Свойство white-space управляет тем, как обрабатываются пробельные символы внутри элемента.
Интерактивный пример
Сводка
/* Ключевые значения */
white-space: normal;
white-space: nowrap;
white-space: pre;
white-space: pre-wrap;
white-space: pre-line;
white-space: break-spaces;
/* Глобальные значения */
white-space: inherit;
white-space: initial;
white-space: unset;
| Начальное значение | normal |
|---|---|
| Применяется к | все элементы |
| Наследуется | да |
| Обработка значения | как указано |
| Animation type | discrete |
Синтаксис
Свойство white-space определяется, как одно ключевое слово, выбранное из списка значений, указанных ниже.
Значения
normal-
Последовательности пробелов объединяются в один пробел. Символы новой строки в источнике обрабатываются, как отдельный пробел. Применение данного значения при необходимости разбивает строки для того, чтобы заполнить строчные боксы.
nowrap-
Объединяет последовательности пробелов в один пробел, как значение
normal, но не переносит строки (оборачивание текста) внутри текста. pre-
Последовательности пробелов сохраняются так, как они указаны в источнике. Строки переносятся только там, где в источнике указаны символы новой строки и там, где в источнике указаны элементы
<br>. pre-wrap-
Последовательности пробелов сохраняются так, как они указаны в источнике. Строки переносятся только там, где в источнике указаны символы новой строки и там, где в источнике указаны элементы
<br>, и при необходимости для заполнения строчных боксов. pre-line-
Последовательности пробелов объединяются в один пробел. Строки разбиваются по символам новой строки, по элементам
<br>, и при необходимости для заполнения строчных боксов.. break-spaces-
Поведение идентично
pre-wrapсо следующими отличиями:- Последовательности пробелов сохраняются так, как они указаны в источнике, включая пробелы на концах строк.
- Строки переносятся по любым пробелам, в том числе в середине последовательности пробелов.
- Пробелы занимают место и не висят на концах строк, а значит влияют на внутренние размеры (min-content и max-content).
В приведённой ниже таблице указано поведение различных значений свойства white-space:
| Новые строки | Пробелы и табуляция | Перенос текста по словам | Пробелы в конце строки | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
normal |
Объединяются в одну | Объединяются в один пробел | Переносится | Удаляются |
nowrap |
Объединяются в одну | Объединяются в один пробел | Не переносится | Удаляются |
pre |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Сохраняются как в источнике | Не переносится | Сохраняются как в источнике |
pre-wrap |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Сохраняются как в источнике | Переносится | Висят |
pre-line |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Объединяются в один пробел | Переносится | Удаляются |
break-spaces |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Сохраняются как в источнике | Переносится | Переносятся |
Формальный синтаксис
white-space =
normal | (en-US)
pre | (en-US)
nowrap | (en-US)
pre-wrap | (en-US)
break-spaces | (en-US)
pre-line
Примеры
Основной пример
code {
white-space: pre;
}
Перенос строк внутри элементов <pre>
pre {
word-wrap: break-word; /* IE 5.5-7 */
white-space: pre-wrap; /* текущие браузеры */
}
Спецификации
| Specification |
|---|
| CSS Text Module Level 3 # white-space-property |
Браузерная совместимость
BCD tables only load in the browser

Read on as we will explain it in great detail along with some code examples that you can use in your project.
Contents
- Possible Values for CSS White-space
- – Normal
- – Nowrap
- – Pre
- – Pre-wrap
- – Pre-line
- – Break-spaces
- Summary of CSS White-space values
- Possible Uses
- – Insert Line Breaks in Definition Lists
- – Typing Animation
- When Things Go Wrong
- – White-space Pre-line Extra Space
- – White-space: Pre Not Working as Expected
- – White-space Pre-wrap Not Working in Internet Explorer
- – White-space Nowrap With Ellipse
- CSS White-space vs Word-wrap
- Web Browser Support
- Conclusion
Possible Values for CSS White-space
The possible values for CSS white-space are:
- normal
- nowrap
- pre
- pre-wrap
- preline
- Break-spaces
In this first part of our article, we will be diving deeper into each of those values, so you fully understand each one’s scope.
– Normal
This is the default value, where the web browser will collapse a sequence of whitespace into a single one. Aso, if need be, the text will wrap into a new line.
The next HTML block has some whitespace, but when you view it in the web browser, they are all collapsed. Feel free to run this and see how it works:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: normal</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-normal”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur.
Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #1560bd;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #1560bd;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-normal {
white-space: normal;
}
– Nowrap
With CSS white space nowrap, the web browser will collapse a good deal of whitespace into a single one. What’s more, the text will not wrap into a new line.
When you run the next code in your browser, you’ll observe that all the text appears on a single line. As a result, it leads to an overflow:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: nowrap</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-nowrap”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur.
Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #c00;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #c00;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-nowrap {
white-space: nowrap;
}
– Pre
White-space: pre behaves like the
tag in HTML
. As a result, the web browser will preserve all the whitespace. The text will wrap if it contains a newline character or a line-break element like <br>.
Moreover, the next code demonstrates will help you understand how this works in a web browser. When you run the code, you’ll observe that all whitespace appears as it is in the HTML:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: pre</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-pre”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur.
Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #321fb7;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #321fb7;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-pre {
white-space: pre;
}
– Pre-wrap
This is like white-space: pre, but the white-space pre-wrap text will wrap the text if required.
Now, when you run the next code block in your web browser, some text will wrap to a new line, even if it’s a single text:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: pre-wrap</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-pre-wrap”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur.
Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #060223;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #060223;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-pre-wrap {
white-space: pre-wrap;
}
– Pre-line
White-space: pre-line will collapse a sequence of white space into a single one. Also, the text will wrap at line breaks, newline characters, and when it’s necessary.
The next code block will show you how white-space: pre-line works in a web browser, so check it out:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: pre-line</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-pre-line”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur.
Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #060223;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #060223;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-pre-line {
white-space: pre-line;
}
– Break-spaces
This is like white-space: pre, with the following exceptions:
- All preserved white space will take up space, even at the end of the line
- White space preservation takes precedence over line break characters. Irrespective of the position of the whitespace character
- The preserved white space affect the box’s min-content size and max-content size
In the next HTML code, there is lots of space added so you can see how this particular value works on the web page:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: break-spaces</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-break-spaces”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur.
Ut enim ad minim veniam,
quis nostrud.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse</p>
</div>
</main>
Summary of CSS White-space values
The table below is a summary of all CSS white space values and what happens when you use each one:
| Text wrapping | Spaces and tabs | New lines | End-of-line spaces | |
| normal | Wrap | Collapse | Collapse | Remove |
| nowrap | No wrap | Collapse | Collapse | Remove |
| pre | No wrap | Preserve | Preserve | Preserve |
| pre-wrap | Wrap | Preserve | Preserve | Hang |
| pre-line | Wrap | Collapse | Preserve | Remove |
| break-spaces | Wrap | Preserve | Preserve | Wrap |
Possible Uses
You can use CSS white-space to create the following:
- Insert line breaks in definition list
- Typing animation
Let’s review each ouse-case so we can see how you can implement it in your code!
– Insert Line Breaks in Definition Lists
The elements of the definition list (<dt> and <dd>) are block-level elements. As a result, each of them will appear on a new line. Moreover, you can use white-space: pre to render the list in a presentable manner in the web browser:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>White-space: Insert space in Definition List</code>
</span>
<dl class=”definition-list”>
<dt class=”definition-term”>Name</dt>
<dd class=”definition-description”>John Doe</dd>
<dt class=”definition-term”>Email</dt>
<dd class=”definition-description”>john.doe@no-mail.com</dd>
<dd class=”definition-description”>john.doe@no-mail.com</dd>
<dt class=”definition-term”>Location</dt>
<dd class=”definition-description”>127.0.0.1</dd>
</dl>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #095a96;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #095a96;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.definition-term,
.definition-description {
display: inline;
}
.definition-description {
margin: 0;
font-weight: bold;
}
.definition-description + .definition-term::before {
content: ‘A’;
white-space: pre;
}
.definition-description + .definition-description::before {
content: ‘, ‘;
font-weight: normal;
}
– Typing Animation
In a typing animation, the text should appear on a single line without breaking into another line. This is achievable with the use of white-space: nowrap. Without it, the text will break into another line.
The next code block will show you how typing animation works in the web browser. Needless to say, white-space: nowrap plays a key role:
<div class=”typing-animation”>
<p>Typing animation</p>
</div>
body {
padding: 2em;
}
.typing-animation p {
font-size: 1em;
border-right: 0.5em solid #1560bd;
overflow: hidden;
width: 7.3em;
animation: typingAnimation 2s steps(40, end);
animation-fill-mode: forwards;
white-space: nowrap;
}
@keyframes typingAnimation {
0% {
width: 0;
}
99.9% {
border-right: 0.5em solid #1560bd;
}
100% {
border: none;
}
}
When Things Go Wrong
We took our time to identify some situations when white-space won’t work as expected. Also, we’ll discuss their potential solutions, which are:
- White-space pre-line extra space
- White-space pre not working as expected
- White-space pre-wrap not working in Internet Explorer
- White-space nowrap with ellipse
This happens when you have line breaks in your HTML code. Line-breaks can be newline characters (enter key on your keyboard) or HTML <br> elements.
So anytime you are using white-space: preline, look out for extra space at the top or bottom of the element in the HTML.
For example, in the next code block, there are four line breaks in the HTML. With white-space: pre-line, the web browser preserves the line breaks. As a result, the web browser will add unusual space at the top of the text:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: pre-line extra space</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-pre-line”>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod
tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #060223;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #060223;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-pre-line {
white-space: pre-line;
}
– White-space: Pre Not Working as Expected
If a text contains many carriage returns and you want to display them on many lines, you can use white-space: pre. However, this will not work as expected. The fix is to use white-space: pre-line.
The next code shows how to do this, so all you have to do is change the white-space value to pre-line, and you’ll get each text on a new line:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: pre not working</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-pre-not-working”>
<p>My name is John,
I am from Boston,
I am a Software Engineer.</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #330ceb;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #330ceb;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-pre-not-working {
/**
* This will not work as intended.
white-space: pre; */
/**
* Instead, use pre-line
*/
white-space: pre-line;
}
– White-space Pre-wrap Not Working in Internet Explorer
At this point, we should mention that the CSS white space pre wrap works in Internet Explorer version eight and higher. Now that you know that, you can avoid possible errors!
– White-space Nowrap With Ellipse
CSS white-space: nowrap will cause all the text to appear on a single line, and so at times, you might truncate the text. If you want the truncated text to have an ellipse at the end, you can use the following CSS code:
.text-selector {
display: block;
width: 50%;
min-width: 1px;
white-space: nowrap;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
The next code block is a full example that you can run in your web browser:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space: no-wrap on text</code>
</span>
<div class=”no-wrap-on-text”>
<p>My name is John,
I am from Boston,
I am a Software Engineer.</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #431c97;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #431c97;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.no-wrap-on-text p {
display: block;
width: 50%;
min-width: 1px;
white-space: nowrap;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
CSS White-space vs Word-wrap
CSS white-space and its values control white space in a text. Word-wrap allows you to break an unbreakable long string into a new line. An “unbreakable long string” means the text should not have any spaces in it.
The next code block shows how word-wrap works in a web browser, so all you have to do is run the code and observe what happens. Also, when you delete the word-wrap from the CSS code, the text will overflow its container:
<main>
<span class=”wrap-info”>
<code>white-space vs word-wrap</code>
</span>
<div class=”white-space-word-wrap”>
<p>Theisisanunbreakabletext.Theisisanunbreakabletext.Theisisanunbreakabletext.Theisisanunbreakabletext.Theisisanunbreakabletext.</p>
</div>
</main>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: grid;
place-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
main {
width: 50%;
border: 5px solid #3677f4;
padding: 2em;
font-size: 1.2em;
line-height: 1.168;
position: relative;
}
.wrap-info {
position: absolute;
bottom: -3.2em;
left: -0.25em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #3677f4;
color: #ffffff;
font-weight: bold;
}
.white-space-word-wrap {
width: 200px; /* This will restrict the text */
}
p {
/*white-space: nowrap;*/
word-wrap: break-word;
}
Web Browser Support
All modern web browsers support CSS white-space property.
Conclusion
At this stage, you’ve learned a lot about CSS white-space, and when you can use it. Here is a summary of everything that you’ve learned in the article:
- You can use CSS white-space to control the white space in your text
- CSS white-space property accepts values such as nowrap, pre, pre-wrap, pre-line, and break-spaces
- You can use CSS white-space to create a typing animation. Also, you can use it to insert line breaks in HTML definition lists
- CSS white-space is different from word-wrap; CSS white-space controls whitespace, whereas word-wrap will break an unbreakable string into a new line
- CSS white-space works in Internet Explorer eight and above

- Author
- Recent Posts
Your Go-To Resource for Learn & Build: CSS,JavaScript,HTML,PHP,C++ and MYSQL. Meet The Team
How can text like aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa which exceeds the width of a div (say 200px) be wrapped?
I am open to any kind of solution such as CSS, jQuery, etc.
trejder
17k27 gold badges123 silver badges215 bronze badges
asked Jul 18, 2009 at 15:56
Satya KalluriSatya Kalluri
5,1084 gold badges27 silver badges37 bronze badges
Try this:
div {
width: 200px;
word-wrap: break-word;
}
answered Jul 18, 2009 at 16:02
Alan Haggai AlaviAlan Haggai Alavi
72.2k19 gold badges101 silver badges127 bronze badges
6
On bootstrap 3, make sure the white-space is not set as ‘nowrap’.
div {
width: 200px;
word-break: break-all;
white-space: normal;
}
answered Nov 12, 2013 at 8:39
2
You can use a soft hyphen like so:
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa­aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
This will appear as
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa-
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
if the containing box isn’t big enough, or as
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
if it is.
Tunaki
131k46 gold badges330 silver badges415 bronze badges
answered Jul 18, 2009 at 16:13
Kim StebelKim Stebel
41.6k12 gold badges125 silver badges142 bronze badges
7
div {
/* Set a width for element */
word-wrap: break-word
}
The ‘word-wrap‘ solution only works in IE and browsers supporting CSS3.
The best cross browser solution is to use your server side language (php or whatever) to locate long strings and place inside them in regular intervals the html entity
This entity breaks the long words nicely, and works on all browsers.
e.g.
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
code
5,1204 gold badges16 silver badges37 bronze badges
answered Jul 18, 2009 at 16:14
Orr SiloniOrr Siloni
1,24010 silver badges20 bronze badges
1
This worked for me
word-wrap: normal;
word-break: break-all;
white-space: normal;
display: block;
height: auto;
margin: 3px auto;
line-height: 1.4;
-webkit-line-clamp: 1;
-webkit-box-orient: vertical;
answered Jun 2, 2016 at 2:04
AmolAmol
9087 silver badges20 bronze badges
1
The only one that works across IE, Firefox, chrome, safari and opera if there are no spaces in the word (such as a long URL) is:
div{
width: 200px;
word-break: break-all;
}
I found this to be bullet-proof.
answered Apr 12, 2013 at 13:56
Kyle DearleKyle Dearle
1291 gold badge2 silver badges9 bronze badges
0
Another option is also using:
div
{
white-space: pre-line;
}
This will set all your div elements in all browsers that support CSS1 (which is pretty much all common browsers as far back as IE 
answered Oct 14, 2014 at 15:59
1
Cross Browser
.wrap
{
white-space: pre-wrap; /* css-3 */
white-space: -moz-pre-wrap; /* Mozilla, since 1999 */
white-space: -pre-wrap; /* Opera 4-6 */
white-space: -o-pre-wrap; /* Opera 7 */
word-wrap: break-word; /* Internet Explorer 5.5+ */
}
answered Apr 20, 2015 at 9:21
TimelessTimeless
7,2898 gold badges60 silver badges94 bronze badges
<p style="word-wrap: break-word; word-break: break-all;">
Adsdbjf bfsi hisfsifisfsifs shifhsifsifhis aifoweooweoweweof
</p>
answered Oct 1, 2020 at 20:23
Manoj AlwisManoj Alwis
1,27911 silver badges24 bronze badges
Example from CSS Tricks:
div {
-ms-word-break: break-all;
/* Be VERY careful with this, breaks normal words wh_erever */
word-break: break-all;
/* Non standard for webkit */
word-break: break-word;
-webkit-hyphens: auto;
-moz-hyphens: auto;
hyphens: auto;
}
More examples here.
answered Feb 4, 2015 at 10:01
In HTML body try:
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<div style="word-wrap: break-word; width: 800px">
Hello world, how are you? More text here to see if it wraps after a long while of writing and it does on Firefox but I have not tested it on Chrome yet. It also works wonders if you have a medium to long paragraph. Just avoid writing in the CSS file that the words have to break-all, that's a small tip.
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
In CSS body try:
background-size: auto;
table-layout: fixed;
John Slegers
44.5k22 gold badges201 silver badges169 bronze badges
answered Feb 6, 2016 at 17:06
Add this CSS to the paragraph.
width:420px;
min-height:15px;
height:auto!important;
color:#666;
padding: 1%;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: normal;
word-wrap: break-word;
text-align: left;
TylerH
20.6k64 gold badges76 silver badges97 bronze badges
answered May 23, 2012 at 9:53
Swapnil GodambeSwapnil Godambe
2,0541 gold badge24 silver badges28 bronze badges
1
Try this
div{
display: block;
display: -webkit-box;
height: 20px;
margin: 3px auto;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 1.4;
-webkit-line-clamp: 1;
-webkit-box-orient: vertical;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}the property text-overflow: ellipsis add … and line-clamp show the number of lines.
answered Nov 27, 2014 at 21:10
I have used bootstrap.
My html code looks like ..
<div class="container mt-3" style="width: 100%;">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-12 wrap-text">
<h6>
text content
</h6>
</div>
</div>
</div>
CSS
.wrap-text {
text-align:justify;
}
Stephen Rauch♦
47.2k31 gold badges110 silver badges133 bronze badges
answered Sep 18, 2018 at 2:24
1
you can use this CSS
p {
width: min-content;
min-width: 100%;
}
answered Dec 27, 2019 at 10:22
Rashid IqbalRashid Iqbal
1,05313 silver badges12 bronze badges
Try this CSS property —
overflow-wrap: anywhere;
answered Jun 9, 2022 at 6:12
A server side solution that works for me is: $message = wordwrap($message, 50, "<br>", true); where $message is a string variable containing the word/chars to be broken up. 50 is the max length of any given segment, and "<br>" is the text you want to be inserted every (50) chars.
answered Jan 23, 2012 at 7:31
1
Try this
div {display: inline;}
answered Jul 18, 2018 at 16:58
try:
overflow-wrap: break-word;
borchvm
3,48411 gold badges45 silver badges43 bronze badges
answered Jan 29, 2020 at 3:00
Use word-wrap:break-word attribute along with required width. Mainly, put
the width in pixels, not in percentages.
width: 200px;
word-wrap: break-word;
JSuar
21.1k4 gold badges43 silver badges82 bronze badges
answered Jan 27, 2011 at 8:36
1
Для разного контента нужны разные правила форматирования: фрагменты кода должны сохранять все переносы строк и табуляцию; текст, написанный случайным посетителем сайта, не должен «порвать» вёрстку и т.п. Форматирование можно контролировать с помощью CSS.
Свойство white-space
CSS свойство white-space описывает то, как будут обрабатываться пробельные символы внутри элемента.
| Новая строка | Пробелы и табуляция | Перенос текста | |
|---|---|---|---|
| normal | схлопывается | схлопываются | есть |
| nowrap | схлопывается | схлопываются | нет |
| pre | остаётся | остаются | нет |
| pre-wrap | остаётся | остаются | есть |
| pre-line | остаётся | схлопываются | есть |
Значения pre-wrap и pre-line
доступны во всех современных версиях браузеров и в IE начиная с версии 8.0.
Подробнее o white-space на w3.org
Свойство word-wrap
Изначально это свойство появилось в линейке браузеров IE и только потом перекочевало в другие браузеры, так и не появившись в спецификации CSS2. В CSS3 аналогичное поведение закреплено за свойством
overflow-wrap, а word-wrap останется в качестве псевдонима.
Это свойство может принимать значения:
- normal
-
Переносы строк будут формироваться только в дозволенных позициях.
- break-word
-
Слово будет разрываться, если в пределах строки нет подходящей позиции для переноса строки.
Это свойство можно использовать для переноса строк в теге <pre> даже в старых версиях IE:
pre {
word-wrap: break-word; /* IE 5.5-7 */
white-space: pre-wrap; /* current browsers */
}
Подробнее o word-wrap (overflow-wrap) на w3.org
Свойство word-break
Когда нужно применить «грубую силу» и переносить любую строку в любом месте (я даже не представляю себе где это может потребоваться), то в дело вступает word-break.
.text_user-generated_yes {
word-break: break-all;
}
Это свойство имеет больший приоритет, чем
word-wrap (overflow-wrap) и будет разрывать слова даже там, где это особо и не требуется.
В браузерах на Webkit это свойство имеет ещё одно нестандартное значение – break-word, которое по своему действию аналогично word-wrap
.
Подробнее o word-break на w3.org
Свойство hyphens
С нетерпением ждём, когда браузеры начнут делать автоматическую расстановку переносов в словах.
.text {
-webkit-hyphens: auto;
-moz-hyphens: auto;
hyphens: auto;
}
Основным препятствием на пути внедрения этой технологии стоит то, что браузеру требуется описание правил переноса слов для различных языков. На сегодняшний день только Safari и Firefox могут похвастаться этим.
Подробнее o hyphens на w3.org
Editor’s note: This complete guide to word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break in CSS was last updated 24 February 2023 to reflect the reflect the most recent version of CSS, include interactive code examples, and include a section on how to wrap text using CSS. To learn more about the overflow property, check out our guide to CSS overflow.
Making a site responsive so that it displays correctly on all devices is very important in this day and age. Unfortunately, despite your best efforts to do so, you may still end up with broken layouts. Broken layouts can happen when certain words are too long to fit in their container. Content overflow can occur when you are dealing with user-generated content you have no control over, such as the comments section of a post. Therefore, you need to apply styling to prevent content from overflowing their container.
Content overflow is a common problem for frontend developers. On the web, overflow occurs when your content doesn’t fit entirely within its containing element. As a result, it spills outside. In CSS, you can manage content overflow mainly using the overflow, word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties. However, our focus in this article will be on the word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties.
Jump ahead:
- Using
word-wrap,overflow-wrap, andword-breakCSS properties- How does content wrapping occur in browsers?
- What is the difference between a soft wrap break and a forced line break?
- Understanding the
Word-wrapandoverflow-wrapCSS propertiesNormalAnywhereBreak-word
- Implementing the
Word-breakCSS property- Setting
word-breaktoNormal - The
Break-allvalue - Using the
Keep-allvalue
- Setting
- What is the difference between
overflow-wrapandword-break? - How to wrap text using CSS
- Troubleshooting CSS content overflow with Chrome DevTools
Using word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties
You can use the word-wrap, overflow-wrap, or word-break CSS properties to wrap or break words that would otherwise overflow their container. This article is an in-depth tutorial on the word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties and how you can use them to prevent content overflow from ruining your nicely styled layout. Before we get started, let us understand how browsers wrap content in the next section.
How does content wrapping occur in browsers?
Browsers and other user agents perform content wrapping at allowed breakpoints, referred to as soft wrap opportunities. A browser will wrap content at a soft wrap opportunity, if one exists, to minimize content overflow. In English and other similar writing systems, soft wrap opportunities occur by default at word boundaries in the absence of hyphenation. Because words are bound by spaces and punctuation, that is where soft wraps occur.
Although soft wraps occur in space characters in English texts, the situation might be different for non-English writing systems. Some languages do not use spaces to separate words, meaning that content wrapping depends on the language or writing system. The value of the lang attribute you specify on the HTML element is mostly used to determine which language system is used.
This article will focus mainly on the English language writing system. The default wrapping at soft wrap opportunities may not be sufficient if you are dealing with long, continuous text, such as URLs or user-generated content, which you have very little or no control over. Before we go into a detailed explanation of these CSS properties, let’s look at the differences between soft wrap break and forced line break in the section below.
What is the difference between a soft wrap break and a forced line break?
Any text wrap that occurs at a soft wrap opportunity is referred to as a soft wrap break. For wrapping to occur at a soft wrap opportunity, you need to make sure you’ve enabled wrapping. For example, setting the value of white-space CSS property to nowrap will disable wrapping. Forced line breaks are caused by explicit line-breaking controls or line breaks marking the end or start of blocks of text.
Understanding the Word-wrap and overflow-wrap CSS properties
The name word-wrap is the legacy name for the overflow-wrap CSS property. Word-wrap was originally a non-prefixed Microsoft extension and was not part of the CSS standard, though most browsers implemented it with the name word-wrap. According to the draft CSS3 specification, browsers should treat word-wrap as a legacy name alias of the overflow-wrap property for compatibility.
Most recent versions of popular web browsers have implemented the overflow-wrap property. The draft CSS3 specification refers to the overflow-wrap property as:
This property specifies whether the browser may break at otherwise disallowed points within a line to prevent overflow when an otherwise-unbreakable string is too long to fit within the line box.
If you have a white-space property on an element, you need to set its value to allow wrapping for overflow-wrap to have an effect. Below are the values of the overflow-wrap property:
overflow-wrap: normal; overflow-wrap: anywhere; overflow-wrap: break-word;
You can also use the global values inherit, initial, revert, and unset with overflow-wrap, but we won’t cover them here. In the subsections below, we will look at the values of the overflow-wrap CSS property outlined above to understand the behavior of this property.
Normal
Applying the value normal will make the browser use the default line-breaking behavior of the system. For English and other related writing systems, line breaks will therefore occur at whitespaces and hyphens, as shown below:
.my-element{
overflow-wrap: normal;
}
In the example below, there is a word in the text that is longer than its container. Because there is no soft wrap opportunity and the value of the overflow-wrap property is normal, the word overflows its container. It describes the default line-breaking behavior of the system:
See the Pen
overflow-wrap-normal by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Anywhere
Using the value anywhere will break an otherwise unbreakable string at arbitrary points between two characters. It will not insert a hyphen character even if you apply the hyphens property on the same element.
The browser will break the word only if displaying the word on its line will cause an overflow. If the word still overflows when placed on its line, it will break the word at the point where an overflow would otherwise occur. When you use anywhere, the browser will consider the soft wrap opportunities introduced by the word break when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes:
.my-element{
overflow-wrap: anywhere;
}
Unlike in the previous section, where we used overflow-wrap: normal, in the example below, we are using overflow-wrap: anywhere. The overflowing word that is otherwise unbreakable is broken into chunks of text using overflow-wrap: anywhere so that it fits in its container:
See the Pen
overlow-wrap-anywhere by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
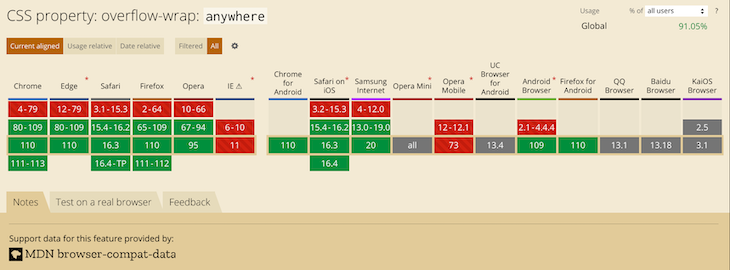
Most recent versions of desktop browsers support overflow-wrap: anywhere. However, support for some mobile browsers is either lacking or unknown. The image below shows the browser support:
Break-word
The value break-word is like anywhere in terms of functionality. If the browser can wrap the overflowing word to its line without overflowing, that is what it will do. However, if the word still overflows its container even when it is on its line, the browser will break it at the point where the overflow would otherwise occur:
.my-element{
overflow-wrap: break-word;
}
The example below shows how the browser breaks the overflowing text when you apply overflow-wrap: break-word:
See the Pen
overflow-wrap-break-word by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Notice that the text appears the same as in the last subsection. The difference between overflow-wrap: anywhere and overflow-wrap: break-word is in the min-content intrinsic sizes.
The difference between anywhere and break-word is apparent when calculating the min-content intrinsic sizes. With break-word, the browser doesn’t consider the soft wrap opportunities introduced by the word break when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes, but it does with anywhere. For more about min-content intrinsic sizes, check out our guide here.
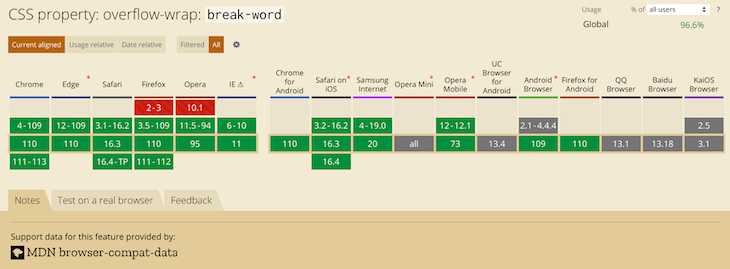
The value break-word has decent coverage among the most recent versions of desktop browsers. Unfortunately, you cannot say the same about their mobile counterpart. It is, therefore, safer to use the legacy word-wrap: break-word instead of the more recent overflow-wrap: break-word.
The image below shows browser support for overflow-wrap: break-word:
The most recent versions of desktop browsers have support, while support for some mobile browsers is unknown.
Implementing the Word-break CSS property
Word-break is another CSS property you can use to specify soft wrap opportunities between characters. You can use this property to break a word at the exact spot where an overflow would occur and wrap it onto the following line.
The draft CSS3 specification refers to the word-break CSS property as:
This property specifies soft wrap opportunities between letters, i.e., where it is “normal” and permissible to break lines of text. It controls what types of letters the browser can glom together to form unbreakable “words” — causing CJK characters to behave like non-CJK text or vice versa.
Below are the possible values of the word-break CSS property. Like overflow-wrap, you can use the global values inherit, initial, revert, and unset with word-break, but we won’t cover them here:
word-break: normal; word-break: break-all; word-break: keep-all;
Break-word is also a value of the word-break CSS property, though it was removed. However, browsers still support it for legacy reasons. Specifying this property has the same effect as word-break: normal and overflow-wrap: anywhere.
Now that we know the break-word CSS property and its corresponding values, let us look at them in the subsections below.
Setting word-break to Normal
Setting the value of the word-break property to normal will apply the default word breaking rules:
.my-element{
word-break: normal;
}
The example below illustrates what happens when you apply the styling word-break: normal to a block of text that contains a word longer than its container:
See the Pen
word-break-normal by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
What you see is the browser’s usual word-breaking rules in effect.
The Break-all value
The value break-all will insert a line break at the exact point where the text would otherwise overflow for non-Chinese, non-Japanese, and non-Korean writing systems. It will not put the word on its own line, even if doing so will prevent the need to insert a line break:
.my-element{
word-break: break-all;
}
In the example below, I am applying word-break: break-all styling to a p element of width 240px containing an overflowing text. The browser will insert a line break at the point where an overflow would occur and wrap the remaining text to the following line:
See the Pen
word-break-break-all by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Using break-all will break a word between two characters at the exact point where an overflow would occur in English and other related language systems. However, it won’t apply the same behavior to Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) texts.
It doesn’t apply the same behavior for CJK texts because CJK writing systems have their own rules for applying breakpoints. Creating a line break between two characters arbitrarily just for the sake of avoiding overflow might significantly change the overall meaning of the text. For CJK systems, the browser will apply line breaks at the point where such breaks are allowed.
Using the Keep-all value
If you use the value keep-all, the browser will not apply word breaks to CJK texts, even if there is content overflow. The effect of applying keep-all value is the same as that of normal for non-CJK writing systems:
.my-element{
word-break: keep-all;
}
In the example below, applying word-break: keep-all will have the same effect as word-break: normal for a non-CJK writing system such as English:
See the Pen
word-break-keep-all by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
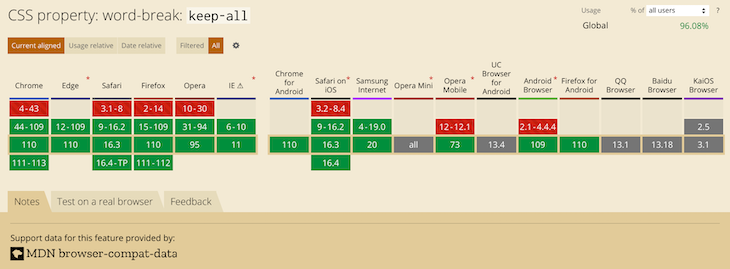
The image below shows the browser support for word-break: keep-all:
This value has support in most popular desktop browsers. Unfortunately, it is not the case for mobile browsers. Now that we have looked at the overflow-wrap and word-break CSS properties, what is the difference between the two? The section below will shed light on that.
What is the difference between overflow-wrap and word-break?
You can use the CSS properties overflow-wrap and word-break to manage content overflow. However, there are differences in the way the two properties handle it.
Using overflow-wrap will wrap the entire overflowing word to its line if it can fit in a single line without overflowing its container. The browser will break the word only if it cannot place it on a new line without overflowing. In most cases, the overflow-wrap property or its legacy name word-wrap might manage content overflow. Using word-wrap: break-word will wrap the overflowing word onto a new line and goes ahead to break it between two characters if it still overflows its container.
Word-break will ruthlessly break the overflowing word between two characters even if placing it on its line will negate the need for word break. Some writing systems, like the CJK writing systems, have strict word breaking rules the browser takes into consideration when creating line breaks using word-break.
How to wrap text using CSS
As hinted above, if you want to wrap text or break a word overflowing the confines of its box, your best bet is the overflow-wrap CSS property. You can also use its legacy name, word-wrap. Try the word-break CSS property if the overflow-wrap property doesn’t work for you. However, be aware of the differences between overflow-wrap and word-break highlighted above.
Below is an illustration of the overflow-wrap and word-wrap CSS properties. You can play with the CodePen to understand their effects:
See the Pen
how-to-wrap-text by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Troubleshooting CSS content overflow with Chrome DevTools
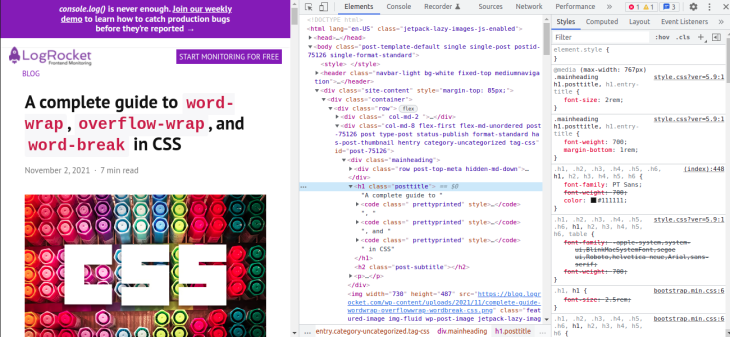
More often than not, you might need to fix broken layouts caused by content overflow, as complex user interfaces are now commonplace in frontend development. Modern web browsers come with tools for troubleshooting such layout issues, such as Chrome DevTools.
It provides the capability to select an element in the DOM tree so that you can view, add, and remove CSS declarations and much more. It will help you track down the offending CSS style in your layout and fix it with ease.
To open the Chrome DevTools, you can use the F12 key. When open, it looks like in the image below. Selecting an element in the DOM tree will display its corresponding CSS styles. You can modify the styles and see the effect on your layout as you track down the source of the bug:
As already mentioned, if you have white-space property on an element, set its value to allow wrapping for overflow-wrap: anywhere or overflow-wrap: break-word to work.
Setting the value of overflow-wrap property to anywhere or break-word on a table content won’t break an overflowing word like in the examples above. The table will overflow its container and create a horizontal scroll if necessary. To get the table to fit within its container and overflow-wrap to work, set the value of the table-layout property to fixed and set the table width to 100% or to some fixed value.
Conclusion
As pointed out in the above sections, overflow-wrap and word-break are similar in so many ways, and you can use both of them for line-breaking controls. The name overflow-wrap is an alias of the legacy word-wrap property. Therefore, you can use the two interchangeably. However, it is worth mentioning that the browser support for the newer overflow-wrap property is still low. You are better off using word-wrap instead of overflow-wrap if you want near-universal browser support.
According to the draft CSS3 specification, browsers and user agents should continue supporting word-wrap for legacy reasons. If you are looking to manage content overflow, overflow-wrap or its legacy name word-wrap might be sufficient. You can also use word-break to break a word between two characters if the word overflows its container. Just like overflow-wrap, you need to tread with caution when using word-break because of limitations in the browser support.
Now that you know the behavior associated with the two properties, you can decide where and when to use them. Did I miss anything? Leave a comment in the comments section. I will be happy to update this article.
Is your frontend hogging your users’ CPU?
As web frontends get increasingly complex, resource-greedy features demand more and more from the browser. If you’re interested in monitoring and tracking client-side CPU usage, memory usage, and more for all of your users in production, try LogRocket.
LogRocket is like a DVR for web and mobile apps, recording everything that happens in your web app, mobile app, or website. Instead of guessing why problems happen, you can aggregate and report on key frontend performance metrics, replay user sessions along with application state, log network requests, and automatically surface all errors.
Modernize how you debug web and mobile apps — Start monitoring for free.