How to Close a Document in Microsoft Word
- Click the gray “X” in the upper-right-hand corner.
- Select Close from the File menu.
Contents
- 1 How do you close a Word document that won’t close?
- 2 How do I close all open Word documents?
- 3 How do I force Word to close?
- 4 How do I force close a document?
- 5 Is there a way to close all Word documents without saving?
- 6 What is the shortcut key to close a document?
- 7 How do I save and close a Word document?
- 8 How do you properly turn off the computer?
- 9 How do I close all files in Windows?
- 10 What is Ctrl N?
- 11 What is Ctrl W?
- 12 What is Ctrl F4?
- 13 What are the steps to close an existing document?
- 14 How do I open and close my computer?
- 15 Is it best to turn off computer when not in use?
- 16 Which button do we click first to shutdown a computer?
- 17 Why is Alt F4 not working?
- 18 How do you close a window using the keyboard?
- 19 How do I close all processes in Windows 10?
- 20 What does Ctrl k do in word?
How do you close a Word document that won’t close?
Using a Mac
- Click on the “Apple” menu in the upper-left corner of the screen.
- Click on the “Force Quit” option in the drop-down menu to open the Force Quit Window.
- Click on the Microsoft Word option in the list of open programs.
- Click on the “Force Quit” button to force quit the Word program.
How do I close all open Word documents?
Close all documents or windows by clicking Taskbar
- Put your cursor on the Taskbar and right click on.
- Click Close all windows, see screenshot:
- Then it will close all documents or windows.
How do I force Word to close?
To quickly force quit on Windows, use the keyboard shortcut Alt + F4.
How to force quit on Windows using Task Manager
- Press Control + Alt + Delete.
- Choose Task Manager.
- Select the application that you want to force quit.
- Click End task.
How do I force close a document?
Certainly, in case you prefer using keyboard shortcuts to clicks, you can press “Ctrl+ W” or “Ctrl+ F4”. Either of it can close only the document.
Is there a way to close all Word documents without saving?
You can close multiple documents in one fell swoop by pressing [Shift] and then going to File | Close All. If any of your documents contain unsaved changes, Word will ask you whether you want to save your changes before closing the particular file.
What is the shortcut key to close a document?
Frequently used shortcuts
| To do this | Press |
|---|---|
| Close the document. | Ctrl+W |
| Cut the selected content to the Clipboard. | Ctrl+X |
| Copy the selected content to the Clipboard. | Ctrl+C |
| Paste the contents of the Clipboard. | Ctrl+V |
How do I save and close a Word document?
How to Save and Close All Open Documents in Word
- Word allows you to open multiple documents at once as well as view multiple documents at once.
- The “Quick Access Toolbar” screen displays on the “Word Options” dialog box.
- Scroll down the list until you find the “Save All” command, select it, and click “Add”.
How do you properly turn off the computer?
So what is the correct way to turn-off a computer? Step 1: Click the ‘Windows’ button at the bottom left-hand corner of your screen. Step 2: Click Shutdown or Restart. Step 3: Wait for the system to power itself down, or start the reboot.
How do I close all files in Windows?
Close all open programs
Press Ctrl-Alt-Delete and then Alt-T to open Task Manager’s Applications tab. Press the down arrow, and then Shift-down arrow to select all the programs listed in the window. When they’re all selected, press Alt-E, then Alt-F, and finally x to close Task Manager.
What is Ctrl N?
Alternatively referred to as Control+N and C-n, Ctrl+N is a keyboard shortcut most often used to create a new document, window, workbook, or other type of file.Ctrl+N in Word and other word processors.
What is Ctrl W?
Alternatively referred to as Control+W and C-w, Ctrl+W is a keyboard shortcut most often used to close a program, window, tab, or document.Ctrl+W in Word and other word processors.
What is Ctrl F4?
Alternatively referred to as Control F4 and C-f4, Ctrl+F4 is a shortcut key most often used to close a tab or window within a program. Tip. If you want to close all tabs and windows as well as the program use the Alt+F4 keyboard shortcut.
What are the steps to close an existing document?
Step 1 − Click the File tab and select the Close option. Step 2 − When you select the Close option and if the document is not saved before closing, it will display the following Warning box asking whether the document should be saved or not.
How do I open and close my computer?
Press Ctrl + Alt + Del and click the power button in the bottom-right corner of the screen. From the Windows desktop, press Alt + F4 to get the Shut down Windows screen and select Shut down.
Is it best to turn off computer when not in use?
Shutting down your computer is when all the software, programs, files, and processes are closed and the memory in the RAM is cleared.It is best to shut down your computer when you don’t need to use it for a while and to save power. Shutting down your computer also allows it to run faster with a clear RAM.
Which button do we click first to shutdown a computer?
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del and click the power button in the bottom-right corner of the screen. From the desktop, press Alt+F4 to get the Shut Down Windows screen.
Why is Alt F4 not working?
If the Alt + F4 combo fails to do what it is supposed to do, then press the Fn key and try the Alt + F4 shortcut again.Try pressing Fn + F4. If you still cannot notice any change, try holding down Fn for a few seconds. If that doesn’t work too, try ALT + Fn + F4.
How do you close a window using the keyboard?
Alt + F4: Close the current app or window.
How do I close all processes in Windows 10?
Terminator 101: How to kill all the processes in Windows 10?
- Go to Search. Type cmd and open Command Prompt.
- Once there, enter this line taskkill /f /fi “status eq not responding” and then press Enter.
- This command should end all processes deemed unresponding.
What does Ctrl k do in word?
In Microsoft Word and other word processors, pressing Ctrl + K inserts a hyperlink at the text cursor’s current location.
When you’re done working with a file, it’s a good idea to close it so you don’t bog down your computer with unused programs.
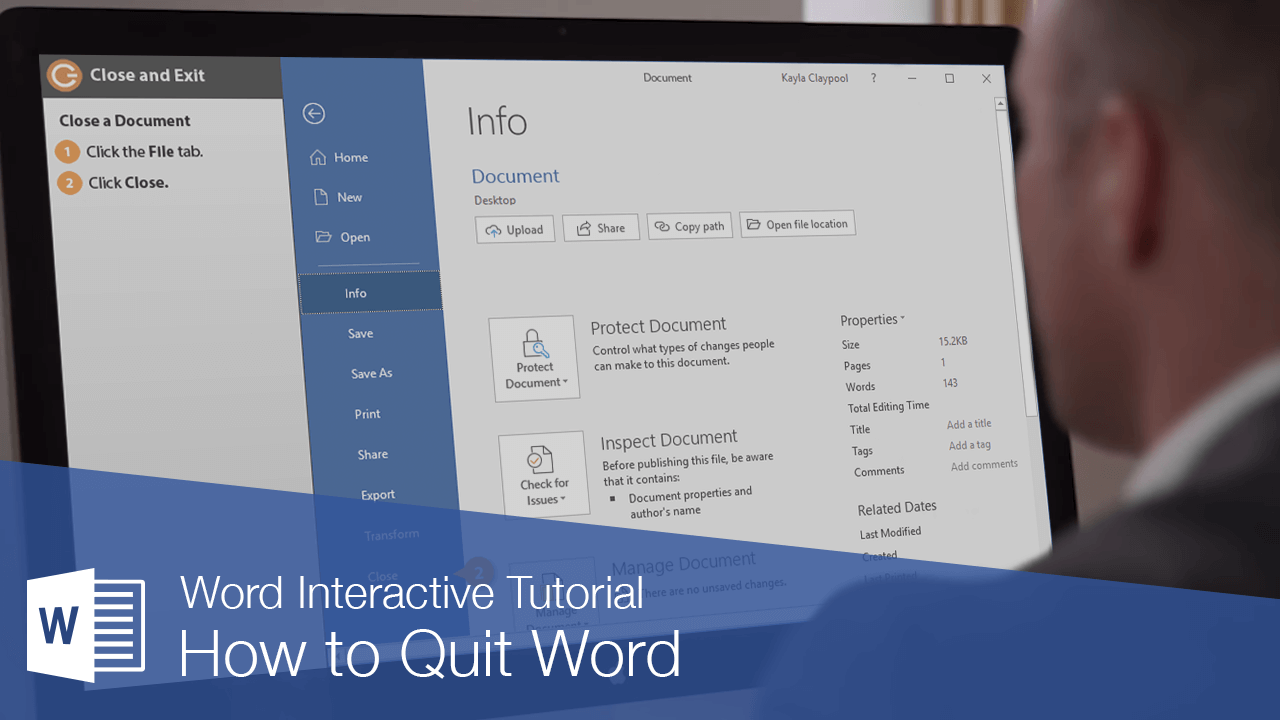
Close a Document
Each document window must be closed individually. If you only have one file open, you can close it from the File menu and keep Word running.
- Click the File tab.
- Click the Close.
The file is closed, but Word is still running. You can still browse for a file to open, create a new document from a template, and access Word’s options.
If you have multiple Word documents open, clicking the Close button on the title bar will close each document individually.
If you have not saved the document since making changes, a dialog box will appear asking if you want to save the changes to the document. Click Save if you wish to save your changes, click Don’t Save Save if you do not want to save your changes, and click Cancel if you do not want to close the document.
Close Word
If you only have one Word document open, closing the document window will also quit Word entirely.
- Click the Close button.
Word quits as the window closes.
FREE Quick Reference
Click to Download
Free to distribute with our compliments; we hope you will consider our paid training.
Saving the data of a project is always very important and necessary, when making a Word document it is necessary to keep the written data . For this reason, it is essential not only to buy this program but the entire Microsoft 365 office to get the most out of it.
How to Close a Document in Word Correctly and not Lose Information
In order not to lose valuable information, it is advisable to download and install the Word 2010 program preferably or a higher one and in this way it allows us to modify text documents or create them and get the most out of this tool.
When Word files are saved incorrectly, you may lose a lot of data, so it is important that you learn how to save this type of file correctly. In this article we are going to teach you how to store the data of these documents on your computer and we will also teach you how to take advantage of the automatic saving of Word documents.
Index( )
- What is the traditional way to save documents in the Word program
- Guide to saving documents using the “Save” icon
- How to benefit from automatic saving of Word documents
- How to benefit from Word’s autosave feature?
- How to recover a document in Word that could not be saved?
What is the traditional way to save documents in the Word program
To start, go to the top right corner of Word where the close option is and click on that option. Once you click on such an option, a box will appear that says “ Do you want to save changes to the document? ” you must click on “save” then select the place where you want to save the document and select the format that the document will have.
Although this is one of the most common ways to save Word documents , not many people trust this method to save data from a file. In case you insert a table you should not worry about losing it, but if it is a large project it is better that you choose to save the documents using the save icon.
Guide to saving documents using the “Save” icon
Once you are done with the document you were editing or making you can go to the top left corner and look for the template icon next to the Word icon . Once you locate it, clicking on it will immediately take you to a new window that has several options.
If you are located in “Save as” you should look for the icon that says “Browse” to find the folder in which you will save the file. Once you are there select the folder in which you will save the document and save it . When you make statistical graphs for a document, this takes a long time and you cannot lose that data so easily.
How to benefit from automatic saving of Word documents
This saving is done automatically while you write in a document, almost all versions of Word office have such a function . To some extent this is one of the best features that Office Word has, something that OpenOffice and WordPad do not have. If you don’t know how to take advantage of this feature and want to know how, then keep reading this article.
How to benefit from Word’s autosave feature?
Doing this is extremely easy, if you already have an important document finished and suddenly your PC shuts down abruptly because it overheated, because they disconnected the plug or because the electricity went out. You just have to turn on the PC again and open the Word office, there you will see a bar on the left side of the screen. You can follow the instructions that appear to recover the lost document.
Since if your PC unexpectedly shuts down again this time it will not save the document so you must save the document immediately. If you do not get any documents recovery box at all then you should look for the section “ recover documents without saving ”.
How to recover a document in Word that could not be saved?
For this, open Word and go to where it says “File” once you click there you will see another window, you will have to look for the option that says “Open”. Now the documents that you have recently opened. In that panel you will have to go to the end, and there you will find the box that says “ Recover unsaved documents ”. When you press that little box you will have a file manager window where all the documents that you did not save previously are.
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts and function keys in Word for Windows.
Notes:
-
To quickly find a shortcut in this article, you can use Search. Press Ctrl+F, and then type your search words.
-
If an action that you use often does not have a shortcut key, you can record a macro to create one. For instructions, go to Create or run a macro or Use a screen reader to create a macro in Word.
-
If you are using Microsoft Word Starter, be aware that not all the features listed for Word are supported in Word Starter. For more information about the features available in Word Starter, go to Word features that are not fully supported in Word Starter.
-
Get these keyboard shortcuts in a Word document at this link: Word 2016 for Windows keyboard shortcuts.
In this topic
-
Frequently used shortcuts
-
Ribbon keyboard shortcuts
-
Navigate the document
-
Preview and print documents
-
Select text and graphics
-
Edit text and graphics
-
Work with web content
-
Work with tables
-
Review a document
-
Work with references, citations, and indexing
-
Work with mail merge and fields
-
Work with text in other languages
-
Work with document views
-
Use function key shortcuts
Frequently used shortcuts
This table shows the most frequently used shortcuts in Microsoft Word.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open a document. |
Ctrl+O |
|
Create a new document. |
Ctrl+N |
|
Save the document. |
Ctrl+S |
|
Close the document. |
Ctrl+W |
|
Cut the selected content to the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Copy the selected content to the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste the contents of the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Select all document content. |
Ctrl+A |
|
Apply bold formatting to text. |
Ctrl+B |
|
Apply italic formatting to text. |
Ctrl+I |
|
Apply underline formatting to text. |
Ctrl+U |
|
Decrease the font size by 1 point. |
Ctrl+Left bracket ([) |
|
Increase the font size by 1 point. |
Ctrl+Right bracket (]) |
|
Center the text. |
Ctrl+E |
|
Align the text to the left. |
Ctrl+L |
|
Align the text to the right. |
Ctrl+R |
|
Cancel a command. |
Esc |
|
Undo the previous action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Redo the previous action, if possible. |
Ctrl+Y |
|
Adjust the zoom magnification. |
Alt+W, Q, then use the Tab key in the Zoom dialog box to go to the value you want. |
|
Split the document window. |
Ctrl+Alt+S |
|
Remove the document window split. |
Alt+Shift+C or Ctrl+Alt+S |
Top of Page
Close a task pane
To close a task pane using the keyboard:
-
Press F6 until the task pane is selected.
-
Press Ctrl+Spacebar.
-
Use the arrow keys to select Close, and then press Enter.
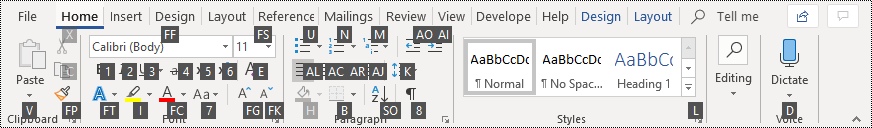
Ribbon keyboard shortcuts
The ribbon groups related options on tabs. For example, on the Home tab, the Font group includes the Font Color option. Press the Alt key to display the ribbon shortcuts, called Key Tips, as letters in small images next to the tabs and options as shown in the image below.
Note: Add-ins and other programs can add new tabs to the ribbon and might provide access keys for those tabs.
You can combine the Key Tips letters with the Alt key to make shortcuts called Access Keys for the ribbon options. For example, press Alt+H to open the Home tab, and Alt+Q to move to the Tell Me or Search field. Press Alt again to see Key Tips for the options for the selected tab.
Depending on the version of Microsoft 365 you are using, the Search text field at the top of the app window might be called Tell Me instead. Both offer a largely similar experience, but some options and search results can vary.
In Office 2013 and Office 2010, most of the old Alt key menu shortcuts still work, too. However, you need to know the full shortcut. For example, press Alt, and then press one of the old menu keys E (Edit), V (View), I (Insert), and so on. A notification pops up saying you’re using an access key from an earlier version of Microsoft 365. If you know the entire key sequence, go ahead and use it. If you don’t know the sequence, press Esc and use Key Tips instead.
Use the Access Keys for ribbon tabs
To go directly to a tab on the ribbon, press one of the following access keys. Additional tabs might appear depending on your selection in the document.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the Tell Me or Search field on the Ribbon to search for assistance or Help content. |
Alt+Q, then enter the search term. |
|
Open the File page to use Backstage view. |
Alt+F |
|
Open the Home tab to use common formatting commands, paragraph styles, and the Find tool. |
Alt+H |
|
Open the Insert tab to insert tables, pictures and shapes, headers, or text boxes. |
Alt+N |
|
Open the Design tab to use themes, colors, and effects, such as page borders. |
Alt+G |
|
Open the Layout tab to work with page margins, page orientation, indentation, and spacing. |
Alt+P |
|
Open the References tab to add a table of contents, footnotes, or a table of citations. |
Alt+S |
|
Open the Mailings tab to manage Mail Merge tasks and to work with envelopes and labels. |
Alt+M |
|
Open the Review tab to use Spell Check, set proofing languages, and to track and review changes to your document. |
Alt+R |
|
Open the View tab to choose a document view or mode, such as Read Mode or Outline view. You can also set the zoom magnification and manage multiple document windows. |
Alt+W |
Top of Page
Work in the ribbon with the keyboard
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the active tab on the ribbon and activate the access keys. |
Alt or F10. To move to a different tab, use access keys or the arrow keys. |
|
Move the focus to commands on the ribbon. |
Tab key or Shift+Tab |
|
Move between command groupings on the ribbon. |
Ctrl+Left or Right arrow key |
|
Move among the items on the ribbon. |
Arrow keys |
|
Show the tooltip for the ribbon element currently in focus. |
Ctrl+Shift+F10 |
|
Activate the selected button. |
Spacebar or Enter |
|
Open the list for the selected command. |
Down arrow key |
|
Open the menu for the selected button. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
When a menu or submenu is open, move to the next command. |
Down arrow key |
|
Expand or collapse the ribbon. |
Ctrl+F1 |
|
Open the context menu. |
Shift+F10 Or, on a Windows keyboard, the Windows Menu key (between the right Alt and right Ctrl keys) |
|
Move to the submenu when a main menu is open or selected. |
Left arrow key |
Top of Page
Navigate the document
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move the cursor one word to the left. |
Ctrl+Left arrow key |
|
Move the cursor one word to the right. |
Ctrl+Right arrow key |
|
Move the cursor up by one paragraph. |
Ctrl+Up arrow key |
|
Move the cursor down by one paragraph. |
Ctrl+Down arrow key |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the current line. |
End |
|
Move the cursor to the beginning the current line. |
Home |
|
Move the cursor to the top of the screen. |
Ctrl+Alt+Page up |
|
Move the cursor to the bottom of the screen. |
Ctrl+Alt+Page down |
|
Move the cursor by scrolling the document view up by one screen. |
Page up |
|
Move the cursor by scrolling the document view down by one screen. |
Page down |
|
Move the cursor to the top of the next page. |
Ctrl+Page down |
|
Move the cursor to the top of the previous page. |
Ctrl+Page up |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the document. |
Ctrl+End |
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the document. |
Ctrl+Home |
|
Move the cursor to the location of the previous revision. |
Shift+F5 |
|
Move the cursor to the location of the last revision made before the document was last closed. |
Shift+F5, immediately after opening the document. |
|
Cycle through floating shapes, such as text boxes or images. |
Ctrl+Alt+5, and then the Tab key repeatedly |
|
Exit the floating shape navigation and return to the normal navigation. |
Esc |
|
Display the Navigation task pane, to search within the document content. |
Ctrl+F |
|
Display the Go To dialog box, to navigate to a specific page, bookmark, footnote, table, comment, graphic, or other location. |
Ctrl+G |
|
Cycle through the locations of the four previous changes made to the document. |
Ctrl+Alt+Z |
Top of Page
Navigate the document using the browse options in Word 2007 and 2010
In Word 2007 and 2010, you can browse the document by various types of objects, such as fields, footnotes, headings, and graphics.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open the list of browse options to define the type of object to browse by. |
Ctrl+Alt+Home |
|
Move to the previous object of the defined type. |
Ctrl+Page up |
|
Move to the next object of the defined type. |
Ctrl+Page down |
Top of Page
Preview and print documents
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Print the document. |
Ctrl+P |
|
Switch to print preview. |
Ctrl+Alt+I |
|
Move around the preview page when zoomed in. |
Arrow keys |
|
Move by one preview page when zoomed out. |
Page up or Page down |
|
Move to the first preview page when zoomed out. |
Ctrl+Home |
|
Move to the last preview page when zoomed out. |
Ctrl+End |
Top of Page
Select text and graphics
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select text. |
Shift+Arrow keys |
|
Select the word to the left. |
Ctrl+Shift+Left arrow key |
|
Select the word to the right. |
Ctrl+Shift+Right arrow key |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the current line. |
Shift+Home |
|
Select from the current position to the end of the current line. |
Shift+End |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the current paragraph. |
Ctrl+Shift+Up arrow key |
|
Select from the current position to the end of the current paragraph. |
Ctrl+Shift+Down arrow key |
|
Select from the current position to the top of the screen. |
Shift+Page up |
|
Select from the current position to the bottom of the screen. |
Shift+Page down |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the document. |
Ctrl+Shift+Home |
|
Select from the current position to the end of the document. |
Ctrl+Shift+End |
|
Select from the current position to the bottom of the window. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Page down |
|
Select all document content. |
Ctrl+A |
Top of Page
Extend a selection
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Start extending the selection. |
F8 In the extend selection mode, clicking a location in the document extends the current selection to that location. |
|
Select the nearest character to the left or right. |
F8, Left or Right arrow key |
|
Expand the selection. |
F8 repeatedly to expand the selection to the entire word, sentence, paragraph, section, and document. |
|
Reduce the selection. |
Shift+F8 |
|
Select a vertical block of text. |
Ctrl+Shift+F8, then press the arrow keys |
|
Stop extending the selection. |
Esc |
Top of Page
Edit text and graphics
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Delete one word to the left. |
Ctrl+Backspace |
|
Delete one word to the right. |
Ctrl+Delete |
|
Open the Clipboard task pane and enable the Office Clipboard, which allows you to copy and paste content between Microsoft 365 apps. |
Alt+H, F, O |
|
Cut the selected content to the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Copy the selected content to the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste the contents of the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Move the selected content to a specific location. |
F2, move the cursor to the destination, and then press Enter. |
|
Copy the selected content to a specific location. |
Shift+F2, move the cursor to the destination, and then press Enter. |
|
Define an AutoText block with the selected content. |
Alt+F3 |
|
Insert an AutoText block. |
The first few characters of the AutoText block, and then press Enter when the ScreenTip appears. |
|
Cut the selected content to the Spike. |
Ctrl+F3 |
|
Paste the contents of the Spike. |
Ctrl+Shift+F3 |
|
Copy the selected formatting. |
Ctrl+Shift+C |
|
Paste the selected formatting. |
Ctrl+Shift+V |
|
Copy the header or footer used in the previous section of the document. |
Alt+Shift+R |
|
Display the Replace dialog box, to find and replace text, specific formatting, or special items. |
Ctrl+H |
|
Display the Object dialog box, to insert a file object into the document. |
Alt+N, J, J |
|
Insert a SmartArt graphic. |
Alt+N, M |
|
Insert a WordArt graphic. |
Alt+N, W |
Top of Page
Align and format paragraphs
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Center the paragraph. |
Ctrl+E |
|
Justify the paragraph. |
Ctrl+J |
|
Align the paragraph to the left. |
Ctrl+L |
|
Align the paragraph to the right. |
Ctrl+R |
|
Indent the paragraph. |
Ctrl+M |
|
Remove a paragraph indent. |
Ctrl+Shift+M |
|
Create a hanging indent. |
Ctrl+T |
|
Remove a hanging indent. |
Ctrl+Shift+T |
|
Remove paragraph formatting. |
Ctrl+Q |
|
Apply single spacing to the paragraph. |
Ctrl+1 |
|
Apply double spacing to the paragraph. |
Ctrl+2 |
|
Apply 1.5-line spacing to the paragraph. |
Ctrl+5 |
|
Add or remove space before the paragraph. |
Ctrl+0 (zero) |
|
Enable AutoFormat. |
Ctrl+Alt+K |
|
Apply the Normal style. |
Ctrl+Shift+N |
|
Apply the Heading 1 style. |
Ctrl+Alt+1 |
|
Apply the Heading 2 style. |
Ctrl+Alt+2 |
|
Apply the Heading 3 style. |
Ctrl+Alt+3 |
|
Display the Apply Styles task pane. |
Ctrl+Shift+S |
|
Display the Styles task pane. |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S |
Top of Page
Format characters
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Display the Font dialog box. |
Ctrl+D or Ctrl+Shift+F |
|
Increase the font size. |
Ctrl+Shift+Right angle bracket (>) |
|
Decrease the font size. |
Ctrl+Shift+Left angle bracket (<) |
|
Increase the font size by 1 point. |
Ctrl+Right bracket (]) |
|
Decrease the font size by 1 point. |
Ctrl+Left bracket ([) |
|
Switch the text between upper case, lower case, and title case. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Change the text to all upper case. |
Ctrl+Shift+A |
|
Hide the selected text. |
Ctrl+Shift+H |
|
Apply bold formatting. |
Ctrl+B |
|
Add a bulleted list. |
Ctrl+Shift+L |
|
Apply underline formatting. |
Ctrl+U |
|
Apply underline formatting to the words, but not the spaces. |
Ctrl+Shift+W |
|
Apply double-underline formatting. |
Ctrl+Shift+D |
|
Apply italic formatting. |
Ctrl+I |
|
Apply small caps formatting. |
Ctrl+Shift+K |
|
Apply subscript formatting. |
Ctrl+Equal sign ( = ) |
|
Apply superscript formatting. |
Ctrl+Shift+Plus sign (+) |
|
Remove manual character formatting. |
Ctrl+Spacebar |
|
Change the selected text to the Symbol font. |
Ctrl+Shift+Q |
Top of Page
Manage text formatting
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Display all nonprinting characters. |
Ctrl+Shift+8 (do not use the numeric keypad) |
|
Display the Reveal Formatting task pane. |
Shift+F1 |
Top of Page
Insert special characters
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a line break. |
Shift+Enter |
|
Insert a page break. |
Ctrl+Enter |
|
Insert a column break. |
Ctrl+Shift+Enter |
|
Insert an em dash (—). |
Ctrl+Alt+Minus sign (on the numeric keypad) |
|
Insert an en dash (–). |
Ctrl+Minus sign (on the numeric keypad) |
|
Insert an optional hyphen. |
Ctrl+Hyphen (-) |
|
Insert a nonbreaking hyphen. |
Ctrl+Shift+Hyphen (-) |
|
Insert a nonbreaking space. |
Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar |
|
Insert a copyright symbol (©). |
Ctrl+Alt+C |
|
Insert a registered trademark symbol (®). |
Ctrl+Alt+R |
|
Insert a trademark symbol (™). |
Ctrl+Alt+T |
|
Insert an ellipsis (…) |
Ctrl+Alt+Period (.) |
|
Insert the Unicode character for the specified Unicode (hexadecimal) character code. For example, to insert the euro currency symbol ( Tip: To find out the Unicode character code for a selected character, press Alt+X. |
The character code, then press Alt+X |
|
Insert the ANSI character for the specified ANSI (decimal) character code. For example, to insert the euro currency symbol, hold down Alt and press 0128 on the numeric keypad. |
Alt+the character code (on the numeric keypad) |
Top of Page
Work with web content
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a hyperlink. |
Ctrl+K |
|
Go back one page. |
Alt+Left arrow key |
|
Go forward one page. |
Alt+Right arrow key |
|
Refresh the page. |
F9 |
Top of Page
Work with tables
Move around in a table
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the next cell in the row and select its content. |
Tab key |
|
Move to the previous cell in the row and select its content. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Move to the first cell in the row. |
Alt+Home |
|
Move to the last cell in the row. |
Alt+End |
|
Move to the first cell in the column. |
Alt+Page up |
|
Move to the last cell in the column. |
Alt+Page down |
|
Move to the previous row. |
Up arrow key |
|
Move to the next row. |
Down arrow key |
|
Move one row up. |
Alt+Shift+Up arrow key |
|
Move one row down. |
Alt+Shift+Down arrow key |
Top of Page
Select table content
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the content in the next cell. |
Tab key |
|
Select the content in the previous cell. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Extend a selection to adjacent cells. |
Shift+Arrow keys |
|
Select a column. |
Select the top or bottom cell of the column, and then press Shift+Up or Down arrow key |
|
Select a row. |
Select the first or last cell in the row, and then press Shift+Alt+End or Home. |
|
Select the whole table. |
Alt+5 on the numeric keypad, with Num Lock switched off |
Top of Page
Insert paragraphs and tab characters in a table
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a new paragraph in a cell. |
Enter |
|
Insert a tab character in a cell. |
Ctrl+Tab |
Top of Page
Review a document
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a comment. |
Ctrl+Alt+M |
|
Turn change tracking on or off. |
Ctrl+Shift+E |
|
Close the Reviewing Pane. |
Alt+Shift+C |
Top of Page
Work with references, citations, and indexing
Use the following shortcuts to add references to your document, such as a table of contents, footnotes, and citations.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Mark a table of contents entry. |
Alt+Shift+O |
|
Mark a table of authorities entry (citation). |
Alt+Shift+I |
|
Choose citation options. |
Alt+Shift+F12, Spacebar |
|
Mark an index entry. |
Alt+Shift+X |
|
Insert a footnote. |
Ctrl+Alt+F |
|
Insert an endnote. |
Ctrl+Alt+D |
|
Go to the next footnote. |
Alt+Shift+Right angle bracket (>) |
|
Go to the previous footnote. |
Alt+Shift+Left angle bracket (<) |
Top of Page
Work with mail merge and fields
To use the following keyboard shortcuts, the Mailings ribbon tab must be selected. To select the Mailings tab, press Alt+M.
Perform a mail merge
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Preview the mail merge. |
Alt+Shift+K |
|
Merge a document. |
Alt+Shift+N |
|
Print the merged document. |
Alt+Shift+M |
|
Edit a mail-merge data document. |
Alt+Shift+E |
|
Insert a merge field. |
Alt+Shift+F |
Top of Page
Work with fields
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a DATE field. |
Alt+Shift+D |
|
Insert a LISTNUM field. |
Ctrl+Alt+L |
|
Insert a PAGE field. |
Alt+Shift+P |
|
Insert a TIME field. |
Alt+Shift+T |
|
Insert an empty field. |
Ctrl+F9 |
|
Update the linked information in a Word source document. |
Ctrl+Shift+F7 |
|
Update the selected fields. |
F9 |
|
Unlink a field. |
Ctrl+Shift+F9 |
|
Switch between a selected field code and its result. |
Shift+F9 |
|
Switch between all field codes and their results. |
Alt+F9 |
|
Run GOTOBUTTON or MACROBUTTON from a field displaying field results. |
Alt+Shift+F9 |
|
Go to the next field. |
F11 |
|
Go to the previous field. |
Shift+F11 |
|
Lock a field. |
Ctrl+F11 |
|
Unlock a field. |
Ctrl+Shift+F11 |
Top of Page
Work with text in other languages
Set the proofing language
Every document has a default language, typically the same default language as your computer’s operating system. If your document also contains words or phrases in a different language, it’s a good idea to set the proofing language for those words. This not only makes it possible to check spelling and grammar for those phrases, but it also enables assistive technologies like screen readers to handle them appropriately.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Display the Language dialog box to set the proofing language. |
Alt+R, U, L |
|
Set default languages. |
Alt+R, L |
Top of Page
Insert international characters
To type a lowercase character by using a key combination that includes the Shift key, hold down the Ctrl+Shift+symbol keys simultaneously, and then release them before you type the letter.
Note: If you type extensively in another language, you might prefer to switch to a different keyboard instead.
|
To insert this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
à, è, ì, ò, ù, |
Ctrl+Grave accent (`), the letter |
|
á, é, í, ó, ú, ý |
Ctrl+Single quotation mark (‘), the letter |
|
â, ê, î, ô, û |
Ctrl+Shift+Caret (^), the letter |
|
ã, ñ, õ |
Ctrl+Shift+Tilde (~), the letter |
|
ä, ë, ï, ö, ü, ÿ, |
Ctrl+Shift+Colon (:), the letter |
|
å, Å |
Ctrl+Shift+At sign (@), a or A |
|
æ, Æ |
Ctrl+Shift+Ampersand (&), a or A |
|
œ, Œ |
Ctrl+Shift+Ampersand (&), o or O |
|
ç, Ç |
Ctrl+Comma (,), c or C |
|
ð, Ð |
Ctrl+Single quotation mark (‘), d or D |
|
ø, Ø |
Ctrl+Forward slash (/), o or O |
|
¿ |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Question mark (?) |
|
¡ |
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Exclamation point (!) |
|
ß |
Ctrl+Shift+Ampersand (&), s |
Top of Page
Use Input Method Editors for East Asian languages
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Switch to the Japanese Input Method Editor (IME) for a 101-key keyboard, if available. |
Alt+Tilde (~) |
|
Switch to the Korean Input Method Editor (IME) for a 101-key keyboard, if available. |
Right Alt |
|
Switch to the Chinese Input Method Editor (IME) for a 101-key keyboard, if available. |
Ctrl+Spacebar |
Top of Page
Work with document views
Word offers several different views of a document. Each view makes it easier to do certain tasks. For example, Read Mode enables you view the document as a horizontal sequence of pages, which you can quickly browse using the Left and Right arrow keys.
Switch the document view
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Switch to the Read Mode view. In Word 2007 and 2010, this is called Full Screen Reading view. |
Alt+W, F |
|
Switch to the Print Layout view. |
Ctrl+Alt+P |
|
Switch to the Outline view. |
Ctrl+Alt+O |
|
Switch to the Draft view. |
Ctrl+Alt+N |
Top of Page
Outline a document
These shortcuts only apply when the document is in the Outline view.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Promote a paragraph. |
Alt+Shift+Left arrow key |
|
Demote a paragraph. |
Alt+Shift+Right arrow key |
|
Demote the paragraph to body text. |
Ctrl+Shift+N |
|
Move the selected paragraphs up. |
Alt+Shift+Up arrow key |
|
Move the selected paragraphs down. |
Alt+Shift+Down arrow key |
|
Expand the text under a heading. |
Alt+Shift+Plus sign (+) |
|
Collapse the text under a heading. |
Alt+Shift+Minus sign (-) |
|
Expand or collapse all text or headings. |
Alt+Shift+A |
|
Hide or display the character formatting. |
Forward slash (/) (on the numeric keypad) |
|
Switch between showing the first line of body text and showing all body text. |
Alt+Shift+L |
|
Show all headings with the Heading 1 style. |
Alt+Shift+1 |
|
Show all headings with the specified heading level. |
Alt+Shift+Heading level number |
|
Insert a tab character. |
Ctrl+Tab |
Top of Page
Move through the document in Read Mode
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the beginning of the document. |
Home |
|
Move to the end of the document. |
End |
|
Go to a specific page. |
Type the page number, then press Enter |
|
Exit Read Mode. |
Esc |
Top of Page
Use function key shortcuts
|
Key |
Description |
|---|---|
|
F1 |
|
|
F2 |
|
|
F3 |
|
|
F4 |
|
|
F5 |
|
|
F6 |
|
|
F7 |
|
|
F8 |
|
|
F9 |
|
|
F10 |
|
|
F11 |
|
|
F12 |
|
Top of Page
See also
Word help center
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Word
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Word
Screen reader support for Word
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts and function keys in Word for Mac.
Notes:
-
The settings in some versions of the Mac operating system (OS) and some utility applications might conflict with keyboard shortcuts and function key operations in Microsoft 365 for Mac. For information about changing the key assignment for a keyboard shortcut, see Mac Help for your version of macOS, your utility application, or refer to Shortcut conflicts.
-
If you don’t find a keyboard shortcut here that meets your needs, you can create a custom keyboard shortcut. For instructions, go to Create a custom keyboard shortcut for Office for Mac.
-
Many of the shortcuts that use the Ctrl key on a Windows keyboard also work with the Control key in Word for Mac. However, not all do.
-
To quickly find a shortcut in this article, you can use Search. Press Command+F, and then type your search words.
For the best experience using your keyboard with the ribbon, enable your keyboard to access all controls.
-
To open the System Preferences, press
+Spacebar, type system preferences, and press Return.
-
To go to Keyboard Settings, type keyboard and press Return.
-
In the Shortcuts tab, press Control+F7 to change the Full Keyboard Access setting from Text boxes and lists only to All Controls.
In this topic
-
Frequently used shortcuts
-
Shortcut conflicts
-
Navigate the document
-
Select text and graphics
-
Edit text and graphics
-
Work with tables
-
Drawing
-
Work with fields
-
Outline a document
-
Review a document
-
Use footnotes and endnotes
-
Work with right-to-left languages
-
Use function key shortcuts
Frequently used shortcuts
This table lists frequently used shortcuts in Word for Mac.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Undo the previous action. |
|
|
Redo the previous action, if possible. |
|
|
Cut the selected content to the Clipboard. |
|
|
Copy the selected content to the Clipboard. |
|
|
Paste the contents of the Clipboard. |
|
|
Display the shortcut menu for the selected item. * |
Shift+F10 |
|
Display the Go To dialog box. |
|
|
Display the Spelling and Grammar dialog box. |
|
|
Enable extended selection mode. |
F8 |
|
Switch to the next window. |
|
|
Switch to the previous window. |
|
|
Display the Save As dialog box. |
|
|
Find text (move focus to the Search in Document box). |
|
|
Display the Find and Replace pane. |
Control+H |
|
Display the Print dialog box. |
|
|
Close the current document. |
|
|
Expand or minimize the ribbon. |
|
|
Find the next spelling or grammatical error. The Check spelling as you type feature must be enabled. |
Option+F7 |
|
Open the Dictionary. |
In Word 2011, Option+Shift+F7 |
Top of Page
Shortcut conflicts
Some Word for Mac keyboard shortcuts conflict with default macOS keyboard shortcuts. This topic flags such shortcuts with an asterisk ( * ). To use these shortcuts, you may have to change your Mac keyboard settings to change the shortcut for the key.
Change system preferences for keyboard shortcuts
-
From the Apple menu, select System Preferences.
-
Select Keyboard.
-
Select the Shortcuts tab.
-
Select Mission Control.
-
Clear the check box for the keyboard shortcut conflicting with the Word for Mac shortcut that you want to use.
Navigate the document
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move the cursor one word to the left. |
Option+Left arrow key |
|
Move the cursor one word to the right. |
Option+Right arrow key |
|
Move the cursor up by one paragraph. |
|
|
Move the cursor down by one paragraph. |
|
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the current line. |
Home |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the current line. |
End |
|
Move the cursor to the top of the previous page. |
On a MacBook, press |
|
Move the cursor to the top of the next page. |
On a MacBook, press |
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the document. |
On a MacBook, press |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the document. |
On a MacBook, press |
|
Move the cursor to the previous insertion point. |
Shift+F5 |
|
Move the cursor by scrolling the document view up by one screen. |
Page up |
|
Move the cursor by scrolling the document view down by one screen. |
Page down |
Top of Page
Select text and graphics
Tip: If you know the key combination to move the cursor, you can generally select the text by using the same key combination while holding down Shift. For example, 
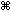
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select multiple items that are not next to each other. |
Select the first item that you want, hold down |
|
Select text. |
Shift+Arrow keys |
|
Select the word to the left. |
Shift+Option+Left arrow key |
|
Select the word to the right. |
Shift+Option+Right arrow key |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the current line. |
Shift+Home |
|
Select from the current position to the end of the current line. |
Shift+End |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the current paragraph. |
|
|
Select from the current position to the end of the current paragraph. |
|
|
Select from the current position to the top of the screen. |
Shift+Page up |
|
Select from the current position to the bottom of the screen. |
Shift+Page down |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the document. |
|
|
Select from the current position to the end of the document. |
|
|
Select from the current position to the bottom of the window. |
|
|
Select all document content. |
|
Top of Page
Extend a selection
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Start extending the selection. * |
F8 In the extend selection mode, clicking a location in the document extends the current selection to that location. |
|
Select the nearest character to the left. |
F8, Left arrow key |
|
Select the nearest character to the right. |
F8, Right arrow key |
|
Expand the selection. |
F8 repeatedly to expand the selection to the entire word, sentence, paragraph, section, and document. |
|
Reduce the selection. * |
Shift+F8 |
|
Select a vertical block of text. |
|
|
Stop extending the selection. |
Esc |
Top of Page
Edit text and graphics
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Cut the selected content to the Clipboard. |
F2 |
|
Copy the selected content to the Clipboard. |
F3 |
|
Paste the contents of the Clipboard. |
F4 |
|
Display the Paste Special dialog box. |
|
|
Cut the selected content to the Spike. |
|
|
Paste the contents of the Spike. |
|
|
Copy the selected formatting. |
|
|
Paste the copied formatting. |
|
|
Create an AutoText entry. |
Option+F3 |
Top of Page
Align and format paragraphs
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Center the paragraph. |
|
|
Justify the paragraph. |
|
|
Align the paragraph to the left. |
|
|
Align the paragraph to the right. |
|
|
Indent the paragraph. |
Control+Shift+M |
|
Remove a paragraph indent. |
|
|
Create a hanging indent. |
|
|
Remove a hanging indent. |
|
|
Apply single-spacing to the paragraph. |
|
|
Apply double-spacing to the paragraph. |
|
|
Apply 1.5-line spacing to the paragraph. |
|
|
Enable AutoFormat. |
|
|
Apply the Normal style. |
|
|
Apply the Heading 1 style. |
|
|
Apply the Heading 2 style. |
|
|
Apply the Heading 3 style. |
|
|
Apply the List style. |
|
|
Insert a nonbreaking space. |
Option+Spacebar |
Top of Page
Format characters
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Increase the font size. |
|
|
Decrease the font size. |
|
|
Increase the font size by 1 point. |
|
|
Decrease the font size by 1 point. |
|
|
Display the Font dialog box. |
|
|
Switch the text between upper case, lower case, and title case. |
Shift+F3 |
|
Change the text to all upper case. |
|
|
Apply bold formatting. |
|
|
Add a bulleted list. |
|
|
Apply underline formatting. |
|
|
Apply underline formatting to the words, but not the spaces. |
|
|
Apply double-underline formatting. |
|
|
Apply italics formatting. |
|
|
Apply small caps formatting. |
|
|
Apply strike-through formatting. |
|
Top of Page
Insert special characters
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert an empty field. |
|
|
Insert a line break. |
Shift+Return |
|
Insert a page break. |
|
|
Insert a column break. |
|
|
Insert a nonbreaking hyphen. |
|
|
Insert a registered trademark symbol (®). |
Option+R |
|
Insert a trademark symbol (™). |
Option+2 |
Top of Page
Work with tables
Move around in a table
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move to the next cell and select its content. |
Tab key |
|
Move to the previous cell and select its content. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Move to the next row. |
Down arrow key |
|
Move to the previous row. |
Up arrow key |
|
Move to the first cell in the row. |
Control+Home |
|
Move to the last cell in the row. |
Control+End |
|
Move to the first cell in the column. |
Control+Page up |
|
Move to the last cell in the column. |
Control+Page down |
|
Add a new row to the bottom of the table. |
Tab key, at the end of the last row |
|
Insert a row. |
|
Top of Page
Select table content
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the content in the next cell. |
Tab key |
|
Select the content in the previous cell. |
Shift+Tab |
|
Extend a selection to adjacent cells. |
Shift+Arrow keys |
|
Select a row. |
Select the first or last cell in the row, and then press Shift+Alt+End or Home. |
Top of Page
Resize table columns with the ruler
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Retain the column sizes to the right and change the table width. |
Drag the column boundary in the ruler |
|
Move a single column line and retain the table width. |
Shift+Drag the column boundary in the ruler |
|
Equally resize all columns to the right and retain the table width. |
|
|
Proportionally resize all columns to the right and retain the table width. |
|
Top of Page
Resize table columns directly in a table
Tip: To finely adjust the column width and display the column’s measurements in the ruler when you resize the column, turn off the snap-to functionality by pressing Option with the shortcut keys.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move a single column line and retain the table width. |
Drag the column boundary |
|
Retain column sizes to the right and change the table width. |
Shift+Drag the column boundary |
|
Equally resize all columns to the right and retain the table width. |
|
|
Proportionally resize all columns to the right and retain the table width. |
|
Top of Page
Insert paragraphs and tab characters in a table
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a new paragraph in a cell. |
Return |
|
Insert a Tab character in a cell. |
Option+Tab |
Top of Page
Drawing
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Toggle drawing mode. |
|
Top of Page
Work with fields
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a DATE field. |
Control+Shift+D |
|
Insert a LISTNUM field. |
|
|
Insert a PAGE field. |
Control+Shift+P |
|
Insert a TIME field. |
Control+Shift+T |
|
Insert an empty field. |
|
|
Update the selected fields. * |
F9 |
|
Switch between a field code and its result. * |
Shift+F9 |
|
Switch between all field codes and their results. |
Option+F9 |
|
Run GOTOBUTTON or MACROBUTTON from a field displaying field results. |
Option+Shift+F9 |
|
Lock a field. |
|
|
Unlock a field. |
|
Top of Page
Outline a document
These shortcuts only apply when the document is in the Outline view.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Promote a paragraph. |
Control+Shift+Left arrow key |
|
Demote a paragraph. |
Control+Shift+Right arrow key |
|
Demote the paragraph to body text. |
|
|
Move the selected paragraphs up. * |
Control+Shift+Up arrow key |
|
Move the selected paragraphs down. * |
Control+Shift+Down arrow key |
|
Expand the text under a heading. |
Control+Shift+Plus sign (+) |
|
Collapse text under a heading. * |
Control+Shift+Minus sign (-) |
|
Expand all body text and headings, or collapse all body text. |
Control+Shift+A |
|
Switch between showing the first line of body text and showing all body text. |
Control+Shift+L |
|
Show all headings with the specified heading level. |
Control+Shift+Heading level number |
Top of Page
Review a document
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a comment. |
|
|
Turn change tracking on or off. |
|
|
Move to the beginning of a comment. |
Home |
|
Move to the end of a comment. |
End (The End key is not available on all keyboards.) |
|
Move to the beginning of the list of comments. |
|
|
Move to the end of the list of comments. |
|
Top of Page
Use footnotes and endnotes
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Insert a footnote. |
|
|
Insert an endnote. |
|
Top of Page
Work with right-to-left languages
Word supports right-to-left functionality for languages that work in a right-to-left or a combined right-to-left, left-to-right environment for writing, editing, and displaying text. In this context, right-to-left languages refers to any writing system that is written from right to left and includes languages that require contextual shaping, such as Arabic, and languages that do not.
Before you can use these keyboard shortcuts, you need to ensure keyboard shortcuts are enabled for the language you are using:
-
Go to Apple > System Preferences > Keyboard.
-
On the Input Sources tab, select the language for which you want to enable shortcuts.
-
On the right side of the tab, select the check box for Enable keyboard shortcuts.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Switch the writing direction to right-to-left. |
Control+ |
|
Switch the writing direction to left-to-right. |
Control+ |
Top of Page
Use function key shortcuts
Word for Mac uses the function keys for common commands, including Copy and Paste. For quick access to these shortcuts, you can change your Apple system preferences so you don’t have to press the Fn key every time you use a function key shortcut.
Note: Changing system function key preferences affects how the function keys work on your Mac, not just in Word. After changing this setting, you can still perform the special features printed on a function key. Just press the Fn key. For example, to use the F12 key to change your volume, press Fn+F12.
If a function key doesn’t work as you expect it to, press the Fn key in addition to the function key. If you don’t want to press the Fn key each time, you can change your Apple system preferences. For instructions, go to Change function key preferences.
The following table provides the function key shortcuts for Word for Mac.
|
Key |
Description |
|---|---|
|
F1 |
|
|
F2 |
|
|
F3 |
|
|
F4 |
|
|
F5 |
|
|
F6 |
|
|
F7 |
|
|
F8 |
|
|
F9 |
|
|
F10 |
|
|
F11 |
|
Top of Page
Change function key preferences
-
In the Apple menu, select System Preferences.
-
Select Keyboard.
-
On the Keyboard tab, select the check box for Use all F1, F2, etc. keys as standard function keys.
See also
Word help center
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Word
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Word
Screen reader support for Word
This article describes the keyboard shortcuts in Word for the web.
Notes:
-
If you use Narrator with the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update, you have to turn off scan mode in order to edit documents, spreadsheets, or presentations with Microsoft 365 for the web. For more information, refer to Turn off virtual or browse mode in screen readers in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update.
-
To quickly find a shortcut in this article, you can use Search. Press Ctrl+F and then type your search words.
-
When you use Word for the web, we recommend that you use Microsoft Edge as your web browser. Because Word for the web runs in your web browser, the keyboard shortcuts are different from those in the desktop program. For example, you’ll use Ctrl+F6 instead of F6 for jumping in and out of the commands. Also, common shortcuts like F1 (Help) and Ctrl+O (Open) apply to the web browser – not Word for the web.
In this topic
-
Frequently used shortcuts
-
Ribbon keyboard shortcuts
-
Navigate the document
-
Edit and format the document
-
Work with comments
Frequently used shortcuts
This table lists the most frequently used shortcuts in Word for the web.
Tip: To quickly create a new document in Word for the web, open your browser, type Word.new in the address bar, and then press Enter.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
In the Reading view, open a PDF-based view tagged to work with screen readers. |
Press the Tab key until you reach the Accessibility Mode button, and then press Enter |
|
Find text in the Reading view. |
Ctrl+F or F3 |
|
Find text in the Editing view. |
Ctrl+F or Ctrl+G |
|
Find and replace text in the Editing view. |
Ctrl+H |
|
Hide the task pane, if one is open. |
Esc |
|
Switch to the Zoom control. |
Alt+Period, W, then Q or Alt+Windows logo key, W, then Q |
|
Print the document. |
Ctrl+P |
|
Move to the next landmark region. |
Ctrl+F6 |
|
Go to the Tell Me or Search text field. |
Alt+Q |
Top of Page
Ribbon keyboard shortcuts
Word for the web offers shortcuts called access keys to navigate the ribbon. If you’ve used access keys to save time on Word for desktop computers, you’ll find access keys very similar in Word for the web.
On a Windows computer, access keys all start with Alt+Period (.) or Alt+Windows logo key, then add a letter for the ribbon tab. For example, to go to the Review tab, press Alt+Period, R or Alt+Windows logo key, R.
If you’re using Word for the web on a Mac computer, press Control+Period (.) to start.
-
To get to the ribbon, press Alt+Period or Alt+Windows logo key. You can alternatively press Ctrl+F6 until you reach the Home tab.
-
To move between tabs on the ribbon, press the Tab key.
-
To hide the ribbon so you have more room to work, press Ctrl+F3. Repeat to display the ribbon again.
Go to the access keys for the ribbon
To go directly to a tab on the ribbon, press one of the following access keys:
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Open the Tell Me or Search text field on the ribbon to type a search term. |
Alt+Period, Q or Alt+Windows logo key, Q |
|
Open the File tab to use the Backstage view. |
Alt+Period, F or Alt+Windows logo key, F |
|
Open the Home tab to format text and use the Find tool. |
Alt+Period, H or Alt+Windows logo key, H |
|
Open the Insert tab to insert a picture, link, comment, header or footer, or a page number. You can also access the Symbol gallery. |
Alt+Period, N or Alt+Windows logo key, N |
|
Open the Page Layout tab to set page margins, orientation, and size, and paragraph spacing. |
Alt+Period, A or Alt+Windows logo key, A |
|
Open the References tab to insert a table of contents, footnotes, or endnotes. |
Alt+Period, S or Alt+Windows logo key, S |
|
Open the Review tab to check spelling, add comments, or track and review changes to your document. |
Alt+Period, R or Alt+Windows logo key, R |
|
Open the View tab to choose a view, open the Navigation pane, edit the Header & Footer, and to Zoom the document view. |
Alt+Period, W or Alt+Windows logo key, W |
Top of Page
Use Search
To find an option or perform an action quickly, use the Search text field. To learn more about the Search feature, go to Find what you need with Microsoft Search.
Note: Depending on the version of Microsoft 365 you are using, the Search text field at the top of the app window might be called Tell Me instead. Both offer a largely similar experience, but some options and search results can vary.
-
Select the item or place in your document, presentation, or spreadsheet where you want to perform an action.
-
To go to the Search text field, press Alt+Q.
-
Type the search words for the action that you want to perform. For example, if you want to add a bulleted list, type bullets.
-
Press the Down arrow key to browse through the search results.
-
Once you’ve found the result that you want, press Enter to select it and to perform the action.
Work in the ribbon tabs and menus
The following shortcuts can save time when you work with the ribbon tabs and ribbon menus.
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Select the active tab on the ribbon, and activate the access keys. |
Alt+Period or Alt+Windows logo key. To move to a different tab, use an access key or the Tab key. |
|
When a Ribbon tab is selected, move the focus to the tab commands. |
Enter, then Tab key or Shift+Tab |
|
Activate a selected button. |
Spacebar or Enter |
|
Open the list for a selected command. |
Spacebar or Enter |
|
Open the menu for a selected button. |
Alt+Down arrow key |
|
When a menu or submenu is open, move to the next command. |
Down arrow key |
|
Collapse or expand the ribbon. |
Ctrl+F3 |
Top of Page
Navigate the document
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Move the cursor right by one word. |
Ctrl+Right arrow key |
|
Move the cursor left by one word. |
Ctrl+Left arrow key |
|
Move the cursor up by one paragraph. |
Ctrl+Up arrow key |
|
Move the cursor down by one paragraph. |
Ctrl+Down arrow key |
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the current line. |
Home |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the current line. |
End |
|
Move the cursor to the beginning of the document. |
Ctrl+Home |
|
Move the cursor to the end of the document. |
Ctrl+End |
|
Select text. |
Shift+Arrow keys |
|
Select the word to the right. |
Shift+Ctrl+Right arrow key |
|
Select the word to the left. |
Shift+Ctrl+Left arrow key |
|
Select the paragraph above. |
Shift+Ctrl+Up arrow key |
|
Select the paragraph below. |
Shift+Ctrl+Down arrow key |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the line. |
Shift+Home |
|
Select from the current position to the end of the line. |
Shift+End |
|
Select from the current position to the beginning of the document. |
Shift+Ctrl+Home |
|
Select from the current position to the end of the document. |
Shift+Ctrl+End |
|
Select all document content. |
Ctrl+A |
Top of Page
Edit and format the document
|
To do this |
Press |
|---|---|
|
Cut the selected content to the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+X |
|
Copy the selected content to the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+C |
|
Paste the content from the Clipboard. |
Ctrl+V |
|
Undo the previous action. |
Ctrl+Z |
|
Redo the previous action. |
Ctrl+Y |
|
Shrink the font size. |
Ctrl+Left bracket ([) |
|
Grow the font size. |
Ctrl+Right bracket (]) |
|
Apply bold formatting to the selected text. |
Ctrl+B |
|
Apply italic formatting to the selected text. |
Ctrl+I |
|
Underline the selected text. |
Ctrl+U |
|
Align the paragraph to the left. |
Ctrl+L |
|
Align the paragraph to the right. |
Ctrl+R |
|
Center the paragraph. |
Ctrl+E |
|
Justify the paragraph. |
Ctrl+J |
|
Create a bulleted list. |
Ctrl+Period (.) |
|
Create a numbered list. |
Ctrl+Slash (/) |
Top of Page
See also
Word help center
Basic tasks using a screen reader with Word
Use a screen reader to explore and navigate Word
Screen reader support for Word
In this lesson, you will learn how to close a Microsoft Word document. When you complete your work with a document. Before closing the document, you will need to Save it on your computer. If you don’t want to save it on the computer, no tension. So how to close a Word document without closing the word program? follow the below simple steps.
- Click the File tab (located at the left upper corner) and choose the Close option and your document will be closed.
- If you have not saved your document on your computer, a warning box will display on the screen asking whether the document should be saved or not. If you want to save your document, click Save and give a name to the document, otherwise click Don’t Save.
- If the document is already saved on your computer and wants to save the changes, just click on Save, otherwise click Don’t Save. So the Word application will not be closed and you will see a blank Word window.
- To go back to the opened document, click

Note: –
If this article is helpful to you, please share it with your friends on the below social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, WhatsApp, Telegram, etc.
In this chapter, we will understand how to close a document in Word 2010. When you finish working with a document, you will proceed to close the document. Closing a document removes it from your computer screen and if you had other documents open, Word displays the last document you used otherwise, you see a blank Word window. Here are simple steps to close an opened document −
Step 1 − Click the File tab and select the Close option.
Step 2 − When you select the Close option and if the document is not saved before closing, it will display the following Warning box asking whether the document should be saved or not.
Step 3 − To save the changes, click Save, otherwise click Don’t Save. To go back to the document, click Cancel. This will close the document and if you have other documents open, Word displays the last document you used, otherwise, you see a blank Word window as shown below −
In this article, we intend to introduce you 4 quick and effectual ways to keep Word program open while closing the only active document.
Normally, to concentrate on a task, we tend to open only one document in Word. However, after editing or revision, there is the matter of closing the document while keeping the program running. To be precise, this is an issue that users of Word 2010 may run into, for in Word 2003, there is the “Close Window” button on the upper left enabling you to close the document only.
Therefore, the content below involves 4 methods for you to choose.
Method 1: Reveal the “Close Window” Button
As mentioned above, in Word 2010, there is no “Close Window” button for a single document. Nevertheless, we can make it appear.
- First off, click “File” tab.
- Then click “Options” to trigger the “Word Options” dialog box.
- Next click “Advanced”.
- Continue to scroll down to the “Display” and uncheck the “Show all windows in the Taskbar” box.
- Lastly, click “OK” to save the change.
Now you can notice the “Close Window” button is available, such as below:
Here is the effect:
Method 2: Close the File instead of Word
- Firstly, click “File” tab too.
- Next click “Close”.
Or you can choose to add the “Close” command to “Quick Access Toolbar” for quick use.
- Go to the “Word Options” dialog box taking the steps in method 1.
- Then click “Quick Access Toolbar” this time.
- Next choose “File Tab” for the category.
- Find and select “Close” command.
- Next, click “Add” button.
- Finally, click “OK”.
Method 3: Use Keyboard Shortcuts
Certainly, in case you prefer using keyboard shortcuts to clicks, you can press “Ctrl+ W” or “Ctrl+ F4”. Either of it can close only the document.
Method 4: Run a Macro
- To start with, click “Developer” tab then the “Visual Basic” to open the VBA editor.
- Next click “Normal” and “Insert”.
- Choose “Module” then.
- Double click on the new module to display the editing area.
- Then paste the bellowing codes there:
'Close the only document open but keep Word running. Sub CloseFileKeepWordOpen() ActiveDocument.Close Word.Application.Activate End Sub
- Ultimately, hit “Run” button.
It’s suggested to assign a button or keyboard to the macro for easy use. For detailed information, you can look up this article: How to Remove the Formatting of Pasted Texts with Macro and VBA in Your Word
Tool to Fix Damaged Word Document
It’s known to all that file loss can wipe out everything or something critical at least. I assume what comes to top of mind after a file loss is the way to piece data back to life. Then the best way is to gain a Word data damage fix product.
Author Introduction:
Vera Chen is a data recovery expert in DataNumen, Inc., which is the world leader in data recovery technologies, including corrupt xls data recovery tool and pdf repair software products. For more information visit www.datanumen.com
This tutorial is here to teach you the various ways to save, or open existing files in Microsoft Word. It will also show you the various nerdy ways you can close a document in Word and how to exit the Word window.
Open a Saved Document (File) in Microsoft Word
While you are creating a document, it is often important to save it for future use. The saved document now becomes a file. A file is a complete, named collection of information, such as a user-created document. It is the basic unit of storage that enables a computer to distinguish one set of information from another. It is a collection of data that a user can retrieve, change, delete, save, or send to an output device, such as a printer or e-mail program.
From the foregoing explanation, you realize that a saved document can be retrieved, viewed and reused. Here are the steps involved in opening/retrieving a saved document/file in Word environment.
- On the Menu bar, click File, and then click Open. The Open dialog box appears.
- In the Look in list, click the drive or folder that contains the file you want to open.
- Click the file.
- You’ll see a preview of the selected file in the Preview box.
- Click Open.
Open a File as Copy in Microsoft Word
This feature allows you to open a copy of a document which you can edit and save, without such changes altering the content of the original file. When you open a file as a copy, a duplicate of the file is created in the older that contains the original file. You can, however, save the copy you opened in a different location (drive and folder) and with a different filename, using the Save As command in the File menu.
Use this method if you want to work on a file of which you do not want the new changes to reflect on the original document.
Steps:
- On the Menu bar, click File and then click Open. The Open dialog box appears.
- In the Look in list, double-click the drive or folder that contains the file you want to open.
- Select the file whose copy you want to open.
- Click the drop-down arrow next to the Open button to display a drop down list.
- From the drop-down list, click Open as Copy.
NOTE:
- A copy of the selected document now opens. Now see the title bar of the document. You’ll find that Word has automatically named the document Copy (1) of ***. The asterisks represent the filename of the original document.
- If you save the document, using the Save command, after making necessary changes to it, the changes are saved into the document with the default name — Copy (1) of ***.
- To save the document with a different filename, you must use the Save As command on the File menu.
Open a File in Read-Only Mode in Microsoft Word
Opening a file in read-only helps protect a sensitive file from inadvertent change. A stray character coming into an important document that has been proof-read and is ready for publishing can ruin the quality of the entire work. If you need to review an already proof-read document but with no intention to make further changes to it, I suggest you use the Open Read-Only option of opening a document. This can help save you of costly/embarrassing mistakes.
In other words, opening a document in Read-Only prevents new changes that are either purposely or mistakenly made to the content or structure of the file from reflecting on the last saved version (i.e. how it was before you opened it) of the file. It simply allows a user to open a file to be read or copied, but not changed and then saved.
If you attempt to re-save/save changes to a document you opened in Read-Only, Word will immediately display the Save As dialog box, enabling you to re-save the document, together with whatever changes you have made to it, with a different filename or location. This way, the original document is protected, unchanged and unaffected.
To open a document in Read-Only in Word:
- In Word window, click File, and then click Open. The Open dialog box appears.
- In the Look in list, double-click the drive or folder that contains the file you want to open in read-only.
- Select the desired file.
- Click the drop-down arrow next to the Open button, and then choose Open Read-Only.
Save a Document in Microsoft Word
As you create a document, you will need to store it for future reference or use.
In Word, you to save your documents in various ways. You can save all open documents at the same time. You can also save a copy of the active document with a different name or in a different location. If you share documents with people who use previous versions of Word, and you want to be sure the documents look the same when they’re opened in the earlier versions, you can turn off features that are not part of that version.
To save a document:
- Open the File menu and click Save. The Save As dialog box appears.
- In the File name box, enter a desired name for the document.
- To save the document in a folder or a drive other than the default, click the drop-down arrow in the Save in box, and then choose the desired folder or drive.
- To save the document in a new folder within the current drive, click the Create New Folder button on the toolbar within the Save As dialog box, directly below the title bar of the Save As dialog box.
- Click Save.
The document is now stored with the name and in the location you specified, and up to the very point (i.e. only the amount of text or objects contained in the document) before you used the Save command.
NOTE:
- As you make changes to the last saved version of the document (i.e. as you type in more characters or insert objects), you will need to use the Save command often to keep updating the saved document.
- You can save time by clicking the Save button on the Standard toolbar or by pressing Ctrl and S keys simultaneously on the keyboard.
- Use the Save button on the Standard toolbar to save your document for the first time, or to save changes to an already saved document, in the same location and with the same filename.
- Use the Save As command on the File menu to save the current document in a different location, or with a different name, or in a different document format, or to assign a password to the document. The Save As command always displays the Save As dialog box, where you can do one or combination of these.
- For a comprehensive list of all keyboard shortcuts in Microsoft Word, click here, and for a detailed list and explanation of the purposes of toolbar buttons in Word, click here
Save a File/Document to another Format in Word
You can save a Word document in a format that makes it possible to access or edit in other/earlier versions of Word or in other word processors such as WordPerfect. When you save your work in Word, it is stored in the default document format of the particular version of Word you are using. The file name of the saved document is automatically followed by a .doc extension. To be able to share documents with people who use other word processors or who use versions of Word that have a different file format, you will have to save documents in file formats that such word processors or other versions of Word can understand/read. For example, you can open a document created in WordPerfect, make changes to it in Word, and then save it in either Word or WordPerfect format.
Steps to save a file to another format in Microsoft Word:
- On the File menu, click Save As.
- In the File name box, enter a new name for the file.
- Click the Save as type list, and then click the file format that you want the file saved in.
- Click Save.
Save Files Automatically When I Work
Word is equipped with an automatic saving function that ensures that a document containing important data is automatically saved at regular intervals. It does so by making an automatic document recovery file at the default interval or the interval you pre-assigned. Sometimes you are unable to save important changes to your document because your computer suddenly stops responding or you lose power unexpectedly. When this happens, Word opens an AutoRecovery file the next time you start Word so that you can open it to recover most of the changes unsaved to the original document. Note that it is still your absolute responsibility to update your document constantly by using the Save command. AutoRecover is not a replacement for the Save command. Also, if you choose not to save the recovery file after opening it, the file is deleted and your unsaved changes are lost. If, however, you save the recovery file, it replaces the original file (unless you specify a new name or directory).
To set up the interval for automatic saving of file when you work
- On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Save tab in the Options dialog box that appears.
- Select the Save AutoRecover info every check box.
- In the minutes spin box, enter the interval for how often you want to save files. Note that the more frequently your files are saved, the more information you will be able to recover on the event of computer crash/hang, power failure or file damage. In other words, the smaller the value you enter in the minutes box, the more frequently your files will be saved and the more information you will be able to recover if the dreaded happens.
- Click Ok to save your settings and close the dialog box
Speed Up Saving a File
Word is also equipped with a feature for speeding up saving by recording only the changes in a document.When you save changes to your document in Word, Word invariably overwrites the last saved version of the file and then re-save the entire document. In other words, it simply re-saves the entire document from scratch. If the document you are working on has grown rather long, or maybe you are saving in a removable disk or floppy, you’ll notice a slight delay while saving changes to the file. So, speeding up saving a file can be handy in helping you reduce such delays. When you finish working in the document, you can then perform a full save of the complete document.
Steps:
- On the Tools menu, click Options, and then click the Save tab, in the Options dialog box that appears.
- Select the Allow fast saves check box, and then click OK.
- Continue working on the document but make sure you save the new changes you make to the document as often as possible.
- To perform a full save of the document, clear the Allow fast saves check box in the Options dialog box, and then save the document. The document is now saved fully, having cleared the Allow fast saves check box.
Close a Document
When you are through working in a document, you need to close it. This will help prevent unintended changes from being made to it, and also to free the computer working memory [Random Access Memory (RAM)] some space.
Note, however, that closing a document means simply closing the active document (using the Close command or alternatives), without actually quitting the entire Word window.
There are several ways of closing a document in Word. These methods use:
- The File menu
- The Close Window button on the menu bar
- Shortcut keys
Closing a Document Using the File Menu
- From the Menu bar, choose File.
- From the File menu, click Close.
NOTE:
- This operation will close the active document, leaving the Word window Grey, ( if you have no other document running in Word) and the Title bar displays only the program name, but no program name.
- If you have not saved the recent changes you made to the document, Microsoft Word or the Office Assistant (if you have been using the Word Help or the Assistant has been on screen) will display a message box, asking whether you want to save the changes to the document. Click Yes, to save the new changes, click No, to discard the recent changes, or click Cancel, to abort the close operation and continue working in the document.
Close a Document Using the Close Window Button on the Menu Bar
Simply click the Close Window (X) button to the extreme right of the Menu bar. The active document will be closed, leaving the Word program still running. Word or the Office Assistant will prompt you to save your document, if you have unsaved changes in the document.
Close a Document Using Shortcut Keys
To close the current document without exiting Word, you can use any of the following shortcut keys, if you are a keyboard fan:
- Press Ctrl and F4 keys simultaneously on the keyboard (Ctrl + F4).
OR
- Press Ctrl and W keys simultaneously on the keyboard (Ctrl + W).
Exit Word
Exit is a command on the File menu used for quitting the Microsoft Word application when you are through working in your document. When you exit Word, the open document is also closed. Microsoft Word or the Office Assistant (if the Assistant has been active on screen, or you have been using Word Help) will display a message box or balloon, prompting you to save any unsaved changes to the document before exiting. Click Yes, to save the document before exiting Word; or click No, to exit Word without saving the document or the changes you’ve made to it; or click Cancel, to terminate executing the Exit command and continue using Word.
There are several ways of exiting/quitting the Word application. The methods use:
- The File menu
- The Close button on the title bar
- The Context menu
- The System menu
- Shortcut keys
Quitting Word Using the File Menu
The Exit option on the File menu is the command used for exiting the Word application. You have learned that the Close command on the File menu closes the only active document, leaving the Word program running still.
To exit Word using the File menu,
- On the Menu bar, click File.
- From the File menu, click Exit.
- The program (together with the running document) will then quit, but you will be prompted to save the document if unsaved changes exist in it. Choose Yes to save document, No to discard the changes while Word exits, or Cancel if you change your mind and want Word to continue running.
Quitting Word Using the Close Button on the Title Bar
This is perhaps the fastest method of exiting Word using the mouse. It involves clicking the Close button, which you can find in all Windows applications on the right-hand side of the title bar. The Close is equally available on the title bar of the Word window.
To exit Word using this method, simply click the Close button once. Word will then quit, but you will have to choose whether or not to save changes to the document, if necessary, in the message box or balloon that may appear.
Quitting Word Using the Context Menu
The context menu is the shortcut menu that pops up when you click the right mouse button on a space or on a window element.
To exit Word using the context menu,
- Right-click the title bar element of the Word screen.
- Click on the Close option.
OR
- Right-click the Word button on the task bar.
- From the context menu, click Close.
Choose an appropriate option when you are prompted to save your document, if necessary.
Quitting Word Using the System Menu
An even fast way of exiting Word is by using the control menu box. All Windows applications always come with a logo (icon), which is usually displayed on the extreme left-hand side of the title bar. This is the System menu. The System menu of the Word program is the blue «W« icon enclosed in a blue frame at the left-hand side of the title bar of the Word interface.
To exit Word using this method,
- Simply double-click the System menu (the Word icon).
OR
- Click the System menu once.
- Click the Close option on the menu that appears.
If unsaved changes exist in the document, you will be prompted to save your document before the application finally exits. Click an appropriate option.
Quitting Word Using Shortcut Keys
For keyboard fans, who’d rather issue commands from the keyboard, here are the combination of keyboard keys you can use to exit Word.
Press Alt and F4 keys simultaneously (Alt + F4).
OR
Press Alt, F and then X keys, one after the other (Alt + F + X).
OR
Press Alt, Spacebar and then click Close from the menu that appears, or simply press X when the menu appears.
Thank you for taking your time to read his tutorial. Please continue to drop by for future updates and helpful tips. Your visits will surely be worth it. I sincerely appreciate your visits and presence here. If you are finding these tutorials and tips informative and helpful, please kindly recommend this blog to your friends. If, on the other hand, there is any area you feel improvement is needed, please kindly forward a piece of advice. These will be highly welcomed and appreciated. Feel free to drop comments or ask questions using the comment box below. Your comments will be promptly reviewed and published and your questions speedily looked into and answered in the best possible manner. Thanks.
Microsoft Word is a word processing program that is part of the Microsoft Office suite of productivity software. When working in Microsoft Word, the program may suddenly freeze up, becoming unresponsive. When this occurs, you might first want to wait and see if the program will recover responsiveness, but if it remains frozen, you can force quit the program. On a Mac, you can do this from the Apple menu, and on a PC you can open the Task Manager to force quit the Word application.
Using a Mac
-
Click on the «Apple» menu in the upper-left corner of the screen.
-
Click on the «Force Quit» option in the drop-down menu to open the Force Quit Window.
-
Click on the Microsoft Word option in the list of open programs.
-
Click on the «Force Quit» button to force quit the Word program.
Using a PC
-
Right-click on the Windows taskbar at the bottom of the screen.
-
Click on «Start Task Manager» from the context menu.
-
Click on the «Applications» tab in the «Task Manager» window.
-
Click on «Microsoft Word» in the list of running applications.
-
Click the «End Task» button.
-
Click «Close the Program» when prompted to confirm that you want to force quit Word.

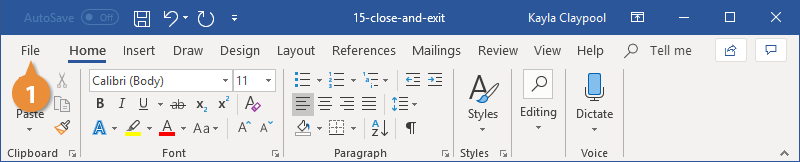
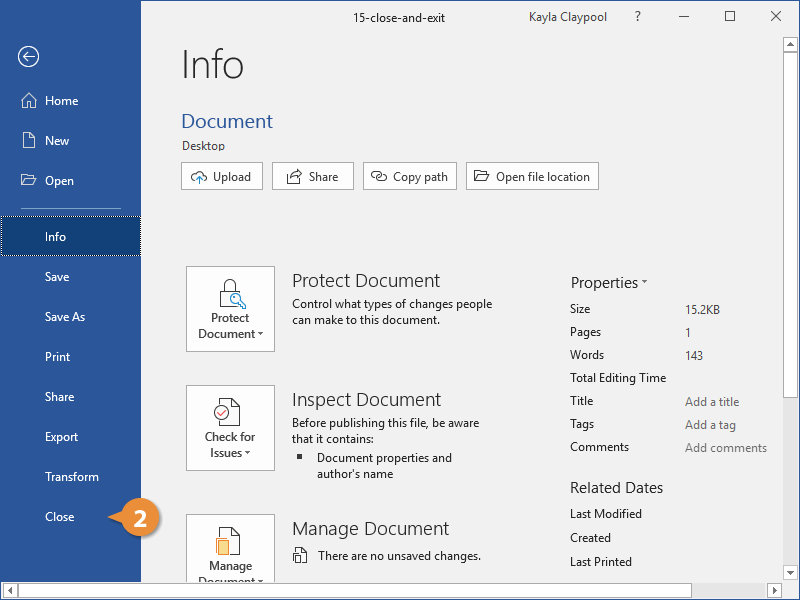
 ), type
), type