which I have written after else.
The secret about writing an IF statement in VBA
Now, you know about all the types of IF and you are also able to choose one of them according to the task you need to perform. Let me tell you a secret.
One Line IF statement Vs. Block IF statement
You can write an IF statement in two different ways and both have advantages and disadvantages. Have a look.
1. One Line Statement
The one-line statement is perfect if you are using the IF-Then statement. The basic to use one line statement is to write your entire code in one line.
If A1 = 10 Then Msgbox("Cell A1 has value 10")In the above statement, we have written an IF statement to evaluate if cell A1 has a value of 10 then it will show a message box. The best practice to use one line statement is when you have to write a simple code. Using one-line code for complex and lengthy statements is hard to understand.
[icon name=”lightbulb-o” unprefixed_] Quick Tip: While writing single-line code you don’t need to use Endif to end the statement.
2. Block Statement
A Block statement is perfect when you want to write your code in a decent and understandable way. When you writing a block statement you can use multiple lines in your macro which give you a neat and clean code.
Sub check_value()
If Range(“A1”).Value = “10” Then
MsgBox ("Cell A1 has value 10")
Else
MsgBox ("Cell A1 has a value other than 10")
End If
End SubIn the above example, we have written an IF-Then-Else statement in blocks. And, you can see that it is easy to read and even easy to debug.
When you will write complex statements (which you will definitely do after reading this guide) using block statements are always good. And, while writing nested If statements you can also add indentation in your line for more clarity.
[icon name=”lightbulb-o” unprefixed_] Quick Tip – You have an exception that you can skip using Else at the end of your code when you are using IF-Then-Elseif-Else. This is very helpful when you do not need to perform any task when none of the conditions is TRUE in your statement.
8 Real Life Examples
Here I have listed some simple but useful examples which you can follow along.
1. Nested IF
The best part of the IF statement is you create nesting statements. You can add a second condition in the first condition.

Sub NestIF()
Dim res As Long
res = MsgBox("Do you want to save this file?", vbYesNo, "Save File")
If res = vbYes Then 'start of first IF statement
If ActiveWorkbook.Saved <> True Then 'start of second IF statement.
ActiveWorkbook.SaveMsgBox ("Workbook Saved")
Else
MsgBox "This workbook is already saved"
End If 'end of second IF statement
Else
MsgBox "Make Sure to save it later"
End If ' end of first IF statement
End SubIn the above example, we have used a nested IF statement. When you run this macro you will get a message box with the OK and Cancel options. Work of conditional statement starts after that.
First, it will evaluate which button you have clicked. If you clicked “Yes” then nest it will evaluate whether your worksheet is saved or not.
If your workbook is not saved, it will save it and you will get a message. And, if the workbook is already saved it will show a message about that.
But, If you click on the button the condition of the first macro will be FALSE and you will only get a message to save your book later.
The basic idea in this code is that the second condition is totally dependent on the first condition if the first condition is FALSE then the second condition will not get evaluated.
More on Nested IF
2. Create Loop With IF and GoTo
You can also create a loop by using goto with IF. Most programmers avoid writing loops this way as we have better ways for a loop. But there is no harm to learn how we can do this.
Sub auto_open()
Alert: If InputBox("Enter Username") <> "Puneet" Then
GoTo Alert
Else
MsgBox "Welcome"
End If
End SubIn the above example, we have used a condition statement to create a loop. We have used auto_open as the name of the macro so that whenever anyone opens the file it will run that macro.
The user needs to enter a username and if that username is not equal to “Puneet” it will repeat the code and show the input box again. And, if you enter the right text then he/she will be able to access the file.
3. Check if a Cell Contains a Number
Here we have used a condition to check whether the active cell contains a numeric value or not.

Sub check_number()
If IsNumeric(Range("B2").Value) Then
MsgBox "Yes, active cell has a number."
Else
MsgBox "No, active cell hasn't a number."
End If
End SubIn the above example, I have written a condition by using the isnumeric function in VBA which is the same as the worksheet’s number function to check whether the value in a cell is a number or not.
If the value is a number it will return TRUE and you will get a message “Yes, Active Cell Has A Numeric Value”. And, if the value is non-number then you will get a message “No Numeric Value In Active Cell”.
4. Using OR and AND With IF
By using IF OR you can specify two or more conditions and perform a task if at least one condition is TRUE from all.
Sub UsingOR()
If Range("A1") < 70 Or Range("B1") < 70 Then
MsgBox "You Are Pass"
Else
If Range("A1") < 40 And Range("B1") < 40 Then
MsgBox "You Are Pass"
Else
MsgBox "You Are Fail"
End If
End If
End SubIn the above example, in line 2, we have two conditions using the OR. If a student gets 70 marks in any of the subjects the result will be a “Pass”. And on line 7, we have two conditions using the AND operator. If a student gets more than 40 marks in both of the subjects the result will be “Pass”.
By using the IF AND you can specify more than one condition and perform a task if all the conditions are TRUE.
5. Using Not With IF
By using NOT in a condition you can change TRUE into FALSE and FALSE into TRUE.
VBA IF Not
Sub IF_Not()
If Range(“D1”) <= 40 And Not Range(“E1”) = “E” Then
MsgBox "You Are Pass."
Else
MsgBox "You Are Fail."
End If
End SubIn the above example, we have used NOT in the condition. We have two cell with the subject score. In one cell score is in numbers and in another cell it has grades.
- If a student has marks above 40 in the first subject and above E grade in the second subject then he/she is a PASS.
- If a student has marks above 40 in the first subject and above E grade in the second subject then he/she is PASS.
So every time when a student’s marks are more than 40 and a grade other than E we will get a message “You are Pass” or else “You are Fail”.
6. IF Statement With a Checkbox
Now, here we are using a checkbox to run a macro.

Sub ship_as_bill()
If Range("D15") = True Then
Range("D17:D21") = Range("C17:C21")
Else
If Range(“D15”) = False Then
Range("D17:D21").ClearContents
Else
MsgBox (“Error!”)
End If
End If
End SubIn the above example, we have used an IF statement to create a condition that if the checkbox is tick marked then range D17:D21 is equal to range C17:C21. And, if the checkbox is not ticked then range D17:D21 will be blank.
Using this technique we can use the billing address as the shipping address and if we need something else we can enter the address manually.
7. Check if a Cell is Merged
And here, we are writing a condition to get an alert if active cell is merged.

Sub MergeCellCheck()
If ActiveCell.MergeCells Then
MsgBox "Active Cell Is Merged"
Else
MsgBox "Active Cell Is Not Merged"
End If
End SubIn the above code, we have used merge cells to check whether the active cell is merged or not. If the active cell is merged then the condition will return an alert for that.
8. Delete the Entire Row if a Cell is Blank
Here we are using IF to check whether a row is blank or not. And, if that row is blank statement will delete that particular row.
Sub DeleteRow()
If Application.CountA(ActiveCell.EntireRow) = 0 Then
ActiveCell.EntireRow.Delete
Else
MsgBox Application.CountA(ActiveCell.EntireRow) & "Cell(s) have values in this row"
End If
End SubIn the above example, it will first check for the cells which have value in them. If the count of cells with a value is zero then the condition will delete the active row else return the alert showing the number of cells having value.
Conclusion
As I said it’s one of the most important parts of VBA and must learn if you want to master VBA. With the IF statement, you can write simple codes as well as complex codes. You can also use logical operators and write nested conditions.
I hope this guide will help you to write better codes.
Now tell me this. Do you write conditions in VBA frequently? What kind of codes do you write? Please share your views with me in the comment section. And, please don’t forget to share this guide with your friends.
Related: Exit IF