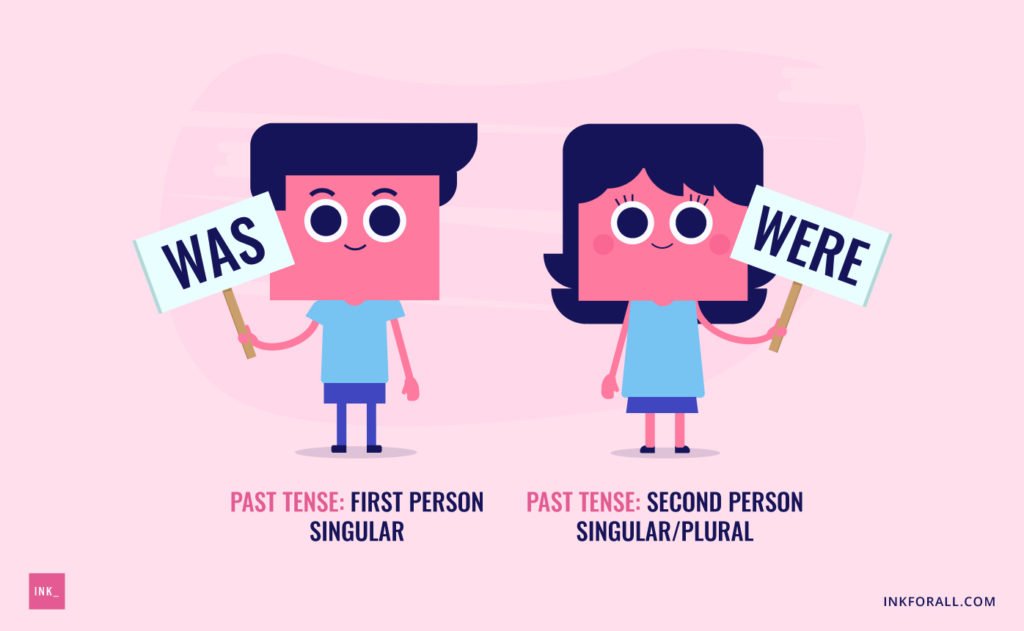
Both was and were are correct forms of the verb “to be.” However, when to use was vs. were depends on whether you’re talking about something imaginary or something real.
Hypothetical situations need the subjunctive mood, so you should use were regardless of the speaker’s point of view. However, situations that actually happened in the past need the indicative mood. This means subject-verb agreement comes into play, so you should use was with I/he/she (She was here) but were with you/we/they (You/we/they were here).
When to Use Was vs. Were at a Glance:
Should you use was or were? This is a grammar question that even native English speakers struggle to answer correctly. Let’s look at the easiest way to know the difference between was and were. What’s more, you’ll see was vs. were example sentences and learn how to correctly use this irregular verb.
| Indicative Mood: Past tense of the verb “to be” | I was | you were | he was | she was | it was | we were | you were | they were |
| Subjunctive Mood: Hypothetical situations with the verb “to be” | I were | you were | he were | she were | it were | we were | you were | they were |
In this way, the difference between was and were comes down to describing something that actually happened in the past vs. an imaginary situation that never happened at all. Moreover, it also depends on who is speaking. Finally, subject-verb agreement also comes into play.
3 Easy Steps That Tell you When to use Was vs. Were
1. Ask yourself these questions:
- Did it really occur in the past?
- Or, are we talking about an imaginary situation that can’t be real?
2. If it actually occurred in the past:
Use was with the first and third person singular points of view:
- I was
- She was
- He was
- It was
- You were
But, use were with the second person (you) or third person (they) plural points of view. This helps ensure correct subject-verb agreement.
- You were
- They were
3. If the situation is imaginary and can’t be real:
Were is the only correct option. As such, use were for every point of view.
Why Second Conditional Uses Were?
A second conditional, or type 2 conditional sentence, describes hypothetical or imaginary situations, like dreams and wishes. In some instances, those situations could happen in the future, but they most likely won’t.
Below is the structure for a second conditional statement:
If + verb to be + condition
In the statement above, we used “were” instead of “was.” That’s even if the latter is considered the proper past simple form of the verb to be to go with the pronoun “I.”
We do this because we’re talking about an imaginary situation. No one can reverse time and be a child again, right? That’s just impossible. By saying “If I were,” we’re changing the mood of the verb to be from indicative to subjunctive.
The indicative mood describes real situations or facts. On the other hand, the subjunctive mood describes situations that are hypothetical or are not real. For second conditional statements, we always use were.
“Was” Usually Refers to the Past
When you see the word “was,” we’re most likely talking about something that previously occurred.
Specifically, was indicates that the first and third singular person points of view acted in the past. For this reason, we use was with the indicative mood.
In other words, the rule for was/were typically comes down to singular vs. plural when using the past tense of the verb “to be.”
However, as with most grammatical rules in English, there is an exception here.
Which is Correct: “If I Was” or “If I Were”
Most statements that include if are subjunctive. In these cases, we use were. Notwithstanding, there is one exception for the first person point of view: I.
On one side, we have was in the indicative mood to indicate reality.
On the other, we have were in the subjunctive mood to refer to imaginary or hypothetical situations.
But, there is also a third option in the middle: what should you use when you aren’t sure if something is real or imaginary?
In this case, “If I was” is the grammatically correct choice. In other words, when it’s not clear if something is real or hypothetical, “I was” is correct.
In the above example, the speaker isn’t sure if they made a mistake or not. This situation might be imaginary, but it might also be real. As a result, the speaker can’t use were since this option is for purely imaginary situations.
Therefore, we use “If I was” to show this doubt grammatically.
Now, let’s compare the “If I was vs. were” in action:
The above example expresses a purely imaginary situation: I don’t live in Los Angeles, so I don’t drive to work. I show that the scenario isn’t real by using the verb “to be” with the subjunctive mood were.
Conversely, the above example expresses doubt. For instance, I did live in Los Angeles in the past, but I don’t anymore. Additionally, I used to drive, but I don’t anymore.
If I don’t remember exactly when I moved or when I stopped driving, I should use the if I was construction to express this doubt to my audience.
When “Were” is Past Tense and When it’s Subjunctive
Was tends to hang out exclusively with the past tense in the indicative mood. However, were can express the real past tense in the indicative mood or an imaginary situation in the subjunctive mood. How do you tell the difference?
Were and Past Tense
The trick here is to associate were and the past tense with subject-verb agreement. In other words, whether you should use was vs. were depends on who is speaking.
For example, use was with these points of view:
- First person singular = I was
- Third person singular = he/she/it was
However, use were with these points of view:
- Second person singular = you were
- Second person plural = you (all) were
- First person plural = wewere
- Third person plural = theywere
Should I use Was or Were with There?
Whether to use was or were with therehas to do with subject-verb agreement. When a sentence starts with the word there, the words following the verb are typically the subject. For example, in the sentence “There are oranges on the table,” the subject is oranges. If the subject is singular, then you should use the verb was (“There was an orange…“). Yet, if the subject is plural, then the correct verb to use is were (“There were oranges…“).
📝 Whether to use was or were depends on several factors, including:
- Subject-verb agreement
- Whether you’re using the subjunctive mood
- Point of view
Were and the Subjunctive Mood
Subjunctive what? Unless you’re a diehard grammarian or advanced polyglot, you’ve probably never heard of subjunctive mood. In simple terms, the phrase describes a verb tense we associate with unreal statements or questions.
Essentially, whereas most statements reveal something that is currently happening or has previously happened, a subjunctive sentence refers to something that hasn’t actually happened. That may be a want, a wish, or a suggestion.
📝 We use the subjunctive mood to express:
- Demands
- Proposals
- Desires
- Wishfulness
- Hypothetical situations
- Possibilities
In both written and spoken English, subjunctive mood usually appears by an indicative verb such aswant, wish, desire, suggest, or recommend. What’s more, sentences that express possibilities often include the word if.
When creating a subjunctive mood, the traditional singular/plural rules for was/were don’t apply. In fact, when it comes to the subjunctive mood, there’s an easy rule for choosing was or were: always choose were.
📝 Phrases used to express subjunctive mood include:
- I were
- You were
- He/she were
- It were
- They were
- This were
- That were
You’ll note that none of these examples describes a current reality. Instead, they all describe hypothetical, desired, or imaginary situations. Therefore, we use were regardless of whether the subject is singular or plural to make this departure from reality clear.
Which is Correct Grammatically: If I Was or If I Were?
Both of the phrases if I was and if I were are grammatically correct, but they mean very different things. Therefore, the difference between if I was and if I weredepends on what you are trying to say. First, use if I was for something that might be real, or to express doubt when you’re not sure if something is true (If I was late responding to you, I apologize). Second, use if I were to express something unreal, imaginary, or hypothetical (If I were a dragon…”
Often, the word if introduces subjunctive mood. When a sentence includes the phrase if I was orif I were, grammatists tend to label this subjunctive mood. That means the sentence refers to something that goes against, or is contrary to, the current truth. In other words, the sentence may express a desire, wish, possibility, or hypothetical situation. For subjunctive statements or questions, the grammatically correct phrase is “If I were“.
Was and Were Sentence Examples
Here are examples of was vs. were in a sentence:
Can you say if I Were?
You can say if I were. In fact, were is typically the correct conjugation of the verb to be in this context. Because this phrase begins with the word if, it’s subjunctive mood. That’s another way of saying it describes a hypothetical or unreal situation. In subjunctive sentences, the correct form of to be is always were.
Is If I Were a Boy Grammatically Correct?
If I were a boy is grammatically correct. This construction is correct because it reflects subjunctive mood. In other words, the phrase refers to a hypothetical or unreal situation. In this particular hypothetical, the writer is speculating about what might happen if her gender were different. When you write a sentence using subjunctive mood, you should always conjugate the the verb “to be” as were— regardless of the speaker’s point of view.
Were vs. Was: a Matter of Style?
It’s also worth noting that more and more writers are opting to use was instead of were in subjunctive sentences. This is particularly true in informal prose. It’s led some grammarians to speculate about the subjunctive were eventually becoming obsolete.
A Brief Was/Were Recap
By following a few basic rules, understanding when to use was and were doesn’t have to leave you with a headache.
- When conjugating the verb to be in the past tense, use was when writing in first or third person singular. Use were when writing in second person singular or plural or first-person or third-person plural.
- Use were when crafting sentences that involve hypothetical situations, speculation, or wishes. This is known as subjunctive mood and is often identified by the inclusion of the word if.
- If a sentence starts with the word there, use was if the subject is singular. Use were if the subject is plural.
Main Was vs. Were Takeaways:
- Was and were are past tense versions of the verb to be. They are both correct, depending on the context.
- When you want to talk about an imaginary, hypothetical, or unreal situation, use the subjunctive mood were across the board (If I were a dinosaur…).
- When you want to talk about reality, follow the normal conjugation for the verb “to be” in the past tense. Use the indicative mood was for I/he/she (She was here) but were with you/we/they (You/we/they were here).
Practice Your Grammar Skills With These Was and Were Exercises
Was and Were Question #1
A. Verbs
B. Adjectives
C. Adverbs
D. Nouns
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is A. “Was” and “were” are past tense versions of the verb “to be.”
Use or When Question #2
A. Point of view
B. Use of subjunctive mood
C. Subject-verb agreement
D. All of the above
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is D. All the factors outlined above can determine whether to use “was” or “when”.
Was vs. Were Question #3
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WAS. “Was” is the correct choice when writing in first person or third person (he, she, it) singular.
Were vs. Was Question #4
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. “Were” is correct when writing in the second-person singular, second-person plural, and first and third-person plural.
Was and Were Question #5
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. Hypothetical situations need the subjunctive mood. So “were” is appropriate.
Was vs. Were Question #6
A. Demands
B. Wishfulness
C. Past events
D. Hypothetical situations
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. A subjunctive sentence refers to something that hasn’t happened.
Were vs. Was Question #7
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. Either can be appropriate, depending on the subject-verb agreement.
Was or Were Question #8
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WAS. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in first-person singular.
Were or Was Question #9
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in third-person plural.
Was vs. Were Question #10
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. The situation is imaginary.
Were vs. Was Question #11
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WAS. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in third-person singular.
Was vs. Were Question #12
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in third-person plural.
Was vs. Were Quiz Result
Expert!
Not bad!
Almost got it! Review the article and try again.
Read More: 🛣️ Toward Vs. Towards: An Easy Guide On When To Use Which
There are plenty of questions associated with the verb to be. “To be or not to be,” for one. On a less existential note, there’s the question of how to use to be in the grammatically correct way. I am, you are, he was, they were—the forms of the verb to be, among many other things, are messy in English.
You might find yourself puzzling out a sentence such as: If she was unhappy, she should have said so. Is this sentence correct? Or should If she was switch to the phrase If she were?
Was vs. were, what’s the difference?
Much of the confusion lies in when to use was versus were, which are the past tense forms of to be. The answer all depends on two factors: 1) is your verb using first, second, or third person? And, 2) is your verb in past indicative or past subjunctive tense? Past indicative is used for ordinary objective statements or questions, and past subjunctive is used for imaginary or hypothetical statements or questions.
Were is always correct in the past subjunctive:
- I were
- You were
- He/she/it were
- We were
- You were
- They were
If this looks a little odd, remember that these constructions are often accompanied by a word like if, as if, and though. You might say, “If I were a rich man …”
Don’t we all wish we were rich … so would you say “wish I was” or “wish I were”?
To conjugate to be in the past indicative, however, using was or were depends on the subject:
- I was
- You were
- He/she/it was
- We were
- You were
- They were
It’s possible to get mixed up even with this straight conjugation in mind. But there are some tips and tricks to remember to make sure you use the correct verb form every time.
When to use was
Was is a past tense indicative form of be, meaning “to exist or live,” and is used in the first person singular (I) and the third person singular (he/she/it).
You use the past indicative when you’re talking about reality and known facts. If you went to the store, for example, then you would say, “I was at the store” because it is something that definitely happened. The same is true if you’re talking about someone else in the third person (or if you make the choice to talk about yourself in the third person). You would say, “Sarah was at the store,” for example, or “She was at the store.”
Another way to use was is as an auxiliary verb with a singular subject in the past continuous tense. An auxiliary verb is used with another verb that follows it in the sentence to express different tenses, aspects, moods, etc., and the past continuous tense refers to something that was ongoing in the past.
If you were to modify the previous example (I was at the store) with an auxiliary verb, you would say, “I was searching for spices at the store.” Was is the auxiliary verb (or helping verb) used to talk about what you were doing in the past (searching).
Examples of was in a sentence
So to recap, if you’re talking about something real that happened in the past, use the past tense indicative: I was or he/she/it was. (Were is used with the other pronouns.) Here are some example sentences:
- I was sick last night.
- He had an amazing imagination when he was a child.
- We turned down the music because it was too loud.
When to use were
Whereas was is the singular past tense of to be, were is used for both the third person plural past tense (they and we) and the second person past tense (you).
In the past indicative, were acts similar to was. “They were at the store,” you could say, for example. It also acts similar as an auxiliary verb, as in “They were searching for spices at the store.”
Things get a little more complicated with were, though, and it’s all thanks to this thing called the subjunctive mood.
The subjunctive mood is the opposite of indicative, and it’s all about things that are unreal or conditional. When you’re talking about your hopes and dreams, you’re using the subjunctive mood. The same goes for talking about something you intend or want to do, as well as for things you know will never be true or are no longer true.
A telltale sign that you’re working with the subjunctive mood is the word if, because this suggests a hypothetical. “If I were to go shopping, I could search for spices,” for example. It doesn’t matter if the subject is singular or plural, or if it’s first, second, or third person. If you’re using the subjunctive mood, the grammatically correct past tense of to be is were.
Speech is always evolving, and the subjunctive mood is used far less extensively than it was in the past. And what’s more, much of the way we talk and write in everyday English isn’t what our old schoolteachers would wag the ruler at us as “grammatically correct.” But if you want to conform with those standards, use were when it comes to the past tense of to be.
Examples of were in a sentence
If you’re discussing things that are unreal or conditional, then use were: I were and he/she/it were. Here are some example sentences:
- If I were in better shape, I would run in the race.
- She took over the meeting as if she were the boss.
- His father talked to him as though he were a child.
When to use was vs. were
To sum it all up, always use was for the past indicative first and third person singular. That goes for whether it’s a simple verb or auxiliary. “I was ready to watch the Auburn Tigers win the game,” and “He was watching number two score the winning touchdown.”
Write smarter with our thesaurus-powered Grammar Coach™! Get spelling help, synonyms suggestions, grammar check and more! Sign up now!
For the past indicative second person and all plural forms, use were. “They were in the stadium,” and “You were standing the whole game.” Also use were for the hypothetical or fantastical subjunctive mood for both singular and plural forms, as in “If they were to bring back popcorn, I would eat it.”
There was vs. there were
Was and were are also used in some instances with the pronoun there. This pronoun introduces a sentence or clause in which the verb comes before its subject (or those instances where the verb has no complement). When the subject that follows is singular, use was: When I opened the fridge, I found there was no more milk left. When the subject that follows is plural, use were: When I opened the fridge, I found there were no more eggs left.
In the end, yes, you were technically correct when you noted that the class lyric “I wish I was a little bit taller” should have been “I wish I were a little bit taller.” But don’t fret if you get it technically wrong at times. Were may be formally correct, but because the subjunctive mood has largely fallen out of common use, was may slip into yours and others’ speech at times.
If you sometimes struggle knowing when to use was and were, you aren’t alone. Many people are confused as to when to use the verb was and when to use the verb were. But the rules for using these terms are clear when you know what to look for.
Were and was are past tenses of the irregular verb to be. The verb to be is an irregular verb, which is a verb that does not follow any pattern or rules in its conjugation.
The verb to be is probably one of the most commonly used and confusing verbs in the English language. It can be particularly hard to understand whether to use were or was in certain situations if you don’t first determine the point of view the subject of the sentence provides.
What Is the Difference Between Was and Were?
Was and were are past tenses of the verb to be. The subject’s point of view determines whether you use was or were.
First Person Point of View: I, Me, My, Mine, Myself, We, Us, Our, Ours
Second Person Point of View: You, Your, Yours, Yourself
Third Person Point of View: He, Him, himself, She, Her, Hers, Herself, It, They, Them, Their, Theirs, Themselves
Was is the first person singular past tense form of the verb to be.
- I was walking to the grocery store.
Was is also the third person singular past tense form of the verb to be.
- She was not friendly when introduced to my sister.
Were is the second person singular and second person plural past tense form of the verb to be.
- You were heading in the wrong direction.
- You all were supposed to meet me after school yesterday.
Were is also the first and third person plural past tense form of the verb to be.
- We were going to the park when you drove by.
- They were heading to the game after school.
Be serves as an irregular verb and an irregular auxiliary verb. But what does being an irregular or irregular auxiliary verb have to do with it? First, let’s look at how to be is conjugated, so you understand how irregular verbs differ from other verbs.
Conjugating To Be
To be conjugates into five different forms:
What Is an Irregular Auxiliary Verb?
As you can see above, to be never used -ed in the past tense. Irregular verbs are defined as verbs that don’t use -ed in the past tense.
Irregular verbs rely on the auxiliary verb (or helping verb) to indicate the future, present, or past tense.
The past tense of to be can be used as a verb and as an auxiliary verb. When used as an auxiliary, it is followed by the verb to describe the tense.
For example:
- She was playing soccer.
- We were playing basketball.
It can also serve as a verb. For example,
- She was fifteen years old.
- They were high school graduates.
When to Use Was in a Sentence
Was is the first person singular past tense form of the verb to be and the third person singular past tense form of the verb to be.
For example:
- I was home last night.
- He was in bed at ten o’clock.
- She was at the restaurant until eleven.
- It was not a late night.
When to Use Were in a Sentence
Were is the second person singular and plural past tense form of the verb to be and the first and third person plural past tense form of the verb to be.
For example:
- We were going to the beach.
- You were home last night.
- The boys were in bed by ten o’clock.
- They were asleep by eleven.
There Were or There Was?
The use of were vs. was can get a little murky in a few situations. The first situation is when using the phrases there were or there was.
To use these terms correctly, you must identify the subject of the sentence and ensure the subject and verb are in agreement. Ensuring that a subject and verb are in agreement means making sure that they are either both plural or singular.
A good rule to remember is when a sentence begins with there, the subject is found after the verb. Once the subject has been identified, use the following rules:
- Use was if the subject is singular.
- Use were if the subject is plural.
Remember this rule when trying to decide whether to use was, were, or some other form of the verb to be.
For example:
- There was a dog on the road. (The subject is “dog,” a singular noun.)
- There were three people trying to lure the dog away from the road. (The subject is “people,” a plural noun.)
Hypothetical Situations
Using the word if or wish is a reliable indicator of using the subjective mood.
A subjunctive mood expresses a hypothetical situation that has not come to pass but might come to pass. It may be conditional, or it may simply be imaginary.
Subjunctive moods are almost always expressed using an if or I wish phrase.
A subjunctive mood always uses the past tense verb were. The verb were is the correct choice, regardless of whether the subject is singular or plural, when speaking of a conditional or hypothetical situation.
For example:
- If I were to ask her out, it’s possible she might tell me no.
- I wish I were there instead of sitting in class.
Using the word if is a reliable indicator of using subjective mood. Now you know that when faced with a choice between the phrases if I were or if I was, the phrase if I were is always correct.
Let’s Review
First Person Singular = Was
Third Person Singular = Was
Second Person Singular = Were
First Person Plural = Were
Second Person Plural = Were
Third Person Plural = Were
If the sentence is a hypothetical statement, always use were no matter whether the subject is singular or plural.
Was and were are both past tenses of the verb to be. The verb be is a tricky one because it is an irregular verb and one that we find ourselves using with great frequency, so it is that much more important that we choose the correct verb for our sentences.
In this post, I want to go over the grammar behind was vs. were, when it’s correct to use which one, and give you a few tips to keep track of them both. After reading this post, you shouldn’t have any trouble correctly choosing between was or were in your future writing.
Forms of Was and Were

Was is used in the first person singular (I) and the third person singular (he, she, it).
Were is used in the second person singular and plural (you, your, yours) and first and third person plural (we, they).
The forms that was and were will take in your sentence are summarized in the chart below,
Singular = I was, You were, He was, She was, It was
Plural = We were, You were, They were
- I was driving to the park.
- You were drinking some water.
- He was about to eat dinner.
- She was at the roller rink.
- It was a great time.
- We were in the right spot.
- They were nowhere to be seen.
If I was vs. If I were
While some people get mixed up on what we’ve covered above, most of the confusion with these two words centers on the use of the subjunctive mood and specifically the two phrases if I was vs. if I were. For example, which of the following two choices is correct?
- If I was a better cook, I could entertain more.
-or-
- If I were a better cook, I could entertain more.
You hear people say both each and every day, so it’s hard to know which is correct. The answer, however, has to do with the subjunctive mood.
Subjunctive Mood

- I wish I weren’t so shy.
- I wish it were warmer outside.
- If I were taller, I could dunk a basketball.
- If John were a rich man, he could drive a fancy car.
- He acts as if he were the one in charge.
- John spends money as if he were a millionaire.
All of the above sentences use the verb were because they aren’t true; they do not describe reality.
In the first two sentences, I am talking about things I wish would happen.
In the third and fourth sentences, I am talking about situations that would happen if I were taller and if John were rich, speaking hypothetically.
And the fifth and sixth sentences are examples of unreal statements.
When to Use Were
Another good example of the subjunctive mood can be found in the musical Fiddler on the Roof. In the song, “If I were a rich man,” the character Tevye sings about how different his life would be and all the things he would do if he were rich.
If I were a rich man, I’d build a big tall house…
If I were a rich man, I’d have the time that I lack.
If I were a wealthy man, I wouldn’t have to work hard.
In these lines, Tevye is fantasizing about life as a wealthy man. He isn’t rich now; he’s just imagining it, so we need to use the subjective “If I were,” not “If I was.”
The correct answer for the example above, therefore, is, “If I were a better cook, I could entertain more.”
Tricks to Remember
Two good clues for the subjunctive mood are the words if and wish. If you see either of these words, there is a good chance you will need to use the subjunctive.
When to Use Was
Since were is used for statements that do not describe reality, was is just the opposite. Was is used for statements of fact. For example,
- Last night, I was watching TV until midnight.
- When I was younger, I wanted to be a singer.
- Your brother was my college roommate.
Summary
These words are used differently in sentences, so it’s important to know when to use were vs. was.
Was is used in the first and third person singular past. It is used for statements of fact.
Were is used in the second person singular and plural and first and third person plural. It is used in the subjunctive mood to indicate unreal or hypothetical statements. The words if and wish usually indicate the subjunctive mood.
< Where versus Were versus Wear
Was versus Were >
Contents
- 1 Forms of Was and Were
- 2 If I was vs. If I were
- 3 Subjunctive Mood
- 4 When to Use Were
- 5 Tricks to Remember
- 6 When to Use Was
- 7 Summary
 Pin
Pin
Was Were Sentences | 50 Examples
- I was disappointed that so few people attended the event.
- You were busy when I called this morning.
- You were helpful because you showed me the way to the airport.
- She was a good teacher because they enjoyed her lessons.
- They were surprised when they learned the truth.
- He was hungry, so he left for dinner early.
- She was going to work when she got in a car accident.
- It was tranquil outside when I woke up.
- All her ideas were well thought out.
- They were the best team members to have on my side.
- I was late for class because my shoelace broke.
- My dog was tired after a long day of play.
- The restaurant I had dinner at was expensive, but the food and waitstaff were great!
- Your application was excellent; however, it was decided to offer the position to a candidate with more experience.
- The last election was fair and square.
- Who was at the door?
- How much sugar was there in the pot?
- Helen was a beautiful girl with red hair.
- He was confident of his success.
- He was a very cunning man.
- You were not at fault.
- She was resting on her oars after her retirement.
- He was planting flowers in his lawn last Sunday.
- All the students were present except Bob.
- He enjoyed his life when he was young.
- He was working as HR Manager in this firm a year ago.
- The novel which I read last night was fascinating.
- Jon was my intimate friend.
- Her opinion was straightforward and honest, as always.
- Last month Tom was traveling to Spain.
- The book was not on the table.
- The children were playing hide and seek in the park yesterday.
- There was no light in the street.
- The beggar was not lame.
- Where were you living last year?
- All the tickets for the concert were sold.
- What were you looking for in my room last night?
- He was weighed down with financial burdens.
- She was at her wit’s end on how to act.
- Jon was Mr. Bob’s blue-eyed boy.
- Who was in the garden last night?
- Was this lesson very difficult?
- Why were you sad yesterday?
- The speaker was cutting a sorry figure because of his wrong pronunciation.
- All the pages of the book were dog-eared.
- Last year he was studying Electrical Engineering.
- We were hardworking students.
- The mechanic was repairing my car an hour ago.
- I was very excited about my new job.
- The wedding was supposed to be simple.
Read also: Is – am – are Sentences (50 Examples)