Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel for iPad Excel for iPhone Excel for Android tablets Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel for Android phones Excel Mobile Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
When you need to perform simple arithmetic calculations on several ranges of cells, sum the results, and use criteria to determine which cells to include in the calculations, consider using the SUMPRODUCT function.
SUMPRODUCT takes arrays and arithmetic operators as arguments. You can use arrays that evaluate as True or False (1 or 0) as criteria by using them as factors (multiplying them by the other arrays).
For example, suppose you want to calculate net sales for a particular sales agent by subtracting expenses from gross sales, as in this example.

-
Click a cell outside the ranges you are evaluating. This is where your result goes.
-
Type =SUMPRODUCT(.
-
Type (, enter or select a range of cells to include in your calculations, then type ). For example, to include the column Sales from the table Table1, type (Table1[Sales]).
-
Enter an arithmetic operator: *, /, +, —. This is the operation you will perform using the cells that meet any criteria you include; you can include more operators and ranges. Multiplication is the default operation.
-
Repeat steps 3 and 4 to enter additional ranges and operators for your calculations. After you add the last range you want to include in calculations, add a set of parentheses enclosing all the involved ranges, so that the entire calculation is enclosed. For example, ((Table1[Sales])+(Table1[Expenses])).
You may need to include additional parentheses inside your calculation to group various elements, depending on the arithmetic you want to perform.
-
To enter a range to use as a criterion, type *, enter the range reference normally, then after the range reference but before the right parenthesis, type =», then the value to match, then «. For example, *(Table1[Agent]=»Jones»). This causes the cells to evaluate as 1 or 0, so when multiplied by other values in the formula the result is either the same value or zero — effectively including or excluding the corresponding cells in any calculations.
-
If you have more criteria, repeat step 6 as needed. After your last range, type ).
Your completed formula might look like the one in our example above: =SUMPRODUCT(((Table1[Sales])-(Table1[Expenses]))*(Table1[Agent]=B8)), where cell B8 holds the agent name.
Need more help?
In this example, the goal is to use a formula to check if a specific value exists in a range. The easiest way to do this is to use the COUNTIF function to count occurences of a value in a range, then use the count to create a final result.
COUNTIF function
The COUNTIF function counts cells that meet supplied criteria. The generic syntax looks like this:
=COUNTIF(range,criteria)Range is the range of cells to test, and criteria is a condition that should be tested. COUNTIF returns the number of cells in range that meet the condition defined by criteria. If no cells meet criteria, COUNTIF returns zero. In the example shown, we can use COUNTIF to count the values we are looking for like this
COUNTIF(data,E5)Once the named range data (B5:B16) and cell E5 have been evaluated, we have:
=COUNTIF(data,E5)
=COUNTIF(B5:B16,"Blue")
=1COUNTIF returns 1 because «Blue» occurs in the range B5:B16 once. Next, we use the greater than operator (>) to run a simple test to force a TRUE or FALSE result:
=COUNTIF(data,B5)>0 // returns TRUE or FALSEBy itself, the formula above will return TRUE or FALSE. The last part of the problem is to return a «Yes» or «No» result. To handle this, we nest the formula above into the IF function like this:
=IF(COUNTIF(data,E5)>0,"Yes","No")This is the formula shown in the worksheet above. As the formula is copied down, COUNTIF returns a count of the value in column E. If the count is greater than zero, the IF function returns «Yes». If the count is zero, IF returns «No».
Slightly abbreviated
It is possible to shorten this formula slightly and get the same result like this:
=IF(COUNTIF(data,E5),"Yes","No")Here, we have remove the «>0» test. Instead, we simply return the count to IF as the logical_test. This works because Excel will treat any non-zero number as TRUE when the number is evaluated as a Boolean.
Testing for a partial match
To test a range to see if it contains a substring (a partial match), you can add a wildcard to the formula. For example, if you have a value to look for in cell C1, and you want to check the range A1:A100 for partial matches, you can configure COUNTIF to look for the value in C1 anywhere in a cell by concatenating asterisks on both sides:
=COUNTIF(A1:A100,"*"&C1&"*")>0
The asterisk (*) is a wildcard for one or more characters. By concatenating asterisks before and after the value in C1, the formula will count the text in C1 anywhere it appears in each cell of the range. To return «Yes» or «No», nest the formula inside the IF function as above.
An alternative formula using MATCH
As an alternative, you can use a formula that uses the MATCH function with the ISNUMBER function instead of COUNTIF:
=ISNUMBER(MATCH(value,range,0))
The MATCH function returns the position of a match (as a number) if found, and #N/A if not found. By wrapping MATCH inside ISNUMBER, the final result will be TRUE when MATCH finds a match and FALSE when MATCH returns #N/A.
To perform complicated and powerful data analysis, you need to test various conditions at a single point in time. The data analysis might require logical tests also within these multiple conditions.
For this, you need to perform Excel if statement with multiple conditions or ranges that include various If functions in a single formula.
Those who use Excel daily are well versed with Excel If statement as it is one of the most-used formula. Here you can check various Excel If or statement, Nested If, AND function, Excel IF statements, and how to use them. We have also provided a VIDEO TUTORIAL for different If Statements.
There are various If statements available in Excel. You have to know which of the Excel If you will work at what condition. Here you can check multiple conditions where you can use Excel If statement.
1) Excel If Statement
If you want to test a condition to get two outcomes then you can use this Excel If statement.
=If(Marks>=40, “Pass”)
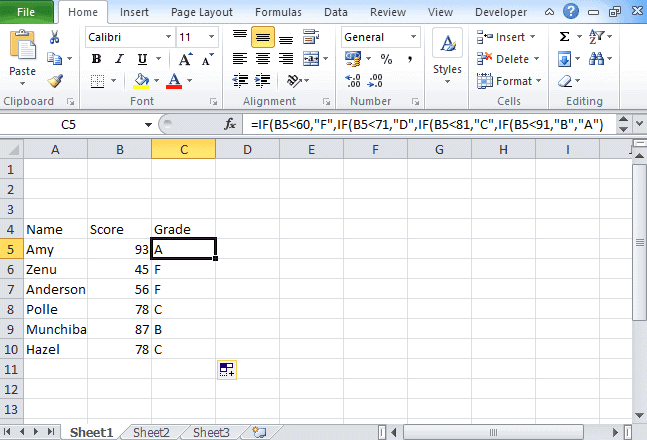
2) Nested If Statement
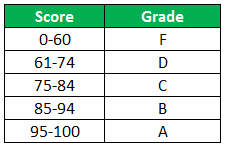
Let’s take an example that met the below-mentioned condition
- If the score is between 0 to 60, then Grade F
- If the score is between 61 to 70, then Grade D
- If the score is between 71 to 80, then Grade C
- If the score is between 81 to 90, then Grade B
- If the score is between 91 to 100, then Grade A
Then to test the condition the syntax of the formula becomes,
=If(B5<60, “F”,If(B5<71, “D”, If(B5<81,”C”,If(B5<91,”B”,”A”)
3) Excel If with Logical Test
There are 2 different types of conditions AND and OR. You can use the IF statement in excel between two values in both these conditions to perform the logical test.
AND Function: If you are performing the logical test based on AND function, then excel will give you TRUE as an outcome in every condition else it will return false.
OR Function: If you are using OR condition for the logical test, then excel will give you an outcome as TRUE if any of the situations match else it returns false.
For this, multiple testing is to be done using AND and OR function, you should gain expertise in using either or both of these with IF statement. Here we have used if the function with 3 conditions.
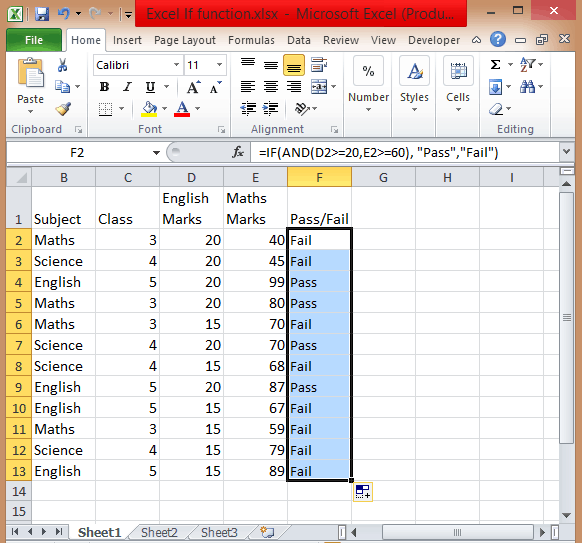
How to apply IF & AND function in Excel
- To perform this multiple if and statements in excel, we will take the data set for the student’s marks that contain fields such as English and Math’s Marks.
- The score of the English subject is stored in the D column whereas the Maths score is stored in column E.
- Let say a student passes the class if his or her score in English is greater than or equal to 20 and he or she scores more than 60 in Maths.
- To create a report in matters of seconds, if formula combined with AND can suffice.
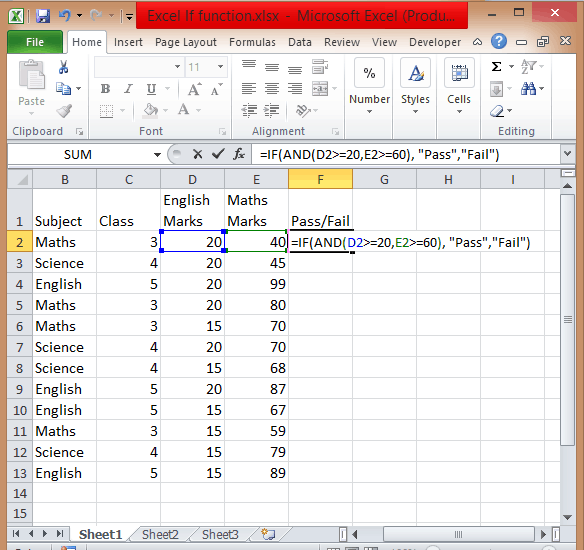
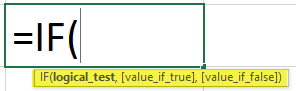
- Type =IF( Excel will display the logical hint just below the cell F2. The parameters of this function are logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false.
- The first parameter contains the condition to be matched. You can use multiple If and AND conditions combined in this logical test.
- In the second parameter, type the value that you want Excel to display if the condition is true. Similarly, in the third parameter type the value that will be displayed if your condition is false.
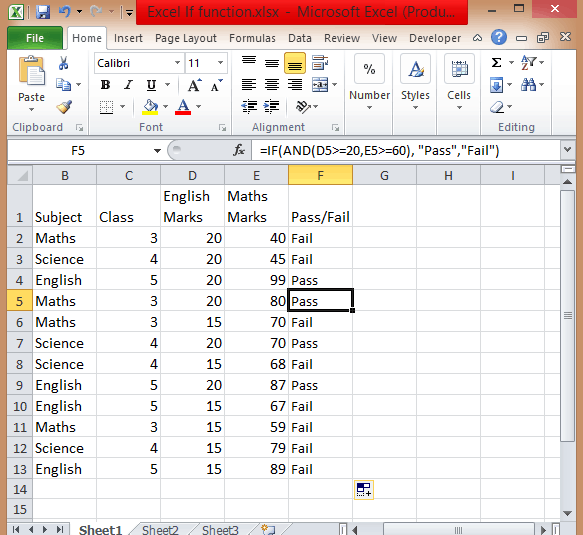
- Apply If & And formula, you will get =IF(AND(D2>=20,E2>=60),”Pass”,”Fail”).
- Add Pass/Fail column in the current table.
- After you have applied this formula, you will find the result in the column.
- Copy the formula from cell F2 and paste in all other cells from F3 to F13.
How to use If with Or function in Excel
To use If and Or statement excel, you need to apply a similar formula as you have applied for If & And with the only difference is that if any of the condition is true then it will show you True.
To apply the formula, you have to follow the above process. The formula is =IF((OR(D2>=20, E2>=60)), “Pass”, “Fail”). If the score is equal or greater than 20 for column D or the second score is equal or greater than 60 then the person is the pass.
How to Use If with And & Or function
If you want to test data based on several multiple conditions then you have to apply both And & Or functions at a single point in time. For example,
Situation 1: If column D>=20 and column E>=60
Situation 2: If column D>=15 and column E>=60
If any of the situations met, then the candidate is passed, else failed. The formula is
=IF(OR(AND(D2>=20, E2>=60), AND(D2>=20, E2>=60)), “Pass”, “Fail”).
4) Excel If Statement with other functions
Above we have learned how to use excel if statement multiple conditions range with And/Or functions. Now we will be going to learn Excel If Statement with other excel functions.
- Excel If with Sum, Average, Min, and Max functions
Let’s take an example where we want to calculate the performance of any student with Poor, Satisfactory, and Good.
If the data set has a predefined structure that will not allow any of the modifications. Then you can add values with this If formula:
=If((A2+B2)>=50, “Good”, If((A2+B2)=>30, “Satisfactory”, “Poor”))
Using the Sum function,
=If(Sum(A2:B2)>=120, “Good”, If(Sum(A2:B2)>=100, “Satisfactory”, “Poor”))
Using the Average function,
=If(Average(A2:B2)>=40, “Good”, If(Average(A2:B2)>=25, “Satisfactory”, “Poor”))
Using Max/Min,
If you want to find out the highest scores, using the Max function. You can also find the lowest scores using the Min function.
=If(C2=Max($C$2:$C$10), “Best result”, “ “)
You can also find the lowest scores using the Min function.
=If(C2=Min($C$2:$C$10), “Worst result”, “ “)
If we combine both these formulas together, then we get
=If(C2=Max($C$2:$C$10), “Best result”, If(C2=Min($C$2:$C$10), “Worst result”, “ “))
You can also call it as nested if functions with other excel functions. To get a result, you can use these if functions with various different functions that are used in excel.
So there are four different ways and types of excel if statements, that you can use according to the situation or condition. Start using it today.
So this is all about Excel If statement multiple conditions ranges, you can also check how to add bullets in excel in our next post.
I hope you found this tutorial useful
You may also like the following Excel tutorials:
- Multiple If Statements in Excel
- Excel Logical test
- How to Compare Two Columns in Excel (using VLOOKUP & IF)
- Using IF Function with Dates in Excel (Easy Examples)
What is IF Function in Excel?
IF function in Excel evaluates whether a given condition is met and returns a value depending on whether the result is “true” or “false”. It is a conditional function of Excel, which returns the result based on the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the given criteria.
For example, the IF formula in Excel can be applied as follows:
“=IF(condition A,“value B”,“value C”)”
The IF excel function returns “value B” if condition A is met and returns “value C” if condition A is not met.
It is often used to make logical interpretations which help in decision-making.
Table of contents
- What is IF Function in Excel?
- Syntax of the IF Excel Function
- How to Use IF Function in Excel?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Example #5
- Guidelines for the Multiple IF Statements
- Frequently Asked Question
- IF Excel Function Video
- Recommended Articles
Syntax of the IF Excel Function
The syntax of the IF function is shown in the following image:
The IF excel function accepts the following arguments:
- Logical_test: It refers to the condition to be evaluated. The condition can be a value or a logical expression.
- Value_if_true: It is the value returned as a result when the condition is “true”.
- Value_if_false: It is the value returned as a result when the condition is “false”.
In the formula, the “logical_test” is a required argument, whereas the “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” are optional arguments.
The IF formula uses logical operators to evaluate the values in a range of cells. The following table shows the different logical operatorsLogical operators in excel are also known as the comparison operators and they are used to compare two or more values, the return output given by these operators are either true or false, we get true value when the conditions match the criteria and false as a result when the conditions do not match the criteria.read more and their meaning.
| Operator | Meaning |
|---|---|
| = | Equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| <> | Not equal to |
How to Use IF Function in Excel?
Let us understand the working of the IF function with the help of the following examples in Excel.
You can download this IF Function Excel Template here – IF Function Excel Template
Example #1
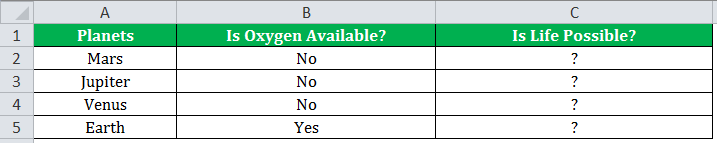
If there is no oxygen on a planet, life is impossible. If oxygen is available on a planet, then life is possible. The following table shows a list of planets in column A and the information on the availability of oxygen in column B. We have to find the planets where life is possible, based on the condition of oxygen availability.
Let us apply the IF formula to cell C2 to find out whether life is possible on the planets listed in the table.
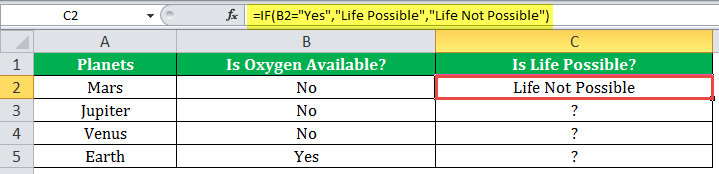
The IF formula is stated as follows:
“=IF(B2=“Yes”, “Life is Possible”, “Life is Not Possible”)
The succeeding image shows the IF formula applied to cell C2.
The subsequent image shows how the IF formula is applied to the range of cells C2:C5.
Drag the cells to view the output of all the planets.
The output in the below worksheet shows life is possible on the planet Earth.
Flow Chart of Generic IF Excel Function
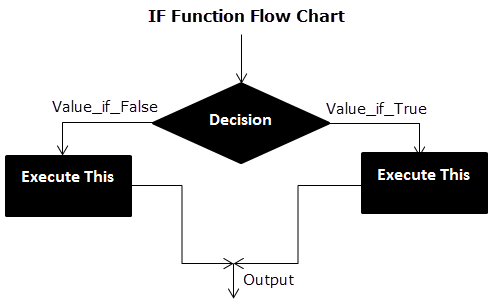
The IF Function Flow Chart for Mars (Example #1)

The flow of IF function flowchart for Jupiter and Venus is the same as the IF function flowchart for Mars (Example #1).
The IF Function Flow Chart for Earth

Hence, the IF excel function allows making logical comparisons between values. The modus operandi of the IF function is stated as: If something is true, then do something; otherwise, do something else.
Example #2
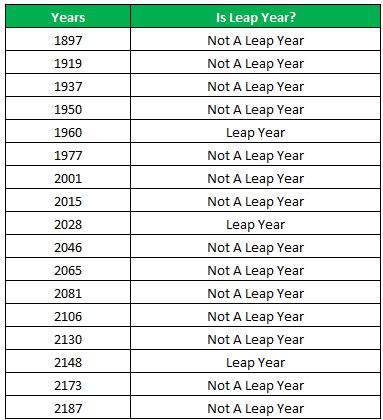
The following table shows a list of years. We want to find out if the given year is a leap year or not.
A leap year has 366 days; the extra day is the 29th of February. The criteria for a leap year are stated as follows:
- The year will be exactly divisible by 4 and not exactly be divisible by 100 or
- The year will be exactly divisible by 400.
In this example, we will use the IF function along with the AND, OR, and MOD functions to find the leap years.
We use the MOD function to find a remainder after a dividend is divided by a divisor.
The AND functionThe AND function in Excel is classified as a logical function; it returns TRUE if the specified conditions are met, otherwise it returns FALSE.read more evaluates both the conditions of the leap years for the value “true”. The OR functionThe OR function in Excel is used to test various conditions, allowing you to compare two values or statements in Excel. If at least one of the arguments or conditions evaluates to TRUE, it will return TRUE. Similarly, if all of the arguments or conditions are FALSE, it will return FASLE.read more evaluates either of the condition for the value “true”.
We will apply the MOD function to the conditions as follows:
If MOD(year,4)=0 and MOD(year,100)<>(is not equal to) 0, then the year is a leap year.
or
If MOD(year,400)=0, then the year is a leap year; otherwise, the year is not a leap year.
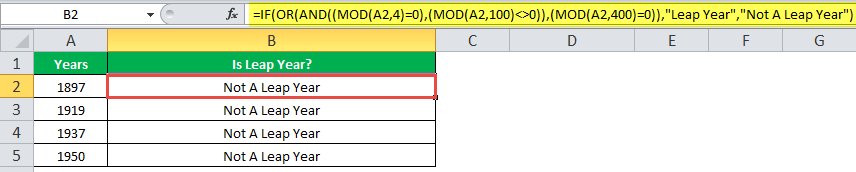
The IF formula is stated as follows:
“=IF(OR(AND((MOD(year,4)=0),(MOD(year,100)<>0)),(MOD(year,400)=0)),“Leap Year”, “Not A Leap Year”)”
The argument “year” refers to a reference value.
The following images show the output of the IF formula applied in the range of cells.
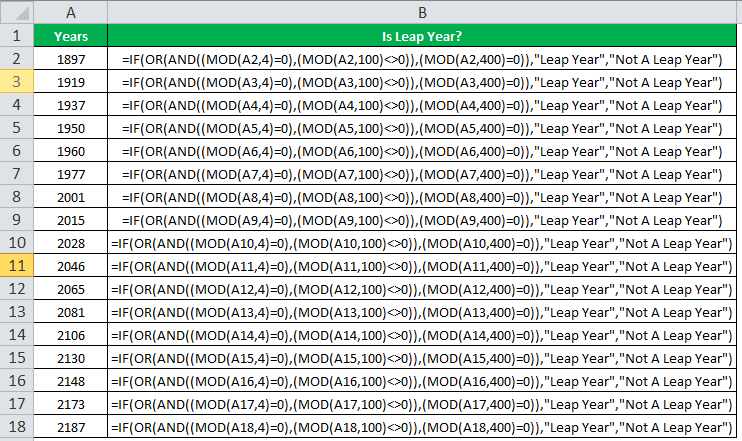
The following image shows how the IF formula is applied to the range of cells B2:B18.
The succeeding table shows the years 1960, 2028, and 2148 as leap years and the remaining as non-leap years.
The result of the IF excel formula is displayed for the range of cells B2:B18 in the following image.
Example #3
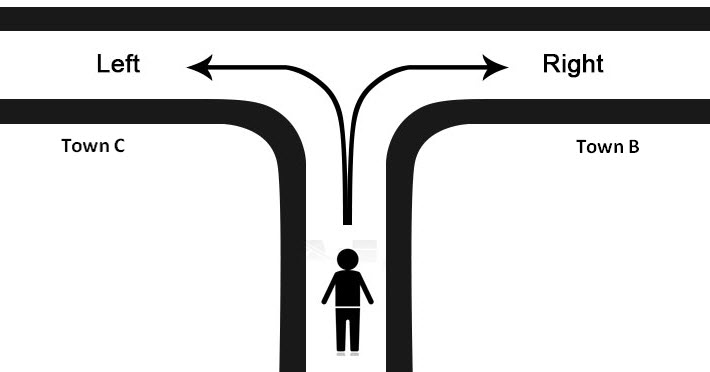
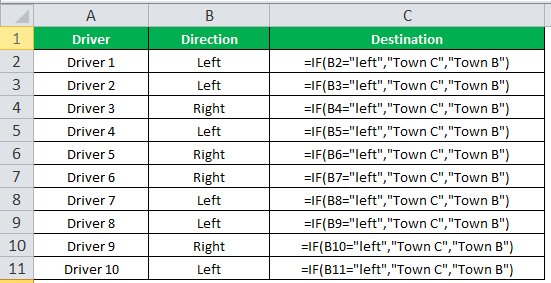
The succeeding table shows a list of drivers and the directions they undertook to reach the destination. It is preceded by an image of the road intersection explaining the turns taken by the drivers and their destinations. The right turn leads to town B, and the left turn leads to town C. Identify the driver’s destination to town B and town C.
Road Intersection Image
Let us apply the IF excel function to find the destination. Here, the condition is mentioned as follows:
- If the driver turns right, he/she reaches town B.
- If the driver turns left, he/she reaches town C.
We use the following IF formula to find the destination:
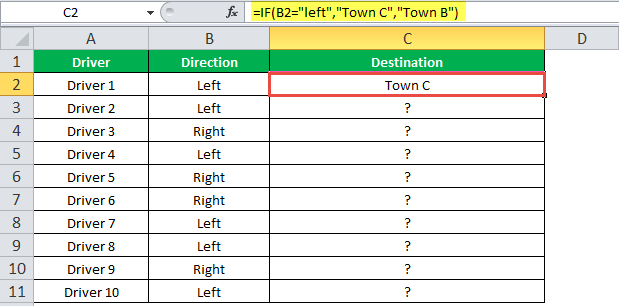
“=IF(B2=“Left”, “Town C”, “Town B”)”
The succeeding image shows the output of the IF formula applied to cell C2.
Drag the cells to use the formula in the range C2:C11. Finally, we get the destinations of each driver for their turning movements.
The below image displays the IF formula applied to the range.
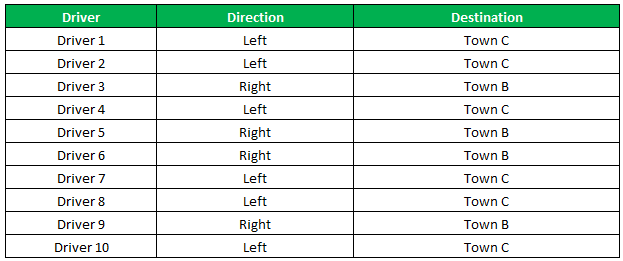
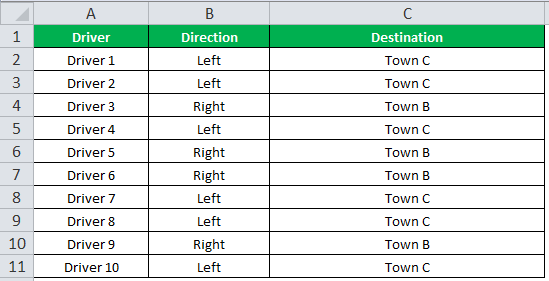
The output of the IF formula and the destinations are displayed in the succeeding image.
The result shows that six drivers reached town C, and the remaining four have reached town B.
Example #4
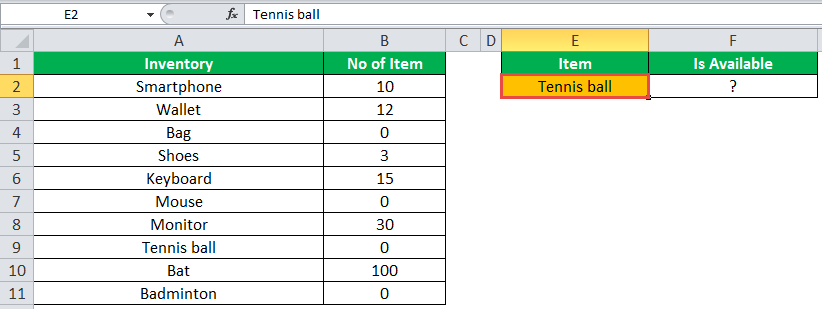
The following table shows a list of items and their inventory levels. We want to check if the specific item is available in the inventory or not using the IF function.
Let us list the name of items in column A and the number of items in column B. The list of data to be validated for the entire items list is shown in the cell E2 of the below image.
We use the Excel IF along with the VLOOKUP functionThe VLOOKUP excel function searches for a particular value and returns a corresponding match based on a unique identifier. A unique identifier is uniquely associated with all the records of the database. For instance, employee ID, student roll number, customer contact number, seller email address, etc., are unique identifiers.
read more to check the availability of the items in the inventory.
The VLOOKUP function looks up the values referring to the number of items, and the IF function will check whether the item number is greater than zero or not.
We will apply the following IF formula in the F2 cell:
“=IF(VLOOKUP(E2,A2:B11,2,0)=0, “Item Not Available”,“Item Available”)”
If the lookup value of an item is equal to 0, then the item is not available; else, the item is available.
The succeeding image shows the result of the IF formula in the cell F2.
Select “bat” in the E2 item cell to know whether the item is available or not in the inventory (as shown in the following image).
Example #5
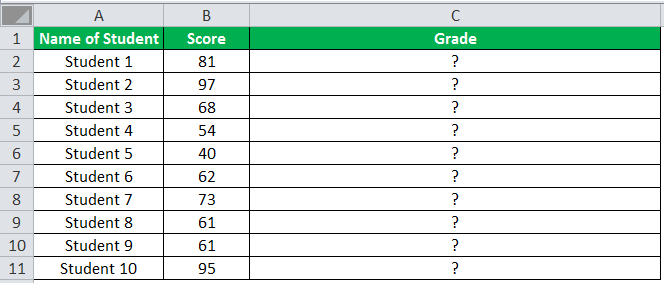
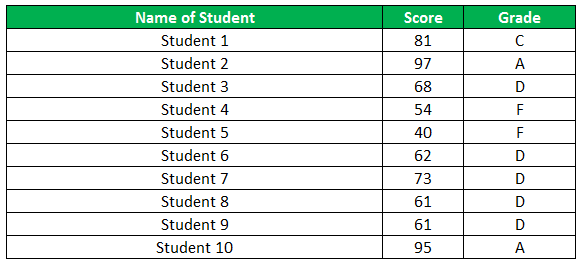
The following table shows the list of students and their marks. The grade criteria are provided based on the marks obtained by the students. We want to find the grade of each student in the list.
We apply the Nested IF in Excel since we have multiple criteria to find and decide each student’s grade.
The Nesting of IF function uses the IF function inside another IF formula when multiple conditions are to be fulfilled.
The syntax of Nesting of IF function is stated as follows:
“=IF( condition1, value_if_true1, IF( condition2, value_if_true2, value_if_false2 ))”
The succeeding table represents the range of scores and the grades, respectively.
Let us apply the multiple IF conditions with AND function in the below-nested formula to find out the grade of the students:
“=IF((B2>=95),“A”,IF(AND(B2>=85,B2<=94),“B”,IF(AND(B2>=75,B2<=84),“C”,IF(AND(B2>=61,B2<=74),“D”,“F”))))”
The IF function checks the logical condition as shown in the formula below:
“=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true],[value_if_false])”
We will split the above-mentioned nested formula and check the IF statements as shown below:
First Logical Test: B2>=95
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “A” (Grade A) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- Value_if_false, then the formula finds another IF condition and enter IF condition
Second Logical Test: B2>=85(logical expression 1) and B2<=94(logical expression 2)
(We use AND function to check the multiple logical expressions as the two given conditions are to be evaluated for “true.”)
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “B” (Grade B) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- Value_if_false, then the formula finds another IF condition and enter IF condition
Third Logical Test: B2>=75(logical expression 1) and B2<=84(logical expression 2)
(We use AND function to check the multiple logical expressions as the two given conditions are to be evaluated for “true.”)
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “C” (Grade C) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- value_if_false, then the formula finds another IF condition and enter IF condition
Fourth Logical Test: B2>=61(logical expression 1) and B2<=74(logical expression 2)
(We use AND function to check the multiple logical expressions as the two given conditions are to be evaluated for “true.”)
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “D” (Grade D) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- Value_if_false, execute: “F” (Grade F)
- Finally, close the parenthesis.
The below image displays the output of the IF formula applied to the range.
The succeeding image shows the IF nested formula applied to the range.
The grades of the students are listed in the following table.
Guidelines for the Multiple IF Statements
The guidelines for the multiple IF statements are listed as follows:
- Use nested IF function to a limited extent as multiple IF statements require a great deal of thought to be accurate.
- Multiple IF statementsIn Excel, multiple IF conditions are IF statements that are contained within another IF statement. They are used to test multiple conditions at the same time and return distinct values. Additional IF statements can be included in the ‘value if true’ and ‘value if false’ arguments of a standard IF formula.read more require multiple parentheses (), which is often difficult to manage. Excel provides a way to check the color of each opening and closing parenthesis to avoid this situation. The last closing parenthesis color will always be black, denoting the end of the formula statement.
- Whenever we pass a string value for the arguments “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” or test a reference against a string value, enclose the string value in double quotes. Passing a string value without quotes will result in “#NAME?” error.
Frequently Asked Question
1. What is the IF function in Excel?
The Excel IF function is a logical function that checks the given criteria and returns one value for a “true” and another value for a “false” result.
The syntax of the IF function is stated as follows:
“=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])”
The arguments are as follows:
1. Logical_test – It refers to a value or condition that is tested.
2. Value_if_true – It is the value returned when the condition logical_test is “true.”
3. Value_if_false – It is the value returned when the condition logical_test is “false.”
The “logical_test” is a required argument, whereas the “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” are optional arguments.
2. How to use the IF Excel function with multiple conditions?
The IF Excel statement for multiple conditions is created by using multiple IF functions in a single formula.
The syntax of IF function with multiple conditions is stated as follows:
“=IF (condition 1_“true”, do something, IF (condition 2_“true”, do something, IF (condition 3_ “true”, do something, else do something)))”
3. How to use the function IFERROR in Excel?
IF Excel Function Video
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the IF function in Excel. Here we discuss how to use the IF function along with examples and downloadable templates. You may also look at these useful functions –
- What is the Logical Test in Excel?A logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more
- “Not Equal to” in Excel“Not Equal to” argument in excel is inserted with the expression <>. The two brackets posing away from each other command excel of the “Not Equal to” argument, and the user then makes excel checks if two values are not equal to each other.read more
- Data Validation ExcelThe data validation in excel helps control the kind of input entered by a user in the worksheet.read more
The logical IF statement in Excel is used for the recording of certain conditions. It compares the number and / or text, function, etc. of the formula when the values correspond to the set parameters, and then there is one record, when do not respond — another.
Logic functions — it is a very simple and effective tool that is often used in practice. Let us consider it in details by examples.
The syntax of the function «IF» with one condition
The operation syntax in Excel is the structure of the functions necessary for its operation data.
=IF(boolean;value_if_TRUE;value_if_FALSE)
Let us consider the function syntax:
- Boolean – what the operator checks (text or numeric data cell).
- Value_if_TRUE – what will appear in the cell when the text or numbers correspond to a predetermined condition (true).
- Value_if_FALSE – what appears in the box when the text or the number does not meet the predetermined condition (false).
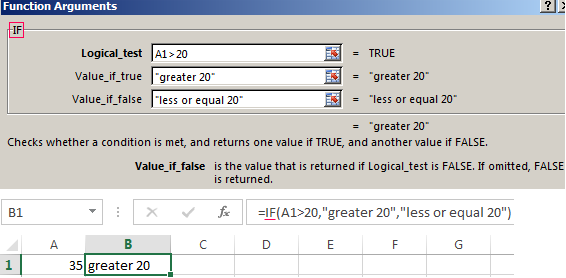
Example:
Logical IF functions.
The operator checks the A1 cell and compares it to 20. This is a «Boolean». When the contents of the column is more than 20, there is a true legend «greater 20». In the other case it’s «less or equal 20».
Attention! The words in the formula need to be quoted. For Excel to understand that you want to display text values.
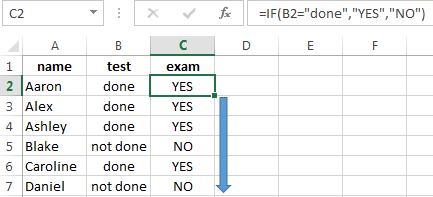
Here is one more example. To gain admission to the exam, a group of students must successfully pass a test. The results are listed in a table with columns: a list of students, a credit, an exam.
The statement IF should check not the digital data type but the text. Therefore, we prescribed in the formula В2= «done» We take the quotes for the program to recognize the text correctly.
The function IF in Excel with multiple conditions
Usually one condition for the logic function is not enough. If you need to consider several options for decision-making, spread operators’ IF into each other. Thus, we get several functions IF in Excel.
The syntax is as follows:
Here the operator checks the two parameters. If the first condition is true, the formula returns the first argument is the truth. False — the operator checks the second condition.
Examples of a few conditions of the function IF in Excel:
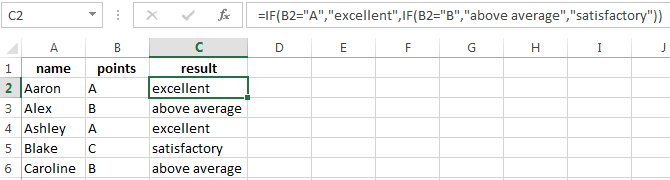
It’s a table for the analysis of the progress. The student received 5 points:
- А – excellent;
- В – above average or superior work;
- C – satisfactory;
- D – a passing grade;
- E – completely unsatisfactory.
IF statement checks two conditions: the equality of value in the cells.
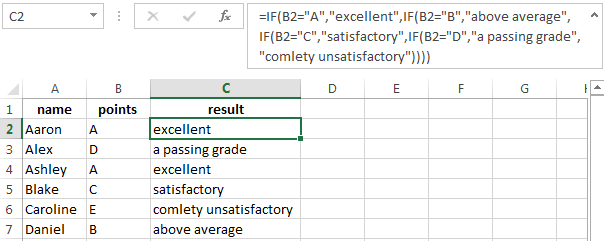
In this example, we have added a third condition, which implies the presence of another report card and «twos». The principle of the operator is the same.
Enhanced functionality with the help of the operators «AND» and «OR»
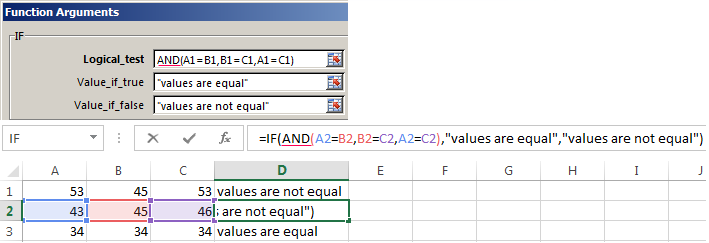
When you need to check out a few of the true conditions you use the function И. The point is: IF A = 1 AND A = 2 THEN meaning в ELSE meaning с.
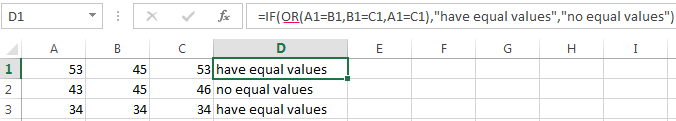
OR function checks the condition 1 or condition 2. As soon as at least one condition is true, the result is true. The point is: IF A = 1 OR A = 2 THEN value B ELSE value C.
Functions AND & OR can check up to 30 conditions.
An example of using the operator AND:
It’s the example of using the logical operator OR.
How to compare data in two tables
Users often need to compare the two spreadsheets in an Excel to match. Examples of the «life»: compare the prices of goods in different bringing, to compare balances (accounting reports) in a few months, the progress of pupils (students) of different classes, in different quarters, etc.
To compare the two tables in Excel, you can use the COUNTIFS statement. Consider the order of application functions.
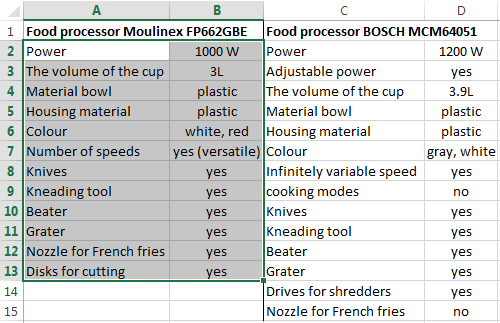
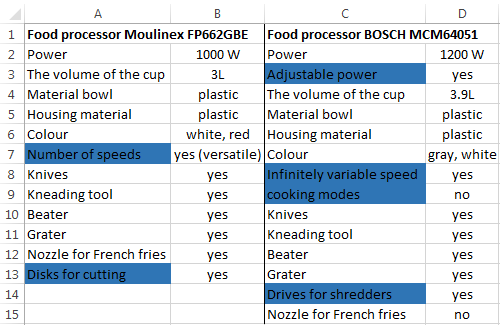
For example, consider the two tables with the specifications of various food processors. We planned allocation of color differences. This problem in Excel solves the conditional formatting.
Baseline data (tables, which will work with):
Select the first table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use a formula to determine the formatted cells:
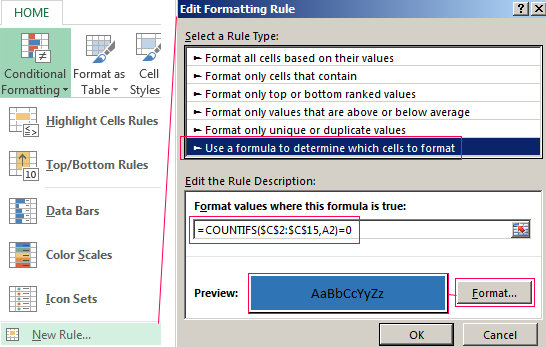
In the formula bar write: = COUNTIFS (comparable range; first cell of first table)=0. Comparing range is in the second table.
To drive the formula into the range, just select it first cell and the last. «= 0» means the search for the exact command (not approximate) values.
Choose the format and establish what changes in the cell formula in compliance. It’s better to do a color fill.
Select the second table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use the formula. Use the same operator (COUNTIFS). For the second table formula:
Download all examples in Excel
Now it is easy to compare the characteristics of the data in the table.