Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 More…Less
If you have tasks in Microsoft Excel that you do repeatedly, you can record a macro to automate those tasks. A macro is an action or a set of actions that you can run as many times as you want. When you create a macro, you are recording your mouse clicks and keystrokes. After you create a macro, you can edit it to make minor changes to the way it works.
Suppose that every month, you create a report for your accounting manager. You want to format the names of the customers with overdue accounts in red, and also apply bold formatting. You can create and then run a macro that quickly applies these formatting changes to the cells you select.
How?
|
|
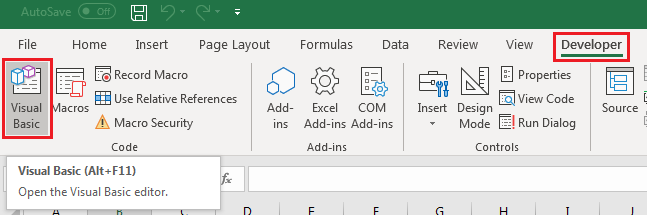
Before you record a macro Macros and VBA tools can be found on the Developer tab, which is hidden by default, so the first step is to enable it. For more information, see Show the Developer tab. |
|
|
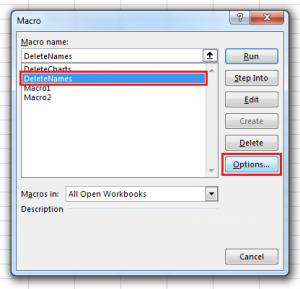
Record a macro
|
|
|
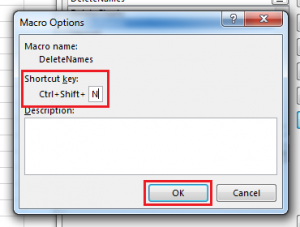
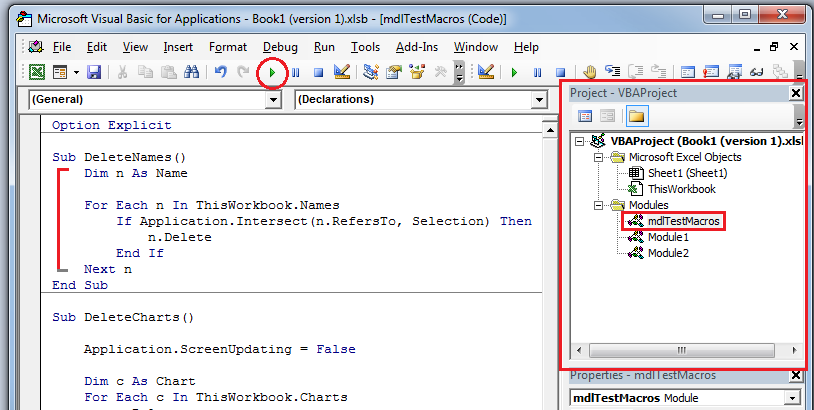
Take a closer look at the macro You can learn a little about the Visual Basic programming language by editing a macro. To edit a macro, in the Code group on the Developer tab, click Macros, select the name of the macro, and click Edit. This starts the Visual Basic Editor. See how the actions that you recorded appear as code. Some of the code will probably be clear to you, and some of it may be a little mysterious. Experiment with the code, close the Visual Basic Editor, and run your macro again. This time, see if anything different happens! |
Next steps
-
To learn more about creating macros, see Create or delete a macro.
-
To learn about how to run a macro, see Run a macro.
How?
|
|
Before you record a macro Make sure the Developer tab is visible on the ribbon. By default, the Developer tab is not visible, so do the following:
|
|
|
Record a macro
|
|
|
Take a closer look at the macro You can learn a little about the Visual Basic programming language by editing a macro. To edit a macro, in the Developer tab, click Macros, select the name of the macro, and click Edit. This starts the Visual Basic Editor. See how the actions that you recorded appear as code. Some of the code will probably be clear to you, and some of it may be a little mysterious. Experiment with the code, close the Visual Basic Editor, and run your macro again. This time, see if anything different happens! |
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Need more help?
Download Article
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to enable, create, run, and save macros in Microsoft Excel. Macros are miniature programs which allow you to perform complex tasks, such as calculating formulas or creating charts, within Excel. Macros can save significant amounts of time when applied to repetitive tasks, and thanks to Excel’s «Record Macro» feature, you don’t have to know anything about programming in order to create a macro.
Things You Should Know
- Macros make it easy to automatic tasks in Microsoft Excel.
- To create macros yourself, you’ll need to enable macros in the Developer menu of Excel.
- Saving a macro-enabled spreadsheet is a little different than saving a spreadsheet without macros.
-
1
Open Excel. Double-click the Excel app icon, which resembles a white «X» on a green box, then click Blank workbook.
- If you have a specific file which you want to open in Excel, double-click that file to open it instead.
-
2
Click File. It’s in the upper-left side of the Excel window.
- On a Mac, click Excel in the upper-left corner of the screen to prompt a drop-down menu.
Advertisement
-
3
Click Options. You’ll find this on the left side of the Excel window.
- On a Mac, you’ll click Preferences… in the drop-down menu.
-
4
Click Customize Ribbon. It’s on the left side of the Excel Options window.[1]
- On a Mac, click instead Ribbon & Toolbar in the Preferences window.
-
5
Check the «Developer» box. This box is near the bottom of the «Main Tabs» list of options.
-
6
Click OK. It’s at the bottom of the window. You can now use macros in Excel.
- On a Mac, you’ll click Save here instead.
Advertisement
-
1
Enter any necessary data. If you opened a blank workbook, enter any data which you want to use before proceeding.
- You can also close Excel and open a specific Excel file by double-clicking it.
-
2
Click the Developer tab. It’s at the top of the Excel window. Doing so opens a toolbar here.
-
3
Click Record Macro. It’s in the toolbar. A pop-up window will appear.
-
4
Enter a name for the macro. In the «Macro name» text box, type in the name for your macro. This will help you identify the macro later.
-
5
Create a shortcut key combination if you like. Press the ⇧ Shift key along with another letter key (e.g., the E key) to create the keyboard shortcut. You can use this keyboard shortcut to run the macro later.
- On a Mac, the shortcut key combination will end up being ⌥ Option+⌘ Command and your key (e.g., ⌥ Option+⌘ Command+T).
-
6
Click the «Store macro in» drop-down box. It’s in the middle of the window. Doing so prompts a drop-down menu.
-
7
Click This Workbook. This option is in the drop-down menu. Your macro will be stored inside your spreadsheet, making it possible for anyone who has the spreadsheet to access the macro.
-
8
Click OK. It’s at the bottom of the window. Doing this saves your macro settings and begins recording.
-
9
Perform the macro’s steps. Any step you perform between clicking OK and clicking Stop Recording while be added to the macro. For example, if you wanted to create a macro which turns two columns’ worth of data into a chart, you would do the following:
- Click and drag your mouse across the data to select it.
- Click Insert
- Select a chart shape.
- Click the chart that you want to use.
-
10
Click Stop Recording. It’s in the Developer toolbar. This will save your macro.
Advertisement
-
1
Understand why you have to save the spreadsheet with macros enabled. If you don’t save your spreadsheet as a macro-enabled spreadsheet (XLSM format), the macro won’t be saved as part of the spreadsheet, meaning that other people on different computers won’t be able to use your macro if you send the workbook to them.
-
2
Click File. It’s in the upper-left corner of the Excel window (Windows) or the screen (Mac). Doing so will prompt a drop-down menu.
-
3
Click Save As. This option is on the left side of the window (Windows) or in the drop-down menu (Mac).
-
4
Double-click This PC. It’s in the column of save locations near the left side of the window. A «Save As» window will open.
- Skip this step on a Mac.
-
5
Enter a name for your Excel file. In the «Name» text box, type in the name for your Excel spreadsheet.
-
6
Change the file format to XLSM. Click the «Save as type» drop-down box, then click Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook in the resulting drop-down menu.[2]
- On a Mac, you’ll replace the «xlsx» at the end of the file’s name with xlsm.
-
7
Select a save location. Click a folder in which you want to save the Excel file (e.g., Desktop).
- On a Mac, you must first click the «Where» drop-down box.
-
8
Click Save. It’s at the bottom of the window. Doing so will save your Excel spreadsheet to your selected location, and your macro will be saved along with it.
Advertisement
-
1
Open the macro-enabled spreadsheet. Double-click the spreadsheet that has the macro in it to open the spreadsheet in Excel.
-
2
Click Enable Content. It’s in a yellow bar at the top of the Excel window. This will unlock the spreadsheet and allow you to use the macro.
- If you don’t see this option, skip this step.
-
3
Click the Developer tab. This option is at the top of the Excel window.
- You can also just press the key combination you set for the macro. If you do so, the macro will run, and you can skip the rest of this method.
-
4
Click Macros. You’ll find it in the Developer tab’s toolbar. A pop-up window will open.
-
5
Select your macro. Click the name of the macro which you want to run.
-
6
Click Run. It’s on the right side of the window. Your macro will begin running.
-
7
Wait for the macro to finish running. Depending on how large your macro is, this can take several seconds.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Can I use a macro that I create in other spreadsheets and future spreadsheets on the same pc?
Yes, you can use a macro that you crate in other spreadsheets and future spreadsheets on the same pc.
-
Question
How can I write macros that will change a spreadsheet as soon as I create it?
You will first need a basic understanding of VBA. There are many tutorials on this.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
Macros are generally useful for automating tasks which you must perform often, such as calculating payroll at the end of the week.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Although most macros are benign, some macros can maliciously change or delete information on your computer. Never open a macro from a source which you don’t trust.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Enable Developer options in Excel.
2. Click the Developer tab.
3. Click Record Macro.
4. Enter the macro name and details.
5. Click OK.
6. Perform the macro’s steps.
7. Click Stop Recording.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 710,278 times.
Is this article up to date?
How to Create Macros in Excel: Step-by-Step Tutorial (2023)
Get ready to have your mind blown! 🤯
Because in this tutorial, you learn how to create your own macros in Excel!
That’s right! And you don’t need to know VBA (Visual Basic for Applications)!
Instead, you will use the Excel macro recording feature to send your spreadsheet experience into overdrive! 🚀
So, read on and try it out yourself using this practice Excel workbook.
What are Excel macros?
A macro is a small program or set of actions that you can run repeatedly. Excel macros are used to automate repetitive tasks to save a lot of time and hassle.
For example, open and take a look at the practice Excel workbook.

Businesses would often have lists like this one. These are potential customers they might want to reach out to and market their products.
Notice how Columns C to H are just pieces of information extracted from Columns A & B.
(Learn how to extract strings from texts in this tutorial!)
To streamline the worksheet, you can hide Columns A & B. You can also hide the rest of the columns on the right starting from Column I.
Let’s do this using Excel macros!
How to record Excel macros
1. Click on the View tab in the Excel ribbon

2. Next, click on the Macros button on the right side of the View ribbon

3. This will open the Macros drop-down.
Click Record Macro.

4. Enter a name for your macro, something like Hide_Columns.

Excel macros can be stored in the Personal Macro Workbook. This is saved in the system files of Microsoft Excel and macros saved here can be used in other workbooks.
For this Excel macro tutorial, you only need to save the macros in the current Excel file.
4. Select Store macro in: This Workbook then click the OK button.
Excel is now recording your actions to create a macro.
5. Select Columns A & B and then right-click on the highlighted Column Bar to Hide them.

6. Then select Column I and press Ctrl + Shift + Right Arrow to include all remaining columns on the right.

7. Right-click on the highlighted Column Bar then click on Hide.
Your worksheet should now look like this:

To end the macro recording:
8. On the View ribbon, click on Macros and select Stop Recording.

Good job! 👏
You have created your first macro in Excel!
But wait, where is the recorded macro?
To view all of the available Excel macros :
1. Select View Macros.

2. This opens the Macro window. Saved macros will be listed here and you can Run whichever one you need.
You can also click on Edit to view the VBA code window.

3. The VBA code editor opens.

Notice the Hide_Columns Sub procedure. You don’t have to write or edit VBA code for the macro.
Excel automatically generated each code line based on the recorded keystrokes and mouse clicks.
The Record Macro feature is powerful enough for general spreadsheet automation needs.
But if you want to customize your own VBA macro, you can learn more about Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) here.
Using the Developer tab
Let’s record another macro to Unhide the hidden columns.
This time, you can record the macro from the Developer tab.
The Developer tab gives you access to a lot of useful Microsoft Excel features such as the Visual Basic Editor. It also allows you to quickly insert form controls such as buttons and checkboxes.
However, the Developer tab is not visible in the Excel ribbon by default.
To add it:
1. Right-click on the Excel ribbon.
Select Customize the Ribbon.

2. This opens the Customize Ribbon window.
On the right side, check the Developer tab checkbox.

3. You should now see the Developer tab.

To start recording the Unhide macro:
1. Click on the Record Macro button in the Developer tab.

2. Name this macro Unhide_Columns.

3. Click OK.
The recording has started.
4. Press Ctrl + A twice to select all cells.
5. Right-click anywhere on the Column Bar then click Unhide.

6. Click on the Stop Recording macro button to finish up.

Great work! 👌
Now you have two recorded macros that can be executed.
How to run an Excel macro
To run your macros:
1. Click on the Macros button from the Developer tab.

2. In the Macro window, select the macro Hide_Columns and click on Run.

The macro executes the actions recorded earlier and hides the unnecessary columns.
You can also run macros from the View ribbon.
Run Excel macro from the View tab
This time, run the Unhide_Columns to show all the columns.
1. On the View ribbon, click the Macros button and select View Macros.
2. Select the Unhide_Columns macro and Run it.

This unhides all the columns in the worksheet.
As you can see, the Macro window allows you to quickly run all the available macros.
But you can execute them even faster by using buttons and shortcuts ❗
Run Excel macro from a button
For this next example, you will assign macros to buttons which will be located on top of the table.
1. Insert 2 rows above the table headers. Select Row 1 then press Ctrl + Shift + Plus Sign(+) twice.

2. To create a button, click on Insert > Illustrations > Shapes.
Then select the Rectangle.

3. Draw a rectangle and format it as you’d like. Label it “HIDE”.

This will be your HIDE button. Place it between columns A & B so it will be hidden with the columns when the macro runs.
4. To assign a macro, right-click the shape and select Assign Macro.

5. In the Assign Macro window, select Hide_Columns and click OK.

The Hide button now works!
Now, do the same for the Unhide_Columns macro.
6. Create another rectangle button and label it “UNHIDE”.

7. Repeat Steps 4 & 5 but this time, assign the Unhide_Columns macro.
Alright! 👍
Now you can quickly run your macros using the HIDE and UNHIDE buttons.

Run Excel macro from a shortcut key
It is sometimes better to run macros using a keyboard shortcut.
For this next example, you want to quickly highlight people on the list that expressed interest in the business.
To create a macro for this:
1. Select any cell within the table.

2. On the Developer tab, toggle ON the Use Relative References button.

3. Start recording with the Record Macro button on the Developer tab.
Or, you can also click the Record Macro button on the Status Bar.

4. Name the macro Mark_Interested.
Then assign a shortcut key. For example, Ctrl + Q.

Click OK. The recording has now started.
4. Highlight the row of the Active Cell using the keyboard shortcut Shift + Space Bar.

When selecting cells or expanding selections while recording a macro, it is best to use keyboard shortcuts.
This is so that Excel can record the selections as relative references.
For example, if you select Row 4 by clicking on the Row Bar, Excel will record this as an absolute reference. This means it will always select Row 4 regardless of the currently Active Cell.
When you use the Shift + Space Bar shortcut instead, it tells Excel to select the row of the current Active Cell.
5. Apply the formatting:
- Fill using the color Green
- Change font color to White

6. End the macro recording from the Status Bar

All done!
Try to use the shortcut Ctrl + Q to quickly apply formatting to entire rows.

Saving macro-enabled workbooks
If you save the practice workbook, this window will pop up:

This is because the practice workbook is currently saved with the .xlsx file extension which does not support macro features.
To save properly, change it to the .xlsm file extension for macro-enable workbooks.
Keep this in mind when saving your work.
Congratulations! 🤩
You are now familiar with Excel macros.
Try to record your own macros and start saving time ⏱️ on your work!
That’s it – Now what?
The examples above are very useful though they are quite simple.
You can record macros for more complex functions. Such as creating custom charts or selectively copying rows of data to another workbook.
But recording and playing macros is just the tip of the iceberg.
With VBA programming, you get access to a whole different level of Excel automation. 🤖
And while Visual Basic may seem overwhelming at first, you can start slow with basic variables and IF statements. These are much easier than you might think!
Learn all that and much more in my free 30-minute online VBA course here.
Other resources
If you want to know more about the inner workings of the record macro feature, check out my Excel macro tutorial for beginners on YouTube.
You can also dive right into VBA by reading this article or watching this introductory video on VBA and macros!
Hope you enjoyed this article!
Kasper Langmann2023-01-19T12:25:15+00:00
Page load link
#Руководства
- 23 май 2022
-
0
Как с помощью макросов автоматизировать рутинные задачи в Excel? Какие команды они выполняют? Как создать макрос новичку? Разбираемся на примере.
Иллюстрация: Meery Mary для Skillbox Media
Рассказывает просто о сложных вещах из мира бизнеса и управления. До редактуры — пять лет в банке и три — в оценке имущества. Разбирается в Excel, финансах и корпоративной жизни.
Макрос (или макрокоманда) в Excel — алгоритм действий в программе, который объединён в одну команду. С помощью макроса можно выполнить несколько шагов в Excel, нажав на одну кнопку в меню или на сочетание клавиш.
Обычно макросы используют для автоматизации рутинной работы — вместо того чтобы выполнять десяток повторяющихся действий, пользователь записывает одну команду и затем запускает её, когда нужно совершить эти действия снова.
Например, если нужно добавить название компании в несколько десятков документов и отформатировать его вид под корпоративный дизайн, можно делать это в каждом документе отдельно, а можно записать ход действий при создании первого документа в макрос — и затем применить его ко всем остальным. Второй вариант будет гораздо проще и быстрее.
В статье разберёмся:
- как работают макросы и как с их помощью избавиться от рутины в Excel;
- какие способы создания макросов существуют и как подготовиться к их записи;
- как записать и запустить макрос начинающим пользователям — на примере со скриншотами.
Общий принцип работы макросов такой:
- Пользователь записывает последовательность действий, которые нужно выполнить в Excel, — о том, как это сделать, поговорим ниже.
- Excel обрабатывает эти действия и создаёт для них одну общую команду. Получается макрос.
- Пользователь запускает этот макрос, когда ему нужно выполнить эту же последовательность действий ещё раз. При записи макроса можно задать комбинацию клавиш или создать новую кнопку на главной панели Excel — если нажать на них, макрос запустится автоматически.
Макросы могут выполнять любые действия, которые в них запишет пользователь. Вот некоторые команды, которые они умеют делать в Excel:
- Автоматизировать повторяющиеся процедуры.
Например, если пользователю нужно каждый месяц собирать отчёты из нескольких файлов в один, а порядок действий каждый раз один и тот же, можно записать макрос и запускать его ежемесячно.
- Объединять работу нескольких программ Microsoft Office.
Например, с помощью одного макроса можно создать таблицу в Excel, вставить и сохранить её в документе Word и затем отправить в письме по Outlook.
- Искать ячейки с данными и переносить их в другие файлы.
Этот макрос пригодится, когда нужно найти информацию в нескольких объёмных документах. Макрос самостоятельно отыщет её и принесёт в заданный файл за несколько секунд.
- Форматировать таблицы и заполнять их текстом.
Например, если нужно привести несколько таблиц к одному виду и дополнить их новыми данными, можно записать макрос при форматировании первой таблицы и потом применить его ко всем остальным.
- Создавать шаблоны для ввода данных.
Команда подойдёт, когда, например, нужно создать анкету для сбора данных от сотрудников. С помощью макроса можно сформировать такой шаблон и разослать его по корпоративной почте.
- Создавать новые функции Excel.
Если пользователю понадобятся дополнительные функции, которых ещё нет в Excel, он сможет записать их самостоятельно. Все базовые функции Excel — это тоже макросы.
Все перечисленные команды, а также любые другие команды пользователя можно комбинировать друг с другом и на их основе создавать макросы под свои потребности.
В Excel и других программах Microsoft Office макросы создаются в виде кода на языке программирования VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). Этот язык разработан в Microsoft специально для программ компании — он представляет собой упрощённую версию языка Visual Basic. Но это не значит, что для записи макроса нужно уметь кодить.
Есть два способа создания макроса в Excel:
- Написать макрос вручную.
Это способ для продвинутых пользователей. Предполагается, что они откроют окно Visual Basic в Еxcel и самостоятельно напишут последовательность действий для макроса в виде кода.
- Записать макрос с помощью кнопки меню Excel.
Способ подойдёт новичкам. В этом варианте Excel запишет программный код вместо пользователя. Нужно нажать кнопку записи и выполнить все действия, которые планируется включить в макрос, и после этого остановить запись — Excel переведёт каждое действие и выдаст алгоритм на языке VBA.
Разберёмся на примере, как создать макрос с помощью второго способа.
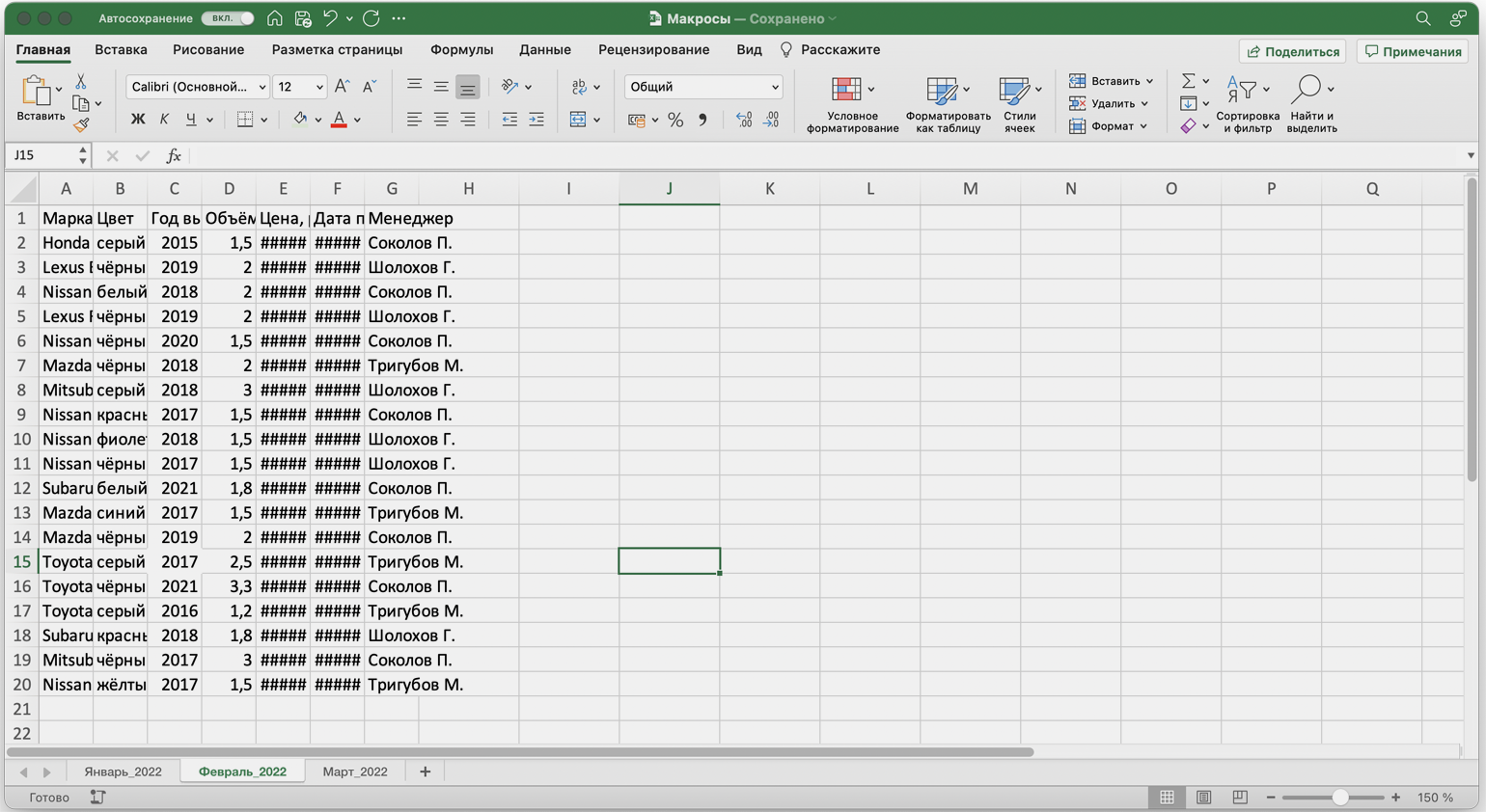
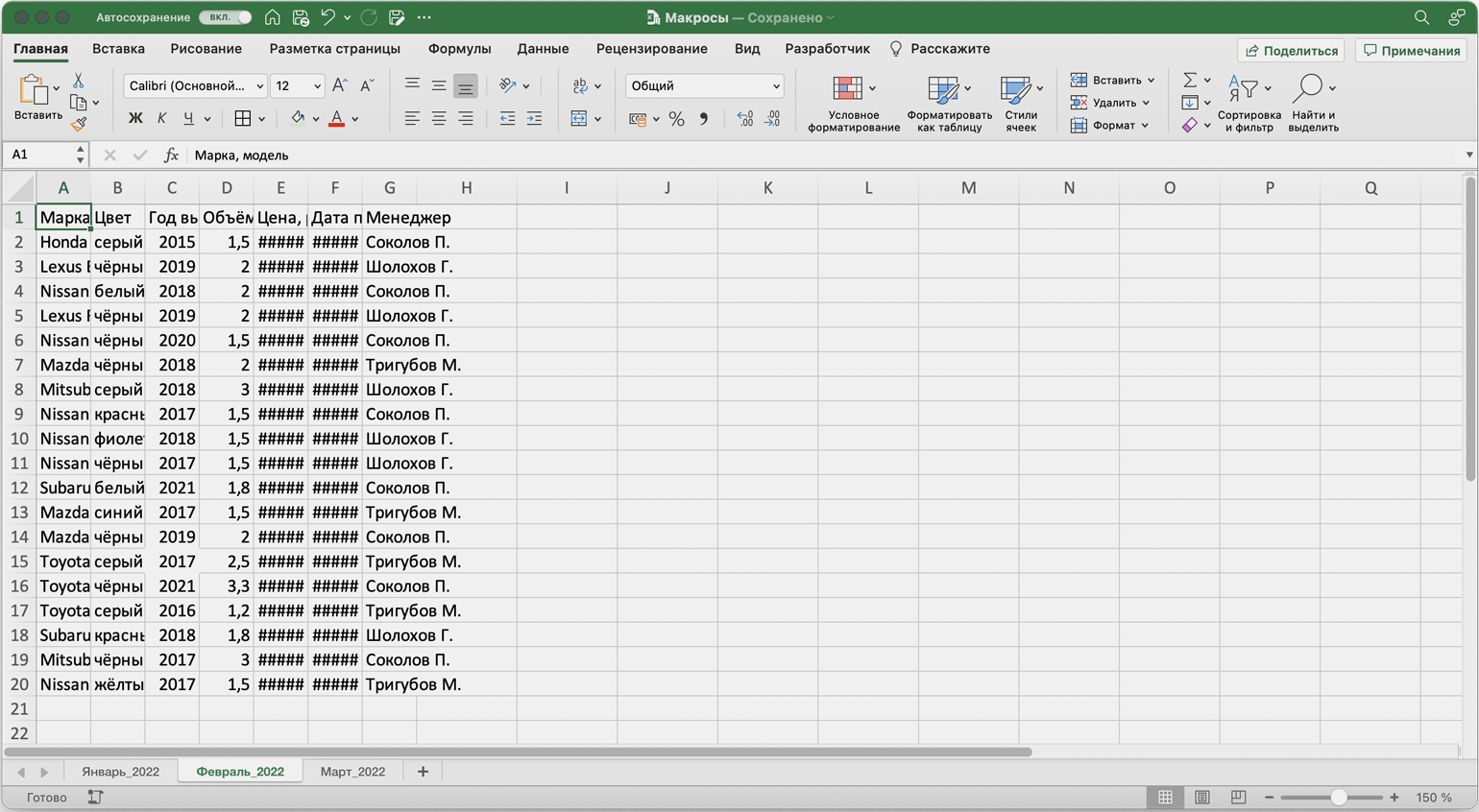
Допустим, специальный сервис автосалона выгрузил отчёт по продажам за три месяца первого квартала в формате таблиц Excel. Эти таблицы содержат всю необходимую информацию, но при этом никак не отформатированы: колонки слиплись друг с другом и не видны полностью, шапка таблицы не выделена и сливается с другими строками, часть данных не отображается.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Пользоваться таким отчётом неудобно — нужно сделать его наглядным. Запишем макрос при форматировании таблицы с продажами за январь и затем применим его к двум другим таблицам.
Готовимся к записи макроса
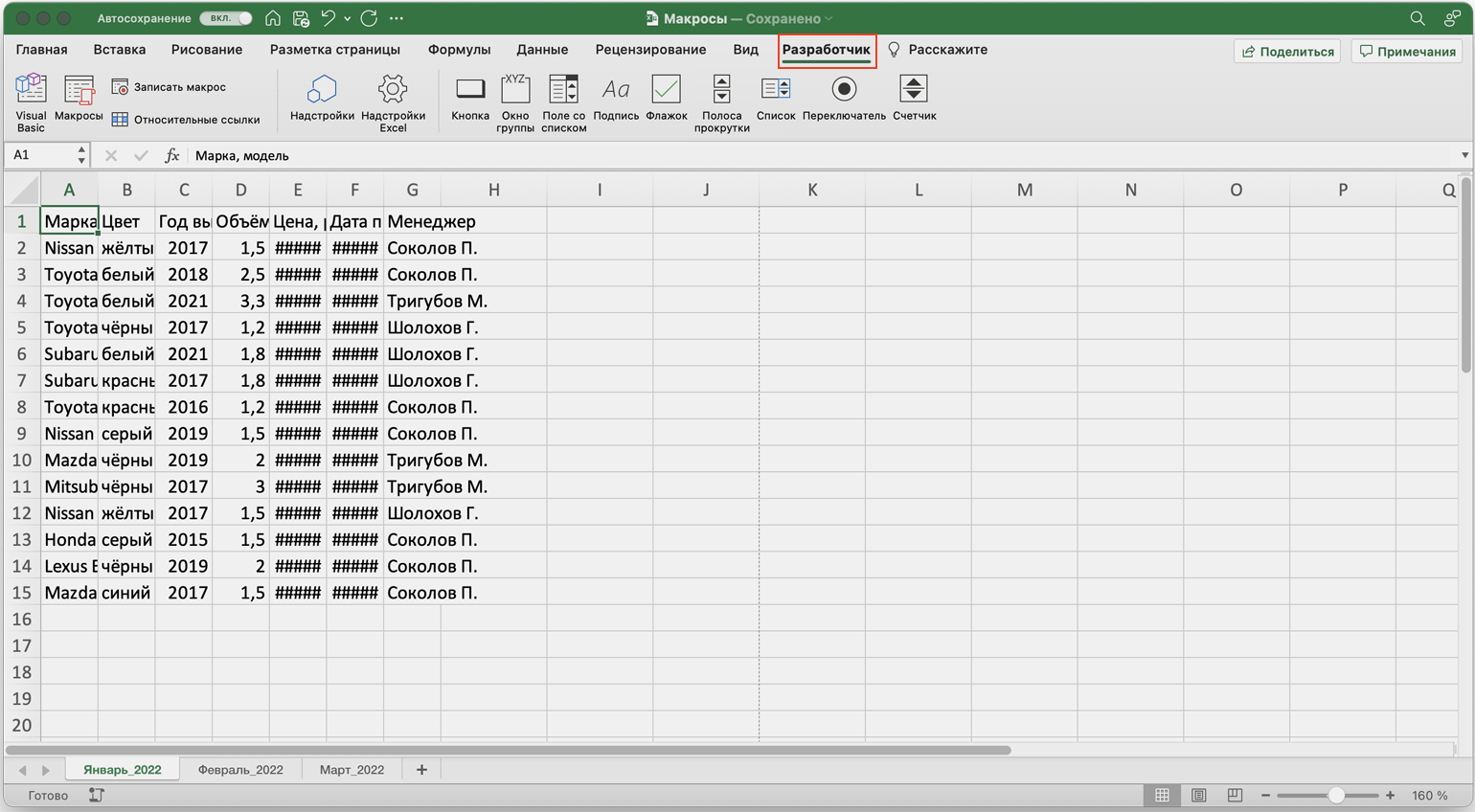
Кнопки для работы с макросами в Excel находятся во вкладке «Разработчик». Эта вкладка по умолчанию скрыта, поэтому для начала разблокируем её.
В операционной системе Windows это делается так: переходим во вкладку «Файл» и выбираем пункты «Параметры» → «Настройка ленты». В открывшемся окне в разделе «Основные вкладки» находим пункт «Разработчик», отмечаем его галочкой и нажимаем кнопку «ОК» → в основном меню Excel появляется новая вкладка «Разработчик».
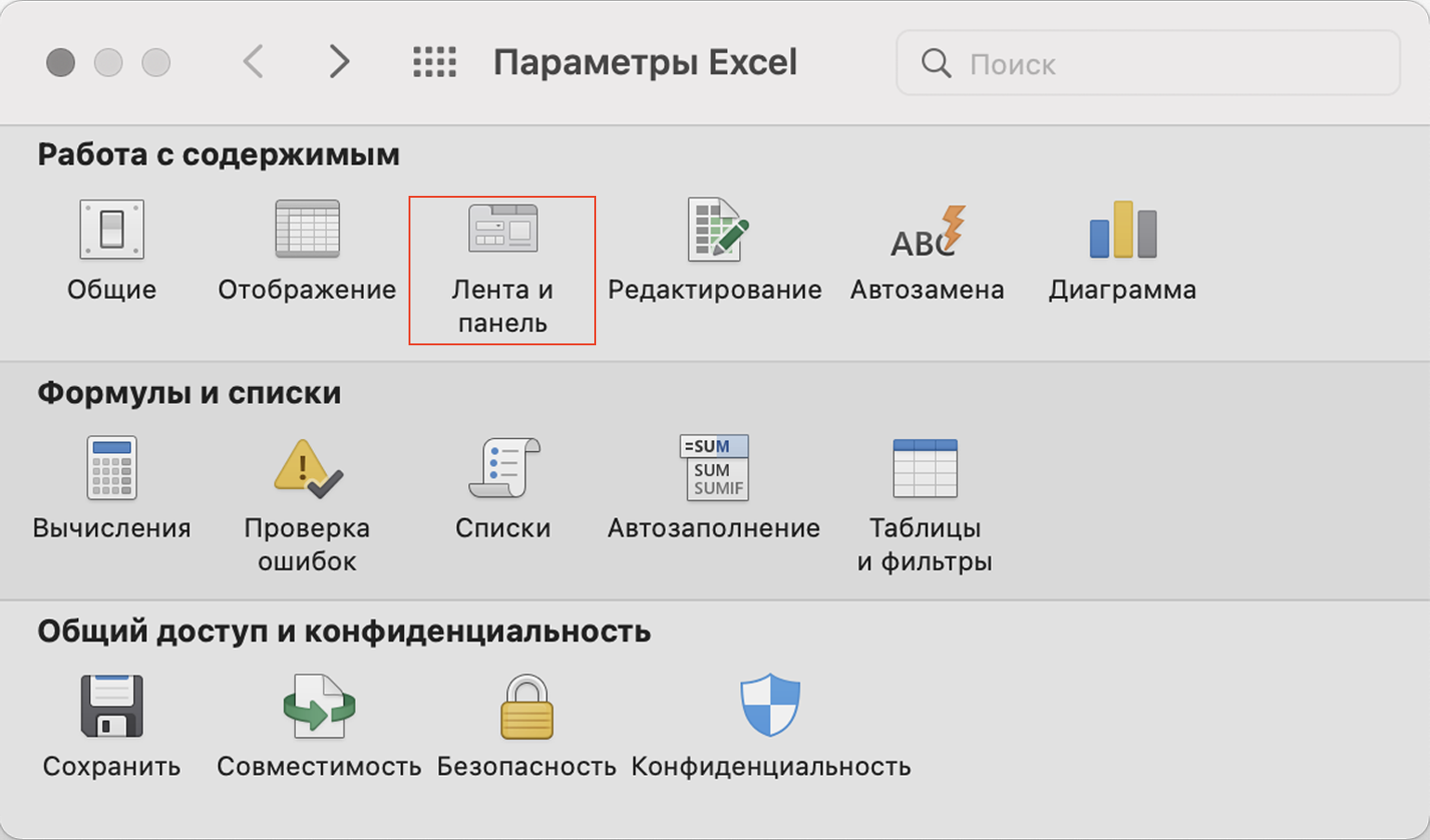
В операционной системе macOS это нужно делать по-другому. В самом верхнем меню нажимаем на вкладку «Excel» и выбираем пункт «Параметры…».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
В появившемся окне нажимаем кнопку «Лента и панель».
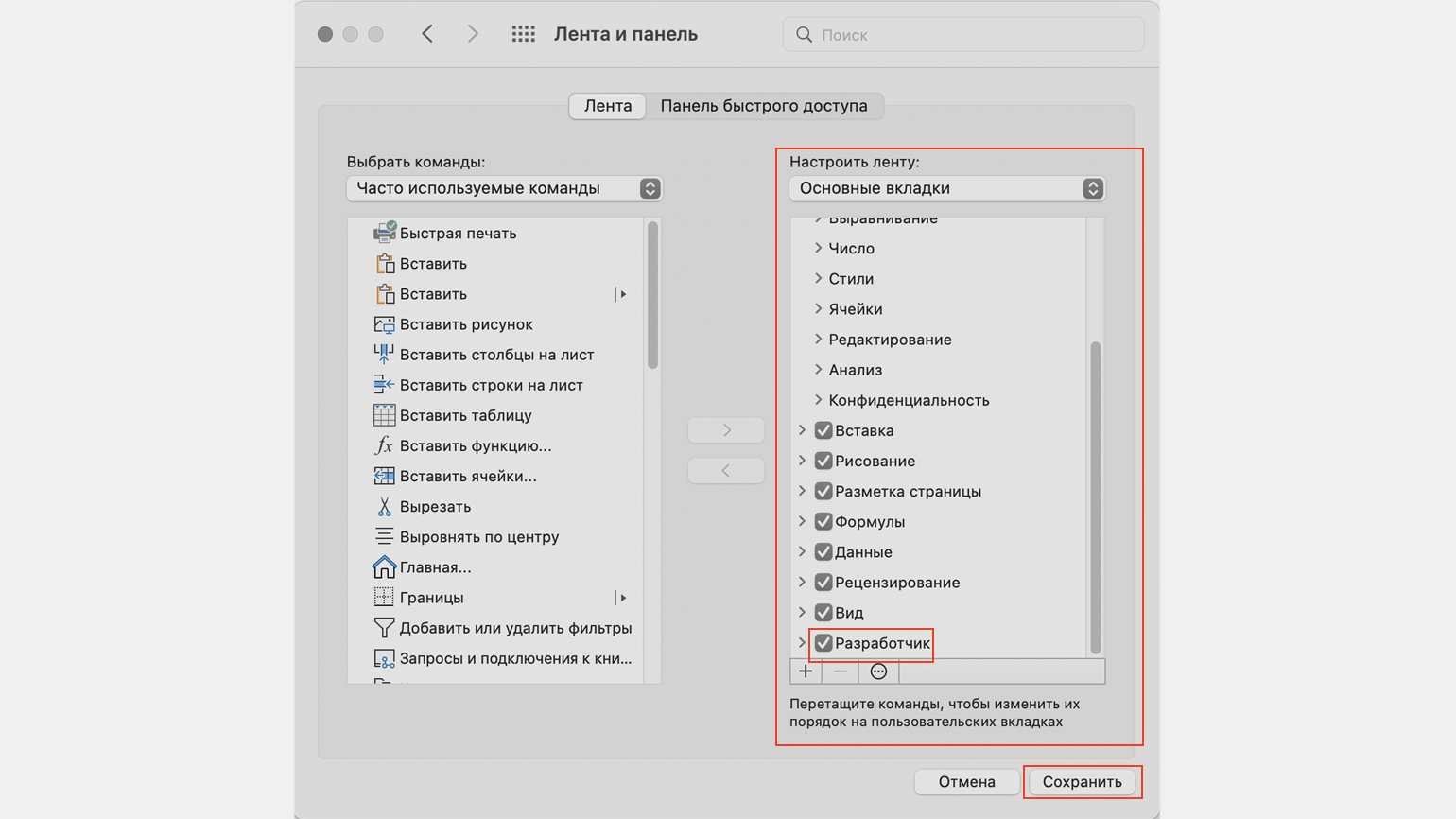
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Затем в правой панели «Настроить ленту» ищем пункт «Разработчик» и отмечаем его галочкой. Нажимаем «Сохранить».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Готово — вкладка «Разработчик» появилась на основной панели Excel.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
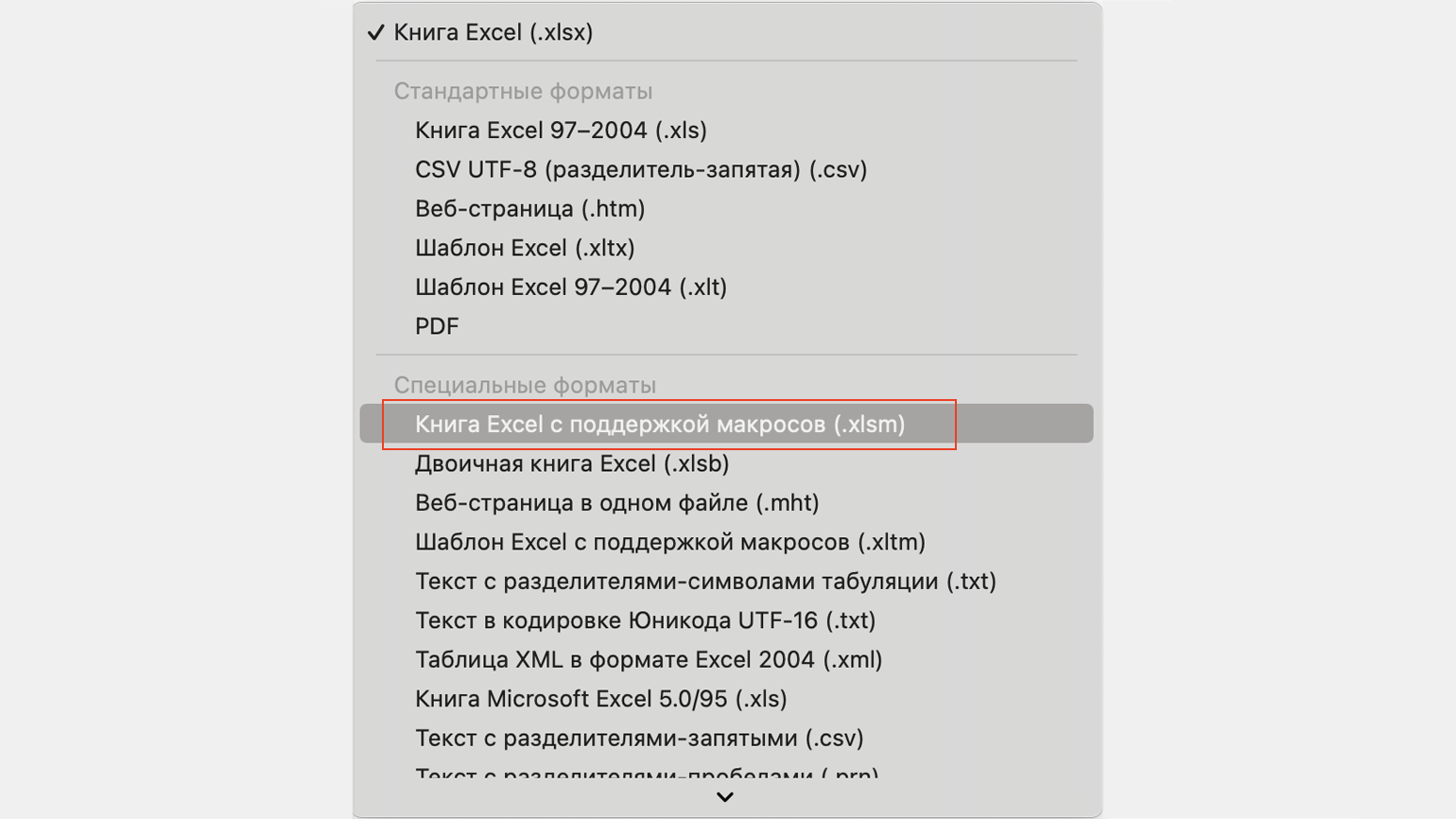
Чтобы Excel смог сохранить и в дальнейшем использовать макрос, нужно пересохранить документ в формате, который поддерживает макросы. Это делается через команду «Сохранить как» на главной панели. В появившемся меню нужно выбрать формат «Книга Excel с поддержкой макросов».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Перед началом записи макроса важно знать об особенностях его работы:
- Макрос записывает все действия пользователя.
После старта записи макрос начнёт регистрировать все клики мышки и все нажатия клавиш. Поэтому перед записью последовательности лучше хорошо отработать её, чтобы не добавлять лишних действий и не удлинять код. Если требуется записать длинную последовательность задач — лучше разбить её на несколько коротких и записать несколько макросов.
- Работу макроса нельзя отменить.
Все действия, которые выполняет запущенный макрос, остаются в файле навсегда. Поэтому перед тем, как запускать макрос в первый раз, лучше создать копию всего файла. Если что-то пойдёт не так, можно будет просто закрыть его и переписать макрос в созданной копии.
- Макрос выполняет свой алгоритм только для записанного диапазона таблиц.
Если при записи макроса пользователь выбирал диапазон таблицы, то и при запуске макроса в другом месте он выполнит свой алгоритм только в рамках этого диапазона. Если добавить новую строку, макрос к ней применяться не будет. Поэтому при записи макроса можно сразу выбирать большее количество строк — как это сделать, показываем ниже.
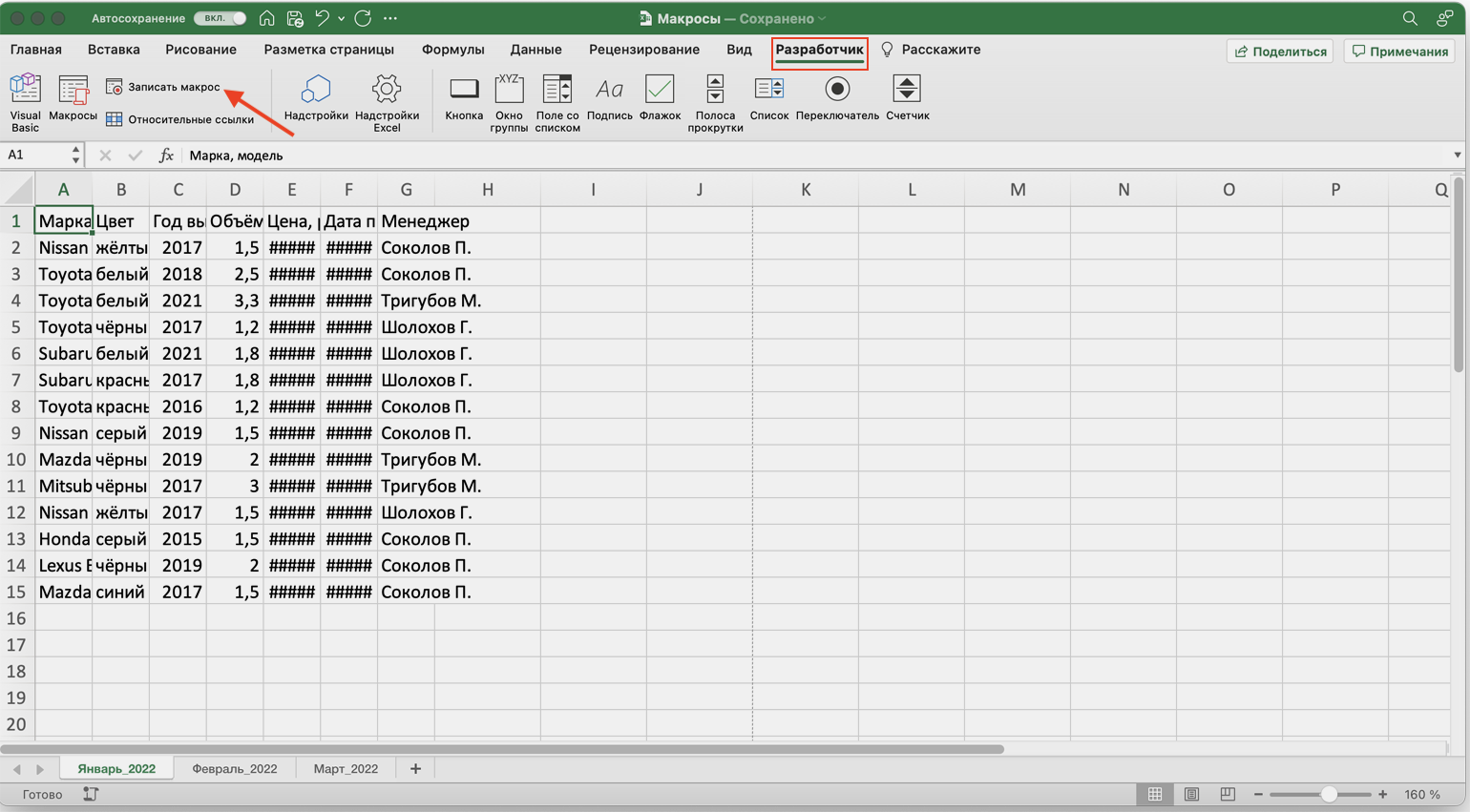
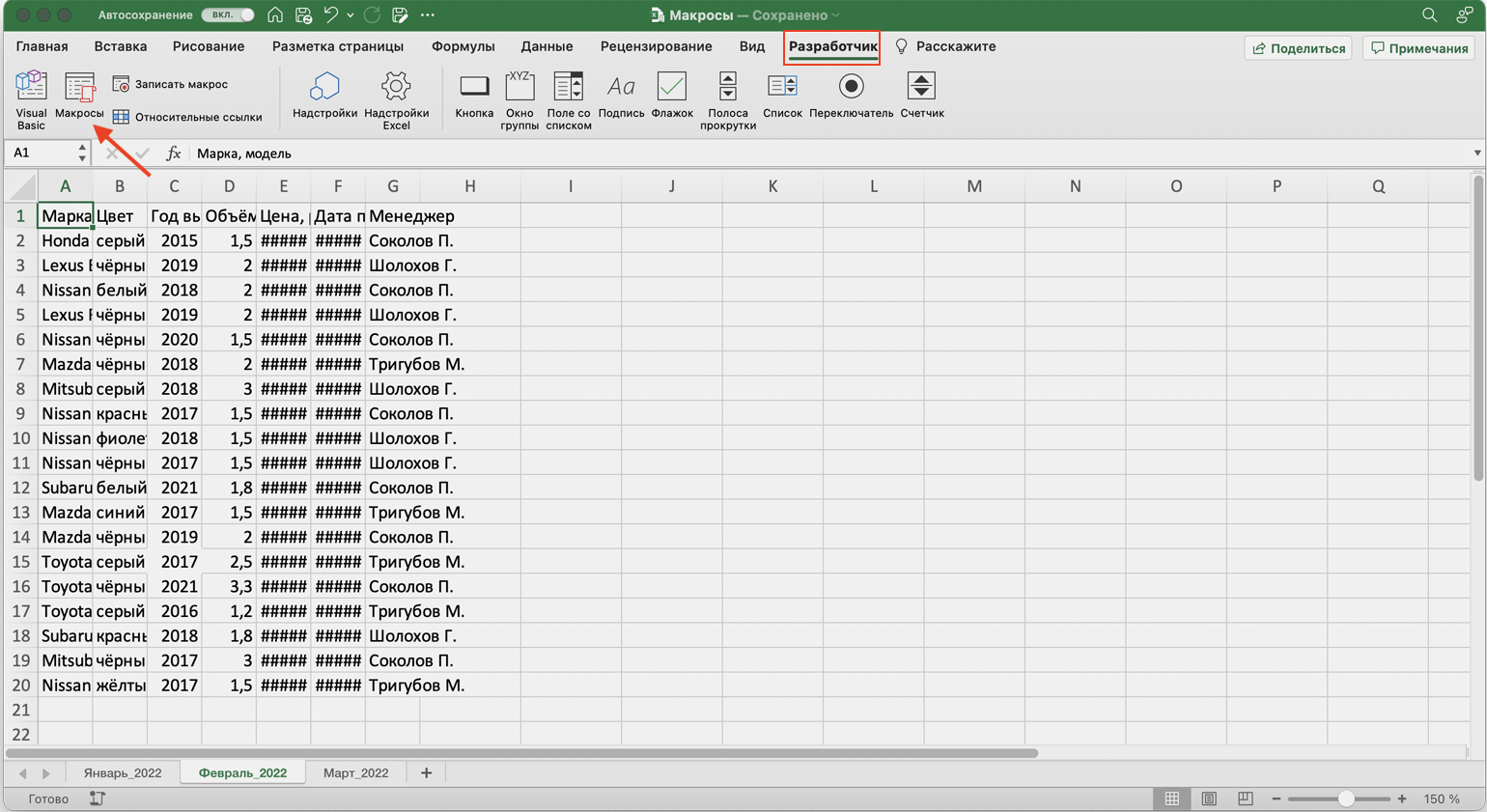
Для начала записи макроса перейдём на вкладку «Разработчик» и нажмём кнопку «Записать макрос».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
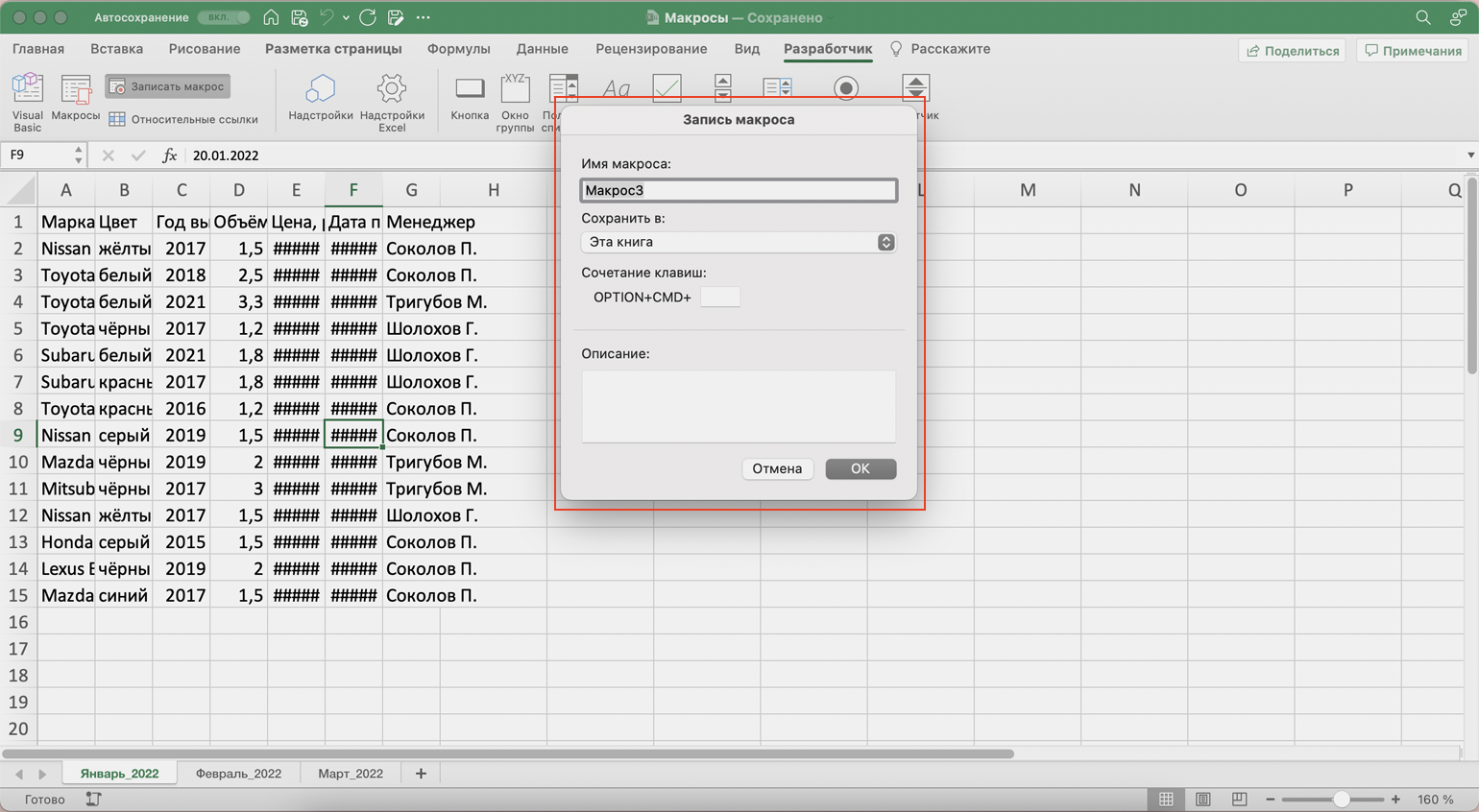
Появляется окно для заполнения параметров макроса. Нужно заполнить поля: «Имя макроса», «Сохранить в», «Сочетание клавиш», «Описание».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
«Имя макроса» — здесь нужно придумать и ввести название для макроса. Лучше сделать его логически понятным, чтобы в дальнейшем можно было быстро его найти.
Первым символом в названии обязательно должна быть буква. Другие символы могут быть буквами или цифрами. Важно не использовать пробелы в названии — их можно заменить символом подчёркивания.
«Сохранить в» — здесь нужно выбрать книгу, в которую макрос сохранится после записи.
Если выбрать параметр «Эта книга», макрос будет доступен при работе только в этом файле Excel. Чтобы макрос был доступен всегда, нужно выбрать параметр «Личная книга макросов» — Excel создаст личную книгу макросов и сохранит новый макрос в неё.
«Сочетание клавиш» — здесь к уже выбранным двум клавишам (Ctrl + Shift в системе Windows и Option + Cmd в системе macOS) нужно добавить третью клавишу. Это должна быть строчная или прописная буква, которую ещё не используют в других быстрых командах компьютера или программы Excel.
В дальнейшем при нажатии этих трёх клавиш записанный макрос будет запускаться автоматически.
«Описание» — необязательное поле, но лучше его заполнять. Например, можно ввести туда последовательность действий, которые планируется записать в этом макросе. Так не придётся вспоминать, какие именно команды выполнит этот макрос, если нужно будет запустить его позже. Плюс будет проще ориентироваться среди других макросов.
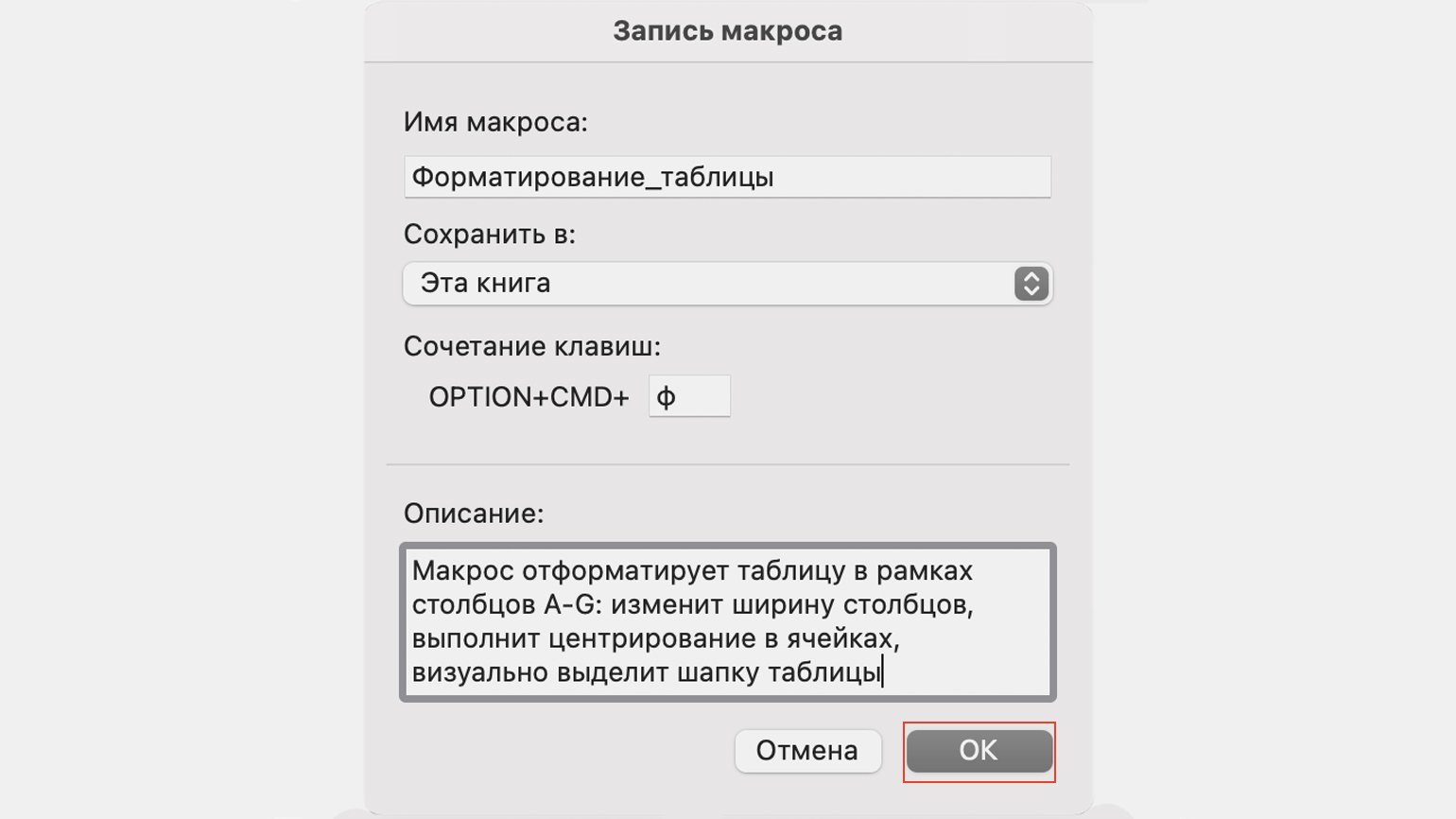
В нашем случае с форматированием таблицы заполним поля записи макроса следующим образом и нажмём «ОК».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
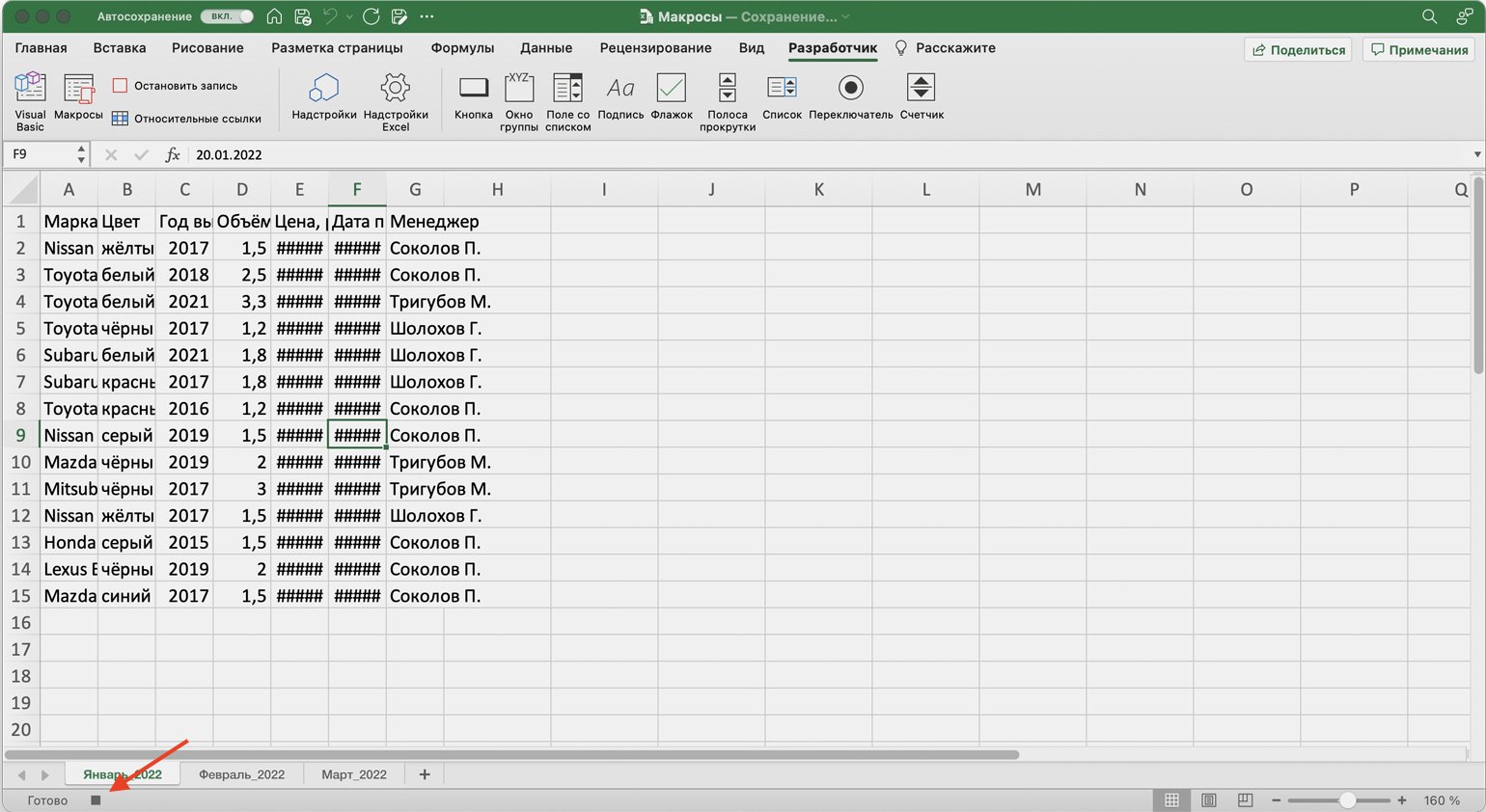
После этого начнётся запись макроса — в нижнем левом углу окна Excel появится значок записи.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Пока идёт запись, форматируем таблицу с продажами за январь: меняем ширину всех столбцов, данные во всех ячейках располагаем по центру, выделяем шапку таблицы цветом и жирным шрифтом, рисуем границы.
Важно: в нашем случае у таблиц продаж за январь, февраль и март одинаковое количество столбцов, но разное количество строк. Чтобы в случае со второй и третьей таблицей макрос сработал корректно, при форматировании выделим диапазон так, чтобы в него попали не только строки самой таблицы, но и строки ниже неё. Для этого нужно выделить столбцы в строке с их буквенным обозначением A–G, как на рисунке ниже.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Если выбрать диапазон только в рамках первой таблицы, то после запуска макроса в таблице с большим количеством строк она отформатируется только частично.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
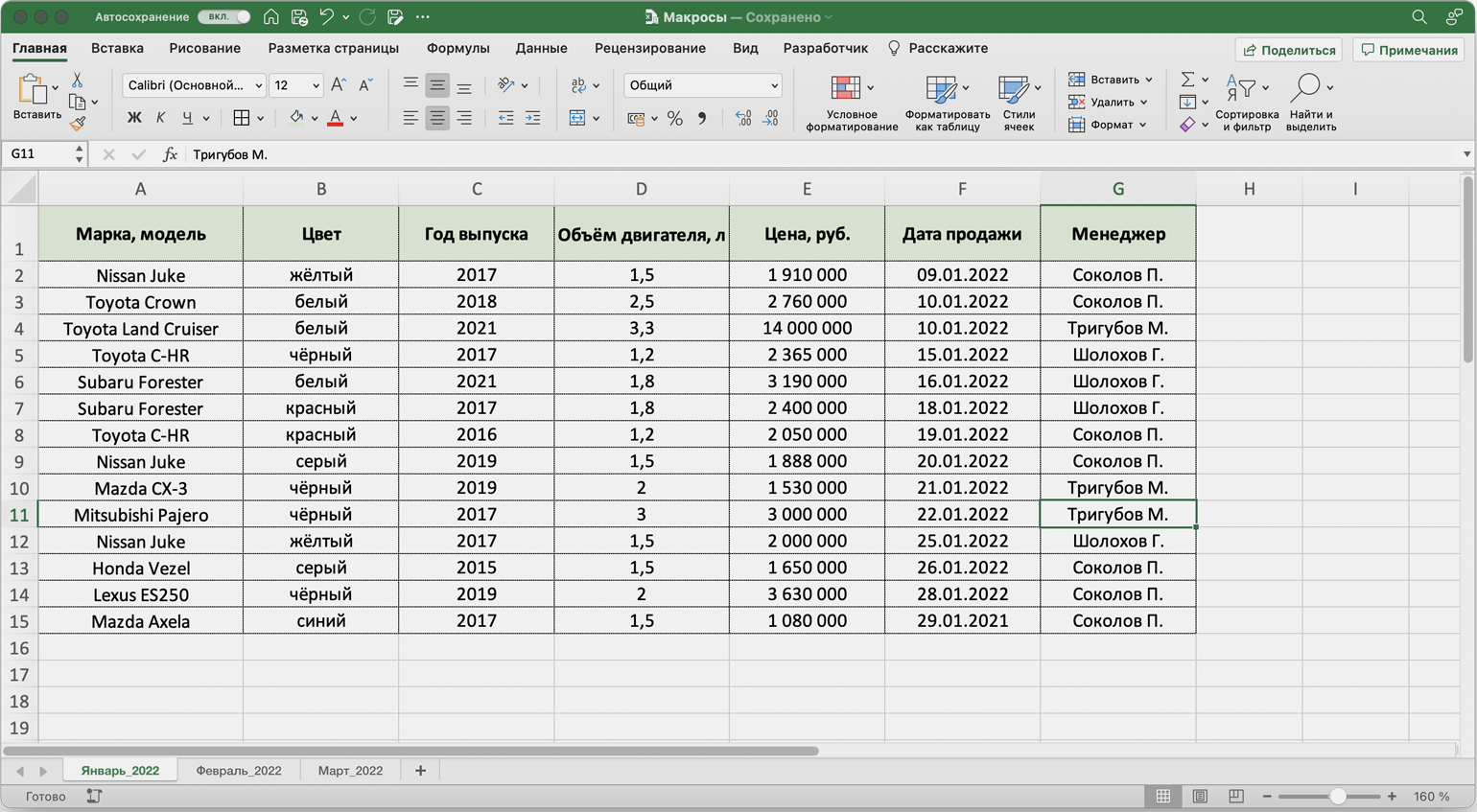
После всех манипуляций с оформлением таблица примет такой вид:
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Проверяем, все ли действия с таблицей мы выполнили, и останавливаем запись макроса. Сделать это можно двумя способами:
- Нажать на кнопку записи в нижнем левом углу.
- Перейти во вкладку «Разработчик» и нажать кнопку «Остановить запись».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Готово — мы создали макрос для форматирования таблиц в границах столбцов A–G. Теперь его можно применить к другим таблицам.
Запускаем макрос
Перейдём в лист со второй таблицей «Февраль_2022». В первоначальном виде она такая же нечитаемая, как и первая таблица до форматирования.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Отформатируем её с помощью записанного макроса. Запустить макрос можно двумя способами:
- Нажать комбинацию клавиш, которую выбрали при заполнении параметров макроса — в нашем случае Option + Cmd + Ф.
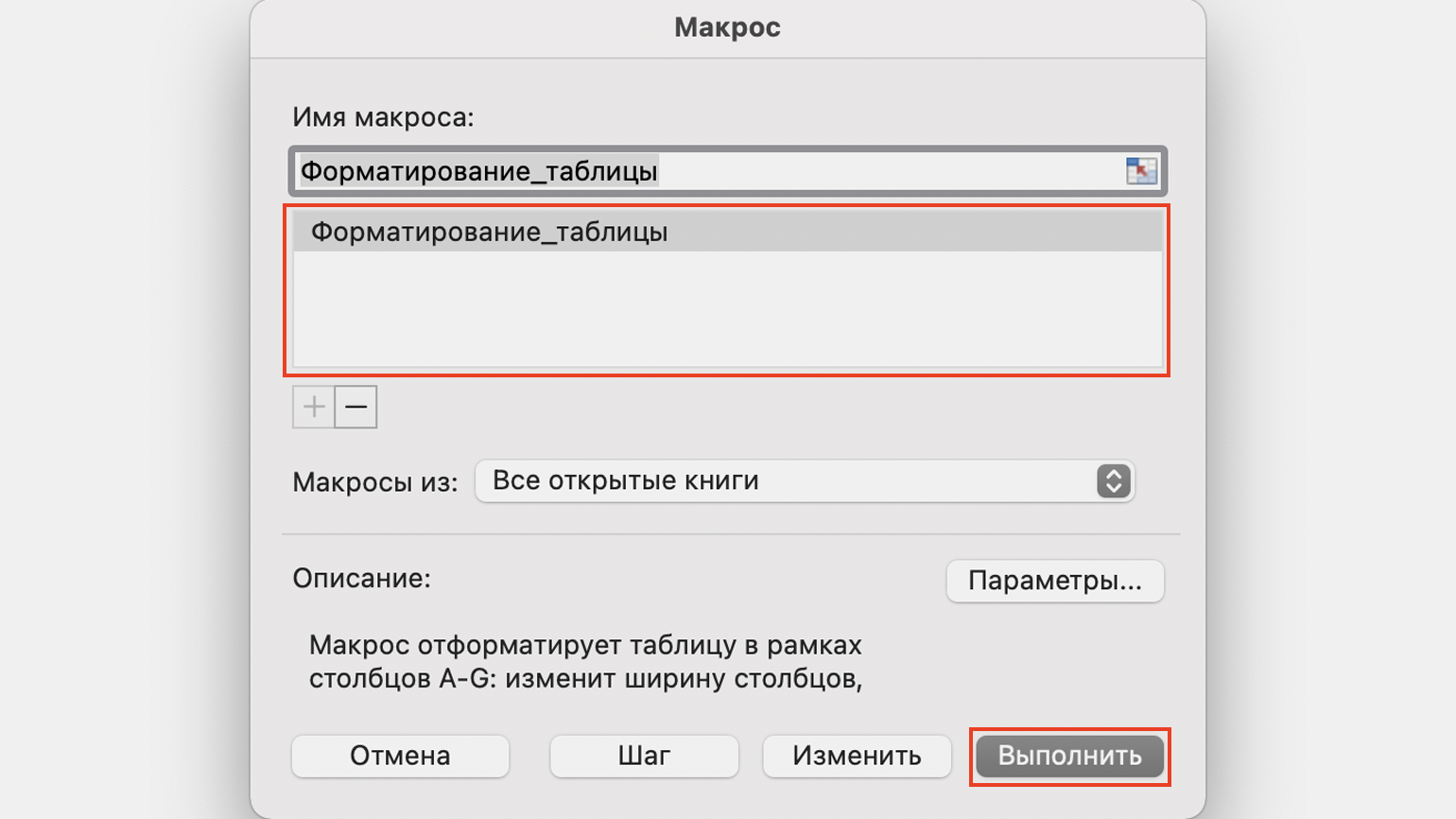
- Перейти во вкладку «Разработчик» и нажать кнопку «Макросы».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
Появляется окно — там выбираем макрос, который нужно запустить. В нашем случае он один — «Форматирование_таблицы». Под ним отображается описание того, какие действия он включает. Нажимаем «Выполнить».
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
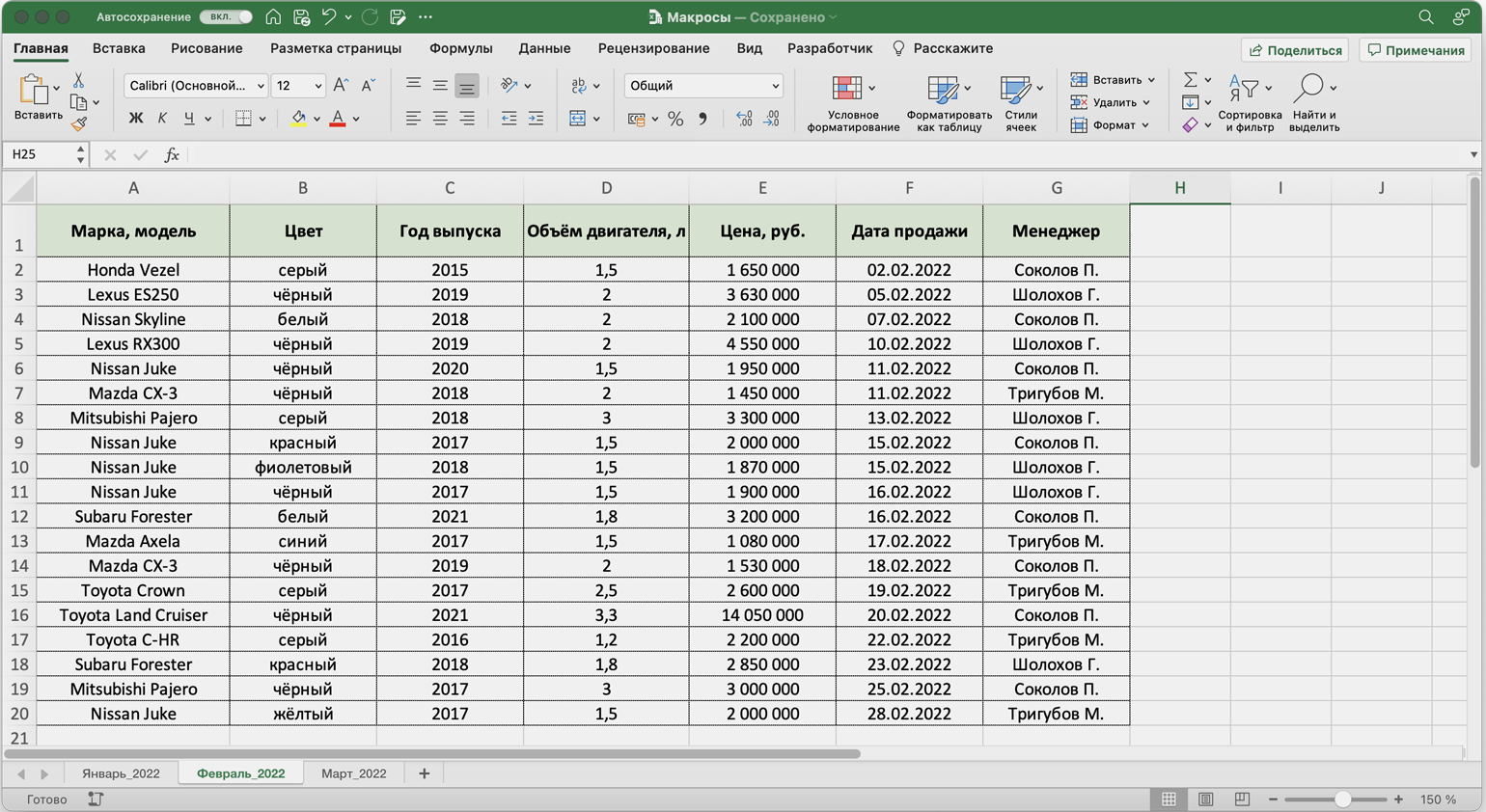
Готово — вторая таблица с помощью макроса форматируется так же, как и первая.
Скриншот: Skillbox Media
То же самое можно сделать и на третьем листе для таблицы продаж за март. Более того, этот же макрос можно будет запустить и в следующем квартале, когда сервис автосалона выгрузит таблицы с новыми данными.
Научитесь: Excel + Google Таблицы с нуля до PRO
Узнать больше
Excel Macro is a record and playback tool that simply records your Excel steps and the macro will play it back as many times as you want. VBA Macros save time as they automate repetitive tasks. It is a piece of programming code that runs in an Excel environment but you don’t need to be a coder to program macros. Though, you need basic knowledge of VBA to make advanced modifications in the macro.
In this Macros in Excel for beginners tutorial, you will learn Excel macro basics:
- What is an Excel Macro?
- Why are Excel Macros Used in Excel?
- What is VBA in a Layman’s Language?
- Excel Macro Basics
- Step by Step Example of Recording Macros in Excel
Why are Excel Macros Used in Excel?
As humans, we are creatures of habit. There are certain things that we do on a daily basis, every working day. Wouldn’t it be better if there were some magical way of pressing a single button and all of our routine tasks are done? I can hear you say yes. Macro in Excel helps you to achieve that. In a layman’s language, a macro is defined as a recording of your routine steps in Excel that you can replay using a single button.
For example, you are working as a cashier for a water utility company. Some of the customers pay through the bank and at the end of the day, you are required to download the data from the bank and format it in a manner that meets your business requirements.
You can import the data into Excel and format. The following day you will be required to perform the same ritual. It will soon become boring and tedious. Macros solve such problems by automating such routine tasks. You can use a macro to record the steps of
- Importing the data
- Formatting it to meet your business reporting requirements.
What is VBA in a Layman’s Language?
VBA is the acronym for Visual Basic for Applications. It is a programming language that Excel uses to record your steps as you perform routine tasks. You do not need to be a programmer or a very technical person to enjoy the benefits of macros in Excel. Excel has features that automatically generated the source code for you. Read the article on VBA for more details.
Excel Macro Basics
Macros are one of the developer features. By default, the tab for developers is not displayed in Excel. You will need to display it via customize report
Excel Macros can be used to compromise your system by attackers. By default, they are disabled in Excel. If you need to run macros, you will need to enable running macros and only run macros that you know come from a trusted source
If you want to save Excel macros, then you must save your workbook in a macro-enabled format *.xlsm
The macro name should not contain any spaces.
Always fill in the description of the macro when creating one. This will help you and others to understand what the macro is doing.
Step by Step Example of Recording Macros in Excel
Now in this Excel macros tutorial, we will learn how to create a macro in Excel:
We will work with the scenario described in the importance of macros Excel. For this Excel macro tutorial, we will work with the following CSV file to write macros in Excel.
You can download the above file here
Download the above CSV File & Macros
We will create a macro enabled template that will import the above data and format it to meet our business reporting requirements.
Enable Developer Option
To execute VBA program, you have to have access to developer option in Excel. Enable the developer option as shown in the below Excel macro example and pin it into your main ribbon in Excel.
Step 1)Go to main menu “FILE”
Select option “Options.”
Step 2) Now another window will open, in that window do following things
- Click on Customize Ribbon
- Mark the checker box for Developer option
- Click on OK button
Step 3) Developer Tab
You will now be able to see the DEVELOPER tab in the ribbon
Step 4) Download CSV
First, we will see how we can create a command button on the spreadsheet and execute the program.
- Create a folder in drive C named Bank Receipts
- Paste the receipts.csv file that you downloaded
Step 5) Record Macro
- Click on the DEVELOPER tab
- Click on Record Macro as shown in the image below
You will get the following dialogue window
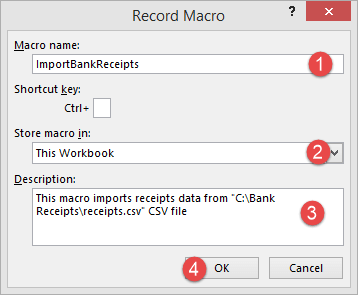
- Enter ImportBankReceipts as the macro name.
- Step two will be there by default
- Enter the description as shown in the above diagram
- Click on “OK” tab
Step 6) Perform Macro Operations/Steps you want to record
- Put the cursor in cell A1
- Click on the DATA tab
- Click on From Text button on the Get External data ribbon bar
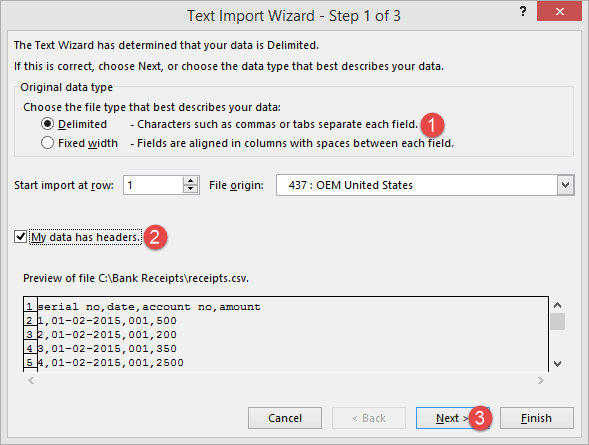
You will get the following dialogue window
- Go to the local drive where you have stored the CSV file
- Select the CSV file
- Click on Import button
You will get the following wizard
Click on Next button after following the above steps
Follow the above steps and click on next button
- Click on Finish button
- Your workbook should now look as follows
Step 7) Format the Data
Make the columns bold, add the grand total and use the SUM function to get the total amount.
Step 
Now that we have finished our routine work, we can click on stop recording macro button as shown in the image below
Step 9) Replay the Macro
Before we save our work book, we will need to delete the imported data. We will do this to create a template that we will be copying every time we have new receipts and want to run the ImportBankReceipts macro.
- Highlight all the imported data
- Right click on the highlighted data
- Click on Delete
- Click on save as button
- Save the workbook in a macro enabled format as shown below
- Make a copy of the newly saved template
- Open it
- Click on DEVELOPER tab
- Click on Macros button
You will get the following dialogue window
- Select ImportBankReceipts
- Highlights the description of your macro
- Click on Run button
You will get the following data
Congratulations, you just created your first macro in Excel.
Summary
Macros simplify our work lives by automating most of the routine works that we do. Macros Excel are powered by Visual Basic for Applications.
You work in Excel every day and do the same things again and again. Why not automate those tasks? Or, maybe, you want Excel to do most of the work for you? Read on to learn what Excel macros are and how they can help you.
What are macros in Excel?
Excel is an extremely powerful tool for processing data in the form of spreadsheets. While most users use formulas, there is another way to manipulate data in Excel.
Excel macros are pieces of code that describe specific actions or contain a set of instructions. Every time you launch the macro, Excel follows those instructions step-by-step.
Why learn macros in Excel?
Macros are a must-have tool for an advanced Excel user. By using Excel macros you can avoid dull, repetitive actions or even create your own order management system for free.
Simple macros in Excel that will make things easier
There are lots of simple Excel macros that take just a few lines of code, but can save you hours. Excel can perform certain operations instantly, where it would take you a very long time to do the job manually.
For example, this macro will sort all worksheets alphabetically:
Sub SortSheetsTabName() Application.ScreenUpdating = False Dim ShCount As Integer, i As Integer, j As Integer ShCount = Sheets.Count For i = 1 To ShCount - 1 For j = i + 1 To ShCount If Sheets(j).Name < Sheets(i).Name Then Sheets(j).Move before:=Sheets(i) End If Next j Next i Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
The following code will unhide all hidden worksheets:
Sub UnhideAllWoksheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next ws End Sub
To unhide all rows and columns on a worksheet, use:
Sub UnhideRowsColumns() Columns.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Rows.EntireRow.Hidden = False End Sub
Advanced Excel macros that can significantly improve your workflow
If you are running a business, you have to store and manipulate data. Small companies can keep records by hand and large enterprises can buy specialized software (which is rather expensive). But what about medium-sized businesses that can no longer settle for manual record-keeping, but still cannot afford costly software? This is where Excel with macros shines.
By combining advanced Excel macros you can create a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system which will help you provide better services. If you sell goods, you need an inventory management tool and Excel spreadsheets enhanced with macros will fit your needs.
If your data is contained in multiple Excel workbooks, you can use Coupler.io to move them around. You can even add third-party sources, like Google Sheets, Airtable, BigQuery, etc. Data integration with Coupler.io does not require any programming skills and can be done in just a few clicks.
Check out the available integrations with Excel.
Other Excel macros examples
Below are a few examples of useful Excel macros.
Sometimes you might accidentally add extra spaces to the data in cells. This mistake will cause errors, thereby preventing you from making correct calculations. To remove unnecessary spaces from the selected cells, use the following code:
Sub TrimTheSpaces() Dim MyRange As Range Dim MyCell As Range Set MyRange = Selection For Each MyCell In MyRange If Not IsEmpty(MyCell) Then MyCell = Trim(MyCell) End If Next MyCell End Sub
It is often the case that you need to protect your workbook with a password. You can do that in the user interface of Excel. However, if you use the same password for all of your workbooks, you have to re-enter it every time. This macro will do the job for you (don’t forget to replace “1234” with your own password!):
Sub ProtectSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet For Each ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets ws.Protect Password:="1234" Next ws End Sub
Using macros in Excel
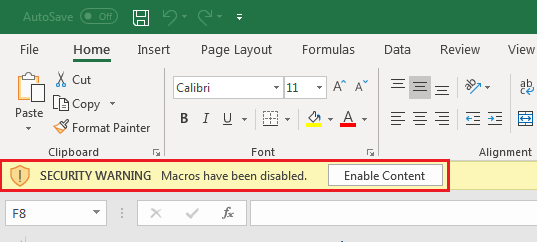
As macros are programs that can do literally anything on your computer, using macros from untrusted sources is very risky. That’s why, when you open a workbook with macros in Excel, they will be disabled and you will see the following notification:
If you trust the source of the file, click Enable Content. That will add the workbook to the list of trusted documents and turn on its macros. The next time you open that workbook, there will be no warning.
You will see the above notification each time you open a workbook if it has been saved to an untrusted location. That can be a folder for temporary files or browser downloads. To avoid that, move the file to another folder or enable macros in the Excel Trust Center.
How to enable macros in Excel
If you do not want to see the security warning when opening Excel workbooks, you can permanently enable macros in the Trust Center.
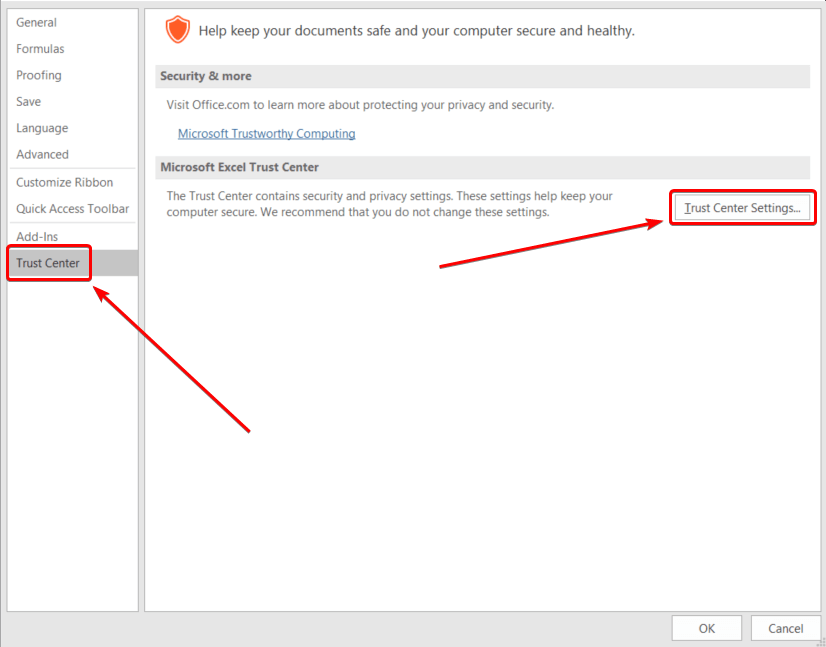
To enable macros in the Excel Trust Center:
- In the upper-left corner, click the File tab and then select Options:
- In the Excel Options window, select Trust Center and then click Trust Center Settings:
- In the Trust Center, go to Macro Settings and then select Enable all macros:
Warning! Enabling macros for all workbooks is potentially risky because files from external sources may contain malicious code. If you open such a workbook, the macros may run automatically and corrupt your data or even cause hardware malfunctions.
How to use macros in Excel
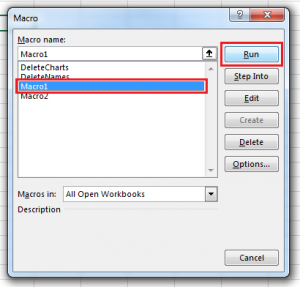
If your workbook contains macros, you can run them by pressing Alt+F8. In the Macro window that opens, select the macro you need and click Run:
If you want to create new macros, you need to enable the Developer tab first.
To enable the Developer tab:
- In the upper-left corner, click the File tab and then select Options.
- In the Excel Options window, select Customize Ribbon and then enable the Developer checkbox in the Main Tabs area:
- Click OK to apply the changes.
In the Developer tab you can run existing macros by clicking the Macros button or create a new macro. For details on creating macros in Excel, see the following sections.
How to delete macros in Excel
To delete a macro in Excel:
- Open the Macro window in one of the following ways:
- Press Alt+F8.
- Select the Developer tab and click Macros.
- Select the macro that you want to delete and click Delete.
- Click Yes in the confirmation window that opens.
How to disable macros in Excel
Enabling Excel macros can make your computer vulnerable. Some macros will run when you open a workbook, which is especially dangerous if you have downloaded the workbook from an untrusted source. To prevent that, you can disable macros in Excel either with or without a notification.
To disable macros in Excel:
- In the upper-left corner, click the File tab and then select Options.
- In the Excel Options window, select Trust Center and then click Trust Center Settings.
- In the Trust Center, go to Macro Settings and then select one of the following options:
- Disable all macros without notification. Macros will be disabled and you will not see a security warning when opening a workbook with macros.
- Disable all macros with notification. Macros will be disabled but you will see a security warning when opening a workbook with macros and will be able to allow macros, if needed.
Writing macros in Excel
In Excel you can not only run ready-to-use macros, but also write your own macros to automate your daily tasks. We will provide a few methods below for creating macros in Excel. Anyone can write macros in Excel: from a complete beginner to an advanced user with programming skills.
How to record a macro in Excel
If you are unfamiliar with programming languages, the easiest way to create your own Excel macro is to record it.
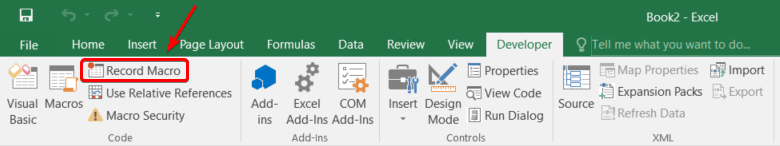
To record a macro in Excel:
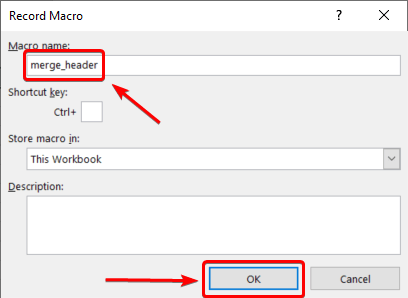
- In the Developer tab, click Record Macro:
- Enter the macro name and click OK:
Excel will start recording the macro.
- Perform the actions, that need to be included in the macro, then click Stop Recording:
The macro will be saved to the workbook.
Creating VBA macros in Excel
If you can write code in any programming language, you can easily learn the basics of Visual Basic for Applications and create Excel macros in the VBA editor.
To open the editor, click Visual Basic in the Developer tab.
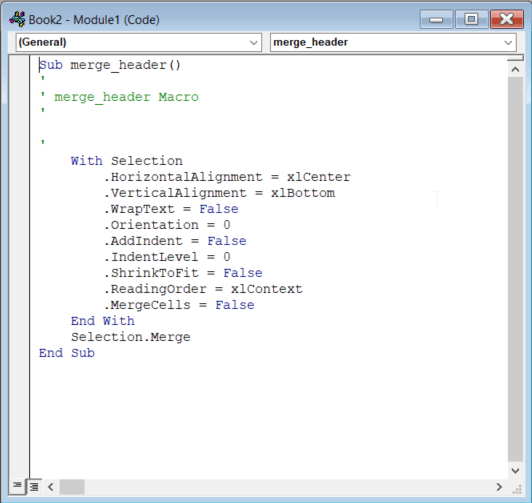
Each workbook is a VBA project in the editor. The project contains worksheets as objects and modules with macros:
By default, macros recorded in the Developer tab are saved to Module1. For example, here is the macro that we recorded in the previous section:
As you can see in the picture above, a macro starts with Sub followed by the macro name and (). You can insert the macro description in the comment lines. Be sure to indent the macro body for better readability. The End Sub string designates the end of the macro.
Excel macros language
Macros in Excel are written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). This programming language is used not only in Excel, but also in other MS office applications.
VBA provides many of the tools that are available in advanced programming languages. For example, to create Excel macros, you can use the following:
- Variables
- ‘If’ statements
- ‘For’ cycles
- Loops
- Arrays
- Events
- Functions
Being an object-oriented language, VBA lets you manipulate the following objects:
- Application object
- Workbook object
- Worksheet object
- Range object
If you decide to turn your Excel worksheet into something much more powerful, like a CRM system, you can even create a graphical user interface with message boxes and user forms. To learn more about VBA, check out the official documentation.
Editing macros in Excel VBA editor
When creating macros in Excel, it may be difficult to get the desired result on the first try. By editing Excel macros and running them again, you can resolve errors and make your system work as expected.
To edit a macro in Excel VBA editor:
- In the Developer tab, click Visual Basic:
- In the VBA project tree, double-click the module with the macro that you want to edit:
- Edit the macro code, then save changes by clicking the Save button or pressing Ctrl+S.
The workbook with the macro will be saved.
You can press F5 or click Run in the editor to launch the macro:
Note: If a macro changes workbook data, those changes cannot be reversed using the Undo command in Excel.
The VBA editor has a built-in debugger that highlights errors in code. The line that follows the error is highlighted:
An easy way of learning how to create macros in Excel
In Excel you can record a macro by using the Record Macro button in the Developer tab. Then you can open the recorded macro in Excel VBA editor.
This is the easiest way to learn the VBA programming language. Just perform actions in the Excel user interface and see how they are interpreted in the macro code. Then you can change values and methods in the code to see how that affects the macro behavior.
Do I need Excel macros?
As you can see, macros can drastically enhance Excel features in many ways. By using macros, you can automate your daily operations and save yourself hours of time. Excel macros can even save you money if you decide to create an Excel-based order management system instead of buying costly software.
When you finish customizing your Excel workbook with macros, you may need to migrate your data from other sources, like Google Sheets or BigQuery.
-
A content manager at Coupler.io whose key responsibility is to ensure that the readers love our content on the blog. With 5 years of experience as a wordsmith in SaaS, I know how to make texts resonate with readers’ queries✍🏼
Back to Blog
Focus on your business
goals while we take care of your data!
Try Coupler.io
Although running a macro in Excel isn’t hard, there are lots of ways to run them. Some ways are meant to make using macros easier, while other ways can change the way a user interacts with your workbook entirely. In this article we’ll cover some obvious ways to run macros run like the Macros List and Button controls, and some more obscure ways like the VB Editor and Events.
First: Ensure Macros are Enabled
Excel’s security features will disable macros by default. When opening a macro-enabled workbook, users are typically prompted if they’d like to enable macros.
If you’re not able to run macros, try following these instructions:
- Save the workbook
- Close the workbook, then open it again
- When the workbook loads, you’ll see a Security Warning prompt (pictured below). Click Enable Content.
Run a Macro from the Macro List
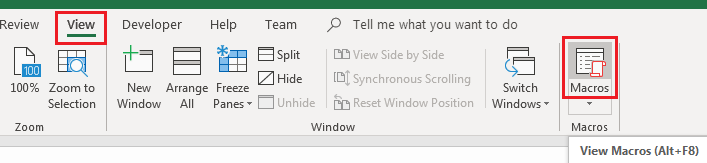
A list of macros can be accessed from the View tab. To view this list:
- Select the View tab
- Click the button labelled Macros to bring up the Macro list
- Select the macro you want to run from the list, then click the Run button
You can also show the Macro List at any time by pressing ALT+F8.
Run a Macro using a Keyboard Shortcut
You can assign a keyboard shortcut to a macro that you use often, in the form of CTRL+<letter> or CTRL+SHIFT+<letter>. To do this:
- Bring up the Macro List (View > Macros, or ALT+F8)
- Select the macro you want to apply a shortcut to
- Click Options… to show the Macro Options sub-dialog
- In the textbox under Shortcut Key, type a single letter and then click OK. If you hold the SHIFT key while typing the letter, the label next to the box will show SHIFT as part of the shortcut
NOTE: it is highly recommended that you use SHIFT when creating a shortcut key! Excel uses CTRL+ shortcuts for itself, e.g. CTRL+C to Copy, or CTRL+V to Save. If you create a macro shortcut using these or other Excel shortcuts, you’ll overwrite the Excel shortcut until you re-assign the macro shortcut.
Run a Macro from the VB Editor
Macros can also be run from the VB Editor. The VB Editor allows you to review a macro’s code and make any changes you want before running it.
To run a macro in the VB Editor:
- Open the VB Editor (Developer tab > Visual Basic, or ALT+F11)
- In the Project window, double-click the module containing the macro you want to test
- In the module’s code window, place the cursor anywhere on the macro’s code between “Sub” and “End Sub”
- Click the Run button on the toolbar, or press keyboard shortcut F5
Run a Macro using a Button or Shape
It’s often useful to have a control on the worksheet that a user can click to run a macro, like a Button control or a Shape. This is much quicker for end-users than opening lists of macros or digging through macro code in the VB Editor.
Information about how to create a clickable Button or Shape can be found here: Add a Button and Assign a Macro in Excel.
Auto-Run a Macro using Events in VBA
It’s possible to make a macro run when something happens in Excel – for example, when a workbook is opened or when a cell value is changed. These are called Events, and you can write VBA code for them to call macros or perform other operations.
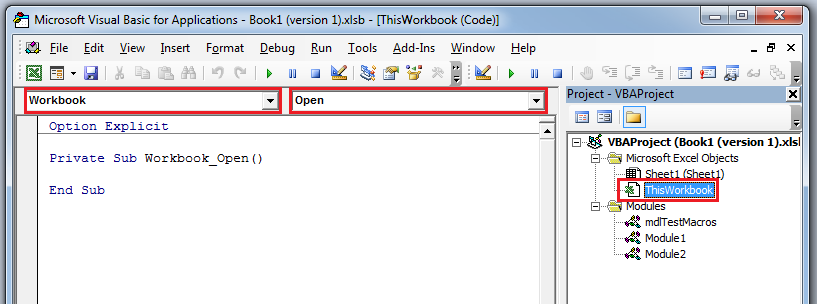
To write code for an event, you’ll need to use the VB Editor. For example, to view events for the workbook:
- Open the VB Editor (ALT+F11)
- Double-click the ThisWorkbook object in the VB Editor’s Project Window
- Choose “Workbook” from the dropdown on the top-left of the code window
- Click the dropdown on the right to see a list of events
The following are a small, but useful sample of Excel Events that you could run macros from.
Workbook_Open()
The Workbook_Open() event fires when a workbook is opened. If you get the Security Warning after opening a workbook, this event fires after clicking “Enable Content”.
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
MsgBox "Workbook Opened!"
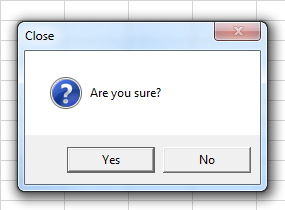
End SubWorkbook_BeforeClose(Cancel as Boolean)
Workbook_BeforeClose() fires when the user tries to close the workbook. It happens before any checks are done to see if the workbook needs to be saved.
The Cancel parameter can be set to True to stop the workbook from closing.
Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean)
If MsgBox("Are you sure?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Close") = vbNo Then
Cancel = True
End If
End SubWorksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
Worksheet_Change() fires when the value of a cell is changed – whether it’s changed by a macro, by a copy/paste operation, or by an external link. It does not fire when a value is recalculated via a formula, though.
The Target parameter represents the cells whose value have changed.
If you change the value of other cells inside this event, the event will fire again. This can possibly cause an infinite loop. If you need to change cell values without triggering this event, consider setting Application.EnableEvents to False first, and then set it back to True at the end of the event procedure.
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
MsgBox "Cells changed: " & Target.Address
Application.EnableEvents = False
Range("A2").Value = Range("A2").Value + Target.Cells.Count
Application.EnableEvents = True
End SubWorksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
This event fires whenever different cells are selected with the targeting reticle. The Target parameter represents the new cells that have been selected.
You can trigger this event with code as well, i.e. “Range(“A1”).Select”. As with Worksheet_Change(), you should be careful about selecting other cells inside this event, since you can cause an infinite loop. Use Application.EnableEvents.
Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Address = "$A$1" Then
MsgBox "Cursor in home position."
End If
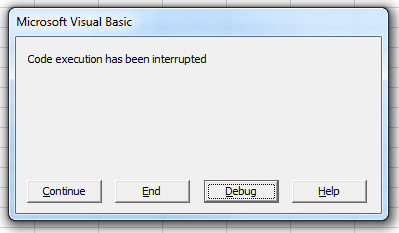
End SubStop a Running Macro
A running macro can be interrupted by pressing ESC or CTRL+BREAK. By default, an interrupted macro will show the following dialog:
Clicking End will stop the macro, while Continue will resume it. Clicking Debug will open the macro in the VB Editor and focus the line of code that execution was paused on. (Inside the VB Editor you can stop or resume the macro using the Run or End buttons on the toolbar.)
Application.EnableCancelKey
You can disable the ability to stop a macro with ESC or CTRL+BREAK by setting the Application.EnableCancelKey property. This property has three possible values:
- xlInterrupt – this is the default value, which makes Excel show the dialog above
- xlDisabled – removes the ability to stop a running macro
- xlErrorHandler – when an interrupt attempt is made, an error is thrown that can be handled in code
Whenever code execution stops, Excel always resets the value of Application.EnableCancelKey back to xlInterrupt.
A good reason for using this property is security. For example, if you had a macro that temporarily unprotected parts of your workbook, a user could potentially stop the macro right after the unprotect and gain access to content you didn’t intend them to have. By setting Application.EnableCancelKey, you can completely disable their ability to do this, or handle their interruption gracefully with an Error Handler that re-protects the workbook.
Sub UpdateBaseData(ByVal NewData As Range, ByVal Target As Range)
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlDisabled
Target.Worksheet.Unprotect "MyPassword"
NewData.Copy Target
Target.Worksheet.Protect "MyPassword"
Application.EnableCancelKey = xlInterrupt
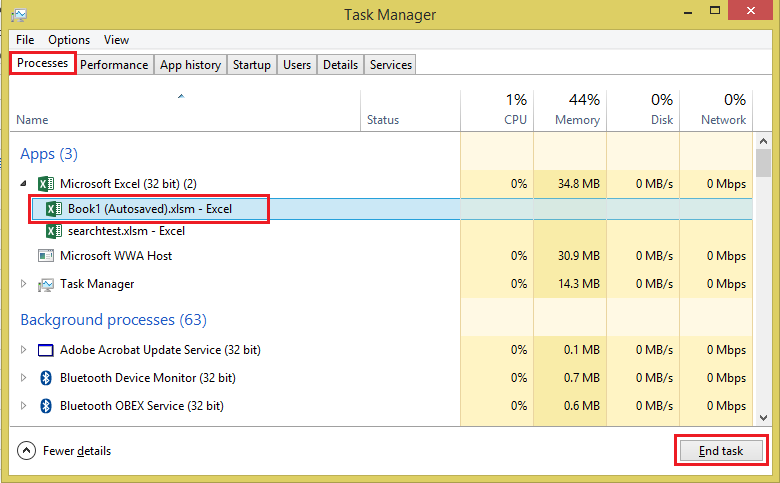
End SubForce-Close Excel with the Windows Task Manager
If the macro has ‘hung’, or Excel has become too busy to acknowledge an interrupt attempt, you may need to force-close Excel itself with the Windows Task Manager. (NOTE: if you do this, you may lose any unsaved work, and have to rely on an auto-recover version of your workbook.)
- Open the Task Manager directly using CTRL+SHIFT+ESC
- Select the “Processes” tab
- Expand the “Microsoft Excel” item to show all workbooks
- Select the workbook you want to close, then click End Task in the bottom-right corner
Содержание
- Способы записи макросов в Excel
- Вариант 1: Автоматическая запись макросов
- Запуск макроса
- Редактирование макроса
- Вариант 2: Написание кода макроса с нуля
- Вопросы и ответы
Макросы в Microsoft Excel позволяют значительно ускорить работу с документами в этом табличном редакторе. Эта возможность достигается путем автоматизации повторяющихся действий, записанных в специальный код. Давайте разберем, как создать макросы в программе и как их можно отредактировать.
Макрос записывается двумя способами: автоматически и вручную. Воспользовавшись первым вариантом, вы просто записываете определенные действия в Microsoft Excel, которые выполняете в данный момент времени. Потом можно будет воспроизвести эту запись. Такой метод очень легкий и не требует знания кода, но применение его на практике довольно ограничено. Ручная запись, наоборот, требует знаний программирования, так как код набирается вручную с клавиатуры. Однако грамотно написанный таким образом код может значительно ускорить выполнение процессов.
Вариант 1: Автоматическая запись макросов
Прежде чем начать автоматическую запись макросов, нужно включить их в программе Microsoft Excel. Для этого воспользуйтесь нашим отдельным материалом.
Подробнее: Включение и отключение макросов в Microsoft Excel
Когда все готово, приступаем к записи.
- Перейдите на вкладку «Разработчик». Кликните по кнопке «Запись макроса», которая расположена на ленте в блоке инструментов «Код».
- Открывается окно настройки записи макроса. Тут можно указать любое имя для него, если установленное по умолчанию вас не устраивает. Главное, чтобы имя это начиналось с буквы, а не с цифры, а также в названии не должно быть пробелов. Мы оставили название по умолчанию – «Макрос1».
- Тут же при желании можно установить сочетание клавиш, при нажатии на которые макрос будет запускаться. Первой клавишей обязательно должна быть Ctrl, а вторую пользователь устанавливает самостоятельно. Мы в качестве примера установили клавишу М.
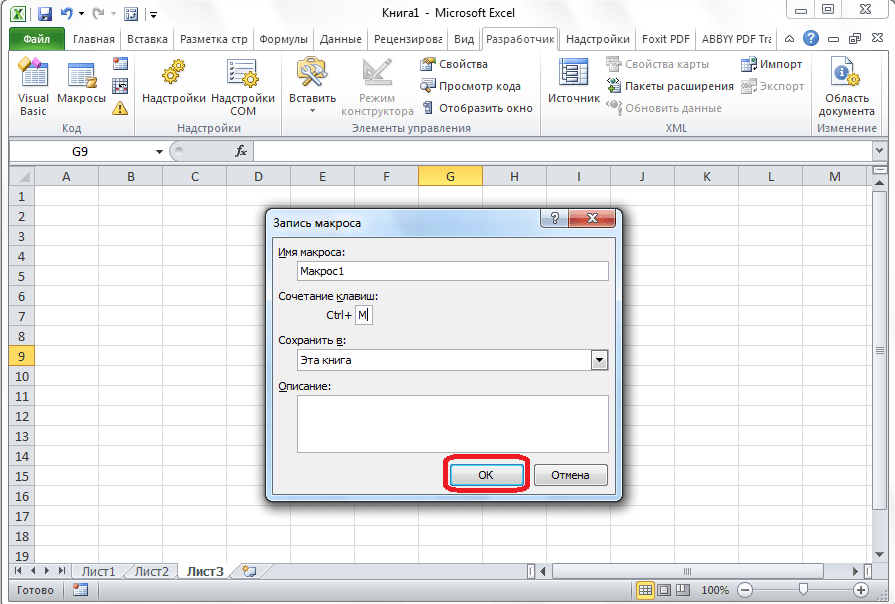
- Далее следует определить, где будет храниться макрос. По умолчанию он расположен в этой же книге (файле), но при желании можно установить хранение в новой книге или в отдельной книге макросов. Мы оставим значение по умолчанию.
- В самом нижнем поле можно оставить любое подходящее по контексту описание макроса, но это делать не обязательно. Когда все настройки выполнены, жмем на кнопку «OK».
- После этого все ваши действия в данной книге (файле) Excel будут записываться в макрос до тех пор, пока вы сами не остановите запись.
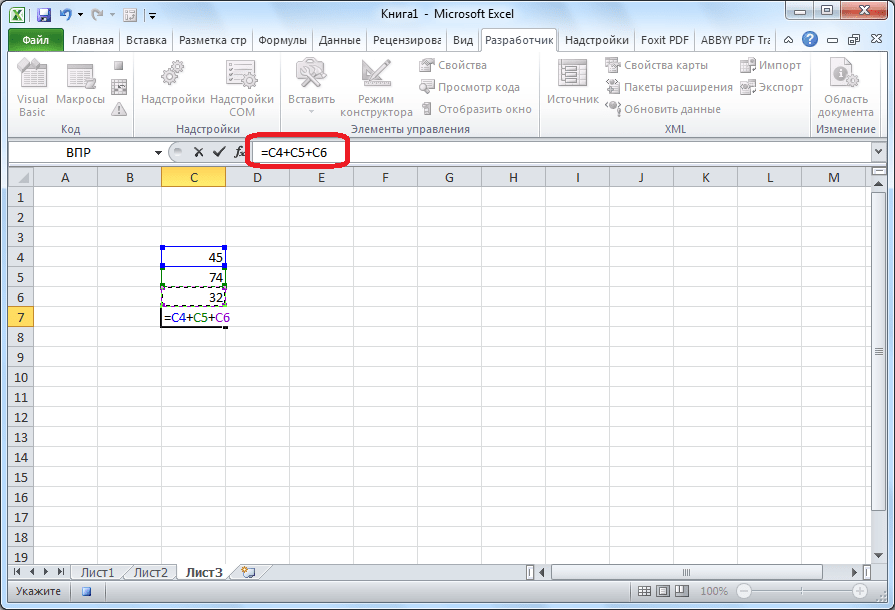
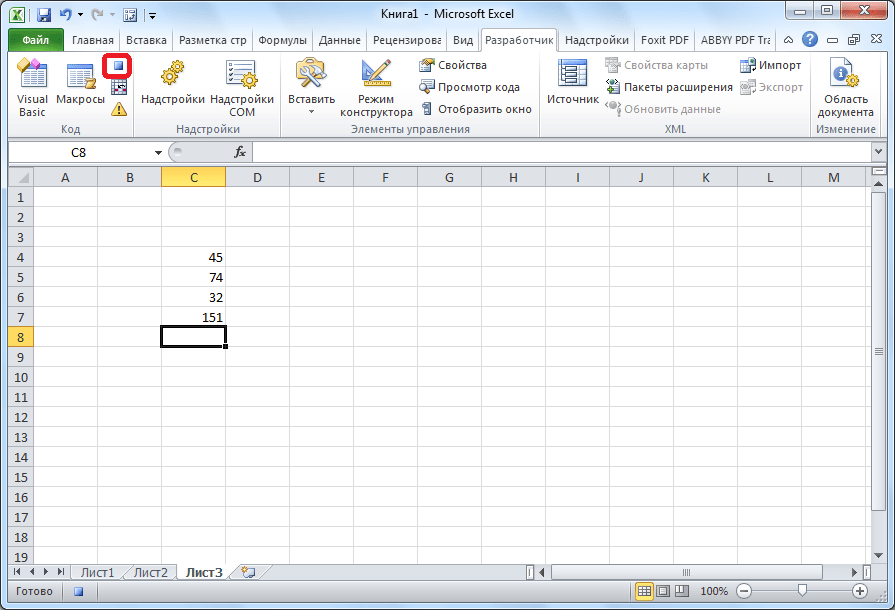
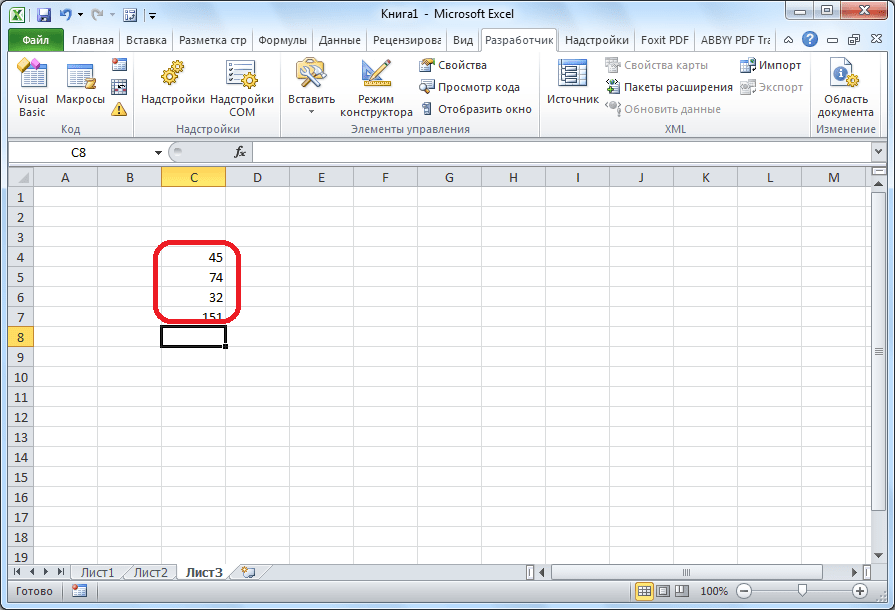
- Для примера запишем простейшее арифметическое действие: сложение содержимого трех ячеек (=C4+C5+C6).
- Когда алгоритм был выполнен, щелкаем на кнопку «Остановить запись». Эта кнопка преобразовалась из кнопки «Запись макроса» после включения записи.
Запуск макроса
Для проверки того, как работает записанный макрос, выполним несколько простых действий.
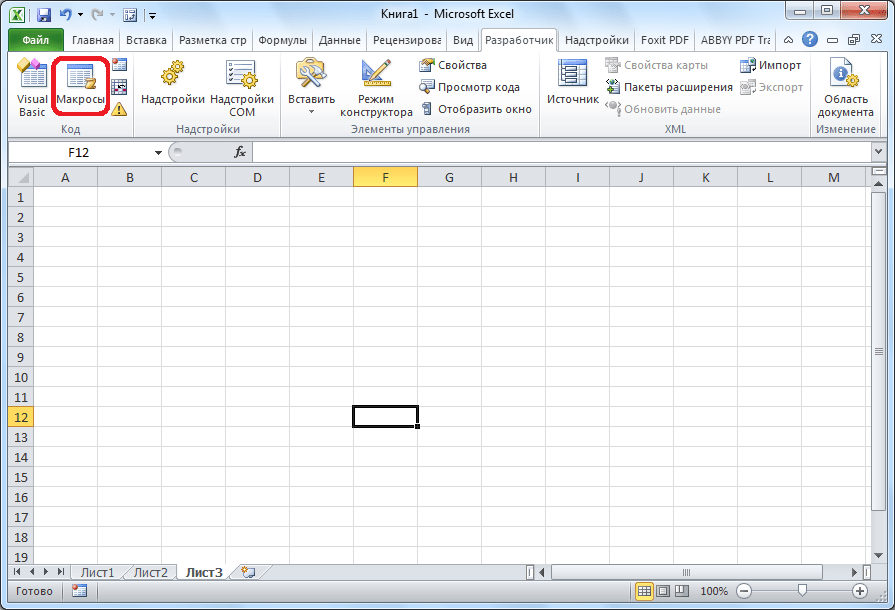
- Кликаем в том же блоке инструментов «Код» по кнопке «Макросы» или жмем сочетание клавиш Alt + F8.
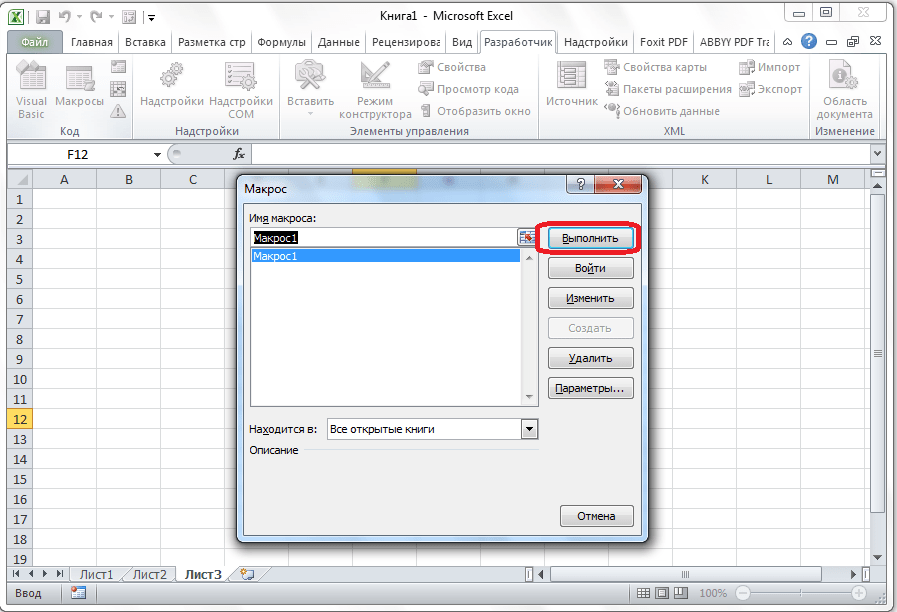
- После этого открывается окно со списком записанных макросов. Ищем макрос, который мы записали, выделяем его и кликаем на кнопку «Выполнить».
- Можно поступить еще проще и не вызывать даже окно выбора макросов, так как на первом этапе мы задали сочетание клавиш для быстрого вызова макроса. В нашем случае это Ctrl + М. Жмем данную комбинацию на клавиатуре, после чего он запускается.
- Как видим, он выполнил в точности все те действия, которые были записаны ранее.
Редактирование макроса
Естественно, при желании вы можете корректировать созданный макрос, чтобы всегда поддерживать его в актуальном состоянии и исправлять некоторые неточности, допущенные во время процесса записи.
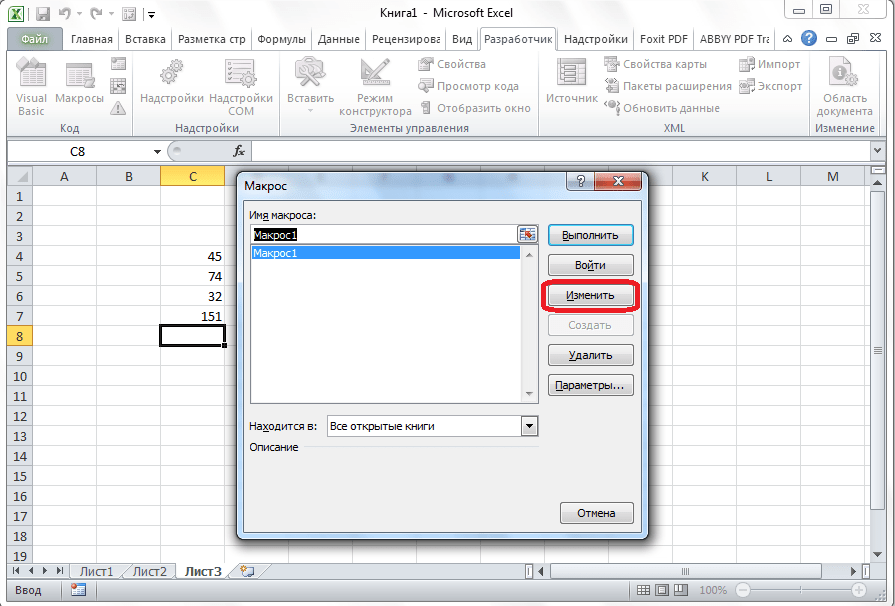
- Снова щелкаем на кнопку «Макросы». В открывшемся окне выбираем нужный и кликаем по кнопке «Изменить».
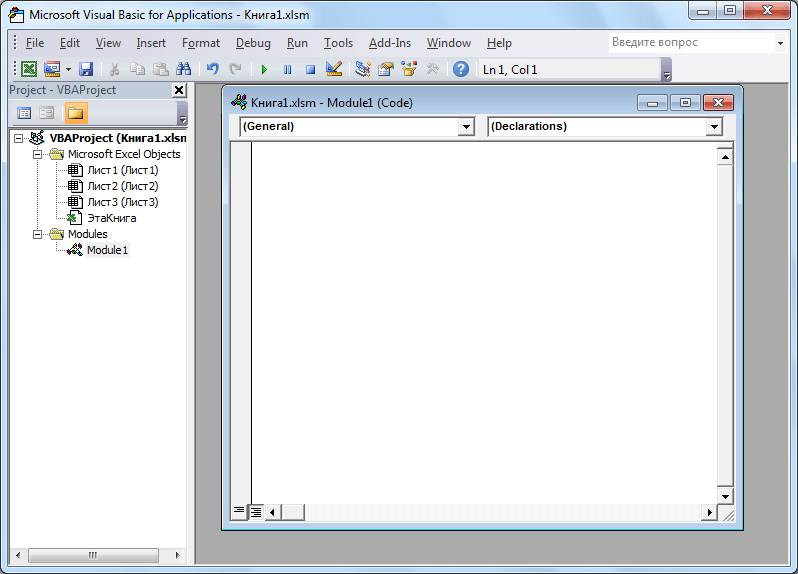
- Открывается «Microsoft Visual Basic» (VBE) – среда, где происходит их редактирование.
- Запись каждого макроса начинается с команды
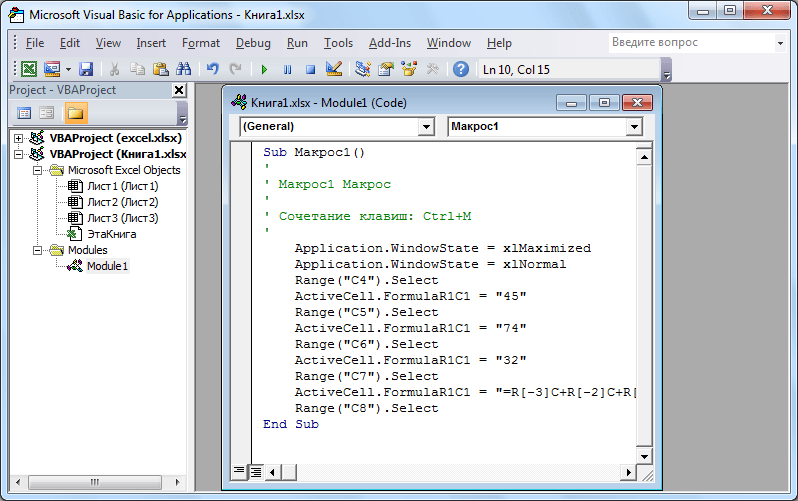
Sub, а заканчивается командойEnd Sub. Сразу же послеSubуказывается имя макроса. ОператорRange("…").Selectуказывает выбор ячейки. Например, при команде «Range(«C4»).Select» выбирается ячейка «C4». ОператорActiveCell.FormulaR1C1используется для записи действий в формулах и других расчетов. - Попытаемся немного изменить макрос, дописав выражение:
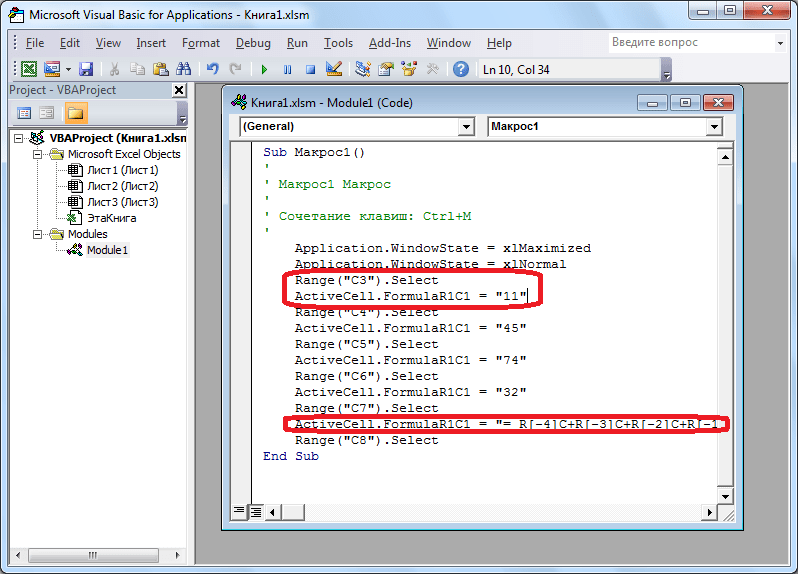
Range("C3").Select
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "11" - Выражение
ActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "=R[-3]C+R[-2]C+R[-1]C"заменим наActiveCell.FormulaR1C1 = "= R[-4]C+R[-3]C+R[-2]C+R[-1]C". - Закрываем редактор и запускаем макрос. Как видим, вследствие введенных нами изменений была добавлена дополнительная ячейка с данными. Она также была включена в расчет общей суммы.
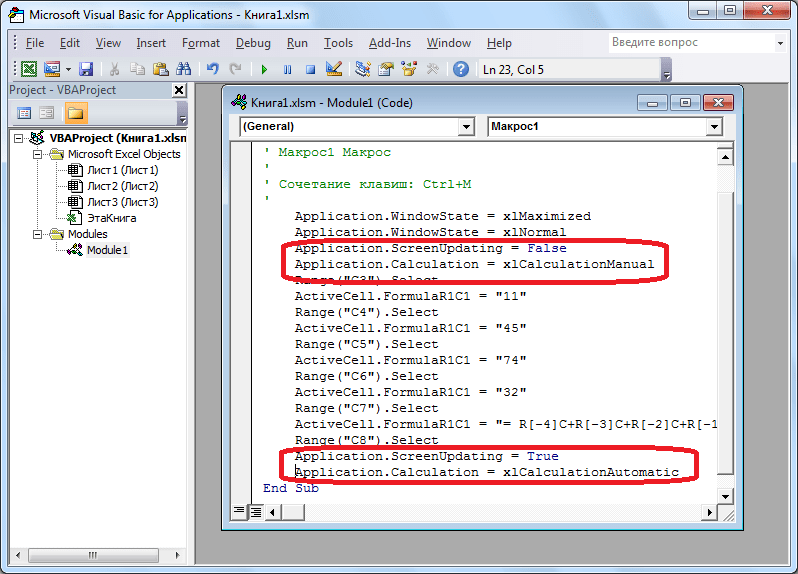
- В случае если макрос слишком большой, его выполнение может занять значительное время, но внесением ручного изменения в код мы можем ускорить процесс. Добавляем команду
Application.ScreenUpdating = False. Она позволит сохранить вычислительные мощности, а значит, ускорить работу. Это достигается путем отказа от обновления экрана во время выполнения вычислительных действий. Чтобы возобновить обновление после выполнения макроса, в его конце пишем командуApplication.ScreenUpdating = True. - Добавим также команду
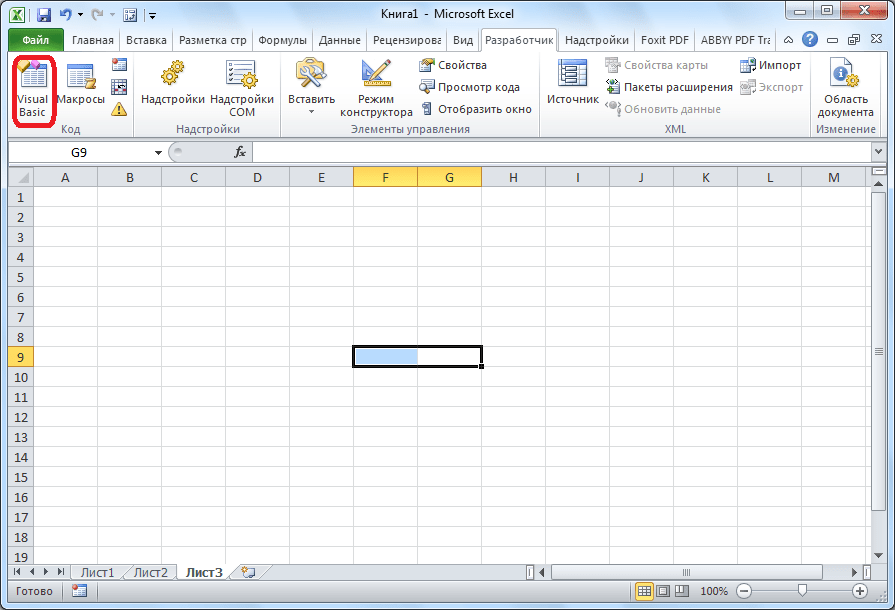
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationManualв начало кода, а в его конец дописываемApplication.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic. Этим мы сначала отключаем автоматический пересчет результата после каждого изменения ячеек, а в конце макроса – включаем. Таким образом, Excel подсчитает результат только один раз, а не будет его постоянно пересчитывать, чем сэкономит время. - Чтобы приступить к этому, нужно нажать на кнопку «Visual Basic», которая расположена в самом начале ленты разработчика.
- Откроется окно редактора VBE, которое уже было продемонстрировано в предыдущем варианте.
- Программист пишет там код макроса вручную.
Вариант 2: Написание кода макроса с нуля
Продвинутые пользователи могут выполнять не только редактирование и оптимизацию записанных макросов, но и записывать их код с нуля.
Как видим, макросы в Microsoft Excel могут значительно упростить выполнение рутинных и однообразных процессов. Тем не менее в большинстве случаев для этого больше подходят макросы, код которых написан вручную, а не автоматически записанные действия. Кроме того, его код можно оптимизировать через редактор VBE для ускорения процесса выполнения задачи.
Еще статьи по данной теме: