“Will” is a really common word in the English language, and used in lots of different ways.
It’s usually a word you hear when you’re talking about the future – but it can also have other uses too! So let’s take a look at the different ways of working with “will”.
“Will” as a modal verb
When you’re talking about the future, “will” is a very common and simple way of describing what you anticipate or plan to happen.
For example, “She will be catching the later train, but I will travel afterwards.”
In this case, the word is actually a modal verb – and follows the same rules as other modals.
So – just like other modal verbs such as “can” and “may”, using “will” as a modal verb means you need to do the following:
— always use the verb with another verb in the base form
— never change, even when using the third person form (he, she or it)
— do not use with the verb “do”, in questions or negatives
Different ways of using will
Although “will” is commonly used as a modal verb to describe the future, there are different ways to express this!
So let’s take a closer look at some of them, and how the word can be used in each case.
Decide to do something now
When you’ve made a decision that you’re going do take an action that is going to happen immediately or soon, you can use “will” to describe this.
For example, “I will catch the bus to work.”
Making a promise
If you are promising to do something in the near future, then you can use “will” in a similar way – in this case, this show that you are definitely planning on doing the action – and it’s not just a suggestion, so only use it when you mean it!
For example, “She will study harder for the next exam.”
Thinking about the future
If you are talking about the future and considering what you think is likely to happen, then using “will” is a good way of expressing the likelihood of it occurring. Unlike other modals such as “may”, “will” expresses that there is a greater certainly of it happening, rather than a slight chance.
For example, “I think the election will have a shocking result.”
Using “will” in the negative
If you have used “be” in a sentence where “will” is used positively, then you simply add the negative word, “not” after “will”. You do not use “not” after the additional verb.
For example, in the positive form it would be written as “I will be coming for dinner.”
In the negative, it would be “I will not be coming for dinner” – not “I will be not coming for dinner.”
Using “will” as a contraction
In spoken or colloquial English, you can contract the use of the word “will” into a shorter word, for convenience or simply to make it easier.
You do this by replacing the word “will” with the following form: “ +’ll”.
This is added on to the end of the subject – for example “I will” becomes “I’ll” and “she will” becomes “she’ll”.
You can also contract the negative form. “Will not” becomes “won’t” and is used in the same way.
For example, “They won’t be going on holiday this year.”
Your turn
Using “will” correctly takes a bit of practice, so try to use it as often as you can in the different contexts! And make sure you include using the contracted or shorter form too, so that you are more familiar with it.
Examples of how to use the word “will” in a sentence. How to connect “will” with other words to make correct English sentences.
will (v, n, modal): If you will something to happen, you try to make it happen by the power of your thoughts; the mental power used to control and direct your thoughts and actions, or a determination to do something, despite any difficulties or opposition; used to talk about what is going to happen in the future, especially things that you are certain about or things that are planned
Use “will” in a sentence
Back to “3000 Most Common Words in English”
Although we can use “will” in English to talk about the future, we normally use “will” to make predictions, talk about spontaneous decisions, and to make promises, offers, requests and threats. In this article, we explain how to use “will” in English with plenty of examples and links to songs that contain “will” in the lyrics.
Grammar rules for using “will” in English
“Will” is a modal auxiliary verb, meaning that there is no “s” on the third person singular conjugations. The main verb in the sentence is in the infinitive form (without “to”). The negative form is “will not” which is usually contracted in spoken English and we say “won’t”. Similarly “will” is sometimes contracted to “‘ll” when speaking.
Examples:
I’ll bring a bottle of wine.
You’ll enjoy the club!
He won’t sign the document.
She will find it difficult.
We will do our homework!
They’ll probably stay the night.
We make yes/no questions by changing the word order, “will” comes first:
Will he sign the contract?
Will they stay the night?
Won’t she find it difficult?
And we can ask open questions by placing a question word in front of the modal verb “will”:
Why won’t he sign the contract?
Where will they stay the night?
When will we do our homework?
How will she find it difficult?
When to use “will” in English:
- to express beliefs and predictions
- Spontaneous decisions
- to talk about willingness (what people want to do or are happy to do) – offers
- to make promises, requests and threats
Using “will” to express beliefs about the present or future
Although we don’t generally use “will” to talk about plans for the future, we can use it to talk about beliefs or predictions.
Examples:
(Doorbell rings) “That will be Jeremy, I invited him for coffee.” (belief – present)
I think it’ll rain this weekend. (prediction)
I’m sure she’ll be a highly acclaimed lawyer one day. (belief and prediction)
I don’t think you will like him. (negative prediction)
Notice that for negative predictions, we make the “think” negative, not the “will”.
Song: Gloria Gaynor’s I will survive uses “will” in this sense. A more modern song with “will” to express beliefs and predictions is “Can’t feel my face” by The Weekend.
We use “will” when we are making spontaneous decisions
We use “will” when we are making spontaneous decisions
In a restaurant when the waiter or waitress asks you what you would like, you normally make a decision at more or less the time of speaking, for this reason we use the expression “I’ll have…” For example:
I’ll have the fish please,
I’ll just have a coffee, I’m not hungry.
We’ll share the starter selection
I’ll have what Phill’s having (a TV show about food)
Of course, we can make spontaneous decisions in other situations such as:
Someone is calling on the other line, I’ll have to call you back.
I’m not sure when I’m free, I’ll let you know by tomorrow.
I’m cold, I think I’ll turn the heating on.
How to use “will” to express willingness – offers
The question form “Will you…” is asking about willingness.
Willingness is a complicated word to explain, however, it is clear that it is derived from the word “will”. If I want to do something, if I am happy to volunteer to do something, I am willing to help. So when I speak to express that I am willing to help or to offer to do something I use “will”.
Examples:
Don’t worry, I’ll go shopping tomorrow.
I’ll help you make dinner!
(Doorbell rings) “ I’ll get it!”
I’ll talk to him if you like
David will finish painting the garage for you.
All of the above examples are offers to help, even the last sentence, where David is being volunteered by someone else.
“Will not” or “won’t” mean to refuse to do something
In the same way that we can show willingness by using “will”, we can show the opposite attitude, a refusal to help with “will not” or “won’t”. Interestingly, this applies to animals and inanimate objects too.
I can’t go with you on the trip today, my car won’t start.
The donkey won’t budge.
She won’t tell you her secrets.
I won’t allow this to continue.
The governors will not permit smoking on school property.
Why won’t you come with me?
The question form “Will you…” is asking about willingness
The famous “Will you marry me?” is a question that asks if you want to marry me. Here are some other examples:
Will you take your dog on holiday?
Will they put their house on the market?
Will Gail teach business English?
Song: Lana Del Rey’s Young and Beautiful uses “Will you” in this sense.
We use “will” to make promises
We use “will” to make promises
We often use words like “I promise, I swear, I assure you… ” to emphasise a promise about the future with will. Here are some examples:
I swear I’ll never cheat on you again.
I assure you we will do our best to get to the bottom of this.
I promise, my dog won’t pee in your garden again
Songs: Calvin Harris, Sam Smith’s – Promises uses “will” in the chorus – “I’ll give you everything”. Additionally, Jess Glynne promises “You’ll never be alone, I’ll be there for you”.
We use “Will you … ?” to make requests:
With this type of question, we are asking if someone is willing to carry out the request.
Examples:
Will you help me on this project, please?
Will you sign this petition?
In reality, we use “Will you…” and “Would you…” to express that we are annoyed and we want someone to behave in a certain way:
Will you please be quiet!
Would you not eat my pants! (hilarious video!)
Will you please just sign the form so that we can all go home!
Would you please get your dog to stop barking!
Song: Will you be there by Michael Jackson is a simple request.
Using “will” to make a threat or give a warning
Admittedly, Peaky Blinders is not the best Netflix show to learn English with, but this clip where Grace warns Thomas Shelby that her song will break his heart is worth watching!
“OK, but I warn you, it’ll break your heart”
Meat Loaf threatens in one of his blasting ballads:
“In every way, I want you out of my life, but I’ll kill you if you don’t come back!”
Hypotheses and conditionals
We use will in first conditional sentences to say what will happen depending on the first clause:
If it rains tomorrow I’ll cancel the trip to the beach.
We’ll never finish the project if Charlotte doesn’t jump on board.
You won’t get promoted unless you stick to the rules.
So we have gone through all the main points you need to know about how to use “will” in English, one final song: Will you by Hazel O’Connor has many examples of “will” in it! In fact, so many that if you can figure out which use of “Will” in English each example is – you will be a champion of this subject! You can find more examples of this grammar topic in our Business English post: 5 ways to stop employees procrastinating in the workplace
WILL – English Grammar Lesson
In general, WILL is used to talk about the future.
- I will help you tomorrow. (Tomorrow is in the future)
- I think we will win on Saturday. (Saturday is a day in the future)
- We will see more uses of the word WILL in a moment. (It is coming in the near future)
Let’s look at how to create sentences and questions with WILL.
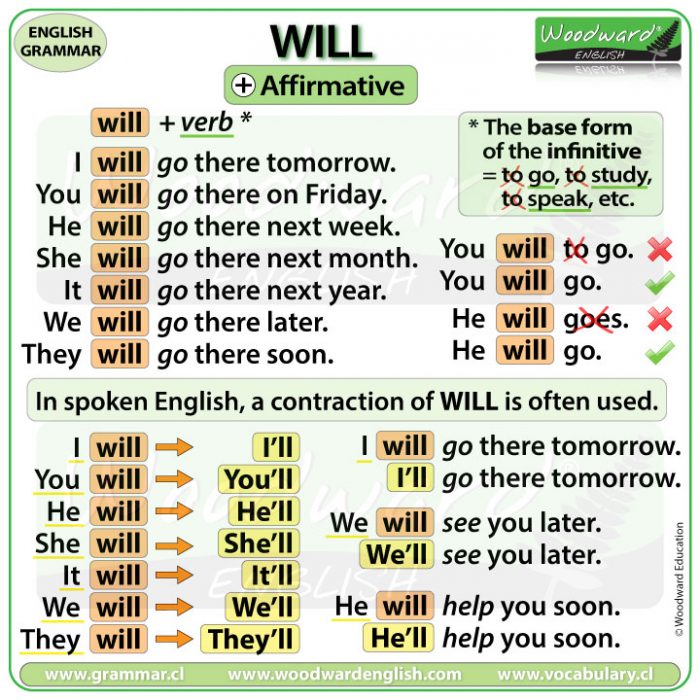
Affirmative Sentences with WILL
WILL is a modal verb. This means it follows the same rules as the other modal verbs.
It only has one form for each subject:
- I will
- You will
- He will
- She will
- It will
- We will
- They will
The word WILL doesn’t change.
You cannot say: He wills … ❌ or She wills … ❌
No! … There is no S at the end of WILL.
He will … ✅ She will … ✅
After WILL we have the base form of the infinitive.
This is the Infinitive without TO at the beginning.
Instead of TO GO, just GO.
Instead of TO STUDY, just STUDY.
Instead of TO SPEAK, just SPEAK is used.
We don’t say: I will TO go. ❌
No, this is NOT correct.
We use the base form of TO GO which is without TO.
You say: You will go. ✅
We don’t say: He will goes. ❌
No, this is NOT correct.
We have the infinitive (TO GO) without TO at the beginning.
You say: He will go. ✅
Let’s look at some example sentences:
- I will go there tomorrow.
- You will go there on Friday.
- He will go there next week.
- She will go there next month.
- It will go there next year.
- We will go there later.
- They will go there soon.
You can see that in these sentences GO is used after WILL for all subjects.
Contractions with WILL
In spoken English, a contraction of WILL is often used.
- I will ➡️ I’ll
- you will ➡️ you’ll
- he will ➡️ he’ll
- she will ➡️ she’ll
- it will ➡️ it’ll
- we will ➡️ we’ll
- they will ➡️ they’ll
Example sentences with contractions:
- I will go there tomorrow. ➡️ I’ll go there tomorrow.
- We will see you later. ➡️ We’ll see you later.
- He will help you soon. ➡️ He’ll help you soon.
Negative Sentences with WILL
To create a negative sentence with WILL, we just add NOT directly after it.
I will (affirmative) becomes I will not (negative)
Let’s look at the rest of the subjects.
Affirmative ➡️ Negative
- I will ➡️ I will not
- You will ➡️ You will not
- He will ➡️ He will not
- She will ➡️ She will not
- It will ➡️ It will not
- We will ➡️ We will not
- They will ➡️ They will not
BUT, in spoken English, the contraction WON’T is used more than WILL NOT.
- I will not = I won’t
- You will not = You won’t
- He will not = He won’t
- She will not = She won’t
- It will not = It won’t
- We will not = We won’t
- They will not = They won’t
Compare these sentences:
- I will be ready in five minutes. (affirmative)
- I will not be ready in five minutes. (negative)
- I won’t be ready in five minutes. (negative – more in spoken English)
- She will arrive on time. (affirmative)
- She will not arrive on time. (negative)
- She won’t arrive on time. (negative – more in spoken English)
See our lesson about the difference between ON TIME and IN TIME.
More examples of negative sentences using WON’T
- He won’t listen to me.
- She won’t find it funny.
- I’m sorry I won’t be at your party.
- It won’t hurt if you stay calm.
- We won’t finish this by the end of the day.
- They won’t accept the offer.
- Don’t worry, I won’t tell anyone.
Questions with WILL
Just like with other modal verbs, we change the order of the SUBJECT and WILL to make it a question.
- You will go there tomorrow.
This is an affirmative sentence.
In order to make it a question, we change the order of the subject (YOU) and WILL. It becomes:
- Will you go there tomorrow?
More examples:
- They will be busy. (affirmative)
- Will they be busy? (question)
- He will visit us. (affirmative)
- Will he visit us? (question)
- You will tell us the truth. (affirmative)
- Will you tell us the truth? (question)
How can you answer a question with WILL?
For short answers, you can use: Yes, I will … OR … No, I won’t.
BUT, we don’t use a contraction with affirmative short answers.
- Will you tell us the truth?
- Yes, I’ll. ❌ (This is NOT correct)
- Yes, I will. ✅ (This is correct)
Another example:
- Will you come with me? Yes, I will. / No, I won’t.
(You cannot say: Yes, I’ll. ❌ – We don’t use a contraction with affirmative short answers.)
Look at this question:
- Will he visit us?
A possible answer is: Yes, he will
BUT, if we want to know the time it will happen, then we can use the question word WHEN at the beginning:
- When will he visit us?
Since this is not a yes/no question, our answer needs to be different.
One possible response is: On Friday.
This means: He will visit us on Friday.
We don’t need to say the whole sentence and it would sound repetitive.
Now look at this question:
- Do you think she will get angry?
Notice the order of subject + will. (Do you think SHE WILL get angry?)
That is because the first part of the sentence “Do you…?” makes it a question so we don’t change the order of the subject and will.
You can answer: Yes, I do … or No, I don’t
BUT, our short answer can also contain WILL if you want to use SHE as the subject:
Yes, she will / No, she won’t.
Question Tags with WILL
WILL and WON’T can also be used in question tags.
- You won’t tell Mum, will you?
- He will arrive on time, won’t he?
See our lesson about Question Tags in English.
In our next lesson, we will look at the different uses of WILL and will also compare WILL vs. GOING TO. (Coming next week)
I hope you found this grammar lesson about WILL useful. If you did, please let other people know about it.
We can use “will” to talk about the future. We also use will to make predictions, talk about decisions, and to make promises, offers, requests and threats.
Grammar rules
“Will” and the negative form “will not” or “won’t” is a modal auxiliary verb.
This means that there is no s on the third person singular, and that it is followed by the infinitive:
I will leave later.
You will leave later.
He / she will leave later.
We will leave later.
They will leave later.
Note: “will” is often abbreviated to ‘ll in spoken English:
“I’ll leave later.”
“He’ll leave later.”
To make the question form, change the word order:
“You will leave later” = “Will you leave later?”
(For more information on the grammar of modal auxiliary verbs, see our page on how to use “can”.)
Using will
Here are some of the ways we use will:
1. To talk about the future
We can often use “will” + infinitive without “to” to refer to future events. This is often called the “pure” future:
“I’ll be back later tonight – don’t bother making me dinner.”
“I’m busy right now – I’ll call you tomorrow.”
2. To make predictions
We also use “will” to talk about what we think will happen in the future.
“I think it’ll rain tonight.”
“I’m sure he’ll be a successful lawyer one day.”
Note: for “negative” predictions, make the “think” negative, not the “will”:
“I don’t think it’ll rain tonight” (Not “I think it won’t rain tonight.”)
3. To make decisions
When we make decisions at the same time as we speak, we use “will”.
For example, in a restaurant:
Waiter: “What would you like to eat?”
Customer: “I think I’ll have the chicken.”
Other examples:
“I’m cold. I think I’ll put the heater on.”
“Look, that’s my bus. I’ll catch up with you later.”
4. To make promises, offers, requests and threats
These are some other ways we can use “will” in English.
Promises: “I’ll help you with your homework tomorrow.”
Offers: “I’ll look after the children for you if you like.”
Requests: “Will you tell Tony I called?”
Threats: “If you cheat again, I’ll tell the teacher.”
(Some of the examples above also show conditional sentences. For more grammar information on conditionals, see our page on If sentences.)
Will
Choose the correct answer.
Now go on to the next page to learn how to book a table in a restaurant and phrases for talking to the waiter. You can also practise your listening: English Conversations: In a Restaurant