Содержание
- IF function
- Simple IF examples
- Common problems
- Need more help?
- IF function
- Simple IF examples
- Common problems
- Need more help?
- Функция ЕСЛИ в Excel. Как использовать?
- Что возвращает функция
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции
- Дополнительная информация
- Функция Если в Excel примеры с несколькими условиями
- Пример 1. Проверяем простое числовое условие с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
- Пример 2. Использование вложенной функции IF (ЕСЛИ) для проверки условия выражения
- Пример 3. Вычисляем сумму комиссии с продаж с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
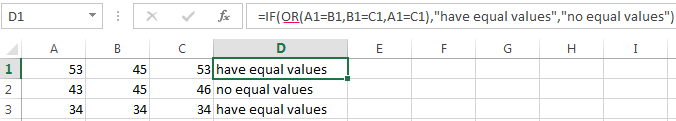
- Пример 4. Используем логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) в функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
- Пример 5. Преобразуем ошибки в значения “0” с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
IF function
The IF function is one of the most popular functions in Excel, and it allows you to make logical comparisons between a value and what you expect.
So an IF statement can have two results. The first result is if your comparison is True, the second if your comparison is False.
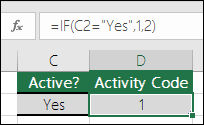
For example, =IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2) says IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2).
Use the IF function, one of the logical functions, to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false.
IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false])
The condition you want to test.
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is TRUE.
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is FALSE.
Simple IF examples
In the above example, cell D2 says: IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2)
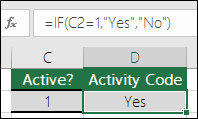
In this example, the formula in cell D2 says: IF(C2 = 1, then return Yes, otherwise return No)As you see, the IF function can be used to evaluate both text and values. It can also be used to evaluate errors. You are not limited to only checking if one thing is equal to another and returning a single result, you can also use mathematical operators and perform additional calculations depending on your criteria. You can also nest multiple IF functions together in order to perform multiple comparisons.
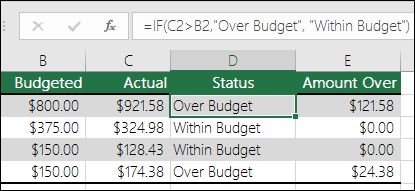
=IF(C2>B2,”Over Budget”,”Within Budget”)
In the above example, the IF function in D2 is saying IF(C2 Is Greater Than B2, then return “Over Budget”, otherwise return “Within Budget”)
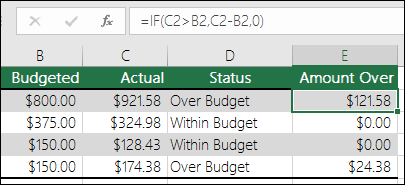
In the above illustration, instead of returning a text result, we are going to return a mathematical calculation. So the formula in E2 is saying IF(Actual is Greater than Budgeted, then Subtract the Budgeted amount from the Actual amount, otherwise return nothing).
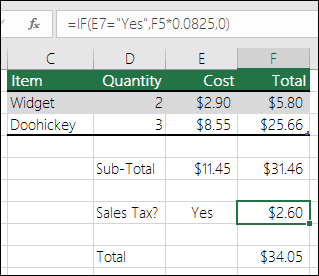
In this example, the formula in F7 is saying IF(E7 = “Yes”, then calculate the Total Amount in F5 * 8.25%, otherwise no Sales Tax is due so return 0)
Note: If you are going to use text in formulas, you need to wrap the text in quotes (e.g. “Text”). The only exception to that is using TRUE or FALSE, which Excel automatically understands.
Common problems
What went wrong
There was no argument for either value_if_true or value_if_False arguments. To see the right value returned, add argument text to the two arguments, or add TRUE or FALSE to the argument.
This usually means that the formula is misspelled.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Источник
IF function
The IF function is one of the most popular functions in Excel, and it allows you to make logical comparisons between a value and what you expect.
So an IF statement can have two results. The first result is if your comparison is True, the second if your comparison is False.
For example, =IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2) says IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2).
Use the IF function, one of the logical functions, to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false.
IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false])
The condition you want to test.
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is TRUE.
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is FALSE.
Simple IF examples
In the above example, cell D2 says: IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2)
In this example, the formula in cell D2 says: IF(C2 = 1, then return Yes, otherwise return No)As you see, the IF function can be used to evaluate both text and values. It can also be used to evaluate errors. You are not limited to only checking if one thing is equal to another and returning a single result, you can also use mathematical operators and perform additional calculations depending on your criteria. You can also nest multiple IF functions together in order to perform multiple comparisons.

=IF(C2>B2,”Over Budget”,”Within Budget”)
In the above example, the IF function in D2 is saying IF(C2 Is Greater Than B2, then return “Over Budget”, otherwise return “Within Budget”)

In the above illustration, instead of returning a text result, we are going to return a mathematical calculation. So the formula in E2 is saying IF(Actual is Greater than Budgeted, then Subtract the Budgeted amount from the Actual amount, otherwise return nothing).
In this example, the formula in F7 is saying IF(E7 = “Yes”, then calculate the Total Amount in F5 * 8.25%, otherwise no Sales Tax is due so return 0)
Note: If you are going to use text in formulas, you need to wrap the text in quotes (e.g. “Text”). The only exception to that is using TRUE or FALSE, which Excel automatically understands.
Common problems
What went wrong
There was no argument for either value_if_true or value_if_False arguments. To see the right value returned, add argument text to the two arguments, or add TRUE or FALSE to the argument.
This usually means that the formula is misspelled.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Источник
Функция ЕСЛИ в Excel. Как использовать?
Функция ЕСЛИ в Excel — это отличный инструмент для проверки условий на ИСТИНУ или ЛОЖЬ. Если значения ваших расчетов равны заданным параметрам функции как ИСТИНА, то она возвращает одно значение, если ЛОЖЬ, то другое.
Что возвращает функция
Заданное вами значение при выполнении двух условий ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ.
Синтаксис
=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false]) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(лог_выражение; [значение_если_истина]; [значение_если_ложь]) — русская версия
Аргументы функции
- logical_test (лог_выражение) — это условие, которое вы хотите протестировать. Этот аргумент функции должен быть логичным и определяемым как ЛОЖЬ или ИСТИНА. Аргументом может быть как статичное значение, так и результат функции, вычисления;
- [value_if_true] ([значение_если_истина]) — (не обязательно) — это то значение, которое возвращает функция. Оно будет отображено в случае, если значение которое вы тестируете соответствует условию ИСТИНА;
- [value_if_false] ([значение_если_ложь]) — (не обязательно) — это то значение, которое возвращает функция. Оно будет отображено в случае, если условие, которое вы тестируете соответствует условию ЛОЖЬ.
Дополнительная информация
- В функции ЕСЛИ может быть протестировано 64 условий за один раз;
- Если какой-либо из аргументов функции является массивом — оценивается каждый элемент массива;
- Если вы не укажете условие аргумента FALSE (ЛОЖЬ) value_if_false (значение_если_ложь) в функции, т.е. после аргумента value_if_true (значение_если_истина) есть только запятая (точка с запятой), функция вернет значение “0”, если результат вычисления функции будет равен FALSE (ЛОЖЬ).
На примере ниже, формула =IF(A1> 20,”Разрешить”) или =ЕСЛИ(A1>20;»Разрешить») , где value_if_false (значение_если_ложь) не указано, однако аргумент value_if_true (значение_если_истина) по-прежнему следует через запятую. Функция вернет “0” всякий раз, когда проверяемое условие не будет соответствовать условиям TRUE (ИСТИНА).|
- Если вы не укажете условие аргумента TRUE(ИСТИНА) (value_if_true (значение_если_истина)) в функции, т.е. условие указано только для аргумента value_if_false (значение_если_ложь), то формула вернет значение “0”, если результат вычисления функции будет равен TRUE (ИСТИНА);
На примере ниже формула равна = IF (A1>20;«Отказать») или =ЕСЛИ(A1>20;»Отказать») , где аргумент value_if_true (значение_если_истина) не указан, формула будет возвращать “0” всякий раз, когда условие соответствует TRUE (ИСТИНА).
Функция Если в Excel примеры с несколькими условиями
Пример 1. Проверяем простое числовое условие с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
При использовании функции ЕСЛИ в Excel, вы можете использовать различные операторы для проверки состояния. Вот список операторов, которые вы можете использовать:

Ниже приведен простой пример использования функции при расчете оценок студентов. Если сумма баллов больше или равна «35», то формула возвращает “Сдал”, иначе возвращается “Не сдал”.
Пример 2. Использование вложенной функции IF (ЕСЛИ) для проверки условия выражения
Функция может принимать до 64 условий одновременно. Несмотря на то, что создавать длинные вложенные функции нецелесообразно, то в редких случаях вы можете создать формулу, которая множество условий последовательно.
В приведенном ниже примере мы проверяем два условия.
- Первое условие проверяет, сумму баллов не меньше ли она чем 35 баллов. Если это ИСТИНА, то функция вернет “Не сдал”;
- В случае, если первое условие — ЛОЖЬ, и сумма баллов больше 35, то функция проверяет второе условие. В случае если сумма баллов больше или равна 75. Если это правда, то функция возвращает значение “Отлично”, в других случаях функция возвращает “Сдал”.
Пример 3. Вычисляем сумму комиссии с продаж с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
Функция позволяет выполнять вычисления с числами. Хороший пример использования — расчет комиссии продаж для торгового представителя.
В приведенном ниже примере, торговый представитель по продажам:
- не получает комиссионных, если объем продаж меньше 50 тыс;
- получает комиссию в размере 2%, если продажи между 50-100 тыс
- получает 4% комиссионных, если объем продаж превышает 100 тыс.
Рассчитать размер комиссионных для торгового агента можно по следующей формуле:
=ЕСЛИ(B2 — русская версия

В формуле, использованной в примере выше, вычисление суммы комиссионных выполняется в самой функции ЕСЛИ . Если объем продаж находится между 50-100K, то формула возвращает B2 * 2%, что составляет 2% комиссии в зависимости от объема продажи.
Пример 4. Используем логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) в функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
Вы можете использовать логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) внутри функции для одновременного тестирования нескольких условий.
Например, предположим, что вы должны выбрать студентов для стипендий, основываясь на оценках и посещаемости. В приведенном ниже примере учащийся имеет право на участие только в том случае, если он набрал более 80 баллов и имеет посещаемость более 80%.

Вы можете использовать функцию AND (И) вместе с функцией IF (ЕСЛИ) , чтобы сначала проверить, выполняются ли оба эти условия или нет. Если условия соблюдены, функция возвращает “Имеет право”, в противном случае она возвращает “Не имеет право”.
Формула для этого расчета:
=IF(AND(B2>80,C2>80%),”Да”,”Нет”) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(И(B2>80;C2>80%);»Да»;»Нет») — русская версия
Пример 5. Преобразуем ошибки в значения “0” с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
С помощью этой функции вы также можете убирать ячейки содержащие ошибки. Вы можете преобразовать значения ошибок в пробелы или нули или любое другое значение.
Формула для преобразования ошибок в ячейках следующая:
=IF(ISERROR(A1),0,A1) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(ЕОШИБКА(A1);0;A1) — русская версия
Формула возвращает “0”, в случае если в ячейке есть ошибка, иначе она возвращает значение ячейки.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Если вы используете Excel 2007 или версии после него, вы также можете использовать функцию IFERROR для этого.
Точно так же вы можете обрабатывать пустые ячейки. В случае пустых ячеек используйте функцию ISBLANK, на примере ниже:
=IF(ISBLANK(A1),0,A1) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(ЕПУСТО(A1);0;A1) — русская версия
Источник
IF function
The IF function is one of the most popular functions in Excel, and it allows you to make logical comparisons between a value and what you expect.
So an IF statement can have two results. The first result is if your comparison is True, the second if your comparison is False.
For example, =IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2) says IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2).
Use the IF function, one of the logical functions, to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false.
IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false])
For example:
-
=IF(A2>B2,»Over Budget»,»OK»)
-
=IF(A2=B2,B4-A4,»»)
|
Argument name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logical_test (required) |
The condition you want to test. |
|
value_if_true (required) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is TRUE. |
|
value_if_false (optional) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is FALSE. |
Simple IF examples
-
=IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2)
In the above example, cell D2 says: IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2)
-
=IF(C2=1,”Yes”,”No”)
In this example, the formula in cell D2 says: IF(C2 = 1, then return Yes, otherwise return No)As you see, the IF function can be used to evaluate both text and values. It can also be used to evaluate errors. You are not limited to only checking if one thing is equal to another and returning a single result, you can also use mathematical operators and perform additional calculations depending on your criteria. You can also nest multiple IF functions together in order to perform multiple comparisons.
-
=IF(C2>B2,”Over Budget”,”Within Budget”)
In the above example, the IF function in D2 is saying IF(C2 Is Greater Than B2, then return “Over Budget”, otherwise return “Within Budget”)
-
=IF(C2>B2,C2-B2,0)
In the above illustration, instead of returning a text result, we are going to return a mathematical calculation. So the formula in E2 is saying IF(Actual is Greater than Budgeted, then Subtract the Budgeted amount from the Actual amount, otherwise return nothing).
-
=IF(E7=”Yes”,F5*0.0825,0)
In this example, the formula in F7 is saying IF(E7 = “Yes”, then calculate the Total Amount in F5 * 8.25%, otherwise no Sales Tax is due so return 0)
Note: If you are going to use text in formulas, you need to wrap the text in quotes (e.g. “Text”). The only exception to that is using TRUE or FALSE, which Excel automatically understands.
Common problems
|
Problem |
What went wrong |
|---|---|
|
0 (zero) in cell |
There was no argument for either value_if_true or value_if_False arguments. To see the right value returned, add argument text to the two arguments, or add TRUE or FALSE to the argument. |
|
#NAME? in cell |
This usually means that the formula is misspelled. |
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.

See Also
IF function — nested formulas and avoiding pitfalls
IFS function
Using IF with AND, OR and NOT functions
COUNTIF function
How to avoid broken formulas
Overview of formulas in Excel
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Функция ЕСЛИ в Excel — это отличный инструмент для проверки условий на ИСТИНУ или ЛОЖЬ. Если значения ваших расчетов равны заданным параметрам функции как ИСТИНА, то она возвращает одно значение, если ЛОЖЬ, то другое.
Содержание
- Что возвращает функция
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы функции
- Дополнительная информация
- Функция Если в Excel примеры с несколькими условиями
- Пример 1. Проверяем простое числовое условие с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
- Пример 2. Использование вложенной функции IF (ЕСЛИ) для проверки условия выражения
- Пример 3. Вычисляем сумму комиссии с продаж с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
- Пример 4. Используем логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) в функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
- Пример 5. Преобразуем ошибки в значения “0” с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
Что возвращает функция
Заданное вами значение при выполнении двух условий ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ.
Синтаксис
=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false]) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(лог_выражение; [значение_если_истина]; [значение_если_ложь]) — русская версия
Аргументы функции
- logical_test (лог_выражение) — это условие, которое вы хотите протестировать. Этот аргумент функции должен быть логичным и определяемым как ЛОЖЬ или ИСТИНА. Аргументом может быть как статичное значение, так и результат функции, вычисления;
- [value_if_true] ([значение_если_истина]) — (не обязательно) — это то значение, которое возвращает функция. Оно будет отображено в случае, если значение которое вы тестируете соответствует условию ИСТИНА;
- [value_if_false] ([значение_если_ложь]) — (не обязательно) — это то значение, которое возвращает функция. Оно будет отображено в случае, если условие, которое вы тестируете соответствует условию ЛОЖЬ.
Дополнительная информация
- В функции ЕСЛИ может быть протестировано 64 условий за один раз;
- Если какой-либо из аргументов функции является массивом — оценивается каждый элемент массива;
- Если вы не укажете условие аргумента FALSE (ЛОЖЬ) value_if_false (значение_если_ложь) в функции, т.е. после аргумента value_if_true (значение_если_истина) есть только запятая (точка с запятой), функция вернет значение “0”, если результат вычисления функции будет равен FALSE (ЛОЖЬ).
На примере ниже, формула =IF(A1> 20,”Разрешить”) или =ЕСЛИ(A1>20;»Разрешить») , где value_if_false (значение_если_ложь) не указано, однако аргумент value_if_true (значение_если_истина) по-прежнему следует через запятую. Функция вернет “0” всякий раз, когда проверяемое условие не будет соответствовать условиям TRUE (ИСТИНА).
|
- Если вы не укажете условие аргумента TRUE(ИСТИНА) (value_if_true (значение_если_истина)) в функции, т.е. условие указано только для аргумента value_if_false (значение_если_ложь), то формула вернет значение “0”, если результат вычисления функции будет равен TRUE (ИСТИНА);
На примере ниже формула равна =IF (A1>20;«Отказать») или =ЕСЛИ(A1>20;»Отказать»), где аргумент value_if_true (значение_если_истина) не указан, формула будет возвращать “0” всякий раз, когда условие соответствует TRUE (ИСТИНА).
Функция Если в Excel примеры с несколькими условиями
Пример 1. Проверяем простое числовое условие с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
При использовании функции ЕСЛИ в Excel, вы можете использовать различные операторы для проверки состояния. Вот список операторов, которые вы можете использовать:
Ниже приведен простой пример использования функции при расчете оценок студентов. Если сумма баллов больше или равна «35», то формула возвращает “Сдал”, иначе возвращается “Не сдал”.
Пример 2. Использование вложенной функции IF (ЕСЛИ) для проверки условия выражения
Функция может принимать до 64 условий одновременно. Несмотря на то, что создавать длинные вложенные функции нецелесообразно, то в редких случаях вы можете создать формулу, которая множество условий последовательно.
В приведенном ниже примере мы проверяем два условия.
- Первое условие проверяет, сумму баллов не меньше ли она чем 35 баллов. Если это ИСТИНА, то функция вернет “Не сдал”;
- В случае, если первое условие — ЛОЖЬ, и сумма баллов больше 35, то функция проверяет второе условие. В случае если сумма баллов больше или равна 75. Если это правда, то функция возвращает значение “Отлично”, в других случаях функция возвращает “Сдал”.
Пример 3. Вычисляем сумму комиссии с продаж с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
Функция позволяет выполнять вычисления с числами. Хороший пример использования — расчет комиссии продаж для торгового представителя.
В приведенном ниже примере, торговый представитель по продажам:
- не получает комиссионных, если объем продаж меньше 50 тыс;
- получает комиссию в размере 2%, если продажи между 50-100 тыс
- получает 4% комиссионных, если объем продаж превышает 100 тыс.
Рассчитать размер комиссионных для торгового агента можно по следующей формуле:
=IF(B2<50,0,IF(B2<100,B2*2%,B2*4%)) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(B2<50;0;ЕСЛИ(B2<100;B2*2%;B2*4%)) — русская версия
В формуле, использованной в примере выше, вычисление суммы комиссионных выполняется в самой функции ЕСЛИ. Если объем продаж находится между 50-100K, то формула возвращает B2 * 2%, что составляет 2% комиссии в зависимости от объема продажи.

Пример 4. Используем логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) в функции IF (ЕСЛИ) в Excel
Вы можете использовать логические операторы (AND/OR) (И/ИЛИ) внутри функции для одновременного тестирования нескольких условий.
Например, предположим, что вы должны выбрать студентов для стипендий, основываясь на оценках и посещаемости. В приведенном ниже примере учащийся имеет право на участие только в том случае, если он набрал более 80 баллов и имеет посещаемость более 80%.
Вы можете использовать функцию AND (И) вместе с функцией IF (ЕСЛИ), чтобы сначала проверить, выполняются ли оба эти условия или нет. Если условия соблюдены, функция возвращает “Имеет право”, в противном случае она возвращает “Не имеет право”.
Формула для этого расчета:
=IF(AND(B2>80,C2>80%),”Да”,”Нет”) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(И(B2>80;C2>80%);»Да»;»Нет») — русская версия
Пример 5. Преобразуем ошибки в значения “0” с помощью функции IF (ЕСЛИ)
С помощью этой функции вы также можете убирать ячейки содержащие ошибки. Вы можете преобразовать значения ошибок в пробелы или нули или любое другое значение.
Формула для преобразования ошибок в ячейках следующая:
=IF(ISERROR(A1),0,A1) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(ЕОШИБКА(A1);0;A1) — русская версия
Формула возвращает “0”, в случае если в ячейке есть ошибка, иначе она возвращает значение ячейки.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Если вы используете Excel 2007 или версии после него, вы также можете использовать функцию IFERROR для этого.
Точно так же вы можете обрабатывать пустые ячейки. В случае пустых ячеек используйте функцию ISBLANK, на примере ниже:
=IF(ISBLANK(A1),0,A1) — английская версия
=ЕСЛИ(ЕПУСТО(A1);0;A1) — русская версия
The logical IF statement in Excel is used for the recording of certain conditions. It compares the number and / or text, function, etc. of the formula when the values correspond to the set parameters, and then there is one record, when do not respond — another.
Logic functions — it is a very simple and effective tool that is often used in practice. Let us consider it in details by examples.
The syntax of the function «IF» with one condition
The operation syntax in Excel is the structure of the functions necessary for its operation data.
=IF(boolean;value_if_TRUE;value_if_FALSE)
Let us consider the function syntax:
- Boolean – what the operator checks (text or numeric data cell).
- Value_if_TRUE – what will appear in the cell when the text or numbers correspond to a predetermined condition (true).
- Value_if_FALSE – what appears in the box when the text or the number does not meet the predetermined condition (false).
Example:
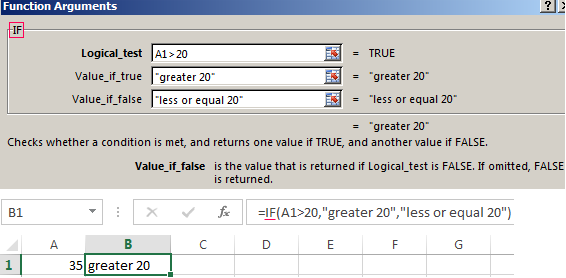
Logical IF functions.
The operator checks the A1 cell and compares it to 20. This is a «Boolean». When the contents of the column is more than 20, there is a true legend «greater 20». In the other case it’s «less or equal 20».
Attention! The words in the formula need to be quoted. For Excel to understand that you want to display text values.
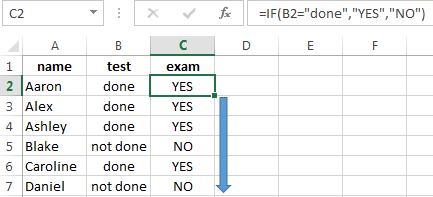
Here is one more example. To gain admission to the exam, a group of students must successfully pass a test. The results are listed in a table with columns: a list of students, a credit, an exam.
The statement IF should check not the digital data type but the text. Therefore, we prescribed in the formula В2= «done» We take the quotes for the program to recognize the text correctly.
The function IF in Excel with multiple conditions
Usually one condition for the logic function is not enough. If you need to consider several options for decision-making, spread operators’ IF into each other. Thus, we get several functions IF in Excel.
The syntax is as follows:
Here the operator checks the two parameters. If the first condition is true, the formula returns the first argument is the truth. False — the operator checks the second condition.
Examples of a few conditions of the function IF in Excel:
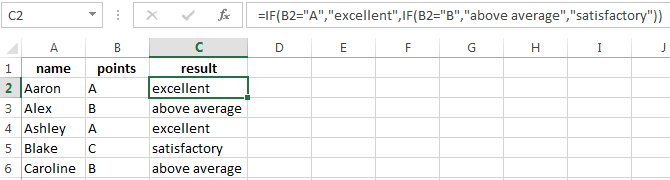
It’s a table for the analysis of the progress. The student received 5 points:
- А – excellent;
- В – above average or superior work;
- C – satisfactory;
- D – a passing grade;
- E – completely unsatisfactory.
IF statement checks two conditions: the equality of value in the cells.
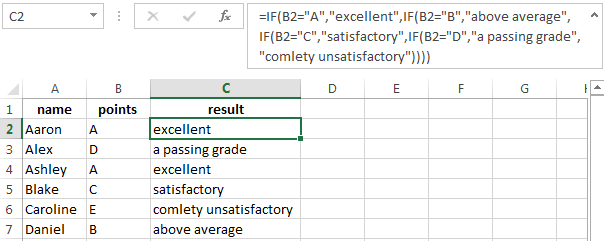
In this example, we have added a third condition, which implies the presence of another report card and «twos». The principle of the operator is the same.
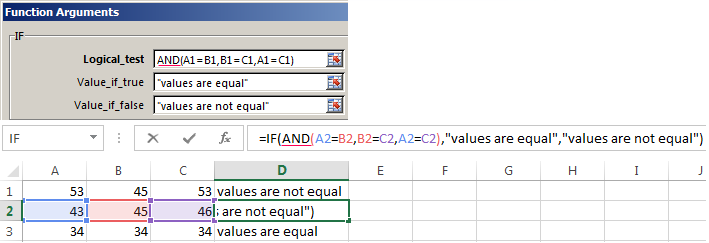
Enhanced functionality with the help of the operators «AND» and «OR»
When you need to check out a few of the true conditions you use the function И. The point is: IF A = 1 AND A = 2 THEN meaning в ELSE meaning с.
OR function checks the condition 1 or condition 2. As soon as at least one condition is true, the result is true. The point is: IF A = 1 OR A = 2 THEN value B ELSE value C.
Functions AND & OR can check up to 30 conditions.
An example of using the operator AND:
It’s the example of using the logical operator OR.
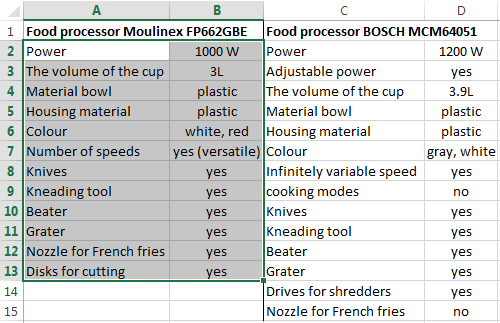
How to compare data in two tables
Users often need to compare the two spreadsheets in an Excel to match. Examples of the «life»: compare the prices of goods in different bringing, to compare balances (accounting reports) in a few months, the progress of pupils (students) of different classes, in different quarters, etc.
To compare the two tables in Excel, you can use the COUNTIFS statement. Consider the order of application functions.
For example, consider the two tables with the specifications of various food processors. We planned allocation of color differences. This problem in Excel solves the conditional formatting.
Baseline data (tables, which will work with):
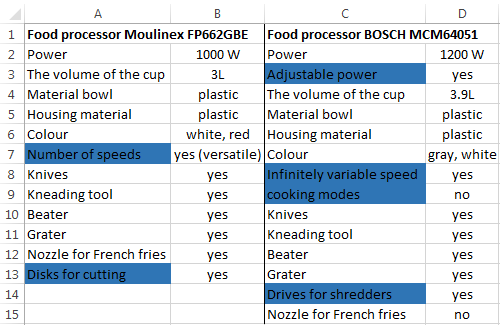
Select the first table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use a formula to determine the formatted cells:
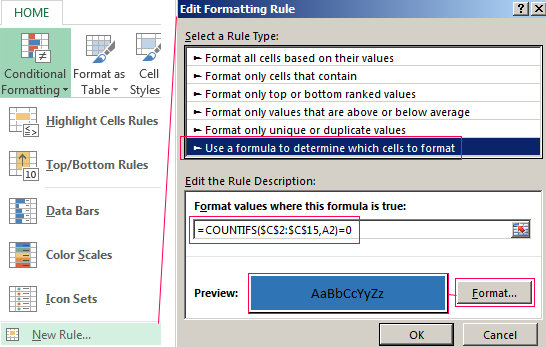
In the formula bar write: = COUNTIFS (comparable range; first cell of first table)=0. Comparing range is in the second table.
To drive the formula into the range, just select it first cell and the last. «= 0» means the search for the exact command (not approximate) values.
Choose the format and establish what changes in the cell formula in compliance. It’s better to do a color fill.
Select the second table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use the formula. Use the same operator (COUNTIFS). For the second table formula:
Download all examples in Excel
Now it is easy to compare the characteristics of the data in the table.
The IF function is one of the most useful Excel functions. It is used to test a condition and return one value if the condition is TRUE and another if it is FALSE.
One of the most common applications of the IF function involves the comparison of values.
These values can be numbers, text, or even dates. However, using the IF statement with date values is not as intuitive as it may seem.
In this tutorial, I will demonstrate some ways in which you can use the IF function with date values.
Syntax and Usage of the IF Function in Excel
The syntax for the IF function is as follows:
IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
Here,
- logical_test is the condition or criteria that you want the IF function to test. The result of this parameter is either TRUE or FALSE
- value_if_true is the value that you want the IF function to return if the logical_test evaluates to TRUE
- value_if_false is the value that you want the IF function to return if the logical_test evaluates to FALSE
For example, say you want to write a statement that will return the value “yes” if the value in cell reference A2 is equal to 10, and “no” if it’s anything but 10.
You can then use the following IF function for this scenario:
=IF(A2=10,"yes","no")

Comparing Dates in Excel (Using Operators)
Unlike numbers and strings, comparison operators, when used with dates, have a slightly different meaning.
Here are some of the comparison operators that you can use when comparing dates, along with what they mean:
| Operator | What it Means When Using with Dates |
|---|---|
| < | Before the given date |
| = | Same as the date with which we are comparing |
| > | After the given date |
| <= | Same as or before the given date |
| >= | Same as or after the given date |
It may look like IF formulas for dates are the same as IF functions for numeric or text values, since they use the same comparison operators.
However, it’s not as simple as that.
Unfortunately, unlike other Excel functions, the IF function cannot recognize dates.
It interprets them as regular text values.
So you cannot use a logical test such as “>05/07/2021” in your IF function, as it will simply see the value “05/07/2021” as text.
Here are a few ways in which you can incorporate date values into your IF function’s logical_test parameter.
Using the IF Function with DATEVALUE Function
If you want to use a date in your IF function’s logical test, you can wrap the date in the DATEVALUE function.
This function converts a date in text format to a serial number that Excel can recognize as a date.
If you put a date within quotes, it is essentially a text or string value.
When you pass this as a parameter to the DATEVALUE function, it takes a look at the text inside the double quotes, identifies it as a date and then converts it to an actual Excel date value.
Let us say you have a date in cell A2, and you want cell B2 to display the value “done” if the date comes before or on the same date as “05/07/2021” and display “not done” otherwise.
You can use the IF function along with DATEVALUE in cell B2 as follows:
=IF(A2<DATEVALUE("05/07/2021"),"done","not done")
Here’s a screenshot to illustrate the effect of the above formula:

Using the IF Function with the TODAY Function
If you want to compare a date with the current date, you can use the IF function with the TODAY function in the logical test.
Let’s say you have a date in cell A2 and you want cell B2 to display the value “done” if it is a date before today’s date.
If not, you want let’s say you want to display the value “not done”. You can use the IF function along with the TODAY function in cell B2 as follows:
=IF(A2<TODAY(),"done","not done")
Here’s a screenshot to illustrate the effect of the above formula (assuming the current date is 05/08/2021):

Using the IF Function with Future or Past Dates
An interesting thing about dates in Excel is that you can perform addition and subtraction operations with them too.
This is because dates are basically stored in Excel as serial numbers, starting from the date Jan 1, 1900.
Each day after that is represented by one whole number.
So, the serial number 2 corresponds to Jan 2, 1900, and so on.
This means that adding n number of days to a date is equivalent to adding the value n to the serial number that the date represents.
If TODAY() is 05/07/2021, then TODAY()+5 is five days after today, or 05/12/2021. Similarly, TODAY()-3 is three days before today or 05/04/2021.
Let’s say you have a date in cell A2 and you want cell B2 to mark it as “within range” if it is within 15 days from the current date.
If not, you want to show “out of range”. You can use the IF function along with the TODAY function in cell B2 as follows:
=IF(A2<TODAY()+15,"within range","out of range")
Here’s a screenshot to illustrate the effect of the above formula (assuming the current date is 05/08/2021):

Points to Remember
Having discussed different ways to use dates with the IF function, here are some important points to remember:
- Instead of hardcoding the dates into the IF function’s logical test parameter, you can store the date in a separate cell and refer to it with a cell reference. For example, instead of typing =IF(A2<”05/07/2021”,”done”,”not done”), you can store the date 05/07/2021 in a cell, say B2 and type the formula: =IF(A2<B2,”done”,”not done”).
- Alternatively, you can use the DATEVALUE function as explained in the first part of this tutorial.
- Another neat technique that you can use is to simply add a zero to the date (which has been enclosed in double quotes). So you can type: =IF(A2<”05/07/2021”+0,”done”,”not done”). This will make Excel take the date inside double quotes as a serial number, and use it in the logical test without having its value changed.
In this tutorial, I showed you some great techniques to use the IF function with dates. I hope the tips covered here were useful for you.
Other articles you may also like:
- Multiple If Statements in Excel (Nested Ifs, AND/OR) with Examples
- How to use Excel If Statement with Multiple Conditions Range [AND/OR]
- How to Convert Month Number to Month Name in Excel
- Why are Dates Shown as Hashtags in Excel? Easy Fix!
- How to Convert Serial Numbers to Date in Excel
- How to Get the First Day Of The Month In Excel?