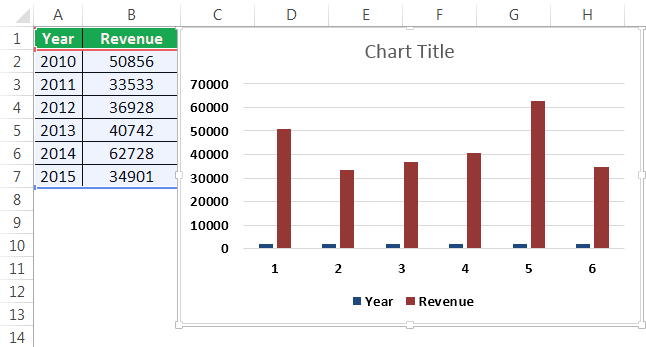
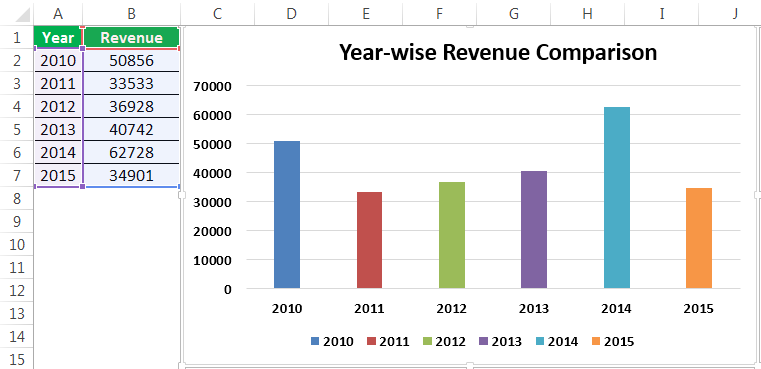
Most companies (and people) don’t want to pore through pages and pages of spreadsheets when it’s so quick to turn those rows and columns into a visual chart or graph. But someone has to do it…and that person must be you.
Ready to turn your boring Excel spreadsheet into something a little more interesting?
In Excel, you’ve got everything you need at your fingertips. Excel users can leverage the power of visuals without any additional extensions. You can create a graph or chart right inside Excel rather than exporting it into some other tool.
What is the difference between Charts and Graphs?
According to reference.com…“The difference between graphs and charts is mainly in the way the data is compiled and the way it is represented. Graphs are usually focused on raw data and showing the trends and changes in that data over time. Charts are best used when data can be categorized or averaged to create more simplistic and easily consumed figures.“
So technically, charts and graphs mean separate things, but in the real world, you’ll hear the terms used interchangeably. People generally accept both so don’t worry too much about it!
In this post, you’ll learn exactly how to create a graph in Excel and improve your visuals and reporting…but first let’s talk about charts. Understanding exactly how charts play out in Excel will help with understanding graphs in Excel.
Charts in Excel
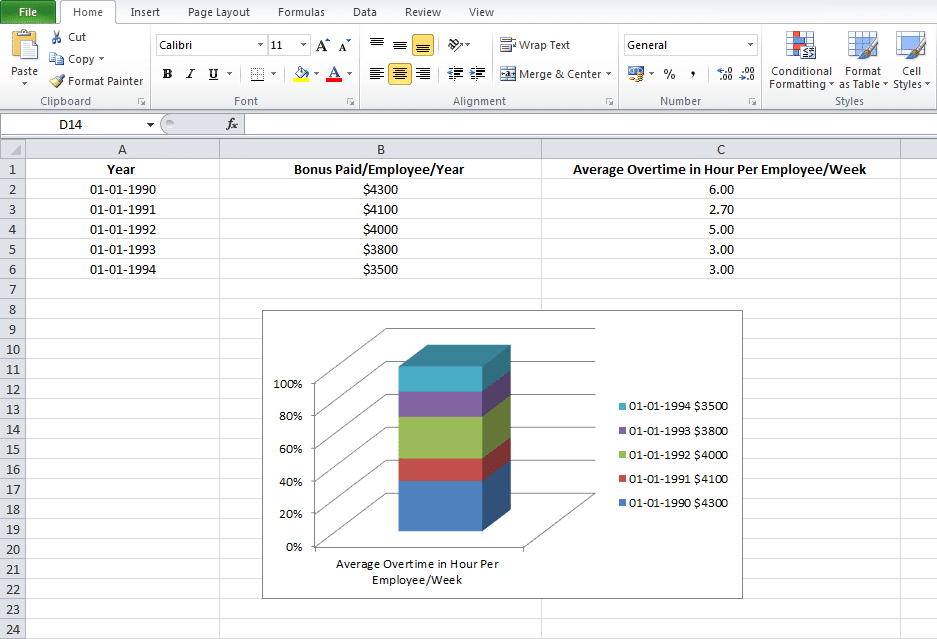
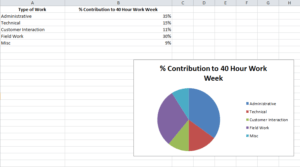
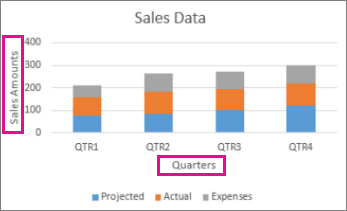
Charts are usually considered more aesthetically pleasing than graphs. Something like a pie chart is used to convey to readers the relative share of a particular segment of the data set with respect to other segments that are available. If instead of the changes in hours worked and annual leaves over 5 years, you want to present the percentage contributions of the different types of tasks that make up a 40 hour work week for employees in your organization then you can definitely insert a pie chart into your spreadsheet for the desired impact.
Graphs in Excel
Graphs represent variations in values of data points over a given duration of time. They are simpler than charts because you are dealing with different data parameters. Comparing and contrasting segments of the same set against one another is more difficult.
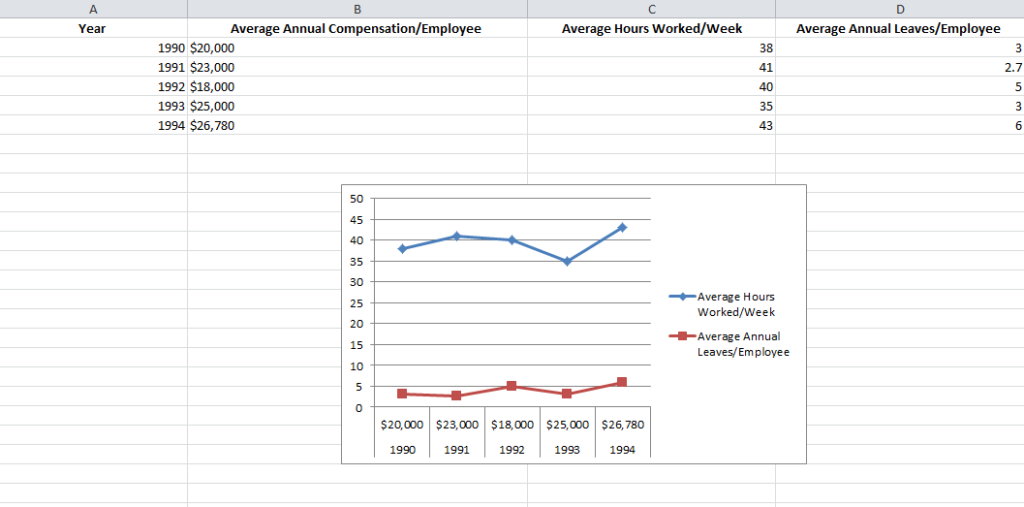
So if you are trying to see how the number of hours worked per week and the frequency of annual leaves for employees in your company has fluctuated over the past 5 years, you can create a simple line graph and track the spikes and dips to get a fair idea.
Types of Graphs Available in Excel
Excel offers three varieties of graphs:
- Line Graphs: Both 2 dimensional and three dimensional line graphs are available in all the versions of Microsoft Excel. Line graphs are great for showing trends over time. Simultaneously plot more than one data parameter – like employee compensation, average number of hours worked in a week and average number of annual leaves against the same X axis or time.
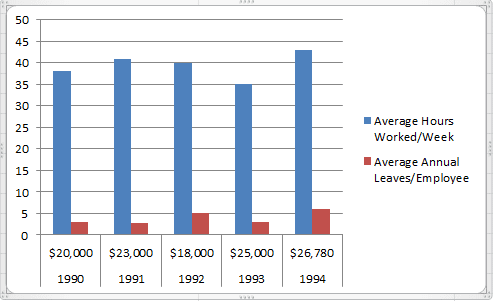
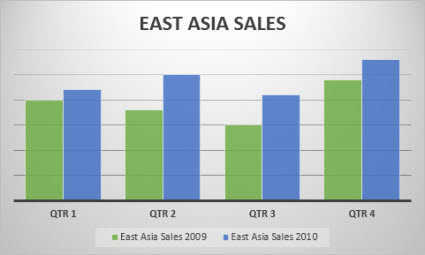
- Column Graphs: Column graphs also help viewers see how parameters change over time. But they can be called “graphs” when only a single data parameter is used. If multiple parameters are called into action, viewers can’t really get any insights about how each individual parameter has changed. As you can see in the Column graph below, average numbers of hours worked in a week and average number of annual leaves when plotted side by side do not provide the same clarity as the Line graph.
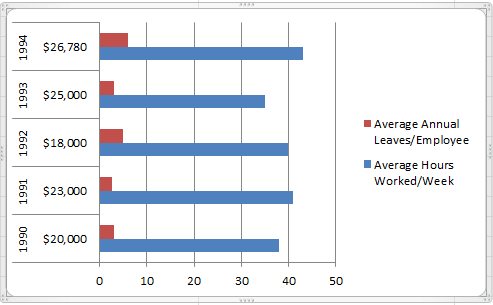
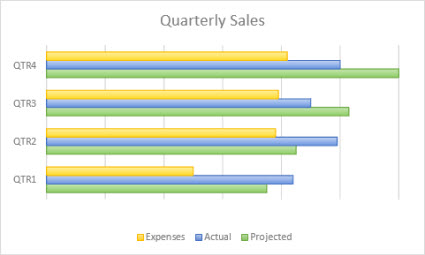
- Bar Graphs: Bar graphs are very similar to column graphs but here the constant parameter (say time) is assigned to the Y axis and the variables are plotted against the X axis.
1. Fill the Excel Sheet with Your Data & Assign the Right Data Types
The first step is to actually populate an Excel spreadsheet with the data that you need. If you have imported this data from a different software, then it’s probably been compiled in a .csv (comma separated values) formatted document.
If this is the case, use an online CSV to Excel converter like the one here to generate the Excel file or open it in Excel and save the file with an Excel extension.
After converting the file, you still may need to clean up the rows and the columns. It is better to work with a clean spreadsheet so that the Excel graph you’re creating is clean and easy to modify or change.
If that doesn’t work, you may also need to manually enter the data into the spreadsheet or copy and paste it over before creating the Excel graph.
Excel has two components to its spreadsheets:
- The rows that are horizontal and marked with numbers
- The columns that are vertical and marked with alphabets
After all the data values have been set and accounted for, make sure that you visit the Number section under the Home tab and assign the right data type to the various columns. If you do not do this, chances are your graphs will not show up right.
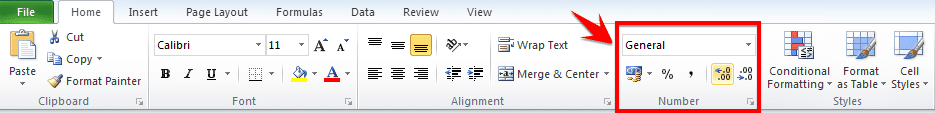
For example if column B is measuring time, ensure that you choose the option Time from the drop down menu and assign it to B.
Choose the Type of Excel Graph You Want to Create
This will depend on the type of data you have and the number of different parameters you will be tracking simultaneously.
If you are looking to take note of trends over time then Line graphs are your best bet. This is what we will be using for the purpose of the tutorial.
Let us assume that we are tracking Average Number of Hours Worked/Week/Employee and Average Number of Leaves/Employee/Year against a five year time span.
Highlight The Data Sets That You Want To Use
For a graph to be created, you need to select the different data parameters.
To do this, bring your cursor over the cell marked A. You will see it transform into a tiny arrow pointing downwards. When this happens, click on the cell A and the entire column will be selected.
Repeat the process with columns B and C, pressing the Ctrl (Control) button on Windows or using the Command key with Mac users.
Your final selection should look something like this:
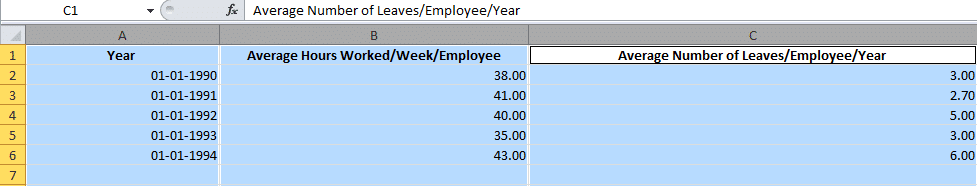
Create the Basic Excel Graph
With the columns selected, visit the Insert tab and choose the option 2D Line Graph.
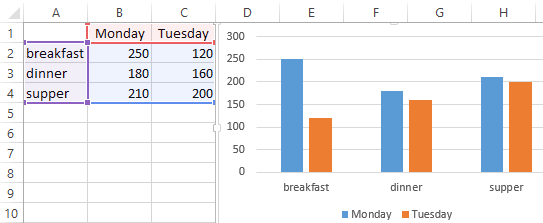
You will immediately see a graph appear below your data values.
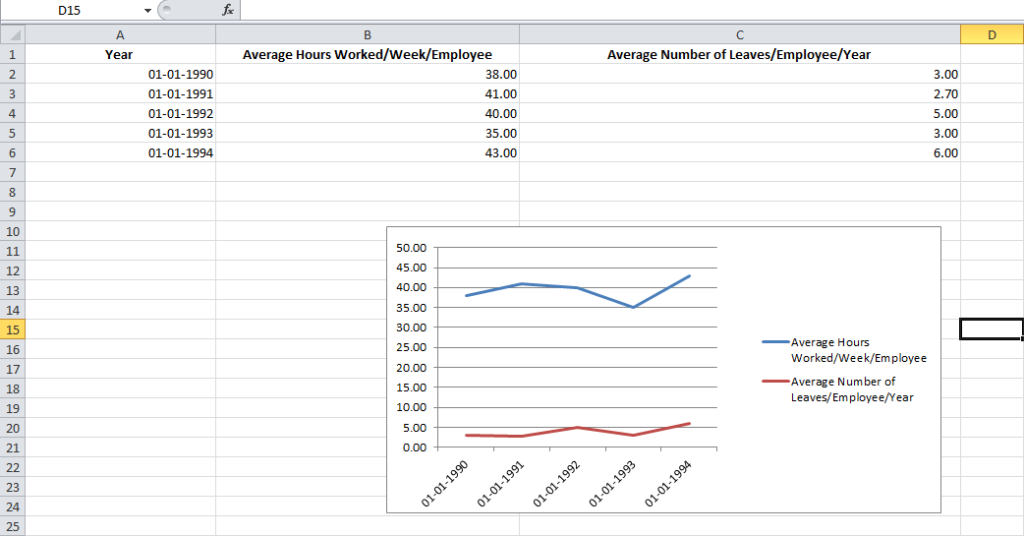
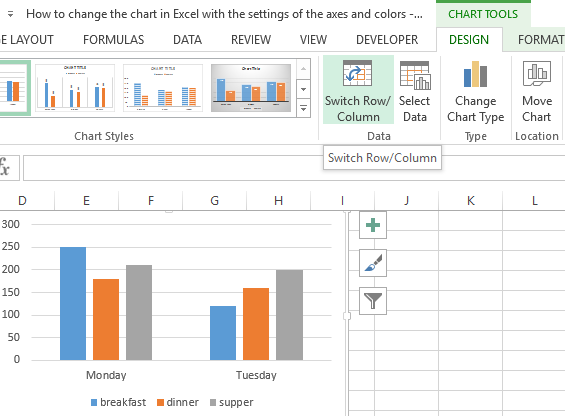
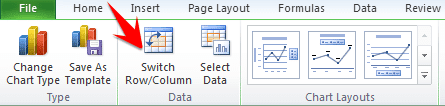
Sometimes if you do not assign the right data type to your columns in the first step, the graph may not show in a way that you want it to. For example, Excel may plot the parameter Average Number of Leaves/Employee/Year along the X axis instead of the Year. In this case, you can use the option Switch Row/Column under the Design tab of Chart Tools to play around with various combinations of X axis and Y axis parameters till you hit on the perfect rendition.
Improve Your Excel Graph with the Chart Tools
To change colors or to change the design of your graph, go to Chart Tools in the Excel header.
You can select from the design, layout and format. Each will change up the look and feel of your Excel graph.
Design: Design allows you to move your graph and re-position it. It gives you the freedom to change the chart type. You can even experiment with different chart layouts. This may conform more to your brand guidelines, your personal style, or your manager’s preference.

Layout: This allows you to change the title of the axis, the title of your chart and the position of the legend. You might go with vertical text along the Y axis and horizontal text along the X axis. You can even adjust the grid lines. You have every formatting tool conceivable at your fingertips to improve the look and feel of your graph.
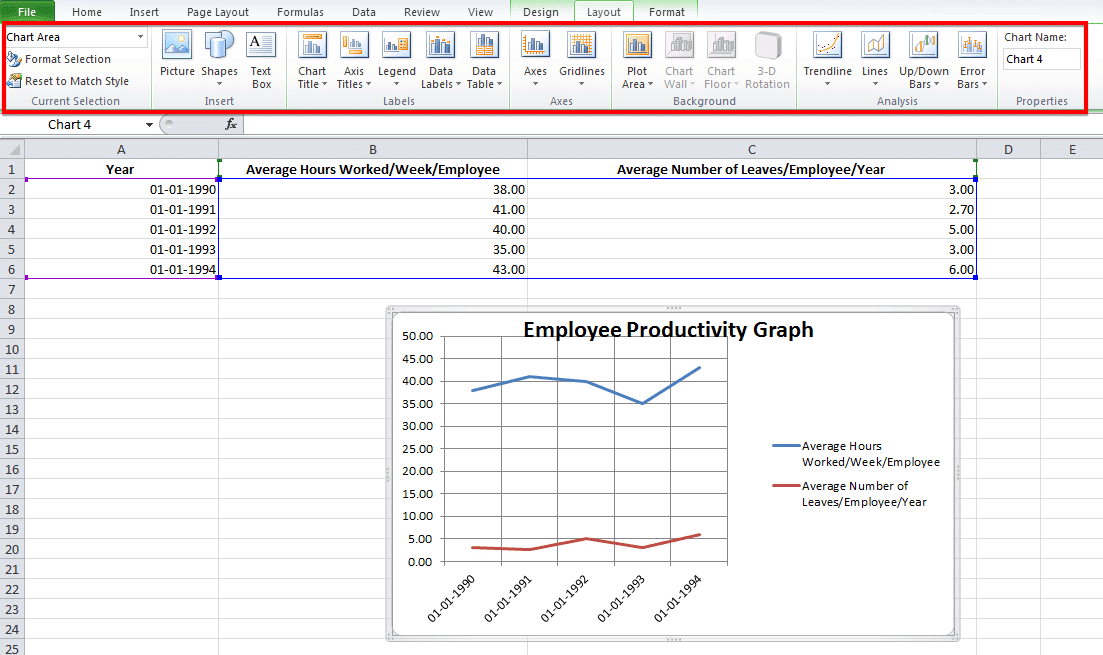
Format: The Format tab allows you to add a border in your chosen width and color around the graph to properly separate it from the data points that are filled in the rows and columns.
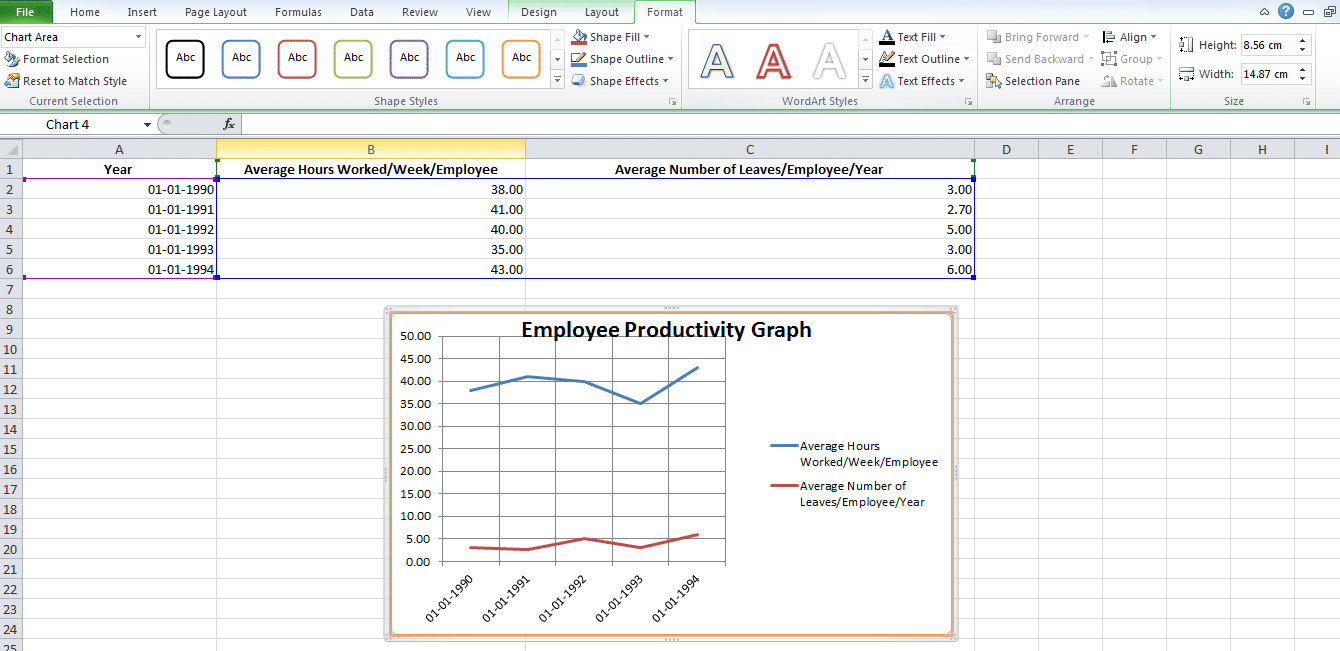
And there you have it. An accurate visual representation of the data that you have imported or entered manually to help your team members and stakeholders better engage with the information and utilize it to create strategies or be more aware of all the constraints while taking decisions!
Challenges with Making a Graph In Excel
When manipulating simple data sets, you can create a graph fairly easily.
But when you start adding in several types of data with multiple parameters, then there will be glitches. Here are some of the challenges that you’re going to have:
- Data sorting can be problematic when creating graphs. Online tutorials might recommend data sorting to make your “charts” look more aesthetically appealing. But beware of when the X axis is a time-based parameter! Sorting data values by magnitude may mess up the flow of the graph because the dates are sorted randomly. You may not be able to spot the trends very well.
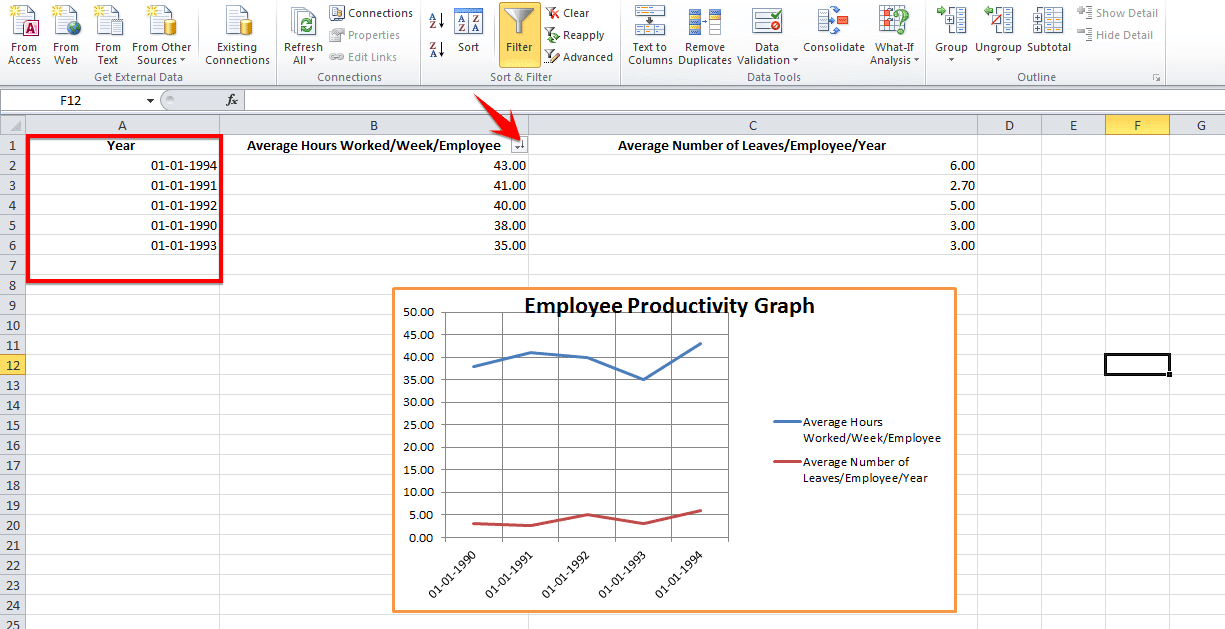
You may forget to remove duplicates. This is especially true if you have imported the data from a third-party application. Generally, this type of information is not filtered of redundancies. And you might end up corrupting the integrity of your information if duplicates sneak into your pictorial representation of trends. When working with copious volumes of data, it is best to use the Remove Duplicates option on your rows.
Creating graphs in Excel doesn’t have to be overly complex, but, much like with creating Gantt charts in Excel, there can be some easier tools to help you do it. If you’re trying to create graphs for workloads, budget allocations or monitoring projects, check out project management software instead.
Many of those functions are automated and without manual data entry. And you won’t be left wondering about who has the latest data sets. Most project management solutions, like Workzone, have file sharing and some visualization capabilities built-in.
Содержание
- Create a chart
- Want more?
- How to Make a Graph in Excel (2023 Guide)
- What are Graphs & Charts in Microsoft Excel?
- Wondering if graphs and charts in Excel are the same?
- Steps To Make a Graph in Excel
- ⭐️ Step 1: fill the Excel sheet with data
- ⭐️ Step 2: determine the Excel graph type you want
- How To Create a Line Graph in Excel – 3 Steps
- ⭐️ Step 1: select data to turn into a line graph
- ⭐️ Step 2: insert line graph
- ⭐️ Step 3: customize your line graph
- 3 Steps To Create a Bar Graph in Excel
- ⭐️ Step 1: select data to turn into a bar graph
- ⭐️ Step 2: insert bar graph
- ⭐️ Step 3: customize your Excel bar graph
- Create Effortless Graphs With ClickUp
- 1. Line Chart Widgets
- 2. Gantt Chart view
- 3. Table view
- Now Showing: ClickUp 🎥🍿
Create a chart
Create a chart (graph) that is recommended for your data, almost as fast as using the chart wizard that is no longer available.
Select the data for which you want to create a chart.
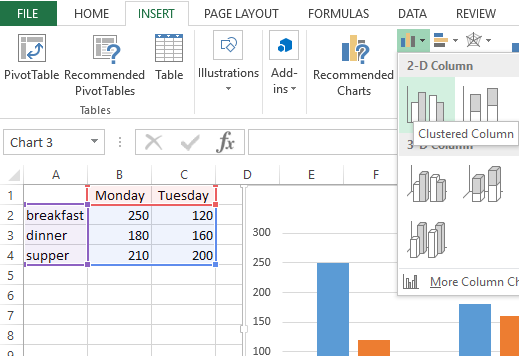
Click INSERT > Recommended Charts.
On the Recommended Charts tab, scroll through the list of charts that Excel recommends for your data, and click any chart to see how your data will look.
If you don’t see a chart you like, click All Charts to see all the available chart types.
When you find the chart you like, click it > OK.
Use the Chart Elements, Chart Styles, and Chart Filters buttons, next to the upper-right corner of the chart to add chart elements like axis titles or data labels, customize the look of your chart, or change the data that is shown in the chart.
To access additional design and formatting features, click anywhere in the chart to add the CHART TOOLS to the ribbon, and then click the options you want on the DESIGN and FORMAT tabs.
Want more?
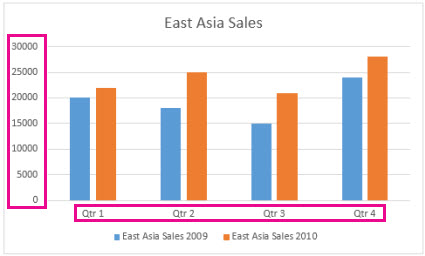
Charts provide a visual representation of your data, making it easier to analyze.
For example, I want to create a chart for Sales, to see if there is a pattern.
I select the cells that I want to use for the chart, click the Quick Analysis button, and click the CHARTS tab.
Excel displays recommended charts based on the data in the cells selected.
You can hover over each one to see what looks good for your data.
Clustered Column is great for comparing data, so I click it.
And now, I have an eye catching chart of the data.
It looks like the Summer months are slower and the Winter months are busier.
Up next, Create pie, bar, and line charts.
Источник
How to Make a Graph in Excel (2023 Guide)
Over the past years, one of the things we’ve learned is that Microsoft Excel is like a Hallmark movie.
Some of us can’t get enough of them and others just can’t stand it. 💔😬
Regardless of your preference, if you’re a manager or business owner, you’ll probably have to rely on Excel for business insights.
And unlike Hallmark movies, you can’t really opt to sit it out.
(Or can you? 🤔)
The point is, tools like Microsoft Excel graphs are helpful for data analysis and tracking.
And wayyy better than endless spreadsheets that can easily trigger a migraine.
Then why not turn your boring Excel spreadsheet into something interesting?
In this article, we’ll learn what an Excel graph is, how to make a graph in Excel, and its drawbacks. We’ll also suggest an alternative to create effortless graphs.
What are Graphs & Charts in Microsoft Excel?
Graphs in Excel are graphical representations of variations in values of data points over a given period.
In other words, it’s a diagram that represents changes in comparison to one or more variables.
Take a look at the image for clarity:
Wondering if graphs and charts in Excel are the same?
Graphs are mostly numerical representations of data as it shows how one variable is affecting or changing another.
On the other hand, charts are visual representations where variables may or may not be associated. They’re also considered more aesthetically pleasing than graphs. For example, a pie chart. 🥧
However, if you’re wondering how to make a chart in Excel, it isn’t very different from making a graph.
But for now, let’s focus on the main plot: graphs!✨
Steps To Make a Graph in Excel
The first (and obvious step) is to open a new Excel file or a blank Excel worksheet.
Then let’s learn how to create a graph in Excel.
⭐️ Step 1: fill the Excel sheet with data
Start by populating your Excel spreadsheet with the data you need.
You may import this data from different software, insert it manually, or copy and paste it.
For our example, let’s say you’re an owner of a movie theater in a small town, and you often screen older movies. You probably want to track the sales of your tickets to see which movie is a hit so you can screen it frequently.
Let’s do that by comparing the ticket sales in January and February.
Here’s what your data might look like:
Column A contains the movie names.
Column B contains tickets sold in January.
And column C contains tickets sold in February.
You can bold headings and center align your text for better readability.
Done? Okay, get ready to pick a graph. 😊
⭐️ Step 2: determine the Excel graph type you want
The type of graph you pick will depend on the data you have and the number of different parameters you want to track.
You’ll find the different graph types under the Excel Insert tab, in the Excel Ribbon, arranged close to one another like this:
Note: The Excel Ribbon is where you can find the Home, Insert, and Draw tabs.
Here are some of the different Excel graph or chart type options you can choose from:
- Line graph
- Column graph or bar graph
- Pie graph or chart
- Combo chart
- Area chart
- Scatter plot chart
➡️ Fun fact: Excel can help you decide the graph or chart type with the Recommended Charts (formerly known as Chart Wizard) option.
If you want to take notes of trends (increase or decrease) over time, then a line graph is perfect.
But for a long time frame and more data, a bar graph is the best option.
We’ll use these two graphs for the purpose of this Excel tutorial.
How To Create a Line Graph in Excel – 3 Steps
A line graph in Excel typically has two axes (horizontal and vertical) to function.
You need to enter the data in two columns.
Lucky for us, we’ve already done this when creating the ticket sales data table.
⭐️ Step 1: select data to turn into a line graph
Click and drag from the top-left cell (A1) in your ticket sales data to the bottom-right cell (C7) to select. Don’t forget to include column headers.
This will highlight all the data you want to display in your line graph.
⭐️ Step 2: insert line graph
Now that you’ve selected your data, it’s time to add the line graph.
Look for the line graph icon under the Insert tab.
With the data selected, go to Insert > Line. Click on the icon, and a dropdown menu will appear to select the type of line chart you want.
For this example, we’ll choose the fourth 2-D line graph (Line with Markers).
Excel will add your line graph representing your selected data series.
You’ll then notice the names of the movies appear on the horizontal axis and the number of tickets sold on the vertical axis.
⭐️ Step 3: customize your line graph
After adding the line graph, you’ll notice a new tab called Chart Design on your Excel Ribbon.
Select the Design tab to make the line graph your own by choosing the chart style you prefer.
You can also change the graph’s title.
Select the Chart Title > double click to name > type in the name you wish to call it. To save it, simply click anywhere outside the graph’s title box or chart area.
We’ll name our graph “Movie Ticket Sales.”
Anything else you need to tweak?
If you spot anything, now is the time to make those edits!
For example, here you can see The Godfather and Modern Times are smooshed together.
Let’s give them some space.
Just drag any corner of the graph until it’s how you desire.
These are just some examples. You can customize every chart element if you like including the Axis Labels (the color of the lines that represent each data point, etc.)
Just double click on any chart element to open a sidebar for formatting like this:
That’s it! You’ve successfully created a line graph in Excel, and it looks like you should screen Modern Times more often.
Now, let’s learn how to make a bar graph. 📊
3 Steps To Create a Bar Graph in Excel
Any Excel graph or Excel chart begins with a populated sheet.
We’ve already done this, so copy and paste the movie ticket sales data to a new sheet tab in the same Excel workbook.
⭐️ Step 1: select data to turn into a bar graph
Like step 1 for the line graph, you need to select the data you wish to turn into a bar graph.
Drag from cell A1 to C7 to highlight the data.
⭐️ Step 2: insert bar graph
Highlight your data, go to the Insert tab, and click on the Column chart or graph icon. A dropdown menu should appear.
Select Clustered Bar under the 2-D bar options.
Note: you can choose a different type of bar chart option like a 3D clustered column or 2D stacked bar, etc.
As soon as you click on the bar graph option, it’ll be added to your Excel sheet.
⭐️ Step 3: customize your Excel bar graph
Now, you can go to the Chart Design tab in the Excel Ribbon to personalize it.
Click on the Design tab to apply a bar style you prefer from the many options.
You know the next step! Change the bar graph’s title.
Select the Excel Chart Title > double click on the title box > type in “Movie Ticket Sales.”
Then click anywhere on the excel sheet to save it.
Note: you can also add other graph elements such as Axis Title, Data Label, Data Table, etc., with the Add Chart Element option. You’ll find it under the Chart Design tab.
And that’s a wrap. 🎬
You’ve successfully created a bar graph in Excel!
Well, that was fun.
But the question is, do you have the time for graphs in your busy work schedule?
And that’s just the teaser when it comes to Excel graph drawbacks.
Read on to watch the full movie. 👀
Create Effortless Graphs With ClickUp
If ClickUp were a Hallmark movie, graphs and this project management tool would be the perfect match.
A forever kind-of-love. ❤️
Whether you want to create graphs to monitor time, projects, people, ticket sales… you name it because we can do it all within a few clicks.
All without the drawbacks of using Excel!
Excel can be:
- Time-consuming and manual
- Complex and pricey
- Error-prone
Most of those functions are automated without manual data entry. Phew.
1. Line Chart Widgets
The Line Chart Widget is a Custom Widget on our Dashboard. Use this ClickUp production to visualize literally anything in the form of a line graph.
It can be tracking profits, total daily sales, or how many movies you’ve watched in a month.
Visualize any set of values as a line graph with the Line Chart Widget on ClickUp’s Dashboard!
And that’s not it. You can visualize your data in many different ways too.
Just use any of these Custom Widgets:
- Calculations
- Bar charts
- Battery chart
- Pie chart
- And more
Present your data visually as a pie chart with Custome Widgets in ClickUp!
2. Gantt Chart view
Just like it’s difficult to love just one movie genre, we totally get that graphs alone don’t work.
And that’s why we have charts too!
Specifically, ClickUp’s Gantt chart, an interactive chart with live updates and progress tracking that can help you:
Drawing a relationship from one task to a future task in ClickUp’s Gantt Chart view!
3. Table view
If you’re a fan of the Excel grids, ClickUp has your back.
This view lets you visualize your tasks in the spreadsheet style.
It’s super fast and allows easy navigation between fields, bulk edits, and data export.
➡️ Fun fact: you can quickly copy and paste your table’s data into other programs, like MS Excel. Just click and drag to highlight the cells you want to copy.
Highlight data from your table in ClickUp to copy and paste into other programs!
And that was just the trailer for you. 📽️
Here are some more powerful ClickUp features in store for:
- Send and receive emails right from your project management tool with Email in ClickUp
- Work even when the wifi acts up with Offline Mode
- Work how you like with multiple ClickUp Views, including Calendar, Mind Maps, Chat, etc.
- Reduce your workload with ClickUp Automations
- Track time spent on tasks with ClickUp’s Native Time Tracker
- Share Table view or Dashboards with clients and external users using Public Sharing and Permissions
- View all graphs and charts on the go with ClickUp mobile apps
Now Showing: ClickUp 🎥🍿
You can surely make tons of graphs in Excel.
But does that make it a smart choice?
I mean, if you have to Google how to make a graph in Excel, maybe that’s your red flag. 🚩
Tools are supposed to make your life easier.
Take ClickUp, for instance.
Our project management tool can be your graph maker, chart creator, spreadsheet builder, time tracker, workload manager…
It’s a hallmark for a quality tool that can be your all-in-one solution.
Get your ClickUp ticket for free today and enjoy watching your graphs come to life in minutes!
Related readings:
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Источник
Building charts and graphs are one of the best ways to visualize data in a clear and comprehensible way.
However, it’s no surprise that some people get a little intimidated by the prospect of poking around in Microsoft Excel.
I thought I’d share a helpful video tutorial as well as some step-by-step instructions for anyone out there who cringes at the thought of organizing a spreadsheet full of data into a chart that actually, you know, means something. But before diving in, we should go over the different types of charts you can create in the software.
Types of Charts in Excel
You can make more than just bar or line charts in Microsoft Excel, and when you understand the uses for each, you can draw more insightful information for your or your team’s projects.
|
Type of Chart |
Use |
|
Area |
Area charts demonstrate the magnitude of a trend between two or more values over a given period. |
|
Bar |
Bar charts compare the frequency of values across different levels or variables. |
|
Column |
Column charts display data changes or a period of time. |
|
Line |
Similar to bar charts, they illustrate trends over time. |
|
Pie |
Pie charts show values as percentages of a whole. |
|
Radar |
Radar charts compare the aggregate of multiple data series. |
|
Scatter |
Scatter charts show the positive or negative relationship between two variables. |
|
Stock |
Stock charts are used to report the fluctuation of stock prices over given periods. |
|
Surface |
Surface charts plot sets of values in the form of a three-dimensional surface. |
The steps you need to build a chart or graph in Excel are simple, and here’s a quick walkthrough on how to make them.
Keep in mind there are many different versions of Excel, so what you see in the video above might not always match up exactly with what you’ll see in your version. In the video, I used Excel 2021 version 16.49 for Mac OS X.
To get the most updated instructions, I encourage you to follow the written instructions below (or download them as PDFs). Most of the buttons and functions you’ll see and read are very similar across all versions of Excel.
Download Demo Data | Download Instructions (Mac) | Download Instructions (PC)
- Enter your data into Excel.
- Choose one of nine graph and chart options to make.
- Highlight your data and click ‘Insert’ your desired graph.
- Switch the data on each axis, if necessary.
- Adjust your data’s layout and colors.
- Change the size of your chart’s legend and axis labels.
- Change the Y-axis measurement options, if desired.
- Reorder your data, if desired.
- Title your graph.
- Export your graph or chart.
Featured Resource: Free Excel Graph Templates
Why start from scratch? Use these free Excel Graph Generators. just input your data and adjust as needed for a beautiful data visualization.
1. Enter your data into Excel.
First, you need to input your data into Excel. You might have exported the data from elsewhere, like a piece of marketing software or a survey tool. Or maybe you’re inputting it manually.
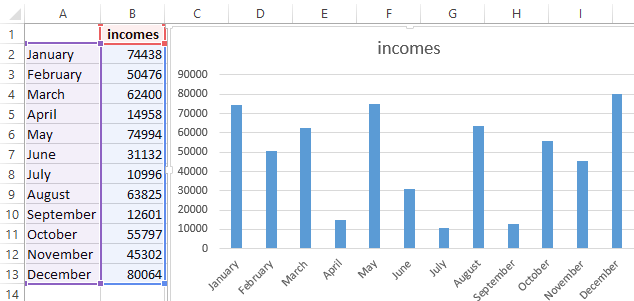
In the example below, in Column A, I have a list of responses to the question, “Did inbound marketing demonstrate ROI?”, and in Columns B, C, and D, I have the responses to the question, “Does your company have a formal sales-marketing agreement?” For example, Column C, Row 2 illustrates that 49% of people with a service level agreement (SLA) also say that inbound marketing demonstrated ROI.
2. Choose from the graph and chart options.
In Excel, your options for charts and graphs include column (or bar) graphs, line graphs, pie graphs, scatter plots, and more. See how Excel identifies each one in the top navigation bar, as depicted below:
To find the chart and graph options, select Insert.
(For help figuring out which type of chart/graph is best for visualizing your data, check out our free ebook, How to Use Data Visualization to Win Over Your Audience.)
3. Highlight your data and insert your desired graph into the spreadsheet.
In this example, a bar graph presents the data visually. To make a bar graph, highlight the data and include the titles of the X and Y-axis. Then, go to the Insert tab and click the column icon in the charts section. Choose the graph you wish from the dropdown window that appears.
I picked the first two dimensional column option because I prefer the flat bar graphic over the three dimensional look. See the resulting bar graph below.
4. Switch the data on each axis, if necessary.
If you want to switch what appears on the X and Y axis, right-click on the bar graph, click Select Data, and click Switch Row/Column. This will rearrange which axes carry which pieces of data in the list shown below. When finished, click OK at the bottom.
The resulting graph would look like this:
5. Adjust your data’s layout and colors.
To change the labeling layout and legend, click on the bar graph, then click the Chart Design tab. Here, you can choose which layout you prefer for the chart title, axis titles, and legend. In my example below, I clicked on the option that displayed softer bar colors and legends below the chart.
To further format the legend, click on it to reveal the Format Legend Entry sidebar, as shown below. Here, you can change the fill color of the legend, which will change the color of the columns themselves. To format other parts of your chart, click on them individually to reveal a corresponding Format window.
6. Change the size of your chart’s legend and axis labels.
When you first make a graph in Excel, the size of your axis and legend labels might be small, depending on the graph or chart you choose (bar, pie, line, etc.) Once you’ve created your chart, you’ll want to beef up those labels so they’re legible.
To increase the size of your graph’s labels, click on them individually and, instead of revealing a new Format window, click back into the Home tab in the top navigation bar of Excel. Then, use the font type and size dropdown fields to expand or shrink your chart’s legend and axis labels to your liking.
7. Change the Y-axis measurement options if desired.
To change the type of measurement shown on the Y axis, click on the Y-axis percentages in your chart to reveal the Format Axis window. Here, you can decide if you want to display units located on the Axis Options tab, or if you want to change whether the Y-axis shows percentages to two decimal places or no decimal places.
Because my graph automatically sets the Y axis’s maximum percentage to 60%, you might want to change it manually to 100% to represent my data on a universal scale. To do so, you can select the Maximum option — two fields down under Bounds in the Format Axis window — and change the value from 0.6 to one.
The resulting graph will look like the one below (In this example, the font size of the Y-axis has been increased via the Home tab so that you can see the difference):
8. Reorder your data, if desired.
To sort the data so the respondents’ answers appear in reverse order, right-click on your graph and click Select Data to reveal the same options window you called up in Step 3 above. This time, arrow up and down to reverse the order of your data on the chart.
If you have more than two lines of data to adjust, you can also rearrange them in ascending or descending order. To do this, highlight all of your data in the cells above your chart, click Data and select Sort, as shown below. Depending on your preference, you can choose to sort based on smallest to largest, or vice versa.
The resulting graph would look like this:
9. Title your graph.
Now comes the fun and easy part: naming your graph. By now, you might have already figured out how to do this. Here’s a simple clarifier.
Right after making your chart, the title that appears will likely be «Chart Title,» or something similar depending on the version of Excel you’re using. To change this label, click on «Chart Title» to reveal a typing cursor. You can then freely customize your chart’s title.
When you have a title you like, click Home on the top navigation bar, and use the font formatting options to give your title the emphasis it deserves. See these options and my final graph below:
10. Export your graph or chart.
Once your chart or graph is exactly the way you want it, you can save it as an image without screenshotting it in the spreadsheet. This method will give you a clean image of your chart that can be inserted into a PowerPoint presentation, Canva document, or any other visual template.
To save your Excel graph as a photo, right-click on the graph and select Save as Picture.
In the dialogue box, name the photo of your graph, choose where to save it on your computer, and choose the file type you’d like to save it as. In this example, it’s saved as a JPEG to a desktop folder. Finally, click Save.
You’ll have a clear photo of your graph or chart that you can add to any visual design.
Visualize Data Like A Pro
That was pretty easy, right? With this step-by-step tutorial, you’ll be able to quickly create charts and graphs that visualize the most complicated data. Try using this same tutorial with different graph types like a pie chart or line graph to see what format tells the story of your data best.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in June 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Download Article
Download Article
If you’re looking for a great way to visualize data in Microsoft Excel, you can create a graph or chart. Whether you’re using Windows or macOS, creating a graph from your Excel data is quick and easy, and you can even customize the graph to look exactly how you want. This wikiHow tutorial will walk you through making a graph in Excel.
Steps
-
1
Open Microsoft Excel. Its app icon resembles a green box with a white «X» on it.
-
2
Click Blank workbook. It’s a white box in the upper-left side of the window.
Advertisement
-
3
Consider the type of graph you want to make. There are three basic types of graph that you can create in Excel, each of which works best for certain types of data:[1]
- Bar — Displays one or more sets of data using vertical bars. Best for listing differences in data over time or comparing two similar sets of data.
- Line — Displays one or more sets of data using horizontal lines. Best for showing growth or decline in data over time.
- Pie — Displays one set of data as fractions of a whole. Best for showing a visual distribution of data.
-
4
Add your graph’s headers. The headers, which determine the labels for individual sections of data, should go in the top row of the spreadsheet, starting with cell B1 and moving right from there.
- For example, to create a set of data called «Number of Lights» and another set called «Power Bill», you would type Number of Lights into cell B1 and Power Bill into C1
- Always leave cell A1 blank.
-
5
Add your graph’s labels. The labels that separate rows of data go in the A column (starting in cell A2). Things like time (e.g., «Day 1», «Day 2», etc.) are usually used as labels.
- For example, if you’re comparing your budget with your friend’s budget in a bar graph, you might label each column by week or month.
- You should add a label for each row of data.
-
6
Enter your graph’s data. Starting in the cell immediately below your first header and immediately to the right of your first label (most likely B2), enter the numbers that you want to use for your graph.
- You can press the Tab ↹ key once you’re done typing in one cell to enter the data and jump one cell to the right if you’re filling in multiple cells in a row.
-
7
Select your data. Click and drag your mouse from the top-left corner of the data group (e.g., cell A1) to the bottom-right corner, making sure to select the headers and labels as well.
-
8
Click the Insert tab. It’s near the top of the Excel window. Doing so will open a toolbar below the Insert tab.
-
9
Select a graph type. In the «Charts» section of the Insert toolbar, click the visual representation of the type of graph that you want to use. A drop-down menu with different options will appear.
- A bar graph resembles a series of vertical bars.
- A line graph resembles two or more squiggly lines.
- A pie graph resembles a sectioned-off circle.
-
10
Select a graph format. In your selected graph’s drop-down menu, click a version of the graph (e.g., 3D) that you want to use in your Excel document. The graph will be created in your document.
- You can also hover over a format to see a preview of what it will look like when using your data.
-
11
Add a title to the graph. Double-click the «Chart Title» text at the top of the chart, then delete the «Chart Title» text, replace it with your own, and click a blank space on the graph.
- On a Mac, you’ll instead click the Design tab, click Add Chart Element, select Chart Title, click a location, and type in the graph’s title.[2]
- On a Mac, you’ll instead click the Design tab, click Add Chart Element, select Chart Title, click a location, and type in the graph’s title.[2]
-
12
Save your document. To do so:
- Windows — Click File, click Save As, double-click This PC, click a save location on the left side of the window, type the document’s name into the «File name» text box, and click Save.
- Mac — Click File, click Save As…, enter the document’s name in the «Save As» field, select a save location by clicking the «Where» box and clicking a folder, and click Save.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I change the horizontal axis to a vertical axis in Excel?
Click «Edit» and then press «Move.» If this doesn’t work, double click the axis and use the dots to move it.
-
Question
How do I print a graph only in Excel?
Type control p on your laptop or go to print on the page font of your screen?
-
Question
How do I label a Series?
Jayna Akanova
Community Answer
Right-click the chart with the data series you want to rename, and click Select Data. In the Select Data Source dialog box, under Legend Entries (Series), select the data series, and click Edit. In the Series name box, type the name you want to use.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
You can change the graph’s visual appearance on the Design tab.
-
If you don’t want to select a specific type of graph, you can click Recommended Charts and then select a graph from Excel’s recommendation window.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Some graph formats won’t include all of your data, or will display it in a confusing manner. It’s important to choose a graph format that works with your data.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Enter the graph’s headers.
2. Add the graph’s labels.
3. Enter the graph’s data.
4. Select all data including headers and labels.
5. Click Insert.
6. Select a graph type.
7. Select a graph format.
8. Add a title to the graph.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,722,650 times.
Is this article up to date?
Charts help you visualize your data in a way that creates maximum impact on your audience. Learn to create a chart and add a trendline. You can start your document from a recommended chart or choose one from our collection of pre-built chart templates.
Create a chart
-
Select data for the chart.
-
Select Insert > Recommended Charts.
-
Select a chart on the Recommended Charts tab, to preview the chart.
Note: You can select the data you want in the chart and press ALT + F1 to create a chart immediately, but it might not be the best chart for the data. If you don’t see a chart you like, select the All Charts tab to see all chart types.
-
Select a chart.
-
Select OK.
Add a trendline
-
Select a chart.
-
Select Design > Add Chart Element.
-
Select Trendline and then select the type of trendline you want, such as Linear, Exponential, Linear Forecast, or Moving Average.
Note: Some of the content in this topic may not be applicable to some languages.
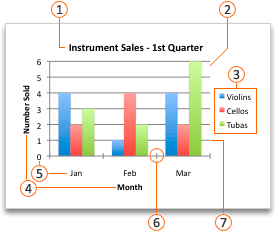
Charts display data in a graphical format that can help you and your audience visualize relationships between data. When you create a chart, you can select from many chart types (for example, a stacked column chart or a 3-D exploded pie chart). After you create a chart, you can customize it by applying chart quick layouts or styles.
Charts contain several elements, such as a title, axis labels, a legend, and gridlines. You can hide or display these elements, and you can also change their location and formatting.

You can create a chart in Excel, Word, and PowerPoint. However, the chart data is entered and saved in an Excel worksheet. If you insert a chart in Word or PowerPoint, a new sheet is opened in Excel. When you save a Word document or PowerPoint presentation that contains a chart, the chart’s underlying Excel data is automatically saved within the Word document or PowerPoint presentation.
Note: The Excel Workbook Gallery replaces the former Chart Wizard. By default, the Excel Workbook Gallery opens when you open Excel. From the gallery, you can browse templates and create a new workbook based on one of them. If you don’t see the Excel Workbook Gallery, on the File menu, click New from Template.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the Insert tab, and then click the arrow next to Chart.
-
Click a chart type, and then double-click the chart you want to add.
When you insert a chart into Word or PowerPoint, an Excel worksheet opens that contains a table of sample data.
-
In Excel, replace the sample data with the data that you want to plot in the chart. If you already have your data in another table, you can copy the data from that table and then paste it over the sample data. See the following table for guidelines for how to arrange the data to fit your chart type.
For this chart type
Arrange the data
Area, bar, column, doughnut, line, radar, or surface chart
In columns or rows, as in the following examples:
Series 1
Series 2
Category A
10
12
Category B
11
14
Category C
9
15
or
Category A
Category B
Series 1
10
11
Series 2
12
14
Bubble chart
In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values and bubble size values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
X-Values
Y-Value 1
Size 1
0.7
2.7
4
1.8
3.2
5
2.6
0.08
6
Pie chart
In one column or row of data and one column or row of data labels, as in the following examples:
Sales
1st Qtr
25
2nd Qtr
30
3rd Qtr
45
or
1st Qtr
2nd Qtr
3rd Qtr
Sales
25
30
45
Stock chart
In columns or rows in the following order, using names or dates as labels, as in the following examples:
Open
High
Low
Close
1/5/02
44
55
11
25
1/6/02
25
57
12
38
or
1/5/02
1/6/02
Open
44
25
High
55
57
Low
11
12
Close
25
38
X Y (scatter) chart
In columns, putting x values in the first column and corresponding y values in adjacent columns, as in the following examples:
X-Values
Y-Value 1
0.7
2.7
1.8
3.2
2.6
0.08
or
X-Values
0.7
1.8
2.6
Y-Value 1
2.7
3.2
0.08
-
To change the number of rows and columns included in the chart, rest the pointer on the lower-right corner of the selected data, and then drag to select additional data. In the following example, the table is expanded to include additional categories and data series.
-
To see the results of your changes, switch back to Word or PowerPoint.
Note: When you close the Word document or the PowerPoint presentation that contains the chart, the chart’s Excel data table closes automatically.
After you create a chart, you might want to change the way that table rows and columns are plotted in the chart. For example, your first version of a chart might plot the rows of data from the table on the chart’s vertical (value) axis, and the columns of data on the horizontal (category) axis. In the following example, the chart emphasizes sales by instrument.
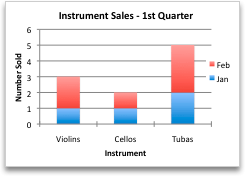
However, if you want the chart to emphasize the sales by month, you can reverse the way the chart is plotted.
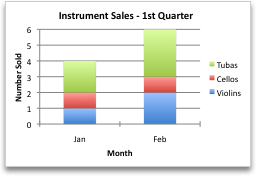
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
Click the Chart Design tab, and then click Switch Row/Column.
If Switch Row/Column is not available
Switch Row/Column is available only when the chart’s Excel data table is open and only for certain chart types. You can also edit the data by clicking the chart, and then editing the worksheet in Excel.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
Click the Chart Design tab, and then click Quick Layout.
-
Click the layout you want.
To immediately undo a quick layout that you applied, press
+ Z .
Chart styles are a set of complementary colors and effects that you can apply to your chart. When you select a chart style, your changes affect the whole chart.
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart.
-
Click the Chart Design tab, and then click the style you want.
To see more styles, point to a style, and then click
.
To immediately undo a style that you applied, press
+ Z .
-
On the View menu, click Print Layout.
-
Click the chart, and then click the Chart Design tab.
-
Click Add Chart Element.
-
Click Chart Title to choose title format options, and then return to the chart to type a title in the Chart Title box.
See also
Update the data in an existing chart
Chart types
Create a chart
You can create a chart for your data in Excel for the web. Depending on the data you have, you can create a column, line, pie, bar, area, scatter, or radar chart.
-
Click anywhere in the data for which you want to create a chart.
To plot specific data into a chart, you can also select the data.
-
Select Insert > Charts > and the chart type you want.
-
On the menu that opens, select the option you want. Hover over a chart to learn more about it.
Tip: Your choice isn’t applied until you pick an option from a Charts command menu. Consider reviewing several chart types: as you point to menu items, summaries appear next to them to help you decide.
-
To edit the chart (titles, legends, data labels), select the Chart tab and then select Format.
-
In the Chart pane, adjust the setting as needed. You can customize settings for the chart’s title, legend, axis titles, series titles, and more.
Available chart types
It’s a good idea to review your data and decide what type of chart would work best. The available types are listed below.
Data that’s arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a column chart. A column chart typically displays categories along the horizontal axis and values along the vertical axis, like shown in this chart:
Types of column charts
-
Clustered column A clustered column chart shows values in 2-D columns. Use this chart when you have categories that represent:
-
Ranges of values (for example, item counts).
-
Specific scale arrangements (for example, a Likert scale with entries, like strongly agree, agree, neutral, disagree, strongly disagree).
-
Names that are not in any specific order (for example, item names, geographic names, or the names of people).
-
-
Stacked column A stacked column chart shows values in 2-D stacked columns. Use this chart when you have multiple data series and you want to emphasize the total.
-
100% stacked column A 100% stacked column chart shows values in 2-D columns that are stacked to represent 100%. Use this chart when you have two or more data series and you want to emphasize the contributions to the whole, especially if the total is the same for each category.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a line chart. In a line chart, category data is distributed evenly along the horizontal axis, and all value data is distributed evenly along the vertical axis. Line charts can show continuous data over time on an evenly scaled axis, and are therefore ideal for showing trends in data at equal intervals, like months, quarters, or fiscal years.
Types of line charts
-
Line and line with markers Shown with or without markers to indicate individual data values, line charts can show trends over time or evenly spaced categories, especially when you have many data points and the order in which they are presented is important. If there are many categories or the values are approximate, use a line chart without markers.
-
Stacked line and stacked line with markers Shown with or without markers to indicate individual data values, stacked line charts can show the trend of the contribution of each value over time or evenly spaced categories.
-
100% stacked line and 100% stacked line with markers Shown with or without markers to indicate individual data values, 100% stacked line charts can show the trend of the percentage each value contributes over time or evenly spaced categories. If there are many categories or the values are approximate, use a 100% stacked line chart without markers.
Notes:
-
Line charts work best when you have multiple data series in your chart—if you only have one data series, consider using a scatter chart instead.
-
Stacked line charts add the data, which might not be the result you want. It might not be easy to see that the lines are stacked, so consider using a different line chart type or a stacked area chart instead.
-
Data that is arranged in one column or row on a worksheet can be plotted in a pie chart. Pie charts show the size of items in one data series, proportional to the sum of the items. The data points in a pie chart are shown as a percentage of the whole pie.
Consider using a pie chart when:
-
You have only one data series.
-
None of the values in your data are negative.
-
Almost none of the values in your data are zero values.
-
You have no more than seven categories, all of which represent parts of the whole pie.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows only on a worksheet can be plotted in a doughnut chart. Like a pie chart, a doughnut chart shows the relationship of parts to a whole, but it can contain more than one data series.
Tip: Doughnut charts are not easy to read. You may want to use a stacked column or stacked bar chart instead.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a bar chart. Bar charts illustrate comparisons among individual items. In a bar chart, the categories are typically organized along the vertical axis, and the values along the horizontal axis.
Consider using a bar chart when:
-
The axis labels are long.
-
The values that are shown are durations.
Types of bar charts
-
Clustered A clustered bar chart shows bars in 2-D format.
-
Stacked bar Stacked bar charts show the relationship of individual items to the whole in 2-D bars
-
100% stacked A 100% stacked bar shows 2-D bars that compare the percentage that each value contributes to a total across categories.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in an area chart. Area charts can be used to plot change over time and draw attention to the total value across a trend. By showing the sum of the plotted values, an area chart also shows the relationship of parts to a whole.
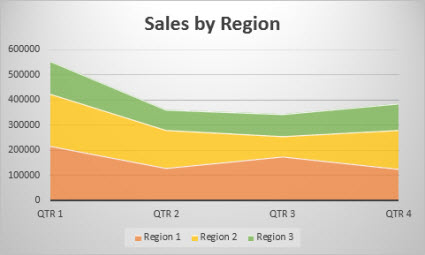
Types of area charts
-
Area Shown in 2-D format, area charts show the trend of values over time or other category data. As a rule, consider using a line chart instead of a non-stacked area chart, because data from one series can be hidden behind data from another series.
-
Stacked area Stacked area charts show the trend of the contribution of each value over time or other category data in 2-D format.
-
100% stacked 100% stacked area charts show the trend of the percentage that each value contributes over time or other category data.
Data that is arranged in columns and rows on a worksheet can be plotted in an scatter chart. Place the x values in one row or column, and then enter the corresponding y values in the adjacent rows or columns.
A scatter chart has two value axes: a horizontal (x) and a vertical (y) value axis. It combines x and y values into single data points and shows them in irregular intervals, or clusters. Scatter charts are typically used for showing and comparing numeric values, like scientific, statistical, and engineering data.
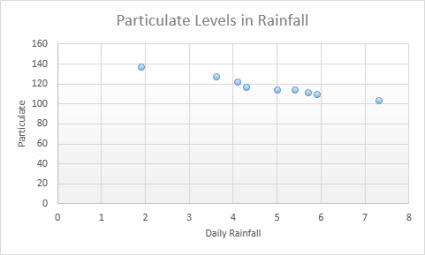
Consider using a scatter chart when:
-
You want to change the scale of the horizontal axis.
-
You want to make that axis a logarithmic scale.
-
Values for horizontal axis are not evenly spaced.
-
There are many data points on the horizontal axis.
-
You want to adjust the independent axis scales of a scatter chart to reveal more information about data that includes pairs or grouped sets of values.
-
You want to show similarities between large sets of data instead of differences between data points.
-
You want to compare many data points without regard to time — the more data that you include in a scatter chart, the better the comparisons you can make.
Types of scatter charts
-
Scatter This chart shows data points without connecting lines to compare pairs of values.
-
Scatter with smooth lines and markers and scatter with smooth lines This chart shows a smooth curve that connects the data points. Smooth lines can be shown with or without markers. Use a smooth line without markers if there are many data points.
-
Scatter with straight lines and markers and scatter with straight lines This chart shows straight connecting lines between data points. Straight lines can be shown with or without markers.
Data that is arranged in columns or rows on a worksheet can be plotted in a radar chart. Radar charts compare the aggregate values of several data series.
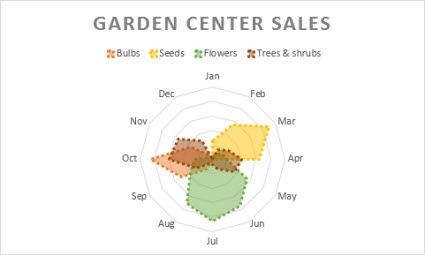
Type of radar charts
-
Radar and radar with markers With or without markers for individual data points, radar charts show changes in values relative to a center point.
-
Filled radar In a filled radar chart, the area covered by a data series is filled with a color.
Add or edit a chart title
You can add or edit a chart title, customize its look, and include it on the chart.
-
Click anywhere in the chart to show the Chart tab on the ribbon.
-
Click Format to open the chart formatting options.
-
In the Chart pane, expand the Chart Title section.
-
Add or edit the Chart Title to meet your needs.
-
Use the switch to hide the title if you don’t want your chart to show a title.
Add axis titles to improve chart readability
Adding titles to the horizontal and vertical axes in charts that have axes can make them easier to read. You can’t add axis titles to charts that don’t have axes, such as pie and doughnut charts.
Much like chart titles, axis titles help the people who view the chart understand what the data is about.
-
Click anywhere in the chart to show the Chart tab on the ribbon.
-
Click Format to open the chart formatting options.
-
In the Chart pane, expand the Horizontal Axis or Vertical Axis section.
-
Add or edit the Horizontal Axis or Vertical Axis options to meet your needs.
-
Expand the Axis Title.
-
Change the Axis Title and modify the formatting.
-
Use the switch to show or hide the title.
Change the axis labels
Axis labels are shown below the horizontal axis and next to the vertical axis. Your chart uses text in the source data for these axis labels.
To change the text of the category labels on the horizontal or vertical axis:
-
Click the cell which has the label text you want to change.
-
Type the text you want and press Enter.
The axis labels in the chart are automatically updated with the new text.
Tip: Axis labels are different from axis titles you can add to describe what is shown on the axes. Axis titles aren’t automatically shown in a chart.
Remove the axis labels
To remove labels on the horizontal or vertical axis:
-
Click anywhere in the chart to show the Chart tab on the ribbon.
-
Click Format to open the chart formatting options.
-
In the Chart pane, expand the Horizontal Axis or Vertical Axis section.
-
From the dropdown box for Label Position, select None to prevent the labels from showing on the chart.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Содержание
- Создание графиков в Excel
- Построение обычного графика
- Редактирование графика
- Построение графика со вспомогательной осью
- Построение графика функции
- Вопросы и ответы
График позволяет визуально оценить зависимость данных от определенных показателей или их динамику. Эти объекты используются и в научных или исследовательских работах, и в презентациях. Давайте рассмотрим, как построить график в программе Microsoft Excel.
Каждый пользователь, желая более наглядно продемонстрировать какую-то числовую информацию в виде динамики, может создать график. Этот процесс несложен и подразумевает наличие таблицы, которая будет использоваться за базу. По своему усмотрению объект можно видоизменять, чтобы он лучше выглядел и отвечал всем требованиям. Разберем, как создавать различные виды графиков в Эксель.
Построение обычного графика
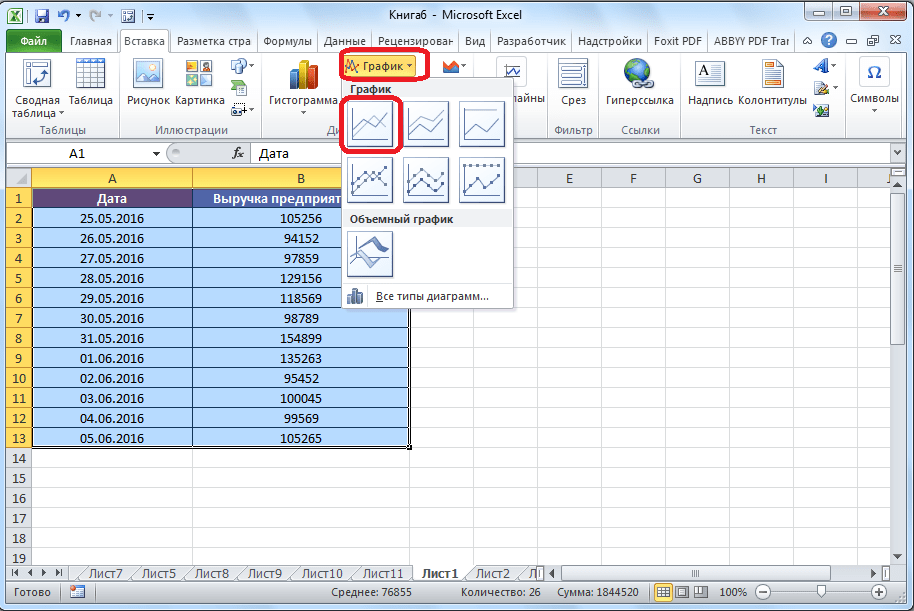
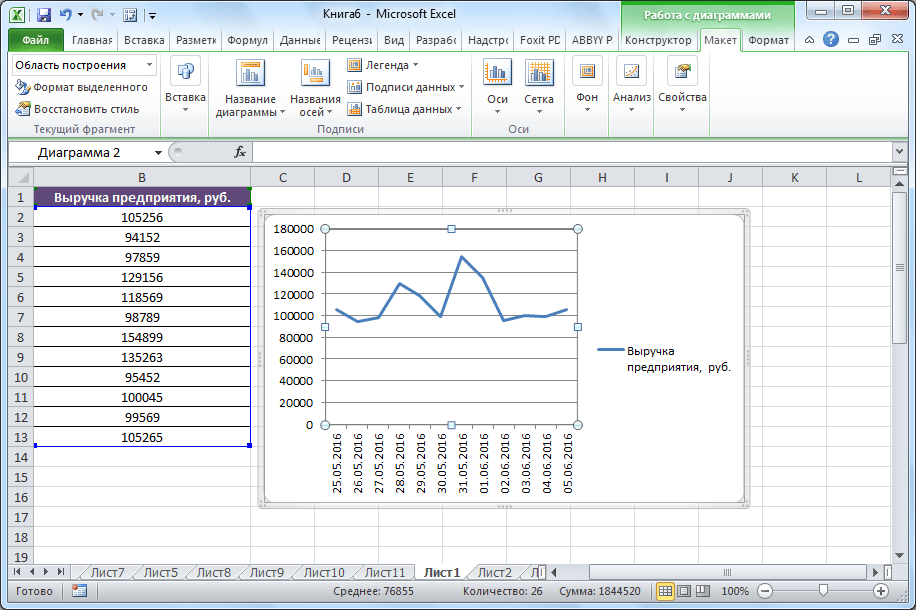
Рисовать график в Excel можно только после того, как готова таблица с данными, на основе которой он будет строиться.
- Находясь на вкладке «Вставка», выделяем табличную область, где расположены расчетные данные, которые мы желаем видеть в графике. Затем на ленте в блоке инструментов «Диаграммы» кликаем по кнопке «График».
- После этого открывается список, в котором представлено семь видов графиков:
- Обычный;
- С накоплением;
- Нормированный с накоплением;
- С маркерами;
- С маркерами и накоплением;
- Нормированный с маркерами и накоплением;
- Объемный.
Выбираем тот, который по вашему мнению больше всего подходит для конкретно поставленных целей его построения.
- Дальше Excel выполняет непосредственное построение графика.
Редактирование графика
После построения графика можно выполнить его редактирование для придания объекту более презентабельного вида и облегчения понимания материала, который он отображает.
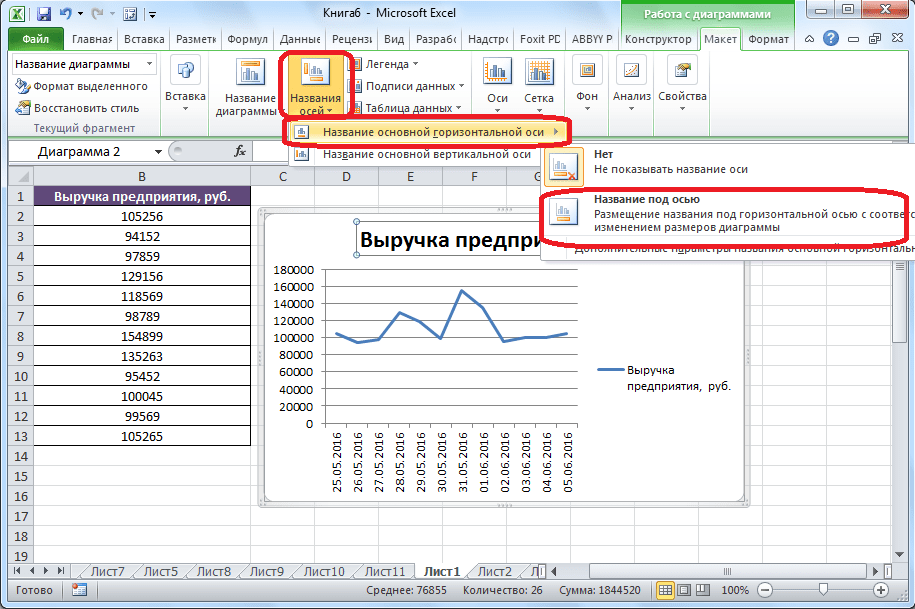
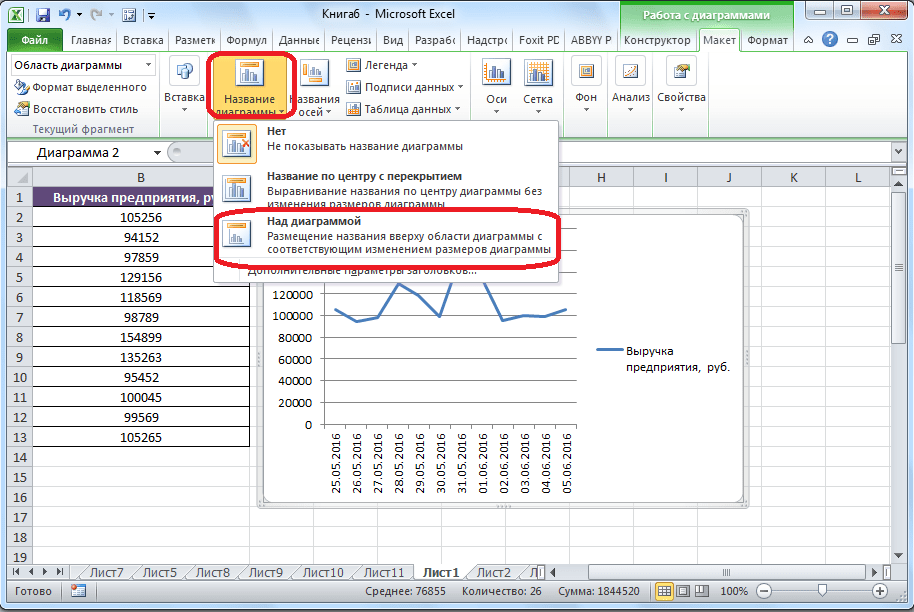
- Чтобы подписать график, переходим на вкладку «Макет» мастера работы с диаграммами. Кликаем по кнопке на ленте с наименованием «Название диаграммы». В открывшемся списке указываем, где будет размещаться имя: по центру или над графиком. Второй вариант обычно более уместен, поэтому мы в качестве примера используем «Над диаграммой». В результате появляется название, которое можно заменить или отредактировать на свое усмотрение, просто нажав по нему и введя нужные символы с клавиатуры.
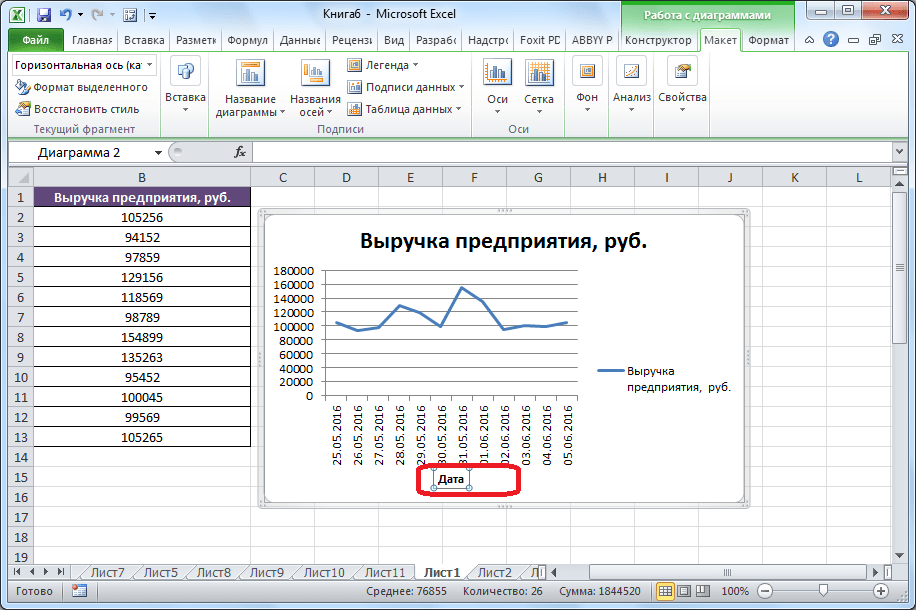
- Задать имя осям можно, кликнув по кнопке «Название осей». В выпадающем списке выберите пункт «Название основной горизонтальной оси», а далее переходите в позицию «Название под осью».
- Под осью появляется форма для наименования, в которую можно занести любое на свое усмотрение название.
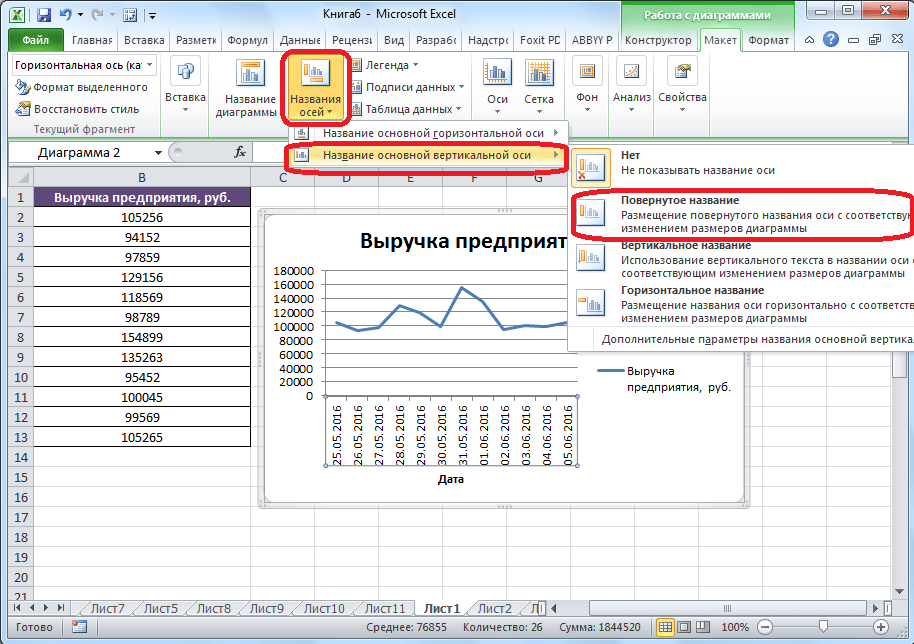
- Аналогичным образом подписываем вертикальную ось. Жмем по кнопке «Название осей», но в появившемся меню выбираем «Название основной вертикальной оси». Откроется перечень из трех вариантов расположения подписи: повернутое, вертикальное, горизонтальное. Лучше всего использовать повернутое имя, так как в этом случае экономится место на листе.
- На листе около соответствующей оси появляется поле, в которое можно ввести наиболее подходящее по контексту расположенных данных название.
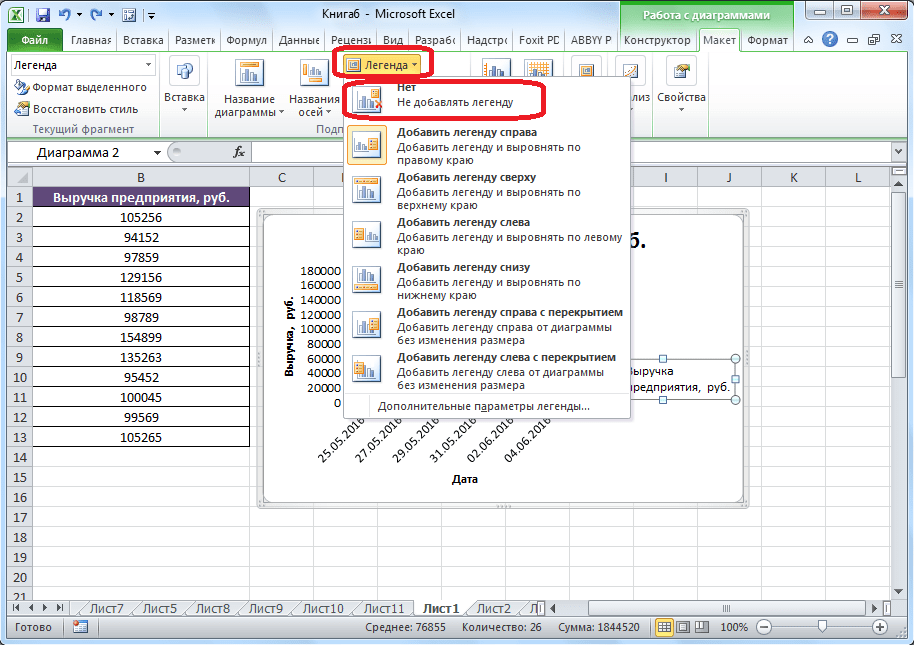
- Если вы считаете, что для понимания графика легенда не нужна и она только занимает место, то можно удалить ее. Щелкните по кнопке «Легенда», расположенной на ленте, а затем по варианту «Нет». Тут же можно выбрать любую позицию легенды, если надо ее не удалить, а только сменить расположение.
Построение графика со вспомогательной осью
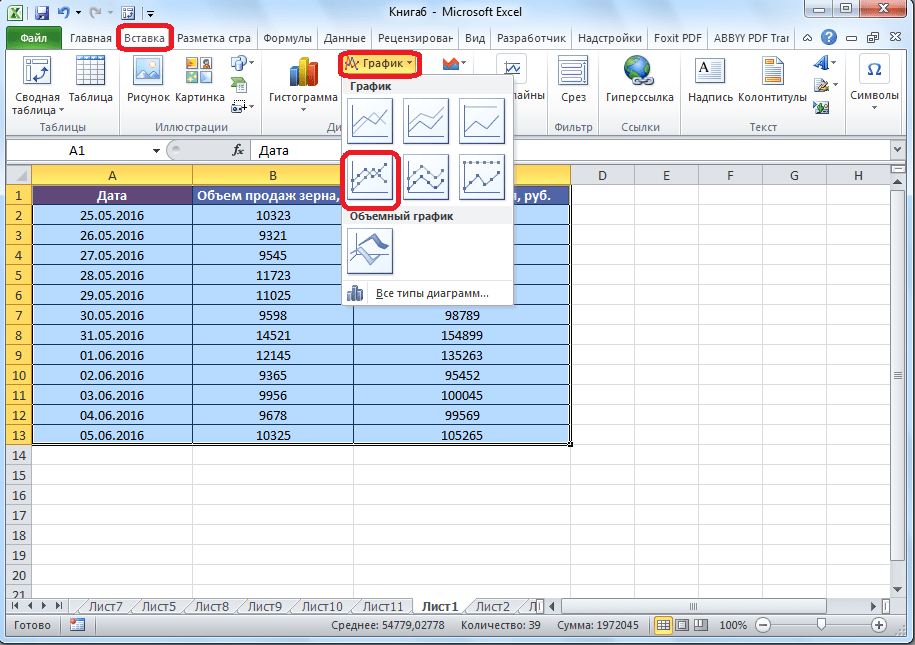
Существуют случаи, когда нужно разместить несколько графиков на одной плоскости. Если они имеют одинаковые меры исчисления, то это делается точно так же, как описано выше. Но что делать, если меры разные?
- Находясь на вкладке «Вставка», как и в прошлый раз, выделяем значения таблицы. Далее жмем на кнопку «График» и выбираем наиболее подходящий вариант.
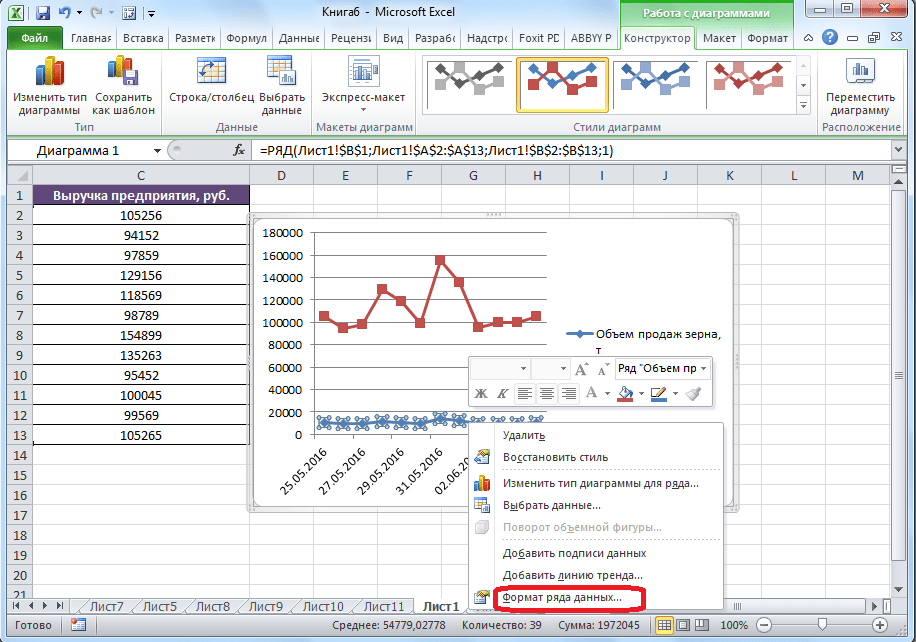
- Как видим, формируются два графика. Для того чтобы отобразить правильное наименование единиц измерения для каждого графика, кликаем правой кнопкой мыши по тому из них, для которого собираемся добавить дополнительную ось. В появившемся меню указываем пункт «Формат ряда данных».
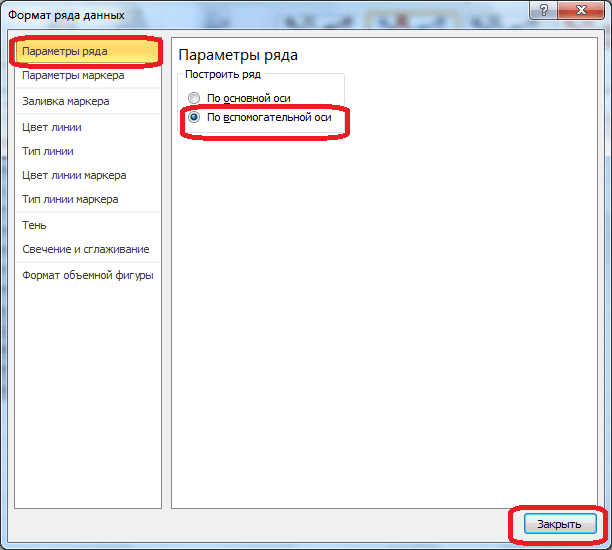
- Запускается окно формата ряда данных. В его разделе «Параметры ряда», который должен открыться по умолчанию, переставляем переключатель в положение «По вспомогательной оси». Жмем на кнопку «Закрыть».
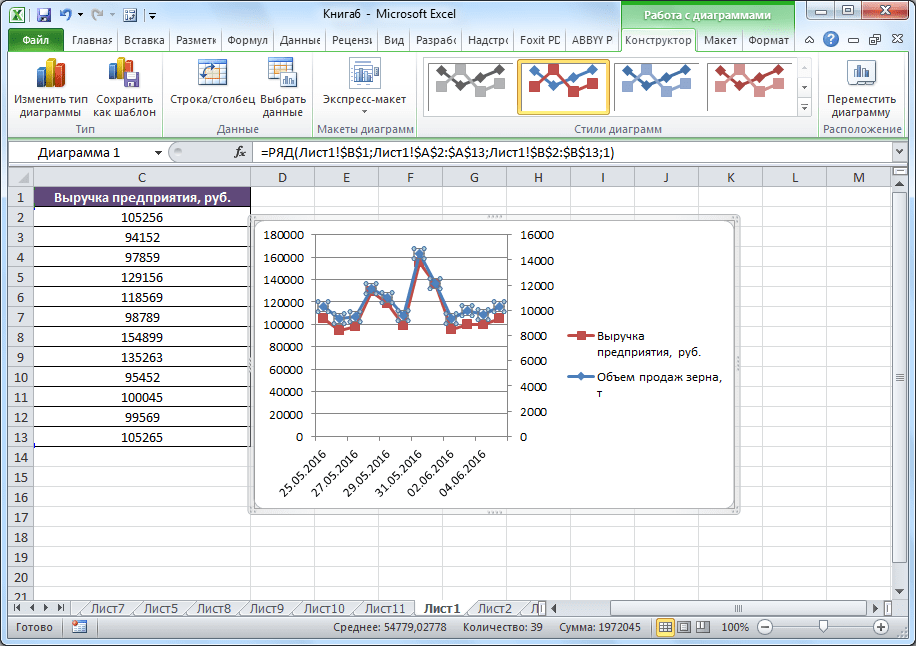
- Образуется новая ось, а график перестроится.
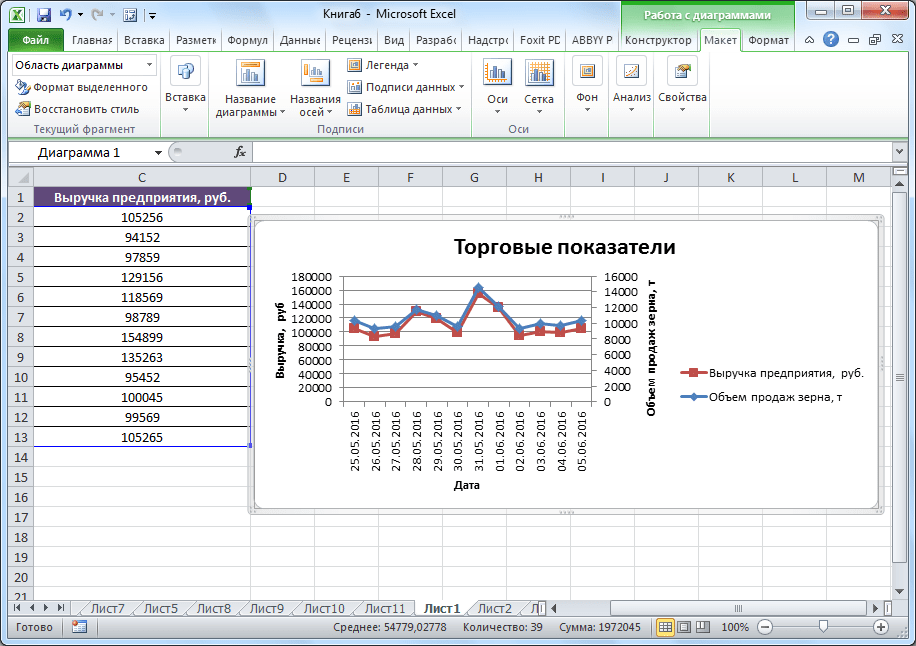
- Нам только осталось подписать оси и название графика по алгоритму, аналогичному предыдущему примеру. При наличии нескольких графиков легенду лучше не убирать.
Построение графика функции
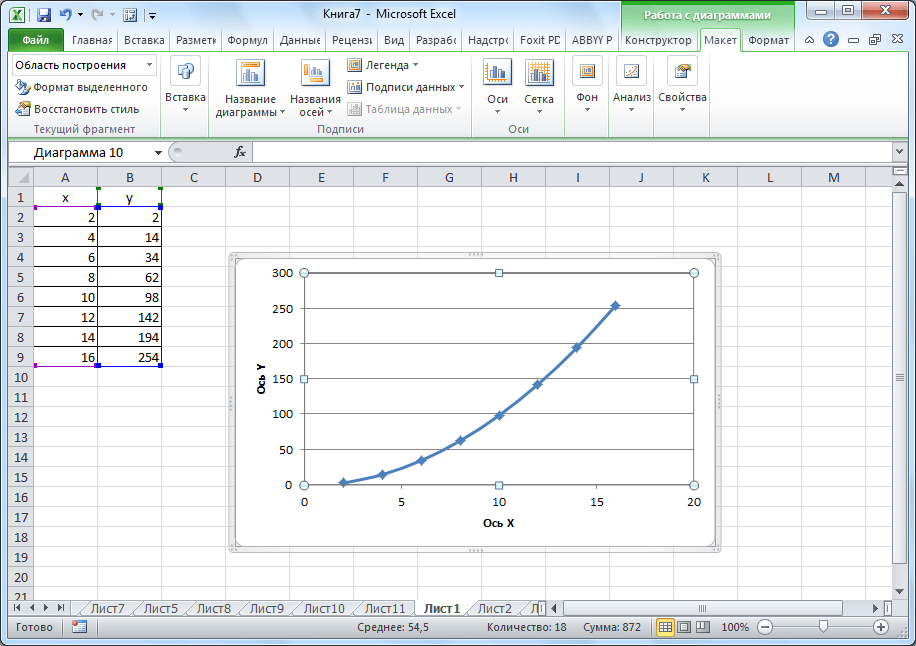
Теперь давайте разберемся, как построить график по заданной функции.
- Допустим, мы имеем функцию
Y=X^2-2. Шаг будет равен 2. Прежде всего построим таблицу. В левой части заполняем значения X с шагом 2, то есть 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 и т.д. В правой части вбиваем формулу. - Далее наводим курсор на нижний правый угол ячейки, щелкаем левой кнопкой мыши и «протягиваем» до самого низа таблицы, тем самым копируя формулу в другие ячейки.
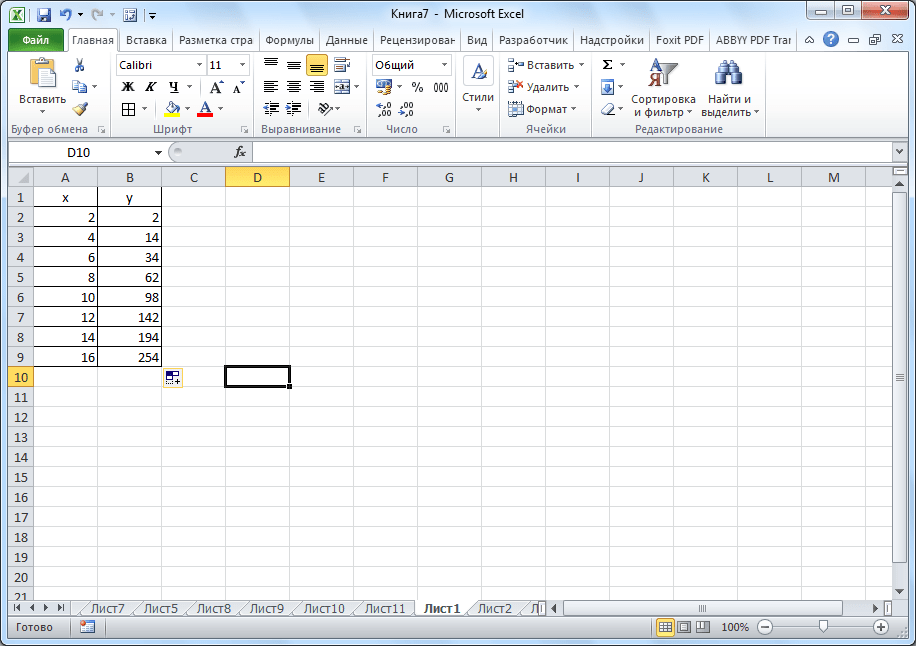
- Затем переходим на вкладку «Вставка». Выделяем табличные данные функции и кликаем по кнопке «Точечная диаграмма» на ленте. Из представленного списка диаграмм выбираем точечную с гладкими кривыми и маркерами, так как этот вид больше всего подходит для построения.
- Выполняется построение графика функции.
- После того как объект был построен, можно удалить легенду и сделать некоторые визуальные правки, о которых уже шла речь выше.

Как видим, Microsoft Excel предлагает возможность построения различных типов графиков. Основным условием для этого является создание таблицы с данными. Созданный график можно изменять и корректировать согласно целевому назначению.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Содержание
- Элементарный график изменения
- Создание графика с несколькими кривыми
- Создание второй оси
- Excel: методика создания графика функции
- Вычисление значений функции
- Создание таблицы и вычисление значений функций
- Построение графиков других функций
- Квадратичная функция y=ax2+bx+c
- Кубическая парабола y=ax3
- Гипербола y=k/x
- Построение точечной диаграммы
- Построение обычного графика
- Редактирование графика
- Как добавить название в график Эксель
- Как подписать оси в графике Excel
- Добавление второй оси
- Наложение и комбинирование графиков
- Особенности оформления графиков в Excel
- Добавление в график вспомогательной оси
- Как построить два графика в Excel
- Как построить график в Excel – Расширение таблицы исходных данных
- Как построить график в Excel – Выбрать данные
- Как построить график в Excel – Выбор источника данных
- Как построить график в Excel – Два графика на одной точечной диаграмме
- Заключение
Элементарный график изменения
График необходим, если от человека требуется продемонстрировать, насколько определенный показатель изменился за конкретный период времени. И обычного графика для выполнения этой задачи вполне достаточно, а вот различные вычурные диаграммы на деле могут только сделать информацию менее читаемой.
Предположим, у нас есть таблица, которая предоставляет информацию о чистой прибыли компании за последние пять лет.
Важно. Эти цифры не представляют фактические данные и могут быть нереалистичными. Они предоставляются только в образовательных целях.
Затем отправьтесь к вкладке «Вставка», где у вас есть возможность осуществить выбор типа графика, который будет подходящим в конкретной ситуации.
Нас интересует тип «График». После нажатия на соответствующую кнопку, появится окошко с настройками внешнего вида будущего графика. Чтобы понять, какой вариант подходит в конкретном случае, вы можете навести указатель мыши на определенный тип, и появится соответствующее приглашение.
После выбора нужного вида диаграммы вам необходимо скопировать таблицу данных связать ее с графиком. Результат будет следующим.
В нашем случае на диаграмме представлено две линии. Первая имеет красный цвет. Вторая – синий. Последняя нам не нужна, поэтому мы можем удалить ее, выбрав ее и нажав кнопку «Удалить». Поскольку мы имеем лишь одну линию, легенда (блок с названиями отдельных линий графика) также может быть удалена. Но маркеры лучше назвать. Найдите панель «Работа с диаграммами» и блок «Подписи данных» на вкладке «Макет». Здесь вы должны определить положение чисел.
Оси рекомендуется называть, чтобы обеспечить большую удобочитаемости графика. На вкладке «Макет» найдите меню «Названия осей» и задайте имя для вертикальной или горизонтальной осей соответственно.
Но вы можете смело обходиться без заголовка. Чтобы удалить его, вам нужно переместить его в область графика, которая невидима для постороннего глаза (над ним). Если вам все еще нужно название диаграммы, вы можете получить доступ ко всем необходимым настройкам через меню «Название диаграммы» на той же вкладке. Вы также можете найти его на вкладке «Макет».
Вместо порядкового номера отчетного года достаточно оставить только сам год. Выберите требуемые значения и щелкните по ним правой кнопкой мышки. Затем кликните по пункту «Выбор данных» – «Изменить подпись горизонтальной оси». Далее вам следует задать диапазон. В случае с нами, это первая колонка таблицы, являющейся источником информации. Результат такой.
Но вообще, можно все оставить, этот график вполне рабочий. Но если есть необходимость сделать привлекательный дизайн графика, то к вашим услугам – Вкладка “Конструктор”, которая позволяет указать фоновый цвет графика, его шрифт, а также разместить его на другом листе.
Создание графика с несколькими кривыми
Предположим, нам надо продемонстрировать инвесторам не одну лишь чистую прибыль предприятия, но и то, сколько в общей сумме будут стоить ее активы. Соответственно, выросло количество информации.
Невзирая на это, в методике создания графика принципиальных отличий нет по сравнению с описанным выше. Просто теперь легенду надо оставить, поскольку ее функция отлично выполняется.
Создание второй оси
Какие же действия необходимо предпринять, чтобы создать еще одну ось на графике? Если мы используем общие метрические единицы, то необходимо применить советы, описанные ранее. Если применяются данные различных типов, то придется добавлять еще одну ось.
Но перед этим нужно построить обычный график, как будто используются одни и те же метрические единицы.
После этого главная ось выделяется. Затем вызовите контекстное меню. В нем будет много пунктов, один из которых – «Формат ряда данных». Его нужно нажать. Затем появится окно, в котором необходимо найти пункт меню «Параметры ряда», а далее выставить опцию «По вспомогательной оси».
Далее закройте окно.
Но это всего лишь один из возможных методов. Никто не мешает, например, использовать для вторичной оси диаграмму другой разновидности. Надо определиться, какая линия требует того, чтобы мы добавили дополнительную ось, и потом кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши по ней и выбрать пункт «Изменить тип диаграммы для ряда».
Далее нужно настроить «внешность» второго ряда. Мы решили остановиться на линейчатой диаграмме.
Вот, как все просто. Достаточно сделать лишь пару кликов, и появляется еще одна ось, настроенная под иной параметр.
Это уже более нетривиальная задача, и для ее выполнения необходимо выполнить два основных действия:
- Сформировать таблицу, служащую источником информации. Сперва следует определиться с тем, какая будет конкретно в вашем случае использоваться функция. Например, y=x(√x – 2). При этом в качестве используемого шага мы выберем значение 0,3.
- Собственно, построить график.
Итак, нам необходимо сформировать таблицу, где есть два столбца. Первый – это горизонтальная ось (то есть, X), второй – вертикальная (Y). Вторая строка содержит первое значение, в нашем случае это единица. На третьей строке нужно написать значение, которое будет на 0,3 большим предыдущего. Это можно сделать как с помощью самостоятельных подсчетов, так и записав непосредственно формулу, которая в нашем случае будет следующей:
=A2+0,3.
После этого нужно применить автозаполнение к следующим ячейкам. Для этого нужно выделить ячейки A2 и A3 и перетащить квадратик на нужное количество строк вниз.
В вертикальной колонке мы указываем формулу, используемую, чтобы на основе готовой формулы построить график функции. В случае с нашим примером это будет =А2*(КОРЕНЬ(А2-2). После этого подтверждает свои действия с помощью клавиши Enter, и программа автоматически рассчитает результат.
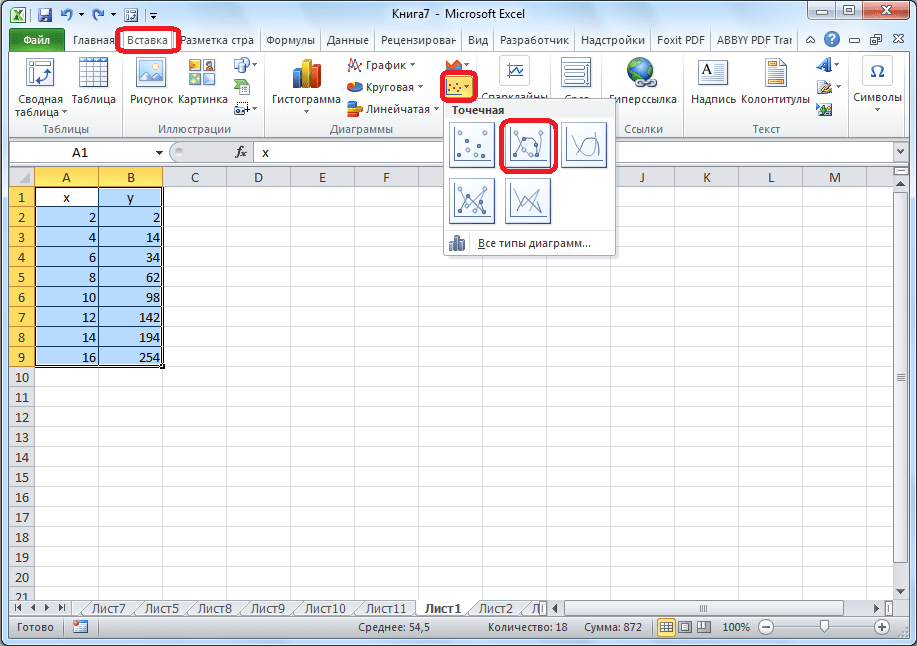
Далее нужно создать новый лист или перейти на другой, но уже существующий. Правда, если есть острая необходимость, можно вставить диаграмму здесь же (не резервируя под эту задачу отдельный лист). Но лишь при условии, что есть много свободного пространства. Затем нажимаем следующие пункты: «Вставка» – «Диаграмма» – «Точечная».
После этого надо решить, какой тип диаграммы нужно использовать. Далее делается правый клик мышью по той части диаграммы, для которой будут определяться данные. То есть, после открытия контекстного меню следует нажать на кнопку «Выбрать данные».
Далее нужно выделить первый столбик, и нажать «Добавить». Появится диалоговое окно, где будут настройки названия ряда, а также значения горизонтальной и вертикальной осей.
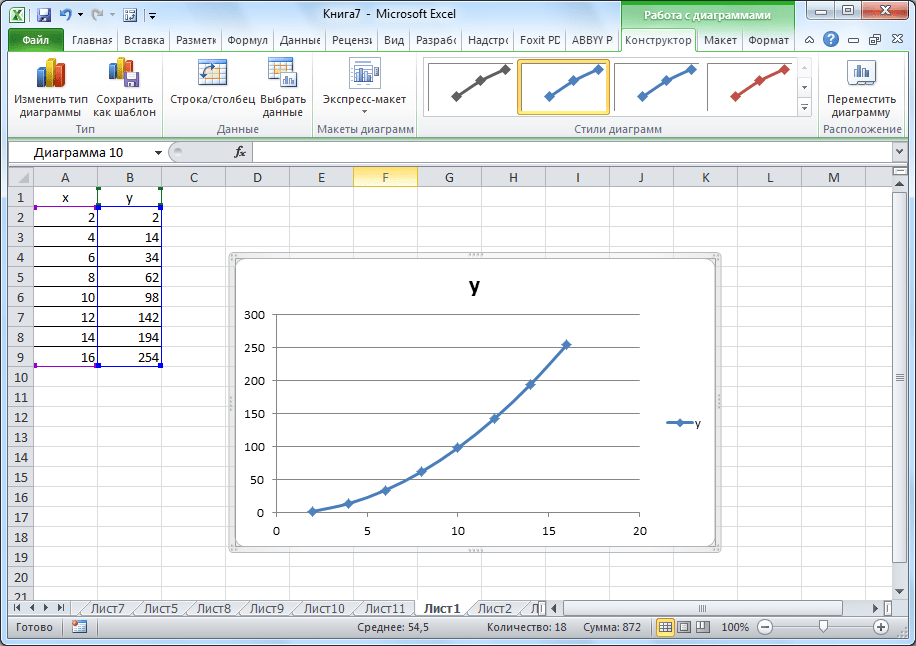
Ура, результат есть, и выглядит очень даже мило.
Аналогично графику, построенному в начале, можно удалять легенду, поскольку мы имеем только одну линию, и нет необходимости ее дополнительно подписывать.
Но есть одна проблема – на оси X не нанесены значения, лишь номер точек. Чтобы скорректировать эту проблему, надо дать названия этой оси. Чтобы это сделать, нужно кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши по ней, а затем выбрать пункт «Выбрать данные» – «Изменить подписи горизонтальной оси». По окончании этих операций выделяется требуемый набор значений, и график станет выглядет так.
Вычисление значений функции
Нужно вычислить значения функции в данных точках. Для этого в ячейке В2 создадим формулу, соответствующую заданной функции, только вместо x будем вводить значение переменной х, находящееся в ячейке слева (-5).
Важно: для возведения в степень используется знак ^, который можно получить с помощью комбинации клавиш Shift+6 на английской раскладке клавиатуры. Обязательно между коэффициентами и переменной нужно ставить знак умножения * (Shift+8).
Ввод формулы завершаем нажатием клавиши Enter. Мы получим значение функции в точке x=-5. Скопируем полученную формулу вниз.
Мы получили последовательность значений функции в точках на промежутке [-5;5] с шагом 1.
Создание таблицы и вычисление значений функций
Таблицу для первой функции мы уже построили, добавим третий столбец — значения функции y=50x+2 на том же промежутке [-5;5]. Заполняем значения этой функции. Для этого в ячейку C2 вводим формулу, соответствующую функции, только вместо x берем значение -5, т.е. ячейку А2. Копируем формулу вниз.
Мы получили таблицу значений переменной х и обеих функций в этих точках.
Построение графиков других функций
Теперь, когда у нас есть основа в виде таблицы и диаграммы, можно строить графики других функций, внося небольшие корректировки в нашу таблицу.
Квадратичная функция y=ax2+bx+c
Выполните следующие действия:
- В первой строке меняем заголовок
- В третьей строке указываем коэффициенты и их значения
- В ячейку A6 записываем обозначение функции
- В ячейку B6 вписываем формулу =$B3*B5*B5+$D3*B5+$F3
- Копируем её на весь диапазон значений аргумента вправо
Получаем результат
Кубическая парабола y=ax3
Для построения выполните следующие действия:
- В первой строке меняем заголовок
- В третьей строке указываем коэффициенты и их значения
- В ячейку A6 записываем обозначение функции
- В ячейку B6 вписываем формулу =$B3*B5*B5*B5
- Копируем её на весь диапазон значений аргумента вправо
Получаем результат
Гипербола y=k/x
Для построения гиперболы заполните таблицу вручную (смотри рисунок ниже). Там где раньше было нулевое значение аргумента оставляем пустую ячейку.
Далее выполните действия:
- В первой строке меняем заголовок.
- В третьей строке указываем коэффициенты и их значения.
- В ячейку A6 записываем обозначение функции.
- В ячейку B6 вписываем формулу =$B3/B5
- Копируем её на весь диапазон значений аргумента вправо.
- Удаляем формулу из ячейки I6.
Для корректного отображения графика нужно поменять для диаграммы диапазон исходных данных, так как в этом примере он больше чем в предыдущих.
- Кликните диаграмму
- На вкладке Работа с диаграммами перейдите в Конструктор и в разделе Данные нажмите Выбрать данные.
- Откроется окно мастера ввода данных
- Выделите мышкой прямоугольный диапазон ячеек A5:P6
- Нажмите ОК в окне мастера.
Получаем результат
Построение точечной диаграммы
Как правило, точечная диаграмма используется для построения графиков функций. Например, возьмем функцию y=x^2.
- Построим таблицу данных из двух столбцов.
Таблица данных y=x^2
- Выделяем данные и вызываем уже упомянутую панель диаграм и выбираем на этот раз точечную.
Виды точечных диаграмм
- После этого получаем диаграмму, я выбрал с маркерами, на листе.
График, построенный при помощи точечной диаграммы
- Как уже было ранее показано, перемещаем диаграмму, меняем название, убираем легенду, заливаем фон.
График функции
- Теперь поработаем на вкладке “Конструктор”. Добавим еще пару рядов данных:
Вторая таблица данных
- Переходим на диаграмму и на вкладке “Конструктор” нажимаем кнопку “Выбрать данные”. Появится окно, где мы можем выбрать в качестве диапазона нашу новую таблицу данных.
Окно выбора данных
- В этом же окне мы можем изменить параметры каждого ряда
Корректировка данных рядов
Можно поставить свое произвольное название ряда. Если вдруг Excel неверно взял какой-то ряд в качестве независимой или зависимой переменной, можно произвольно определить нужные диапазоны.
- Добавляем легенду, меняем название диаграммы и получаем вот такую картинку
Итоговый график
Построение обычного графика
Рисовать график в Excel можно только после того, как готова таблица с данными, на основе которой он будет строиться.
- Находясь на вкладке «Вставка», выделяем табличную область, где расположены расчетные данные, которые мы желаем видеть в графике. Затем на ленте в блоке инструментов «Диаграммы» кликаем по кнопке «График».
- После этого открывается список, в котором представлено семь видов графиков:
- Обычный;
- С накоплением;
- Нормированный с накоплением;
- С маркерами;
- С маркерами и накоплением;
- Нормированный с маркерами и накоплением;
- Объемный.
Выбираем тот, который по вашему мнению больше всего подходит для конкретно поставленных целей его построения.
- Дальше Excel выполняет непосредственное построение графика.
Редактирование графика
После построения графика можно выполнить его редактирование для придания объекту более презентабельного вида и облегчения понимания материала, который он отображает.
- Чтобы подписать график, переходим на вкладку «Макет» мастера работы с диаграммами. Кликаем по кнопке на ленте с наименованием «Название диаграммы». В открывшемся списке указываем, где будет размещаться имя: по центру или над графиком. Второй вариант обычно более уместен, поэтому мы в качестве примера используем «Над диаграммой». В результате появляется название, которое можно заменить или отредактировать на свое усмотрение, просто нажав по нему и введя нужные символы с клавиатуры.
- Задать имя осям можно, кликнув по кнопке «Название осей». В выпадающем списке выберите пункт «Название основной горизонтальной оси», а далее переходите в позицию «Название под осью».
- Под осью появляется форма для наименования, в которую можно занести любое на свое усмотрение название.
- Аналогичным образом подписываем вертикальную ось. Жмем по кнопке «Название осей», но в появившемся меню выбираем «Название основной вертикальной оси». Откроется перечень из трех вариантов расположения подписи: повернутое, вертикальное, горизонтальное. Лучше всего использовать повернутое имя, так как в этом случае экономится место на листе.
- На листе около соответствующей оси появляется поле, в которое можно ввести наиболее подходящее по контексту расположенных данных название.
- Если вы считаете, что для понимания графика легенда не нужна и она только занимает место, то можно удалить ее. Щелкните по кнопке «Легенда», расположенной на ленте, а затем по варианту «Нет». Тут же можно выбрать любую позицию легенды, если надо ее не удалить, а только сменить расположение.
Как добавить название в график Эксель

На примерах выше мы строили графики курсов Доллара и Евро, без заголовка сложно понять про что он и к чему относится. Чтобы решить эту проблему нам нужно:
- Нажать на графике левой клавишей мыши;
- Нажать на “зеленый крестик” в правом верхнем углу графика;
- Во всплывающем окне поставить галочку напротив пункта “Название диаграммы”:
- Над графиком появится поле с названием графика. Кликните по нему левой клавишей мыши и внесите свое название:
Как подписать оси в графике Excel
Для лучше информативности нашего графика в Excel есть возможность подписать оси. Для этого:
- Щелкните левой клавишей мыши по графику. В правом верхнем углу графика появится “зеленый крестик”, нажав на который раскроются настройки элементов диаграммы:
- Щелкните левой клавишей мыши на пункте “Названия осей”. На графике под каждой осью появятся заголовки, в которые вы можете внести свой текст:
Добавление второй оси
Как добавить вторую (дополнительную) ось? Когда единицы измерения одинаковы, пользуемся предложенной выше инструкцией. Если же нужно показать данные разных типов, понадобится вспомогательная ось.
Сначала строим график так, будто у нас одинаковые единицы измерения.

Выделяем ось, для которой хотим добавить вспомогательную. Правая кнопка мыши – «Формат ряда данных» – «Параметры ряда» – «По вспомогательной оси».

Нажимаем «Закрыть» – на графике появилась вторая ось, которая «подстроилась» под данные кривой.

Это один из способов. Есть и другой – изменение типа диаграммы.
Щелкаем правой кнопкой мыши по линии, для которой нужна дополнительная ось. Выбираем «Изменить тип диаграммы для ряда».

Определяемся с видом для второго ряда данных. В примере – линейчатая диаграмма.

Всего несколько нажатий – дополнительная ось для другого типа измерений готова.
Наложение и комбинирование графиков
Построить два графика в Excel не представляет никакой сложности. Совместим на одном поле два графика функций в Excel. Добавим к предыдущей Z=X(√x – 3). Таблица с данными:

Выделяем данные и вставляем в поле диаграммы. Если что-то не так (не те названия рядов, неправильно отразились цифры на оси), редактируем через вкладку «Выбрать данные».
А вот наши 2 графика функций в одном поле.

Особенности оформления графиков в Excel
Несколько советов по оформлению графиков в Excel:
- Первое, что следует сделать пользователю, — ввести правильно название зависимости. Для этого нужно выделить щелчком мыши блок «Название диаграммы», щёлкнуть по нему ещё раз и ввести требуемое наименование. При необходимости этот блок можно удалить, выделив его и нажав клавишу Delete.
- Если требуется изменить не только название, но и стиль написания, следует, снова выделив блок, вызвать контекстное меню и выбрать в нём раздел «Шрифт». Подобрав подходящий вариант, юзер может нажимать на «ОК» и переходить к дальнейшим действиям.
- Вызвав меню «Формат названия диаграммы», можно определить, в какой части рисунка будет располагаться наименование: в центре, в левом верхнем, нижнем правом углу и так далее.
- Чтобы добавить на график названия осей, следует щёлкнуть мышью по «плюсику» справа от рисунка и в выплывающем списке установить галочку в соответствующем чекбоксе.
- Если изначальное расположение названий не устраивает пользователя, он может свободно перетаскивать их по полю графика, а также менять их наименования описанным ранее способом.
- Чтобы добавить на любую линию графика подписи (размещаются прямо на сетке) или выноски данных (в отдельных окошечках), нужно выделить её щелчком правой клавишей мыши и выбрать соответствующий параметр во вложенном меню «Добавить подписи данных».
- Юзер может свободно сочетать способы размещения подписей, выбирая любой из пунктов в расширенном меню окошка «Элементы диаграммы».
- Выбрав в том же меню «Дополнительные параметры», в боковом меню следует указать категорию представленных данных: простые числа, дроби, проценты, деньги и так далее.
- Чтобы добавить таблицу с данными непосредственно на график, нужно вызвать нажатием на «плюсик» всё те же «Дополнительные параметры» и установить галочку в одноимённом чекбоксе.
- Сетку, позволяющую найти значения графика в каждой точке, с помощью того же меню можно совсем убрать или добавить на неё основную и вспомогательную разметку.
- «Легенда» — не самый полезный, но привычный блок графиков Excel. Убрать или перенести его можно, сняв галочку в окне «Дополнительные параметры» или вызвав вложенное меню. Более простой вариант — выделить блок щелчком мыши и нажать клавишу Delete или перетащить по полю графика.
- Понять общее направление движения графика поможет линия тренда; добавить её для каждого ряда значений можно в том же окне.
- Перейдя на вкладку «Конструктор», пользователь может кардинально изменить вид графика, выбрав один из стандартных шаблонов в разделе «Стили диаграмм».
- А вызвав находящееся там же меню «Изменить цвета» — подобрать палитру для каждой линии в отдельности или для всего графика в целом.
- Меню «Стили» вкладки «Формат» позволяет найти оптимальное представление для текстовых элементов графика.
- Изменить фон, оставив нетронутым тип диаграммы, можно с помощью раздела «Стили фигур».
- На этом настройку графика можно считать оконченной. Пользователь может в любой момент изменить тип диаграммы, перейдя в одноимённое меню и выбрав понравившийся вариант.
Добавление в график вспомогательной оси
Нередко возникает необходимость на одной диаграмме разместить несколько графиков. В этом нет никакой сложности, если они имеют одинаковые меры исчисления. Но порой приходится совмещать несколько графиков с различными мерами исчисления, к примеру, чтобы показать зависимость одних данных от других. Делается это следующим образом.
- Первые шаги такие же, как и описанные выше. Выделяем таблицу, переходим во вкладку “Вставка” и выбираем наиболее подходящий вариант графика.
- В полученной диаграмме построено несколько графиков в соответствии с количеством столбцов выделенной таблицы. Теперь нужно нажать правой кнопкой мыши на тот, для которого необходима вспомогательная ось. Внизу появившегося списка выбираем «Формат ряда данных…».
- Откроются настройки формата данных, в котором выбираем “Построить ряд по вспомогательной оси”.
- После этого будет добавлена вспомогательная ось, и график перестроится. Далее можно скорректировать название, подписи данных, легенду, и выбрать для них подходящее место.
Примечание: в диаграмму можно добавить только одну дополнительную ось, что ограничивает возможность построения графиков для трёх и более различных мер исчисления.
Как построить два графика в Excel
Перейдем к вопросу, как построить два графика в Excel. Добавим еще один график кубической параболы. Создадим в таблице еще один столбец (столбец С), в котором введем формулу кубической параболы. Теперь наша таблица выглядит следующим образом:
Как построить график в Excel – Расширение таблицы исходных данных
Теперь во вкладке «Конструктор» выбираем пункт «Выбрать данные».
Как построить график в Excel – Выбрать данные
В появившемся окне, Excel предлагает выбрать источник данных.
Как построить график в Excel – Выбор источника данных
Мы можем либо изменить «Диапазон данных для диаграммы», выбрав нашу обновленную таблицу; либо добавить еще один ряд с помощью кнопки «Добавить». Мы воспользуемся вторым способом, и просто добавим еще один ряд.
В открывшемся окне в поле «Имя ряда» выбираем ячейку с заголовком столбца, в поле «Значения Х» – выбираем первый столбец таблицы, «Значения У» – третий. Нажимаем кнопку «ОК».
Как построить график в Excel – Два графика на одной точечной диаграмме
Для удобства добавим легенду и название диаграммы, и выберем желаемый стиль. Ну вот, график функции в Excel построен:
Заключение
Наряду с работой данных в табличном виде, в программе Microsoft Excel можно строить графики. Программа предлагает большое разнообразие видов и подвидов, которые прекрасно покрывают потребности пользователей в предоставлении информации в наиболее наглядном виде, значительно облегчающем ее восприятие.
Источники
- https://office-guru.ru/excel/diagrammy-grafika/grafik-v-excel-s-nulya.html
- https://pedsovet.su/excel/5883_grafik_funkcii
- https://tvojkomp.ru/kak-postroit-grafik-funktsii-v-microsoft-excel/
- http://excelpractic.ru/kak-postroit-grafik-v-excel.html
- https://lumpics.ru/how-to-make-a-graph-in-excel/
- https://excelhack.ru/kak-postroit-grafik-v-excel-po-dannym-tablicy/
- https://exceltable.com/grafiki/grafiki-i-diagrammi-v-excel
- https://konekto.ru/kak-postroit-grafik-v-excel.html
- https://MicroExcel.ru/postroenie-grafikov/
- https://naprimerax.org/kak-postroit-grafik-v-excel
Taxes are better calculated on the basis of information from the tables. And for the presentation of the company’s achievements it is better to use charts and diagrams.
The graphs are well suited for analyzing of relative data. For example, the forecast of sales growth dynamics or the assessment of the overall trend of growth in the capacity of the enterprise.
How to build a chart in Excel?
The fastest way to build a chart in Excel – is to create graphs by template:
- The range of the cells A1:C4. You need to fill it with values as shown in the figure:
- Select the range A1:C4 and choose the tool on the «INSERT» tab – «Insert Column Chart» – «Clustered Column».
- Click on the graph to activate it and call the additional menu «CHART TOOLS». There are also three tool tabs available: «DESIGN» and «FORMAT».
- To change the axes in the graph, select to the «Constructor» tab, and on it the «Switch Row/Column» tool. Thus, you change the values in the graph: rows per columns.
- Click on any cell to deselect the chart and thus to deactivate its setting mode.
Now you can work in the normal mode.
How to build a chart on the table in Excel?
Now we are constructing the diagram according to the data of the Excel table, which must be signed with the title:
- Select the A1:B4 range in the source table.
- Select «INSERT» – «Insert Pie or Doughnut». From the group of different chart types, select the «Doughnut».
- Sign the title of your chart. To do this, make a double-click on the title with the left mouse button and enter the text as shown in the picture:
After you sign a new title, click on any cell to deactivate the chart settings and go to normal mode.
Diagrams and charts in Excel
How not to create a table, its data will be less readable than the graphical representation in diagrams and charts. For example, pay attention to the picture:
According to the table, you do not immediately to notice in what month the company’s revenues were the highest, and in what the smallest ones. You can, of course, use the «Sorting» tool, but then the general idea of the seasonality of the firm’s activity is lost.
Pay attention to the chart, which is built according to the same table. Here you do not have to blame your eyes to notice the months with the smallest and the largest indicator of the company’s profitability. And the general presentation of the schedule allows you to track the seasonality of activity of sales, which bring more or less profit in certain periods of the year. The data recorded in the table, is perfectly suitable for detailed calculations and calculations. But the charts and the diagrams provide us with its indisputable advantages:
- improve to the readability of data;
- simplify the general orientation of large amounts of the data;
- allow you to create high-quality presentations of reports.
How to Make Charts or Graphs in Excel?
Steps in making graphs in Excel:
- Numerical Data: The first thing required in your Excel is numerical data. Charts or graphs can only be built using numerical data sets.
- Data Headings: These are often called data labels. The headings of each column should be understandable and readable.
- Data in Proper Order: It is very important how the data looks in Excel. If the information to build a chart is bits and pieces, we might find it difficult to construct a chart. So arrange the data properly.
Table of contents
- How to Make Charts or Graphs in Excel?
- Examples (Step by Step)
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- Examples (Step by Step)
Examples (Step by Step)
Below are some examples of how to make charts in Excel.
You can download this Make Chart Excel Template here – Make Chart Excel Template
Example #1
Assume we have passed six years of sales data. We want to show them in visuals or graphs.
- First, we must select the date range we are using for a graph.
- Then, go to the “INSERT” tab > under the “Charts” section, and select the “COLUMN” chart. We can see many other types under the “Column” chart but prefer the first one.
- As soon as we have selected the chart, we can see the below chart in Excel.
- It is not the finished product yet. We need to make some arrangements here. So, we must select the blue-colored bars and press the “Delete” button. Else, right-click on bars and choose “Delete.”
- Now, we do not know which bar represents which year. So, right-click on the chart and select “Select Data.”
- In the below window, we must click on “EDIT,” which is on the right-hand side.
- After we click on the “EDIT option,” we will see a small dialog box below. It will ask to select the “Horizontal Axis Labels.” So, choose the “Year” column.
- Now, we have the “Year” name below each bar.
- After that, change the heading or title of the chart as per the requirement by double-clicking on the existing header.
- Add “Data Labels” for each bar. The “Data Labels” are each bar’s numbers to convey the message perfectly. Right-click on the column bars and select “Add Data Labels.”
- Change the color of the column bars to different colors. Next, select the bars and press “Ctrl + 1.” We may see the format chart dialog box on the right-hand side.
- Now, go to the “FILL” option, and select the option “Vary colors by point.”
Now, we have a neatly arranged chart in front of us.
Example #2
We have seen how to create a graph with auto-selection of the data range. Next, we will show you how to build an Excel chart with a manual data selection.
- Step 1: First, we must place the cursor in the empty cell and click on the “Insert Chart.”
- Step 2: After we click on the “Insert Chart,” we can see a blank chart.
- Step 3: Right-click on the chart and choose the “Select Data” option.
- Step 4: In the below window, click on “Add.”
- Step 5: In the below window, under “Series name,” select the heading of the data series, and under the “Series values,” select data series values.
- Step 6: Now, the default chart is ready.
Now, we must apply the steps shown in the previous example to modify the chart. Next, refer to steps 5 to 12 to alter the chart.
Things to Remember
- For the same data, we can insert all types of charts. It is important to identify a suitable chart.
- If the data is smaller, it is easy to plot a graph without any hurdles.
- In the case of percentage data, we must select the PIE chartMaking a pie chart in excel can help you with the pictorial representation of your data and simplifies the analysis process. There are multiple kinds of pie chart options available on excel to serve the varying user needs.read more.
- We must try using different charts for the same data to identify the best fit chart for the data set.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Making Charts in Excel. Here, we discuss how to make charts or graphs in Excel, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Organization Chart in Excel
- Examples of Line Chart in Excel
- Excel Chart Templates
- 8 Types of Charts in Excel
- Infographics in Excel
Reader Interactions











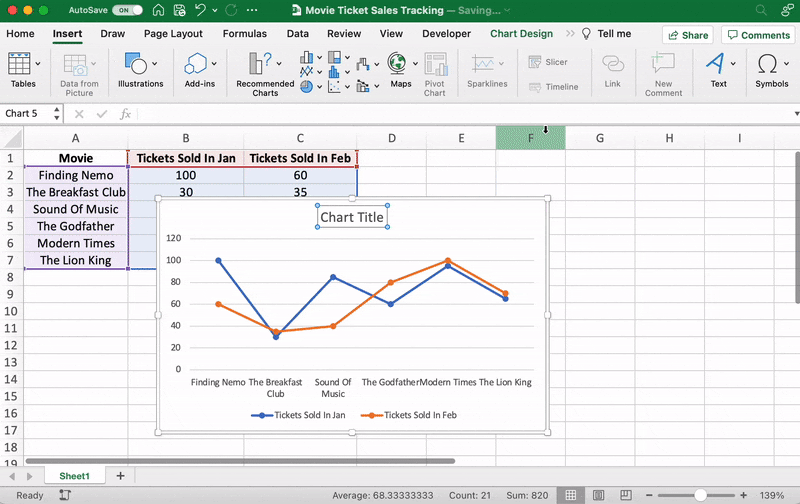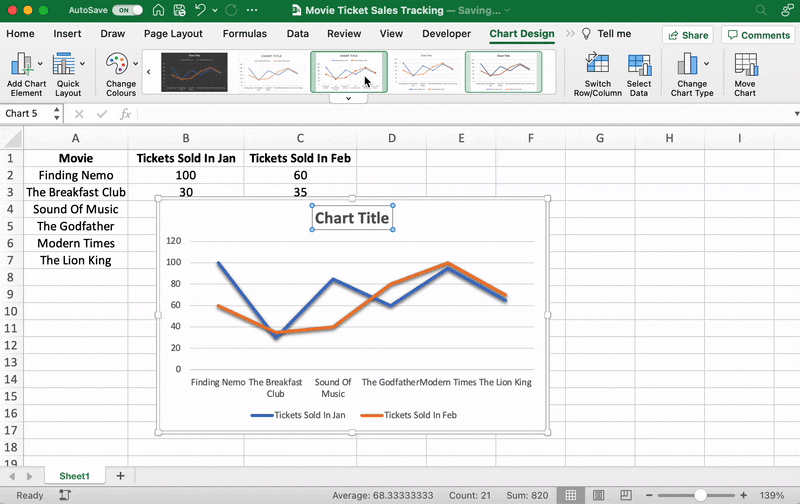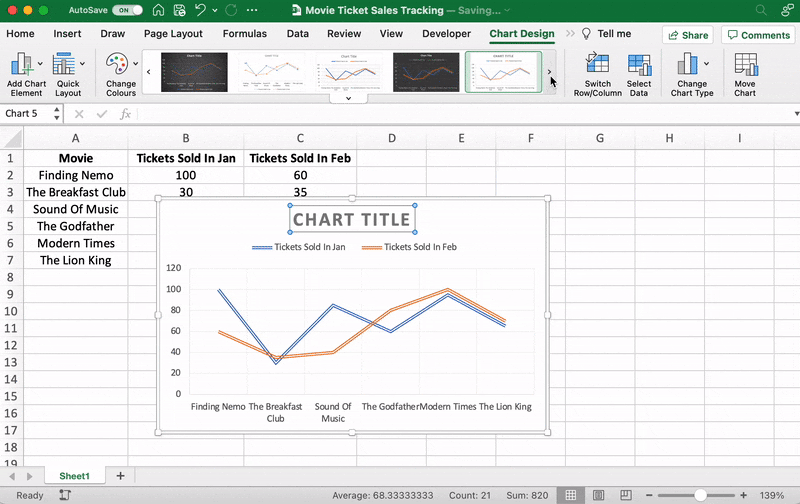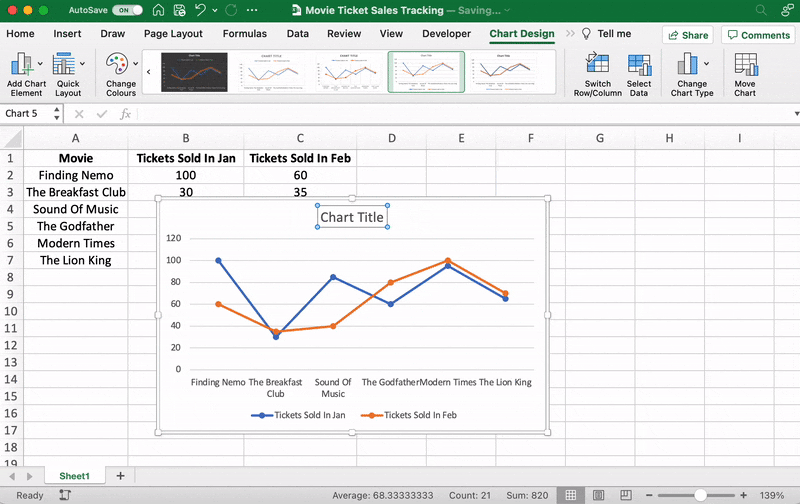
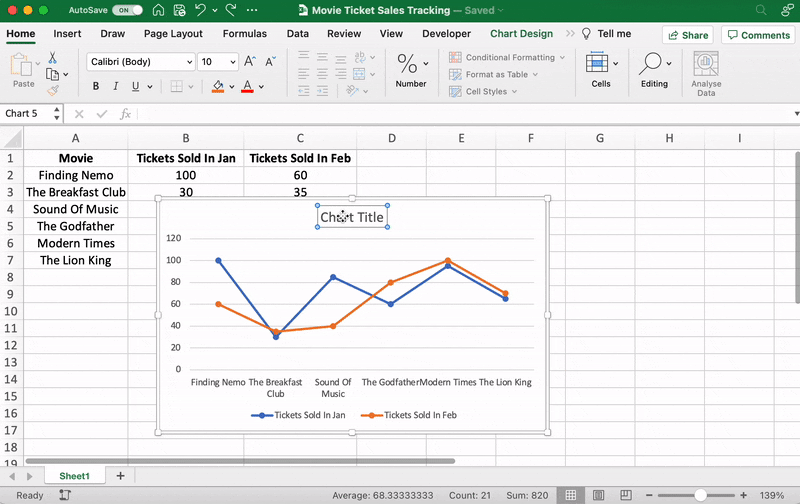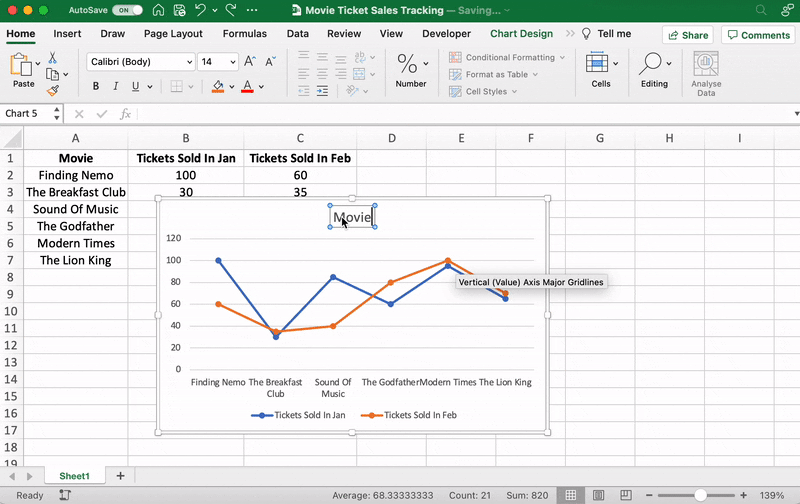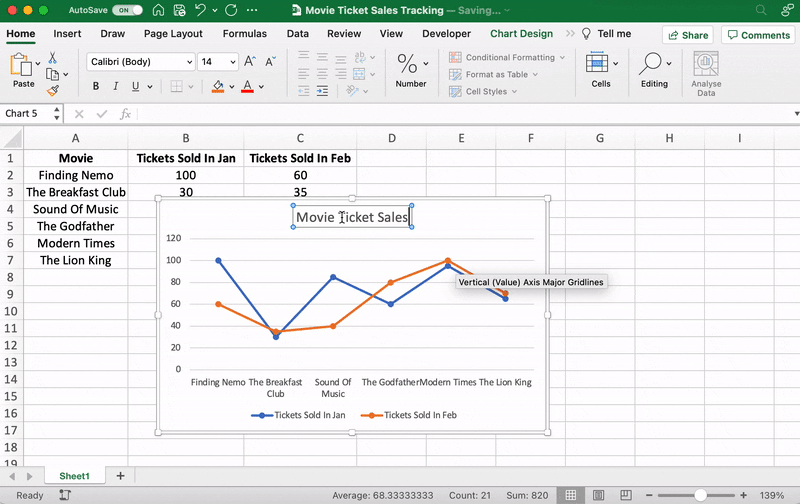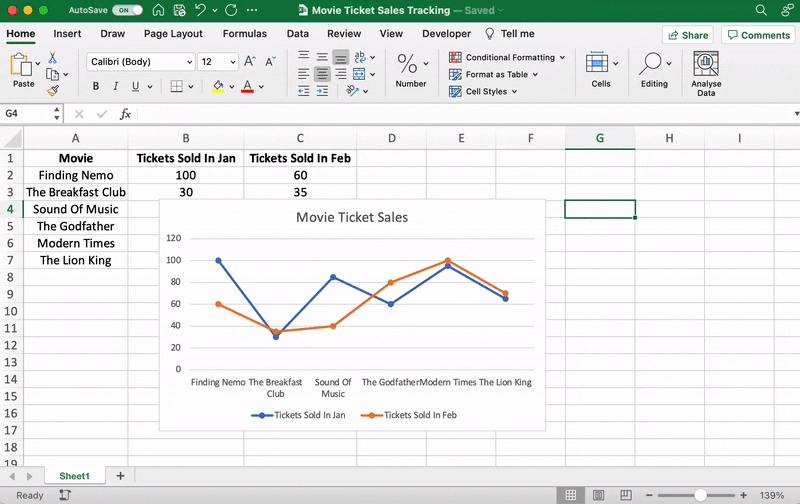

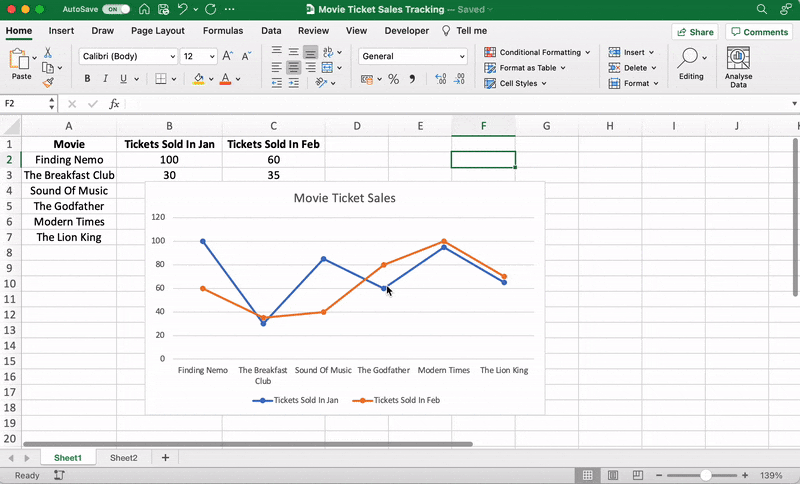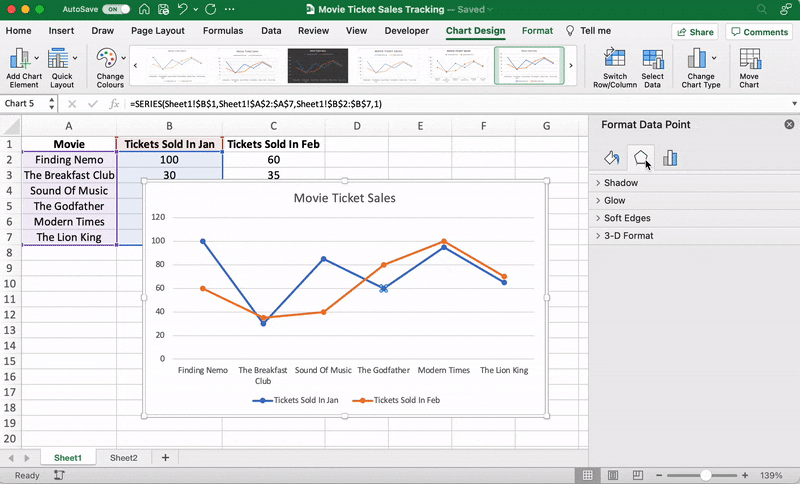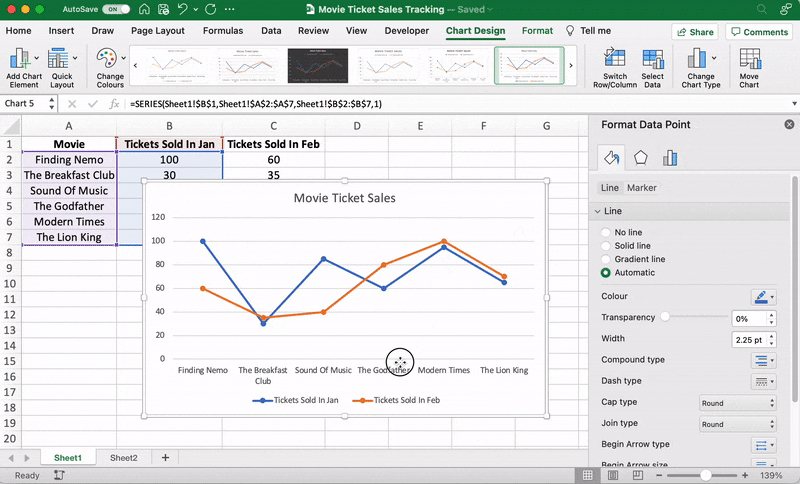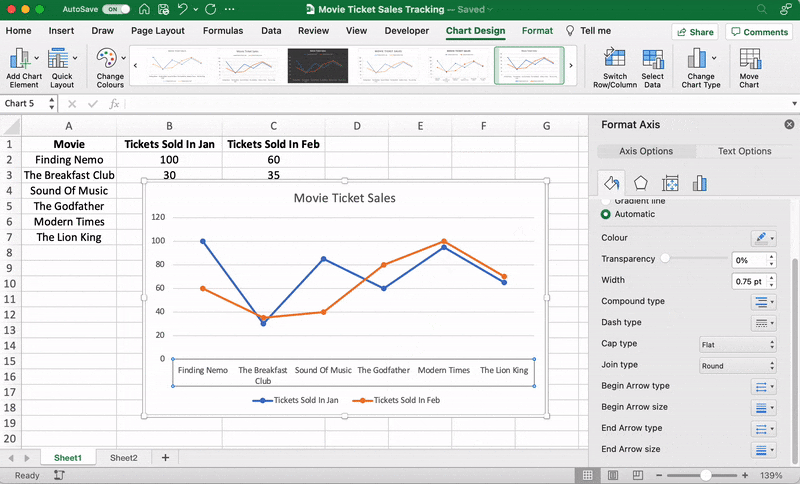
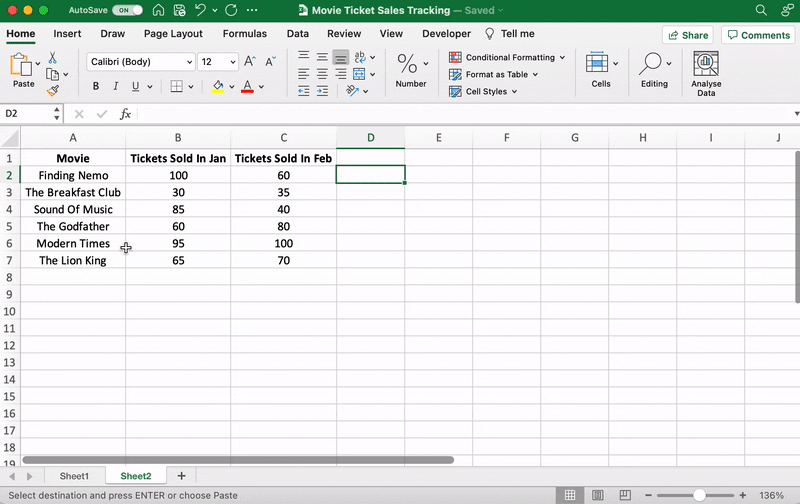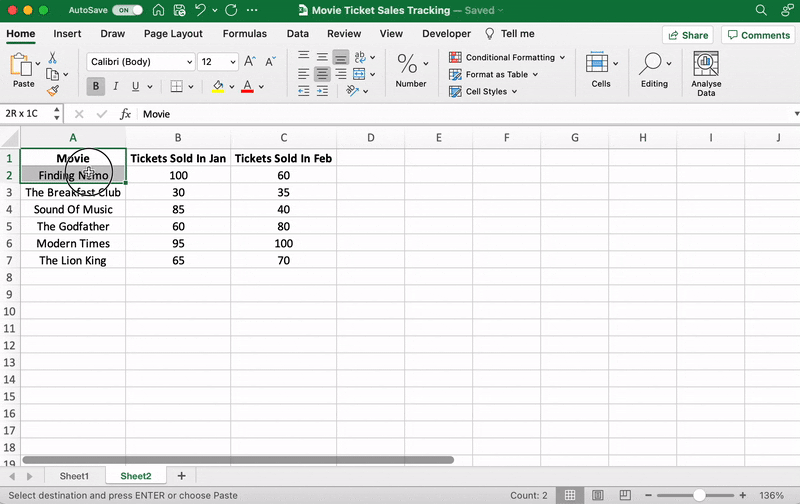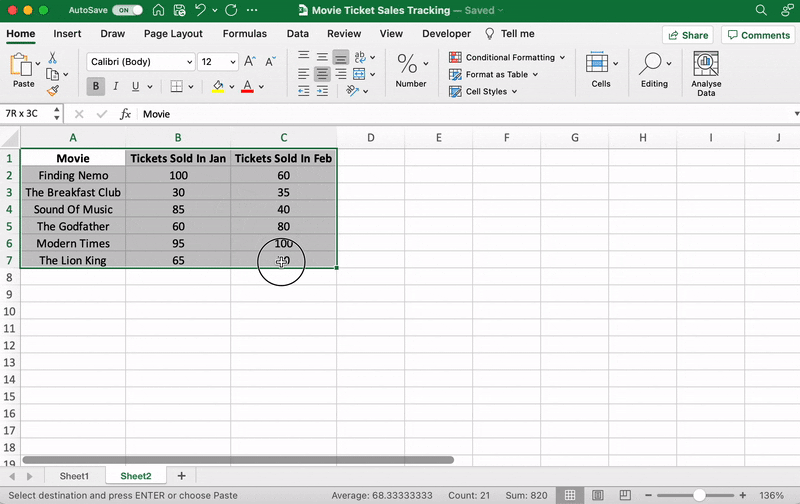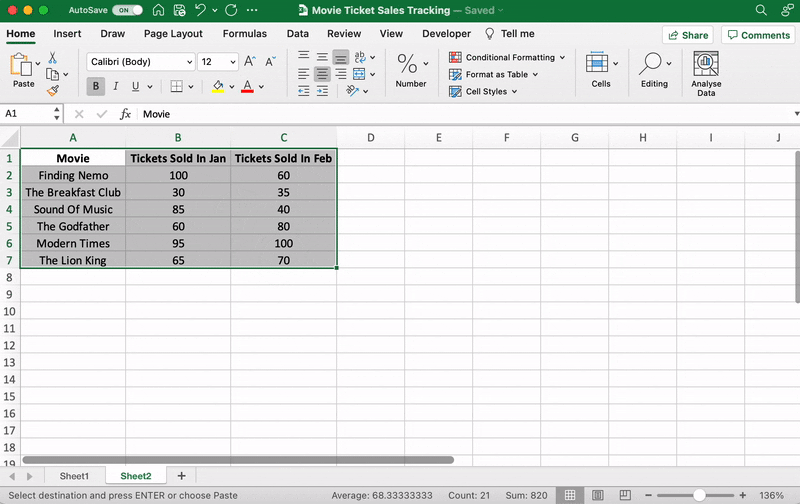

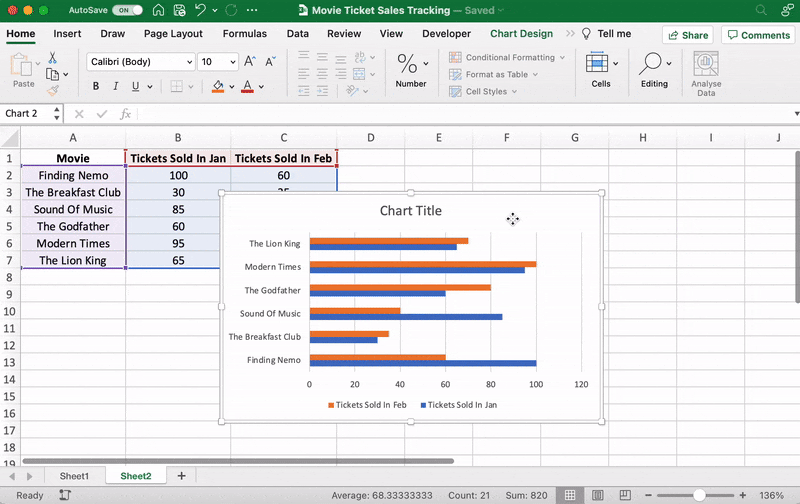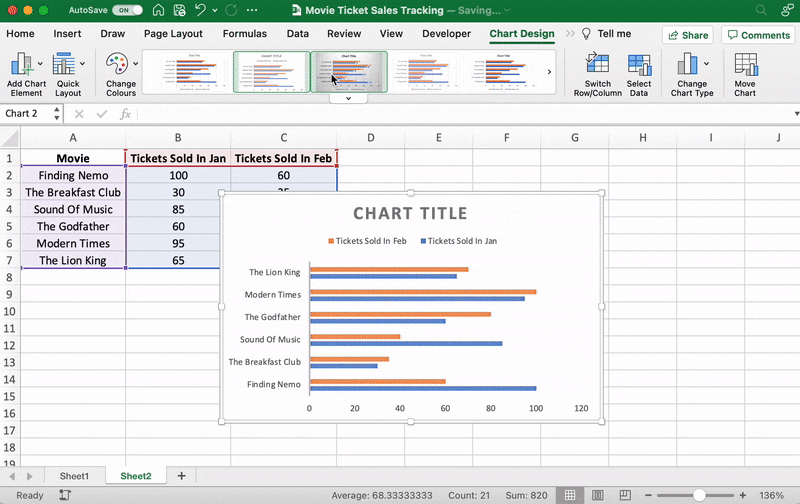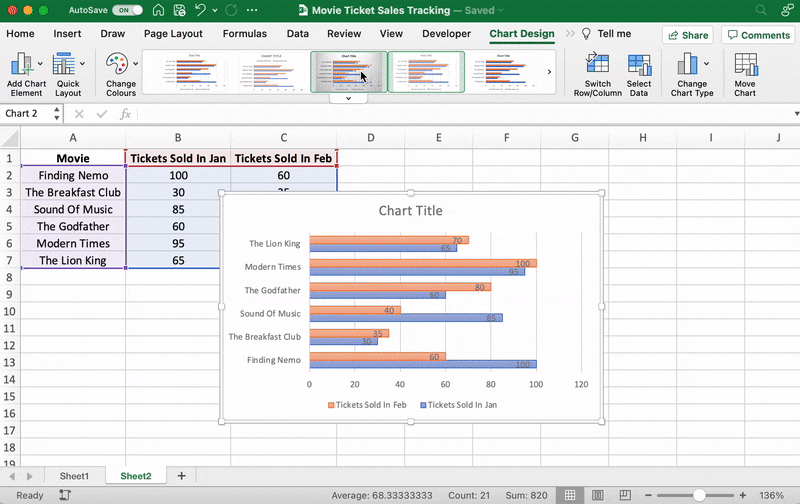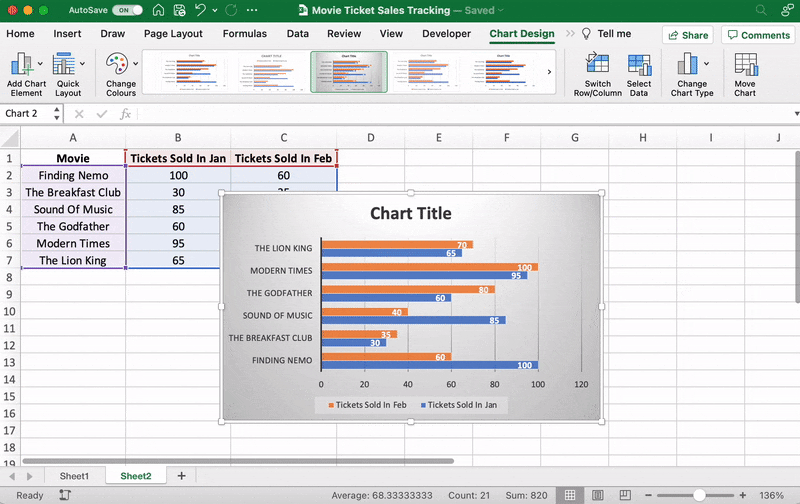




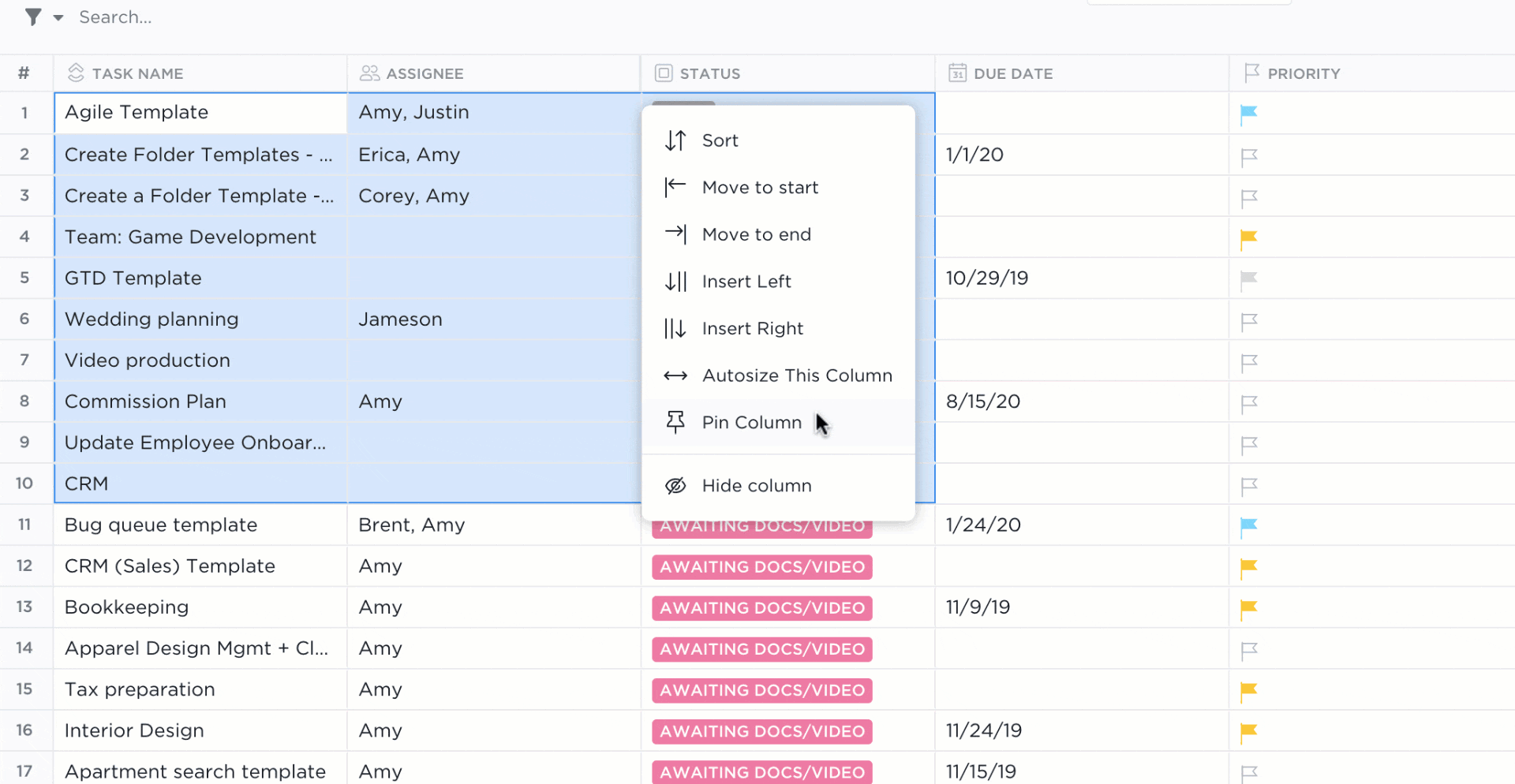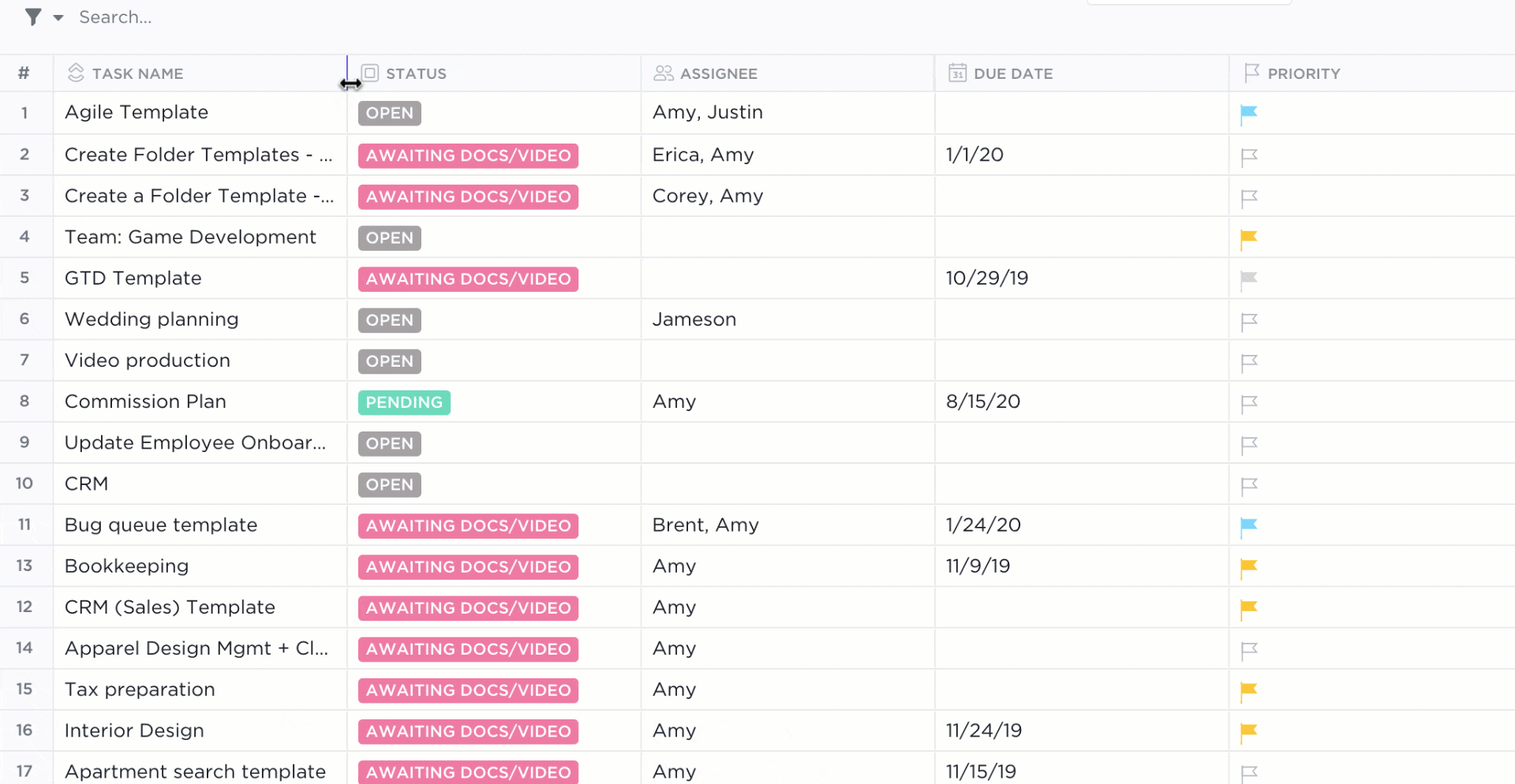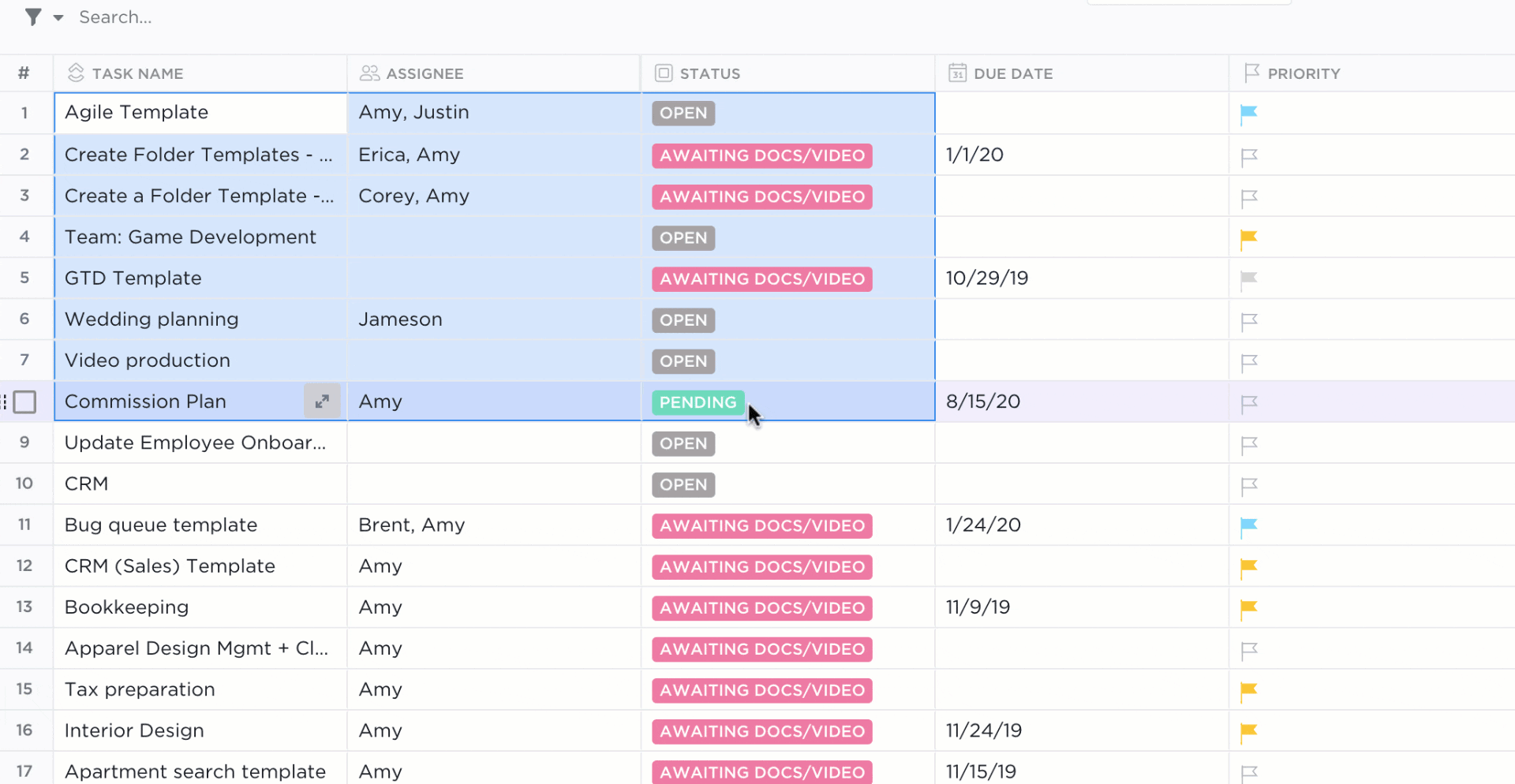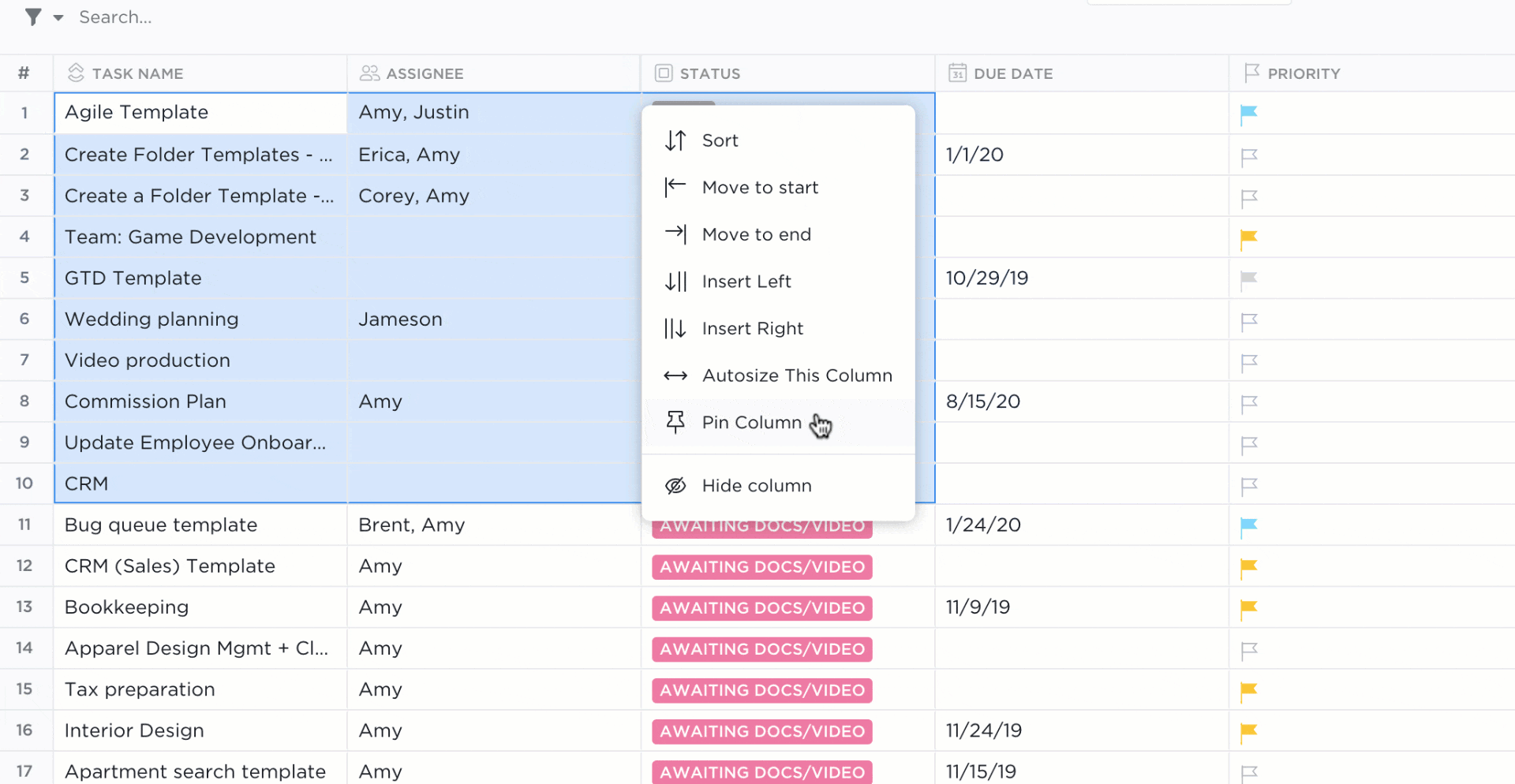



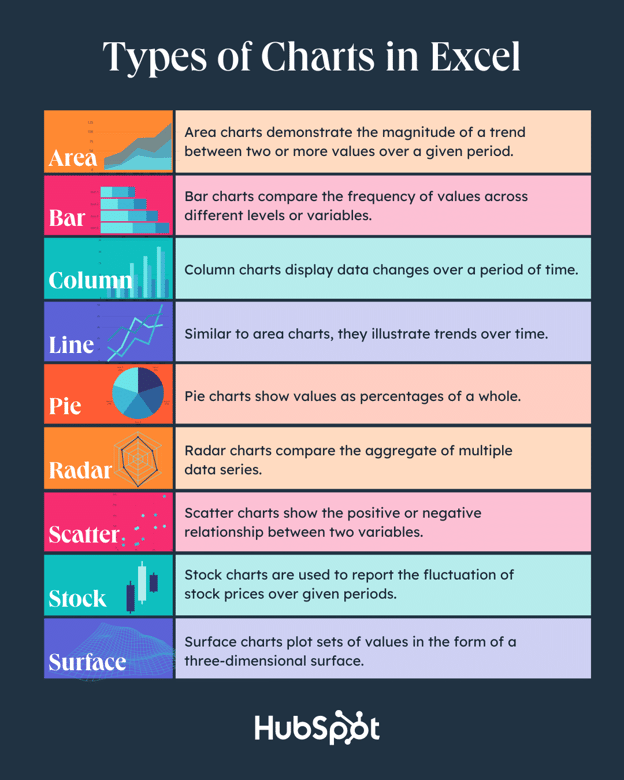
.png)
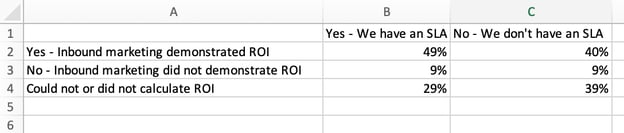
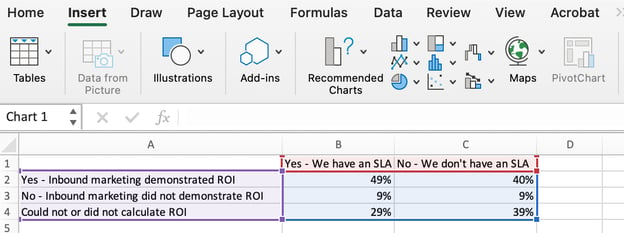
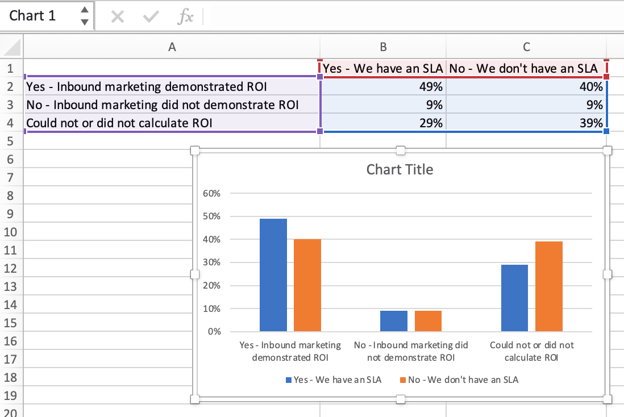
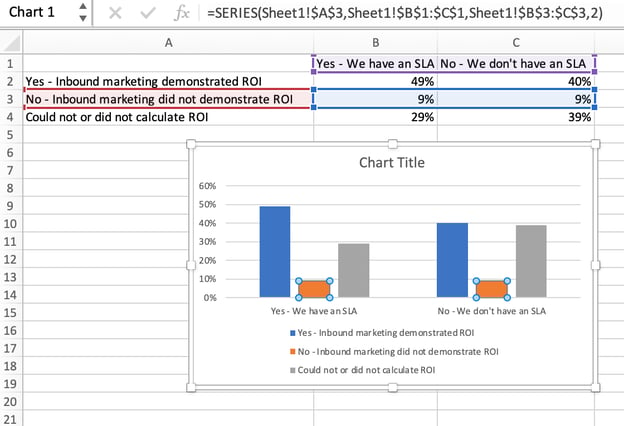
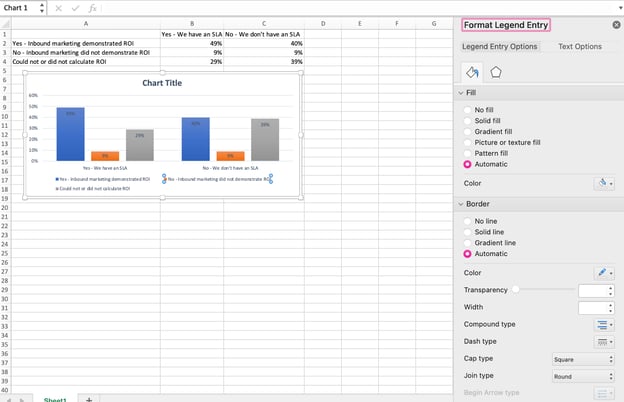
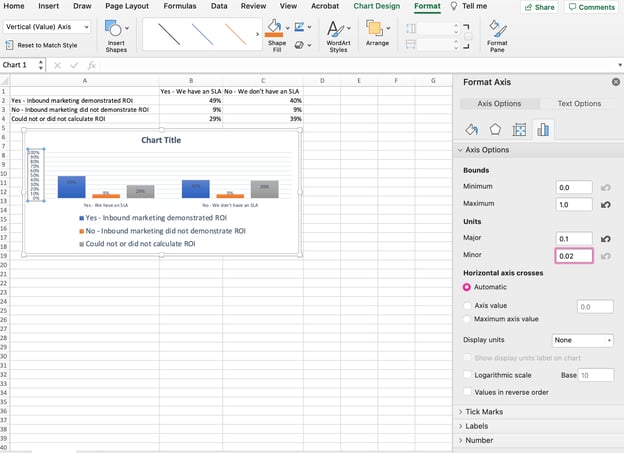
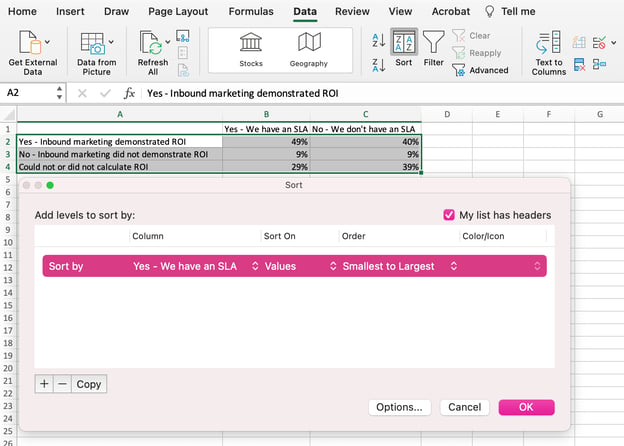
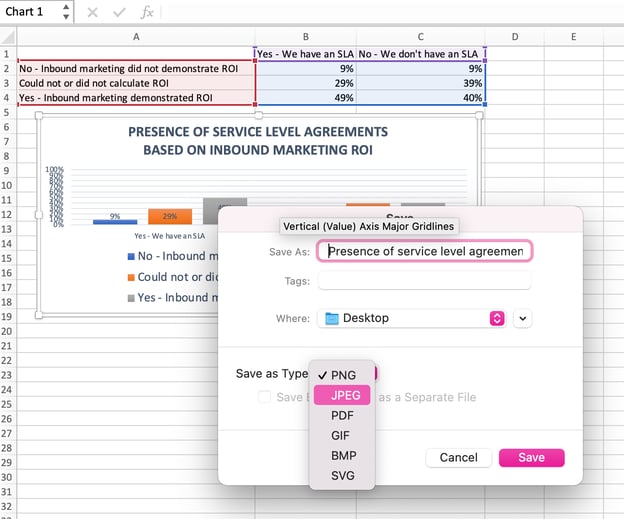













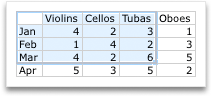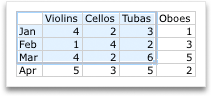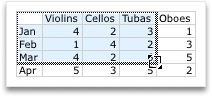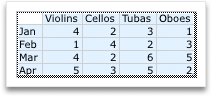
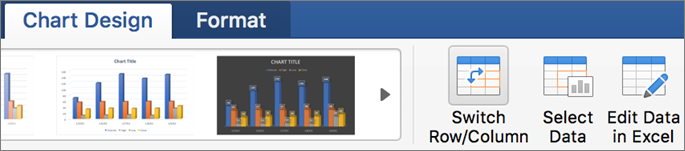
 + Z .
+ Z .
 .
.