VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT
Let’s say you want to process a customer order. For that, you want to first check to see if the ordered product exists or not. If it does, you also want to check if the quantity on hand is enough. Logical operators come in handy in such cases. Logical operators are used to evaluate more than one condition.
The main Excel VBA logical operators AND, OR, NOT are listed in the table below:
| S/N | Operator | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AND | AND: This is used to combine more than one condition. If all the conditions are true, AND evaluates to true. If any of the condition is false, AND evaluates to false | If true = true AND false = true THEN | false |
| 2 | OR | OR: This is used to combine more than one condition. If any of the conditions evaluate to true, OR returns true. If all of them are false, OR returns false | If true = true OR true = false THEN | true |
| 3 | NOT | NOT: This one works like an inverse function. If the condition is true, it returns false, and if a condition is false, it returns true. | If NOT (true) Then | false |
VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
For the sake of simplicity, we will be comparing hard coded numbers.
Add ActiveX buttons to the sheet from the “Insert option.”
Set the properties as shown in the image below
The following table shows the properties that you need to change and the values that you need to update too.
| S/N | Control | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CommandButton1 | Name | btnAND |
| Caption | AND Operator (0 = 0) | ||
| 2 | CommandButton2 | Name | btnOR |
| Caption | OR Operator (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) | ||
| 3 | CommandButton3 | Name | btnNOT |
| Caption | NOT Operator Not (0 = ) |
Add the following code to btnAND_Click
Private Sub btnAND_Click()
If (1 = 1) And (0 = 0) Then
MsgBox "AND evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "AND operator"
Else
MsgBox "AND evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "AND operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If AND Operator
- “If (1 = 1) And (0 = 0) Then” the if statement uses the AND logical operator to combine two conditions (1 = 1) And (0 = 0). If both conditions are true, the code above ‘Else’ keyword is executed. If both conditions are not true, the code below ‘Else’ keyword is executed.
Add the following code to btnOR_Click
Private Sub btnOR_Click()
If (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) Then
MsgBox "OR evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "OR operator"
Else
MsgBox "OR evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "OR operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If OR Operator
- “If (1 = 1) Or (5 = 0) Then” the if statement uses the OR logical operator to combine two conditions (1 = 1) And (5 = 0). If any of the conditions is true, the code above Else keyword is executed. If both conditions are false, the code below Else keyword is executed.
Add the following code to btnNOT_Click
Private Sub btnNOT_Click()
If Not (0 = 0) Then
MsgBox "NOT evaluated to TRUE", vbOKOnly, "NOT operator"
Else
MsgBox "NOT evaluated to FALSE", vbOKOnly, "NOT operator"
End If
End Sub
VBA If NOT Operator
- “If Not (0 = 0) Then” the VBA If Not function uses the NOT logical operator to negate the result of the if statement condition. If the conditions is true, the code below ‘Else’ keyword is executed. If the condition is true, the code above Else keyword is executed.
Download Excel containing above code
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- IF…AND
- IF…OR
- IF NOT…
This article will demonstrate how to use the VBA If statement with And, Or and Not.
When we us an IF statement in Excel VBA, the statement will execute a line of code if the condition you are testing is true.
- We can use AND statement and OR statements in conjunction with IF statements to test for more than one condition and direct the code accordingly.
- We can also use a NOT statement with an IF statement to check if the condition is NOT true – it basically is the inverse of the IF statement when used alone.
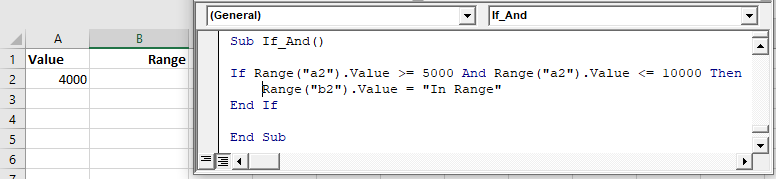
IF…AND
We can use the IF…AND combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where all the conditions need to be true for the next line of code to execute.
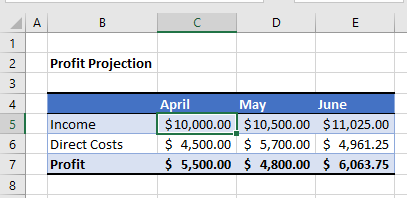
For example, consider the following sheet:
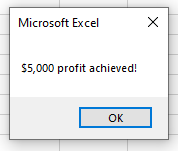
To check if the Profit is over $5,000, we can run the following macro:
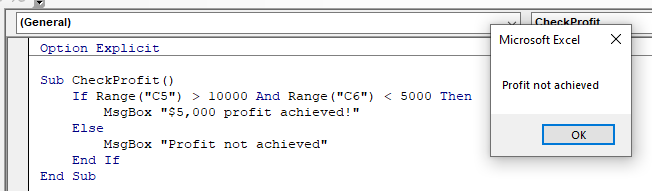
Sub CheckProfit()
If Range("C5") >= 10000 And Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubThis macro will check that the cell C5 is greater or equal to $10,000 AND check that the cell B6 is less than $5,000. If these conditions are BOTH true, it will show the message box.
If we amend the macro to check if C5 is just greater than $10,000, then the profit would not be achieved!
IF…OR
We can use the IF…OR combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where only one of the conditions needs to be true for the next line of code to execute.
The format for this is almost identical to the IF…AND example above.
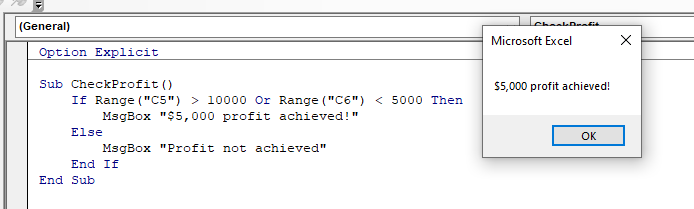
Sub CheckProfit()
If Range("C5") > 10000 Or Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubHowever, with this macro, because we are using an IF …OR statement, only one of the conditions needs to be true.
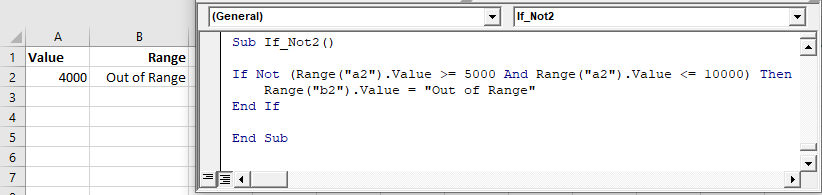
IF NOT…
IF..NOT changes the IF statement around – it will check to see if the condition is NOT true rather than checking to see if the condition is true.
Sub CheckProfit()
If NOT Range("C5")< 10000 Or Range("C6") < 5000 Then
MsgBox "$5,000 profit achieved!"
Else
Msgbox "Profit not achieved!"
End If
End SubIn this example above, the IF statement is checking to see if the value in C5 is NOT smaller than 10000.
Therefore this line of code:
IF Range("C5") > 10000and this this line of code:
IF NOT Range("C5") < 10000are testing for the same thing!
Содержание
- VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT, IF NOT in Excel VBA
- Excel VBA Logical Operators
- VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
- VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
- Use OR with IF
- Multiple Conditions with IF OR
- VBA If – And, Or, Not
- IF…AND
- IF NOT…
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
- VBA IF OR
- IF OR Function in VBA
- How to Use IF with OR Function in VBA?
- IF OR VBA Function with Loops (Advanced)
- Recommended Articles
- VBA If, ElseIf, Else (Ultimate Guide to If Statements)
- VBA If Statement
- If Then
- End If
- ElseIF – Multiple Conditions
- If-Else
- Nested IFs
- VBA Coding Made Easy
- IF – Or, And, Xor, Not
- If Or
- If And
- If Xor
- If Not
- If Comparisons
- Comparing Text
- VBA If Like
- If Loops
- If Else Examples
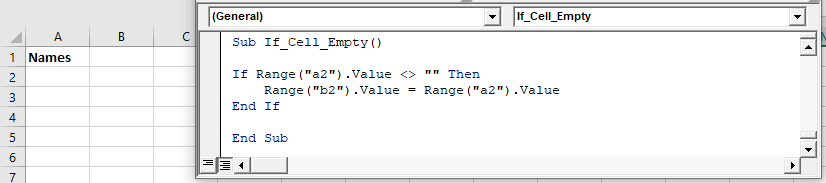
- Check if Cell is Empty
- Check if Cell Contains Specific Text
- Check if cell contains text
- If Goto
- Delete Row if Cell is Blank
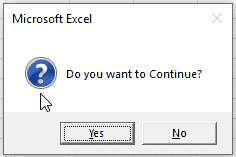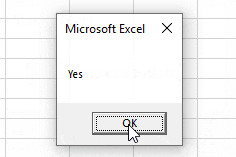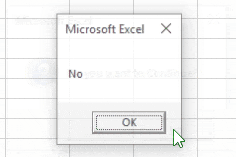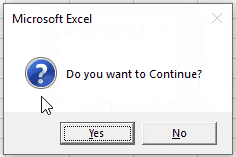
- If MessageBox Yes / No
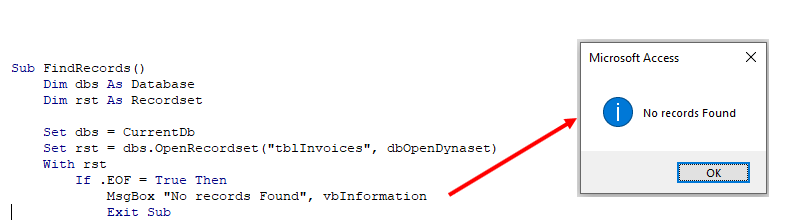
- VBA If, ElseIf, Else in Access VBA
- VBA Code Examples Add-in
VBA Logical Operators: AND, OR, NOT, IF NOT in Excel VBA
Updated January 20, 2023
Excel VBA Logical Operators
Let’s say you want to process a customer order. For that, you want to first check to see if the ordered product exists or not. If it does, you also want to check if the quantity on hand is enough. Logical operators come in handy in such cases. Logical operators are used to evaluate more than one condition.
The main Excel VBA logical operators AND, OR, NOT are listed in the table below:
| S/N | Operator | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AND | AND: This is used to combine more than one condition. If all the conditions are true, AND evaluates to true. If any of the condition is false, AND evaluates to false | If true = true AND false = true THEN | false |
| 2 | OR | OR: This is used to combine more than one condition. If any of the conditions evaluate to true, OR returns true. If all of them are false, OR returns false | If true = true OR true = false THEN | true |
| 3 | NOT | NOT: This one works like an inverse function. If the condition is true, it returns false, and if a condition is false, it returns true. | If NOT (true) Then | false |
VBA Logical Operators Example Source Code
For the sake of simplicity, we will be comparing hard coded numbers.
Add ActiveX buttons to the sheet from the “Insert option.”
Set the properties as shown in the image below

The following table shows the properties that you need to change and the values that you need to update too.
Источник
VBA IF OR (Test Multiple Conditions)
You can use the OR operator with the VBA IF statement to test multiple conditions. When you use it, it allows you to test two or more conditions simultaneously and returns true if any of those conditions are true. But if all the conditions are false only then it returns false in the result.
Use OR with IF
- First, start the IF statement with the “IF” keyword.
- After that, specify the first condition that you want to test.
- Next, use the OR keyword to specify the second condition.
- In the end, specify the second condition that you want to test.
To have a better understanding let’s see an example.
If you look at the above example, we have specified two conditions one if (1 = 1) and the second is (2
Now let’s see if both conditions are false, let me use a different code here.
In the above code, both conditions are false, and when you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified if the result is false.
Multiple Conditions with IF OR
In the same way, you can also test more than two conditions at the same time. Let’s continue the above example and add the third condition to it.
Now we have three conditions to test, and we have used the OR after the second condition to specify the third condition. As you learned above that when you use OR, any of the conditions need to be true to get true in the result. When you run this code, it executes the line of code that we have specified for the true.
And if all the conditions are false, just like you have in the following code, it returns false.
Источник
VBA If – And, Or, Not
In this Article
This article will demonstrate how to use the VBA If statement with And, Or and Not.
When we us an IF statement in Excel VBA, the statement will execute a line of code if the condition you are testing is true.
- We can use AND statement and OR statements in conjunction with IF statements to test for more than one condition and direct the code accordingly.
- We can also use a NOT statement with an IF statement to check if the condition is NOT true – it basically is the inverse of the IF statement when used alone.
IF…AND
We can use the IF…AND combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where all the conditions need to be true for the next line of code to execute.
For example, consider the following sheet:
To check if the Profit is over $5,000, we can run the following macro:
This macro will check that the cell C5 is greater or equal to $10,000 AND check that the cell B6 is less than $5,000. If these conditions are BOTH true, it will show the message box.
If we amend the macro to check if C5 is just greater than $10,000, then the profit would not be achieved!
We can use the IF…OR combination of logical operators when we wish to test for more than one condition where only one of the conditions needs to be true for the next line of code to execute.
The format for this is almost identical to the IF…AND example above.
However, with this macro, because we are using an IF …OR statement, only one of the conditions needs to be true.
IF NOT…
IF..NOT changes the IF statement around – it will check to see if the condition is NOT true rather than checking to see if the condition is true.
In this example above, the IF statement is checking to see if the value in C5 is NOT smaller than 10000.
Therefore this line of code:
and this this line of code:
are testing for the same thing!
VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
Источник
VBA IF OR
IF OR is not a single statement. Rather, these are two logical functions used together in VBA when we have more than one criteria to check. When we use the IF statement, if any criteria meet, we get the TRUE result. OR statement is used between the two criteria of the IF statement.
IF OR Function in VBA
Logical functions are the heart of any criteria-based calculations. The IF function is the most popular logical function, be it a worksheet function or a VBA function because it serves excellently for our needs. But one more logical function, OR in excel, is the most underrated. It is also important to master when it comes to solving complex calculations. This article will take you through the VBA IF OR function in detail. Read the full article to get the function in detail.
Table of contents
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA IF OR (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Use IF with OR Function in VBA?
We will show you a simple example of using the IF OR function in VBA.
A combination of logical functions is the best pair in Excel. However, combining many logical formulas inside the other logical formula suggests that calculation requires many conditions to test.
Now, look at the syntax of the IF OR function in VBA.
It is the same as we saw in the worksheet example. For a better understanding, look at the below example.
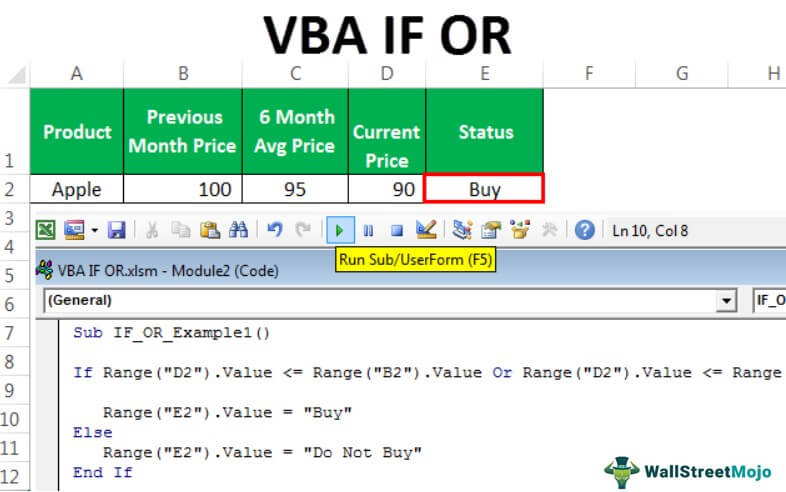
We have the previous month’s price, the last 6-month average price, and the current monthly price here.
To decide whether to buy the product, we need to do some tests here, and those tests are.
If the Current Price is less than or equal to any of the other two prices, we should get the result as “Buy” or else should get the result as “Do Not Buy.”
Step 1: Open the IF condition inside the Sub procedure.
Code:
Step 2: Inside the IF condition, apply the first logical test as Range(“D2”).Value
Step 3: The first logical condition completes. Now, open OR statement.
Code:
Step 4: Now, apply the second logical condition as Range(“D2”).Value
Step 5: We are done with the logical tests here. After the logical tests, put the word “Then.”
Code:
Step 6: In the next line, write what the result should be if the logical test Logical Test A logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test. read more is TRUE. If the condition is TRUE, we need the result as “Buy” in cell E2.
Code:
Step 7: If the result is FALSE, we should get the result as “Do Not Buy.” So in the next line, put “Else” and write the code in the next line.
Code:
Step 8: Close the IF statement with “End If.”
Code:
We complete the coding part.
Let us run this code using F5 or manually through the run option and see the result in cell E2.
We got the result as “Buy” because the current monthly price of Apple is less than the price of both “Previous Month” as well as “6 Month Average Price”.
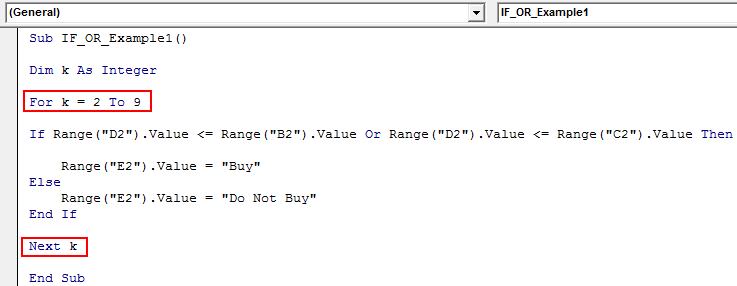
IF OR VBA Function with Loops (Advanced)
Once you understand the formula, try to use it with a larger number of cells. In the case of a larger number of cells, we cannot write any line of code, so we need to use VBA loops Use VBA Loops A VBA loop in excel is an instruction to run a code or repeat an action multiple times. read more .
We have added a few more lines for the above data set.
We need to use the For Next Loop here.
Just keep the current code as it is.
Declare the variable as an Integer.
Now, open For Next Loop from 2 to 9.
For example, Range (“D2”).Value should be Range (“D” & k).Value
Now, run the code. First, we should get the status in all the cells.
You can copy the code below.
Code:
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA IF OR. Here, we learn how to use IF Condition with OR function in Excel VBA, examples, and downloadable templates. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
Источник
VBA If, ElseIf, Else (Ultimate Guide to If Statements)
In this Article
VBA If Statement
If Then
VBA If Statements allow you to test if expressions are TRUE or FALSE, running different code based on the results.
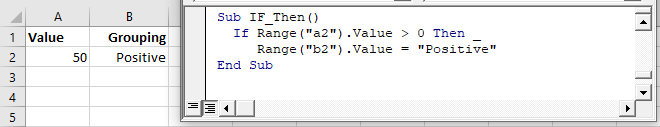
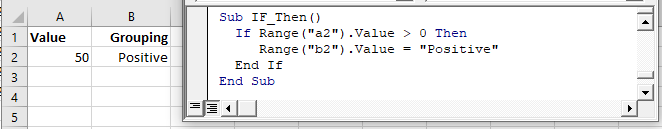
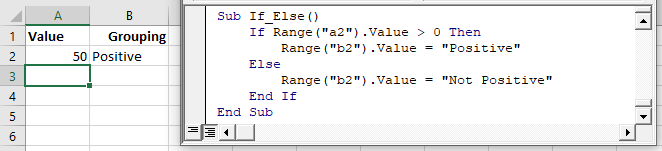
Let’s look at a simple example:
This tests if the value in Range A2 is greater than 0. If so, setting Range B2 equal to “Positive”
Note: When testing conditions we will use the =, >, , = comparison operators. We will discuss them in more detail later in the article.
Here is the syntax for a simple one-line If statement:
To make it easier to read, you can use a Line Continuation character (underscore) to expand the If Statements to two lines (as we did in the above picture):
End If
The above “single-line” if statement works well when you are testing one condition. But as your IF Statements become more complicated with multiple conditions, you will need to add an “End If” to the end of the if statement:
Here the syntax is:
The End If signifies the end of the if statement.
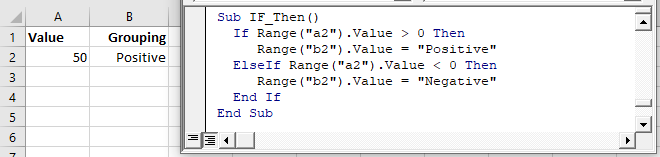
Now let’s add in an ElseIF:
ElseIF – Multiple Conditions
The ElseIf is added to an existing If statement. ElseIf tests if a condition is met ONLY if the previous conditions have not been met.
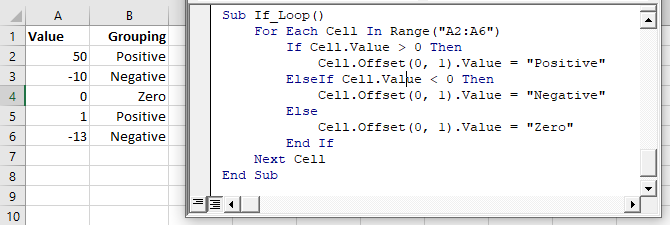
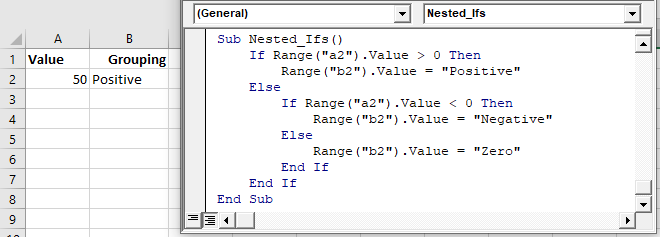
In the previous example we tested if a cell value is positive. Now we will also test if the cell value is negative with an ElseIf:
You can use multiple ElseIfs to test for multiple conditions:
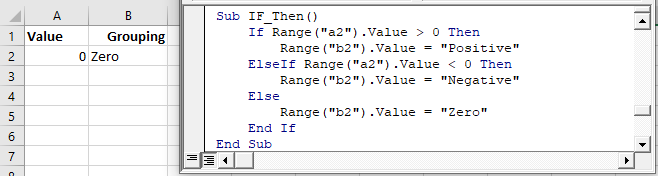
Now we will add an Else:
The Else will run if no other previous conditions have been met.
We will finish our example by using an Else to indicate that if the cell value is not positive or negative, then it must be zero:
If-Else
The most common type of If statement is a simple If-Else:
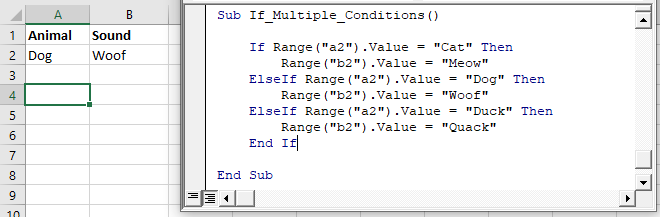
Nested IFs
You can also “nest” if statements inside of each other.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
IF – Or, And, Xor, Not
Next we will discuss the logical operators: Or, And, Xor, Not.
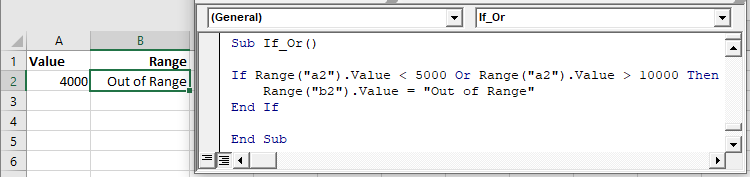
If Or
The Or operator tests if at least one condition is met.
The following code will test if the value in Range A2 is less than 5,000 or greater than 10,000:
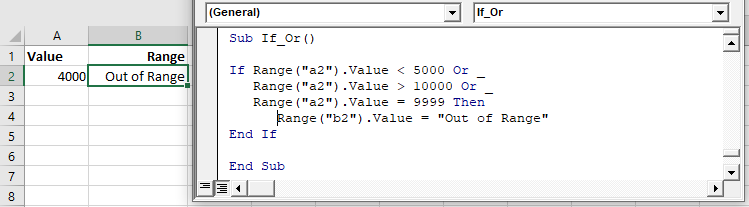
You can include multiple Ors in one line:
If you are going to use multiple Ors, it’s recommended to use a line continuation character to make your code easier to read:
If And
The And operator allows you to test if ALL conditions are met.
If Xor
The Xor operator allows you to test if exactly one condition is met. If zero conditions are met Xor will return FALSE, If two or more conditions are met, Xor will also return false.
I’ve rarely seen Xor used in VBA programming.
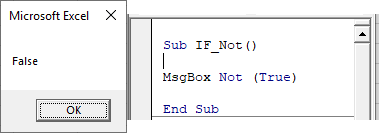
If Not
The Not operator is used to convert FALSE to TRUE or TRUE To FALSE:
Notice that the Not operator requires parenthesis surrounding the expression to switch.
The Not operator can also be applied to If statements:
If Comparisons
When making comparisons, you will usually use one of the comparison operators:
| Comparison Operator | Explanation | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = | Equal to | |||||||||||
| <> | Not Equal to | |||||||||||
| > | Greater than | |||||||||||
| >= | Greater than or Equal to | |||||||||||
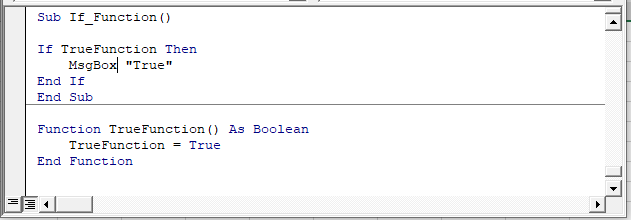
| If – Boolean Function
When build expressions for If Statements, you can also use any function that generates TRUE or False. VBA has a few of these functions:
They can be called like this: Excel also has many additional functions that can be called using WorksheetFunction. Here’s an example of the Excel IsText Function: You can also create your own User Defined Functions (UDFs). Below we will create a simple Boolean function that returns TRUE. Then we will call that function in our If statement: Comparing TextYou can also compare text similar to comparing numbers: When comparing text, you must be mindful of the “Case” (upper or lower). By default, VBA considers letters with different cases as non-matching. In other words, “A” <> “a”. If you’d like VBA to ignore case, you must add the Option Compare Text declaration to the top of your module: After making that declaration “A” = “a”: VBA If LikeThe VBA Like Operator allows you to make inexact comparisons of text. Click the “Like Operator” link to learn more, but we will show a basic example below: Here we’re using an asterisk “*” wildcard. The * stands for any number of any characters. So the above If statement will return TRUE. The Like operator is an extremely powerful, but often under-used tool for dealing with text. If LoopsVBA Loops allow you to repeat actions. Combining IF-ELSEs with Loops is a great way to quickly process many calculations. Continuing with our Positive / Negative example, we will add a For Each Loop to loop through a range of cells: If Else ExamplesNow we will go over some more specific examples. Check if Cell is EmptyThis code will check if a cell is empty. If it’s empty it will ignore the cell. If it’s not empty it will output the cell value to the cell to the right: Check if Cell Contains Specific TextThe Instr Function tests if a string of text is found in another string. Use it with an If statement to check if a cell contains specific text: Check if cell contains textThis code will test if a cell is text: If GotoYou can use the result of an If statement to “Go to” another section of code. Delete Row if Cell is BlankIf MessageBox Yes / NoWith VBA Message Boxes you’re able to ask the user to select from several options. The Yes/No Message Box asks the user to select Yes or No. You can add a Yes / No Message Box to a procedure to ask the user if they would like to continue running the procedure or not. You handle the user’s input using an If statement. Here is the Yes/No Message Box in practice: VBA If, ElseIf, Else in Access VBAThe If, ElseIf and Else functions work exactly the same in Access VBA as in Excel VBA. You can use an If statement to check if there are records in a Recordset. VBA Code Examples Add-inEasily access all of the code examples found on our site. Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in. Источник Adblock |
Logical Operator And | Logical Operator Or | Logical Operator Not
The three most used logical operators in Excel VBA are: And, Or and Not. As always, we will use easy examples to make things more clear.
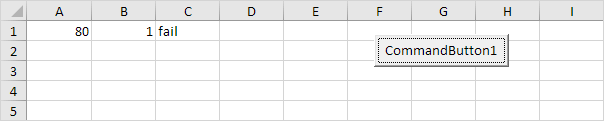
Logical Operator And
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
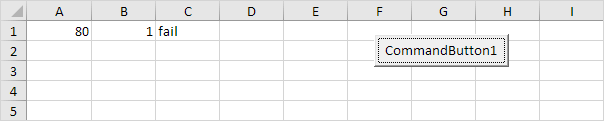
Dim score1 As Integer, score2 As Integer, result As String
score1 = Range(«A1»).Value
score2 = Range(«B1»).Value
If score1 >= 60 And score2 > 1 Then
result = «pass»
Else
result = «fail»
End If
Range(«C1»).Value = result
Explanation: if score1 is greater than or equal to 60 and score2 is greater than 1, Excel VBA returns pass, else Excel VBA returns fail.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Conclusion: Excel VBA returns fail because score2 is not greater than 1.
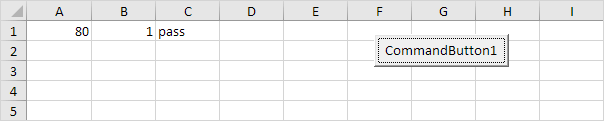
Logical Operator Or
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim score1 As Integer, score2 As Integer, result As String
score1 = Range(«A1»).Value
score2 = Range(«B1»).Value
If score1 >= 60 Or score2 > 1 Then
result = «pass»
Else
result = «fail»
End If
Range(«C1»).Value = result
Explanation: if score1 is greater than or equal to 60 or score2 is greater than 1, Excel VBA returns pass, else Excel VBA returns fail.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Conclusion: Excel VBA returns pass because score1 is greater than or equal to 60.
Logical Operator Not
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim score1 As Integer, score2 As Integer, result As String
score1 = Range(«A1»).Value
score2 = Range(«B1»).Value
If score1 >= 60 And Not score2 = 1 Then
result = «pass»
Else
result = «fail»
End If
Range(«C1»).Value = result
Explanation: if score1 is greater than or equal to 60 and score2 is not equal to 1, Excel VBA returns pass, else Excel VBA returns fail.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Conclusion: Excel VBA returns fail because score2 is equal to 1.
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel OR function (in VBA) with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel OR function returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE. Otherwise, it returns FALSE.
The OR function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Please read our OR function (WS) page if you are looking for the worksheet version of the OR function as it has a very different syntax.
Syntax
The syntax for the OR function in Microsoft Excel is:
condition1 Or condition2 [... Or condition_n] )
Parameters or Arguments
- condition1, condition2, … condition_n
- Expressions that you want to test that can either be TRUE or FALSE.
Returns
The OR function returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE.
The OR function returns FALSE if all conditions are FALSE.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- VBA function (VBA)
Example (as VBA Function)
The OR function with this syntax can only be used in VBA code in Microsoft Excel.
Let’s look at some Excel OR function examples and explore how to use the OR function in Excel VBA code.
This first example combines the OR function with the IF Statement in VBA:
If LWebsite = "TechOnTheNet.com" Or LCount > 25 Then LResult = "Great" Else LResult = "Fair" End If
This would set the LResult variable to the string value «Great» if either LWebsite was «TechOnTheNet.com» or LCount > 25. Otherwise, it would set the LResult variable to the string value «Fair».
You can use the OR function with the AND function in VBA, for example:
If (LWebsite = "TechOnTheNet.com" Or LWebsite = "CheckYourMath.com") And LPages <= 10 Then LBandwidth = "Low" Else LBandwidth = "High" End If
This would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «Low» if LWebsite was either «TechOnTheNet.com» or «CheckYourMath.com» and LPages <= 10. Otherwise, it would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «High».