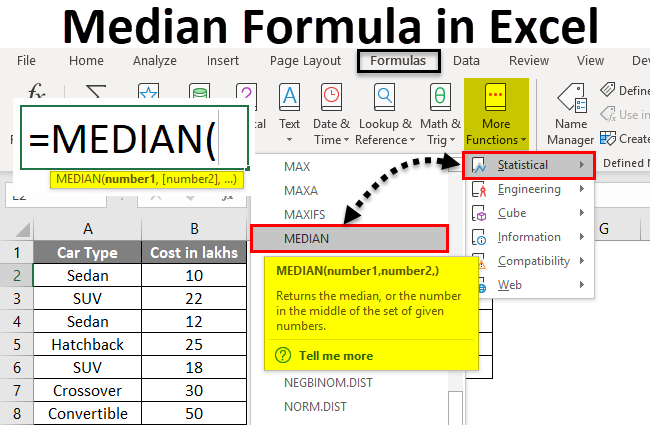
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the MEDIAN function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns the median of the given numbers. The median is the number in the middle of a set of numbers.
Syntax
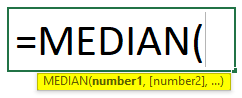
MEDIAN(number1, [number2], …)
The MEDIAN function syntax has the following arguments:
-
Number1, number2, … Number1 is required, subsequent numbers are optional. 1 to 255 numbers for which you want the median.
Remarks
-
If there is an even number of numbers in the set, then MEDIAN calculates the average of the two numbers in the middle. See the second formula in the example.
-
Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
-
Logical values and text representations of numbers that you type directly into the list of arguments are counted.
-
If an array or reference argument contains text, logical values, or empty cells, those values are ignored; however, cells with the value zero are included.
-
Arguments that are error values or text that cannot be translated into numbers cause errors.
Note: The MEDIAN function measures central tendency, which is the location of the center of a group of numbers in a statistical distribution. The three most common measures of central tendency are:
-
Average which is the arithmetic mean, and is calculated by adding a group of numbers and then dividing by the count of those numbers. For example, the average of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 30 divided by 6, which is 5.
-
Median which is the middle number of a group of numbers; that is, half the numbers have values that are greater than the median, and half the numbers have values that are less than the median. For example, the median of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 4.
-
Mode which is the most frequently occurring number in a group of numbers. For example, the mode of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 3.
For a symmetrical distribution of a group of numbers, these three measures of central tendency are all the same. For a skewed distribution of a group of numbers, they can be different.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Data |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
||
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=MEDIAN(A2:A6) |
Median of the 5 numbers in the range A2:A6. Because there are 5 values, the third is the median. |
3 |
|
=MEDIAN(A2:A7) |
Median of the 6 numbers in the range A2:A7. Because there are six numbers, the median is the midway point between the third and fourth numbers. |
3.5 |
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
How to Find the Median in Excel: Step-by-Step (2023 Guide)
“When Bill Gates walks into a bar, everyone becomes a millionaire on average”.
Outliers (like Mr. Bill) can skew data so much that simple statistical indicators (like averages) become misguiding.
In some of those cases, finding the median is more insightful 💡
Let me show you how to do that in Excel with the MEDIAN function, in just a few minutes.
Please download this workbook if you want to follow along as you read this guide.
What is a median?
Median refers to the middle term in a sorted set of data. It separates a group of numbers into two equal parts and acts as the center of data when arranged symmetrically.
If there are any empty cells in the selected data range, the MEDIAN function will ignore them.
If your data consists of an odd number of values, the middle term will be the median of your data set.

But if your data set contains an even number of values, the average of the two middle values will make the median.

Luckily, Excel offers a built-in MEDIAN Function that you can use to calculate the median of a data range. Its syntax is:
=MEDIAN (number1, [number2], ..)
Number1, Number2 are the numeric values whose median is to be calculated.
The first argument, Number 1, is mandatory. It can be a cell reference, named range, date, or even logical values. Number 2 uses the same types of values, but its use is optional.
You can use up to 255 arguments for the Excel MEDIAN formula in Excel. But the first two arguments suffice for most cases.
How to find the median in Excel
Let’s now see how to find the median in Excel.
Say we have the following data set.

We want to find the median salary.
For that, we will apply the following formula:
=MEDIAN (C2:C10)

Press Enter.
Excel returns the result as:

As evident, the MEDIAN returns a value of ‘69,740’, which isn’t even included in the list.
That’s because the total count of list entries is an even number. And for even numbers, Excel returns the median as the average of the two middle numbers.
You can use the formula with odd numbers as well. Excel will divide the list in half and return the middle number as result.

Pro Tip!
The MEDIAN function also counts logical values TRUE and FALSE. You can enter them directly into a MEDIAN formula.
If a set is (FALSE, TRUE, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), its median returned will be 4. The TRUE and FALSE values here represent 1, and 0, respectively.
Let’s now also calculate the median of the joining year.
We will first find the median of an even number of values.
The MEDIAN function returns the result:

Similarly, for an odd number of values, the result is:

That was pretty easy, no? 😀
That’s it – Now what?
And that’s how simple it is to use the MEDIAN function. All you need to do is sort the data in the proper order and apply the formula. Excel will return your median just as you expect 🤓
In this article, we learned what a median was and its uses. We also saw how to find the median of a data set having odd and even numbers of values.
MEDIAN truly is a fantastic function of Excel that helps ease your calculations. Similar to this, there are many other functions in Excel that you are missing out on.
If you have just started out, you should try practicing Excel’s SUM, AVERAGE, and COUNT functions.
You can learn them in my 30-minute free email course here. It’s delivered right into your inbox only at the cost of your email address 🤗
Kasper Langmann2023-01-10T18:58:46+00:00
Page load link
You can use the following formulas to find the mean, median, and mode of a dataset in Excel:
=AVERAGE(A1:A10) =MEDIAN(A1:A10) =MODE.MULT(A1:A10)
It’s worth noting that each of these formulas will simply ignore non-numeric or blank values when calculating these metrics for a range of cells in Excel.
The following examples shows how to use these formulas in practice with the following dataset:
Example: Finding the Mean in Excel
The mean represents the average value in a dataset.
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the mean of a dataset in Excel:
The mean turns out to be 19.11.
Example: Finding the Median in Excel
The median represents the middle value in a dataset, when all of the values are arranged from smallest to largest.
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the median of a dataset in Excel:
The median turns out to be 20.
Example: Finding the Mode in Excel
The mode represents the value that occurs most often in a dataset. Note that a dataset can have no mode, one mode, or multiple modes.
The following screenshot shows how to calculate the mode(s) of a dataset in Excel:
The modes turn out to be 7 and 25. Each of these values appears twice in the dataset, which is more often than any other value occurs.
Note: If you use the =MODE() function instead, it will only return the first mode. For this dataset, only the value 7 would be returned. For this reason, it’s always a good idea to use the =MODE.MULT() function in case there happens to be more than one mode in the dataset.
Additional Resources
How to Calculate the Interquartile Range (IQR) in Excel
How to Calculate the Midrange in Excel
How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Excel
There is a formula can help you quickly median the range. Select a blank cell and type this formula =MEDIAN(A1:C6) (A1:C6 indicates the range you want to calculate median from), press Enter key, and then you can get the median in the cell.
Contents
- 1 How do you calculate the median in Excel?
- 2 Is there a median if in Excel?
- 3 How is median calculated?
- 4 How do you figure out the median?
- 5 How do you calculate the median return?
- 6 What is a median example?
- 7 How do I use the IF function in Excel?
- 8 How do I write a formula in Excel?
- 9 How do you do an if and/or command in Excel?
- 10 How do you write an IF THEN statement?
How do you calculate the median in Excel?
Enter the MEDIAN IF Nested Formula
- Select cell E10.
- Type the following formula in the cell: =MEDIAN(IF(D3:D8=D10,E3:E8))
- Press and hold the Ctrl and Shift keys.
- Press the Enter key to create the array formula.
- The answer 15875 ($15,875 with formatting) appears in cell E10 since this is the middle tender for Project A.
Is there a median if in Excel?
A MEDIAN IF array formula in Excel will identify the middle number of values that meet certain criteria. An array formula performs an operation on multiple values instead of a single value.This formula can be used to complete the College Board’s Net Price Calculator.
How is median calculated?
Add up all of the numbers and divide by the number of numbers in the data set. The median is the central number of a data set. Arrange data points from smallest to largest and locate the central number. This is the median.
How do you figure out the median?
Count how many numbers you have. If you have an odd number, divide by 2 and round up to get the position of the median number. If you have an even number, divide by 2. Go to the number in that position and average it with the number in the next higher position to get the median.
How do you calculate the median return?
To find the median value in a list with an even amount of numbers, one must determine the middle pair, add them, and divide by two. Again, arrange the numbers in order from lowest to highest.
What is a median example?
Median: The middle number; found by ordering all data points and picking out the one in the middle (or if there are two middle numbers, taking the mean of those two numbers). Example: The median of 4, 1, and 7 is 4 because when the numbers are put in order (1 , 4, 7) , the number 4 is in the middle.
How do I use the IF function in Excel?
Use the IF function, one of the logical functions, to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false. For example: =IF(A2>B2,”Over Budget”,”OK”) =IF(A2=B2,B4-A4,””)
How do I write a formula in Excel?
Create a simple formula in Excel
- On the worksheet, click the cell in which you want to enter the formula.
- Type the = (equal sign) followed by the constants and operators (up to 8192 characters) that you want to use in the calculation. For our example, type =1+1. Notes:
- Press Enter (Windows) or Return (Mac).
How do you do an if and/or command in Excel?
When you combine each one of them with an IF statement, they read like this:
- AND – =IF(AND(Something is True, Something else is True), Value if True, Value if False)
- OR – =IF(OR(Something is True, Something else is True), Value if True, Value if False)
- NOT – =IF(NOT(Something is True), Value if True, Value if False)
How do you write an IF THEN statement?
Another way to define a conditional statement is to say, “If this happens, then that will happen.” The hypothesis is the first, or “if,” part of a conditional statement. The conclusion is the second, or “then,” part of a conditional statement. The conclusion is the result of a hypothesis.
Excel Median Formula (Table of Contents)
- Median Formula in Excel
- How to Calculate the Median in Excel using Formula?
Median Formula in Excel is one of the prime members of the statistical measure of central tendency (the rest two are mean and mode). It gives a more decent approach to finding out the middle most value for the given data.
If we are having a group of observations arranged in ascending or descending order, then the median of that group will be the middle most value. This means exactly 50% (half of the observations) are above median value, and exactly 50% (or half of the observations) are below the median value.
If the data set is with an odd number of observations, the median will be the middle observation. If the data set is with an even number of observations, the median will be the average of the middle two observations.
In cases where we need to calculate the exact center of the data, e.g. Calculation containing data of salary are the ones where the mean value would not be with that efficiency. The reason behind it is, our mean value might have extremely low or high observations, which may affect the average salary. However, the median is least affected by such extreme observations, due to which we prefer calculating it.
In Microsoft Excel, we can calculate the median using the MEDIAN function. It is an in-built function in excel that works on a range of data and calculates the median for that group.
The Formula for Excel MEDIAN function is as below:
Where, number1, number2 … are the arguments for the function. Excel MEDIAN Formula can take numbers, arrays, named ranges, dates, or cell references as input arguments. This function requires at least one argument to provide an output (i.e. number1 is fixed/required argument, the rest all are optional).
How to Calculate the Median in Excel using Formula?
To calculate the Median in excel using a formula is very simple and easy. Let’s understand how to calculate the Median in excel with some examples.
You can download this Median Formula Excel Template here – Median Formula Excel Template
Example #1 – Group with an Odd Number of Observation
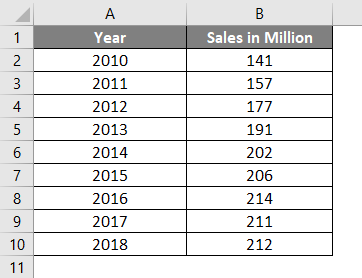
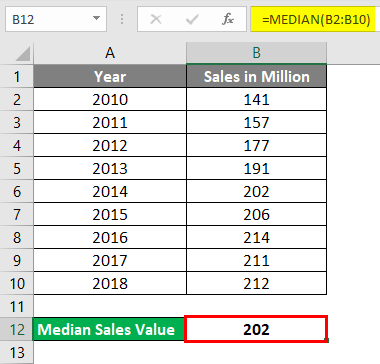
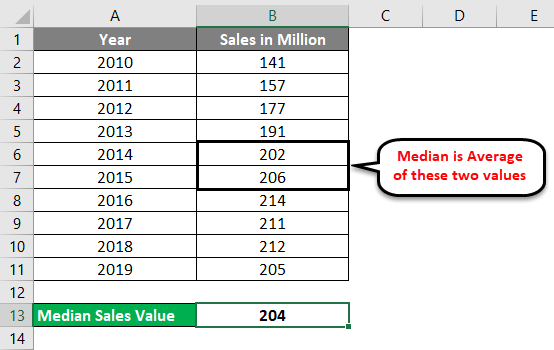
Suppose I have data on vehicle sales in a million from 2010 to 2018 for the USA. (9 observations in total which is an odd number).
In the image below, you can see that the observations are listed in ascending order by year.
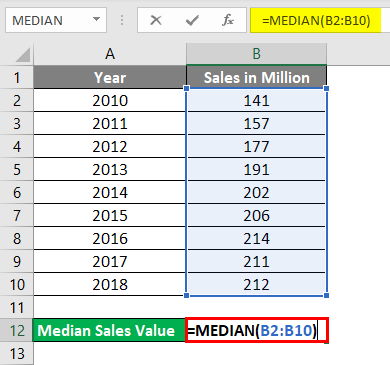
Put the following formula in cell B12. i.e.=MEDIAN(B2:B10). See the image below:
What you expect to be an output using this formula?
As you might have rightly guessed, this function allows excel to print the Median value for the given range (B2:B10), which is 202 in this case.
- Press enter once you are done with the formula, and you’ll get the following output:
The year associated with the median value can be considered as Median Year (in this case, 2014). It seems logical, right?
Please note that we have arranged the data Year wise and not the Sales wise. So, don’t get confused if the sales value seems to be not in ascending or descending order.
Now, what if I have an even number of observations?
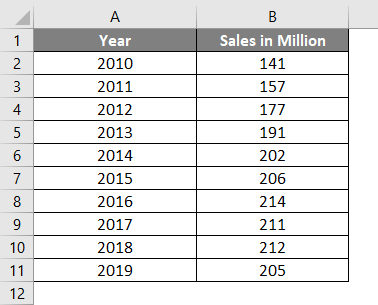
Example #2 – Group with Even Number of Observation
Suppose I have sales detail for one more the year 2019. That means even the number (10) of observations. Let’s see how the median formula works on such data.
Suppose I have data as below:
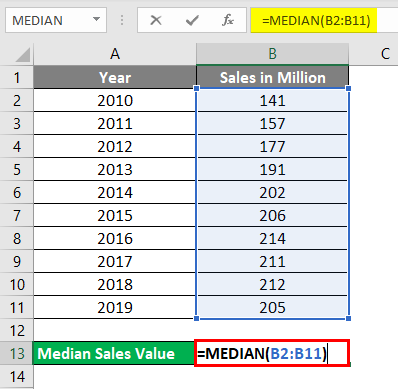
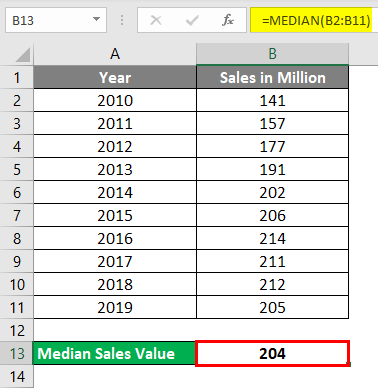
In cell D2, input the formula =MEDIAN(B2:B11)
Press enter once done and see the output.
When you are having an even number of observations, the Median value is an average of two middlemost values.
Conditional Median Formula
While working on the AVERAGE function in Excel, you might have seen some customized formulas like AVERAGEIF & AVERAGEIFS, which are allowing you to customize the AVERAGE function based on condition/conditions. That means giving an average of a group following specific criteria. Unfortunately, for MEDIAN, there is no such customized formula available ready-made in Excel. However, you can use your own logic and create one of such conditional formulas for the calculation of the Median of a group of observations.
Following is the formula which can be used:
Example #3 – Excel Median If Formula
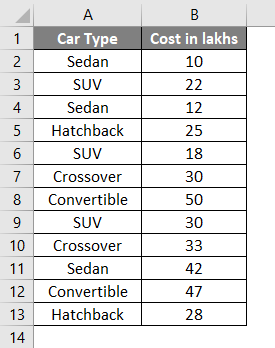
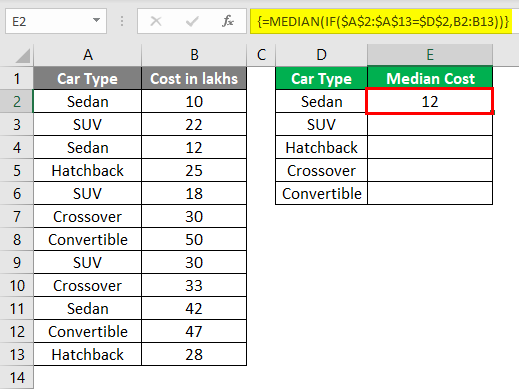
Suppose you have data of cars type and their costs in Lakhs as below:
You wanted a median cost for Car Type Sedan in your data; what can you do?
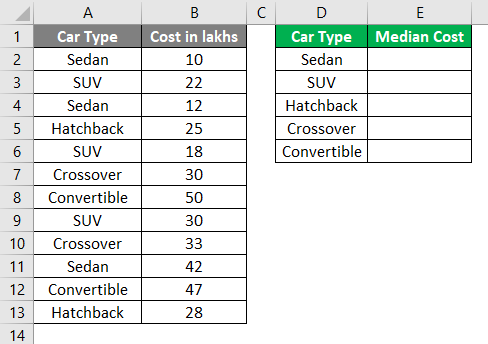
For that, put the Car Type values in one separate column, say column D.
Use the conditional formula below:
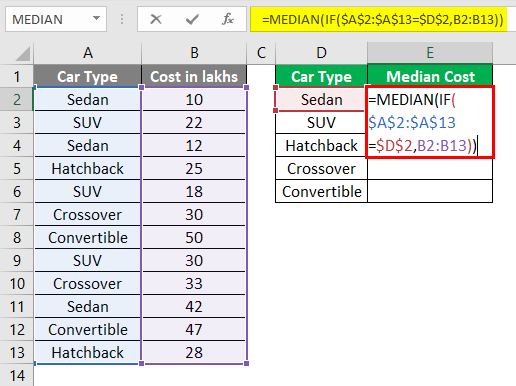
=MEDIAN(IF($A$2:$A$13 = $D$2, $B$2:$B$13))
See the image below:
Hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter at the same time after you have completed the formula.
Because you are working on a range of cells (i.e. Array), the dollar sign ($) makes the cell ranges absolute and is helpful when you have the same range of data for different other categories.
Moreover, as you can see through the formula, you are working on a range of cells which is array now, to make the array formula work, you need to hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
What this formula has done is, it has selected all the Sedan’s and their costs in lakhs, arranged those in ascending order (which is by default) and then selected the median from the available set of value.
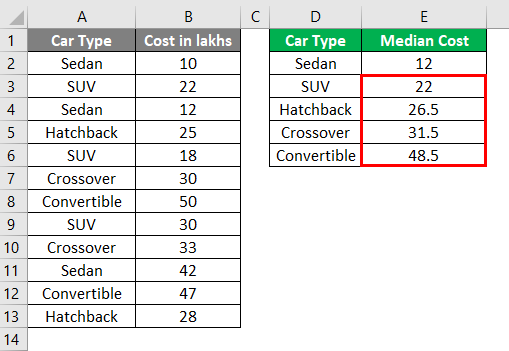
Do the same procedure for other cells in column D (cell D3, D4, D5, D6).
You also can add multiple conditions in this formula and make it work like AVERAGEIFS.
That’s it from this article. Let’s wrap up with some things to remember.
Things to Remember About Median Formula in Excel
- When the group of observations has an odd number of values, the MEDIAN formula considers the middle most value as a median. If the group of observations has an even number of values, the MEDIAN formula considers an average of two middlemost values as a median.
- Your group of observation should be sorted in ascending or descending order before you start using this formula.
- If any cell has zero value, it still is a part of median calculations.
- In most of the cases, the median has preference over the mean. Because it is least affected by extreme low/high observations.
- While calculating empty cells, cells with text or logical values are neglected automatically.
- Excel 2003 and earlier allows 30 arguments per formula for the MEDIAN function. In Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, this limit has been extended from 30 to 255. It means that you can pass till 255 arguments.
- Logical values of TRUE and FALSE gets counted in the MEDIAN formula. For example, MEDIAN(FALSE, TRUE, 2, 3) will be outputting 1.5 as a median which is nothing but an average of Logical value of TRUE (TRUE =1) and a number 2.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Median Formula in Excel. Here we discuss How to calculate Median in Excel along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Excel Frequency Formula
- Excel FV Formula
- Statistics in Excel
- How to Find Mean in Excel
Purpose
Get the median of a group of numbers
Return value
A number representing the median.
Usage notes
The MEDIAN function returns the median (middle number) in a set of data. The calculation performed by MEDIAN varies according to the number of numeric values provided. When the number is odd, MEDIAN returns the middle number in the group. When the number is even, MEDIAN returns the average of the two numbers in the middle.
The MEDIAN function takes multiple arguments in the form number1, number2, number3, etc. Arguments can be a hardcoded constant, a cell reference, or a range, in any combination. MEDIAN ignores empty cells, text values, and the logical values TRUE and FALSE. The MEDIAN function will accept up to 255 separate arguments.
Examples
When the number of values provided is odd, MEDIAN returns the middle number:
=MEDIAN(1,2,3,4,5) // returns 3
=MEDIAN(1,4,5,7,11) // returns 5
When the number of values provided is even, MEDIAN returns the average of the two middle numbers:
=MEDIAN(1,2,3,4,5,6) // returns 3.5
=MEDIAN(1,2,4,6,8,9) // returns 9
In the worksheet shown above, the formulas in H5 and H6 are:
=MEDIAN(B5:B16) // returns 83.5
=MEDIAN(D5:D16) // returns 80
Note that MEDIAN ignores the empty cell in D5:D16 and returns the middle number in the eleven values provided.
Notes
- When the count of numbers is odd, MEDIAN returns the middle number.
- When the count of numbers is even, MEDIAN returns the average of the two middle numbers.
- MEDIAN ignores empty cells, the logical values TRUE and FALSE, and text.
- MEDIAN returns a #NUM! error if no numeric values are provided.
- Arguments can be numbers, names, arrays, or references, up to 255 total.
Содержание
- Функция МЕДИАНА
- Описание
- Синтаксис
- Замечания
- Пример
- Calculate the median of a group of numbers
- Example
- MEDIAN function
- Description
- Syntax
- Remarks
- Example
- Mean, median and mode in Excel
- How to calculate mean in Excel
- How to find median in Excel
- How to calculate mode in Excel
- Mean vs. median: which is better?
- MEDIAN Function
- Related functions
- Summary
- Purpose
- Return value
- Arguments
- Syntax
- Usage notes
- Examples
В этой статье описаны синтаксис формулы и использование функции МЕДИАНА в Microsoft Excel.
Описание
Возвращает медиану заданных чисел. Медиана — это число, которое является серединой множества чисел.
Синтаксис
Аргументы функции МЕДИАНА описаны ниже.
Число1, число2. Аргумент «число1» является обязательным, последующие числа необязательные. От 1 до 255 чисел, для которых требуется определить медиану.
Замечания
Если в наборе имеется ряду чисел, медиана вычисляет среднее значение двух чисел в середине. См. вторую формулу в примере.
Аргументы могут быть либо числами, либо содержащими числа именами, массивами или ссылками.
Учитываются логические значения и текстовые представления чисел, которые непосредственно введены в список аргументов.
Если аргумент, который является массивом или ссылкой, содержит текст, логические значения или пустые ячейки, то такие значения пропускаются; однако ячейки, которые содержат нулевые значения, учитываются.
Аргументы, которые являются значениями ошибки или текстами, не преобразуемыми в числа, приводят в возникновению ошибок.
Примечание: Функция МЕДИАНА измеряет центральную тенденцию, которая является центром множества чисел в статистическом распределении. Существует три наиболее распространенных способа определения центральной тенденции:
Среднее значение — это среднее арифметическое, которое вычисляется путем сложения набора чисел с последующим делением полученной суммы на их количество. Например, средним значением для чисел 2, 3, 3, 5, 7 и 10 будет 5, которое является результатом деления их суммы, равной 30, на их количество, равное 6.
Медиана — это число, которое является серединой множества чисел, то есть половина чисел имеют значения большие, чем медиана, а половина чисел имеют значения меньшие, чем медиана. Например, медианой для чисел 2, 3, 3, 5, 7 и 10 будет 4.
Мода — это число, наиболее часто встречающееся в данном наборе чисел. Например, модой для чисел 2, 3, 3, 5, 7 и 10 будет 3.
При симметричном распределении множества чисел все три значения центральной тенденции будут совпадать. При смещенном распределении множества чисел значения могут быть разными.
Пример
Скопируйте образец данных из следующей таблицы и вставьте их в ячейку A1 нового листа Excel. Чтобы отобразить результаты формул, выделите их и нажмите клавишу F2, а затем — клавишу ВВОД. При необходимости измените ширину столбцов, чтобы видеть все данные.
Источник
Let’s say you want to find out what the midpoint is in a distribution of student grades or a quality control data sample. To calculate the median of a group of numbers, use the MEDIAN function.
The MEDIAN function measures central tendency, which is the location of the center of a group of numbers in a statistical distribution. The three most common measures of central tendency are:
Average which is the arithmetic mean, and is calculated by adding a group of numbers and then dividing by the count of those numbers. For example, the average of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 30 divided by 6, which is 5.
Median which is the middle number of a group of numbers; that is, half the numbers have values that are greater than the median, and half the numbers have values that are less than the median. For example, the median of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 4.
Mode which is the most frequently occurring number in a group of numbers. For example, the mode of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 3.
For a symmetrical distribution of a group of numbers, these three measures of central tendency are all the same. For a skewed distribution of a group of numbers, they can be different.
The screen shots in this article were taken in Excel 2016. If you have a different version your view might be slightly different, but unless otherwise noted, the functionality is the same.
Example
The example may be easier to understand if you copy it to a blank worksheet.
Open a blank workbook or worksheet.
How to copy an example
Select the example below.
Note: Do not select the row or column headers.
Источник
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the MEDIAN function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
Returns the median of the given numbers. The median is the number in the middle of a set of numbers.
Syntax
The MEDIAN function syntax has the following arguments:
Number1, number2, . Number1 is required, subsequent numbers are optional. 1 to 255 numbers for which you want the median.
If there is an even number of numbers in the set, then MEDIAN calculates the average of the two numbers in the middle. See the second formula in the example.
Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
Logical values and text representations of numbers that you type directly into the list of arguments are counted.
If an array or reference argument contains text, logical values, or empty cells, those values are ignored; however, cells with the value zero are included.
Arguments that are error values or text that cannot be translated into numbers cause errors.
Note: The MEDIAN function measures central tendency, which is the location of the center of a group of numbers in a statistical distribution. The three most common measures of central tendency are:
Average which is the arithmetic mean, and is calculated by adding a group of numbers and then dividing by the count of those numbers. For example, the average of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 30 divided by 6, which is 5.
Median which is the middle number of a group of numbers; that is, half the numbers have values that are greater than the median, and half the numbers have values that are less than the median. For example, the median of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 4.
Mode which is the most frequently occurring number in a group of numbers. For example, the mode of 2, 3, 3, 5, 7, and 10 is 3.
For a symmetrical distribution of a group of numbers, these three measures of central tendency are all the same. For a skewed distribution of a group of numbers, they can be different.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
Источник

When analyzing numerical data, you may often be looking for some way to get the «typical» value. For this purpose, you can use the so-called measures of central tendency that represent a single value identifying the central position within a data set or, more technically, the middle or center in a statistical distribution. Sometimes, they are also classified as summary statistics.
The three main measures of central tendency are Mean, Median and Mode. They all are valid measures of central location, but each gives a different indication of a typical value, and under different circumstances some measures are more appropriate to use than others.
How to calculate mean in Excel
Arithmetic mean, also referred to as average, is probably the measure you are most familiar with. The mean is calculated by adding up a group of numbers and then dividing the sum by the count of those numbers.
For example, to calculate the mean of numbers <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6>, you add them up, and then divide the sum by 6, which yields 3: (1+2+2+3+4+6)/6=3.
In Microsoft Excel, the mean can be calculated by using one of the following functions:
- AVERAGE- returns an average of numbers.
- AVERAGEA — returns an average of cells with any data (numbers, Boolean and text values).
- AVERAGEIF — finds an average of numbers based on a single criterion.
- AVERAGEIFS — finds an average of numbers based on multiple criteria.
For the in-depth tutorials, please follow the above links. To get a conceptual idea of how these functions work, consider the following example.
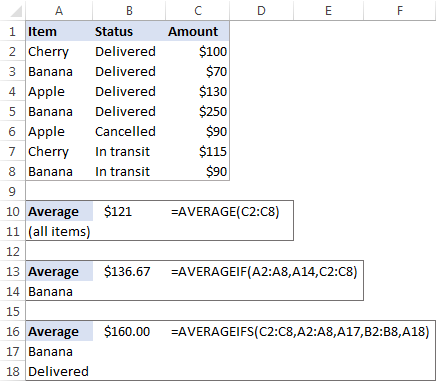
In a sales report (please see the screenshot below), supposing you want to get the average of values in cells C2:C8. For this, use this simple formula:
To get the average of only «Banana» sales, use an AVERAGEIF formula:
=AVERAGEIF(A2:A8, «Banana», C2:C8)
To calculate the mean based on 2 conditions, say, the average of «Banana» sales with the status «Delivered», use AVERAGEIFS:
=AVERAGEIFS(C2:C8,A2:A8, «Banana», B2:B8, «Delivered»)
You can also enter your conditions in separate cells, and reference those cells in your formulas, like this:
Median is the middle value in a group of numbers, which are arranged in ascending or descending order, i.e. half the numbers are greater than the median and half the numbers are less than the median. For example, the median of the data set <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9>is 3.
This works fine when there are an odd number of values in the group. But what if you have an even number of values? In this case, the median is the arithmetic mean (average) of the two middle values. For example, the median of <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6>is 2.5. To calculate it, you take the 3rd and 4th values in the data set and average them to get a median of 2.5.
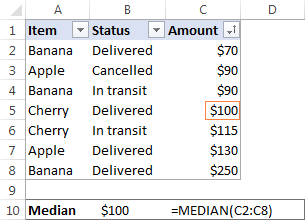
In Microsoft Excel, a median is calculated by using the MEDIAN function. For example, to get the median of all amounts in our sales report, use this formula:
To make the example more illustrative, I’ve sorted the numbers in column C in ascending order (though it is not actually required for the Excel Median formula to work):
In contrast to average, Microsoft Excel does not provide any special function to calculate median with one or more conditions. However, you can «emulate» the functionality of MEDIANIF and MEDIANIFS by using a combination of two or more functions like shown in these examples:
How to calculate mode in Excel
Mode is the most frequently occurring value in the dataset. While the mean and median require some calculations, a mode value can be found simply by counting the number of times each value occurs.
For example, the mode of the set of values <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6>is 2. In Microsoft Excel, you can calculate a mode by using the function of the same name, the MODE function. For our sample data set, the formula goes as follows:
=MODE(C2:C8)
In situations when there are two or more modes in your data set, the Excel MODE function will return the lowest mode.
Generally, there is no «best» measure of central tendency. Which measure to use mostly depends on the type of data you are working with as well as your understanding of the «typical value» you are attempting to estimate.
For a symmetrical distribution (in which values occur at regular frequencies), the mean, median and mode are the same. For a skewed distribution (where there are a small number of extremely high or low values), the three measures of central tendency may be different.
Since the mean is greatly affected by skewed data and outliers (non-typical values that are significantly different from the rest of the data), median is the preferred measure of central tendency for an asymmetrical distribution.
For instance, it is generally accepted that the median is better than the mean for calculating a typical salary. Why? The best way to understand this would be from an example. Please have a look at a few sample salaries for common jobs:
- Electrician — $20/hour
- Nurse — $26/hour
- Police officer — $47/hour
- Sales manager — $54/hour
- Manufacturing engineer — $63/hour
Now, let’s calculate the average (mean): add up the above numbers and divide by 5: (20+26+47+54+63)/5=42. So, the average wage is $42/hour. The median wage is $47/hour, and it is the police officer who earns it (1/2 wages are lower, and 1/2 are higher). Well, in this particular case the mean and median give similar numbers.
But let’s see what happens if we extend the list of wages by including a celebrity who earns, say, about $30 million/year, which is roughly $14,500/hour. Now, the average wage becomes $2,451.67/hour, a wage that no one earns! By contrast, the median is not significantly changed by this one outlier, it is $50.50/hour.
Agree, the median gives a better idea of what people typically earn because it is not so strongly affected by abnormal salaries.
This is how you calculate mean, median and mode in Excel. I thank you for reading and hope to see you on our blog next week!
Источник
Summary
The Excel MEDIAN function returns the median (middle number) in the supplied set of data. For example, =MEDIAN(1,2,3,4,5) returns 3.
Purpose
Return value
Arguments
- number1 — A number or cell reference that refers to numeric values.
- number2 — [optional] A number or cell reference that refers to numeric values.
Syntax
Usage notes
The MEDIAN function returns the median (middle number) in a set of data. The calculation performed by MEDIAN varies according to the number of numeric values provided. When the number is odd, MEDIAN returns the middle number in the group. When the number is even, MEDIAN returns the average of the two numbers in the middle.
The MEDIAN function takes multiple arguments in the form number1, number2, number3, etc. Arguments can be a hardcoded constant, a cell reference, or a range, in any combination. MEDIAN ignores empty cells, text values, and the logical values TRUE and FALSE. The MEDIAN function will accept up to 255 separate arguments.
Examples
When the number of values provided is odd, MEDIAN returns the middle number:
When the number of values provided is even, MEDIAN returns the average of the two middle numbers:
In the worksheet shown above, the formulas in H5 and H6 are:
Note that MEDIAN ignores the empty cell in D5:D16 and returns the middle number in the eleven values provided.
Источник
Today, we’ll learn to find the median and mode in Excel. In statistics, the median is the value that separates the upper and lower halves of a data sample or population or simply the middle number in a sorted list of numbers. Excel has an inbuilt function MEDIAN to find the median value of a dataset.
Also read: How to calculate mean in Excel? [Easy Step-by-Step Method]
Using the MEDIAN function
The MEDIAN function returns the median of a list of numbers. Syntax: =MEDIAN(n), where n is the list of numbers or reference to the cell ranges containing the numbers.
Let us consider a list of numbers whose median we are interested in calculating:
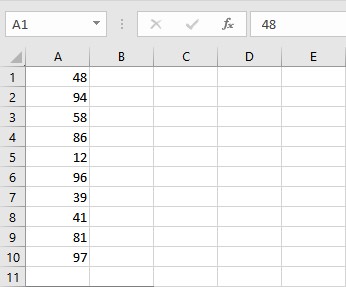
- Go to the cell where you want to display the median value.
- Type =MEDIAN(, select the cells containing the numbers and complete the formula with ).
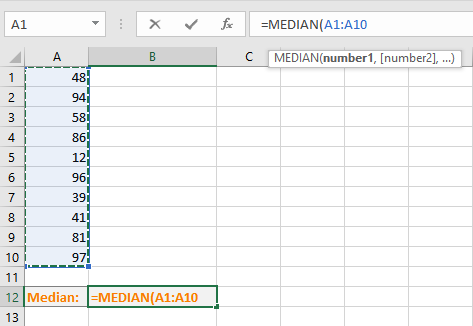
- Press Enter key to display the calculated median value.
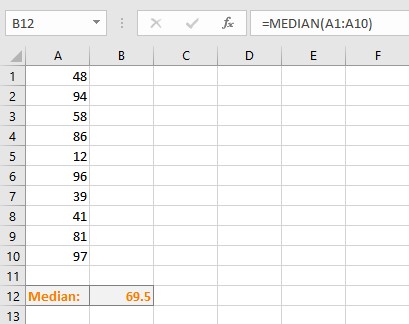
Note:
- The Excel MEDIAN function returns the middle number in the dataset when the total number of items is odd. It returns the average of the two middle numbers when the total number of items in the dataset is even.
- In calculating median using the MEDIAN function, cells with values as zero (0) are included.
- The MEDIAN function ignores empty cells as well as cells containing text or logical values.
- TRUE and FALSE logical values put directly into the MEDIAN function’s parameters are counted as 1 and 0 respectively. The formula MEDIAN(FALSE, TRUE,2,3,4), returns 2 as the dataset is read as {0,1,2,3,4}.
Using the MEDIAN IF formula
Sometimes you want to exclude zero values while calculating the median of a dataset. Excel does not have a dedicated function to do this, but a workaround is available using a MEDIAN IF formula. The syntax for this formula is MEDIAN(IF(criteria_range=criteria, cell_ranges)), where criteria are the condition to be satisfied by the values in the cells, cell_ranges is the reference to the cell ranges containing the values.
Let us consider a list of numbers whose median we are interested in calculating excluding zero values:
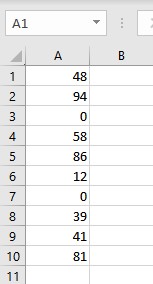
- Go to the cell where you want to display the median value.
- Type =MEDIAN(IF(A1:A10>0,A1:A10)).
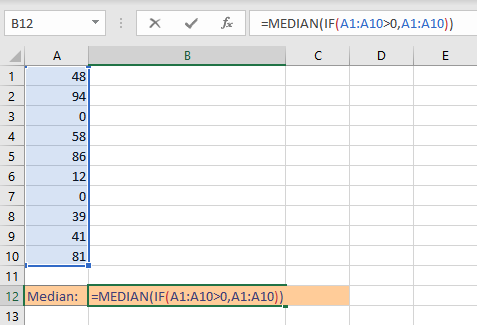
- Press Enter key to display the calculated median value of the numbers excluding zero values.
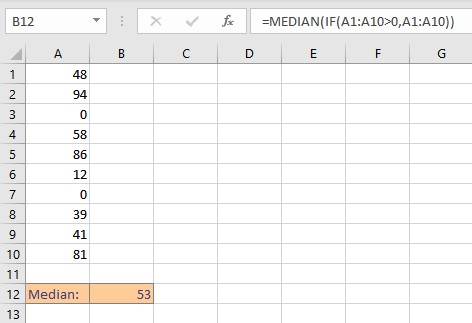
To illustrate the difference in the median, we calculated the mean of the above dataset including zeroes.
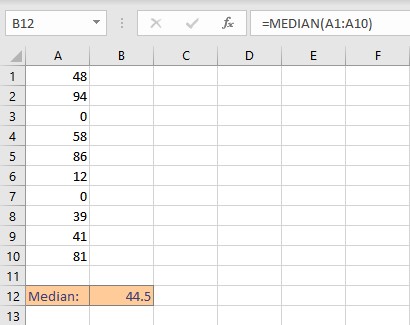
As you can see, the median is different in both cases.
Finding mode in Excel
The mode is a statistical term that refers to the most frequently occurring number found in a set of numbers. A data set can have none, one, or multiple modes. In Excel, there are three functions to find the mode/modes of a dataset which are discussed below:
Using the MODE function
This function returns a single mode. Syntax: MODE(n), where n is the list of numbers or reference to the cell ranges containing the numbers. Follow these steps to find the mode of a dataset using the MODE function:
- Go to the cell where you want to display the mode value.
- Type =MODE(, select the cells containing the numbers and complete the formula with ).
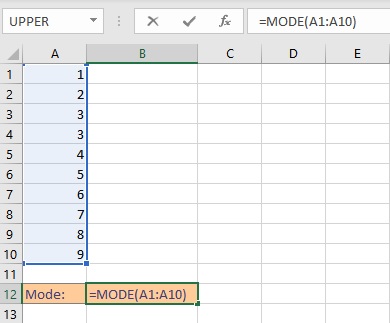
- Press Enter key to display the result.
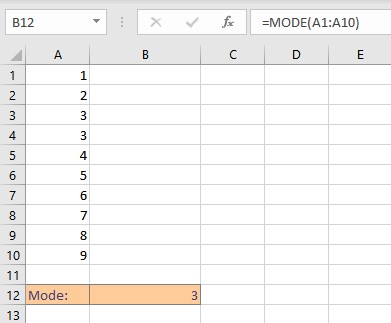
Note:
- If the data set contains no data value that has at least one duplicate value, the MODE function returns the #N/A error value.
- The MODE function ignores empty cells as well as cells containing text or logical values.
Using the MODE.MULT function
This function returns more than one result if there are multiple modes in the dataset. Syntax: MODE.MULT(n), where n is the list of numbers or reference to the cell ranges containing the numbers. Follow these steps to find the Mode of a dataset using the MODE.MULT function:
- Go to the cell where you want to display the mode value.
- Type =MODE.MULT(, select the cells containing the numbers and complete the formula with ).
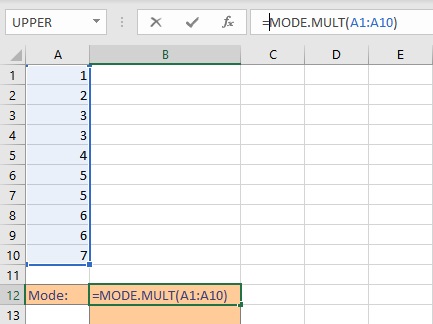
- Press Enter key to display the result.
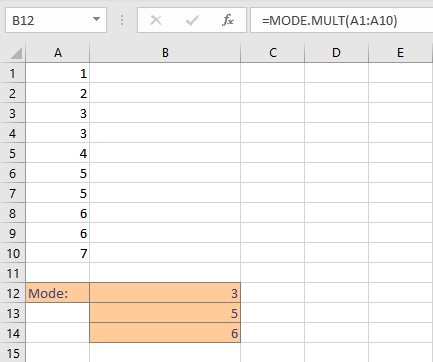
Note:
- If the data set contains no data value that has at least one duplicate value, the MODE.MULT function returns the #N/A error value.
- The MODE.MULT function ignores empty cells as well as cells containing text or logical values.
Using the MODE.SNGL function
This function is an advanced version of the MODE function and returns a single most frequently occurring value in a dataset. Syntax: MODE.SNGL(n), where n is the list of numbers or reference to the cell ranges containing the numbers. Follow these steps to find the mode of a dataset using the MODE.SNGL function:
- Go to the cell where you want to display the mode value.
- Type =MODE.SNGL(, select the cells containing the numbers and complete the formula with ).
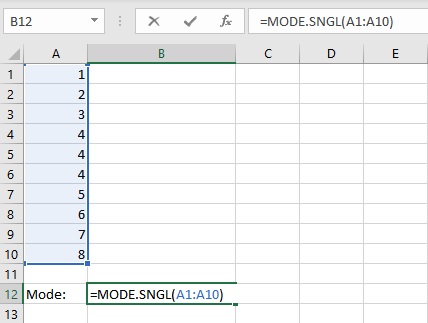
- Press the Enter key to display the result.
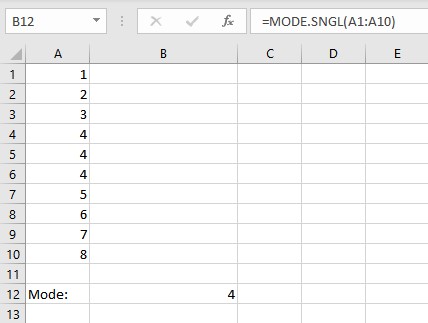
Note:
- If the data set contains no data value that has at least one duplicate value, the MODE.SNGL function returns the #N/A error value.
- The MODE.SNGL function ignores empty cells as well as cells containing text or logical values.
Conclusion
We discussed simple and quick ways of calculating the median and the mode of a dataset in Excel.
MEDIAN function in Excel is used to analyze a range of numeric values and returns a number that is the midpoint of the set being examined. That is, this function conditionally divides the set of numbers into two subsets, the first of which contains numbers less than the median, and the second — more. This is one of several methods for determining the central trend of the range studied.
Examples of using the MEDIAN function in Excel
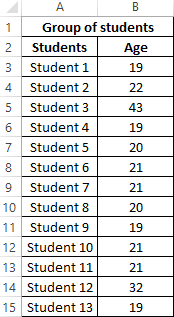
Example 1. In the study of age groups of students used data from a randomly selected group of students in the university. The task is to determine the average age of students.
Initial data:
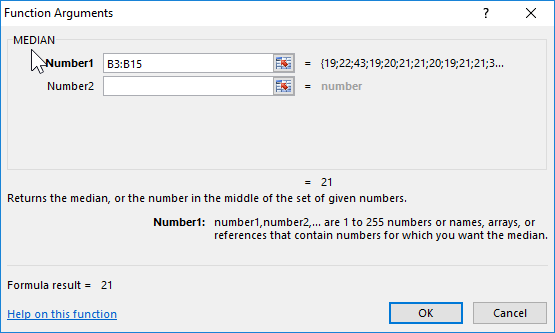
The formula for calculating:
Argument Description:
- B3:B15 — the range of the investigated ages.
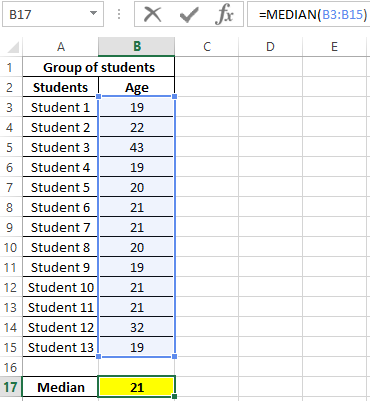
The result:
That is, there are students in the group whose age is less than 21 years and more than this value.
Comparison of MEDIAN and average functions to calculate the average
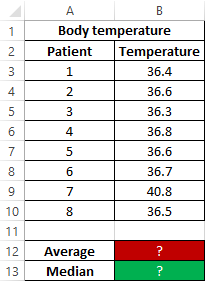
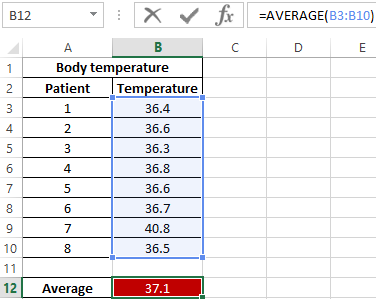
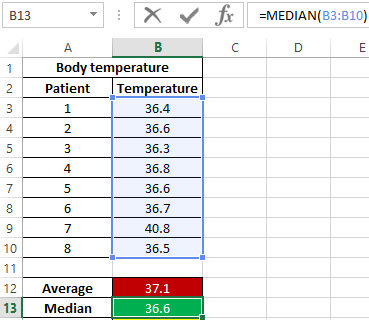
Example 2. During the evening tour in the hospital, each patient was measured body temperature. Demonstrate the feasibility of using the parameter median instead of the average value for the study of a number of values obtained.
Initial data:
The formula for finding the average value:
The formula for finding the median value:
As can be seen from the average value, the average temperature in patients is above the norm, but this is not true. The median shows that at least half of the patients have a normal body temperature that does not exceed 36.6.
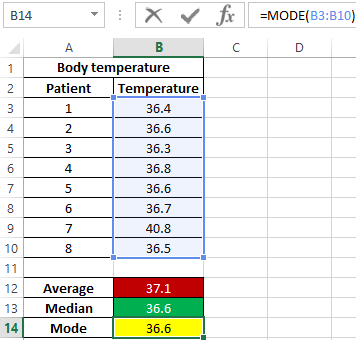
Attention! Another method for determining the central trend is fashion (the most common value in the range under study). To determine the central trend in Excel, use the MODE function. In this example, the values of the median and the mode are the same:
That is, the median value dividing one set into subsets of smaller and larger values is also the most frequently occurring value in the set. As can be seen, in most patients the temperature is 36.6.
Example of calculating the MEDIAN for statistical analysis in Excel
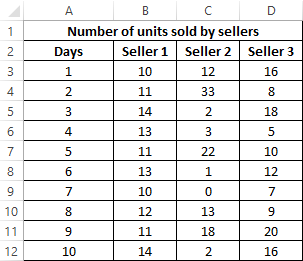
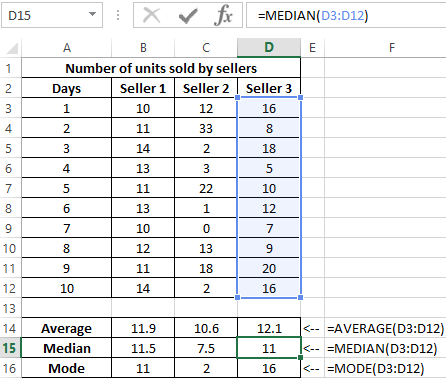
Example 3. The store has 3 sellers. According to the results of the last 10 days, it is necessary to determine the employee who will receive the award. When choosing the best employee, the degree of effectiveness of his work, and not the number of goods sold, is taken into account.
Source data table:
To characterize the efficiency, we will use three indicators at once: the average value, the median and the mode. We define them for each employee using the formula AVERAGE, MEDIAN and MODE, respectively:
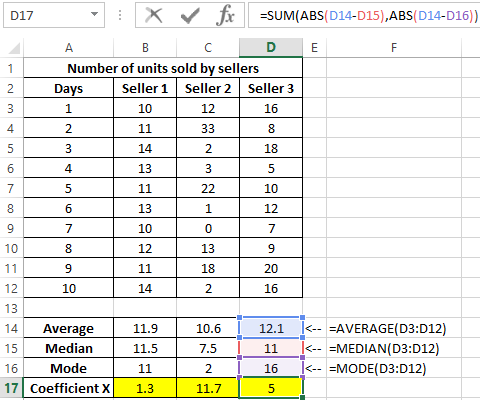
To determine the degree of scatter of data, we use a value that is the total value of the modulus of the difference between the mean and the mode, the mean and the median, respectively. That is, the coefficient x = | av-med | + | av-mod |, where:
- av is average;
- med is median;
- mod is a mode.
Calculate the value of the coefficient x for the first seller:
Similarly, we will carry out calculations for the remaining sellers. Results:
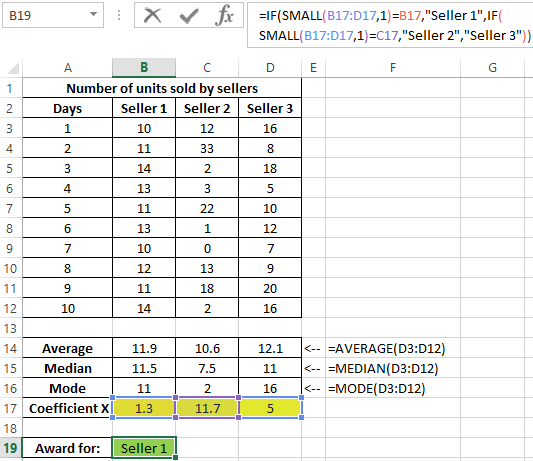
Determine the seller to whom the bonus will be issued:
Note: the SMALL function returns the first minimum value from the considered range of x values.
The coefficient x is a quantitative characteristic of the stability of the work of sellers, which was introduced by the economist of the store. With its help, it was possible to determine the range with the smallest deviations of values. This method demonstrates how three methods of determining the central tendency can be used at once to obtain the most reliable results.
Features of using the MEDIAN function in Excel
The function has the following syntax:
=MEDIAN(number1,[number2],…)
Argument Description:
- number1 is a required argument characterizing the first numerical value contained in the range under study;
- [num2] — optional second (and subsequent arguments, up to 255 arguments in total), characterizing the second and subsequent values of the studied range.
Notes 1:
- When calculating, it is more convenient to transfer the whole range of values under investigation instead of sequentially entering arguments.
- Arguments are data of a numeric type, names containing numbers, data of a reference type, and arrays (for example, =MEDIAN({1,2,3,5,7,10})).
- The calculation of the median takes into account cells containing empty values or logical TRUE, FALSE, which will be interpreted as numerical values 1 and 0, respectively. For example, the result of executing a function with logical values in arguments (TRUE,FALSE) is equivalent to the result of executing with arguments =MEDIAN(1,0) and is equal to 0.5.
- If one or more function arguments take text values that cannot be converted to numeric values, or contain error codes, the result of the function is the error code #VALUE!.
- Other Excel functions can be used to determine the median of the sample: PERCENTILE.INC, QUARTILE.INC, LARGE examples. Examples:
- =PERCENTILE.INC(A1:A10,0.5), since by definition the median is the 50th percentile.
- =QUARTILE.INC(A1:A10,2), since the median is the 2nd quartile.
- =LARGE(A1:A9,COUNT(A1:A9)/2), but only if the number of numbers in the range is an odd number.
Notes 2:
- If in the studied range all numbers are distributed symmetrically with respect to the average value, the arithmetic mean and median for this range will be equivalent.
- With large deviations of data in the range («spread» of values), the median better reflects the trend in the distribution of values than the arithmetic average. An excellent example is the use of a median to determine the real level of wages among the population of a state in which officials receive an order of magnitude more than ordinary citizens.
- The range of tested values may contain:
Download examples MEDIAN function in Excel
- Odd number of numbers. In this case, the median will be a single number dividing the range into two subsets of large and small values, respectively;
- Even number of numbers. Then is calculated as the arithmetic average for two numerical values dividing the set into the two subsets indicated above.