Skip to content
В статье описано, как использовать функцию ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel для обнаружения ошибок и замены их пустой ячейкой, другим значением или определённым сообщением. Покажем примеры, как использовать функцию ЕСЛИОШИБКА с функциями визуального просмотра и сопоставления индексов, а также как она сравнивается с ЕСЛИ ОШИБКА и ЕСНД.
«Дайте мне точку опоры, и я переверну землю», — сказал однажды Архимед. «Дайте мне формулу, и я заставлю ее вернуть ошибку», — сказал бы пользователь Excel. Здесь мы не будем рассматривать, как получить ошибки в Excel. Мы узнаем, как предотвратить их, чтобы ваши таблицы были чистыми, а формулы — понятными и точными.
Итак, вот о чем мы поговорим:
Что означает функция Excel ЕСЛИОШИБКА
Функция ЕСЛИОШИБКА (IFERROR по-английски) предназначена для обнаружения и устранения ошибок в формулах и вычислениях. Это значит, что функция ЕСЛИОШИБКА должна выполнить определенные действия, если видит какую-либо ошибку. Более конкретно, она проверяет формулу и, если вычисление дает ошибку, то она возвращает какое-то другое значение, которое вы ей укажете. Если же всё хорошо, то просто возвращает результат формулы.
Синтаксис функции Excel ЕСЛИОШИБКА следующий:
ЕСЛИОШИБКА(значение; значение_если_ошибка)
Где:
- Значение (обязательно) — что проверять на наличие ошибок. Это может быть формула, выражение или ссылка на ячейку.
- Значение_если_ошибка (обязательно) — что возвращать при обнаружении ошибки. Это может быть пустая строка (получится пустая ячейка), текстовое сообщение, числовое значение, другая формула или вычисление.
Например, при делении двух столбцов чисел можно получить кучу разных ошибок, если в одном из столбцов есть пустые ячейки, нули или текст.
Рассмотрим простой пример:
Чтобы этого не произошло, используйте формулу ЕСЛИОШИБКА, чтобы перехватывать и обрабатывать их нужным вам образом.
Если ошибка, то пусто
Укажите пустую строку (“”) в аргументе значение_если_ошибка, чтобы вернуть пустую ячейку, если обнаружена ошибка:
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(A4/B4; «»)
Вернемся к нашему примеру и используем ЕСЛИОШИБКА:
Как видите по сравнению с первым скриншотом, вместо стандартных сообщений мы видим просто пустые ячейки.
Если ошибка, то показать сообщение
Вы также можете отобразить собственное сообщение вместо стандартного обозначения ошибок Excel:
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(A4/B4; «Ошибка в вычислениях»)
Перед вами – третий вариант нашей небольшой таблицы.
5 фактов, которые нужно знать о функции ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel
- ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel обрабатывает все типы ошибок, включая #ДЕЛ/0!, #Н/Д, #ИМЯ?, #NULL!, #ЧИСЛО!, #ССЫЛКА! и #ЗНАЧ!.
- В зависимости от содержимого аргумента значение_если_ошибка функция может заменить ошибки вашим текстовым сообщением, числом, датой или логическим значением, результатом другой формулы или пустой строкой (пустой ячейкой).
- Если аргумент значение является пустой ячейкой, он обрабатывается как пустая строка (»’), но не как ошибка.
- ЕСЛИОШИБКА появилась в Excel 2007 и доступна во всех последующих версиях Excel 2010, Excel 2013, Excel 2016, Excel 2019, Excel 2021 и Excel 365.
- Чтобы перехватывать ошибки в Excel 2003 и более ранних версиях, используйте функцию ЕОШИБКА в сочетании с функцией ЕСЛИ, например как показано ниже:
=ЕСЛИ(ЕОШИБКА(A4/B4);»Ошибка в вычислениях»;A4/B4)
Далее вы увидите, как можно использовать ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel в сочетании с другими функциями для выполнения более сложных задач.
ЕСЛИОШИБКА с функцией ВПР
Часто встречающаяся задача в Excel – поиск нужного значения в таблице в соответствии с определёнными критериями. И не всегда этот поиск бывает успешным. Одним из наиболее распространенных применений функции ЕСЛИОШИБКА является сообщение пользователям, что искомое значение не найдено в базе данных. Для этого вы заключаете формулу ВПР в функцию ЕСЛИОШИБКА примерно следующим образом:
ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР( … );»Не найдено»)
Если искомое значение отсутствует в таблице, которую вы просматриваете, обычная формула ВПР вернет ошибку #Н/Д:
Для лучшего понимания таблицы и улучшения ее внешнего вида, заключите функцию ВПР в ЕСЛИОШИБКА и покажите более понятное для пользователя сообщение:
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР(D3; $A$3:$B$5; 2;ЛОЖЬ); «Не найдено»)
На скриншоте ниже показан пример ЕСЛИОШИБКА вместе с ВПР в Excel:
Если вы хотите перехватывать только #Н/Д, но не все подряд ошибки, используйте функцию ЕНД вместо ЕСЛИОШИБКА. Она просто возвращает ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ в зависимости от появления ошибки #Н/Д. Поэтому нам здесь еще понадобится функция ЕСЛИ, чтобы обработать эти логические значения:
=ЕСЛИ(ЕНД(ВПР(D3; $A$3:$B$5; 2;ЛОЖЬ)); «Не найдено»;ВПР(D3; $A$3:$B$5; 2;ЛОЖЬ))
Дополнительные примеры формул Excel ЕСЛИОШИБКА ВПР можно также найти в нашей статье Как убрать сообщение #Н/Д в ВПР?
Вложенные функции ЕСЛИОШИБКА для выполнения последовательных ВПР
В ситуациях, когда вам нужно выполнить несколько операций ВПР в зависимости от того, была ли предыдущая ВПР успешной или неудачной, вы можете вложить две или более функции ЕСЛИОШИБКА одну в другую.
Предположим, у вас есть несколько отчетов о продажах из региональных отделений вашей компании, и вы хотите получить сумму по определенному идентификатору заказа. С ячейкой В9 в качестве критерия поиска (номер заказа) и тремя небольшими таблицами поиска (таблица 1, 2 и 3), формула выглядит следующим образом:
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР(B9;A3:B6;2;0);ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР(B9;D3:E6;2;0);ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР(B9;G3:H6;2;0);»Не найден»)))
Результат будет выглядеть примерно так, как на рисунке ниже:
То есть, если поиск завершился неудачей (то есть, ошибкой) первой таблице, начинаем искать во второй, и так далее. Если нигде ничего не нашли, получим сообщение «Не найден».
ЕСЛИОШИБКА в формулах массива
Как вы, наверное, знаете, формулы массива в Excel предназначены для выполнения нескольких вычислений внутри одной формулы. Если вы в аргументе значение функции ЕСЛИОШИБКА укажете формулу или выражение, которое возвращает массив, она также обработает и вернет массив значений для каждой ячейки в указанном диапазоне. Пример ниже поможет пояснить это.
Допустим, у вас есть Сумма в столбце B и Цена в столбце C, и вы хотите вычислить Количество. Это можно сделать с помощью следующей формулы массива, которая делит каждую ячейку в диапазоне B2:B4 на соответствующую ячейку в диапазоне C2:C4, а затем суммирует результаты:
=СУММ(($B$2:$B$4/$C$2:$C$4))
Формула работает нормально, пока в диапазоне делителей нет нулей или пустых ячеек. Если есть хотя бы одно значение 0 или пустая строка, то возвращается ошибка: #ДЕЛ/0! Из-за одной некорректной позиции мы не можем получить итоговый результат.
Чтобы исправить эту ситуацию, просто вложите деление внутрь формулы ЕСЛИОШИБКА:
=СУММ(ЕСЛИОШИБКА($B$2:$B$4/$C$2:$C$4;0))
Что делает эта формула? Делит значение в столбце B на значение в столбце C в каждой строке (3500/100, 2000/50 и 0/0) и возвращает массив результатов {35; 40; #ДЕЛ/0!}. Функция ЕСЛИОШИБКА перехватывает все ошибки #ДЕЛ/0! и заменяет их нулями. Затем функция СУММ суммирует значения в итоговом массиве {35; 40; 0} и выводит окончательный результат (35+40=75).
Примечание. Помните, что ввод формулы массива должен быть завершен нажатием комбинации Ctrl + Shift + Enter (если у вас не Office365 или Excel2021 – они понимают формулы массива без дополнительных телодвижений).
ЕСЛИОШИБКА или ЕСЛИ + ЕОШИБКА?
Теперь, когда вы знаете, как использовать функцию ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel, вы можете удивиться, почему некоторые люди все еще склоняются к использованию комбинации ЕСЛИ + ЕОШИБКА. Есть ли у этого старого метода преимущества по сравнению с ЕСЛИОШИБКА?
В старые недобрые времена Excel 2003 и более ранних версий, когда ЕСЛИОШИБКА не существовало, совместное использование ЕСЛИ и ЕОШИБКА было единственным возможным способом перехвата ошибок. Это просто немного более сложный способ достижения того же результата.
Например, чтобы отловить ошибки ВПР, вы можете использовать любую из приведенных ниже формул.
В Excel 2007 — Excel 2016:
ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР( … ); «Не найдено»)
Во всех версиях Excel:
ЕСЛИ(ЕОШИБКА(ВПР(…)); «Не найдено»; ВПР(…))
Обратите внимание, что в формуле ЕСЛИ ЕОШИБКА ВПР вам нужно дважды выполнить ВПР. Чтобы лучше понять, расшифруем: если ВПР приводит к ошибке, вернуть «Не найдено», в противном случае вывести результат ВПР.
А вот простой пример формулы Excel ЕСЛИ ЕОШИБКА ВПР:
=ЕСЛИ(ЕОШИБКА(ВПР(D2; A2:B5;2;ЛОЖЬ)); «Не найдено»; ВПР(D2; A2:B5;2;ЛОЖЬ ))
ЕСЛИОШИБКА против ЕСНД
Представленная в Excel 2013, ЕСНД (IFNA в английской версии) — это еще одна функция для проверки формулы на наличие ошибок. Его синтаксис похож на синтаксис ЕСЛИОШИБКА:
ЕСНД(значение; значение_если_НД)
Чем ЕСНД отличается от ЕСЛИОШИБКА? Функция ЕСНД перехватывает только ошибки #Н/Д, тогда как ЕСЛИОШИБКА обрабатывает все типы ошибок.
В каких ситуациях вы можете использовать ЕСНД? Когда нецелесообразно скрывать все ошибки. Например, при работе с важными данными вы можете захотеть получать предупреждения о возможных ошибках в вашем наборе данных (случайном делении на ноль и т.п.), а стандартные сообщения об ошибках Excel с символом «#» могут быть яркими визуальными индикаторами проблем.
Давайте посмотрим, как можно создать формулу, отображающую сообщение «Не найдено» вместо ошибки «Н/Д», которая появляется, когда искомое значение отсутствует в наборе данных, но при этом вы будете видеть все другие ошибки Excel.
Предположим, вы хотите получить Количество из таблицы поиска в таблицу с результатами, как показано на рисунке ниже. Проще всего было бы использовать ЕСЛИОШИБКА с ВПР. Таблица приобрела бы красивый вид, но при этом за надписью «Не найдено» были бы скрыты не только ошибки поиска, но и все другие ошибки. И мы не заметили бы, что в исходной таблице поиска у нас есть ошибка деления на ноль, так как не заполнена цена персиков. Поэтому более разумно использовать ЕСНД, чтобы с ее помощью обработать только ошибки поиска:
=ЕСНД(ВПР(F3; $A$3:$D$6; 4;ЛОЖЬ); «Не найдено»)
Или подойдет комбинация ЕСЛИ ЕНД для старых версий Excel:
=ЕСЛИ(ЕНД(ВПР(F3; $A$3:$D$6; 4;ЛОЖЬ));»Не найдено»; ВПР(F3; $A$3:$D$6; 4;ЛОЖЬ))
Как видите, формула ЕСНД с ВПР возвращает «Не найдено» только для товара, которого нет в таблице поиска (Сливы). Для персиков она показывает #ДЕЛ/0! что указывает на то, что наша таблица поиска содержит ошибку деления на ноль.
Рекомендации по использованию ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel
Итак, вы уже знаете, что функция ЕСЛИОШИБКА — это самый простой способ отлавливать ошибки в Excel и маскировать их пустыми ячейками, нулевыми значениями или собственными сообщениями. Однако это не означает, что вы должны обернуть каждую формулу в функцию обработки ошибок.
Эти простые рекомендации могут помочь вам сохранить баланс.
- Не ловите ошибки без весомой на то причины.
- Оберните в ЕСЛИОШИБКА только ту часть формулы, где по вашему мнению могут возникнуть проблемы.
- Чтобы обрабатывать только определенные ошибки, используйте другую функцию обработки ошибок с меньшей областью действия:
- ЕСНД или ЕСЛИ ЕНД для обнаружения только ошибок #H/Д.
- ЕОШ для обнаружения всех ошибок, кроме #Н/Д.
Мы постарались рассказать, как можно использовать функцию ЕСЛИОШИБКА в Excel. Примеры перехвата и обработки ошибок могут быть полезны и для «чайников», и для более опытных пользователей.
Также рекомендуем:
Функция IFERROR (ЕСЛИОШИБКА) в Excel лучше всего подходит для обработки случаев, когда формулы возвращают ошибку. Используя эту функцию, вы можете указать, какое значение функция должна возвращать вместо ошибки. Если функция в ячейке не возвращает ошибку, то возвращается её собственный результат.
Содержание
- Видеоурок
- Что возвращает функция
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции
- Дополнительная информация
- Примеры использования функции IFERROR (ЕСЛИОШИБКА) в Excel
- Пример 1. Заменяем ошибки в ячейке на пустые значения
- Пример 2. Заменяем значения без данных при использовании функции VLOOKUP (ВПР) на “Не найдено”
- Пример 3. Возвращаем значение “0” вместо ошибок формулы
Видеоурок
Что возвращает функция
Указанное вами значение, в случае если в ячейке есть ошибка.
Синтаксис
=IFERROR(value, value_if_error) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(значение;значение_если_ошибка) — русская версия
Аргументы функции
- value (значение) — это аргумент, который проверяет, есть ли в ячейке ошибка. Обычно, ошибкой может быть результат какого либо вычисления;
- value_if_error (значение_если_ошибка) — это аргумент, который заменяет ошибку в ячейке (в случае её наличия) на указанное вами значение. Ошибки могут выглядеть так: #N/A, #REF!, #DIV/0!, #VALUE!, #NUM!, #NAME?, #NULL! (английская версия Excel) или #ЗНАЧ!, #ДЕЛ/0, #ИМЯ?, #Н/Д, #ССЫЛКА!, #ЧИСЛО!, #ПУСТО! (русская версия Excel).
Дополнительная информация
- Если вы используете кавычки («») в качестве аргумента value_if_error (значение_если_ошибка), ячейка ничего не отображает в случае ошибки.
- Если аргумент value (значение) или value_if_error (значение_если_ошибка) ссылается на пустую ячейку, она рассматривается как пустая.
Примеры использования функции IFERROR (ЕСЛИОШИБКА) в Excel
Пример 1. Заменяем ошибки в ячейке на пустые значения
Если вы используете функции, которые могут возвращать ошибку, вы можете заключить ее в функцию и указать пустое значение, возвращаемое в случае ошибки.
В примере, показанном ниже, результатом ячейки D4 является # DIV/0!.
Для того, чтобы убрать информацию об ошибке в ячейке используйте эту формулу:
=IFERROR(A1/A2,””) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(A1/A2;»») — русская версия
В данном случае функция проверит, выдает ли формула в ячейке ошибку, и, при её наличии, выдаст пустой результат.
В качестве результата формулы, исправляющей ошибки, вы можете указать любой текст или значение, например, с помощью следующей формулы:

=IFERROR(A1/A2,”Error”) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(A1/A2;»») — русская версия
Если вы пользуетесь версией Excel 2003 или ниже, вы не найдете функцию IFERROR (ЕСЛИОШИБКА). Вместо нее вы можете использовать обычную функцию IF или ISERROR.
Пример 2. Заменяем значения без данных при использовании функции VLOOKUP (ВПР) на “Не найдено”
Когда мы используем функцию VLOOKUP (ВПР), часто сталкиваемся с тем, что при отсутствии данных по каким либо значениям, формула выдает ошибку “#N/A”.
На примере ниже, мы хотим с помощью функции VLOOKUP (ВПР) для выбранных студентов подставить данные из результатов экзамена.
На примере выше, в списке студентов с результатами экзамена нет данных по имени Иван, в результате, при использовании функции VLOOKUP (ВПР), формула нам выдает ошибку.
Как раз в этом случае мы можем воспользоваться функцией IFERROR (ЕСЛИОШИБКА), для того, чтобы результат вычислений выглядел корректно, без ошибок. Добиться этого мы можем с помощью формулы:
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(D2,$A$2:$B$12,2,0),”Не найдено”) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИОШИБКА(ВПР(D2;$A$2:$B$12;2;0);»Не найдено») — русская версия
Пример 3. Возвращаем значение “0” вместо ошибок формулы
Если у вас нет конкретного значения, которое вы бы хотели использовать для замены ошибок — оставляйте аргумент функции value_if_error (значение_если_ошибка) пустым, как показано на примере ниже и в случае наличия ошибки, функция будет выдавать “0”:
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel Web App Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
You can use the IFERROR function to trap and handle errors in a formula. IFERROR returns a value you specify if a formula evaluates to an error; otherwise, it returns the result of the formula.
Syntax
IFERROR(value, value_if_error)
The IFERROR function syntax has the following arguments:
-
value Required. The argument that is checked for an error.
-
value_if_error Required. The value to return if the formula evaluates to an error. The following error types are evaluated: #N/A, #VALUE!, #REF!, #DIV/0!, #NUM!, #NAME?, or #NULL!.
Remarks
-
If value or value_if_error is an empty cell, IFERROR treats it as an empty string value («»).
-
If value is an array formula, IFERROR returns an array of results for each cell in the range specified in value. See the second example below.
Examples
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter.
|
Quota |
Units Sold |
|
|---|---|---|
|
210 |
35 |
|
|
55 |
0 |
|
|
23 |
||
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=IFERROR(A2/B2, «Error in calculation») |
Checks for an error in the formula in the first argument (divide 210 by 35), finds no error, and then returns the results of the formula |
6 |
|
=IFERROR(A3/B3, «Error in calculation») |
Checks for an error in the formula in the first argument (divide 55 by 0), finds a division by 0 error, and then returns value_if_error |
Error in calculation |
|
=IFERROR(A4/B4, «Error in calculation») |
Checks for an error in the formula in the first argument (divide «» by 23), finds no error, and then returns the results of the formula. |
0 |
Example 2
|
Quota |
Units Sold |
Ratio |
|---|---|---|
|
210 |
35 |
6 |
|
55 |
0 |
Error in calculation |
|
23 |
0 |
|
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=C2 |
Checks for an error in the formula in the first argument in the first element of the array (A2/B2 or divide 210 by 35), finds no error, and then returns the result of the formula |
6 |
|
=C3 |
Checks for an error in the formula in the first argument in the second element of the array (A3/B3 or divide 55 by 0), finds a division by 0 error, and then returns value_if_error |
Error in calculation |
|
=C4 |
Checks for an error in the formula in the first argument in the third element of the array (A4/B4 or divide «» by 23), finds no error, and then returns the result of the formula |
0 |
|
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas. |
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Содержание
- If cell is not blank
- Related functions
- Summary
- Generic formula
- Explanation
- IF function
- ISBLANK function
- LEN function
- Null in Excel
- Null in Excel
- ISBLANK Function to Find NULL Value in Excel
- #1 – How to Find NULL Cells in Excel?
- #2 – Shortcut Way of Finding NULL Cells in Excel
- #3 – How to Fill Our Values to NULL Cells in Excel?
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- NULL in Excel
- What is Null Error in Excel?
- Examples of NULL in Excel
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Example #5
- Things to Remember About NULL in Excel
- Recommended Articles
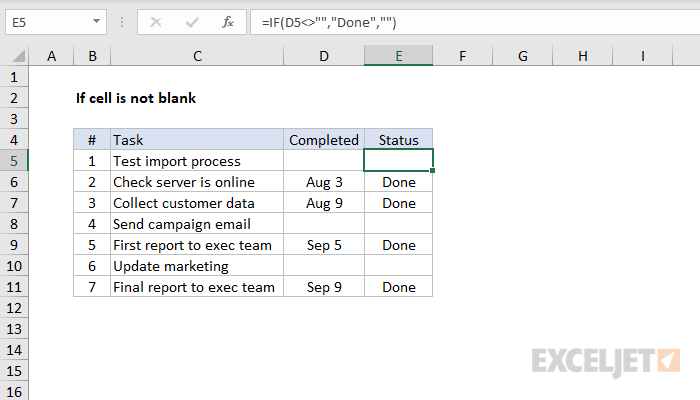
If cell is not blank
Summary
To test if a cell is not blank (i.e. has content), you can use a formula based on the IF function. In the example shown, the formula in cell E5 is:
As the formula is copied down it returns «Done» when a cell in column D is not blank and an empty string («») if the cell is blank.
Generic formula
Explanation
In this example, the goal is to create a formula that will return «Done» in column E when a cell in column D contains a value. In other words, if the cell in column D is «not blank», then the formula should return «Done». In the worksheet shown, column D is is used to record the date a task was completed. Therefore, if the column contains a date (i.e. is not blank), we can assume the task is complete. This problem can be solved with the IF function alone or with the IF function and the ISBLANK function. It can also be solved with the LEN function. All three approaches are explained below.
IF function
The IF function runs a logical test and returns one value for a TRUE result, and another value for a FALSE result. You can use IF to test for a blank cell like this:
In the first example, we test if A1 is empty with =»». In the second example, the <> symbol is a logical operator that means «not equal to», so the expression A1<>«» means A1 is «not empty». In the worksheet shown, we use the second idea in cell E5 like this:
If D5 is «not empty», the result is «Done». If D5 is empty, IF returns an empty string («») which displays as nothing. As the formula is copied down, it returns «Done» only when a cell in column D contains a value. To display both «Done» and «Not done», you can adjust the formula like this:
ISBLANK function
Another way to solve this problem is with the ISBLANK function. The ISBLANK function returns TRUE when a cell is empty and FALSE if not. To use ISBLANK directly, you can rewrite the formula like this:
Notice the TRUE and FALSE results have been swapped. The logic now is if cell D5 is blank. To maintain the original logic, you can nest ISBLANK inside the NOT function like this:
The NOT function simply reverses the result returned by ISBLANK.
LEN function
One problem with testing for blank cells in Excel is that ISBLANK(A1) or A1=»» will both return FALSE if A1 contains a formula that returns an empty string. In other words, if a formula returns an empty string in a cell, Excel interprets the cell as «not empty». To work around this problem, you can use the LEN function to test for characters in a cell like this:
This is a much more literal formula. We are not asking Excel if A1 is blank, we are literally counting the characters in A1. The LEN function will return a positive number only when a cell contains actual characters.
Источник
Null in Excel
Null is an error that occurs in Excel when the two or more cell references provided in a formula are incorrect, or the position they have been placed in is erroneous. For example, suppose we use space in formulas between two cell references; we will encounter a null error. In that case, there are two reasons to meet this error, one if we used an incorrect range reference and another when we use the intersect operator, which is the space character.
Null in Excel
NULL is nothing but nothing or blank in Excel. Usually, when working in Excel, we encounter many NULL or blank cells. We can use the formula and find out whether the particular cell is blank (NULL) or not.
We have several ways of finding the NULL cells in Excel. Today’s article will take a tour of dealing with NULL values in Excel.
How do you find which cell is blank or null? Yes, we must look at the particular cell and decide. Let us discover many methods of finding the null cells in Excel.
Table of contents
ISBLANK Function to Find NULL Value in Excel
The syntax is straightforward. Value is nothing but the cell reference; we are testing whether it is blank or not.
Note: ISBLANK will treat the single space as one character; if the cell has only space value, it will be recognized as a non-blank or non-null cell.
#1 – How to Find NULL Cells in Excel?
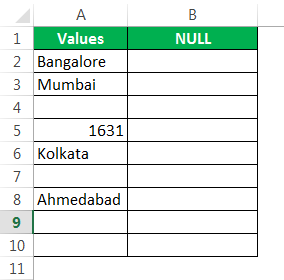
Assume we have the values below in the Excel file and want to test all the null cells in the range.
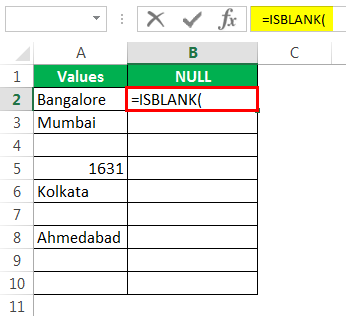
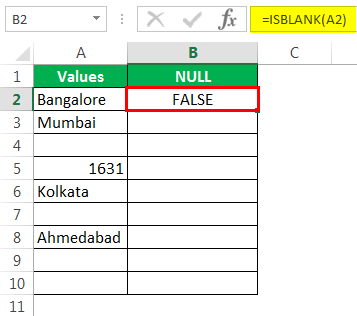
- Let us open the ISBLANK formula in cell B2 cell.
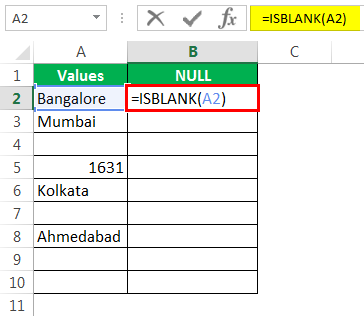
Select cell A2 as the argument. Since there is only one argument, close the bracket.
We got the result as given below:
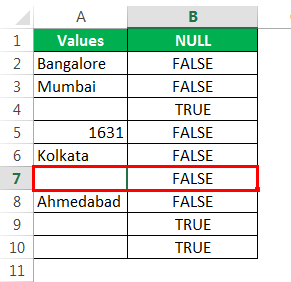
Then, drag and drop the formula to other remaining cells.
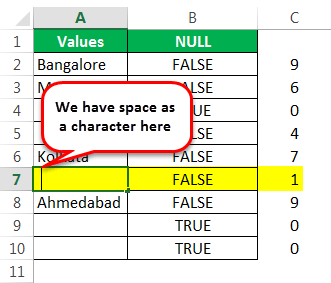
We got the results. But look at cell B7. Even though there is still no value in cell A7, the formula returned the result as a FALSE, non-null cell.
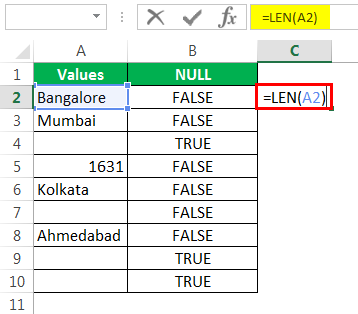
It counts the no. of characters and gives the result.
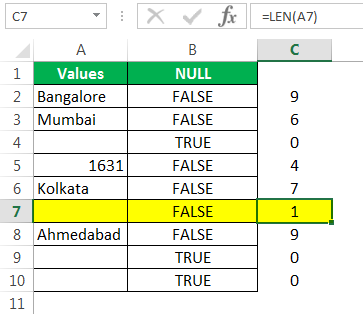
The LEN function returned the no. of character in the A7 cell as 1. So, there should be a character in it.
Let us edit the cell now. So, we found the space character here. Let us remove the space character to make the formula show accurate results.
We have removed the space character, and the ISBLANK formula returned the result as TRUE. That is because even the LEN function says there are zero characters in cell A7.
#2 – Shortcut Way of Finding NULL Cells in Excel
We have seen the traditional formula way to find the null cells. Without using the ISBLANK function, we can find the null cells.
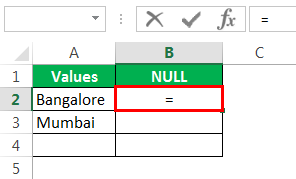
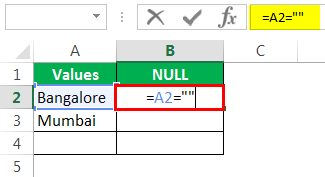
Let us open the formula with an equal sign (=).
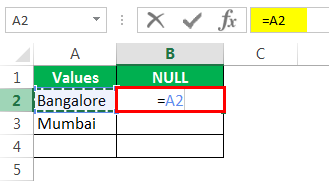
After the equal sign, select cell A2 as the reference.
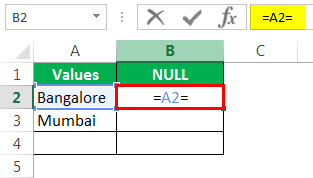
Now open one more equal sign after the cell reference.
Now mention open double-quotes and close double-quotes. (“”)
The sign double quotes (“”) says the selected cell is NULL or not. If the selected cell is NULL, we will get TRUE. Else, we will get FALSE.
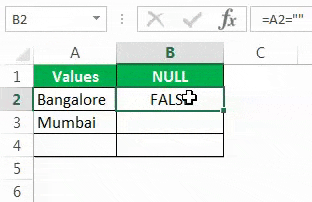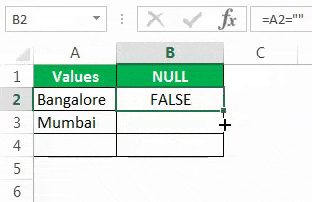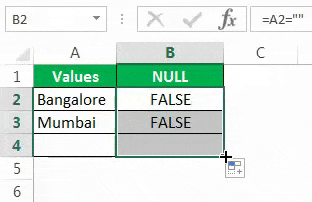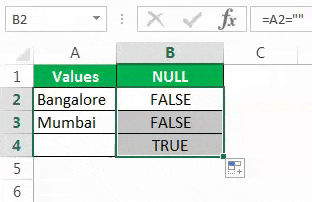
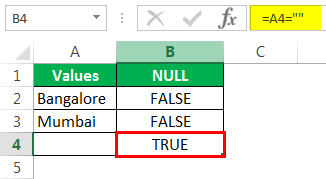
Drag the formula to the remaining cells.
We can see that in cell B7, we got the result as “TRUE.” So it means it is a null cell.
#3 – How to Fill Our Values to NULL Cells in Excel?
We have seen how to find the NULL cells in the Excel sheet. In our formula, we could only get TRUE or FALSE. But we can also receive our values for the NULL cells.
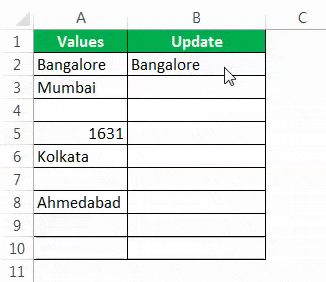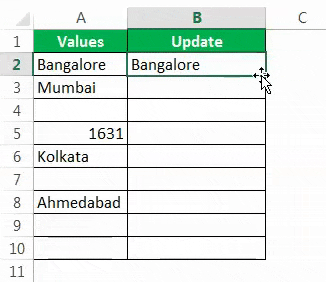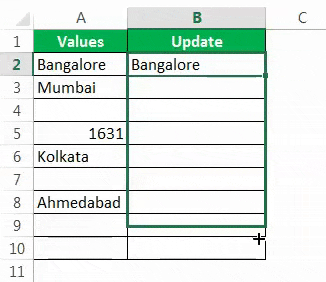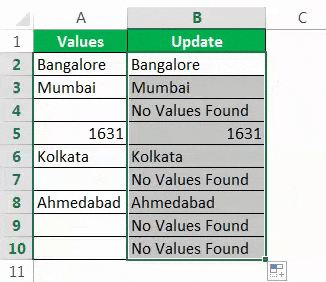
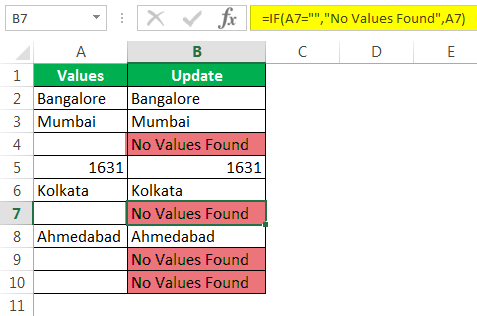
Consider the below data for an example.
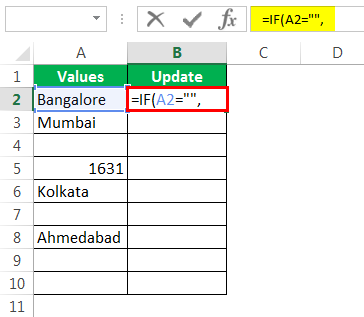
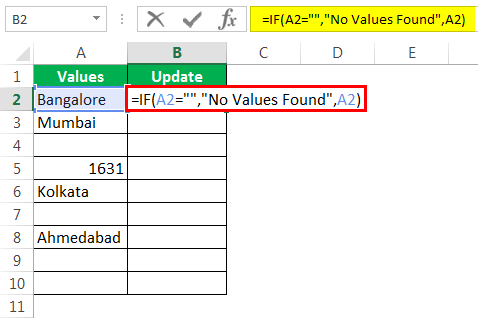
Step 1: Open the IF condition first.
Step 2: Here, we need to do a logical test. We need to test whether the cell is NULL or not. So apply A2=”.”
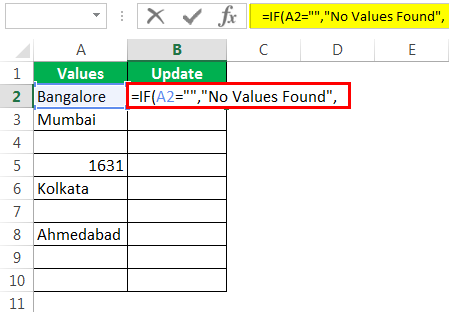
Step 3: If the logical test is TRUE (TRUE means cell is NULL), we need the result as “No Values Found.”
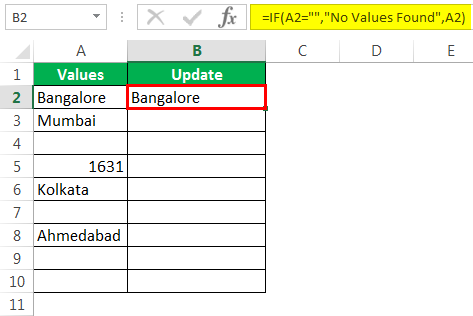
Step 4: If the logical test is FALSE (which means the cell contains values), then we need the same cell value.
We got the result as the same cell value.
Step 5: Drag the formula to the remaining cells.
So, we have got our value of No Values Found for all the NULL cells.
Things to Remember
- Even space will be considered a character and treated as a non-empty cell.
- Instead of ISBLANK, we can also use double quotes (“ ”) to test the NULL cells.
- If the cell seems blank and the formula shows it as a non-null cell, then you need to test the number of characters using the LEN function.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Null in Excel. We discuss the top methods to find null values in Excel using ISBLANK and shortcuts to replace those null cells, along with practical examples and a downloadable template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
Источник
NULL in Excel
NULL in Excel (Table of Contents)
What is Null Error in Excel?
Null is an error value in a cell when Excel cannot properly evaluate a worksheet formula or function. This error is shown when you use an incorrect range operator in a formula or when you use an intersection operator. The error value itself plus the Error Option Button, displayed in the error formula, helps identify the problem by showing a small green triangle containing error values. The small green triangle indicates one of the cell contents is violating one of Excel’s errors checking rules.
Excel functions, formula, charts, formatting creating excel dashboard & others
So here below, we will show you how it looks like.
As shown in the above screenshot, the green triangle and a yellow diamond-shaped button which is next to that cell marked with Red Arrows and when you click that Yellow Diamond shaped icon in the cell will show you the Excel’s error options button, which contains the options in the drop-down list to correct the perceived error.
Examples of NULL in Excel
Excel display some of the #Null! Errors which are very common. We will show you the list of those common error values along with some examples.
Example #1
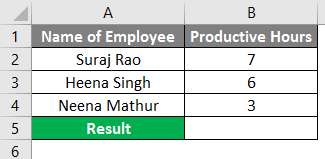
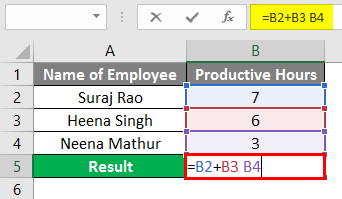
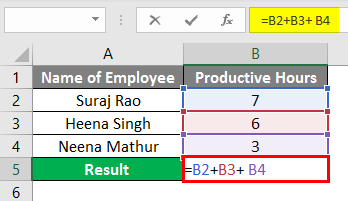
As shown below, we have the employees name in Column A and Productive Hours in Column B, so if we want to get the Total Productive hours of the below employees, we will Sum the hours from Column B2 to B4 but we have to input the Formula (=B2+B3 B4).
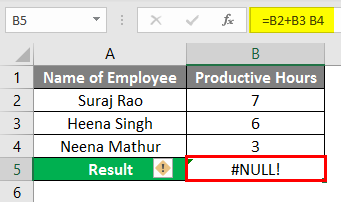
We have given space instead of the plus sign(+), so we got the #NULL! Error in Column B5.
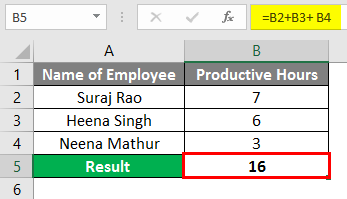
Now to rectify the error, we can click the Yellow Diamond Icon, and we will show that we need to input the correct formula in the formula bar, which is (=B2+B3+B4), which will give us the Total Productive Hours and rectify the #NULL! Error. Refer to the below screenshot.
After applying the formula, the result is shown below.
Example #2
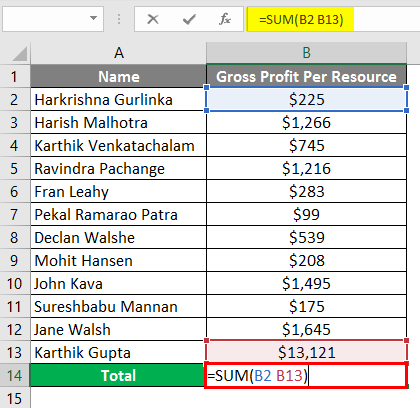
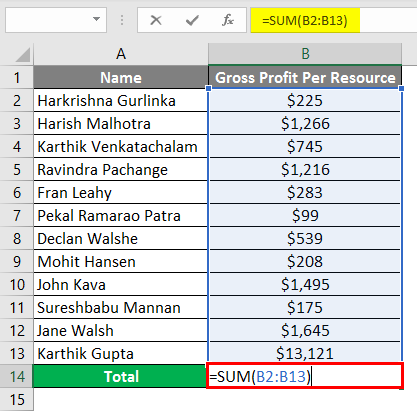
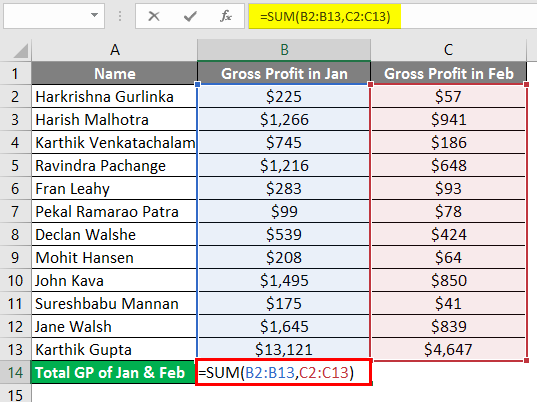
Suppose we need to take the Total Gross Profit of the resources in the below example for 12 resources with their gross profits in column B3 to B14.
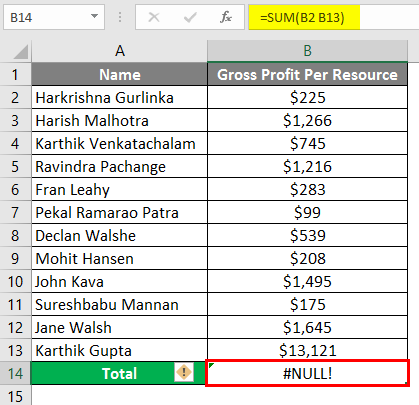
You can see that in column B13, we are getting the #NULL! Error. This is because, in the Formula bar, we have input the formula (=SUM (B2 B13)).
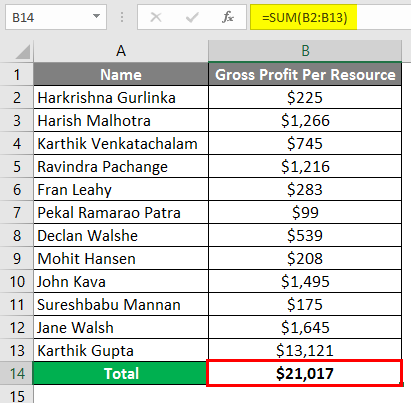
Suppose you want to rectify the #NULL! error you can add “Colon (:)” instead of “Space” in the formula bar (=SUM (B2:B13)) as shown in the below screenshot.
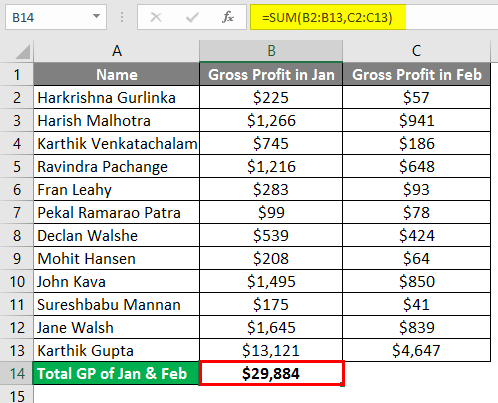
After applying the formula, the result is shown below.
Example #3
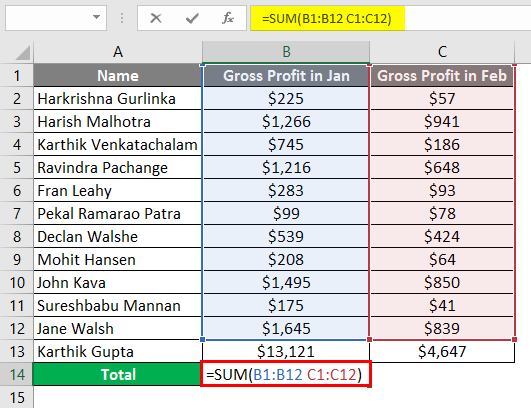
Another example shows where you are adding up Multiple ranges, and instead of adding “Comma”, we give space for those individual ranges, which as a result will give us the NULL Error and rectify that we will use Comma as the Union operator.
We need the Total Gross Profit of resources for both January and February month, so we insert the Sum formula for the Total Gross Profit (=SUM (B1:B12 C1:C12)) in the formula bar, but it will give us the #NULL! Error.
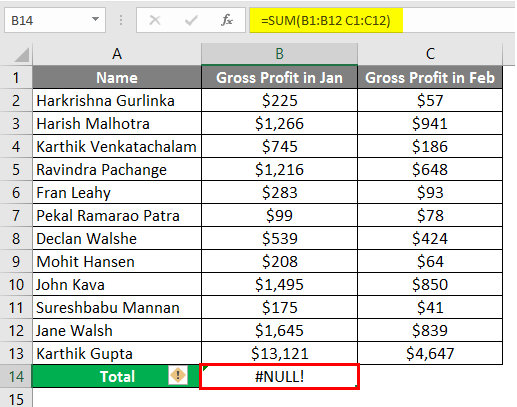
To eradicate the Null Error, input “Comma (,)” between both ranges.
After using the above formula, the output is shown below.
Example #4
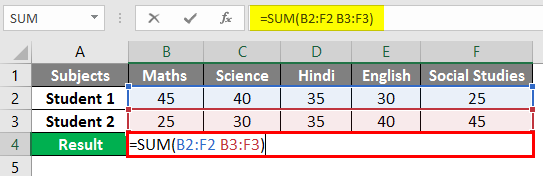
In the below example, we have taken two students marks in 5 subjects in 2 different rows, which do not intersect. This is when we get the Null error in Excel.
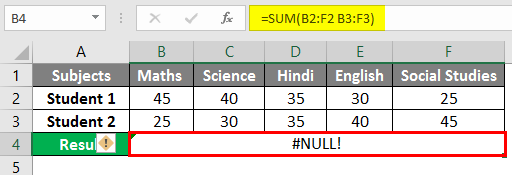
After using the formula, the output is shown below.
To eradicate the Null Error, input “Comma (,)” between both ranges.
After using the formula, the output is shown below.
Example #5
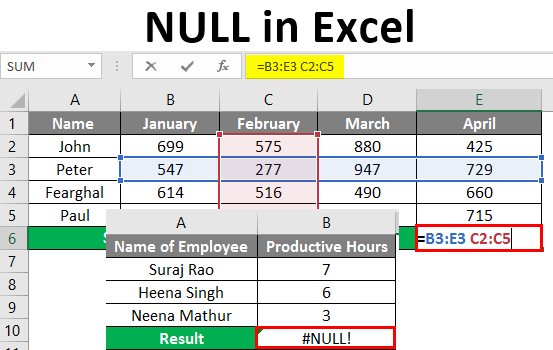
Intersect operator is basically used when you need the values which come from the intersection of one or more columns or rows. “Intersect Operator” allows performing the calculation on the ranges that intersect.
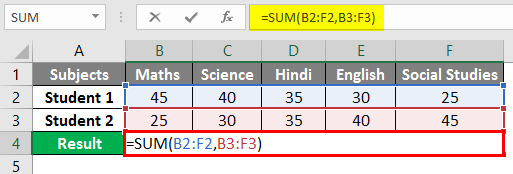
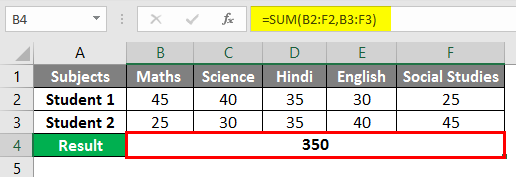
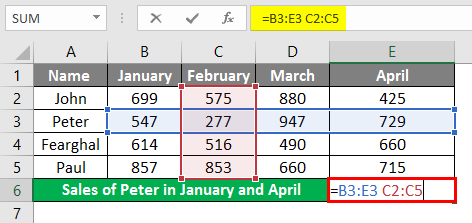
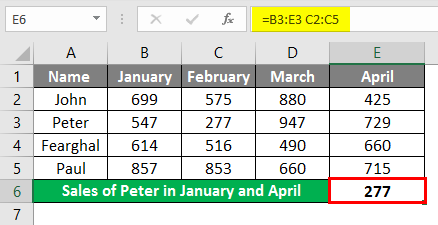
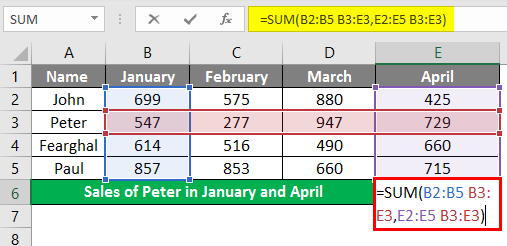
Let us try to use the intersection operator in the below example where you need to calculate Peter’s sales in February Month. We would input the Formula in the formula bar =(B3:E3 C2:C5) in cell B7.
Once the formula is applied, we will get the sales value for Peter in February month which is 277.
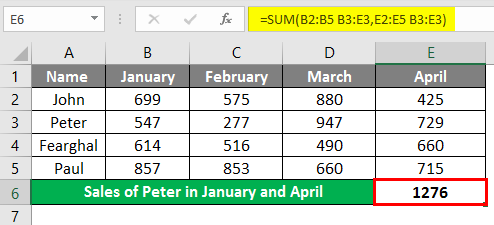
If you want to calculate the sales of Peter for January and April also, you could use=SUM (Peter Jan, Peter Apr), which means we need to input the formula in the formula bar “=SUM (B2:B5 B3:E3, E2:E5 B3:E3)”.
In cell B6, to get the sales value of Peter which is 1276 for both the months. The space between the two named ranges is the Intersect Operator.
Things to Remember About NULL in Excel
- If error checking is turned on in Excel, then you can easily fix your #NULL! error by clicking the Yellow Diamond icon next to the cell, which shows the error. Click on Help or Show Calculation Steps if it’s available and pick the resolution that works for your data.
- Excel #NULL! error will appear in case of two reasons. Whether you have used an incorrect range operator or trying to use the intersect operator where there is no intersection of ranges. #Null! Error gets returned when Excel can’t figure out the range specified in the cell.
- Use of Colon, Comma, Space, and mathematical operator (plus sign (+) needs be to input correctly in the formula to avoid the #NULL! Error in Excel.
- Excel display some of the #Null! Errors which are very common. We will show you the list of those common error values along with some common causes and solutions which will be helpful to correct them. #Null! Error Values occur when incorrectly or unintentionally, a “SPACE” character is used as the intersect operator between two or more cells. This error is shown when you use an incorrect range operator in a formula. The error occurs if the Multiple cell references in a formula are separated by a space instead of a mathematical operator such as a plus sign (+).
- #NULL! error occurs when the intersect operator (the space character) is used intentionally, but specified ranges do not intersect.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to NULL in Excel. Here we discuss How to use NULL in Excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
Источник
Return value
The value you specify for error conditions.
Usage notes
The IFERROR function is used to catch errors and return a more friendly result or message when an error is detected. When a formula returns a normal result, the IFERROR function returns that result. When a formula returns an error, IFERROR returns an alternative result. IFERROR is an elegant way to trap and manage errors. The IFERROR function is a modern alternative to the ISERROR function.
Use the IFERROR function to trap and handle errors produced by other formulas or functions. IFERROR checks for the following errors: #N/A, #VALUE!, #REF!, #DIV/0!, #NUM!, #NAME?, or #NULL!.
Example #1
In the example shown, the formula in E5 copied down is:
=IFERROR(C5/D5,0)
This formula catches the #DIV/0! error that occurs when Qty is empty or zero, and replaces it with zero.
Example #2
For example, if A1 contains 10, B1 is blank, and C1 contains the formula =A1/B1, the following formula will catch the #DIV/0! error that results from dividing A1 by B1:
=IFERROR (A1/B1,"Please enter a value in B1")
As long as B1 is empty, C1 will display the message «Please enter a value in B1» if B1 is blank or zero. When a number is entered in B1, the formula will return the result of A1/B1.
Example #3
You can also use the IFERROR function to catch the #N/A error thrown by VLOOKUP when a lookup value isn’t found. The syntax looks like this:
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(value,data,column,0),"Not found")
In this example, when VLOOKUP returns a result, IFERROR functions that result. If VLOOKUP returns #N/A error because a lookup value isn’t found, IFERROR returns «Not Found».
IFERROR or IFNA?
The IFERROR function is a useful function, but it is a blunt instrument since it will trap many kinds of errors. For example, if there’s a typo in a formula, Excel may return the #NAME? error, but IFERROR will suppress the error and return the alternative result. This can obscure an important problem. In many cases, it makes more sense to use the IFNA function, which only traps the #N/A error.
Other error functions
Excel provides a number of error-related functions, each with a different behavior:
- The ISERR function returns TRUE for any error type except the #N/A error.
- The ISERROR function returns TRUE for any error.
- The ISNA function returns TRUE for #N/A errors only.
- The ERROR.TYPE function returns the numeric code for a given error.
- The IFERROR function traps errors and provides an alternative result.
- The IFNA function traps #N/A errors and provides an alternative result.
Notes
- If value is empty, it is evaluated as an empty string («») and not an error.
- If value_if_error is supplied as an empty string («»), no message is displayed when an error is detected.
- In Excel 2013+, you can use the IFNA function to trap and handle #N/A errors specifically.