-
Create a table
Video
-
Sort data in a table
Video
-
Filter data in a range or table
Video
-
Add a Total row to a table
Video
-
Use slicers to filter data
Video
Sign in with Microsoft
Sign in or create an account.
Hello,
Select a different account.
You have multiple accounts
Choose the account you want to sign in with.
Thank you for your feedback!
×
Do you want to make a table in Excel? This post is going to show you how to create a table from your Excel data.
Entering and storing data is a common task in Excel. If this is something you’re doing, then you need to use a table.
Tables are containers for your data! They help you keep all your related data together and organized.
Tables have a lot of great features and work well with other tools inside and outside of Excel, so you should definitely be using them with your data.
This post is going to show you all the ways you can create a table from your data in Excel. Get your copy of the example workbook used in this post and follow along!
Tabular Data Format for Excel Tables
Excel tables are the perfect container for tabular datasets due to their row and column structure. Just make sure your data follows these rules.
- The first row of your dataset should contain a descriptive column heading.
- Your data should have no blank column headings.
- Your data should have no blank columns or blank rows.
- Your data should have no subtotals or grand totals.
- One row in your data should represent exactly one record of data.
- One column should contain exactly one type of data.
If your data is rectangular in shape and adheres to the above rules, then it’s ready to be put into a table.
Create a Table from the Insert Tab
Now that your data is ready to be placed inside a table, how can you do that?
It’s very easy and will only take a few clicks!
You’ll be able to add your data in a table from the Insert tab. Follow these steps to get your data into a table!
- Select a cell inside your data.
- Go to the Insert tab.
- Select the Table command in the Tables section.
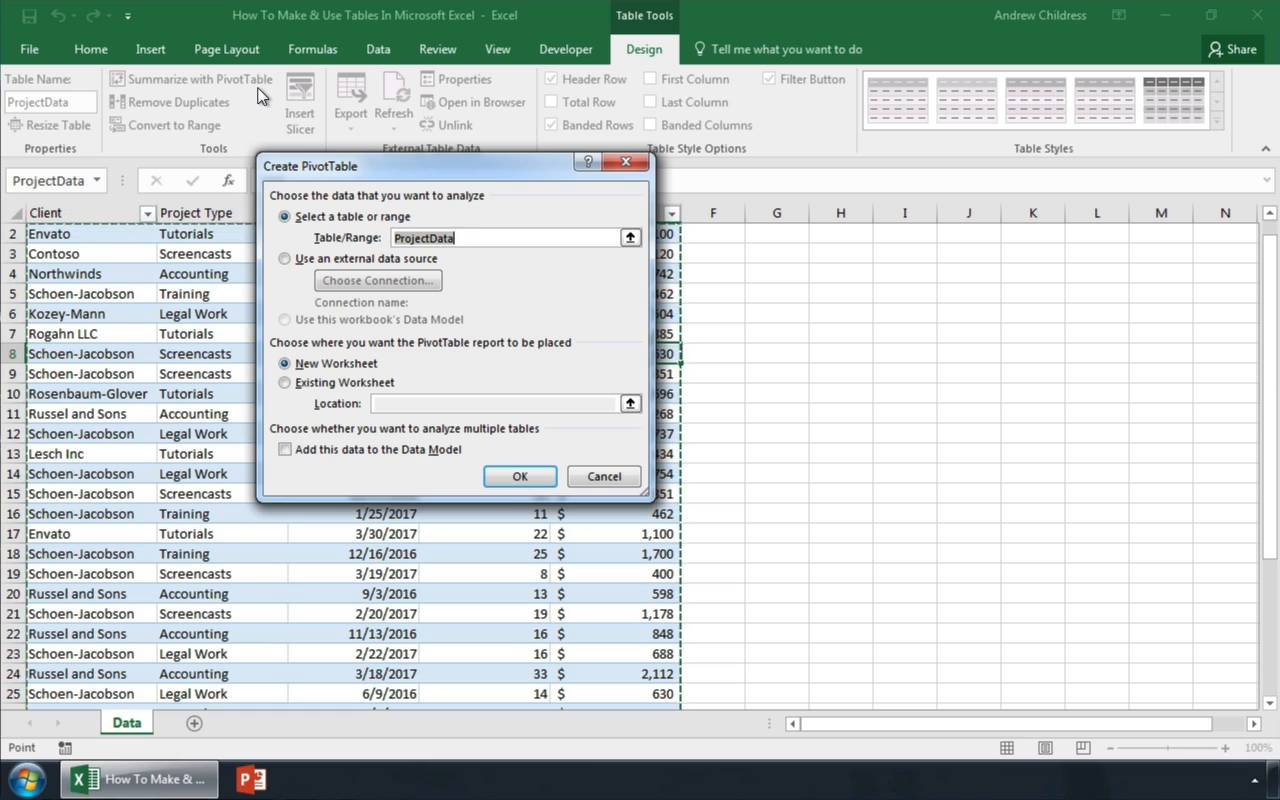
This is going to open the Create Table menu with your data range selected. You should see a green dash line around your selected data and you can adjust the selection if needed.
- Check the My table has headers option. This is needed if the first row of your data contains column name headings.
- Press the OK button.
Your data is now inside a table! You’ll easily be able to tell the data is inside an Excel Table now because a default table formatting is automatically applied.
You can go to the Table Design tab and select other style options from the Table Styles section.
💡 Tip: Your table will get a default name such as Table1. You should give your new table a descriptive name as this is how you will refer to it in formulas and other tools.
Create a Table from the Home Tab
Another place you can access the table command is from the Home tab.
You can use the Format as Table command to create a table.
- Select a cell inside your data.
- Go to the Home tab.
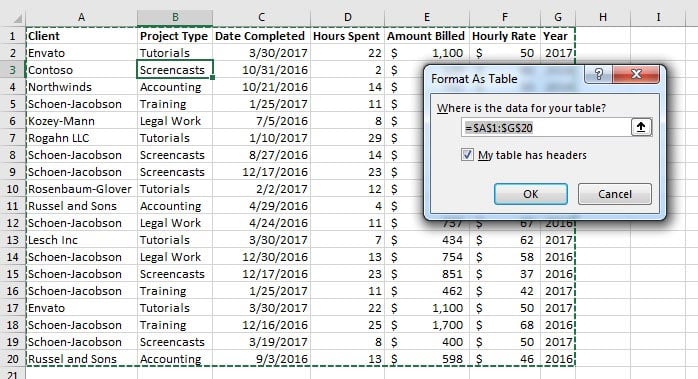
- Select the Format as Table command in the Styles section.
- Select a style option for your table.
- Check the option for My table has headers.
- Press the OK button.
This is a great option as you get to choose the table style during the process of making your table.
Create a Table with a Keyboard Shortcut
Creating a table is such a common task that there is a keyboard shortcut for it.
Select your data and press Ctrl + T on your keyboard to turn your dataset into a table.
This is an easy shortcut to remember since T stands for Table.
There is also a legacy shortcut available from when tables were called lists. Select your data and if you press Ctrl + L this will also make a table. In this case, L stands for List.
Create a Table with Quick Analysis
When you select any range Excel will show you the Quick Analysis options in the lower right corner.
This will give you quick access to conditional formatting, pivot tables, charts, totals, and sparklines. The menu also includes the table command to convert the data into a table.
You can follow these steps to create a table from the Quick Analysis tools.
- Select your entire dataset. You can select any cell in the data and press Ctrl + A and this will select the full range.
This should automatically show the Quick Analysis tool in the lower right corner of the selected range.
- Click on the Quick Analysis tools or press Ctrl + Q to open the Quick Analysis menu.
- Go to the Tables tab.
- Click on the Table command. When you hover your cursor over the Table command it will show you a preview of your data inside a table!
📝 Note: This method allows you to skip the Create Table menu and the Quick Analysis will guess if your data has column headings or not. Excel will apply any column headings to your table accordingly.
Quick Analysis can be disabled from the Excel Options menu if the pop-up command is something you find annoying.
- Go to the File tab.
- Select the Options menu.
- Go to the General tab of the Excel Options menu.
- Uncheck the Show Quick Analysis options on selection option.
- Press the OK button.
📝 Note: This will only disable the small pop-up command from showing when you select your data. You can still use the Ctrl + Q keyboard shortcut to access the Quick Analysis tools for any selected range.
Create a Table with Power Query
Power Query is a very useful tool for transforming your data, but you can also create a table during the process of building your queries.
If your data isn’t already inside a table, you can use the From Table/Range query to make a table.
- Select your data.
- Go to the Data tab.
- Press the From Table/Range command in the Get & Transform Data section.
This will open the Create Table menu.
- Check the My table has headers option if the first row in your data contains column headings.
- Press the OK button.
This will add your data to a table and then open the Power Query Editor where you will be able to build your query based on the new table.
When you are finished building your query, you can go to the Home tab of the Power Query editor and press the Close and Load command.
This will give you the option to create another table filled with the transformed data. Select the Table option and press the OK button to load the transformed data into a table.
⚠️ Warning: This method does create a table, but doesn’t give you the opportunity to name the table before you build your queries. This means your queries will reference the generic table name such as Table1, and if you later change the table name you will also have to update the reference in your query.
Create Multiple Tables from a List with VBA
Suppose you need to create multiple tables in your Excel file. Maybe you need to create a table of sales data for each month of the year. Doing this manually could be a time-consuming process.
This is where you could use VBA to create multiple tables with the required columns.
Go to the Developer tab and select the Visual Basic command to open the visual basic editor. Then go to the Insert tab of the visual basic editor and select the Module option to create a new module to add your VBA macro.
Sub AddTables()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim sheetTest As Boolean
Dim myHeadings As Variant
Dim colCount As Integer
Set myRange = Selection
myHeadings = [{"ID","Date","Item","Quantity","Price"}]
colCount = UBound(myHeadings)
For Each c In myRange.Cells
sheetTest = False
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name = c.Value Or c.Value = "" Then
sheetTest = True
End If
Next ws
If Not (sheetTest) Then
With Sheets
Sheets.Add.Name = c.Value
Sheets(c.Value).Select
Range("A1").Resize(1, colCount).Value = myHeadings
ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range("A1").Resize(1, colCount), , xlYes).Name = c.Value & "Sales"
End With
End If
Next c
End SubThis code will loop through the selected range and add a new sheet for each cell in the range. The code tests if the sheet name exists and if it doesn’t then it creates a new sheet named from the cell value.
The column headings are added to the new sheet starting at cell A1. This is then turned into a table and the table is named based on the sheet name.
myHeadings = [{"ID","Date","Item","Quantity","Price"}]The above line of code is used to create the column headings in each table. You can adjust this to suit your needs.
You can then run this macro to create multiple tables.
- Select the range of cells that contain the list the names for each table you want to create. For example, you might want a list of month names to create a table for each month.
- Press the Alt + F8 keyboard shortcut to open the Macro menu.
- Select your macro.
- Press the Run button.
This will run and create a new sheet for each item in your selection. Each sheet will contain a table with the same column headings and be named based on the items in the selected list.
Create Multiple Tables from a List with Office Scripts
If you are using Excel online and want to automate the process of creating multiple tables from a list, then you will need to use Office Scripts.
This is a JavaScript based language that can help you automate tasks in Excel online.
Go to the Automate tab and select the New Script command to open the Office Script Editor.
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
//Create an array with the column headings
let myHeaders = [["ID", "Date", "Item", "Quantity", "Price"]]
let colCount = myHeaders[0].length;
//Create an array with the values from the selected range
let selectedRange = workbook.getSelectedRange();
let selectedValues = selectedRange.getValues();
//Get dimensions of selected range
let rowHeight = selectedRange.getRowCount();
let colWidth = selectedRange.getColumnCount();
//Loop through each item in the selected range
for (let i = 0; i < rowHeight; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < colWidth; j++) {
try {
//Create a new sheet with name from the selected range
let thisSheet = workbook.addWorksheet(selectedValues[i][j]);
//Add column headings to new sheet and convert to table
thisSheet.getRange("A1").getAbsoluteResizedRange(1, colCount).setValues(myHeaders);
let newTable = workbook.addTable(thisSheet.getRange("A1").getAbsoluteResizedRange(1, colCount), true);
newTable.setName(selectedValues[i][j] + "Sales");
}
catch (e) {
//do nothing
};
};
};
};Copy and paste the above code into the Code Editor. Press the Save script button to save the script and then you can use the Run button to execute the script.
This Office Script code will loop through the active range in your workbook and create a new sheet for each cell in the selected range and name it based on the value in the cell.
let myHeaders = [["ID", "Date", "Item", "Quantity", "Price"]]The column headings are added to each new sheet starting in cell A1. You can adjust the above line of code to change the column headings to suit your needs.
These column headings are then turned into a table and the table is named based on the sheet name.
You can then run this script using the following steps.
- Select a range of cells that contain the list of tables you want to create.
- Click on the Run button in the Code Editor.
The code will run and create all the sheets with tables in each sheet.
Conclusions
Tables are a very useful feature for your tabular data in Excel.
Your data can be added to a table in several ways such as from the Insert tab, from the Home tab, with a keyboard shortcut, or using the Quick Analysis tools.
Tables work well with other tools in Excel such as Power Query. Because of this, Excel will even automatically convert your data into a table before using Power Query.
Creating multiple tables in your workbook can also be automated using either VBA or Office Scripts.
How do you make your tables? Do you know any other tips? Let me know in the comments section below!
About the Author
John is a Microsoft MVP and qualified actuary with over 15 years of experience. He has worked in a variety of industries, including insurance, ad tech, and most recently Power Platform consulting. He is a keen problem solver and has a passion for using technology to make businesses more efficient.
Содержание
- Основы создания таблиц в Excel
- Способ 1: Оформление границ
- Способ 2: Вставка готовой таблицы
- Способ 3: Готовые шаблоны
- Вопросы и ответы
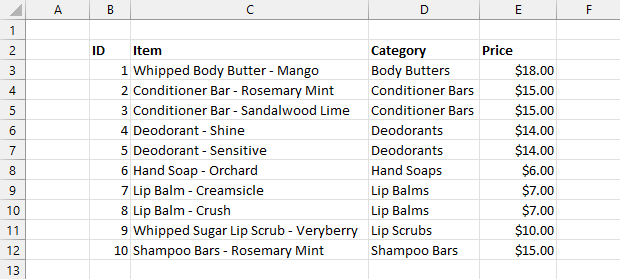
Обработка таблиц – основная задача Microsoft Excel. Умение создавать таблицы является фундаментальной основой работы в этом приложении. Поэтому без овладения данного навыка невозможно дальнейшее продвижение в обучении работе в программе. Давайте выясним, как создать таблицу в Экселе.
Таблица в Microsoft Excel это не что иное, как набор диапазонов данных. Самую большую роль при её создании занимает оформление, результатом которого будет корректное восприятие обработанной информации. Для этого в программе предусмотрены встроенные функции либо же можно выбрать путь ручного оформления, опираясь лишь на собственный опыт подачи. Существует несколько видов таблиц, различающихся по цели их использования.
Способ 1: Оформление границ
Открыв впервые программу, можно увидеть чуть заметные линии, разделяющие потенциальные диапазоны. Это позиции, в которые в будущем можно занести конкретные данные и обвести их в таблицу. Чтобы выделить введённую информацию, можно воспользоваться зарисовкой границ этих самых диапазонов. На выбор представлены самые разные варианты чертежей — отдельные боковые, нижние или верхние линии, толстые и тонкие и другие — всё для того, чтобы отделить приоритетную информацию от обычной.
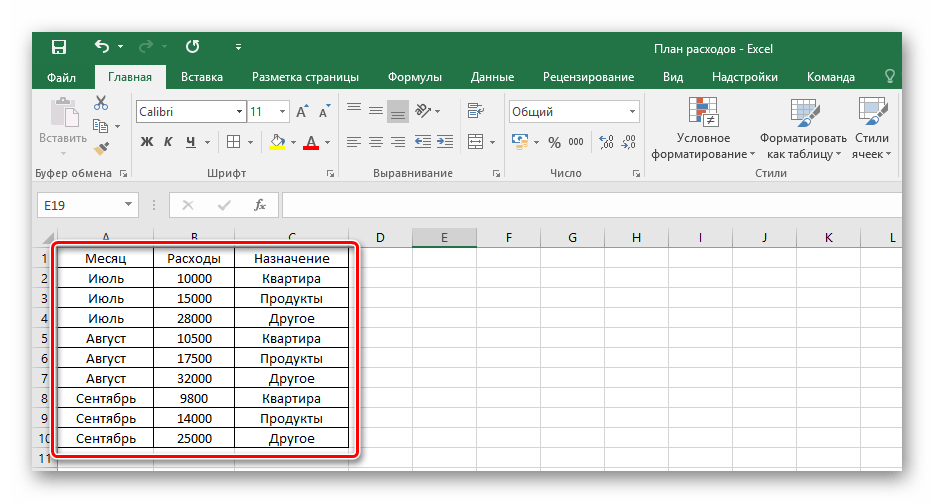
- Для начала создайте документ Excel, откройте его и введите в желаемые клетки данные.
- Произведите выделение ранее вписанной информации, зажав левой кнопкой мыши по всем клеткам диапазона.
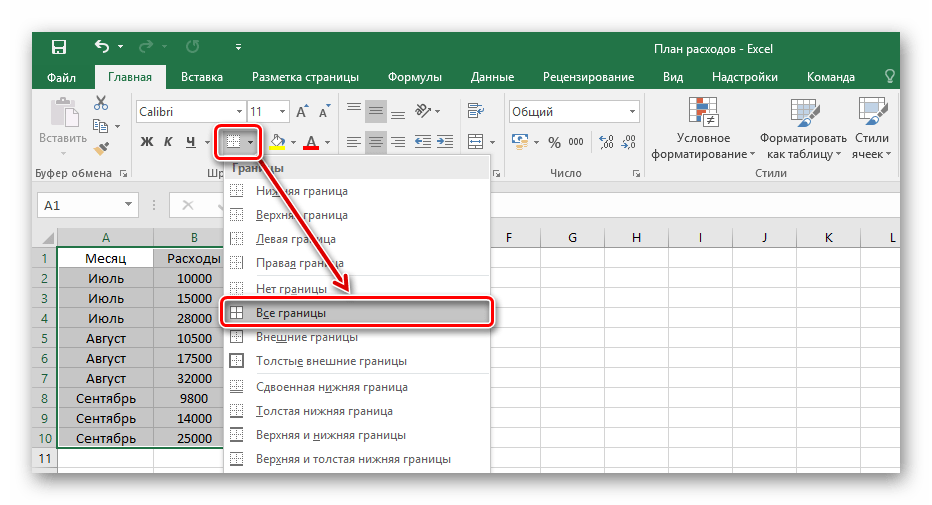
- На вкладке «Главная» в блоке «Шрифт» нажмите на указанную в примере иконку и выберите пункт «Все границы».
- В результате получится обрамленный со всех сторон одинаковыми линиями диапазон данных. Такую таблицу будет видно при печати.
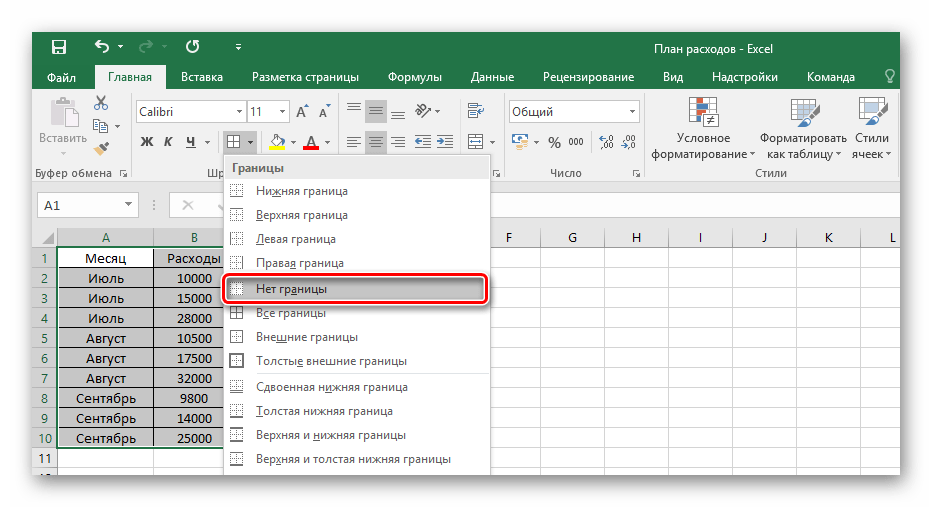
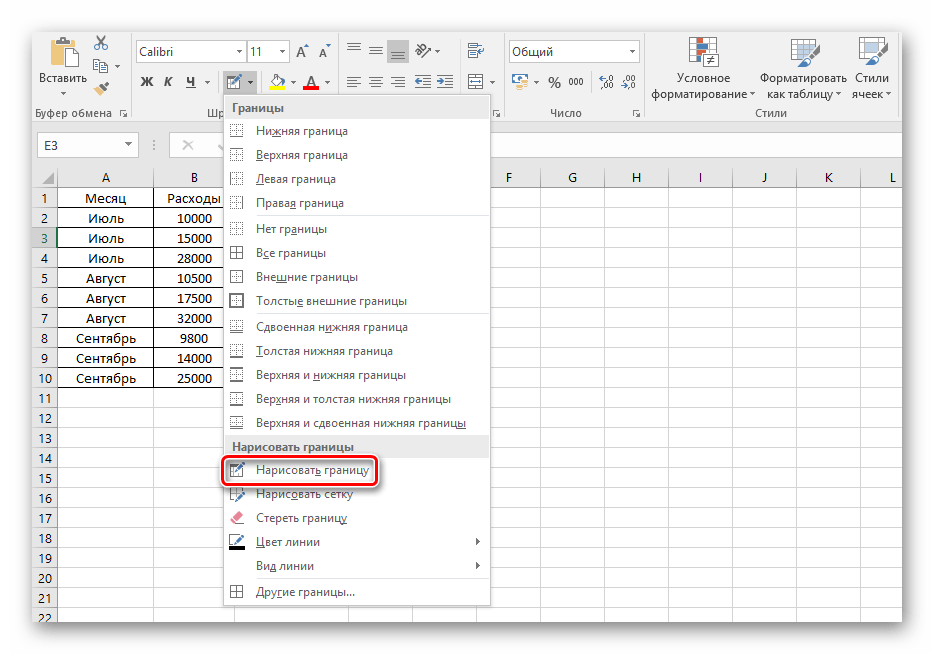
- Для ручного оформления границ каждой из позиций можно воспользоваться специальным инструментом и нарисовать их самостоятельно. Перейдите уже в знакомое меню выбора оформления клеток и выберите пункт «Нарисовать границу».
Соответственно, чтобы убрать оформление границ у таблицы, необходимо кликнуть на ту же иконку, но выбрать пункт «Нет границы».
Пользуясь выбранным инструментом, можно в произвольной форме разукрасить границы клеток с данными и не только.
Обратите внимание! Оформление границ клеток работает как с пустыми ячейками, так и с заполненными. Заполнять их после обведения или до — это индивидуальное решение каждого, всё зависит от удобства использования потенциальной таблицей.
Способ 2: Вставка готовой таблицы
Разработчиками Microsoft Excel предусмотрен инструмент для добавления готовой шаблонной таблицы с заголовками, оформленным фоном, границами и так далее. В базовый комплект входит даже фильтр на каждый столбец, и это очень полезно тем, кто пока не знаком с такими функциями и не знает как их применять на практике.
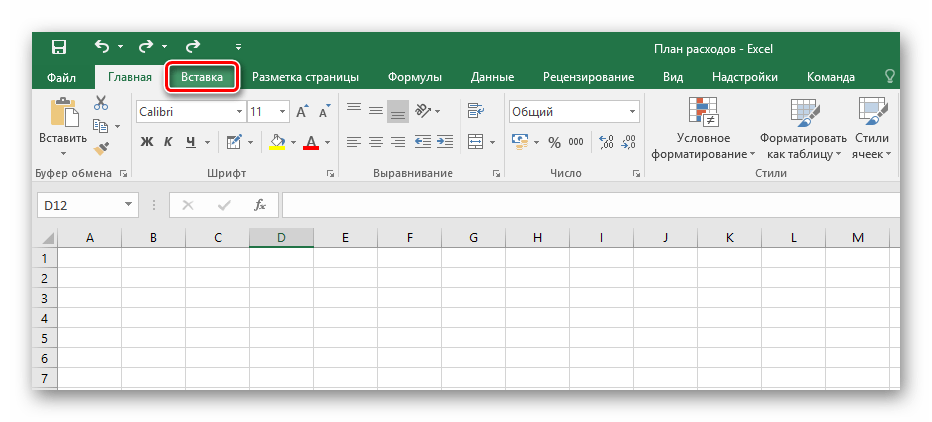
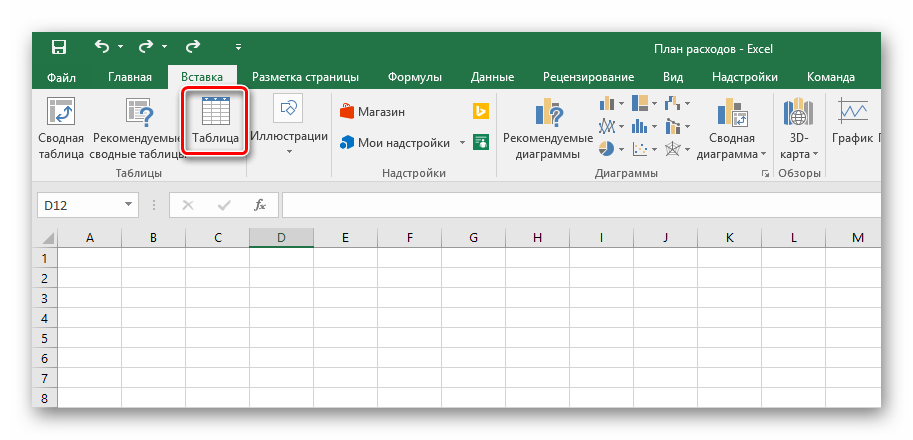
- Переходим во вкладку «Вставить».
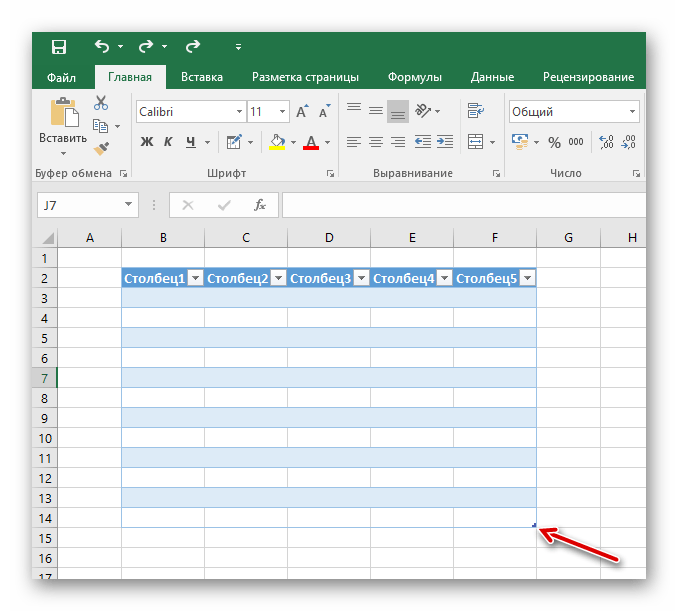
- Среди предложенных кнопок выбираем «Таблица».
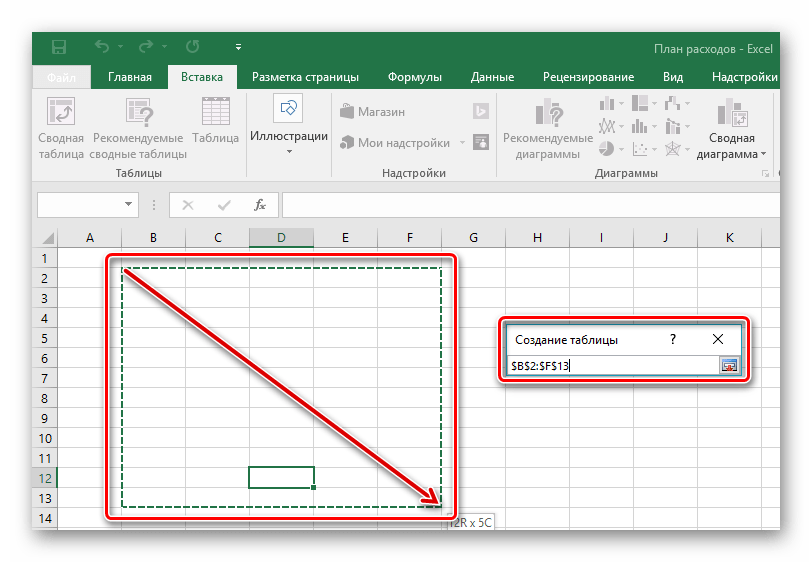
- После появившегося окна с диапазоном значений выбираем на пустом поле место для нашей будущей таблицы, зажав левой кнопкой и протянув по выбранному месту.
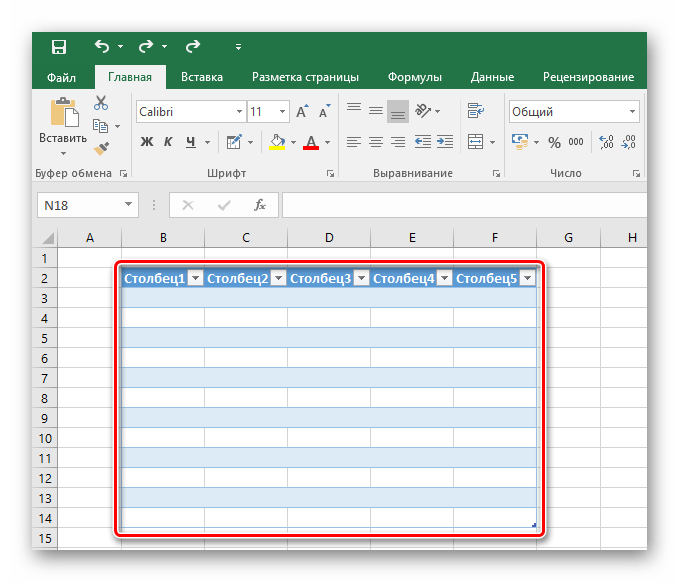
- Отпускаем кнопку мыши, подтверждаем выбор соответствующей кнопкой и любуемся совершенно новой таблице от Excel.
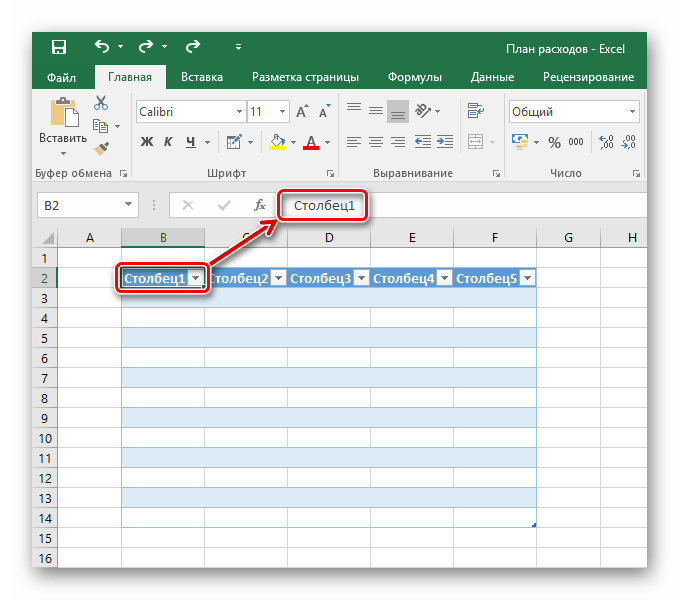
- Редактирование названий заголовков столбцов происходит путём нажатия на них, а после — изменения значения в указанной строке.
- Размер таблицы можно в любой момент поменять, зажав соответствующий ползунок в правом нижнем углу, потянув его по высоте или ширине.
Таким образом, имеется таблица, предназначенная для ввода информации с последующей возможностью её фильтрации и сортировки. Базовое оформление помогает разобрать большое количество данных благодаря разным цветовым контрастам строк. Этим же способом можно оформить уже имеющийся диапазон данных, сделав всё так же, но выделяя при этом не пустое поле для таблицы, а заполненные клетки.
Способ 3: Готовые шаблоны
Большой спектр возможностей для ведения информации открывается в разработанных ранее шаблонах таблиц Excel. В новых версиях программы достаточное количество готовых решений для ваших задач, таких как планирование и ведение семейного бюджета, различных подсчётов и контроля разнообразной информации. В этом методе всё просто — необходимо лишь воспользоваться шаблоном, разобраться в нём и пользоваться в удовольствие.
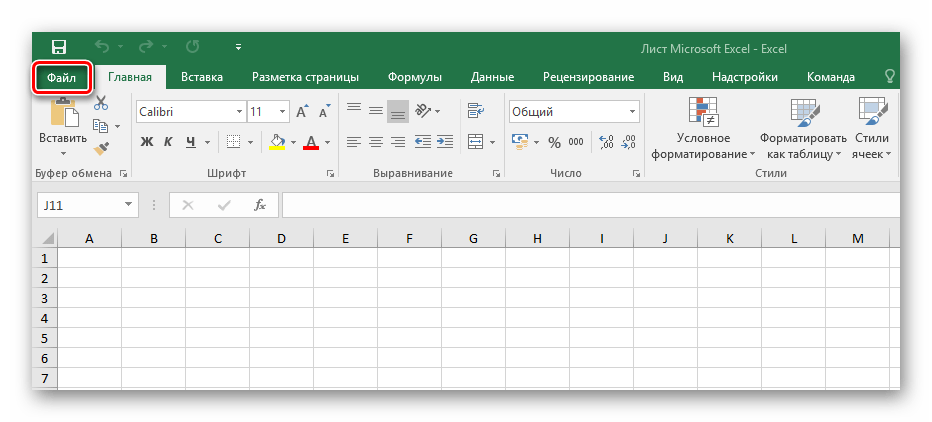
- Открыв Excel, перейдите в главное меню нажатием кнопки «Файл».
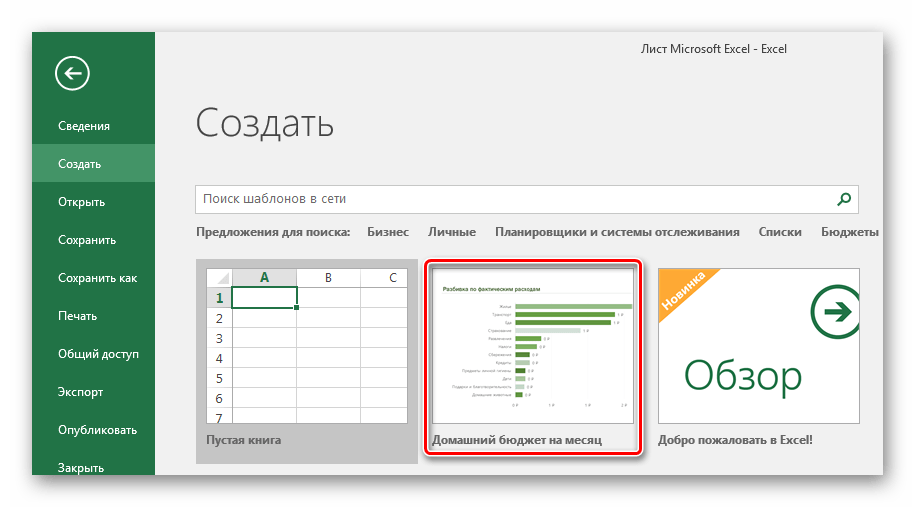
- Нажмите вкладку «Создать».
- Выберите любой понравившийся из представленных шаблон.
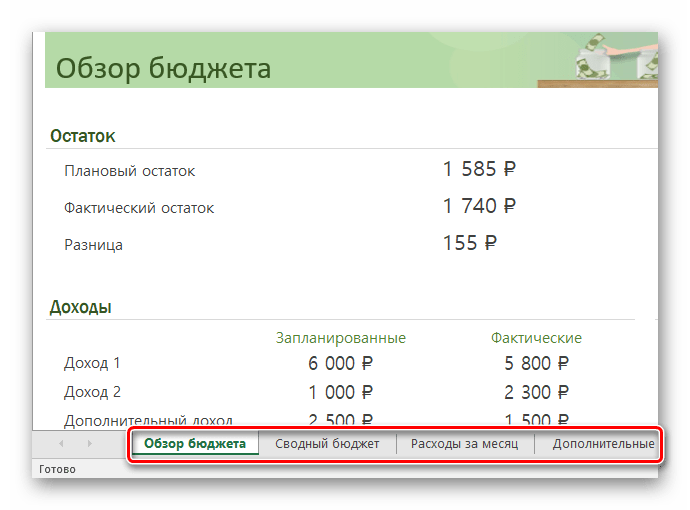
- Ознакомьтесь с вкладками готового примера. В зависимости от цели таблицы их может быть разное количество.
- В примере с таблицей по ведению бюджета есть колонки, в которые можно и нужно вводить свои данные — воспользуйтесь этим.
Таблицы в Excel можно создать как вручную, так и в автоматическом режиме с использованием заранее подготовленных шаблонов. Если вы принципиально хотите сделать свою таблицу с нуля, следует глубже изучить функциональность и заниматься реализацией таблицы по маленьким частицам. Тем, у кого нет времени, могут упростить задачу и вбивать данные уже в готовые варианты таблиц, если таковы подойдут по предназначению. В любом случае, с задачей сможет справиться даже рядовой пользователь, имея в запасе лишь желание создать что-то практичное.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Creating a table in Excel may seem unusual at first. But it becomes clear that this is the best tool for solving this problem when you have mastered the first skills to work with this.
In fact Excel is a table consisting of a plurality of cells. All that is required from the user is to pick up table format for the subsequent work.
Let’s begin from next: highlight Excel cells you need using a mouse (holding the left button). After that you may choose formatting and apply it to the selected cells.
Following provisions will help to make a table in Excel as desired.
How to change the height and width of the selected cells? If you want to change cell sizes use fields with headers [A B C D] in horizontally way and [1 2 3 4] in vertically dimension. You have to move the cursor of a mouse on the border between the two cells. Holding down the left mouse button draw the border of the way and let it go.
In order not to waste time and may set the desired size to multiple cells or columns in Excel. To do this you have to activate the columns / rows by selecting them with the mouse on the gray field. It remains only to conduct already above described operation.
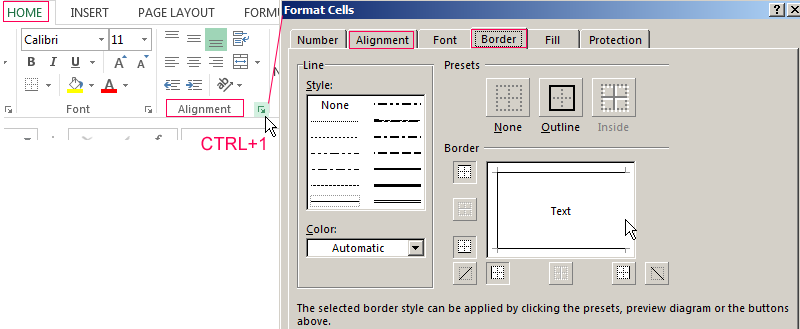
The window «Format Cells» can be caused by three simple ways:
- The key combination Ctrl + 1 (the “1” is not on the numeric keypad, it’s above the letter «Q») is the fastest and most convenient way.
- The context menu (right click).
- Using the main menu «HOME» on the tab «Alignment».
Next, perform the following steps:
- Click on the tab «Format Cells» hovering the mouse cursor
- A window pops up with such tabs as «Number», «Alignment», «Font», «Border», «Fill» and «Protection».
- You must use a tabs «Border» and «Alignment» to solve this task.
Tools in «Alignment» tab are the key capabilities for effective editing previously entered text in the cells, namely:
- Merge the selected cells.
- The ability to transfer the words.
- Aligning the entered text vertically and horizontally (tab located in the top menu box as well as quick access).
- Text orientation including vertical angle.
Excel makes it possible to carry out a rapid alignment of all previously typed text in vertical orientation using the tabs located in the Main Menu.
On the «Border» tab we are working with the lines style of table borders.
Flip the table: how to do it?
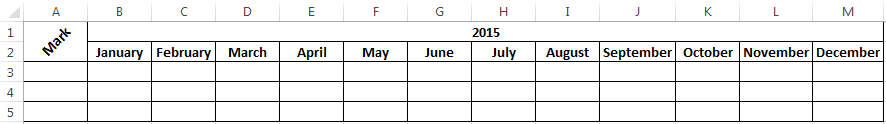
For example a user has created an Excel spreadsheet file of the following form:
According to the task it is necessary to do so headlines in the table were positioned vertically and not horizontally as it is now. Proceed as follows.
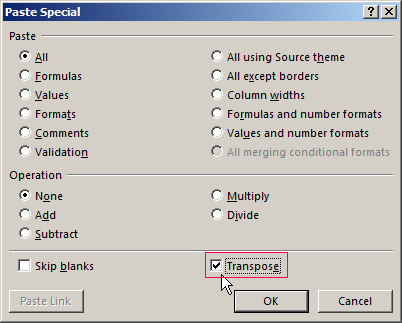
First we need to highlight and copy the entire table. After that you must activate any empty cell in Excel. And then via the right mouse button displays a menu where you need to click the tab «Paste Special». Or you may press the key combination CTRL + ALT + V.
Next you need to establish a tick in the «Transpose» tab.
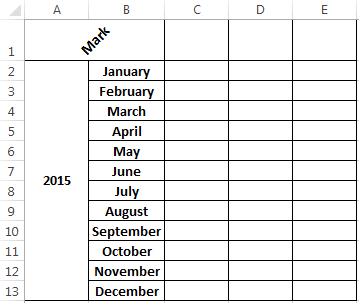
And press «OK» via the left button. As a result the user will receive:
Using transposition button you can easily transfer the values even in cases where a single table header stands vertically and in the other header stands horizontally.
How to transfer values from the vertical into the horizontal table
Many users are often faced with the seemingly impossible task — transferring values from one table to another, despite the fact that values are arranged horizontally in one table, and the other placed in the vertical way.
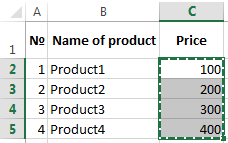
Assume that the user has an Excel price list which spelled out with the prices of the following form:
There is also a table where the total cost of the order is already calculated:
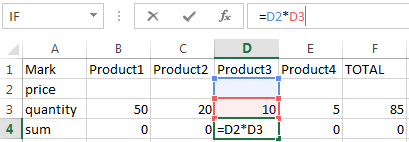
User task is to copy the values of the vertical price-list with prices and paste it into another horizontal table. It’s a long while and inconvenient to perform these actions manually by copying the value of each cell.
Use the tab «Paste Special» and transpose function in order to be able to copy all the values
Procedure:
- The table with a price list and prices you must use the mouse to select all values. Then while holding the mouse over the previously selected field you must right-click and bring up a menu to select the «Copy»:
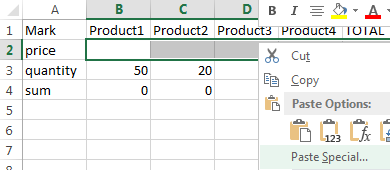
- Then selected range will be highlighted and you may paste previously allocated prices.
- Using the right mouse button call menu and then, you must select the button «Paste Special» while holding the cursor over the selected area.
- Finally set the check mark in «Transpose» button and press «OK».
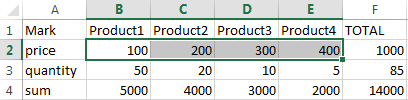
As a result you get the following output:
Using the window «Transpose» you can completely turn the table. Function of transferring values from one table to another (taking into account their different locations) is a very handy tool. For example, it allows you to adjust the value quickly in the price list in case of the company’s pricing policy has changed.
Changing the size of the table during the adjustment in Excel
It happens often when filled Excel table simply does not fit on the screen. And you have to move from side to side which is inconvenient and time consuming. You can simply change the table scale to solve this problem. it’s very comfortably to work changing scale if you have small or big display.
To reduce the size of the table go to the tab «VIEW» and select there the tab «Zoom». Then pick up an appropriate size for your screen. For example choose 80 or 95 percent. It also might be another scale.
To increase the size of the table use the same procedure with the slight difference that the scale is placed over one hundred percent. For example choose 115 or 125 percent.
Excel offers a wide range of possibilities for building fast and efficient work. For example using a special formula (for example, = OFFSET ($a$1;0;0счеттз($а:$а);2) you can adjust the dynamic range used by the table. That can be very convenient during work especially when you are working simultaneously with multiple tables.
Tables might be the best feature in Excel that you aren’t yet using. It’s quick to create a table in Excel. With just a couple of clicks (or a single keyboard shortcut), you can convert your flat data into a data table with a number of benefits.
The advantages of an Excel table include all of the following:
- Quick Styles. Add color, banded rows, and header styles with just one click to style your data.
- Table Names. Give a table a name to make it easier to reference in other formulas.
- Cleaner Formulas. Excel Formulas are much easier to read and write when working in tables.
- Auto Expand. Add a new row or column to your data, and the Excel table automatically updates to include the new cells.
- Filters & Subtotals. Automatically add filter buttons and subtotals that adapt as you filter your data.
In this tutorial, I’ll teach you to use tables (also called data tables) in Microsoft Excel. You’ll discover how to use all of these features and master working with data tables. Let’s get started learning all about MS Excel tables.
What is a Table in Microsoft Excel?
A table is a powerful feature to group your data together in Excel. Think of a table as a specific set of rows and columns in a spreadsheet. You can have multiple tables on the same sheet.
You might think that your data in an Excel spreadsheet is already in a table, simply because it’s in rows and columns and all together. However, your data isn’t in a true «table» unless you’ve used the specific Excel data table feature.
In the screenshot above, I’ve converted a standard set of data to a table in Excel. The obvious change is that the data was styled, but there’s so much power inside this feature.
Tables make it easier to work with data in Microsoft Excel, and there’s no real reason not to use them. Let’s learn how to convert your data to tables and reap the benefits.
How To Make a Table in Excel Quickly (Watch & Learn)
The screencast below is a guided tour to convert your flat data into an Excel table. I’ll teach you the keyboard shortcut as well as the one-click option to convert your data to tables. Then, you’ll learn how to use all the features that make MS Excel tables so powerful.
If you want to learn more, keep reading the tutorial below for an illustrated guide to Excel tables.
To follow along with this tutorial, you can use the sample data I’ve included for free in this tutorial. It’s a simple spreadsheet with example data you can use to convert to a table in Excel.
How to Convert Data to a Table in Excel
Here’s how to quickly create a table in Excel:
Start off by clicking inside a set of data in your spreadsheet. You can click anywhere in a set of data before converting it to a table.
Now, you have two choices for how to convert your flat, ordinary data to a table:
- Use the keyboard shortcut, Ctrl + T to convert your data to a table.
- Make sure you’re working on the Home tab on Excel’s ribbon, and click on Format as Table and choose a style (theme) to convert your data to a table.
In either case, you’ll receive this pop-up menu asking you to confirm the table settings:
Confirm two settings on this menu:
- Make sure all of your data is selected. You’ll see the green marching ants box around the cells that will be included in your table.
- If your data has headers (titles at the top of the column), leave the My table has headers box checked.
I highly recommend embracing the keyboard shortcut (Ctrl + T) to create tables quickly. When you learn Excel keyboard shortcuts, you’re much more likely to use the feature and embrace it in your own work.
Now that you’ve converted your ordinary data to a table, it’s time to use the power of the feature. Let’s learn more:
How to Use Table Styles in Excel
Tables make it easy to style your data. Instead of spending time highlighting your data, applying background colors and tweaking individual cell styles, tables offer one click styles.
Once you’ve converted your data to a table, click inside of it. A new Excel ribbon option called Table Tools > Design appears on the ribbon.
Click on this ribbon option and find the Table Styles dropdown. Click on one of these style thumbnails to apply the selected color scheme to your data.
Instead of spending time manually styling data, you can use a table to clean up the look of your data. If you only use tables to apply quick styles, it’s still a great feature. But, there’s more you can do with Excel tables:
How to Apply Table Names
One of my favorite table features is the ability to add a name to a table. This makes it easy to reference the table’s data in formulas.
Click inside the table to select it. Then, click on the Design tab on Excel’s ribbon. On the left side of this menu, find the Table Name box and type in a new name for your table. Make sure that it’s a single word (no spaces are allowed in table names.)
Now, you can use the name of the table when you write your formulas. In the example screenshot below, you can see that I’ve pointed a new PivotTable to the table we created in the previous step. Instead of typing out the cell references, I’ve simply typed the name of the table.
Best of all, if the table changes with new rows or columns, these references are smart enough to update as well.
Table names are a must when you create large, robust Excel workbooks. It’s a housekeeping step that ensures you know where your cell references point to.
How to Make Cleaner Excel Formulas
When you write a formula in a table, the formula is more readable and cleaner to review than standard Excel formulas.
In the example below, I’m writing a formula to divide the Amount Billed by the Hours Spent to calculate an Hourly Rate. Notice that the formula that Excel generates isn’t «E2/D2», but instead includes the column names.
Once you press enter, the Excel table will pull the formula down to all of the rows in the table. I prefer the formulas that tables generate when creating calculations. Not only are they cleaner, but you don’t have to pull the formula down manually.
Time-Saving Excel Table Feature: Auto Expand
Tables might evolve over time to include new columns or rows. When you add new data to your tables, they automatically update to include the new columns or rows.
In the example below, you can see an example of what I mean. Once I add a new column in column G and press enter, the table automatically expands and all of the styles are pulled over as well. This means that the table has expanded to include these new columns.
The best part of this feature is that when you’re referencing tables in other formulas, it will automatically include the new rows and columns as well. For example, a PivotTable linked to an Excel data table will update with the new columns and rows when refreshed.
How to Use Excel Table Filters
When you convert data to a table in Excel, you may notice that filter buttons appear at the top of each column. These give you an easy way to restrict the data that appears in the spreadsheet. Click on the dropdown arrow to open the filtering box.
You can check the boxes for the data you want to remove, or uncheck a box to remove it from the table view.
Again, this is a feature that makes using Excel tables worthwhile. You can add filtering without using tables, sure—but with so many features, it makes sense to convert to tables instead.
How to Quickly Apply Subtotals
Subtotals are another great feature that make tables worth using. Turn on totals from the ribbon by clicking on Total Row.
Now, the bottom of each column has a dropdown option to add a total or another math formula. In the last row, click the dropdown arrow to choose an average, total, count, or another math formula.
With this feature, a table becomes a reporting and analysis tool. The subtotals and other figures at the bottom of the table will help you understand your data better.
These subtotals will also adapt if you use filters. For example, if you filter for a single client, the totals will update to only show for that single client.
Recap and Keep Learning More About Excel
It doesn’t matter how much time you spend learning Excel, there’s always more to learn and better ways to use it for controlling your data. Check out these Excel tutorials to keep learning useful spreadsheet skills:
If you haven’t been using tables, are you going to start using them after this tutorial? Let me know in the comments section below.
Did you find this post useful?
I believe that life is too short to do just one thing. In college, I studied Accounting and Finance but continue to scratch my creative itch with my work for Envato Tuts+ and other clients. By day, I enjoy my career in corporate finance, using data and analysis to make decisions.
I cover a variety of topics for Tuts+, including photo editing software like Adobe Lightroom, PowerPoint, Keynote, and more. What I enjoy most is teaching people to use software to solve everyday problems, excel in their career, and complete work efficiently. Feel free to reach out to me on my website.