Download Article
Learn the basics of formatting a Microsoft Word document
Download Article
- Formatting the Layout
- Formatting Text
- Adding Pictures, Graphs, & Tables
- Using a Formatted Template
- Saving in Other Formats
- Q&A
|
|
|
|
|
Microsoft Word is the world’s most popular word processing app. Depending on what kind of legal, formal, or personal paper you’re writing, each has its own formatting guidelines. Fortunately, Microsoft Word makes it easy to format the layout, text, and other objects in your document. If you’re new to using Microsoft Word, don’t worry. You can be formatting your document like a pro in no time. This wikiHow guide will teach you simple ways to format a Word document on your PC or Mac computer.
Things You Should Know
- You can find most of the formatting tools you’ll need in the Ribbon menu at the top of your document.
- If you don’t want to do all the formatting from scratch, try using one of Word’s premade templates.
- Save your document in different file formats using the Save a Copy or Save As menu.
-
1
Explore the Word user interface. You can access most of Word’s formatting tools from the Menu Bar or the Ribbon at the top of the window. You can modify which tools are visible using the View menu.
- The Menu Bar is the area at the top of the screen where you will find File, Edit, View, and other important menu commands.
- The Ribbon is at the top of your workspace and contains icons, menus, and shortcuts to common tasks.
-
2
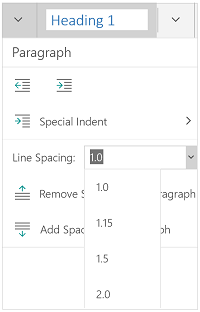
Align your document. Different types of documents call for different text alignments. You can choose whether to align your entire document to the left, right, or at the center on the Home tab by clicking the Alignment buttons in the «Paragraph» section.
- These are the buttons that look like a small version of a document, with small black lines arranged according to their button’s alignment function.
- You can also adjust alignment by selecting the text and objects you want to align, right-clicking the selection, and choosing Paragraph. Select your preferred alignment from the Alignment menu under the General header.
- You can either set the alignment for the whole document or just a selected piece of text.
Advertisement
-
3
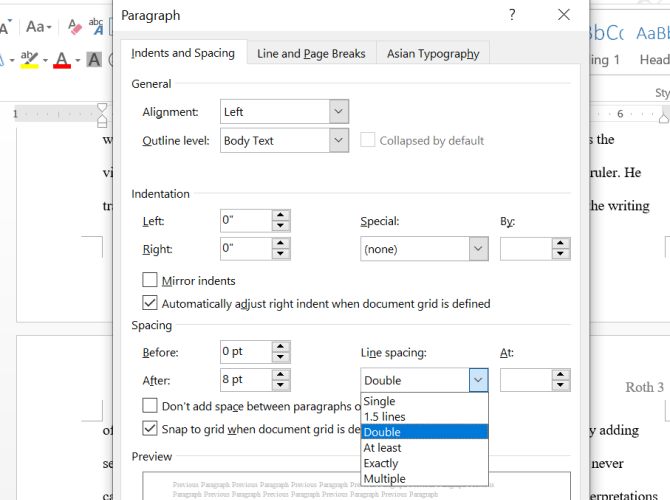
Set the line spacing of your document. Need to change your document to single or double-space? You can adjust the spacing of your entire document, or for selected text.
- If you haven’t begun typing or adding content to your Word document, click the Home tab, click the «Line and Paragraph Spacing» icon (a row of lines with vertical arrows to the left of the lines pointing up and down, and select an option.
- If your document already has text or other content, press Ctrl + A (PC) or Cmd + A (Mac) to select everything in the document, right-click the selection, and choose Paragraph. You can then choose your desired spacing from the «Line Spacing» menu.
- For a single-spaced document, choose 1.0. For double-spacing, choose 2.0.
- Many professional documents, like college essays and cover letters, should be double-spaced.
-
4
Adjust the page orientation. If you need to write the document in a different orientation, click the Layout tab at the top of Word, select Orientation, and choose either Portrait or Landscape.
-
5
Change the size of the paper. If you need to print the document on a specific paper size, click the Layout tab, click Size, and then select your desired size from the drop-down list.
- This will change the virtual size of the document you’re writing as well as the actual size of the printout.
-
6
Adjust the headers and footers. A header contains details that will appear on every page of the paper, such as page numbers, your name, or the document title.
- To set the header of your document, double-click on the topmost part of the page, and the header field will appear. You can also click the Insert tab and select Header.
- Footers are just like headers. All text in the footer will appear at the bottom of each page of your document. To set the footer, double-click on the bottommost part of the page, and the footer field will appear. You can also use the Footer button on the Insert tab.
- You can also format your headers and footers by selecting the View tab and clicking Header and Footer on the list. This action will open the headers and footers on your page and allow you to edit them.
-
7
Insert page or section breaks with the Breaks menu. Go to the Layout tab in the and click Breaks if you want to start a new page or section in your document. You can choose from a variety of types of breaks, including Page, Column, and Section. This is a very useful tool if you need to format different sections of your document in different ways.[1]
- For example, you can use section or page breaks to help you format your page numbers so that the numbering restarts with each new section.
-
8
Adjust the margin size with the Margins tool. Click the Margins button in the Layout tab and select a margin from the pre-defined margin settings listed on the drop-down list.
- If you want to use your own margin measurements, click Custom Margins at the very bottom of the drop-down list to set your own.
-
9
Add columns to split your text vertically on the page. If you need to create a newspaper-like document, you can do so by adjusting the format of the document to columns. Click the Layout tab, select the Columns option, and choose the number and alignment of columns from the drop-down list.
- The Columns button looks like a rectangle with two vertical columns of blue lines on it.
- If you want to create one, two, or three columns, you can do so from the preset options. If you’d like to create more, you’ll need to choose More Columns from the bottom of the dropdown menu.
- Note that this column option is different from the columns you get when you insert items like tables on your document.
-
10
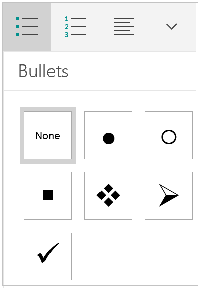
Add bullets and numbers to make lists. Highlight the text that you would like to be numbered or bulleted and click the Numbering or Bullets button on the Home tab of the Ribbon.
- These buttons can be found side by side on the Ribbon, near the alignment buttons. The Numbering button displays three small lines with numbers to the left of the lines and the Bullets button displays three small lines with bullet points to the left of the lines.
- There’s also a third button that allows you to create more elaborate multi-level list styles, which is useful for formatting outlines.
-
11
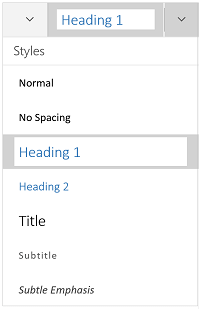
Experiment with document styles. All documents have standard built-in styles (for example, Normal, Title, Heading 1). The default style for text is Normal. The template that a document is based on (for example, Normal.dotx) determines which styles appear on the Ribbon and on the Styles tab. You can see the current style presets for your document in the Home tab of the Ribbon.
- Before you apply a style, you can see all of the available styles and preview how they will appear when applied.
- On the Home tab, click a style to apply it to selected text.
- Click the Styles Pane button (the arrow pointing down and to the right) to view and select from advanced Style options.
- By default, Word applies a paragraph style (for example, Heading 1) to the entire paragraph. To apply a paragraph style to part of a paragraph, select only the specific part that you wish to modify.
-
12
Reveal hidden formatting symbols if you’re having trouble. Word documents often contain hidden code that can cause frustrating problems when you’re trying to modify your formatting. For instance, an invisible extra paragraph mark or section break can create unwanted spaces between paragraphs or lines of text. To see formatting symbols that are normally hidden so you can delete or modify them, you can click the ¶ button in the Home tab, or try one of the following:[2]
- On Windows, open File, select Options, and click Display. Tick the box next to Show all formatting marks.
- In Word for Mac, open the Word menu, then Preferences, then View. Check the box next to All in the Show Non-Printing Characters section of the View menu.
-
13
Use the View menu to change your view of the document. The View menu can let you change how your document looks in Word without actually making changes to the format. For example, Print Layout will show approximately what your document will look like when it’s printed out, while Web Layout will display the whole document in one long chunk without any page breaks.
- The View menu also lets you zoom in and out on your document.
- You can also change your view with the buttons and zoom slider at the bottom right side of the document pane, or with the View tab in the Ribbon.
Advertisement
-
1
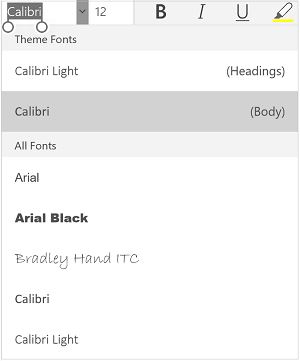
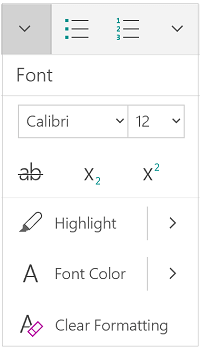
Change the font face. On the Home tab, you will a drop-down menu containing a list of fonts to choose from. Use your mouse to select the text you want to change, then choose a font from the list.
-
2
Change font size and color. Also on the Home tab, you can change the size, color, and highlighting for your font. Select the text you want to format, then choose your options.
- By default, they will be set to the size and font associated with your document’s current Style settings. For example, if you’re using Word’s default template, the Normal style will use Calibri as the default font and 12 pt. as the default text size.
- Always consider the formatting guidelines of the document you are writing when choosing the font style and size.
- The standard font for most college and professional papers is Times New Roman font, text size 12.
-
3
Make text bold, underlined, or italicized. Besides setting the font style and size, you can also adjust the emphasis of words and lines in your document. Near the font and text size menus, you will see the Bold, Italics, and Underline buttons.
- Just click the buttons to make your text bold, underlined, or italicized.
- In this section, you can also find special text formatting options such as Strikethrough, Subscript, and Superscript.
-
4
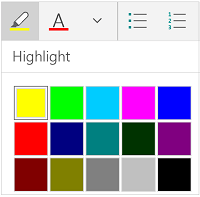
Highlight text on the page. If you would like to change the background color behind selected text, similar to using a highlighter on a printed page, click the Text Highlight icon, which is a pen above a colored line.
- You can also add special text effects with the Text Effects button, which looks like a capital A with a glowing blue border.
Advertisement
-
1
Drag an image into your document. This is a quick way to add a picture to your Word document. Simply select an image on your desktop and drag and drop it into the document window. Make sure your image is placed exactly where you want it before you drop it.
- You can also insert an image by going to the Insert tab, then clicking Pictures. Select one of the options to browse for images on your computer, the web, or Word’s gallery of stock photos.
- You can also insert graphics or other media (such as video or audio clips) using the Shapes, Icons, or 3D Models, and Media buttons.
-
2
Enable text wrapping. Text wrapping changes the layout of your document, allowing the text to flow around the image no matter where it is placed. To turn on text wrapping:
- Right-click (or ctrl-click, on a Mac) on the image and hover over Wrap Text. Select the alignment that best suits your document. You will see a preview as you hover over each option.
- To change the location of the image in the document, select the image and then hold the Ctrl key. While holding the key, use the arrow keys to move the picture around the document.
- When you right-click or ctrl-click your image, you’ll also see an option in the context menu to add a caption under your image.
-
3
Edit your image in the Picture Format tab. Once you insert your image, you can select it to open a new Picture Format tab in the ribbon. From there, you can choose from a variety of tools, such as:
- Making corrections or adding artistic filters to the image
- Adding style effects, such as a drop shadow or frame, to the picture
- Entering alt text
- Tweaking the position of your image or changing the text-wrap settings
-
4
Add a graph or chart in the Insert tab. Click the Insert tab on the Ribbon, and then click the Chart option. Choose your preferred type of graph, such as a pie or bar chart, from the dropdown menu.
- Depending on the type of chart or graph you choose, Word may automatically launch Excel and create a new spreadsheet, where you can enter data for your chart.
-
5
Modify your graph. When you choose a graph type, a new tab will appear in the Ribbon menu called Chart Design. Navigate to that tab with the chart selected to make changes to the look of your graph or chart, or choose the Edit in Excel button to make changes to the data in your chart.
-
6
Use the Table tool to insert a table. If you want to add a table to your document, head over to the Insert tab and click the Table button. A menu will pop open where you can either scroll over a grid of squares to select your number of rows and columns, or select an option like Insert Table or Draw Table.
- Insert Table opens a pop-up menu where you can specify parameters like the number of rows and columns and whether or not the contents of the table autofit your document window.
- The Draw Table tool allows you to draw the table with your mouse directly in the document.
- Once you start creating a table, you’ll see several new table editing tools in the Layout tab.
Advertisement
-
1
Choose a template from the New Documents pane. Templates are a great way to create a nice-looking document without having to do all the formatting from scratch. To use one, open Word and select New from the side menu to create a new document, or select New from Template from the File menu. Click one of the templates on the screen to select it.[3]
- If you don’t see a template you like, use the Search bar at the top of the window to find one that fits your needs. For instance, use keywords like “flyer,” “resume,” or “research paper” to find different styles of templates.
-
2
Click Create to open the template. The template will open as a new document.
-
3
Select text within the template to modify it. Word templates are simply preformatted documents with text, graphics, and other elements already in place. To add your own text, select text anywhere on the document and type in your own. The new text will have the same format as whatever text you selected and replaced. You can also click on a blank area of the document and start typing to add new text.
- To select a single word, double-click it. You can select longer pieces of text by clicking and dragging your mouse, or positioning your cursor at the start of the selection and holding down Shift while pressing the Right Arrow key.
- You can also select and move, delete, or replace other elements in the template, such as images, graphs, or tables.
-
4
Modify your template with the Styles pane. Templates use styles to create their distinctive looks. If you want to change the look of the template, click the Styles button in the Home tab of the ribbon toolbar. Click the down arrow next to any of the style elements and select Modify Style… to make changes.
- You can also make any other types of changes you like using the rest of the tools in the ribbon menu or Format menu.
-
5
Save your modified template as a document. When you’ve made the changes you want to the template, save it the same way you would any other Microsoft Word document.
Advertisement
-
1
Click the file menu and select Save a Copy…. If you want to save a document as a file type other than .DOCX, you can do so with the Save a Copy function.
- If it’s a brand-new document that you haven’t already saved, select Save As… instead.
-
2
Open the File Format dropdown menu. You’ll see this menu at the bottom of the Save a Copy or Save As window.
-
3
Select the format you want from the menu. In addition to common formats like .DOC, .DOCX, .TXT and .RTF, you can also save your document as a PDF, an XML file, or a macro-enabled Word file.
- Check out the list of file formats that are supported in word here.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What is Microsoft publishing?
UK_Gamer05
Community Answer
Publisher is a tool for making posters, leaflets, booklet,s etc. It’s for when you need to create something that isn’t a standard document.
-
Question
How do I move from page one to page two of a Word document?
UK_Gamer05
Community Answer
In Word 2016, on the insert tab, either select insert new page or page break.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Tip
- Unless free-handedly writing your paper, consult the guidelines of your document first before adjusting its format.
- Besides the header, footer, and page layout formats (which affect the entire document), all the other formatting tools can be applied only on specific parts of the document.
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 309,741 times.
Is this article up to date?
Word for iPad Word for Android tablets Word Mobile More…Less
You can use Word on your Android tablet, iPad, or Windows tablet to select and format text, change line and paragraph spacing, change indentation, and add lists. You can also use the edit menu to cut, copy, paste, and delete text that you select.
On your Android tablet
You can select words, sentences, or paragraphs.
-
To select a word, double-tap it.
-
To select a group of words or a block of text, select the first word and then drag the handles (
) to the end of your selection.
-
To select a paragraph, triple-tap it.
-
Change the font: Select some text and then tap the font name box. Choose a font from the drop-down list.
-
Change the font size: Select some text, tap the font size box, and then choose a size from the drop-down list.
-
Change the font color: Tap the font color icon, and then choose a color.
-
Add bold, italics, underlining, or strikethrough: Select some text and then tap the appropriate icon to apply the formatting.
-
Highlight text: Select some text, tap the highlight icon, and then choose a highlight color.
-
Apply a style: Select some text, tap the style icon, and then select from the list of defined styles.
Notes:
-
If you are using your device in portrait mode, many of the formatting options will appear on the Font menu.
-
-
-
Remove formatting: Select the text that has the formatting you want to remove, and then tap the clear formatting icon (
).
-
Add subscript or superscript: Select the text you want to make subscript or superscript, tap the font icon, and select subscript or superscript.
-
Add bullet or numbered lists: Select the text and then tap the bullet or the numbered list icon.
You can select a bullet or numbering style.
-
Indent a paragraph: Tap anywhere in the paragraph, and then tap the indent icon or the negative indent icon.
-
Align the text: Tap the text and then tap the alignment icon to align the text left, center, right, or justified.
-
Line spacing: To add or remove space before or after a line or paragraph, tap your text, tap the spacing icon, and then make your selection.
-
Insert or remove tabs: Tap the place where you want the tab to be located, tap the tab icon, and then tap the insert tab or remove tab icon.
To indent only the first line or use a hanging indent, tap the paragraph tab icon, tap Special Indent, and then make your selection.
You can also select formatting options from the edit menu.
-
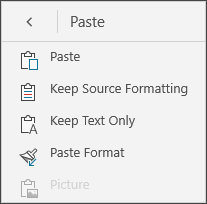
Cut and paste or copy and paste: Select some text, tap the scissors icon or the copy icon, tap to select a new location, and then tap the clipboard icon. Tap the arrow next to the clipboard to see the Paste menu. You can select Paste, Keep Source Formatting,Keep Text Only or Paste Format.
On your iPad
You can select words, sentences, or paragraphs.
-
To select a word, double-tap it.
-
To select a group of words or a block of text, select the first word and then drag the handles (
) to the end of your selection.
-
To select a paragraph, triple-tap it.
You can use the formatting options available on the Home tab to format text.
Tip: Use the back and forward arrows on the Home tab to undo or redo a change.
-
Change the font: Select some text and then tap the font name box. Choose a font from the drop-down list.
-
Change the font size: Select some text, tap the font size box, and then choose a size from the drop-down list.
-
Add bold, italics, or underlining: Select some text and then tap the appropriate icon to apply the formatting.
-
Add special formatting: To add formatting such as strikethrough or subscript, select some text, and then tap the formatting icon.
You can also choose from case options or special text effects, and you can clear formatting.
-
Highlight text: Select some text, tap the highlight icon, and then choose a highlight color.
-
Change the font color: Tap the font color icon and then choose a color.
-
Apply a style: To select a text style, tap the style icon, and then select from the list of defined styles.
-
Add bullet or numbered lists: Tap the text and then tap the bullet or the numbered list icon.
You can select a bullet or numbering style.
-
Indent a paragraph: Tap the text, and then tap the indent icon to move the text to the right. Tap the negative indent icon to move the text to the left.
-
Align the text: Tap the text and then tap the appropriate icon to align the text left, right, center, or justified.
-
Change the line spacing: Tap anywhere in the paragraph, and then tap the line spacing icon. Choose a spacing option.
You can also select formatting options from the edit menu.

-
Cut and paste or copy and paste: Select some text, tap Cut or Copy, tap to select a new location, and then tap Paste.
-
Copy formatting: Select the text that has the formatting you want to use, tap Copy, select the text that you want to format, and then tap Paste Format.
-
Delete text: Select the text that you want to remove, and then tap Delete.
-
Look up a definition: Select a word and then tap Define.
-
Add a comment: Select the text, tap New Comment, and then type your comment in the comment box.
-
Add tabs and line breaks: Tap at the location where you want the tab or line break, tap Insert, and then tap Tab or Line Break on the context menu.
On your Windows 10 tablet
-
To select a word, double-tap it.
-
To select a group of words or a block of text, select the first word and then drag the handles (
) to the end of your selection.
-
To select a paragraph, triple-tap it.
You can use the formatting options available on the Home tab to format text.
-
Change the font: Select some text and then tap the font name box. Choose a font from the drop-down list.
-
Change the font size: Select some text, tap the font size box, and then choose a size from the drop-down list.
-
Add bold, italics, or underlining: Select some text and then tap the appropriate icon to apply the formatting.
-
Highlight text: Select some text, tap the highlight icon, and then choose a highlight color.
-
Change the font color: Tap the font color icon, and then choose a color.
-
Add strikethrough: Select the text, and then tap the down arrow. Tap the strikethrough icon on the Font menu.
-
Remove formatting: Select the text that has the formatting you want to remove, and then tap the down arrow. Tap Clear Formatting on the Font menu.
-
Add subscript or superscript: Select some text, tap the down arrow, and select subscript or superscript on the Font menu
Notes:
-
If you are using your device in portrait mode, many of the formatting options will appear on the Font menu.
-
-
-
Apply a style: Select some text, tap the style icon, and then select from the list of defined styles.
-
Add bullet or numbered lists: Select the text and then tap the bullet or the numbered list icon.
You can select a bullet or numbering style.
-
Indent a paragraph: Tap anywhere in the paragraph, and then tap the indent icon or the negative indent icon.
-
Align the text: Tap the text and then tap the alignment icon to align the text left, center, right, or justified.
-
Line spacing: To add or remove space before or after a line or paragraph, tap the arrow and then select from the spacing options.
-
Insert or remove tabs: Tap the place where you want the tab to be located, tap the paragraph tab icon, and then tap the insert tab or remove tap icon.
To indent only the first line or use a hanging indent, tap the paragraph tab icon, tap Special Indent, and then make your selection.
You can also select formatting options from the edit menu.

-
Cut and paste or copy and paste: Select some text, tap the scissors icon to cut the text or the copy icon to copy the text, tap a new location, and then tap the clipboard icon. Tap the arrow next to the clipboard to see the Paste menu. You can select Paste, Keep Source Formatting,Keep Text Only, or Paste Format.
-
Look up a definition: Select a word and then tap Smart Lookup.
Need more help?
Has this ever happened to you? You’re plugging along on a Microsoft Word document only to freeze because you can’t recall how to do a relatively simple formatting function. I think it’s happened to all of us at one point or another and I hope the following will be your go-to resource whenever an instance like that takes place. (Bookmark the link so you can easily find it whenever a brain freeze occurs!)
My goal is not to cover all Microsoft Word formatting capabilities, just the basic ones that can increase your efficiency greatly. If you need more information or other guidance, look to the ‘HELP’ feature within the software itself.
How do I capitalize (or uncapitalize) text in microsoft Word?
You can change the capitalization, or case, of selected text in a document by clicking a single button on the Home tab called Change Case.
To change capitalization (or case) in Word, follow these steps:
- Select the text for which you want to change the case.
- On the Home tab, in the Font group, click the Change Case button.
- Then choose one of the following:
- To capitalize the first letter of a sentence and leave all other letters as lowercase, click Sentence case.
- To exclude capital letters from your text, click lowercase.
- To capitalize all of the letters, click UPPERCASE.
- To capitalize the first letter of each word and leave the other letters lowercase, click Capitalize Each Word.
- To shift between two case views (for example, to shift between Capitalize Each Word and the opposite, cAPITALIZE eACH wORD), click tOGGLE cASE.
To apply small capital (Small Caps) to your text:
- Select the text, and then on the Home tab, in the Font group, click the Font Dialog Box Launcher (the arrow in the lower-right corner). In the Font dialog box, under Effects, select the Small Caps checkbox.
To use a keyboard shortcut to change between lowercase, UPPERCASE, and Capitalize Each Word:
- Select the text and press SHIFT + F3 until the case you want is applied.
How do I add text effects in a Word document?
Besides WordArt and color fills and outlines, you can change the look of your text by adding effects, such as shadows, reflections, or glows.
To add text effects in Word, do the following:
- Select the text to which you want to add an effect.
- On the Home tab, in the Font group, click the Text Effect button.
- Point to the effect that you want (Shadow, Reflection, or Glow) and then when more choices appear click the effect that you want to add.
NOTE: To remove an effect, click the Clear Formatting button (eraser) on the Home tab in the Font group.
How do I change or set the default font in microsoft word?
The default font for new documents in Word 2016 is Calibri, 11 point but you can change/set it to your preference.
NOTE: When you set a default font, every new document you open will use the font settings that you selected and set as the default. The default font applies to new documents based on the active template, usually Normal.dotm.
To change/set the default in Word, follow these steps:
- Start with a blank document, or if your document already contains text formatted with the properties that you want to use, select that text.
- On the Home tab, click the Font Dialog Box Launcher, and then click the Font tab.
- Select the options that you want to apply to the default font, such as font style and font size. NOTE: If you selected text in step 1, the properties of the selected text are already set in the dialog box.
- Click Set As Default, and set the scope of your changes:
- This document only: (if you want your changes to apply to only the current document)
- Select all documents based on the Normal template: (if you want your changes to apply to any document based on the Normal template)
- Click OK to apply your changes.
How do I format paragraphs in word?
To change spacing between paragraphs in Word, do this:
- Click Design, then Paragraph Spacing.
- Pick which spacing you want (the default is Open) and notice your whole document will preview as you mouse over the different settings.
- If you do not like those options, click Custom Paragraph Spacing and change the numbers under Paragraph Spacing.
To change the spacing in only part of a document:
- Click anywhere in the paragraph you want to change.
- Go to Page Layout and under Spacing, click the up or down arrows to adjust the distance before or after the paragraph. You can also type a number directly.
To format a Word document with columns, follow these steps:
- Select the text you want formatted in columns.
- On the Layout tab, click Columns.
- Click More Columns.
- Click the number of columns that you want.
- Optional: To add a vertical line between the columns, select the Line Between checkbox. You can also adjust the column width and spacing.
- In the Apply to list, click Whole Document, Selected Text or This Point Forward.
To control how text flows between columns:
- Insert a column break. For example, to end a paragraph in one column and start a new paragraph at the top of the next column.
To Stop Using Columns:
- On the Layout tab, click Columns and then click One to return to one-column format. NOTE: You may need to insert a section break if you want two-columns in one section of your document and one-column formatting in another section of the document.
To add leaders between tab stops in Word, do this:
Leaders are those special characters—dots, dashes, underlines—that create a visual link between tab stops. Most often, you see leaders in a table of contents or an index.
NOTE: If you want to use tab stops and leaders to format a Table of Contents, consider using Word to create one automatically.
- Type the text that you want to appear before the leader.
- On the horizontal ruler, set the tab stop where you want (just click on the ruler), and then double-click it.
- In the Tabs dialog box under Leader, choose none, dots, dashes, or underline to set a series of characters.
- Click OK, and then press Tab on your keyboard.
- Type the text that you want to appear after the leader.
If you’d like to dive deeper into the formatting tools of Microsoft Word, and other applications within the Microsoft Office Suite, sign up for a one-day training class at Centriq.
View Centriq’s Microsoft Office Training Classes
Get specific information by speaking with a Training Advisor by email, by phone at 913.322.7062 and 314.644.6400, or by completing the following form.
Whether you’re a one-person business operating out of your kitchen, or a billion-dollar company on Wall Street, the expectation is the same. Your business documents must be the paragon of professionalism and competence.
This expectation shouldn’t be a cause for worry. With applications like Microsoft Word you can create professional-looking documents with your own computer. Through the years, Word has become more powerful, yet more intuitive. Anyone with basic computer skills can use Word to create well-designed documents.
In this article, you’ll learn how to format text in Word to make your business documents easier to read and understand. You’ll also pick up tips on how to make sure your formatting doesn’t look amateurish—even if you’re getting started with Word.
Formatting Text in Word
Formatting text in Microsoft Word refers to controlling how text appears in your document. This includes the size, color, and font of the text. It also covers text alignment, spacing, and letter case.
Microsoft Word styles make it easy to change and apply styles throughout a document. A “style” is a set of formatting settings applied to a specific kind of text.
For example, you can set up a style for headings that’s bold, 14 points, aligned left, and uses the Tahoma font. This means all text in your document with the heading style will be formatted the same way. You don’t have to manually format each heading in your document.
In this post, you’ll see how to use MS Word styles.
How to Format Text in Word
To show you how to format text in Word, we’ll walk through formatting a completely unformatted business document file.
This is what my marketing report looks like without any formatting in Word:
As you can see, it’s plain and boring. Nobody would be inspired to read it, let alone act on the findings of the report!
Some basic Word text formatting can fix that.
1. How to Apply Typographic Emphasis
1. For starters, let’s use typographic emphasis (bold, italic, underline) to make the report title stand out.
To do this, select the text you want to emphasize. Click on the bold button on the Microsoft Word ribbon.
Note that the ribbon also has the buttons to apply italic, underline, strikethrough, and other formatting effects for text. Follow the same steps to apply those effects.
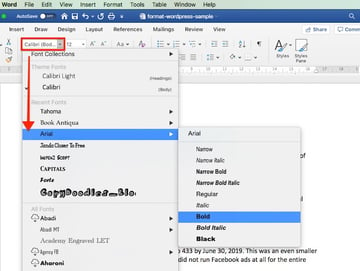
2. Now, let’s change the font, font size, and color of the title.
Again, select the text. Click the drop-down arrow on the font section of the ribbon, then select the font you want to apply. In this case, I’m using Arial bold.
3. To change the font size, highlight the text. Click the drop-down arrow on the font size indicator on the ribbon. Click on the font size of your choice.
Or, after highlighting the text, you can type the font size into the font size indicator on the ribbon. This is especially useful when the font size you want isn’t available in the font size selector.
4. You can also use the Increase Font Size or Decrease Font Size buttons on the ribbon to quickly change the font size.
5. We can easily change the font color as well.
Highlight the text, then click the down arrow beside the Font Color selector. Click on the color of your choice.
Choose More Colors… if you wish to apply a custom color.
2. How to Change Capitalization in Word
Microsoft Word also allows you to easily and quickly change the capitalization of your text. For example, if we want to make the title all uppercase, we don’t have to retype it.
Highlight the title, then click the Change Case button on the ribbon.
Or, highlight the text, go to Format > Change Case…
… then click on the radio button for the case you want to apply. Click OK.
Now the title is looking much better. It’s the most prominent part of the document and commands the reader’s attention. However, we can still improve its readability.
3. How to Format Paragraphs
One way to make your document easier to read is by increasing white space around lines and paragraphs.
1. To adjust the line spacing, select the text. Click on the arrow on the Line and Paragraph Spacing button. Select the line spacing you wish to apply.
2. To change the spacing around a paragraph, select the paragraph. Click on the arrow on the Line and Paragraph Spacing button > Line Spacing Options…. Then, type the amount of spacing before and after the paragraph. (Tip: You can adjust other settings from this dialog box as well.)
For the title, I’ll add a generous amount of space after the paragraph, to set it apart from the rest of the document.
3. Finally, let’s change the alignment of the title. Select the text, click on either the Align Left, Center Text, Align Right, or Justify button on the ribbon. Since this is a title, let’s use Center Text.
These simple formatting effects make the title stand out from the rest of the document.
4. How to Work With MS Word Styles
As much as Word makes it easy to format text, if you need to apply formatting effects on the entire document, the process becomes tedious.
Word solves that through styles. MS Word Styles allow you to define a set of formatting commands and apply them automatically to every item in the document with that style.
Let’s look at a specific example:
1. How to Modify a Paragraph Style
Let’s follow the steps above to define a style for the main headings of the report with the following characteristics:
- Font: Arial
- Size: 14 points
- Color: Blue-grey
- Typographic Emphasis: Bold
- Case: Capitalize each word
- Alignment: Left
- Line spacing: Single
- Paragraph spacing: 6 pts before paragraph, 0 pts after paragraph
It would look like this:
One way to apply this exact formatting on every main heading is to modify the existing Heading 1 style in our document. Place your cursor anywhere in the main heading. Go to Styles, right-click on Heading 1, then choose Update Heading 1 to Match Selection.
You can also modify any style by going to Format > Style…. The Style dialog box opens.
Select the style you want to modify from the Style list. This gives you a preview of the paragraph and character, as well as a description of the current style settings of the selected style.
Click Modify…. The Modify Style dialog box pops up.
Change the text and paragraph format settings. You can control the font, font size, font color, typographic emphasis, alignment, and spacing. When you’re done, click OK.
2. How to Apply a Paragraph Style
Now, go to each main heading in the document and apply the Heading 1 style to it. Place the cursor on a heading, go to Styles > Heading 1.
The selected text instantly takes on the formatting of Heading 1.
3. How to Create a List Paragraph Style
You can also create a new paragraph style from scratch, instead of modifying an existing one. To demonstrate, let’s create a list-type paragraph style.
1. Go to Format > Style…. Fill in the Properties section of the dialog box that opens. For Style based on, you may wish to use one of the pre-existing list styles as a starting point.
2. Next, change the formatting options. The box below gives you a preview of what the list paragraph would look like with those settings. There’s also a summary of the formatting properties you’ve specified.
You also have the option to do the following for this style:
- Add to template. Adds the style you’re creating to the document template.
- Add to Quick Style list. Shows the new style to the Quick Style list, making it quickly accessible from the ribbon.
- Automatically update. Automatically updates the style when you manually format a paragraph with that style.
When you’re happy with the settings you’ve made, click OK. Notice how the new Bullet style you created is now included in the Quick Style popup.
Once the bullet style is applied, our list now looks like this:
4. How to Use Character Styles in Microsoft Word
You can also define a style to an individual word or a block of text, rather than a paragraph. In the next example, I’d like to apply a character style for every URL in the document.
1. Select the text. Then, go to Format > Styles…. From the Style dialog, click New…. The Create New Style from Formatting dialog opens.
2. Give the new character style a name. For Style type, choose Character. Then, make the formatting settings you want to apply to this character. Note that you can’t change alignment and spacing for a character style. The preview box shows you a sneak peek of the text based on the settings you specified.
3. When you’re done, click OK.
To apply the character style, place your cursor in a word or select a set of words. Go to Format > Style…. Find the character style you wish to apply. Click Apply.
Tip: To quickly find the MS Word styles you’ve created, for List, choose User-defined styles.
5. How to Use Table Styles in Word
We can also define a table style to provide a consistent look to the tables in our document.
1. Create the table. Go to Insert > Table…, then indicate the number of columns and rows you need in your table (you can always add or remove these later). Click OK.
2. Add your text to the table. If necessary, click and drag any of the borderlines to adjust the width or a column, or the height of a row.
3. To apply a table style, click anywhere on the table, then go to Table Design. The Table Design ribbon appears.
4. Click on the down-arrow for table styles to display the table styles gallery.
5. Click on any style to apply it to your table.
Expand the table styles gallery again to change the existing style, clear the style you applied, or create your own table style.
Discover Great Microsoft Word Templates for 2020
Some experts say it’s a good idea to set up your formatting styles in Word first before typing or copying the text into the document. One quick way to do this is by starting with a Microsoft Word template. Templates come pre-formatted by professional designers to look current and impressive.
You can find thousands of Word templates for all kinds of business documents in Envato Elements.
For a small monthly subscription fee, you get unlimited downloads of all the templates at Elements. You also have unlimited access to everything else in the Elements catalog:
- presentation templates
- web templates
- fonts
- photos
- graphics
- other digital assets
Use as many of these assets as you want, as often as you want, without paying more. This makes Elements a terrific source for all the creative assets you need to create remarkable marketing and communication materials.
You can also pay as you go at GraphicRiver. This marketplace also offers a huge library of templates for Microsoft Word and other digital assets for all your marketing and communication needs. The difference is, you only pay each time you use an item. This can be a very economical option.
Below are some of the best print templates for Word available on Envato Elements and GraphicRiver:
After downloading any of these Microsoft Word templates, you can apply what you’ve learned about formatting text in Word. This way, you can personalize the template so that it aligns with your visual branding and preferences. You now know how to take any Word template and make it your own!
5 Top FAQs on Formatting Text in Microsoft Word
Below are some of the questions that come up as people format text in Word.
1. How Do You Make a Word Document Easier for the Reader to Scan?
Your primary goal when formatting text in Word is to make it easy for people to scan, read, and understand the content of the document. The different formatting options in Word help you achieve this:
- Use typographic emphasis like bold, italics, and underline to emphasize specific text and add variety to your document.
- Break up the document into sections with headings and sub-headings to help the reader scan and navigate their way through it.
- Use either bulleted or numbered lists where appropriate to shorten paragraphs and make lists easier to comprehend.
- Set up line and paragraph spacing so that there’s plenty of white spaces throughout the document.
2. How Many Fonts Should I Use in a Word Document?
It’s easy—and fun—to apply different fonts in Word. Too easy, in fact, that you could end up overwhelming your reader and making your document look like someone played with the formatting.
Avoid this by sticking to a maximum of two different fonts in a single document. For instance, you could choose a sans serif font for your title and headings, and a serif font for all other text. You could even use one font for the entire document, relying on typographical emphasis and color to distinguish different types of text from each other.
3. Why Should I Use Microsoft Word Text Styles?
Use Microsoft Word text styles because they let you apply formatting settings globally throughout your document. This is important in long documents, where formatting each line or paragraph is too onerous. With text styles, you only need to determine what style you want for each piece of text. Word will do the rest.
4. How Can I Make My Document Formatting Consistent?
Using MS Word styles, as you’ve learned in this article, is an easy way to make your document formatting consistent. You decide and set how you want each type of text to be formatted. Then you can apply those styles consistently through your entire document.
Beyond Microsoft Word styles, also make sure that the recurring parts of your document are consistent as well. These include your headers and footers, for example. You must also be consistent with the placement of images: Do they have borders? Are they always within the document’s margins or do they bleed to the edge of the page?
When you use a Word template, these design decisions are already made for you. So, if you want a consistent design without all the hard work, then starting with a template for Word is the way to go.
5. How do You Copy text into Word without also copying junk code?
When you copy text from one application and paste it into Word, you run the risk of also copying the underlying formatting code for it. This code or set of formatting commands is invisible so you won’t know you’re copying it inadvertently. This can mess up your formatting in Word. Soon, you’ll be pulling your hair wondering why Word won’t “follow” your commands.
To avoid this grief, make sure you strip all formatting when you copy and paste the text into Word. Here’s how: Copy the text. In Word, click Edit > Paste and Match Style.
That’s all there is to it!
Using Microsoft Word, Style Your Business Document for Maximum Impact
You’ve learned how to format a document in Word to make it easier to scan and read. Good formatting is also essential to make sure the final document represents you and your business in a favorable light.
You’ve seen how doable formatting is, even if you’re starting from scratch with completely unformatted text. You’ve also discovered that you can rely on professional designers to make the formatting decisions for you by starting with a template for Word.
For unlimited downloads of print templates for Word at a fixed subscription fee, look to Envato Elements. Here, you can also have your fill of fonts, icons, photos, and other design assets you’ll need without having to pay more. Or, get your premium Word templates from GraphicRiver on a pay-per-use basis. You also get a wide range of choices without having to commit to a subscription.
With Microsoft Word styles and formatting tools, there’s no more excuse to have poorly designed business documents. Make your next business document one you’ll be proud of.
Содержание
- Выбор шрифта и типа написания текста
- Выделение заголовка
- Выравнивание текста
- Изменение интервалов
- Добавление маркированных и нумерованных списков
- Дополнительные операции
- Вопросы и ответы
Мы уже неоднократно писали об инструментах для работы с текстом в MS Word, о тонкостях его оформления, изменения и редактирования. О каждой из этих функций мы рассказывали в отдельных статьях, вот только для того, чтобы сделать текст более привлекательным, удобным для чтения, понадобится большинство из них, причем, выполненных в правильном порядке.
Урок: Как добавить новый шрифт в Ворд
Именно о том, как правильно выполнить форматирование текста в документе Microsoft Word и пойдет речь в данной статье.
Выбор шрифта и типа написания текста
О том, как изменять шрифты в Ворде мы уже писали. Вероятнее всего, вы изначально набирали текст в понравившемся шрифте, выбрав подходящий размер. Более подробно о том, как работать со шрифтами, вы можете узнать в нашей статье.
Урок: Как изменить шрифт в Word
Выбрав подходящий шрифт для основного текста (заголовки и подзаголовки пока что не торопитесь изменять), пройдитесь по всему тексту. Возможно, некоторые есть фрагменты нужно выделить курсивом или полужирным шрифтом, что-то нужно подчеркнуть. Вот пример того, как может выглядеть статья на нашем сайте.
Урок: Как подчеркнуть текст в Ворде
Выделение заголовка
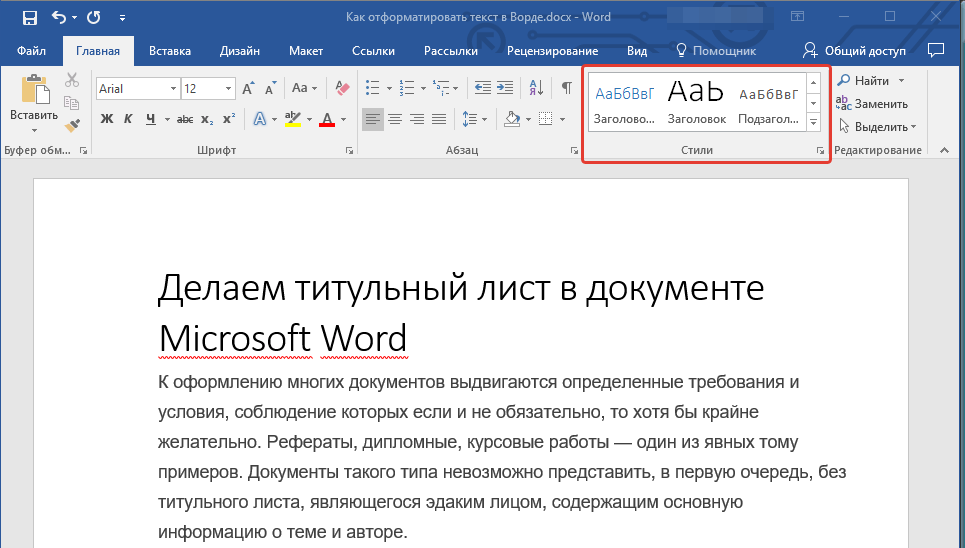
С вероятностью в 99,9% у статьи, которую вы хотите отформатировать, есть заголовок, и, скорее всего, подзаголовки в ней тоже имеются. Конечно же, их нужно отделить от основного текста. Сделать это можно с помощью встроенных стилей Word, а более подробно с тем, как работать с этими инструментами, вы можете ознакомиться в нашей статье.
Урок: Как сделать заголовок в Ворде
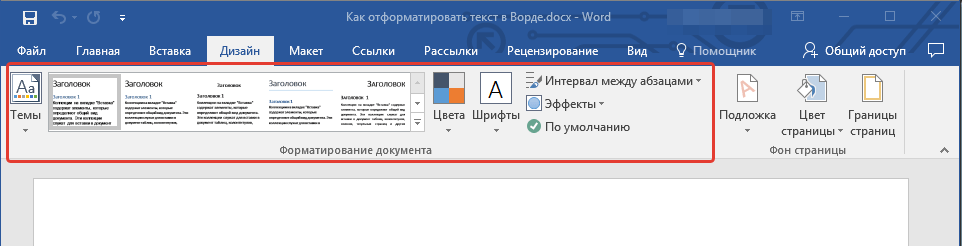
Если вы используете последнюю версию MS Word, дополнительные стили для оформления документа вы можете найти во вкладке “Дизайн” в группе с говорящим названием “Форматирование текста”.
Выравнивание текста
По умолчанию текст в документе выравнивается по левому краю. Однако, если это необходимо, вы можете изменить выравнивание всего текста или отдельно выделенного фрагмента так, как вам это необходимо, выбрав один из подходящих вариантов:
Урок: Как выровнять текст в Ворде
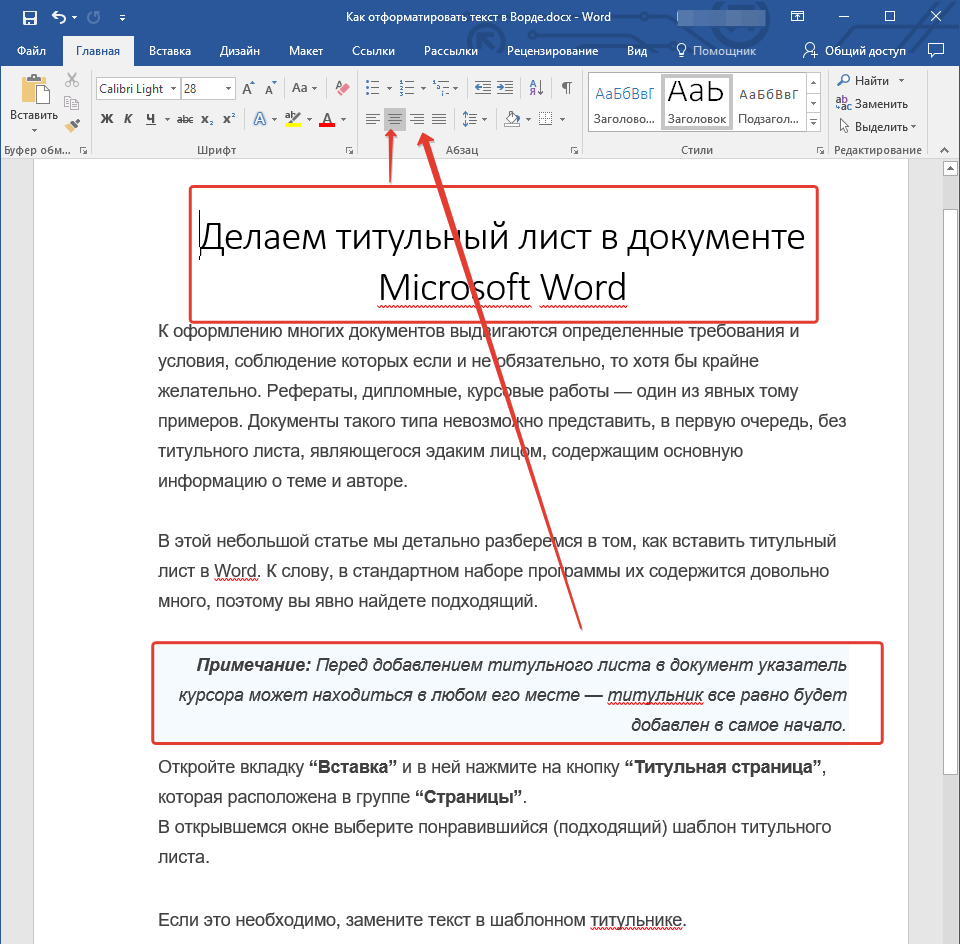
Инструкция, представленная на нашем сайте, поможет вам правильно расположить текст на страницах документа. Выделенные красным прямоугольником фрагменты текста на скриншоте и связанные с ними стрелки показывают, какой стиль выравнивания выбран для данных частей документа. Остальное содержимое файла выровнено по стандарту, то есть, по левому краю.
Изменение интервалов
Расстояние между строчками в MS Word по умолчанию составляет 1,15, однако, его всегда можно изменить на большее или меньшее (шаблонное), а также вручную задать любое подходящее значение. Более подробную инструкцию касательно того, как работать с интервалами, изменять и настраивать их вы найдете в нашей статье.
Урок: Как изменить межстрочный интервал в Ворде
Помимо интервала между строками, в Word также можно изменить и расстояние между абзацами, причем, как до них, так и после. Опять-таки, вы можете выбрать шаблонное значение, которое вас устраивает, или задать собственное вручную.
Урок: Как изменить интервал между абзацами в Ворде
Примечание: Если заголовок и подзаголовки, которые имеются в вашем текстовом документе, оформлены с помощью одного из встроенных стилей, интервал определенного размера между ними и следующими абзацами задается автоматически, а зависит он от выбранного стиля оформления.
Добавление маркированных и нумерованных списков
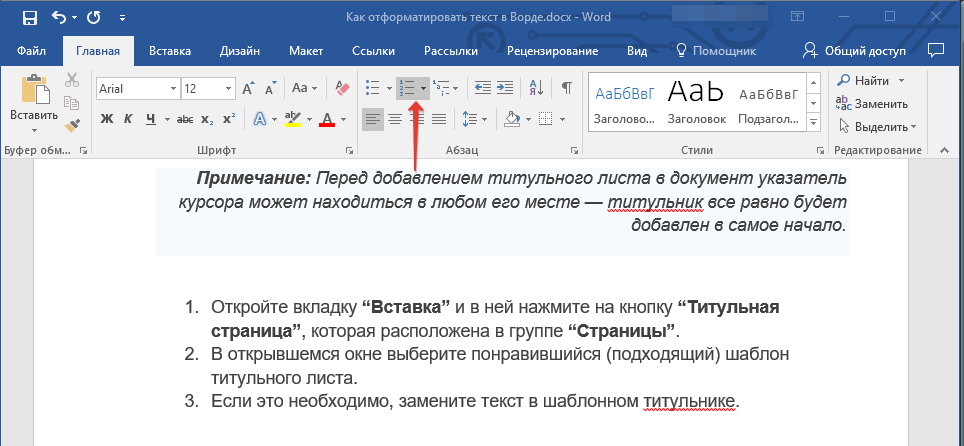
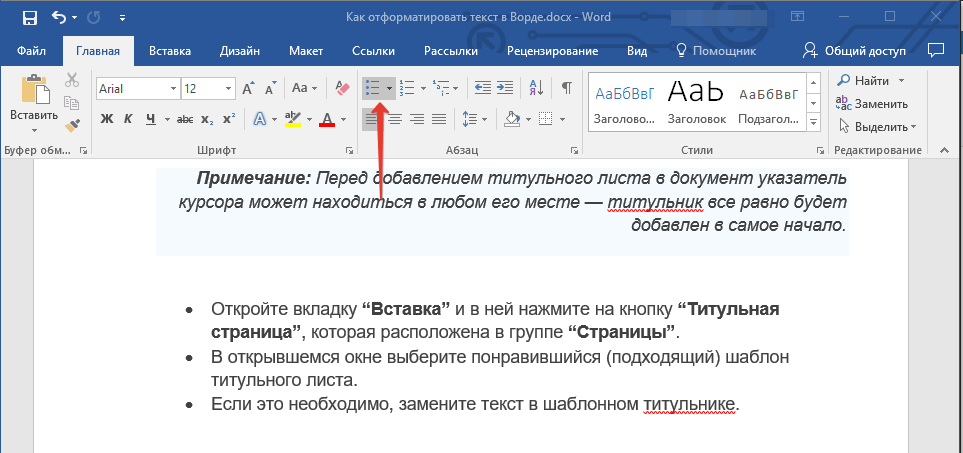
Если в вашем документе содержатся списки, незачем нумеровать или уж тем более маркировать их вручную. В Microsoft Word для этих целей предусмотрены специальных инструменты. Они, как и средства для работы с интервалами, расположены в группе “Абзац”, вкладка “Главная”.
1. Выделите фрагмент текста, который необходимо преобразовать в маркированный или нумерованный список.
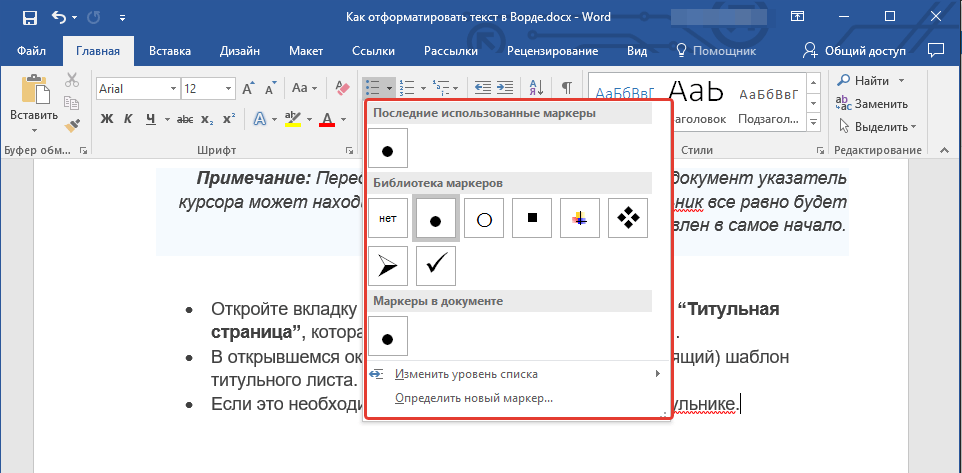
2. Нажмите одну из кнопок (“Маркеры” или “Нумерация”) на панели управления в группе “Абзац”.
3. Выделенный фрагмент текста преобразуется в красивый маркированный или нумерованный список, в зависимости от того, какой из инструментов вы выбрали.
- Совет: Если развернуть меню кнопок, отвечающих за списки (для этого нужно нажать на небольшую стрелочку справа от значка), вы можете увидеть дополнительные стили оформления списков.
Урок: Как в Ворде сделать список в алфавитном порядке
Дополнительные операции
В большинстве случаев того, что мы уже описали в данной статье и остальном материале по теме форматирования текста более, чем достаточно для оформления документов на должном уровне. Если же вам этого будет мало, либо же вы просто пожелаете внести какие-то дополнительные изменения, коррективы и т. д. в документ, с большой вероятность, вам будут очень полезны следующие статьи:
Уроки по работе с Microsoft Word:
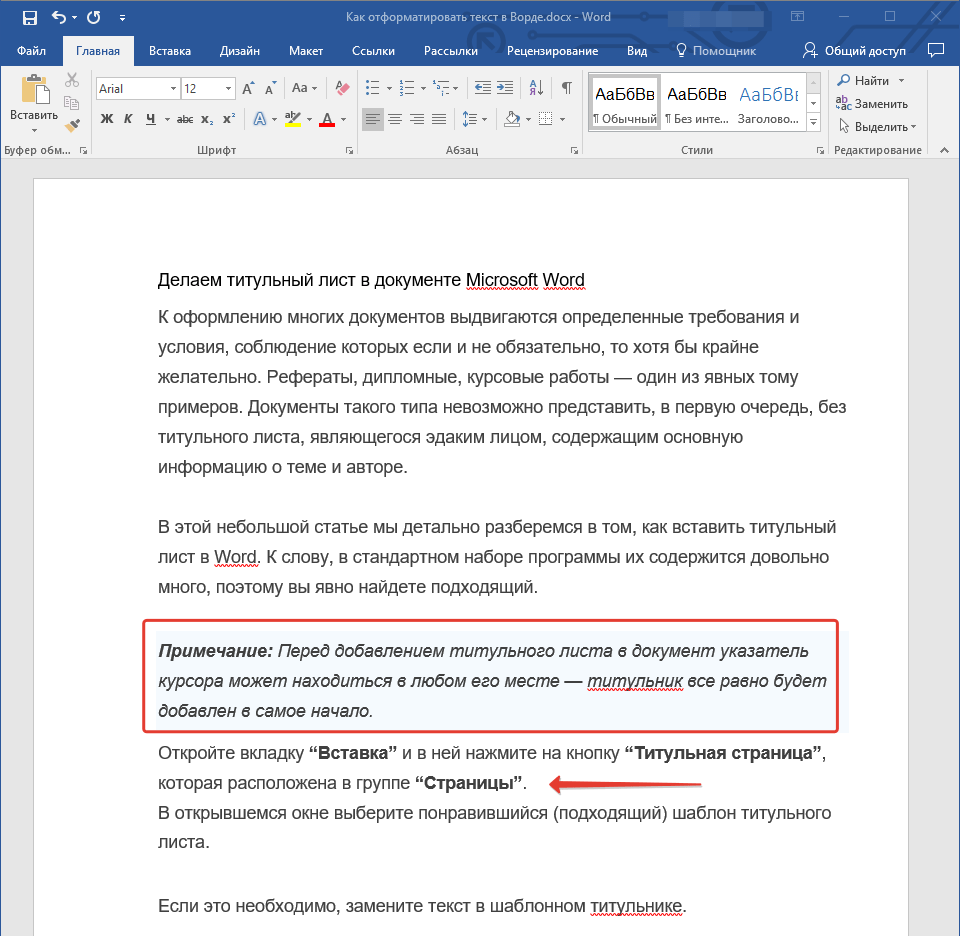
Как сделать отступы
Как сделать титульный лист
Как пронумеровать страницы
Как сделать красную строку
Как сделать автоматическое содержание
Табуляция
- Совет: Если во время оформления документа, при выполнении той или иной операции по его форматированию, вы допустили ошибку, ее всегда можно исправить, то есть, отменить. Для этого просто нажмите на закругленную стрелку (направленную влево), расположенную возле кнопки “Сохранить”. Также, для отмены любого действия в Ворде, будь то форматирование текста или любая другая операция, можно использовать комбинацию клавиш “CTRL+Z”.
Урок: Горячие клавиши в Word
На этом мы смело можем закончить. Теперь вы точно знаете, как отформатировать текст в Ворде, сделав его не просто привлекательным, а хорошо читабельным, оформленным в соответствии с выдвигаемыми требованиями.

Published: 2012-10-05
Browse All Articles > How to format your Word document
Introduction
This tutorial provides instructions on how to properly format your Word document using the inbuilt tools provided.
The benefits of using these tools means your documents are more accessible and easily portable to other applications and formats.
Where to start?
I always recommend the best way to write a document in Word is simply content and ignore the urge to style the document until you have entered all the content and are ready to format. I understand that some people find it hard to work this way as the document appears to lack structure and makes it difficult to know where you are. In that case I recommend you begin your document by typing out all the headings before adding any content; this gives the document structure and will also help you plan your document.
Using this method, type in your headings such as ‘Introduction’, ‘Requirements’, ‘Conclusion’ etc and convert each one to Heading 1 by putting the cursor anywhere in the word and pressing the key combination Ctrl+Alt+1.
If you wish to add sub headings to each section repeat the process but this time the key combination will be Ctrl+Alt+2.
Paragraphs and spacing and page breaks
When you’re ready to start adding the body text, simply type the way you would if you were using a Word processor (if you’re old enough to know what that is). What I mean by this is resist the urge to do anything more than type and then press ‘enter’ at the end of each paragraph. I find a lot of documents I receive have double spaces because the author pressed ‘enter’ twice. I also find documents where the author has pressed ‘enter’ multiple times tocontinue on a new page(you know who you are). These methods are wrong and should be avoided because your document would look different from pc to pc.
Paragraphs and spacing
Once you have finished typing your paragraphs, you can adjust the space before and after each paragraph by placing the cursor anywhere in the paragraph, right-clicking in the paragraph and in the context menu choosing ‘paragraph’ then in the dialog box that opens you can choose how much space you want before and after each paragraph. 12pt would normally give you a double space after your paragraph.
Page breaks
To continue on a new page the correct way would be to place the cursor where you want the section tend then go to the menu under ‘insert’ and choose ‘page break’ . You can then choose whether to have the new page as a new section or simply to make it a page break. Creating new sections is useful if you might want to have different layouts within your document or different headers and footers.
Styles and formatting
Once you have created your headings, sub headings, created desired spacing between your paragraphs and decided your page breaks, you can save your preferences by using the styles and formatiing pane. This allows you to determine everything about your headings and paragraphs from what typeface, colour and size they will be to what spacing to apply before and after them.
I tend to include my page breaks in the formatting for my Heading 1 format so that a new heading starts on a new page without having to manually insert a page break every time. Another helpful tool is the Widow/orphan control which will keep your headings and a certain number of lines together so you don’t have that annoying thing of a heading at the bottom of a page and the text that comes after it on the next page.
Creating a table of Contents
One of the advantages of using the inbuilt formatting tools for creating headings is that it automatically creates bookmarks which can be used for useful things like an automatic table of contents.
To create your table of contents, place the cursor where you would like the table to be and go to the ‘References’ tab and click on the ‘Table of Contents’ icon. Towards the bottom of the drop down that appears you will see ‘Insert Table of Contents…’, click on this and a dialog box will open.
The dialog will give you the option to add a number of levels to your table with three being the default. If you only want your heading 1 level to appear in the contents, change ‘Show levels’ to 1. You can play around with the other options in the dialog to change formatting etc or just leave the defaults in place.
Click OK and your table of contents will be created for you. The advantage to working in this way means that every time you update the table, it will display the correct location of that chapter and the current spelling you have used. It also acts as a bookmark which will allow you to jump straight to the page by clicking (or Ctrl clicking) on the entry in the table.
Conclusion
Formatting your document this way increases the accessibility of the document and makes it easier for others to use your document and export it to different formats such as PDF, XML or HTML. In addition to that you can make DAISY files which are audio files created from Word documents for people who use audio to read documents.
I hope you find this article interesting and that it helps you in your work or study.
Microsoft Word is packed with so many features that you can produce pretty much whatever you want with it. But these features don’t always result in the kind of beautiful, high-quality, and professional document designs that you may expect.
It’s one thing to know everything about Microsoft Word, all of its intricacies and quirks and functions—it’s something else entirely to know what makes a great document. Here, we’ll show you how to format a Word document to make it look professional.
1. Keep It Simple, Less Is More
Want to know how to make a Word document look good? Just keep it simple, and take advantage of the hidden features that Microsoft Word comes with. If you remember one thing from this article, let it be this, and you’ll be able to make the right design decisions in the future!
When writing a document, the content should be the main focus. Document formatting guidelines exist to make that content easier to read and digest.
Eliminate the temptation to introduce eye-catching elements that only serve to distract. Maximize whitespace. Keep your wording tight and revise any wordy sentences or paragraphs. Simple and minimal rules overall.
2. Choose a Context-Appropriate Typeface

Your first big design decision should be which typeface you’re going to use. Traditional knowledge says that serif fonts are easier to read in printed documents, whereas sans-serif fonts are better on the eyes when read on a digital screen.
Good examples of serif fonts include Garamond, Georgia, Hoefler Text, and Palatino, while good examples of sans-serif fonts include Arial, Gill Sans, Helvetica, and Lucida Sans.
Skip Comic Sans if you want to avoid one of the most common presentation design mistakes. And whatever you end up using, stick to the same typeface throughout to make your Word document professional. If desired, you can use a different typeface for headings.
3. Use Standard Font Size and Color
You can’t learn how to format a word document to look professional without paying attention to the look of the text. Business and academic papers generally use 12-point font sizes, which produce the most readable paragraphs when used in combination with the guidelines discussed below for page size, margins, and line spacing.
Some information-dense reports may sometimes go down to 10-point font size, but never less than that.
In general, it’s best to keep your hands off of anything related to colors, especially for printed documents. You’ll have to pay more for the color ink, and it won’t carry over if the document ever gets copied. For digital documents, reserve colored text for critical warnings and the like. Prefer to emphasize using bolded and italic text.
4. Use Standard Page Size and Margins
Nearly all office documents are formatted to the same page size as they are printed for standard 8½» x 11″ pages, known as US Letter size (also known as A4 elsewhere, which is 210mm x 297mm). This is the only size that’s guaranteed to be available regardless of which printer you use.
As for margins, most style manuals and style guides call for a 1″ margin on all sides of the page, which produces the best readability for line lengths and allows for written annotations if necessary. In Word, you can select Normal under Margins to do so. However, if the document is going to be bound in a binder, you may want to use Custom Margins to increase the side margins to 1½» to accommodate the rings.
5. Align Paragraphs to the Left
You may be tempted to use justified alignment because that’s what’s used in newspapers, novels, and some textbooks, but it’s the wrong choice for office and academic documents. Why is it important to make a document formal? Without formality, your document becomes unreadable.
What you want is left alignment for text. This produces jaggedness on the right side of paragraphs, but it keeps letter spacing as intended by whatever typeface you’re using, and that means optimal legibility.
Otherwise, you may end up with typographic rivers, which are extremely distracting and simply look ugly. This is something you certainly want to avoid when you want to make your Word document look professional.
6. Indent the First Lines of Paragraphs
Paragraphs should have no extra spacing between them, and the first lines of paragraphs should be indented to make each paragraph stand out. The only exception is for paragraphs that directly follow a section heading, which can be left unindented because the surrounding context makes it clear that it’s its own paragraph.
To make a document look professional, a general rule of thumb is to have the indent size the same as the font size. Make sure you use Word’s paragraph styling features to handle the indents rather than using the Tab key!
7. Place Images Between Paragraphs
Inserting images is a part of designing your Word document. It may be okay to place images inside a paragraph and allow the surrounding text to flow around it, and if your organization follows this document formatting guideline, then go ahead and do that.
But generally speaking, it can damage readability, especially in data-driven reports. The safest option, particularly for graphs, charts, and tables, is to put images in between paragraphs and keep them center aligned. That way, your images help to make your document attractive, but they are never vying for attention with the surrounding text. It also helps captions to stand out.
8. Choose Context-Appropriate Line Spacing
To format a document to look professional, the right choice for line spacing (the whitespace that separates a line of text from the next line of text) really depends on what kind of document you’re writing.
Academic papers should first follow any academic style guides in place, then prefer double-spacing if no style guide exists. Business and office documents tend to be single-spaced to minimize the number of pages needed when printing, but digital documents may be easier to read if spaced at somewhere between 120-150 percent.
9. Break Up Text With Headings and Lists
The longer the document, the more important headings become. Would you rather read a 20-page report that’s nothing but a wall of text from end to end? Or a 30-page report that’s organized into proper sections, subsections, and headings? It’s highly likely you’ll prefer the latter.
Lists are also good for breaking up walls of text and drawing eyes to important points. In Word, use Numbering to create numbered lists when counting a set of items (e.g., «the five attributes of a successful entrepreneur») or when providing step-by-step instructions. Otherwise, use Bullets to make bulleted lists.
Just be sure to avoid overusing lists, which detracts readability from your Word document design. This is especially important when it comes to using Word to format a screenplay.
10. Separate Sections With Breaks
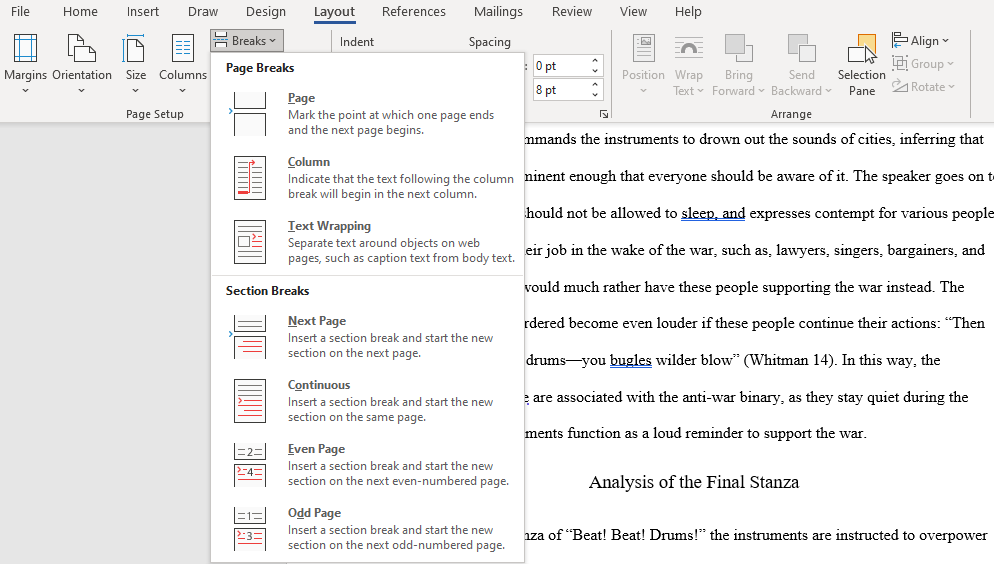
When you want to learn how to make your report look professional, you need to get acquainted with section breaks. In Microsoft Word, section breaks allow you to differentiate certain pages with changes in orientation, columns, headers, footers, page numbers, and more. Section breaks come in four forms:
- Next Page: Start the next section on the following page.
- Continuous: Start the next section on the current page.
- Even Page: Start the next section on the next even page.
- Odd Page: Start the next section on the next even page.
If your document is large enough to need chapters, this is the best way to format them in a clean way. Each chapter should be made with a Next Page section break, or the Even Page or Odd Page section breaks if you’re going to place it within a binder. We’ve shown how to remove page breaks if needed, too.
Learn How to Format a Word Document to Look Professional
Unless your organization or school requires a specific layout and format, you can skip the hard work of setting up your own template and just download one instead. This helps you quickly achieve a professional document design.
Microsoft Word is the global standard for word processing. At the same time, it’s one of the most maddening applications to master, which is why this Geek School series is all about learning how to format documents in Word.
Word 2013 and a Little Perspective
Microsoft is far more than a typical staid word processor. Word is one of the most affordable and closest things you can get to your very own printing press. In fact, it is for all With Word, you can write textbooks, create full magazine and newspaper layouts with graphics, write a novel with indices, and much, much more. You can do in mere hours, what twenty years ago might have taken an entire editorial team days or even weeks.
Microsoft Word completely eliminates the aggravation of typos (in theory at least). There is no need to retype whole chapters in order to add or rearrange content. Instead you can add, move, or even remove complete sentence, paragraphs, and chapters in mere seconds!
Of course, we take this power for granted but we can tell you, it really beats using a typewriter (let alone movable type) – making a mistake using a typewriter meant stopping what you were doing, rolling the platen up to better expose your typo, and then either using an eraser to remove the offending characters, or carefully dabbing on White-Out and patiently blowing it dry. Then, of course, you’d have to roll the platen back to the line you were typing on, taking further care to make sure it all lined up perfectly.
If you can imagine how many daily typing errors you make then you can probably get an idea of how long it took to produce even simple documents. Needless-to-say, it paid to be accurate, and unless you were a really good typist, typing an essay or book report, could be a long arduous process. And forget about adding pictures into your document. Doing that kind of stuff at home was nearly impossible. Oh sure, you could include your illustrations and photos and then refer to them, but it wasn’t as simple and elegant as cut-copy-paste we’ve become so accustomed to.
Nevertheless, all this power and control does arrive with a fairly steep learning curve. It can be a pain to get the hang of and be fluent in effectively formatting eye-catching documents. Luckily, that’s where we come in – with How-To Geek School’s Formatting Documents with Microsoft Word 2013.
What We Will Cover
This series aims to introduce you to a large swath of Word 2013’s document formatting features through five lessons.
In this lesson, we first cover some Word basics like the Ribbon and page structure like tabs, margins, and indents. Additionally, we show you how to manipulate formatting marks or simply turn them on/off. Our first lesson concludes with an exploration of fonts, and finally templates.
Lesson 2 begins with paragraphs, specifically alignment, indentation, and line spacing. After that we move on to shading and borders, and then lists (bulleted, numbered, and multilevel). We’ll also briefly touch upon AutoCorrect options.
After that, Lesson 3 begins with a lengthy exploration of tables (inserting, drawing, formatting, etc.) and then we dive into other formatting options, including links, headers, footers, equations, and symbols.
Lesson 4’s primary focus will be illustrations and multimedia such as pictures, shapes, WordArt, and more. We move on from there to briefly cover working with more than one language.
Finally, in Lesson 5, we wrap up with styles and themes, covering the gamut, new styles, inspecting styles, managing and modifying, and lastly themes.
Before we do all that however, let’s take some time to orient ourselves with Word’s anatomy and layout.
The Ribbon
As you may be familiar, Microsoft employs a “Ribbon” interface throughout their products. These ribbons are prominent in Office and Windows 8 (File Explorer and WordPad).
Here we see the Ribbon in Word 2013, the application we’ll be using for all our work.
The Ribbon is further subdivided into tabs (Home, Insert, Design, etc.) and each tab is further broken down into sections (Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, etc.).
Each of these sections can be expanded by clicking the small arrow in the lower-right corner.
Here, if we click on the arrow on the “Font” section, it opens to the trusty “Font” dialog:
While some menus may open to dialogs, others may spawn panes that slide out from one side of the screen. Also, if you use a computer with a lower resolution screen and need more screen real estate, you can click the small arrow to the very far lower-right corner of the ribbon.
This will cause the Ribbon to collapse, giving you more vertical space to work with. To get the Ribbon back, simply click on a tab and it will spring back into view (you can pin it if you want it to stay open).
Alternatively, you can quickly hide/unhide the Ribbon by typing “CTRL + F1.”
Home is Where Word’s Heart is
We’ll take some time before diving into actual document formatting, to talk about the “Home” tab. Even if you never touch another part of Word for the rest of your life (fairly impossible but still), the Home tab contains its most essential functions and is vital to formatting your documents consistently well.
See here how the “Home” tab has a total of five sections: “Clipboard,” “Font,” “Paragraph,” “Styles,” and “Editing.”
Clipboard
“Clipboard” functions are pretty rudimentary; you should know them by now: cut, copy, paste. Most likely you use right-click menus to do many of your cut-copy-paste functions, or keyboard shortcuts: “CTRL + X”, “CTRL + C”, “CTRL + V,” respectively.
Opening the “Clipboard” pane however, reveals a goldmine of functionality that can actually prove quiet useful when formatting documents. The Word clipboard collects everything you cut or copy for later use. This is particularly useful if you need to paste several distinct passages of text and/or images throughout your document. You can simply place your pointer at the correct insertion point, open the “Clipboard” viewer and select the piece you want to paste.
Font
The “Font” section and applicable dialog should be pretty familiar to the majority of Word users. Even if you’re not a Word pro, you’ve used the font functions in Word every time you create a document. Each time you bold or italicize something, you’re employing font functions. So knowing your way around the “Font” section and dialog is an excellent approach to mastering Word’s formatting bells and whistles.
We’ll go further into depth on fonts and typefaces in this lesson, for now, take a little time to familiarize yourself with its various functions.
Paragraph
Important also is the “Paragraph” section, which lets you set critical formatting features such as indenting, line spacing, and page breaks. Further, adjusting paragraph controls lets you play with borders, shading, and turn paragraph marks on or off. We’ll talk more about this in Lesson 2.
Styles
Styles are a great way to manage the way your entire document’s headers, titles, and text quickly and easily. Rather than going through a document and adding or changing headers one by one, you can simply apply a style, and then make changes to it using the “Styles” section. We’ll go into styles a great deal more in our final lesson of this series.
The Page
Your page is where all the magic happens, it’s where you compose your masterpieces and as such, knowing your way around is essential. Let’s dive in by turning on the “Ruler” and then explain how to set tabs and margins.
To turn on the ruler, we’ll first click the “View” tab and in the “Show” section, check the box next to “Ruler.” Note the horizontal and vertical rulers that appear along the page edges.
If you want to work according to another measurement system, you can change it from “File” -> “Options” -> “Advanced.”
Tabs
With the ruler on, we can cover how to use tabs and set margins. The ruler is used to show to show the positions of tab stops and margins.
Tabs are used to position text by using the “Tab” key. This works better than spacing everything manually, and with most fonts, tabs are the surest way to make sure everything lines up properly.
Microsoft Word sets tabs by default to ½-inch intervals. When you hit “Tab,” the insertion point will automatically jump right (½-inch per tab).
You set tabs by clicking on the ruler to indicate where you want to place them. You’ll see a vertical dotted line allowing your more precise control over where they go.
You can set tabs in any section of the document, meaning the top of the page can have different tabs than the middle or the bottom. Basically, you can a different tabbing scheme on each and every line of your document if you need or desire.
Types of Tabs
There are several different kinds of tabs you can use. To pick the type, click the tab selector located at the far left-hand side of the screen as shown below.
Here we see a left tab, note all the text is aligned to the left.
And similarly, a right tab:
A center tab:
A decimal tab allow you to create columns of numbers and easily line them up by decimal point:
A vertical bar tab, which doesn’t act like a tab, allows you to demarcate text. It looks the same as if you typed | however the advantage is that you can grab the “bar tab” in the ruler and move them together.
You can exert more control over tabs by double-clicking on any one to bring up the tabs dialog window. Note here you can have more precise control over tab stop positions, alignment, and clearing them.
Margins
You can see your margins by making sure Word is viewed in “Print Layout.”
Here in this example, we see our left margin is set at two inches and our left is set at four inches, giving us two inches of horizontal printable area. The margin indicators are the bottom arrows, while top arrow is a hanging indent, which we’ll cover in the very next section.
On a normal document, the left and right margins default to one-inch and 6 ½ inches. This means on a regular 8.5 x 11 sheet of paper, you will have one-inch margins where print will not appear, giving you 6.5 inches of horizontal printable area.
To move margins and the hanging indent, hover over each one with the mouse pointer until it changes to arrows and then drag them to the size you desire.
If you simply grab the left margin, it will leave the hanging indent behind.
And on that note, let’s briefly discuss indents in a bit more detail.
Indents
Indents are used to position the paragraph with margins or within the columns in a table.
You can tweak your margins further depending on what you’re writing. For example, you can create a “first line indent.” This is more of an old school style wherein the first line of each paragraph will be indented.
This is a more traditional way of formatting paragraphs, allowing you to denote where new paragraphs begin in a single-spaced document. Today, text is usually formatted in a block style with a double space between paragraphs.
A second line, or “hanging indent,” will automatically indent every line after the first one. One confusing part with indents is you can move them outside of the margin, which is counterintuitive unless you consider that a printer can print outside the margins, and is limited only by the width of the paper.
There’s not a whole lot to master when it comes to tabs, margins, and indents. That said, it pays to understand how they work so you can get more precise results in your documents. And it gives you a better understanding of why a documents looks the way it does or more importantly, why it may not look the way you want it to look.
Formatting marks
Before we proceed any further, we should point out that you might be noticing now that in some of our screenshots, there are formatting marks that show paragraphs, spaces, tabs, and others. To see the tabs and other text-formatting marks in the document select the ¶ (paragraph) symbol here on the “Paragraph” section on the “Home” tab.
To choose which formatting marks are seen, you can select them in Word “Options.” To open the options dialog, first click on the “File” tab and then choose “Options.” Finally, under “Display” you will see that you can select formatting options that always appear.
For example, if you want to turn off all the formatting marks except paragraphs and spaces, you would select only those two. Then you can turn off all or individual formatting marks in the “Paragraph” section.
Formatting marks are very important for creating clean, consistently formatted documents and they don’t show up in the final, printed document, plus you can turn them on or off as needed, so learn to use them to your advantage.
Fonts vs. Typefaces
Typefaces and fonts will be a routine part of your daily document formatting unless you’re happy with one single font for every document you write. Good font use is very important as it can allow you to better express yourself and get your point across. For that reason, you want to at least understand the very basics of how they work and what font is appropriate where and why.
For the sake of clarification, a “typeface” is basically the way a collection of letters, numbers, and symbols looks across its entirety. Here we see the Times New Roman typeface, which will have the same characteristics no matter which font you use. In other words, Times looks like Time, whether it is bolded, italicized, or whatever formatting you apply to it.
A font may be understood as the entire collection of typefaces. For example, Times New Roman and all its various forms (bold, italic, bold italic) is a “font family.” Each of the variations (regular, bold, italic, and bold italic) within the family is a font:
For the sake of simplicity, rather than split hairs and confuse you with talk of typefaces and fonts, we’ll just refer to everything type-related as a font.
Serif fonts
There are two types of fonts you should understand.
First, there are so-called serif fonts; serifs are those little bits that stick out from a letter as in the example below.
In many cases, a serif font will look best in formal of official documents. One of those most immediately identifiable and iconic examples of a serif font is seen on the New York Times masthead:
Sans serif
Conversely, a sans serif font will obviously not have serifs, hence the “sans” part. Here you see the Arial font, which is one of Windows’ default fonts.
Sans serif fonts are widely used in advertising and logos because they often tend to look new and modern. Without a doubt the most notable sans serif font is Helvetica, upon which Arial is obviously based. You can find dozens of examples of Helvetica-derived fonts in modern culture. Check out Microsoft, Target, and Panasonic for just a few examples.
You can add different fonts to Windows, and by extension Word, by downloading them from the web.
If you want to read up more about typefaces and fonts, Microsoft provides more information its typography homepage.
Point size
Point size relates to the size of the font, leading, and other page items. It is not connected to any established unit of measurement. In typography, a point is the smallest whole unit of measurement.
For most fonts in Word, the smallest point size is 8 points tall. The smallest lines and other graphic objects can have is a point size of 1. Here are some example of various point sizes:
Font Styles and Effects
You can apply various font styles and effects from the “Font” tab on the “Home” ribbon.
You can access further font effects from the full font dialog accessible by clicking the arrow in the bottom right corner.
You have a whole range of effects, including colors and different underline styles you can apply.
Before we end this lesson, we should take a moment to briefly acquaint you with templates, since they can often make short work of complex layouts.
Templates are pre-configured documents, like a resume or business cards that you can use to speed creating forms. There are templates for pretty much anything you can think of.
The goal of Microsoft Word is twofold: (1) provide sets of themes and styles so that the Word user can create professional-looking documents and (2) give the user the ability to create documents of graphic-designer quality by providing tools and pre-configured set of objects from which the user can select.
When you open Microsoft Word or click on the “New” from the “File” tab, the first screen it shows you are the templates available to you, either already included with the program, or available for quick download. If you don’t immediately see what you want, try “suggested searches” or use the search box.
Right-click on any template and you can “Preview” or “Create” the template. You can also pin a preferred template so it is always available at the top of the list.
Creating a template will cause it to open if it is stored locally on your computer, or it will download if it isn’t. Note that some these templates, such as the gift certificate pictured below are offered by third-party sites, so they may not all be free.
If you decide you want to purchase a third-party template, you will be provided with further instructions on how to do so.
After you pick a template, it will open as a new document, and you can fill it in and tweak it to your liking. We see here the template for the “Basic Resume.”
Note how Word will automatically fill in your name and the template provides instructions on how to use it. In reality, this template is really nothing more than a table (discussed in Lesson 3) with a Theme (discussed in Lesson 5) applied to it.
When you are done filling out the template, you can then save it as a new document. You can also take a template, make changes to it, and then save it as a new template. Let’s say for example, that you wanted to apply a different style to our “Basic Resume.” You’d simply need to open the template, affect the changes you want, and then save it as a new template.
There’s a whole lot to discover with templates. Best of all, you don’t have to worry about creating every single document on your own. Need a quick business card or invitations to your retirement party? Word templates make quick work of a lot of formatting headaches, leaving you time to actually design something you’ll be happy with!
Coming up Next…
That concludes our lesson for today, you should now have a fairly firm grasp on Word’s layout, tabs, margins, indents, fonts, and templates.
Tomorrow we’ll go over how to change the appearance and behavior of paragraphs on your pages, shading and borders, as well as introduce you to lists and all their various parts!
READ NEXT
- › Google Chrome Is Getting Faster
- › This New Google TV Streaming Device Costs Just $20
- › How to Adjust and Change Discord Fonts
- › The New NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 Is Like an RTX 3080 for $599
- › BLUETTI Slashed Hundreds off Its Best Power Stations for Easter Sale
- › HoloLens Now Has Windows 11 and Incredible 3D Ink Features
































 ) to the end of your selection.
) to the end of your selection.


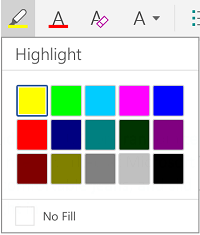
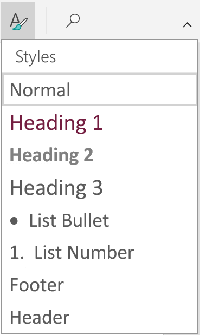
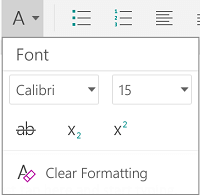
 ).
).


 ) to the end of your selection.
) to the end of your selection.





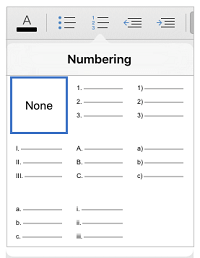


 ) to the end of your selection.
) to the end of your selection.