Excel provides many options for refreshing data, including when you open the workbook and at timed intervals. Note: To stop a refresh, press Esc. To refresh a worksheet, press Ctrl + F5. To refresh a workbook, press Ctrl + Alt + F5.
Contents
- 1 How do I refresh Excel in Windows 10?
- 2 How do I refresh Excel in Office 365?
- 3 How do I create a refresh button in Excel?
- 4 What does refresh all do in Excel?
- 5 How do I refresh Excel data in SharePoint?
- 6 How do I update Excel Online?
- 7 What is the difference between refresh and refresh all in Excel?
- 8 How do you refresh data on a protected sheet?
- 9 How do I automatically refresh excel online?
- 10 How do I feed Excel with live data?
- 11 How can I edit an Excel spreadsheet without Microsoft Office?
- 12 How do you automatically refresh formulas in Excel?
- 13 How do you automatically refresh Excel without opening and closing?
- 14 How do you refresh Excel on a Mac?
- 15 How do I allow an external data refresh in a protected worksheet in Excel?
- 16 How do I allow pivot tables to refresh a protected worksheet?
- 17 How do I unprotect a pivot table in Excel?
- 18 How do I show real time in Excel?
- 19 How do I get a live value in Excel?
How do I refresh Excel in Windows 10?
Windows 10
- Click on the Windows “start” icon (bottom-left corner of your screen).
- Click on “Settings”.
- Click on “Apps”.
- Select “Microsoft Office” (or “Microsoft Excel” if you do not have the full Office installation).
- Click “Modify”.
- Choose from “Quick Repair” or “Online Repair”.
How do I refresh Excel in Office 365?
Open the workbook that contains the data that you want to update. Click the Data icon on the toolbar. Do one of the following: Select Refresh All Connections to refresh all data connections in the workbook.
How do I create a refresh button in Excel?
There are 3 steps:
Step 1: Go to the Insert menu, choose Icons and type “Refresh” in the search field. Choose the icon you want, and click on Insert. Resize and place the icon where you want to have it. Step 3: Go back to Excel, right-click on the Refresh Icon and choose “Assign Macro”.
What does refresh all do in Excel?
According to the Excel VBA help, RefreshAll “Refreshes all external data ranges and PivotTable reports in the specified workbook.”
How do I refresh Excel data in SharePoint?
Refresh the Excel chart
- Click on the Refresh button under the ANALYZE tab and select Refresh All.
- Click on the Refresh All button under the DATA tab.
How do I update Excel Online?
Go to File > Help > Check for Updates. Choose Install Updates or Check for Updates.
What is the difference between refresh and refresh all in Excel?
My gut tells me that “Refresh” refreshes the pivot from the new data on the current worksheet, and “Refresh All” refresh the pivots on all worksheets found in the xlsx file.
How do you refresh data on a protected sheet?
When you want to refresh an Excel pivot table on a protected sheet, you will need to temporarily unprotect the worksheet, refresh the pivot table, and then protect the sheet again.
How do I automatically refresh excel online?
Automatically refresh data at regular intervals
- Click a cell in the external data range.
- On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
- Click the Usage tab.
- Select the Refresh every check box, and then enter the number of minutes between each refresh operation.
How do I feed Excel with live data?
Quick Importing of Live Data
- Open a worksheet in Excel.
- From the Data menu select either Import External Data or Get External Data.
- Select New Web Query.
- In Excel XP: Enter the URL of the web page from which you want to import the data and click Go.
- In Excel 2000:
- Choose how often you want to refresh the data.
How can I edit an Excel spreadsheet without Microsoft Office?
Best of all, these alternatives to Excel are free.
- Google Sheets. Image: Google.
- Microsoft Office Excel Online.
- Apache OpenOffice Calc.
- LibreOffice Calc.
- WPS Office Spreadsheets.
How do you automatically refresh formulas in Excel?
In the Excel for the web spreadsheet, click the Formulas tab. Next to Calculation Options, select one of the following options in the dropdown: To recalculate all dependent formulas every time you make a change to a value, formula, or name, click Automatic. This is the default setting.
How do you automatically refresh Excel without opening and closing?
No, you cannot. The closed workbook will recalculate to update its results only after it has been opened. Your only option will be to open up the calculation file (perhaps in a hidden window) while you change the values in the input file and update the results in the output file.
How do you refresh Excel on a Mac?
How to Refresh Reports in MS Excel for Mac
- To Refresh the data in the report, click on the Data ribbon button, then click on the Refresh button.
- If the values show as zeros in the pivot tables after refreshing, please check your MacOS language and text settings.
- Related articles.
How do I allow an external data refresh in a protected worksheet in Excel?
How to allow external data refresh in protected worksheet in…
- Allow external data refresh in protected worksheet with VBA code.
- In the protected worksheet, press the Alt + F11 keys simultaneously to open the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications window.
How do I allow pivot tables to refresh a protected worksheet?
Refresh Pivot Table on Protected Sheet. When a worksheet is protected, you can’t refresh the pivot tables on that sheet. You could manually unprotect the worksheet, refresh the pivot table, and then protect the sheet again.
How do I unprotect a pivot table in Excel?
Allow Excel Pivot Table Use on Protected Sheet
- Select any cells in which users are allowed to make changes. In this example, users can make changes to cell E2.
- On the Ribbon, click the Home tab.
- In the Cells group, click Format. If the Lock Cell command is enabled, click Lock Cell to unlock the selected cell.
How do I show real time in Excel?
Insert a static date or time into an Excel cell
- To insert the current date, press Ctrl+; (semi-colon).
- To insert the current time, press Ctrl+Shift+; (semi-colon).
- To insert the current date and time, press Ctrl+; (semi-colon), then press Space, and then press Ctrl+Shift+; (semi-colon).
How do I get a live value in Excel?
Simply select the cells that contain the stock names/ticker symbols and navigate to the Data tab in the Excel Ribbon. Next click the Stocks button within the Data Types group. After clicking the Stocks button, Excel will attempt to convert as many of the selected cell’s values into stock data types.
Содержание
- Refresh external data in a workbook in the browser
- What do you want to do?
- Learn about data refresh
- Excel options for data refresh
- Refresh data from an external data source
- Refresh PivotTable data
- Need more help?
- How to Refresh Pivot Table in Excel (Manually + Auto-Refresh with VBA)
- Refresh Pivot Table
- Update Pivot Table by Changing the Data Source
- Autorefresh Pivot Table Using a VBA Macro
- How To Refresh Excel?
- How do I refresh Excel in Windows 10?
- How do I refresh Excel in Office 365?
- How do I create a refresh button in Excel?
- What does refresh all do in Excel?
- How do I refresh Excel data in SharePoint?
- How do I update Excel Online?
- What is the difference between refresh and refresh all in Excel?
- How do you refresh data on a protected sheet?
- How do I automatically refresh excel online?
- How do I feed Excel with live data?
- How can I edit an Excel spreadsheet without Microsoft Office?
- How do you automatically refresh formulas in Excel?
- How do you automatically refresh Excel without opening and closing?
- How do you refresh Excel on a Mac?
- How do I allow an external data refresh in a protected worksheet in Excel?
- How do I allow pivot tables to refresh a protected worksheet?
- How do I unprotect a pivot table in Excel?
- How do I show real time in Excel?
- How do I get a live value in Excel?
Refresh external data in a workbook in the browser
When you use a workbook in the browser, the Web-based viewer displays data that is either stored directly in the workbook, or stored in an external data source, such as in a database or in an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) cube. If the workbook that you are using contains data from an external data source, you can refresh the data. This operation retrieves the most recent version of the data, which includes any changes that were made to the data since it was last refreshed.
What do you want to do?
Learn about data refresh
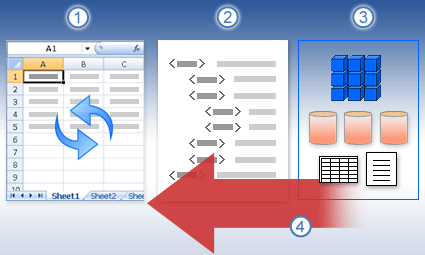
The following illustration explains the basic process of what happens when you refresh data connected to an external data source.
1. The user initiates a refresh operation to get the most recent data.
2. The refresh makes a connection to the data source, often saved to a connection file that defines all the information needed to access and retrieve data from an external data source.
3. There are a variety of data sources you can access, such as OLAP, SQL Server, OLEDB providers, and ODBC drivers.
4. The refresh adds the most recent data to the workbook.
Excel options for data refresh
You cannot define the information that is required to connect a workbook to an external data source while you work in the browser. Instead, you have to open the workbook in Microsoft Excel 2010 to define the connection information and other settings, such as how you want the data to be refreshed. When you configure the settings in Excel 2010, the settings are preserved when you publish the workbook to Microsoft SharePoint Server 2010.
The following table provides a brief description of options for refreshing data that you can select when you configure data connections in Excel.
Refresh on open
The viewer automatically refreshes external data when it opens the workbook.
This option applies only to PivotTables. The user manually refreshes the data by clicking Refresh Selected Connection.
Refresh all connections
This option refreshes all data connections in the workbook when the user clicks the Refresh All Connections button.
Refresh at regular intervals
This option refreshes data automatically at a specific interval of time that the workbook author specifies.
For specific information about how to define connections to external data sources in an Excel workbook, see Connect to (import) external data in Microsoft Excel Help.
Refresh data from an external data source
To refresh data from an external data source in a workbook in the browser, take these steps:
Open the workbook that contains the data that you want to update.
Click the Data icon on the toolbar.
Do one of the following:
Select Refresh All Connections to refresh all data connections in the workbook
Select Refresh Selected Connection to refresh a specific connection for a PivotTable.
Источник
Refresh PivotTable data
At any time, you can click Refresh to update the data for the PivotTables in your workbook. You can refresh the data for PivotTables imported from Power Query, such as a database (SQL Server, Oracle, Access, and so on), Analysis Services cube, a data feed, and many other sources. You can also refresh data from an Excel table, which automatically includes all changes to its external data source.
By default, PivotTables are not refreshed automatically, but you can specify that the PivotTable is automatically refreshed when you open the workbook that contains the PivotTable.
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Tools on the ribbon.
Click Analyze > Refresh, or press Alt+F5.

Tip: You can also refresh the PivotTable by right-clicking on the PivotTable, and then selecting Refresh.
To update all PivotTables in your workbook at once, click Analyze > Refresh arrow > Refresh All.
If refreshing takes longer than you expect, click Analyze > Refresh arrow > Refresh Status to check the refresh status.
To stop refreshing, click Cancel Refresh.
If the column widths and cell formatting of your data adjust when you refresh the PivotTable data, and you don’t want that to happen, make sure the following options are checked:
Click Analyze > Options.
On the Layout & Format tab, check the Autofit column widths on update and Preserve cell formatting on update boxes.
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Tools on the ribbon.
Click Analyze > Options.
On the Data tab, check the Refresh data when opening the file box.
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Tools on the ribbon.
Click Analyze > Refresh, or press Alt+F5.
Tip: You can also refresh the PivotTable by right-clicking on the PivotTable, and then selecting Refresh.
To update all PivotTables in your workbook at once, click Analyze > Refresh arrow > Refresh All.
If refreshing takes longer than you expect, click Analyze > Refresh arrow > Refresh Status to check the refresh status.
To stop refreshing, click Cancel Refresh.
If the column widths and cell formatting of your data adjust when you refresh the PivotTable data, and you don’t want that to happen, make sure the following options are checked:
Click Analyze > Options.
On the Layout & Format tab, check the Autofit column widths on update and Preserve cell formatting on update boxes.
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Tools on the ribbon.
Click Analyze > Options.
On the Data tab, check the Refresh data when opening the file box.
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Tools on the ribbon.
Click Analyze > Refresh, or press Alt+F5.
Tip: You can also refresh the PivotTable by right-clicking on the PivotTable, and then selecting Refresh.
To update all PivotTables in your workbook at once, click Analyze > Refresh arrow > Refresh All.
If refreshing takes longer than you expect, click Analyze > Refresh arrow > Refresh Status to check the refresh status.
To stop refreshing, click Cancel Refresh.
If the column widths and cell formatting of your data adjust when you refresh the PivotTable data, and you don’t want that to happen, make sure the following options are checked:
Click Analyze > Options.
On the Layout & Format tab, check the Autofit column widths on update and Preserve cell formatting on update boxes.
Click anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Tools on the ribbon.
Click Analyze > Options.
On the Data tab, check the Refresh data when opening the file box.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Источник
How to Refresh Pivot Table in Excel (Manually + Auto-Refresh with VBA)
Once you have created a Pivot Table, it doesn’t automatically refresh when you add new data or change the existing data.
Since your Pivot Table is created using the Pivot Cache, when the existing data changes or when you add new rows/columns to the data, the Pivot Cache does not update itself automatically, and hence, the Pivot Table also does not update.
You need to force a refresh every time there are changes. Once you force a refresh, the Pivot Cache gets updated, which is reflected in the Pivot Table.
This tutorial covers a couple of ways to do this.
This Tutorial Covers:
Refresh Pivot Table
This option is best suited when there are changes in the existing data source and you want to refresh the pivot table to reflect these changes.
Here are the steps to refresh a Pivot Table:
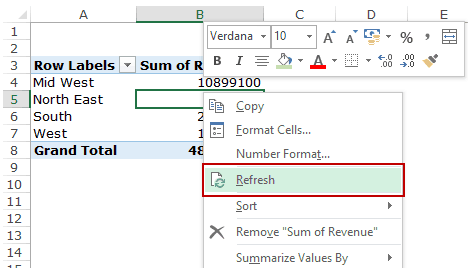
- Right-click on any cell in the Pivot Table.
- Select Refresh.
This will instantly refresh the Pivot Table.
You can also by selecting any cell in the Pivot Table and use the keyboard shortcut ALT + F5.
Quick Tip: It’s a good practice to convert the data source into an Excel Table, and use this Excel Table to create the Pivot Table. If you do this, you can also use the refresh technique to update the Pivot Table even when new data (rows/columns) are added to the data source (since an Excel Table automatically accounts for new rows/columns that are added).
Update Pivot Table by Changing the Data Source
If you’ve added new rows/columns to the data source, you need to change the data source to make sure new rows/columns are a part of the dataset.
Note that if you change the data source into an Excel Table and then use the Excel table to create the Pivot Table, you don’t need to use the change data source option. You can simply refresh the Pivot Table and it’ll account for the new rows/columns.
Autorefresh Pivot Table Using a VBA Macro
While refreshing a Pivot table is as easy as two clicks, you still need to do this every time there is a change.
To make it more efficient and auto-refresh the Pivot Table whenever there is a change in the data source, you can use a simple one-line VBA macro code.
Here is the VBA code:
Decoding the Code: This is a change event which gets triggered whenever there is a change in the sheet that contains the source data. As soon as there is a change, the code refreshes the Pivot Cache of the Pivot Table with the name PivotTable1.
You need to modify this code to make it work for your workbook:
- “Sheet1” – change this part of the code with the name of the sheet that has the Pivot Table.
- “PivotTable1” – change this to the name of your Pivot Table. To know the name, click anywhere in the Pivot Table and click the Analyze Tab. The name would be visible in the left part of the ribbon under the ‘PivotTable Name’ header.
Where to put this VBA code:
Now when you change anything in the data source, the Pivot Table would automatically get refreshed.
Click here to download the example file.
Note: Since there is a macro in the workbook, save this with .xls or .xlsm extension.
You May Also Like the Following Pivot Table Tutorials:
Источник
How To Refresh Excel?
Excel provides many options for refreshing data, including when you open the workbook and at timed intervals. Note: To stop a refresh, press Esc. To refresh a worksheet, press Ctrl + F5. To refresh a workbook, press Ctrl + Alt + F5.
How do I refresh Excel in Windows 10?
Windows 10
- Click on the Windows “start” icon (bottom-left corner of your screen).
- Click on “Settings”.
- Click on “Apps”.
- Select “Microsoft Office” (or “Microsoft Excel” if you do not have the full Office installation).
- Click “Modify”.
- Choose from “Quick Repair” or “Online Repair”.
How do I refresh Excel in Office 365?
Open the workbook that contains the data that you want to update. Click the Data icon on the toolbar. Do one of the following: Select Refresh All Connections to refresh all data connections in the workbook.
How do I create a refresh button in Excel?
There are 3 steps:
Step 1: Go to the Insert menu, choose Icons and type “Refresh” in the search field. Choose the icon you want, and click on Insert. Resize and place the icon where you want to have it. Step 3: Go back to Excel, right-click on the Refresh Icon and choose “Assign Macro”.
What does refresh all do in Excel?
According to the Excel VBA help, RefreshAll “Refreshes all external data ranges and PivotTable reports in the specified workbook.”
Refresh the Excel chart
- Click on the Refresh button under the ANALYZE tab and select Refresh All.
- Click on the Refresh All button under the DATA tab.
How do I update Excel Online?
Go to File > Help > Check for Updates. Choose Install Updates or Check for Updates.
What is the difference between refresh and refresh all in Excel?
My gut tells me that “Refresh” refreshes the pivot from the new data on the current worksheet, and “Refresh All” refresh the pivots on all worksheets found in the xlsx file.
How do you refresh data on a protected sheet?
When you want to refresh an Excel pivot table on a protected sheet, you will need to temporarily unprotect the worksheet, refresh the pivot table, and then protect the sheet again.
How do I automatically refresh excel online?
Automatically refresh data at regular intervals
- Click a cell in the external data range.
- On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
- Click the Usage tab.
- Select the Refresh every check box, and then enter the number of minutes between each refresh operation.
How do I feed Excel with live data?
Quick Importing of Live Data
- Open a worksheet in Excel.
- From the Data menu select either Import External Data or Get External Data.
- Select New Web Query.
- In Excel XP: Enter the URL of the web page from which you want to import the data and click Go.
- In Excel 2000:
- Choose how often you want to refresh the data.
How can I edit an Excel spreadsheet without Microsoft Office?
Best of all, these alternatives to Excel are free.
- Google Sheets. Image: Google.
- Microsoft Office Excel Online.
- Apache OpenOffice Calc.
- LibreOffice Calc.
- WPS Office Spreadsheets.
How do you automatically refresh formulas in Excel?
In the Excel for the web spreadsheet, click the Formulas tab. Next to Calculation Options, select one of the following options in the dropdown: To recalculate all dependent formulas every time you make a change to a value, formula, or name, click Automatic. This is the default setting.
How do you automatically refresh Excel without opening and closing?
No, you cannot. The closed workbook will recalculate to update its results only after it has been opened. Your only option will be to open up the calculation file (perhaps in a hidden window) while you change the values in the input file and update the results in the output file.
How do you refresh Excel on a Mac?
How to Refresh Reports in MS Excel for Mac
- To Refresh the data in the report, click on the Data ribbon button, then click on the Refresh button.
- If the values show as zeros in the pivot tables after refreshing, please check your MacOS language and text settings.
- Related articles.
How do I allow an external data refresh in a protected worksheet in Excel?
How to allow external data refresh in protected worksheet in…
- Allow external data refresh in protected worksheet with VBA code.
- In the protected worksheet, press the Alt + F11 keys simultaneously to open the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications window.
How do I allow pivot tables to refresh a protected worksheet?
Refresh Pivot Table on Protected Sheet. When a worksheet is protected, you can’t refresh the pivot tables on that sheet. You could manually unprotect the worksheet, refresh the pivot table, and then protect the sheet again.
How do I unprotect a pivot table in Excel?
Allow Excel Pivot Table Use on Protected Sheet
- Select any cells in which users are allowed to make changes. In this example, users can make changes to cell E2.
- On the Ribbon, click the Home tab.
- In the Cells group, click Format. If the Lock Cell command is enabled, click Lock Cell to unlock the selected cell.
How do I show real time in Excel?
Insert a static date or time into an Excel cell
- To insert the current date, press Ctrl+; (semi-colon).
- To insert the current time, press Ctrl+Shift+; (semi-colon).
- To insert the current date and time, press Ctrl+; (semi-colon), then press Space, and then press Ctrl+Shift+; (semi-colon).
How do I get a live value in Excel?
Simply select the cells that contain the stock names/ticker symbols and navigate to the Data tab in the Excel Ribbon. Next click the Stocks button within the Data Types group. After clicking the Stocks button, Excel will attempt to convert as many of the selected cell’s values into stock data types.
Источник
To keep imported external data up-to-date, you can refresh it to see recent updates and deletes. Excel provides many options for refreshing data, including when you open the workbook and at timed intervals.
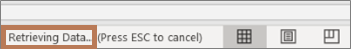
Note: To stop a refresh, press Esc. To refresh a worksheet, press Ctrl + F5. To refresh a workbook, press Ctrl + Alt + F5.
Learn about refreshing data in the Excel app
The following table summarizes the refresh actions, shortcut keys, and commands.
|
To |
Press |
Or |
|---|---|---|
|
Refresh selected data in the worksheet |
Alt + F5 |
Select Data > The drop-down arrow next to Refresh All > Refresh |
|
Refresh all data in the workbook |
Ctrl + Alt + F5 |
Select Data > Refresh All |
|
Check refresh status |
Double-click the message, «Retrieving Data» on the status bar. |
|
|
Stop a refresh |
Esc |
|
|
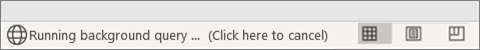
Stop a background refresh |
Double-click the message on the status bar. And then select Stop Refresh in the External Data Refresh Status dialog box. |
Data in a workbook may be stored directly in the workbook, or it may be stored in an external data source, such as a text file, a database, or the cloud. The first time you import external data, Excel creates connection information, sometimes saved to an Office Data Connection (ODC) file, which describes how to locate, log in, query, and access the external data source.
When you are connected to an external data source, you can perform a refresh operation to retrieve the updated data. Each time that you refresh data, you see the most recent version of the data, including any changes that were made to the data since it was last refreshed.
Learn more about refreshing data
This explains the basic process of what happens when you refresh data connected to an external data source:
-
Someone starts refreshing the workbook’s connections to get up-to-date data.
-
Connections are made to external data sources that are used in the workbook.
Note: There are a variety of data sources you can access, such as OLAP, SQL Server, OLEDB providers, and ODBC drivers.
-
The data in the workbook is updated.
Learn about security concerns
When you are connected to an external data source and you attempt to refresh the data, it’s important to be aware of potential security issues, and to know what you can do about any security issues.
Trust Connections — External data may be currently disabled on your computer. To refresh the data when you open a workbook, you must enable the data connections by using the Trust Center bar, or you must place the workbook in a trusted location. For more information, see these articles:
-
Add, remove, or modify a trusted location for your files
-
Trusted documents
-
Add, remove, or view a trusted publisher
-
View my options and settings in the Trust Center.
ODC file — A data connection file (.odc) often contains one or more queries that are used to refresh external data. By replacing this file, a user who has malicious intent can design a query to access confidential information and distribute it to other users or perform other harmful actions. Therefore, it’s important to ensure that the connection file was authored by a reliable individual, and the connection file is secure and comes from a trusted Data Connection Library (DCL).
Credentials — Accessing an external data source usually requires credentials (such as a user name and a password) that are used to authenticate the user. Make sure that these credentials are provided to you in a safe and secure manner, and that you do not inadvertently reveal these credentials to others. If your external data source requires a password to gain access to the data, you can require that the password is entered each time the external data range is refreshed.
Sharing — Are you sharing this workbook with other people who might want to refresh data? Help your colleagues avoid data refresh errors by reminding them to request permissions on the data sources providing the data.
For more information, see Manage data source settings and permissions.
You can refresh an external data range automatically when you open the workbook. You can also save the workbook without saving the external data to shrink the size of the file.
-
Select a cell in the external data range.
-
Select Data > Queries & Connections > Connections tab, right click a query in the list, and then select Properties.
-
In the Connection Properties dialog box, on the Usage tab, under Refresh control, select the Refresh data when opening the file check box.
-
If you want to save the workbook with the query definition but without the external data, select the Remove data from the external data range before saving the workbook check box.
-
Select a cell in the external data range.
-
Select Data > Queries & Connections > Connections tab, right click a query in the list, and then select Properties.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Select the Refresh every check box, and then enter the number of minutes between each refresh operation.
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. Consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish.
Note: You can’t run an OLAP query in the background and you can’t run a query for any connection type that retrieves data for the Data Model.
-
Select a cell in the external data range.
-
Select Data > Queries & Connections > Connections tab, right click a query in the list, and then select Properties.
-
Select the Usage tab.
-
Select the Enable background refresh check box to run the query in the background. Clear this check box to run the query while you wait.
Tip While you record a macro that includes a query, Excel doesn’t run the query in the background. To change the recorded macro so that the query runs in the background, edit the macro in the Visual Basic Editor. Change the refresh method for the QueryTable object from BackgroundQuery := False to BackgroundQuery := True.
Stored passwords aren’t encrypted, so they’re not recommended. If your data source needs a password to connect to it, you can require that users enter the password before they can refresh the external data range. The following procedure doesn’t apply to data retrieved from a text file (.txt) or a Web query (.iqy).
Tip: Use strong passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Weak passwords don’t mix these elements. For example, Strong password: Y6dh!et5. Weak password: House27. Passwords should be 8 or more characters in length. A pass phrase that uses 14 or more characters is better.
It’s critical that you remember your password. If you forget your password, Microsoft cannot retrieve it. Store the passwords that you write down in a secure place away from the information that they help protect.
-
Select a cell in the external data range.
-
Select Data > Queries & Connections > Connections tab, right click a query in the list, and then select Properties.
-
Select the Definition tab, and then clear the Save password check box.
Note: Excel prompts you for the password only the first time that the external data range is refreshed in each Excel session. The next time you start Excel, you’ll be prompted for the password again if you open the workbook that contains the query and then attempt a refresh operation.
Detailed help for refreshing data
When you shape your data in Power Query, you typically load the changes to a worksheet or Data Model. It’s important to understand the difference when you are refreshing data and how you refresh it.
Note: When you refresh, new columns added since the last refresh operation are added to Power Query. To see these new columns, re-examine the Source step in the query. For more information, see Create Power Query formulas.
Most queries are based on external data resources of one kind or another. However, there is a key difference between Excel and Power Query. Power Query caches the external data locally to help improve performance. Furthermore, Power Query doesn’t automatically refresh the local cache to help prevent incurring costs for data sources in Azure.
Important: If you receive a message in the yellow message bar at the top of your window, that states “This preview may be up to n days old.”, it usually means the local cache is out-of-date. You should select Refresh to bring it up-to-date.
Refresh a query in the Power Query Editor
When you refresh a query from the Power Query Editor, you are not only bringing in updated data from the external data source, you are also updating the local cache. But this refresh operation does not update the query in the worksheet or Data Model.
-
In Power Query Editor, select Home
-
Select Refresh Preview > Refresh Preview (the current query in Preview Data) or Refresh All (all opened queries from the Queries pane.)
-
At the bottom of the Power Query Editor on the right, a message displays, “Preview downloaded at <hh:mm> AM/PM”. This message displays upon first importing, and after each subsequent refresh operation in the Power Query Editor.
Refresh a query in a worksheet
-
In Excel, select a cell in a query in a worksheet.
-
Select the Query tab in the ribbon, and then select Refresh > Refresh.
-
The worksheet and the query are refreshed from the external data source and the Power Query cache.
Notes:
-
When you refresh a query that was imported from an Excel table or named range, pay attention to your current worksheet. If you want to change the data in the worksheet that contains the Excel table, make sure you have selected the correct worksheet and not the worksheet that contains the loaded query.
-
This is especially important if you are changing the column headers in the Excel Table. They often look similar and it’s easy to confuse the two. It’s a good idea to rename the worksheets to reflect the difference. For example, you could rename them to “TableData” and “QueryTable” to emphasize the distinction.
At any time, you can select Refresh to update the data for the PivotTables in your workbook. You can refresh the data for PivotTables connected to external data, such as a database (SQL Server, Oracle, Access, or other), Analysis Services cube, data feed, as well as data from a source table in the same or a different workbook. PivotTables can be refreshed manually or automatically when you open the workbook.
Manually refresh
-
Select the anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Analyze tab in the ribbon.
Note: To refresh a PivotTable in Excel for the web, right-click anywhere on the PivotTable, and then select Refresh.
-
Select Refresh or Refresh All.
-
To check the refresh status if refreshing takes longer than you expect, select the arrow under Refresh > Refresh Status.
-
To stop refreshing, select Cancel Refresh, or press Esc.
Prevent column widths and cell formatting from adjusting
If the column widths and cell formatting of your data adjust when you refresh the PivotTable data, and you don’t want that to happen, make sure the following options are checked:
-
Select the anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Analyze tab in the ribbon.
-
Select the PivotTable Analyze tab > in the PivotTable group, select Options.
-
On the Layout & Format tab > select the checkboxes for Autofit column widths on update and Preserve cell formatting on update.
Refresh data automatically when opening the workbook
-
Select the anywhere in the PivotTable to show the PivotTable Analyze tab in the ribbon.
-
Select the PivotTable Analyze tab > in the PivotTable group, select Options.
-
On the Data tab, select Refresh data when opening the file.
Refreshing an offline cube file, which recreates the file by using the most recent data from the server cube, can be time consuming and require a lot of temporary disk space. Start the process at a time when you don’t need immediate access to other files in Excel, and make sure you have adequate disk space to save the file again.
-
Select the PivotTable connected to the offline cube file.
-
On the Data tab, in the Queries & Connections group, click the arrow under Refresh All, and then click Refresh.
For more information, see Work with offline cube files.
-
On the worksheet, click a mapped cell to select the XML map that you want to refresh.
-
If the Developer tab isn’t available, do the following to display it:
-
Click File, click Options, and then click Customize Ribbon.
-
Under Main Tabs, select the Developer check box, and then click OK.
-
-
On the Developer tab, in the XML group, click Refresh Data.
For more information, see Overview of XML in Excel.
When you refresh a Data Model in Power Pivot , you can also see whether your refresh succeeds, fails, or is cancelled. For more information, see Power Pivot: Powerful data analysis and data modeling in Excel.
Note: Addition of data, changing data, or editing filters always triggers recalculation of DAX formulas that depend on that data source.
Refresh and view the status of refresh
-
In Power Pivot, select Home > Get External Data > Refresh or Refresh All to refresh the current table or all of the tables in the Data Model.
-
Status of the refresh is indicated for each connection used in the data model. There are three possible outcomes:
-
Success — Reports on the number of rows imported into each table.
-
Error — Occurs if the database is offline, you no longer have permissions, or a table or column is deleted or renamed in the source. Verify the database is available, perhaps by creating a new connection in a different workbook.
-
Cancelled — Excel did not issue the refresh request, probably because refresh is disabled on the connection.
Use table properties to show the queries used in data refresh
Data refresh is simply rerunning the same query that was used to get the data in the first place. You can view, and sometimes modify, the query by viewing table properties in the Power Pivot window.
-
To view the query used during data refresh, select Power Pivot > Manage to open the Power Pivot window.
-
Select Design > Table Properties.
-
Switch to Query Editor to view the underlying query.
Queries are not visible for every type of data source. For example, queries are not shown for data feed imports.
Set connection properties to cancel data refresh
In Excel, you can set connection properties that determine the frequency of data refresh. If refresh is not allowed on a particular connection, you’ll get a cancellation notice when you run Refresh All or attempt to refresh a specific table that uses the connection.
-
To view connection properties, in Excel, select Data > Queries & Connections to view a list of all connections used in the workbook.
-
Select the Connections tab, right-click a connection, and then click Properties.
-
In the Usage tab, under Refresh control, if the checkbox is cleared for Refresh this connection on Refresh All, you will get a cancellation when you try Refresh All in the Power Pivot window.
Refresh data on SharePoint Server 2013
On SharePoint Server, you can schedule unattended data refresh on the server, but doing so requires that Power Pivot for SharePoint 2013 is installed and configured in your SharePoint environment. Check with your SharePoint administrator to find out if scheduled data refresh is available. For more information, see Configure scheduled data refresh for Power Pivot.
When the data you use for your map changes, you can refresh it manually in 3D Maps. The changes will then be reflected on your map. Here’s how:
-
In 3D Maps, select Home > Refresh Data.
Add data to Power Map
To add new data to your 3D MapsPower Map:
-
In 3D Maps, go to the map you want to add data to.
-
Leave the 3D Maps window open.
-
In Excel select the worksheet data you want to add.
-
On the Excel ribbon, click Insert > Map arrow > Add Selected Data to Power Map. Your 3D Maps will automatically update to show the additional data. For more information, see Get and prep your data for Power Map.
Refreshing external data in Excel Services has unique requirements.
Control how data is refreshed
You can control how to refresh data from an external data source by doing one or more of the following.
Refresh on open with
Excel Services
In Excel, you can create a workbook that automatically refreshes external data when the file is opened. In this case, Excel Services always refreshes the data before it displays a workbook and creates a new session. Use this if you want to ensure that up-to-date data is always displayed when you open the workbook in Excel Services.
-
In a workbook with external data connections, select the Data tab.
-
In the Connections group, select Connections > select the connection > Properties.
-
Select the Usage tab and then select Refresh data when opening the file.
Warning: If you clear the Refresh data when opening the file check box, the data that is cached with the workbook is displayed, which means that when a user manually refreshes the data, the user sees up-to-date data during the current session, but the data is not saved to the workbook.
Refresh with an .odc file
If you are using an Office Data Connection file (.odc), make sure you also set the Always use connection file check box:
-
In a workbook with external data connections, select the Data tab.
-
In the Connections group, select Connections > select the connection > Properties.
-
Select the Definition tab and then select Always use connection file.
The trusted file location site settings, Short Session Timeout and External Data Cache Lifetime, can also have an impact on refresh operations. For more information, see your administrator or the Help system.
Manual refresh
-
Select a cell in the PivotTable report.
-
On the Excel Web Access toolbar, under the Update menu, select Refresh Selected Connection.
Notes:
-
If this Refresh command is not visible, then the Web Part author has cleared the Refresh Selected Connection, Refresh All Connections property. For more information, see Excel Web Access Web Part custom properties.
-
Any interactive operation that causes a re-query of an OLAP data source initiates a manual refresh operation.
-
-
Refresh all connections — On the Excel Web Access toolbar, under the Update menu, click Refresh All Connections.
-
Periodic refresh — You can specify that data automatically refreshes at a specified interval after the workbook is opened for each connection in the workbook. For example, an inventory database may be updated every hour, and so the workbook author has defined the workbook to automatically refresh every 60 minutes.
A Web Part author can select or clear the Allow Excel Web Access Periodic Data Refresh property to allow or prevent periodic refresh. When the time interval elapses, by default, you’ll see a refresh alert display at the bottom of the Excel Web Access Web Part.
An Excel Web Access Web Part author can also set the Display Periodic Data Refresh Prompt property to control the behavior of the message that is displayed when Excel Services performs a periodic data refresh during a session:
For more information, see Excel Web Access Web Part custom properties.
-
Always — means that the message is displayed with a prompt at each interval.
-
Optionally — means that a user can choose to continue periodic refresh without displaying a message.
-
Never — means that Excel Web Access performs a periodic refresh without displaying a message or prompt.
-
Cancel a refresh — While the workbook is refreshing, Excel Services displays a message with a prompt because it could take longer than you expect. You can select Cancel to stop refreshing so you can finish it later at a more convenient time. Data returned by queries before you canceled the refresh will display.
When you use a workbook in the browser, you are viewing data that is stored directly in the workbook or external data where the data is stored elsewhere and requires a connection to a source or database.
This explains the basic process of what happens when you refresh data connected to an external data source:
-
Someone starts refreshing the workbook’s connections to get up-to-date data.
-
Connections are made to external data sources that are used in the workbook.
Note: There are a variety of data sources you can access, such as OLAP, SQL Server, OLEDB providers, and ODBC drivers.
-
The data in the workbook is updated.

If you are viewing a workbook in a browser window, and you want to refresh the data, you can typically do this in one of two modes: view mode or edit mode.
View mode
When you refresh a workbook in view mode, you simply update the data displayed in the workbook. You can do this in a browser window or in Excel, in read-only (not edit) mode.
In this case, the workbook is not tracked as a changed file. This means that in the location where the workbook is stored, your user credentials are not displayed as someone who recently edited the workbook.
Edit mode
When you refresh a workbook in edit mode, you open the workbook for editing (either in a browser window or in Excel). The workbook is tracked as a changed file. This means that your user credentials are displayed as someone who recently edited the workbook.
If you’re editing a workbook and you refresh the data, your changes are automatically saved after the data refresh has occurred. Anyone who has permissions to view the workbook will see your changes as soon as the workbook is saved.
You must use Excel to define external data connections for a workbook. You cannot define such settings while viewing a workbook in a browser window. The settings that you specify by using Excel are preserved when you publish a workbook to a SharePoint library.
To specify data refresh options, choose the Properties button for a particular data connection in Excel. The following table provides a brief description of various data refresh options that you can select.
-
Refresh every __ minutes — This option causes the workbook to attempt to refresh data at intervals of time that you specify (in minutes.)
-
Refresh data when opening the file — This option causes the workbook to attempt to refresh data automatically when the workbook is opened.
-
Refresh this connection on Refresh All — When selected, this option refreshes the data when you or other users click the Refresh All button.
When unselected, this option prevents this connection from refreshing data when you or others click the Refresh All button. This is useful when you want to avoid data refresh errors, such as timeout errors for a particular connection in Excel Services.
Depending on how your environment is configured, data refresh might not occur. For example, if someone created a workbook that uses secure, external data connections to on-premises servers, those data connections will probably not work in Microsoft 365. If you run into a situation where you can’t refresh the data in a browser window, try opening the workbook in Excel.
You can also contact a SharePoint administrator.
For most connections, click any cell in the range or table that uses the connection, and then do one of the following:
-
Update only the selected data Press ALT+F5, or on the Data tab, in the Connections group, click the arrow under Refresh All, and then click Refresh.
-
Update all data in the workbook Press CTRL+ALT+F5, or on the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All.
-
Control how or when the connection is refreshed On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click the arrow under Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
In the dialog box that opens, choose the options you want on the Usage tab, under Refresh Control.
Some refresh operations require more steps, as detailed in the following sections. If you see your data source listed, review the corresponding section.
You can refresh an external data range automatically when you open the workbook. Optionally, you can save the workbook without saving the external data to shrink the size of the file.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Under Refresh control, select the Refresh data when opening the file check box.
-
If you want to save the workbook with the query definition but without the external data, select the Remove data from the external data range before saving the workbook check box.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Select the Refresh every check box, and then enter the number of minutes between each refresh operation.
Stored passwords aren’t encrypted, so they’re not recommended. If your data source needs a password to connect to it, you can require that users enter the password before they can refresh the external data range. The following procedure doesn’t apply to data retrieved from a text file (.txt) or a Web query (.iqy).
Use strong passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Weak passwords don’t mix these elements. For example, Strong password: Y6dh!et5. Weak password: House27. Passwords should be 8 or more characters in length. A pass phrase that uses 14 or more characters is better.
It’s critical that you remember your password. If you forget your password, Microsoft cannot retrieve it. Store the passwords that you write down in a secure place away from the information that they help protect.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
-
Click the Definition tab, and then clear the Save password check box.
Note: Excel prompts you for the password only the first time that the external data range is refreshed in each Excel session. The next time you start Excel, you’ll be prompted for the password again if you open the workbook that contains the query and then attempt a refresh operation.
For very large data sets, consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
Note: You can’t run an OLAP query in the background.
Note: You can’t run a query for any connection type that retrieves data for the Data Model.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Select the Enable background refresh check box to run the query in the background. Clear this check box to run the query while you wait.
While you record a macro that includes a query, Excel doesn’t run the query in the background. To change the recorded macro so that the query runs in the background, edit the macro in the Visual Basic Editor. Change the refresh method for the QueryTable object from BackgroundQuery := False to BackgroundQuery := True.
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on the refresh, or to cancel it, do one of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
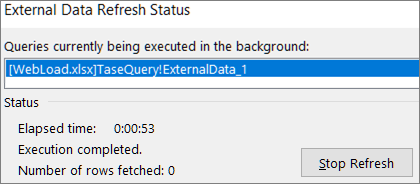
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
If you used Get & Transform to query a text file, no further steps are needed. If you imported the text file, the steps to refresh are as follows:
-
Click any cell in the range or table that contains the link to the imported text file.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All.
To update only the selected data, click Refresh.
You can also right-click a cell in the range or table, and then click Refresh.
-
In the Import Text File dialog box, browse to your text file, and then click Import.
Refreshing an offline cube file, which recreates the file by using the most recent data from the server cube, can be time consuming and require a lot of temporary disk space. Start the process at a time when you don’t need immediate access to other files in Excel, and make sure you have adequate disk space to save the file again.
-
Click the PivotTable connected to the offline cube file.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Refresh.
-
On the worksheet, click a mapped cell to select the XML map that you want to refresh.
-
If the Developer tab isn’t available, do the following to display it:
-
Click File, click Options, and then click Customize Ribbon.
-
Under Main Tabs, select the Developer check box, and then click OK.
-
-
On the Developer tab, in the XML group, click Refresh Data.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All.
If you have multiple connections, and you only want to update a certain one, select any cell within that data range, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Refresh.
Control how or when the connection is refreshed
-
Click any cell that contains your connected data.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Connection Properties.
-
On the Usage tab, set any options you want to change.
For very large data sets, consider checking the Enable background refresh option. This returns control of Excel to you as soon as the refresh begins, instead of making you wait for the refresh to finish.
Cancel or check the status of a refresh
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on the refresh, or to cancel it, do one of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
When you use the Power Pivot add-in to refresh previously imported data, you can see whether refresh succeeds, fails, or is cancelled.
In Power Pivot, click Home > Get External Data > Refresh or Refresh All to re-import the current table or all of the tables in the data model.
Status of the refresh is indicated for each connection used in the data model. There are three possible outcomes.

“Success” reports on the number of rows imported into each table.
“Error” can occur if the database is offline, you no longer have permissions, or a table or column is deleted or renamed in the source. Verify the database is available, perhaps by creating a new connection in a different workbook.
“Cancelled” means that Excel did not issue the refresh request, probably because refresh is disabled on the connection.
Tip: Are you sharing this workbook with other people who might want to refresh data? Help your colleagues avoid data refresh errors by reminding them to request permissions on the data sources providing the data.
Table properties show queries used in data refresh
Data refresh is simply rerunning the same query that was used to get the data in the first place. You can view, and sometimes modify, the query by viewing table properties in the Power Pivot window.
-
To view the query used during data refresh, click Power Pivot > Manage to open the Power Pivot window.
-
Click Design > Table Properties.
-
Switch to Query Editor to view the underlying query.
Queries are not visible for every type of data source. For example, queries are not shown for data feed imports.
Connection properties that cancel data refresh
In Excel, you can set connection properties that determine the frequency of data refresh. If refresh is not allowed on a particular connection, you’ll get a cancellation notice when you run Refresh All or attempt to refresh a specific table that uses the connection.
-
To view connection properties, in Excel, click Data > Connections to view a list of all connections used in the workbook.
-
Select a connection and click Properties.
-
In Usage, under Refresh control, if the checkbox is cleared for Refresh this connection on Refresh All, you will get a cancellation when you try Refresh All in the Power Pivot window.
Refresh data on SharePoint Server 2013 or later
On SharePoint Server, you can schedule unattended data refresh on the server, but doing so requires that Power Pivot for SharePoint 2013 is installed and configured in your SharePoint environment. Check with your SharePoint administrator to find out if scheduled data refresh is available.
With the Power Query Editor, you can refresh a query to import the latest data into a table without having to recreate the query.
To refresh a query:
-
Click Get & Transform > Show Queries.
-
In the Workbook Queries pane, select the query you want to refresh.
-
In the Power Query Editor ribbon, click Home > Query > Refresh preview.
When the data you use for your map changes, you can refresh it manually in 3D Maps. The changes will then be reflected on your map. Here’s how:
-
In 3D Maps, click Home > Refresh Data.
Add data to Power Map
To add new data to your 3D MapsPower Map:
-
In 3D Maps, go to the map you want to add data to.
-
Leaving the 3D Maps window open, click in Excel and select the worksheet data you want to add.
-
On the Excel ribbon, click Insert > Map arrow > Add Selected Data to Power Map.
Your 3D Maps will automatically update to show the additional data.
Data in a Microsoft Office Excel workbook that has been displayed in Excel Services can come from two different locations. The data may be stored directly in the workbook, or it may be stored in an external data source, such as in a database or in an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) cube.
If the data comes from an external data source, the workbook author or administrator has defined the connection information, often in an Office data connection (.odc) file, which describes how to locate, log in, query, and access the external data source.
When you are connected to an external data source, you can perform a refresh operation to retrieve the updated data. Each time that you refresh data, you see the most recent version of the data, including any changes that were made to the data since it was last refreshed.
Learn about refreshing data
The following illustration explains the basic process of what happens when you refresh data connected to an external data source.

-
A refresh operation gets up-to-date data.
-
A connection, often saved to a connection file, defines all the information needed to access and retrieve data from an external data source.
-
There are a variety of data sources you can access, such as OLAP, SQL Server, OLEDB providers, and ODBC drivers.
-
Up-to-date data is added to the current workbook.
Learn about security concerns
When you are connected to an external data source and you attempt to refresh the data, it’s important to be aware of potential security issues, and to know what you can do about any security issues.
A data connection file often contains one or more queries that are used to refresh external data. By replacing this file, a user who has malicious intent can design a query to access confidential information and distribute it to other users or perform other harmful actions. Therefore, it’s important to ensure that the connection file was authored by a reliable individual, and the connection file is secure and comes from a trusted Data Connection Library (DCL).
For more information on how an administrator can author connection files, create trusted locations, and secure connection files, see Microsoft Office Excel Help and Office SharePoint Server Central Administration Help.
Note: Accessing an external data source usually requires credentials (such as a user name and a password) that are used to authenticate the user. Make sure that these credentials are provided to you in a safe and secure manner, and that you do not inadvertently reveal these credentials to others.
Control how data is refreshed
You can control how to refresh data from an external data source by doing one or more of the following:
-
Refresh on open In Excel, a workbook author can create a workbook that automatically refreshes external data when the workbook is opened by selecting the Refresh data when opening the file check box in the Connection Properties dialog box. (On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Connections, select the connection, click Properties, click the Usage tab, and then click Refresh data when opening the file.) In this case, Excel Services always refreshes the data before it displays a workbook and creates a new session. If the workbook author clears the Refresh data when opening the file check box, the data that is cached with the workbook is displayed, which means that when a user manually refreshes the data, the user sees refreshed, up-to-date data during the current session, but the data is not saved to the workbook. If you want to ensure that up-to-date data is always displayed when you display the workbook in Excel Services, select the Refresh data when opening the file check box by using Office Excel.
If you are using an Office Data Connection file (.odc), make sure you also set the Always use connection file check box in the Connection Properties dialog box (On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Connections, select the connection, click Properties, click the Definition tab, and then click Always use connection file).
The trusted file location site settings, Short Session Timeout and External Data Cache Lifetime, can also have an impact on refresh operations. For more information, see your administrator or the Microsoft Office SharePoint Server Central Administration Help system.
-
Manual refresh
Note: You can manually refresh only a PivotTable report.
-
Select a cell in a PivotTable report.
-
On the Excel Web Access toolbar, under the Update menu, click Refresh Selected Connection.
Notes:
-
Any interactive operation that causes a requery of an OLAP data source initiates a manual refresh operation.
-
If this Refresh command is not visible, then the Web Part author has cleared the Refresh Selected Connection, Refresh All Connections property. For more information, see Excel Web Access Web Part custom properties.
-
-
-
Refresh all connections On the Excel Web Access toolbar, under the Update menu, click Refresh All Connections.
-
Periodic refresh By using Excel, the workbook author can specify that data automatically refreshes at a specified interval after the workbook is opened for each connection in the workbook. For example, an inventory database may be updated every hour, and so the workbook author has defined the workbook to automatically refresh every 60 minutes.
A Web Part author can select or clear the Allow Excel Web Access Periodic Data Refresh property to enable or disable this periodic refresh operation, if the property has been defined by the workbook author. When the time interval elapses, by default, the following refresh alert prompt is displayed at the bottom of the Excel Web Access Web Part:
Refresh data for <List of Connections>? (Now) (Always) (Don’t ask me again)
An Excel Web Access Web Part author can also set the Display Periodic Data Refresh Prompt property to control the behavior of the message that is displayed when Excel Services performs a periodic data refresh during a session:
-
Always means that the message is displayed with a prompt at each interval.
-
Optionally means that a user can choose to continue periodic refresh without displaying a message.
-
Never means that Excel Web Access performs a periodic refresh without displaying a message or prompt.
For more information, see Excel Web Access Web Part custom properties.
-
-
Cancel a refresh Because a refresh operation may take longer than you expect, you can cancel it. While the refresh operation occurs, Excel Services displays a message with a prompt. Click Cancel to interrupt the operation, so that you can complete the refresh operation at a more convenient time. Data returned by queries before you cancelled the refresh operation will display.
-
Click any cell in the range or table that contains the link to the external data.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All.
To update only the selected data, click Refresh.
You can also right-click a cell in the range or table, and then click Refresh.
Note: If you have more than one workbook open, you’ll need to repeat the operation in each workbook.
-
Click any cell in the range or table that contains the link to the imported text file.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All.
To update only the selected data, click Refresh.
You can also right-click a cell in the range or table, and then click Refresh.
-
In the Import Text File dialog box, browse to your text file, and then click Import.
Refreshing an offline cube file, which recreates the file by using the most recent data from the server cube, can be time consuming and require a lot of temporary disk space. Start the process at a time when you don’t need immediate access to other files in Excel, and make sure you have adequate disk space to save the file again.
-
Click the PivotTable connected to the offline cube file.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Refresh.
-
On the worksheet, click a mapped cell to select the XML map that you want to refresh.
-
If the Developer tab isn’t available, do the following to display it:
-
Click File, click Options, and then click Customize Ribbon.
-
Under Main Tabs, select the Developer check box, and then click OK.
-
-
On the Developer tab, in the XML group, click Refresh Data.
-
On the Data tab, click Refresh All.
If you have multiple connections, and you only want to update a certain one, select any cell within that data range, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Refresh.
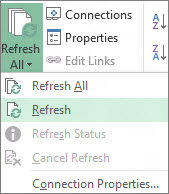
Control how or when the connection is refreshed
-
Click any cell that contains your connected data.
-
On the Data tab, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Connection Properties.
-
On the Usage tab, set any options you want to change.
For very large data sets, consider checking the Enable background refresh option. This returns control of Excel to you, instead of making you wait for the refresh to finish.
Cancel or check the status of a refresh
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on the refresh, or to cancel it, do one of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
When you use the Power Pivot add-in to refresh previously imported data, you can see whether refresh succeeds, fails, or is cancelled.
-
In Power Pivot, click Home > Get External Data > Refresh or Refresh All to re-import the current table or all of the tables in the data model.
Status of the refresh is indicated for each connection used in the data model. There are three possible outcomes.
“Success” reports on the number of rows imported into each table.
“Error” can occur if the database is offline, you no longer have permissions, or a table or column is deleted or renamed in the source. Verify the database is available, perhaps by creating a new connection in a different workbook.
“Cancelled” means that Excel did not issue the refresh request, probably because refresh is disabled on the connection.
Tip: Are you sharing this workbook with other people who might want to refresh data? Help your colleagues avoid data refresh errors by reminding them to request permissions on the data sources providing the data.
Table properties show queries used in data refresh
Data refresh is simply rerunning the same query that was used to get the data in the first place. You can view, and sometimes modify, the query by viewing table properties in the Power Pivot window.
-
To view the query used during data refresh, click Power Pivot > Manage to open the Power Pivot window.
-
Click Design > Table Properties.
-
Switch to Query Editor to view the underlying query.
Queries are not visible for every type of data source. For example, queries are not shown for data feed imports.
Connection properties that cancel data refresh
In Excel, you can set connection properties that determine the frequency of data refresh. If refresh is not allowed on a particular connection, you’ll get a cancellation notice when you run Refresh All or attempt to refresh a specific table that uses the connection.
-
To view connection properties, in Excel, click Data > Connections to view a list of all connections used in the workbook.
-
Select a connection and click Properties.
-
In Usage, under Refresh control, if the checkbox is cleared for Refresh this connection on Refresh All, you will get a cancellation when you try Refresh All in the Power Pivot window.
Refresh data on SharePoint Server 2013
On SharePoint Server 2013, you can schedule unattended data refresh on the server, but doing so requires that Power Pivot for SharePoint 2013 is installed and configured in your SharePoint environment. Check with your SharePoint administrator to find out if scheduled data refresh is available.
With Power Query, you can refresh a query to import the latest data into a table without having to recreate the query.
Important:
-
Excel 2010 Power Query is not included in Excel 2010, but you can download, install, and activate the Power Query Add-In.
-
To activate the Power Query add-in, click File > Options > Add-Ins. In the Manage section at the bottom, choose the COM Add-ins option from the drop-down list, then click Go. Click the Power Query check box, then OK. The Power Query ribbon should appear automatically, but if it doesn’t, close and restart Excel.
To refresh a query:
-
In the Query Editor ribbon, click Refresh preview.

Note: The Query Editor only appears when you load, edit, or create a new query using Power Query. The following video shows the Query Editor window appearing after editing a query from an Excel workbook. To view the Query Editor without loading or editing an existing workbook query, from the Get External Data section in the Power Query ribbon tab, select From Other Sources > Blank Query. The following video shows one way to display the Query Editor.
If your Excel workbook has a connection to a table or query in an Access database, you can make sure it shows the most up to date information. Use the Refresh command (on the Data tab) to do this.
-
On your worksheet, click any cell that contains your Access data.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and then click Refresh.

To control how or how often the connection is refreshed:
-
Click any cell that contains your Access data.
-
In the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Connection Properties.
For very large data sets, consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish.
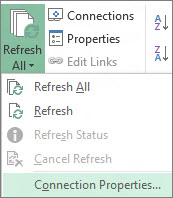
-
On the Usage tab, set any options you want to change.
Check the status of or cancel a refresh
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on the refresh, or to cancel it, do one or more of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
If your Excel workbook has a connection to a table or query in a SQL Server database, you can make sure it shows the most up to date information. Use the Refresh command (on the Data tab) to do this.
-
On your worksheet, click any cell that contains your SQL Server data.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and then click Refresh.

To control how or how often the connection is refreshed:
-
Click any cell that contains your SQL Server data.
-
In the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Connection Properties.
For very large data sets, consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish.

-
On the Usage tab, set any options you want to change, such as enabling a background refresh.
Cancel or check the status of a refresh
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on the refresh, or to cancel it, do one of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
If your Excel workbook has a connection to a table or query in an OLE DB data source, you can make sure it shows the most up to date information. Use the Refresh command (on the Data tab) to do this.
-
On your worksheet, click any cell that contains your OLE DB data.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and then click Refresh.

To control how or how often the connection is refreshed:
-
Click any cell that contains your OLE DB data.
-
In the Connections group, click the arrow next to Refresh All, and click Connection Properties.
For very large data sets, consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish.

-
On the Usage tab, set any options you want to change.
Check or cancel a refresh
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on or cancel a refresh, do one of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
When the data you use for your map changes, you can refresh it manually in 3D Maps. The changes will then be reflected on your map. Here’s how:
-
In 3D Maps, click Home > Refresh Data.

Add data to Power Map
To add new data to your 3D MapsPower Map:
-
In 3D Maps, go to the map you want to add data to.
-
Leaving the 3D Maps window open, click in Excel and select the worksheet data you want to add.
-
On the Excel ribbon, click Insert > Map arrow > Add Selected Data to Power Map.

Your 3D Maps will automatically update to show the additional data.
Manually refresh
-
Click anywhere in the PivotTable.
This displays the PivotTable Tools, adding an Options and a Design tab.
-
On the Options tab, in the Data group, do one of the following:
-
To update the information to match the data source, click the Refresh button, or press ALT+F5.
You can also right-click the PivotTable, and then click Refresh.
-
To refresh all PivotTables in the workbook, click the Refresh button arrow, and then click Refresh All.
If refreshing takes longer than you expect, click Options > Refresh > Refresh Status to check the refresh status.
To stop refreshing, click Cancel Refresh.
Prevent column widths and cell formatting from adjusting
If the column widths and cell formatting of your data adjust when you refresh the PivotTable data, and you don’t want that to happen, make sure the following options are checked:
-
Click Options > Options.
-
On the Layout & Format tab, check the Autofit column widths on update and Preserve cell formatting on update boxes.
Refresh PivotTable data automatically when opening the workbook
-
Click anywhere in the PivotTable.
-
On the Options tab, in the PivotTable group, click Options.
-
In the PivotTable Options dialog box, on the Data tab, select the Refresh data when opening the file check box.
Data in a Microsoft Office Excel workbook that has been displayed in Excel Services can come from two different locations. The data may be stored directly in the workbook, or it may be stored in an external data source, such as in a database or in an Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) cube.
If the data comes from an external data source, the workbook author or administrator has defined the connection information, often in an Office data connection (.odc) file, which describes how to locate, log in, query, and access the external data source.
When you are connected to an external data source, you can perform a refresh operation to retrieve the updated data. Each time that you refresh data, you see the most recent version of the data, including any changes that were made to the data since it was last refreshed.
Learn about refreshing data
The following illustration explains the basic process of what happens when you refresh data connected to an external data source.

-
A refresh operation gets up-to-date data.
-
A connection, often saved to a connection file, defines all the information needed to access and retrieve data from an external data source.
-
There are a variety of data sources you can access, such as OLAP, SQL Server, OLEDB providers, and ODBC drivers.
-
Up-to-date data is added to the current workbook.
Learn about security concerns
When you are connected to an external data source and you attempt to refresh the data, it’s important to be aware of potential security issues, and to know what you can do about any security issues.
A data connection file often contains one or more queries that are used to refresh external data. By replacing this file, a user who has malicious intent can design a query to access confidential information and distribute it to other users or perform other harmful actions. Therefore, it’s important to ensure that the connection file was authored by a reliable individual, and the connection file is secure and comes from a trusted Data Connection Library (DCL).
For more information on how an administrator can author connection files, create trusted locations, and secure connection files, see Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Help and Office SharePoint Server Central Administration Help.
Security Note: Accessing an external data source usually requires credentials (such as a user name and a password) that are used to authenticate the user. Make sure that these credentials are provided to you in a safe and secure manner, and that you do not inadvertently reveal these credentials to others.
Control how data is refreshed
You can control how to refresh data from an external data source by doing one or more of the following:
-
Refresh on open In Microsoft Office Excel 2007, a workbook author can create a workbook that automatically refreshes external data when the workbook is opened by selecting the Refresh data when opening the file check box in the Connection Properties dialog box. (On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Connections, select the connection, click Properties, click the Usage tab, and then click Refresh data when opening the file.) In this case, Excel Services always refreshes the data before it displays a workbook and creates a new session. If the workbook author clears the Refresh data when opening the file check box, the data that is cached with the workbook is displayed, which means that when a user manually refreshes the data, the user sees refreshed, up-to-date data during the current session, but the data is not saved to the workbook. If you want to ensure that up-to-date data is always displayed when you display the workbook in Excel Services, select the Refresh data when opening the file check box by using Office Excel.
If you are using an Office Data Connection file (.odc), make sure you also set the Always use connection file check box in the Connection Properties dialog box (On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Connections, select the connection, click Properties, click the Definition tab, and then click Always use connection file).
The trusted file location site settings, Short Session Timeout and External Data Cache Lifetime, can also have an impact on refresh operations. For more information, see your administrator or the Microsoft Office SharePoint Server Central Administration Help system.
-
Manual refresh
Note: You can manually refresh only a PivotTable report.
-
Select a cell in a PivotTable report.
-
On the Excel Web Access toolbar, under the Update menu, click Refresh Selected Connection.
Notes:
-
Any interactive operation that causes a requery of an OLAP data source initiates a manual refresh operation.
-
If this Refresh command is not visible, then the Web Part author has cleared the Refresh Selected Connection, Refresh All Connections property. For more information, see Excel Web Access Web Part custom properties.
-
-
-
Refresh all connections On the Excel Web Access toolbar, under the Update menu, click Refresh All Connections.
-
Periodic refresh By using Office Excel 2007, the workbook author can specify that data automatically refreshes at a specified interval after the workbook is opened for each connection in the workbook. For example, an inventory database may be updated every hour, and so the workbook author has defined the workbook to automatically refresh every 60 minutes.
A Web Part author can select or clear the Allow Excel Web Access Periodic Data Refresh property to enable or disable this periodic refresh operation, if the property has been defined by the workbook author. When the time interval elapses, by default, the following refresh alert prompt is displayed at the bottom of the Excel Web Access Web Part:
Refresh data for <List of Connections>? (Now) (Always) (Don’t ask me again)
An Excel Web Access Web Part author can also set the Display Periodic Data Refresh Prompt property to control the behavior of the message that is displayed when Excel Services performs a periodic data refresh during a session:
-
Always means that the message is displayed with a prompt at each interval.
-
Optionally means that a user can choose to continue periodic refresh without displaying a message.
-
Never means that Excel Web Access performs a periodic refresh without displaying a message or prompt.
For more information, see Excel Web Access Web Part custom properties.
-
-
Cancel a refresh Because a refresh operation may take longer than you expect, you can cancel it. While the refresh operation occurs, Excel Services displays a message with a prompt. Click Cancel to interrupt the operation, so that you can complete the refresh operation at a more convenient time. Data returned by queries before you cancelled the refresh operation will display.
You can refresh an external data range automatically when you open the workbook. Optionally, you can save the workbook without saving the external data to shrink the size of the file.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Under Refresh control, select the Refresh data when opening the file check box.
-
If you want to save the workbook with the query definition but without the external data, select the Remove data from the external data range before saving the workbook check box.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Select the Refresh every check box, and then enter the number of minutes between each refresh operation.
Stored passwords aren’t encrypted, so they’re not recommended. If your data source needs a password to connect to it, you can require that users enter the password before they can refresh the external data range. The following procedure doesn’t apply to data retrieved from a text file (.txt) or a Web query (.iqy).
Use strong passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Weak passwords don’t mix these elements. For example, Strong password: Y6dh!et5. Weak password: House27. Passwords should be 8 or more characters in length. A pass phrase that uses 14 or more characters is better.
It’s critical that you remember your password. If you forget your password, Microsoft cannot retrieve it. Store the passwords that you write down in a secure place away from the information that they help protect.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
-
Click the Definition tab, and then clear the Save password check box.
Note: Excel prompts you for the password only the first time that the external data range is refreshed in each Excel session. The next time you start Excel, you’ll be prompted for the password again if you open the workbook that contains the query and then attempt a refresh operation.
For very large data sets, consider running a background refresh. This returns control of Excel to you instead of making you wait several minutes or more for the refresh to finish.
-
Click a cell in the external data range.
-
On the Data tab, in the Connections group, click Refresh All, and then click Connection Properties.
Note: You can’t run an OLAP query in the background.
Note: You can’t run a query for any connection type that retrieves data for the Data Model.
-
Click the Usage tab.
-
Select the Enable background refresh check box to run the query in the background. Clear this check box to run the query while you wait.
While you record a macro that includes a query, Excel doesn’t run the query in the background. To change the recorded macro so that the query runs in the background, edit the macro in the Visual Basic Editor. Change the refresh method for the QueryTable object from BackgroundQuery := False to BackgroundQuery := True.
If your workbook is connected to a large data source, refreshing it might take a little longer than you expect. To check on the refresh, or to cancel it, do one of the following:
-
Check the status of a query A message appears on the Excel status bar to indicate that the query is running. Double-click the message to check the status of the query.
-
Stop a background refresh To stop a query that’s running in the background, double-click the query status message on the status bar to display the External Data Refresh Status dialog box, and then click Stop Refresh.
-
Stop a query To stop a query from running when background refresh is turned off, press the Esc key.
See Also
Power Query for Excel Help
Refresh external data in a workbook in SharePoint Server
Change formula recalculation, iteration, or precision in Excel
Block or unblock external content in Office documents
A key advantage of Excel is the ability to link multiple workbooks together. Let’s learn how to refresh data in Microsoft Excel.
A key advantage of Excel is the ability to link multiple workbooks together. Data can exist in one file and be referenced in another. This avoids the need to store multiple copies of the same information. But it’s very important to keep data up to date. Fortunately, Excel offers a quick and easy way to do exactly that. Let’s learn how to refresh data in Microsoft Excel.
Imagine that you have a master spreadsheet containing numerical data. In another workbook, you’ve linked to this data with a series of cell references. You’re preparing to share this second file, and you want to ensure that all of the data inside is current and up to date. Changes are made in the first file, and then reflect in your second file.
To refresh data in Excel, you’ll be working on the Data tab. This is found on Excel’s ribbon, the list of menus across the top of your screen. Click on Data, and examine the options that appear.
The button you’re looking for is the Refresh All dropdown menu, found on the left side of the Data tab. Click on it, and you’ll see a list of additional options to refresh your data. The most commonly used option is listed first: Refresh All.
Click Refresh All, and Excel will update your data. It will be matched to your linked file or files. Keep in mind, if you have a large volume of data, the syncing process may take a few moments. But it’s always worthwhile to perform a refresh if you are using linked data. While files will generally update automatically, it’s important to be sure your data remains in perfect sync.
As you can see, it’s easy to refresh data in Excel. This helps ensure that you always share current, meaningful, and accurate data.
Calculate Part of a Formula
While in Cell Edit Mode, this Excel Shortcut calculates part of a formula.
PC Shorcut:F9
Mac Shorcut:fn+F9
Remember This Shortcut:
F9 is also the standard shortcut to calculate. So, within a cell F9 calculates just the selected piece.
Calculate Now
This Excel Shortcut calculates the active Excel workbooks.
PC Shorcut:F9
Mac Shorcut:fn+F9
Remember This Shortcut:
F9 is the universal shortcut for refresh
Calculate Active Sheet
This Excel Shortcut calculates the active worksheet.
PC Shorcut:Shift+F9
Mac Shorcut:fn+⇧+F9
Remember This Shortcut:
F9 is the universal shortcut for refresh
Force Calculate
This Excel Shortcut forces the active Excel workbooks to recalculate even if cells have not been changed.
PC Shorcut:Ctrl+ALT+F9
Mac Shorcut:n/a
Remember This Shortcut:
F9 is the universal shortcut for refresh
Refresh
This Excel Shortcut calculates the active Excel workbooks.

PC Shorcut:F9
Mac Shorcut:fn+F9
Remember This Shortcut:
F9 is the universal shortcut for refresh
Once you have created a Pivot Table, it doesn’t automatically refresh when you add new data or change the existing data.
Since your Pivot Table is created using the Pivot Cache, when the existing data changes or when you add new rows/columns to the data, the Pivot Cache does not update itself automatically, and hence, the Pivot Table also does not update.
You need to force a refresh every time there are changes. Once you force a refresh, the Pivot Cache gets updated, which is reflected in the Pivot Table.
This tutorial covers a couple of ways to do this.
Refresh Pivot Table
This option is best suited when there are changes in the existing data source and you want to refresh the pivot table to reflect these changes.
Here are the steps to refresh a Pivot Table:
- Right-click on any cell in the Pivot Table.
- Select Refresh.
This will instantly refresh the Pivot Table.
You can also by selecting any cell in the Pivot Table and use the keyboard shortcut ALT + F5.
Quick Tip: It’s a good practice to convert the data source into an Excel Table, and use this Excel Table to create the Pivot Table. If you do this, you can also use the refresh technique to update the Pivot Table even when new data (rows/columns) are added to the data source (since an Excel Table automatically accounts for new rows/columns that are added).
Update Pivot Table by Changing the Data Source
If you’ve added new rows/columns to the data source, you need to change the data source to make sure new rows/columns are a part of the dataset.
To do this:
Note that if you change the data source into an Excel Table and then use the Excel table to create the Pivot Table, you don’t need to use the change data source option. You can simply refresh the Pivot Table and it’ll account for the new rows/columns.
Autorefresh Pivot Table Using a VBA Macro
While refreshing a Pivot table is as easy as two clicks, you still need to do this every time there is a change.
To make it more efficient and auto-refresh the Pivot Table whenever there is a change in the data source, you can use a simple one-line VBA macro code.
Here is the VBA code:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range) Worksheets("Sheet1").PivotTables("PivotTable1").PivotCache.Refresh End Sub
Decoding the Code: This is a change event which gets triggered whenever there is a change in the sheet that contains the source data. As soon as there is a change, the code refreshes the Pivot Cache of the Pivot Table with the name PivotTable1.
You need to modify this code to make it work for your workbook:
- “Sheet1” – change this part of the code with the name of the sheet that has the Pivot Table.
- “PivotTable1” – change this to the name of your Pivot Table. To know the name, click anywhere in the Pivot Table and click the Analyze Tab. The name would be visible in the left part of the ribbon under the ‘PivotTable Name’ header.
Where to put this VBA code:
Now when you change anything in the data source, the Pivot Table would automatically get refreshed.
Click here to download the example file.
Note: Since there is a macro in the workbook, save this with .xls or .xlsm extension.
You May Also Like the Following Pivot Table Tutorials:
- How to Group Dates in Pivot Tables in Excel.
- How to Group Numbers in Pivot Table in Excel.
- How to Filter Data in a Pivot Table in Excel.
- Preparing Source Data For Pivot Table.
- How to Apply Conditional Formatting in a Pivot Table in Excel.
- How to Add and Use an Excel Pivot Table Calculated Field.
- How to Replace Blank Cells with Zeros in Excel Pivot Tables.
- Using Slicers in Excel Pivot Table.
- Move Pivot Table to Different Worksheet or Workbook
It’s easy to forget to refresh your Pivot Tables when you add new source data. Here’s an effective solution to that problem: Add a Refresh button in your Excel report!
This is very easy, and only takes a minute:
There are 3 steps:
Step 1: Go to the Insert menu, choose Icons and type “Refresh” in the search field. Choose the icon you want, and click on Insert. Resize and place the icon where you want to have it.
Step 2: Open the VBA editor (Alt + F11). Go to the Insert menu and choose Module. Type this code:
Sub RefreshAll()
ActiveWorkbook.RefreshAll
End Sub
Step 3: Go back to Excel, right-click on the Refresh Icon and choose “Assign Macro”. Choose the “RefreshAll” macro and click OK.
The next time you add data to your Pivot Table, or you want to get the most recent data from your Datawarehouse, simply click on your new Refresh button!
Important: When you save the workbook, you need to save it as either Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook or Excel Binary Workbook!
BONUS TRICK:
Add one more line to the code and get a popup message when the refresh is done:
Sub RefreshAll()
ActiveWorkbook.RefreshAll
MsgBox “All tables refreshed!”
End Sub
Of course, you can write any text you want between the double quotes.
More Excel tutorials:
- Use Excel to validate a dataset according to Benford’s Law
- How to use a Logarithmic Scale in Excel Diagrams
- How to Calculate Grades in Excel
- How to Find Duplicates and Triplicates in Excel
- Unhide all sheets in Excel with a simple macro that works for all your documents
Are you using a non-English version of Excel? Click here for translations of the 140 most common functions in 17 different languages:
Catalan
Czech
Danish
Dutch
Finnish
French
Galician
German
Hungarian
Italian
Norwegian
Polish
Portuguese (Brazilian)
Portuguese (European)
Russian
Spanish
Swedish
Turkish
There are two ways to make Excel automatically refresh data connections and recalculate a worksheet. These tricks are important with the Stock and Currency data type in Excel 365 but also other situations.
Normally Excel will update itself when you change a cell value. These days there are situations where cells change value but Excel does NOT update the worksheet. In other words, modern Excel has changed in ways that Microsoft hasn’t yet fully adapted to.
Ideally, Excel would have an overall setting to refresh the worksheet every ‘n’ seconds or minutes. In 2022, Microsoft finally added some Stock/Currency auto-refresh options but they are incomplete and limited.
This article has TWO different ways to force updates in Excel. One is a ‘traditional’ macro approach, the other is a newer trick using PowerQuery in conjunction with single macro.
Either option gives you more control over updating than Microsoft’s simplistic ‘tick the box’ addition to Excel 365.
Stock Data Type
With the Stock Data Type the ability to update automatically is more important. Users will want their worksheets to grab the latest prices automatically, something the current preview releases can’t do. Instead of having a nice automatic ‘ticker’, we’re expected to click ‘Refresh’ to get the latest prices.
The Stock, Currency and other linked data types are curious beasts. They are data connections to external sources but do NOT appear as Excel Data Connections. That means you can’t setup an automatic data refresh, as you would with normal data connections. In fact, there’s no exposed controls for the Stock, Currency or other linked data types.
NOW() and other volatile functions
The NOW() function updates to the latest date and time whenever Excel recalculates the worksheet. But if there’s nothing to make that happen, Now() doesn’t change value. Some external factor is needed to make Excel update Now() and the rest of the worksheet. In other words, you should be able to glance at a worksheet and know it’s up to the second but that’s not possible with Excel ‘out of the box’.
Microsoft calls NOW() and similar functions ‘volatile’ because their values can change even if no other cells have changed. Other volatile functions are Today(), Randbetween(), Offset() and Indirect(). In some situations Info(), Cell() and SumIf() can also be volatile.
VBA custom functions can also be tagged as volatile using this line in the function code:
Application.Volatile
That line makes the function run anytime Excel updates/recalcs the worksheet.
The trick is to make an Excel macro which forces data connections to update then mark that function as Volatile so it will be run whenever the workbook is updating.
Maybe you want your worksheet to update automatically as a precaution? Many old Excel hands remember situations where Excel hasn’t properly updated so they like the ‘belt and braces’ approach (at least occasionally).
Automatic update code
The standard method of forcing automatic update of Excel is a short snippet of VBA code. Here’s what we use, there are many variations on the same theme. The full code is at the bottom of the article.
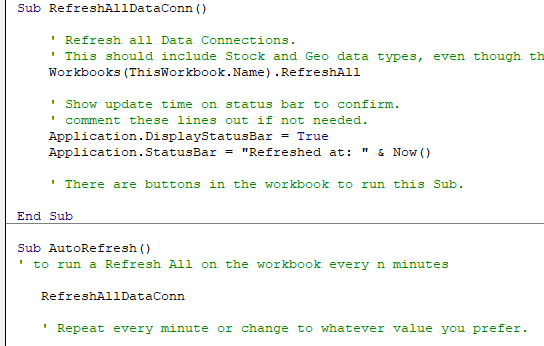
There are three functions.
RefreshAllDataConn
does the actual refreshing of data connections ( Workbooks(ThisWorkbook.Name).RefreshAll ) and we added two, optional, lines to display the last time refreshed on the bottom status bar.
If you wanted to be extra careful, add line to explicitly force recalculation. Either ActiveSheet.Calculate or the extreme Application.CalculateFull (use sparingly, this would slow down a large worksheet).
AutoRefresh
run the RefreshAllDataConn sub every minute or whatever value you set on the line Application.OnTime Now + TimeValue(“00:01:00”), “AutoRefresh”
Workbook_Open
an in-built Excel function that runs automatically when the worksheet is opened. In this case it starts AutoRefresh.
PowerQuery data Connection workaround
The disadvantage of the VBA approach is that a .xlsm worksheet is necessary (macro enabled Excel worksheet). There can be problems sharing macro enabled files because of security concerns.
The arrival of PowerQuery / Get and Transform means there’s another way to force a worksheet recalculation. It’s a workaround and not perfect, but it’s possible and doesn’t need a macro-enabled worksheet.
In short, ensure that there’s a data query setup with auto-refresh. If there isn’t a data connection, add a small one to the worksheet.
Once you have an auto-refreshing query, the worksheet including any volatile functions should also refresh.
Ideally the Stock and Geo data types should also refresh.
Any Excel data query comes with some refresh options in the Query properties. Most of them default OFF.
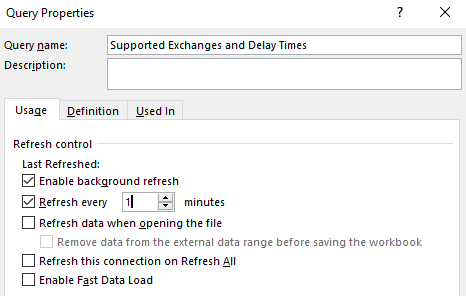
Refresh every nnn minutes – defaults off with 60 minutes suggested.
Refresh data when opening the file
Enable background refresh
Refresh this connection on Refresh All
The auto-refresh workaround is to create a small and practically insignificant data connection. Then configure that data connection to update every minute or whatever time you wish. That should force the worksheet to update including the volatile functions mentioned above.
Some versions of this workaround add a link to a tiny csv file on the same computer. We’ve got the same result using a data connection from a table in the worksheet.
Create a small table with a single cell. The cell can have anything but we create a cell with NOW() in it, for reasons we’ll explain later.

Select the table then choose Data | Get Data | From other sources | from Table/Range. The exact menu item maybe different depending on your version of Excel.

When the Query Editor opens, just Close and Load it. In the data connections pane, you’ll see a query.

Right-click the query, choose properties to see the settings we need.
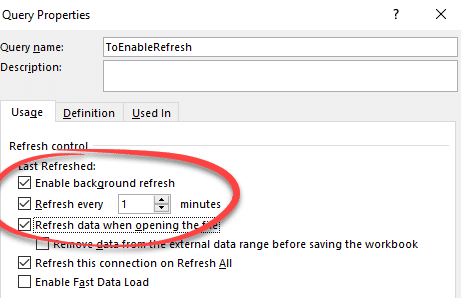
Set the refresh rate that suits you.
To be tidy, we move the source table (right) onto the same sheet at the loaded query (left). Because we used NOW() in the source table cell, it’ll be easy to see when/if the worksheet has refreshed.

VBA Code example
Sub RefreshAllDataConn()
' Refresh all Data Connections.
' This should include Stock and Currency data types, even though they aren't listed.
Workbooks(ThisWorkbook.Name).RefreshAll
' Show update time on status bar to confirm.
' comment these lines out if not needed.
Application.DisplayStatusBar = True
Application.StatusBar = "Refreshed at: " & Now()
End Sub
Sub AutoRefresh()
' to run a Refresh All on the workbook every n minutes
RefreshAllDataConn
' Repeat every minute or change to whatever value you prefer.
Application.OnTime Now + TimeValue("00:01:00"), "AutoRefresh"
' this is a simple example. There's no coded way to exit this function.
End Sub
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
' Starts the automatic refresh when the workbook is opened,
' commented out as a precaution.
' AutoRefresh
End Sub
Excel’s Stock / Currency data (kinda, sorta) gets auto-refresh
Make automatic Excel worksheet list or table of contents
Complete Excel NetworkDays() solution with holidays & vacations
This can be done without having a macro constantly running. It relies on the Application.OnTime method which allows an action to be scheduled out in the future. I have used this approach to force Excel to refresh data from external sources.
The code below is based nearly exclusively on the code at this link: http://www.cpearson.com/excel/ontime.aspx
The reference for Application.OnTime is at: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/office/ff196165.aspx
Dim RunWhen As Date
Sub StartTimer()
Dim secondsBetween As Integer
secondsBetween = 1
RunWhen = Now + TimeSerial(0, 0, secondsBetween)
Application.OnTime EarliestTime:=RunWhen, Procedure:="CodeToRun", Schedule:=True
End Sub
Sub StopTimer()
On Error Resume Next
Application.OnTime EarliestTime:=RunWhen, Procedure:="CodeToRun", Schedule:=False
End Sub
Sub EntryPoint()
'you can add other code here to determine when to start
StartTimer
End Sub
Sub CodeToRun()
'this is the "action" part
[A1] = WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(0, 100)
'be sure to call the start again if you want it to repeat
StartTimer
End Sub
In this code, the StartTimer and StopTimer calls are used to manage the Timers. The EntryPoint code gets things started and CodeToRun includes the actual code to run. Note that to make it repeat, you call StartTimer within CodeToRun. This allows it to loop. You can stop the loop by calling the StopTimer or simply not calling StartTimer again. This can be done with some logic in CodeToRun.
I am simply putting a random number in A1 so that you can see it update.