-
Word stress, its acoustic
nature. -
The
linguistic function of a word stress. -
Degree
and position of a word stress.
-1-
The
sequence of syllables in the word is not pronounced identically. The
syllable or syllables which are pronounced with more prominence than
the other syllables of the word are said to be stressed or accented.
The correlation of varying prominences of syllables in a word is
understood as the accentual structure of the word.
According
to A.C. Gimson, the effect of prominence is achieved by any or all of
four factors: force, tone, length and vowel colour. The dynamic
stress implies greater force with which the syllable is pronounced.
In other words in the articulation of the stressed syllable greater
muscular energy is produced by the speaker. The European languages
such as English, German, French, Russian are believed to possess
predominantly dynamic word stress. In Scandinavian languages the word
stress is considered to be both dynamic and musical (e.g. in Swedish,
the word komma
(comma) is distinguished from the word komma
(come) by a difference in tones). The musical (tonic) word stress is
observed in Chinese, Japanese. It is effected by the variations of
the voice pitch in relation to neighbouring syllables. In Chinese the
sound sequence “chu” pronounced with the level tone means “pig”,
with the rising tone “bamboo”, and with the falling tone “to
live”.
It is fair
to mention that there is a terminological confusion in discussing the
nature of stress. According to D. Crystal, the terms “heaviness,
intensity, amplitude, prominence, emphasis, accent, stress” tend to
be used synonymously by most writers. The discrepancy in terminology
is largely due to the fact that there are 2 major views depending on
whether the productive or receptive aspects of stress are discussed.
The main
drawback with any theory of stress based on production of speech is
that it only gives a partial explanation of the phenomenon but does
not analyze it on the perceptive level.
Instrumental
investigations study the physical nature of word stress. On the
acoustic level the counterpart of force is the intensity of the
vibrations of the vocal cords of the speaker which is perceived by
the listener as loudness. Thus the greater energy with which the
speaker articulates the stressed syllable in the word is associated
by the listener with greater loudness. The acoustic counterparts of
voice pitch and length are frequency and duration respectively. The
nature of word stress in Russian seems to differ from that in
English. The quantitative component plays a greater role in Russian
accentual structure than in English word accent. In the Russian
language of full formation and full length in unstressed positions,
they are always reduced. Therefore the vowels of full length are
unmistakably perceived as stressed. In English the quantitative
component of word stress is not of primary importance because of the
non-reduced vowels in the unstressed syllables which sometimes occur
in English words (e.g. “transport”, “architect”).
-2-
In discussing accentual
structure of English words we should turn now to the functional
aspect of word stress. In language the word stress performs 3
functions:
-
constitutive– word
stress constitutes a word, it organizes the syllables of a word into
a language unit. A word does not exist without the word stress. Thus
the function is constitutive – sound continuum becomes a phrase
when it is divided into units organized by word stress into words. -
Word
stress enables a person to identify a succession of syllables as a
definite accentual pattern of a word. This function is known as
identificatory (or
recognitive). -
Word
stress alone is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or
their forms, thus performing its distinctive
function. The accentual patterns of
words or the degrees of word stress and their positions form
oppositions (“/import – im /port”, “/present – pre
/sent”).
-3-
There are
actually as many degrees of word stress in a word as there are
syllables. The British linguists usually distinguish three degrees of
stress in the word. The primary stress is the strongest (e.g.
exami/nation), the secondary stress is the second strongest one (e.g.
ex,ami/nation). All the other degrees are termed “weak stress”.
Unstressed syllables are supposed to have weak stress. The American
scholars, B. Bloch and J. Trager, find 4 contrastive degrees
of word stress: locid, reduced locid, medial and weak.
In
Germanic languages the word stress originally fell on the initial
syllable or the second syllable, the root syllable in the English
words with prefixes. This tendency was called recessive. Most English
words of Anglo-Saxon origin as well as the French borrowings are
subjected to this recessive tendency.
Languages
are also differentiated according to the placement of word stress.
The traditional classification of languages concerning the place of
stress in a word is into those with a
fixed stress and a free stress. In
languages with a fixed stress the occurrence of the word stress is
limited to a particular syllable in a multisyllabic word. For
example, in French the stress falls on the last syllable of the word
(if pronounced in isolation), in Finnish and Czech it is fixed on the
first syllable.
Some
borrowed words retain their stress.
In languages with a free
stress its place is not confined to a specific position in the word.
The free placement of stress is exemplified in the English and
Russian languages
(e.g. E. appetite – begin –
examination
R.
озеро – погода
– молоко)
The word
stress in English as well as in Russian is not only free but it may
also be shifting performing semantic function of differentiating
lexical units, parts of speech, grammatical forms. It is worth noting
that in English word stress is used as a means of word-building (e.g.
/contrast – con/trast, /music – mu /sician).
Questions:
-
What
features characterize word accent? -
Identify
the functions of word stress. -
What
are the types of word stress? -
Do AmE and
BE have any differences in the system of word stress? Give your
examples.
Lecture 8. Intonation
-
Intonation.
-
The
linguistic function of intonation. -
The
implications of a terminal tone. -
Rhythm.
-1-
Intonation is a language
universal. There are no languages which are spoken as a monotone,
i.e. without any change of prosodic parametres. On perceptional level
intonation is a complex, a whole, formed by significant variations of
pitch, loudness and tempo closely related. Some linguists regard
speech timber as the fourth component of intonation. Though it
certainly conveys some shades of attitudinal or emotional meaning
there’s no reason to consider it alongside with the 3
prosodic components of intonation (pitch, loudness and tempo).
Nowadays the term “prosody” substitutes the term “intonation”.
On the acoustic level pitch
correlates with the fundamental frequency of the vibrations of the
vocal cords; loudness correlates with the amplitude of vibrations;
tempo is a correlate of time during which a speech unit lasts.
The auditory level is very
important for teachers of foreign languages. Each syllable of the
speech chain has a special pitch colouring. Some of the syllables
have significant moves of tone up and down. Each syllable bears a
definite amount of loudness. Pitch movements are inseparably
connected with loudness. Together with the tempo of speech they form
an intonation pattern which is the basic unit of intonation.
An intonation pattern contains
one nucleus and may contain other stressed or unstressed syllables
normally preceding or following the nucleus. The boundaries of an
intonation pattern may be marked by stops of phonation, that is
temporal pauses.
Intonation patterns serve to
actualize syntagms in oral speech. The syntagm
is a group of words which are semantically and syntactically
complete. In phonetics they are called intonation
groups. The
intonation group is a stretch of speech which may have the length of
the whole phrase. But the phrase often contains more than one
intonation group. The number of them depends on the length of phrase
and the degree of semantic impotence or emphasis given to various
parts of it. The position of intonation groups may affect the
meaning.
-2-
The communicative
function of
intonation is realized in various ways which can be grouped under
five – six general headings:
-
to
structure the intonation content of a textual unit. So as to show
which information is new or can not be taken for granted, as against
information which the listener is assumed to possess or to be able
to acquire from the context, that is given information; -
to
determine the speech function of a phrase, to indicate whether it is
intended as a statement, question, etc; -
to
convey connotational meanings of attitude, such as surprise, etc. In
the written form we are given only the lexics and the grammar; -
to
structure a text. Intonation is an organizing mechanism. It divides
texts into smaller parts and on the other hand it integrates them
forming a complete text; -
to
differentiate the meaning of textual units of the same phonetic
structure and the same lexical composition (distinctive or
phonological function); -
to
characterize a particular style or variety of oral speech which may
be called a stylistic function.
-3-
Classification of intonation
patterns:
Different combinations of
pitch sections (pre-heads, heads and nuclei) may result in more than
one hundred pitch-and-stress patterns. But it is not necessary to
deal with all of them, because some patterns occur very rarely. So,
attention must be concentrated on the commonest ones:
-
The Low (Medium) Fall
pitch-and-stress group -
The
High Fall group -
Rise
Fall group -
The
Low Rise group -
The
High Rise group -
The
Fall Rise group -
The
Rise-Fall-Rise group -
The
Mid-level group
No intonation pattern is used
exclusively with this or that sentence type. Some sentences are more
likely to be said with one intonation pattern than with any other. So
we can speak about “common intonation” for a particular type of
sentence.
-
Statements are most widely
used with the Low Fall preceded by the Falling or the High level
Head. They are final, complete and definite. -
Commands,
with the Low Fall are very powerful, intense, serious and strong. -
Exclamations
are very common with the High Fall.
-4-
We cannot fully describe
English intonation without reference to speech rhythm. Rhythm
seems to be a kind of framework of speech organization. Some
linguists consider it to be one of the components of intonation.
Rhythm is understood as
periodicity in time and space. We find it everywhere in life. Rhythm
as a linguistic notion is realized in lexical, syntactical and
prosodic means and mostly in their combinations.
In speech,
the type of rhythm depends on the language. Linguists divide
languages into two groups:
-
syllable-timed(French, Spanish);
-
stress-timed(English, German, Russian).
In a
syllable-timed language the speaker gives an approximately equal
amount of time to each syllable, whether the syllable is stressed or
unstressed.
In a
stress-timed language the rhythm is based on a larger unit, than
syllable. Though the amount of time given on each syllable varies
considerably, the total time of uttering each rhythmic unit is
practically unchanged. The stressed syllables of a rhythmic unit form
peaks of prominence. They tend to be pronounced at regular intervals
no matter how many unstressed syllables are located between every 2
stressed ones. Thus the distribution of time within the rhythmic unit
is unequal.
Speech
rhythm is traditionally defined as recurrence of stressed syllables
at more or less equal intervals of time in a speech continuum.
Questions:
-
Name
the basic components of intonation. -
What
is the connection between pitch and tempo? -
What
for do we need different nuclear tones? -
Which
nuclei are the commonest?
Lecture
9. Territorial varieties of English pronunciation
-
Varieties
of language. -
English
variants.
-1-
The
varieties of the language are conditioned by language communities
ranging from small groups to nations. National
language is the language of a nation,
the standard of its form, the language of a nation’s literature.
The literary spoken form has its national
pronunciation standard. A “standard”
may be defined as a socially accepted variety of a language
established by a codified norm of correctness. It is generally
accepted that for the “English English” it is “Received
Pronunciation” or RP; for the “American English” – “General
American pronunciation”; for the Australian English – “Educated
Australian”.
Though
every national variant of English has considerable differences in
pronunciation, lexics and grammar, they all have much in common which
gives us ground to speak of one and the same language – the English
language.
Every
national variety of the language falls into territorial
or regional dialects. Dialects are
distinguished from each other by differences in pronunciation,
grammar and vocabulary. When we refer to varieties in pronunciation
only, we use the word “accent”.
The social
differentiation of language is closely connected with the social
differentiation of society. Every language community, ranging from a
small group to a nation has its own social
dialect, and consequently, its own
social accent.
The
“language situation” may be spoken about in terms of the
horizontal and vertical differentiations of the language, the first
in accordance with the sphere of social activity, the second – with
its situational variability. Situational varieties of the language
are called functional dialects or functional styles and situational
pronunciation varieties – situational accents or phonostyles.
-2-
Nowadays
two main types of English are spoken in the English-speaking world:
English English and American English.
According to British
dialectologists (P. Trudgill, J. Hannah, A. Hughes and others) the
following variants of English are referred to the English-based
group: English English, Welsh English, Australian English, New
Zealand English; to the American-based group: United States English,
Canadian English.
Scottish English and Irish
English fall somewhere between the two being somewhat by themselves.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #

By
Last updated:
April 13, 2022
8 English Word Stress Rules to Promote Clear Communication
There should be a rhythm to English sentences—it shouldn’t sound flat, monotone (all in the same tone) and boring!
I know it sounds like an additional challenge, especially when speaking English is already difficult.
However, when you pronounce every bit of a word and sentence with the same pitch, volume and length, it might make it difficult for native speakers to understand you.
Contents
- Why Word Stress Matters
- What Is Word Stress?
-
- Identifying syllables to understand word stress
- Features of a stressed syllable
- 8 Word Stress Rules to Improve Your English Pronunciation
-
- 1. Nouns and adjectives with two syllables
- 2. Verbs and prepositions with two syllables
- 3. Words that are both a noun and a verb
- 4. Three syllable words ending in “er” and “ly”
- 5. Words ending in “ic,” “sion” and “tion”
- 6. Words ending in “cy,” “ty,” “phy,” “gy” and “al”
- 7. Compound nouns
- 8. Compound adjectives and verbs
- Resources to Perfect Your Word Stress Skills
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Why Word Stress Matters
In her head, this sentence was understandable to Saskia:
“Dessert is my favorite thing!”
But when she said this to a friend, a native English speaker, he looked confused and asked her:
“Why? It’s just sand and has no life. It could also be dangerous!”
Then it was Saskia’s turn to be puzzled.
Can you guess the source of the problem?
Well, the problem here is word stress. Saskia got the word (“dessert”—the sweet heavenly thing) right, but she said it with the emphasis in the wrong place and the word sounded like “desert”—a dry perilous place.
This is just one example of how important word stress is to improving your pronunciation and speaking English like a native speaker. Perhaps you don’t know much (or anything at all) about the stress in English words yet, but trust me, it’s the key to improving your communication skills, both with speaking to a native English speaker and listening to English.
Also, I’m not just telling you how important word stress is. This guide will take you through the basics of this pronunciation challenge and provide you with eight rules to start doing it right.
Learning word stress is a crucial part of becoming an advanced English learner.
In addition to word stress, it is important to learn the pronunciation of the English dialect you want to speak.
What Is Word Stress?
In English, the individual sounds of a word (i.e. syllables—which we’ll discuss in just a moment) aren’t pronounced with the same weight. One syllable receives more emphasis than the others.
For example, there are three syllables in the word “beautiful” /BEAU-ti-ful/ and the word stress falls on the first one /BEAU/. (Please note that in this guide, I’ll demonstrate the stress in a word by capitalizing all the letters that make up the syllable.)
Now that you have the definition of word stress, let’s dive deeper into syllables to comprehend word stress.
Identifying syllables to understand word stress
A syllable is a unit of pronunciation that has one vowel sound. A word might have one syllable (like “an” or “can”) or more, such as “po-lice” (two syllables), “com-pa-ny” (three syllables), “ne-ce-ssa-ry” (four syllables), etc.
Just for fun, do you know the English word with the most syllables?
The answer is “antidisestablishmentarianism.” (The opposition of the belief that there shouldn’t be an official church in a country.)
The word has 12 syllables!
Remember that syllables aren’t similar to letters. For example, “scratch” has seven letters but one syllable, while “umami” has five letters but three syllables. Whatever the word, pay attention to the vowels because one of them will be where you find the stress of a word.
Features of a stressed syllable
Now you know that you need to emphasize a particular vowel in a specific syllable of a word. However, you might still wonder exactly how to do so. Let’s take a look at a native speaker’s speech pattern.
When a native speaker stresses a syllable in a word, this is what they do:
- Produce a longer vowel
- Raise the pitch of the syllable to a higher level
- Say the syllable louder
- Pronounce it with clarity
- Create a more distinctive facial movement
Don’t forget these five features next time you pronounce a word!
8 Word Stress Rules to Improve Your English Pronunciation
1. Nouns and adjectives with two syllables
The rule: When a noun (a word referring to a person, thing, place or abstract quality) or an adjective (a word that gives information about a noun) has two syllables, the stress is usually on the first syllable.
Examples:
table /TA-ble/
scissors /SCI-ssors/
pretty /PRE-tty/,
clever /CLE-ver/
Exceptions: Unfortunately, there are exceptions to this rule. It could be that a word was borrowed from another language or it could be totally random. You just have to learn these “outsiders” by heart. Here are three words you can start with:
hotel /ho-TEL/
extreme /ex-TREME/
concise /con-CISE/
2. Verbs and prepositions with two syllables
The rule: When a verb (a word referring to an action, event or state of being) or a preposition (a word that comes before a noun, pronoun or the “-ing” form of a verb, and shows its relation to another word or part of the sentence) has two syllables, the stress is usually on the second syllable.
Examples:
present /pre-SENT/
export /ex-PORT/
aside /a-SIDE/
between /be-TWEEN/
3. Words that are both a noun and a verb
The rule: Some words in English can be both a noun and a verb. In those cases, the noun has its word stress on the first syllable, and with the verb, the stress falls on the second syllable.
If you’ve been paying attention, you’ll see that this rule is a derivation from the prior two sections and notice some of the same words. However, this is a separate section since those pairs of words are relatively common in English and they’re likely to cause misunderstanding due to the same spelling.
Examples:
present /PRE-sent/ (a gift) vs. present /pre-SENT/ (give something formally)
export /EX-port/ (the practice or business of selling goods to another country or an article that is exported) vs. export /ex-PORT/ (to sell goods to another country)
suspect /SU-spect/ (someone who the police believe may have committed a crime) vs suspect /su-SPECT/ (to believe that something is true, especially something bad)
There are, however, exceptions to this rule. For example, the word “respect” has a stress on the second syllable both when it’s a verb and a noun.
4. Three syllable words ending in “er” and “ly”
The rule: Words that have three syllables and end in “-er” or “-ly” often have a stress on the first syllable.
Examples:
orderly /OR-der-ly/
quietly /QUI-et-ly/
manager /MA-na-ger/
5. Words ending in “ic,” “sion” and “tion”
The rule: When a word ends in “ic,” “sion” or “tion,” the stress is usually on the second-to-last syllable. You count syllables backwards and put a stress on the second one from the end.
Examples:
creation /cre-A-tion/
commission /com-MI-ssion/
photographic /pho-to-GRA-phic/
6. Words ending in “cy,” “ty,” “phy,” “gy” and “al”
The rule: When a word ends in “cy,” “ty,” “phy,” “gy” and “al,” the stress is often on the third to last syllable. Similarly, you count syllables backwards and put a stress on the third one from the end.
Examples:
democracy /de-MO-cra-cy/
photography /pho-TO-gra-phy/
logical /LO-gi-cal/
commodity /com-MO-di-ty/
psychology /psy-CHO-lo-gy/
7. Compound nouns
The rule: In most compound nouns (a noun made up of two or more existing words), the word stress is on the first noun.
Examples:
football /FOOT-ball/
keyboard /KEY-board/
8. Compound adjectives and verbs
The rule: In most compound adjectives (a single adjective made of more than one word and often linked with a hyphen) and compound verbs (a multi-word verb that functions as a single verb), the stress is on the second word.
Examples:
old-fashioned /old-FA-shioned/
understand /un-der–STAND/
Resources to Perfect Your Word Stress Skills
Here are some resources to learn about this important factor of English pronunciation:
- Forvo — Forvo is definitely one of the more popular audio dictionaries on the market. Translations are provided if you type in a word in English, and a map is shown to give you audio clips of how people say the particular word in varying dialects. For your convenience, we’ve linked the words in the guide to this resource so you’ll be able to hear the pronunciation immediately.
- Merriam-Webster — Merriam-Webster is a well-known dictionary and has high-quality definitions—all available offline. It lets you save favorites, has a word of the day and keeps track of recent searches you did. It’s also available as an app on both iOS and Android devices. Other dictionaries with pronunciation citations you can check out are MacMillan and Cambridge.
- FluentU — FluentU is a language learning website and app that teaches with videos made by, and for, native English speakers. This means you can learn and get used to the sounds of the language in context. Each clip comes with interactive subtitles where you can click on a word to get its definition as well as information on pronunciation. You can also practice writing and speaking vocabulary with personalized quizzes.
- English Club — English Club is a popular site for both English learners and teachers. It provides grammar lessons in small, easy-to-understand parts. There are also fun quizzes and games so you can practice the knowledge you learn. It’s entirely free. You can also find more word stress quizzes and exercises from Word Stress Rules and esl-lounge.
Constant practice will improve your stress pronunciation quickly and effectively! Soon, you can confidently apply what you learned to real conversations and sound like a true native speaker.
Mastering the subject of word stress isn’t easy, as there are many rules and exceptions. While native speakers do it naturally, English learners have to get there through a lot of practice and repetition.
These eight English speaking and word stress rules in this guide might seem a bit overwhelming but they work as references. Next time you hear a word or look something up in a dictionary, come back to these rules.
Make it a habit to be more aware of what you learn and soon you’ll perfect your pronunciation.
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1
Описание слайда:
Word Stress
Lecture 5
Слайд 2
Описание слайда:
Plan
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word Stress.
Placement of Word Stress.
Common Rules of Word Stress in English.
Functions of Word Stress.
Слайд 3
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Слайд 4
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the other syllables of the word
Слайд 5
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.
A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.
Слайд 6
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky: Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase of expiratory and articulatory activity.
S. F. Leontyeva: Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.
Слайд 7
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel Quality
These 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.
Слайд 8
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;
the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).
Слайд 9
Описание слайда:
The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.
Слайд 10
Описание слайда:
Types of Word Stress
Слайд 11
Описание слайда:
Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German);
musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).
Слайд 12
Описание слайда:
Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.
Слайд 13
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
Слайд 14
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees of stress in a word as there are syllables.
In English there are 3 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).
Слайд 15
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony: ´dictioˏnary.
weak (unstressed).
Слайд 16
Описание слайда:
Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]
Слайд 17
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Слайд 18
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting
Слайд 19
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).
Слайд 20
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on any syllable of the word):
English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.
Слайд 21
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´music — mu´sician
Слайд 22
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of factors:
phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.
Слайд 23
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is related to the status of a particular syllables in terms of the degree of sonority.
The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a´rrive — de´velop
Слайд 24
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on.
In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.
Слайд 25
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
Suffixes are divided into:
stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).
Слайд 26
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, -ful, -ing, -ish, -less, -ness, -ly, -ment):
´comfort – ´comfortable;
stress-fixing (-ion, -ic, -ity, -ial, -ive):
´curious — curi´osity;
stress-attracting(-ade, -eer, -ee, -esque, -ette, -ain):
ˏrefu´gee, ˏciga´rette.
Слайд 27
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast – to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record – to re´cord
´present – to pre´sent
Слайд 28
Описание слайда:
Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:
compound adjectives: ´hard-´working, ´blue-´eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´sit´down, ´take´off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four´teen, ´six´teen.
Слайд 29
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Слайд 30
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a´pply, a´ssist. But! ´honest.
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´enter, ´open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´money;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong: es´tate.
Слайд 31
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short vowel and ends with one consonant: de´termine.
the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.
Слайд 32
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:
di´saster;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´cinema
´insolent
Слайд 33
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the prefix:
im´possible, re´call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏex-´minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in´crease – ´increase.
Слайд 34
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate, -ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, — ade have stress on themselves or the preceding syllable:
ˏmari´nade, ˏspecia´lize;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco´nomic, ma´jority.
Слайд 35
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e´mergency
his´torical
Слайд 36
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Compounds are written as one word: ´bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of a verb and an adv.:´make-up.
The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole: ˏapple ´tart.
Parts of the house are implied: ˏfront ´door.
Слайд 37
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people:
ˏthick-´skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing are followed by adverbs:
ˏpasser´by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second-´class, three -´wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb:
head-´first.
Слайд 38
Описание слайда:
Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)
´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki´lometer – ´kilometer
Слайд 39
Описание слайда:
Functions of Word Stress
Слайд 40
Описание слайда:
Word Stress
Слайд 41
Описание слайда:
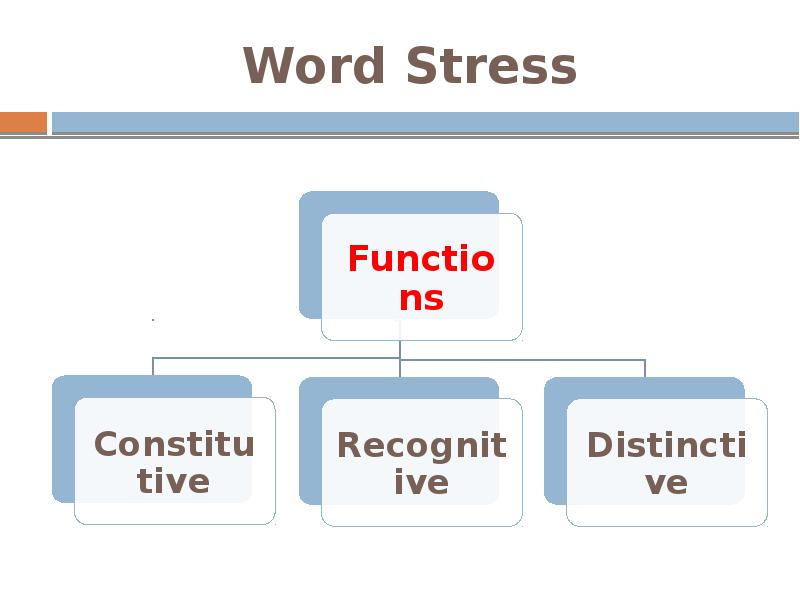
Functions of Word Stress
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the syllables into a word
The recognitive (identicatory) function:
word stress makes it possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.
The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´import — im´port.
Слайд 42
Описание слайда:
Questions:
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?
What factors determine the place of word stress?
Слайд 43
Описание слайда:
Literature
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.
O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.
Слайд 44
Описание слайда:
Thank you for your attention!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|















![Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]](https://myslide.ru/documents_7/36592529c536c90e3814b98ded49d489/img15.jpg)