Word for Microsoft 365 Word 2021 Word 2019 Word 2016 Word 2013 Word 2010 Word 2007 More…Less
In this article
-
Add a cell
-
Add a row above or below
-
Add a column to the left or right
-
About the Table Tools contextual tabs
Add a cell
-
Click in a cell that is to the right of or above where you want to insert a cell.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Click the arrow at the bottom, right-hand corner of the Rows & Columns section.
-
Click one of the following options.
Click
To
Shift cells right
Insert a cell and move all other cells in that row to the right.
Note: Word does not insert a new column. This may result in a row that has more cells than the other rows.
Shift cells down
Insert a cell and move the existing cells down one row. A new row is added at the bottom of the table.
Insert entire row
Insert a row above the cell that you clicked in.
Insert entire column
Insert a column to the left of the cell that you clicked in.
Top of Page
Add a row above or below
-
Click in a cell above or below where you want to add a row.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, do one of the following:
-
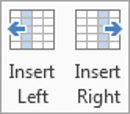
To add a row above the cell, click Insert Above in the Rows and Columns group.
-
To add a row below the cell, click Insert Below in the Rows and Columns group.
-
Tip: To insert more than one row (or column) at the same time, select as many rows or columns as you want to add before you click the insert control. For example, to insert two rows above a row, first select two rows in your table and then click Insert Above.
Top of Page
Add a column to the left or right
-
Click in a cell to the left or right of where you want to add a column.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, do one of the following:
-
To add a column to the left of the cell, click Insert Left in the Rows and Columns group.
-
To add a column to the right of the cell, click Insert Right in the Rows and Columns group.
-
Top of Page
About the Table Tools contextual tabs
You will need to know where the Design and LayoutTable Tools contextual tabs are when working on the design and structural layout of a table. The Design and Layout tabs are only visible after you have clicked inside of a table, and appear at the top of the screen on the ribbon.
Top of Page
See Also
Delete a row, column, or cell from a table
Add columns and rows to a table
Keyboard shortcuts for Microsoft Word on Windows
Need more help?
Tables in Word are useful in so many situations. In this post you’ll discover how to create tables, then manipulate and design them in the quickest and easiest way to provide that visual punch.
Clickable Table of Contents
Enhance your Word tables with these advanced features
1. What are tables in Word good for?
Tables are useful for 2 distinct reasons.
- To show an actual table of data, or
- To organise and postion text, images and other elements on the page.
Many years ago, typewriters ruled the world. And a feature of a good typewriter was the tab stop, which was a device that essentially let you control indentation.
Over the years many people have continued to use tabs to indent text, because of its convenience, but they are hard work to set up properly.
Tables provide a much easier way to organise content on a page.
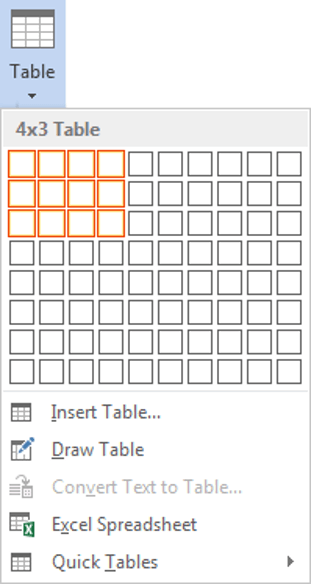
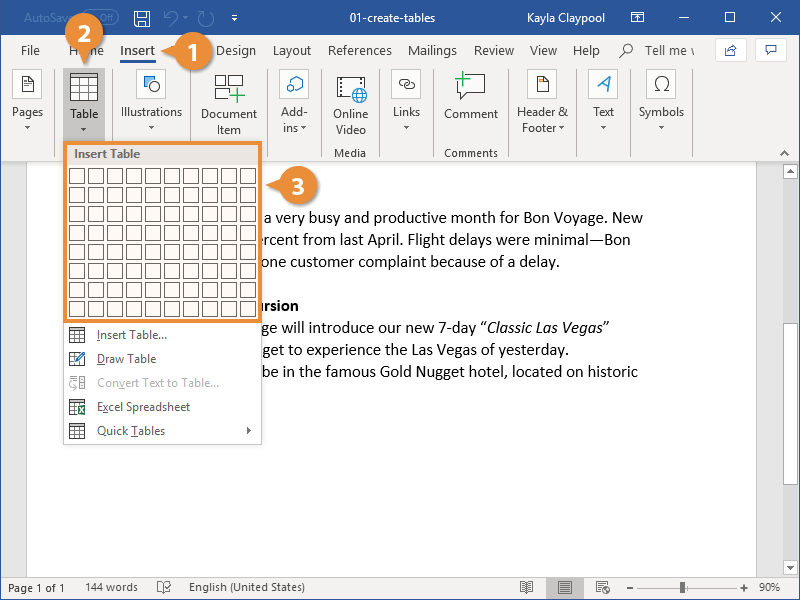
1. Select the Insert tab.
2. Click the Tables icon in the Tables group.
3. Move your mouse pointer into the table grid until the required number of rows and columns are highlighted orange, then left-click.
An empty table is inserted into the document.
Two new tabs, Design and Layout are also added to the ribbon area, under the banner of Table Tools.
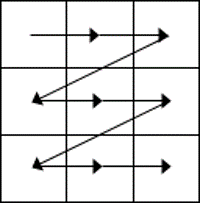
3. MOVING AROUND A Word TABLE
- While the table is empty, you can use the cursor keys to move around the cells. However, when the cells contain information, using the cursor keys will move through the cell content first before moving to the next cell
- You can left-click in any cell to position the cursor.
- Press Tab to move to the next cell. The cursor will move across and then down the table.
- Press Shift + Tab to move to the previous cell.
NB. Using Tab is better than using the cursors as it will move to the next/previous cell regardless of whether there is information in the cells.
NB2. If you press Tab while you are in the last cell, a new row will be added to the bottom of your table
4. SELECTING A CELL, ROW, COLUMN OR THE ENTIRE TABLE
To select a cell:
1. Position the mouse pointer inside the cell on the bottom-left corner of the cell.
The pointer will change shape to a solid black arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a row of a table:
1. Position the mouse pointer in the left margin in line with the row you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a white arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a column
1. Position the mouse pointer so that it rests on the top border of the table, above the column you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a solid black arrow pointing down.
2. Left-click.
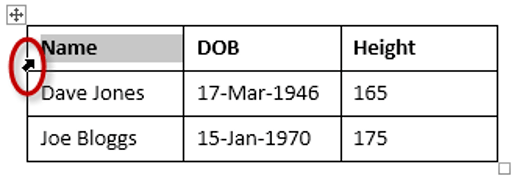
To select the entire table:
1. Position your mouse pointer over the 4-headed arrow icon situated at the top-left of the table.
2. Left-click.
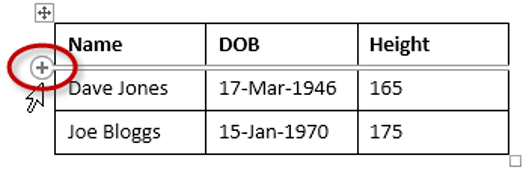
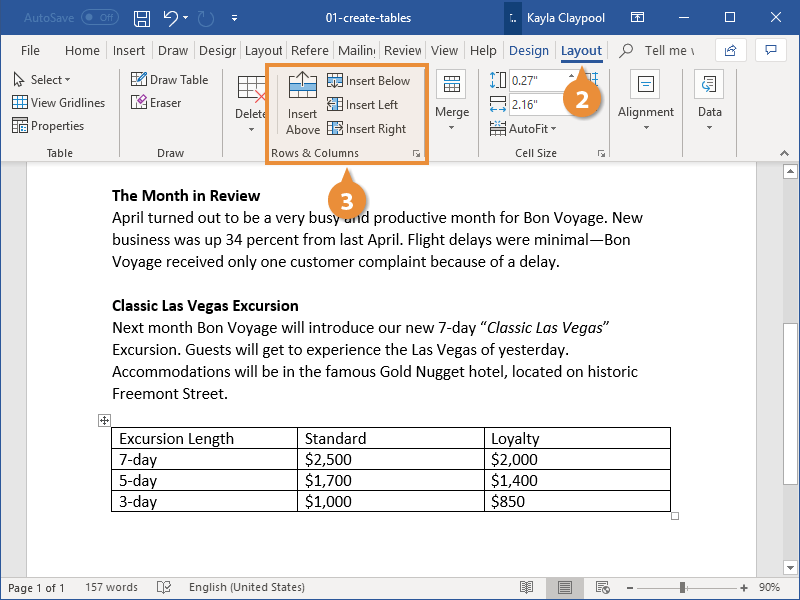
5. INSERTING AN EXTRA ROW OR COLUMN
To insert an extra row:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Above or Insert Below in the Rows and Columns group
Here is a quick way to insert new rows:
1. Position the cursor to the left of the table, but in close proximity.
2. A plus symbol will appear above or below the mouse pointer indicating where the new row will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer up or down to move the plus sign above or below.
4. Left-click to insert the new row,
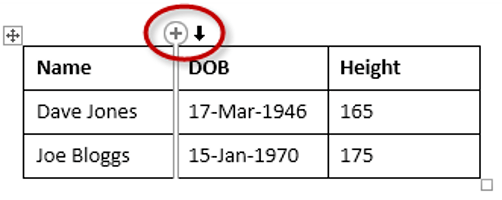
To insert an extra column:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Left or Insert Right in the Rows and Columns group
Here is a quick way to insert a new column:
1. Position the cursor above a column, but in close proximity to the table.
2. A plus symbol will appear to the left or right of the mouse pointer indicating where the new column will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer left or right to move the plus sign to the left or the right of the column.
4. Left-click to insert the new column,
6. DELETING A ROW OR COLUMN
To delete the current row or column:
1. Position the cursor in any cell of the row you want to delete.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Delete icon in the Rows and Columns group.
4. Choose Delete Row or Delete Column from the drop-down menu.
7. Quickly fORMATTING tables in Word
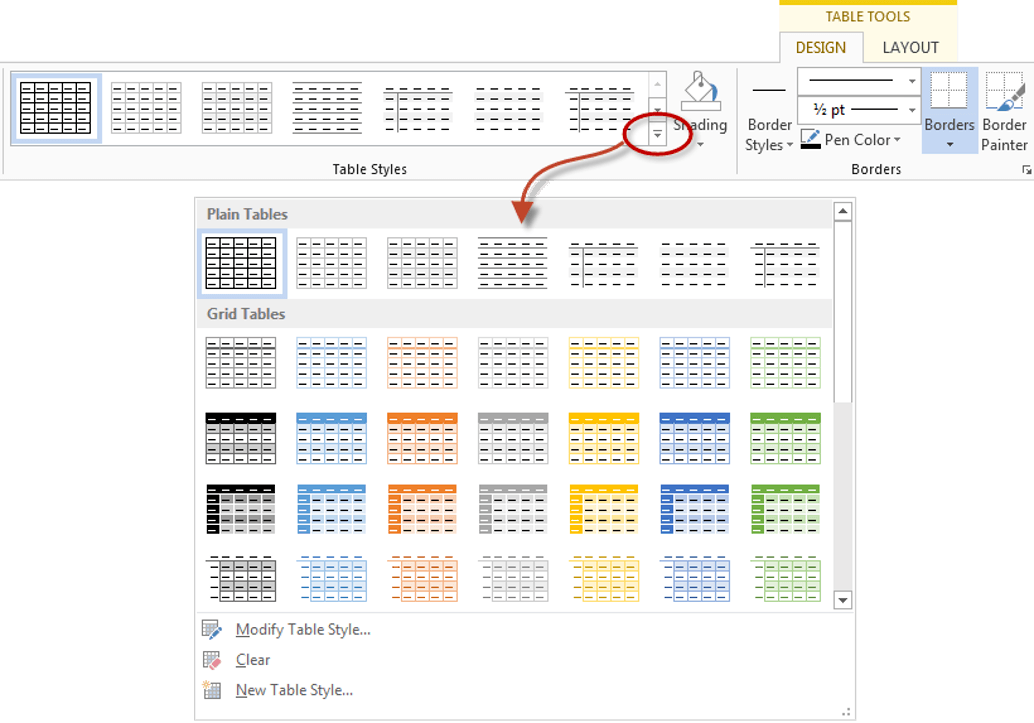
Word provides you with a number of pre-set table designs. This means that it formats the headings and the data, applies a variety of borders and colours the cells in a way that makes it look like a professionally produced table. As a beginner this simple technique will give you a good-looking table.
1. Position the cursor in any cell in the table.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
The Table Styles group lists a number of table designs. To get the full list, click the More button beneath the table styles scroll bar
The default table style is Table Grid in the Plain Tables category which adds simple gridlines but no shading to your table.
Live Preview allows you to hover over a design and see it applied to your table. If you like what you see, click to select the table design.
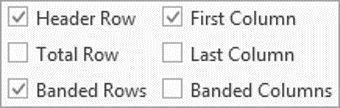
In the Table Style Options group of the Design tab, tick the components that you have in your table. For example, if your table has column headings, tick Header Row. In doing this, the various parts of your table are formatted accordingly
Header Row
This will emphasise the header row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Total Row
This will emphasise the bottom table row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
First Column
This will emphasise the first column (for labels etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Last Column
This will emphasise the last column (for row totals etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Banded Rows
This will make odd rows one colour and even rows a different colour. This helps readability.
Banded Columns
This will make odd columns one colour and even columns a different colour. This helps readability.
8. SETTING THE BORDERS AND SHADING
The Table Styles Gallery allows you to completely format a table with one click. Whereas you used to need some nous, anybody can now create a professional looking design.
However, you will often still need to apply your own border and shading, and manually change a table design. With a little effort can add a lot of flavour to your page and dramatically enhance the overall appearance of the document.
To set the borders for tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to set the borders for. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
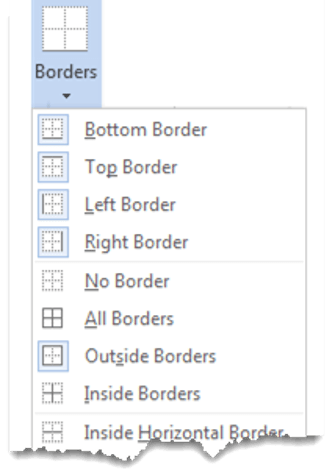
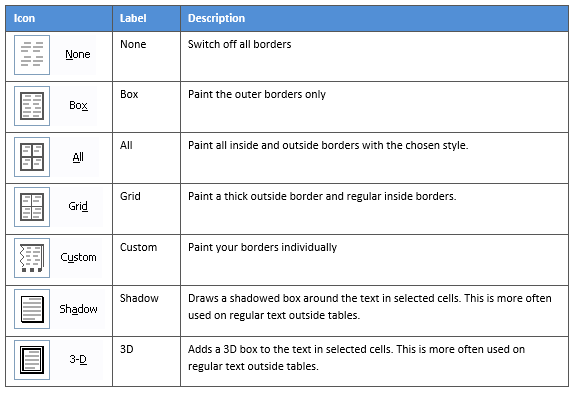
3. Select the Borders icon. A drop-down list appears. This list shows every combination of border that can be turned on or off. The icons with a shaded background are currently switched on. The rest are switched off.
4. Click any icon to switch the border on or off. The border style that is applied is the default style (½ pt solid black line ) or the last style that was used.
5. To apply customised borders, with different colours, styles and widths, click the Borders & Shading option at the bottom of the list to display the Borders and Shading dialog box.
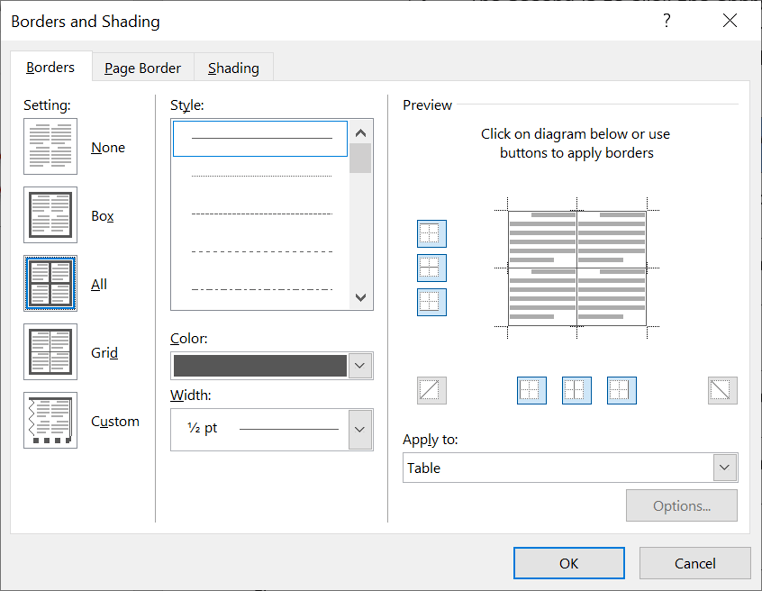
Your selection will always have an outer border, and if you selected more than one cell, you will have some inside borders as well. The easiest way to use the dialog box is to start on the bottom-middle and work your way up and right.
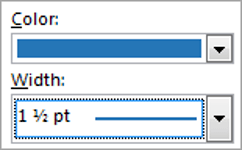
1. Select the colour and width (thickness) that you would like for your border.
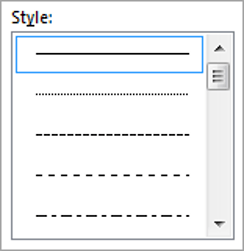
2. Choose a style (e.g. dotted, dashed, double, solid etc.)
3. Paint your borders. There are two ways to do this.
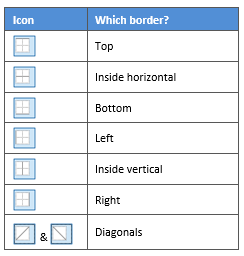
- The first way is to click directly on a border in the Preview itself.
- The second way is to click the appropriate icon around the edge of the Preview section that represents each border. Depending on which cells you selected in your table, some of these icons may not be available.
On the left-hand side of the dialog box, there are some pre-defined border combinations which you can use to save yourself some time. Depending on your selection of cells, the pre-defined options may differ. Here’s a run-down:
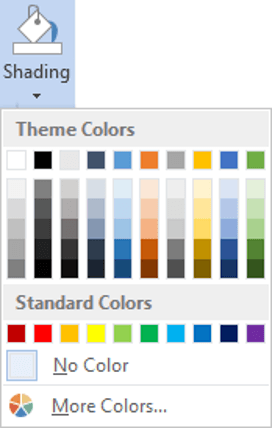
To shade the cells of tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to shade. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Shading icon.
The colours that you see displayed match the current them of the document. Themes were discussed earlier in the course.
4. Click a colour in the palette.
While you can pick any colour, it is recommended to stick with the light colour shades, otherwise your tables will appear very loud and ugly, like they’re shouting in your face. Subtle is the order of the day. The exception to this is column headings or other cells that you wish to differentiate. Under these circumstances, you can use a dark colour, but use a light font with it.
If you cannot find the exact colour you need,
- Click the More Colours link underneath the palette. This displays a larger, more accurate colour palette.
- And if that’s not enough, click the Custom tab and you’ll get a really fine selection of colours (you can even enter your own RGB settings if you know them)
9. REPEATING table HEADINGS ON EVERY PAGE WHEN PRINTING
When you have large tables that occupy two or more pages, many people insert manual page breaks, then copy and paste their table header rows at the top of each page.
When rows are added or removed from tables in Word, the table headers end up half way down the page.
There is a simple tool that will eliminate this problem
1. Ensure that the table is a single table, with no manual page breaks in the middle, and one header at the top. The table header may occupy more than one row, it doesn’t affect the way this feature works.
2. Position the cursor somewhere in the top row of the table.
3. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
4. Click the Repeat Header Rows icon ion the Data group.
Now, it doesn’t matter how many rows tables in Word contain, if the table ever spills across into another page, the header row (which normally displays the column headings) will always appear at the top of the table.
10. All the key points again
- Tables in Word serve 2 distinct purpose: to display a table of data and to organise and position items on the page
- To create table, select 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- There are 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- You can press the TAB key to move direct to the next cell and SHIFT and TAB together to move backwards through a table.
- The four elements of a table are cells, rows, columns and the whole table. Each can be selected.
- Rows can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert Above or Insert Below icons. Alternatively, hover to the left of a row and click the plus symbol that appears above or below the mouse pointer.
- Columns can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert
Left or Insert Right icons. Alternatively, hover above a table column and click the plus symbol that appears to the left or right of the mouse pointer. - Columns and rows and be removed from the table, by positioning the cursor in the row or column to be removed, then clicking the Delete icon on the Layout tab of Table Tools and choosing Delete
Row or Delete Column. - Tables can be formatted using the Table Style gallery or by manually setting the shading and borders manually. Both sets of tools are found on the Design ribbon of the Table Tools.
- When using the Microsoft Table Styles, you can control the behaviour of the formatting by setting the Table Style options – 6 tick boxes that define the structure of your table.
- For long tables that spill across onto subsequent pages, the top row, which normally contains the column headings can be set to repeat automatically. So there is no excuse for cutting and pasting headings midway through your table or taping pages together to make sense of the table!
I hope you found plenty of value in this post. I’d love to hear your biggest takeaway in the comments below together with any questions you may have.
Have a fantastic day.
About the author
Jason Morrell
Jason loves to simplify the hard stuff, cut the fluff and share what actually works. Things that make a difference. Things that slash hours from your daily work tasks. He runs a software training business in Queensland, Australia, lives on the Gold Coast with his wife and 4 kids and often talks about himself in the third person!
SHARE
-
1
Open Microsoft Word. Its icon resembles a blue background with a white «W» on top.
- If you’d rather edit an existing document, simply double-click the document in question.
-
2
Click Blank document. It’s in the top-left corner of the templates page.
- If you’re editing an existing document, skip this step.
Advertisement
-
3
Click the Insert tab. This tab is to the right of the «Home» tab in the top-left corner of the Word window.
-
4
Click Table. It’s the grid icon directly beneath the «Insert» tab.
-
5
Hover the mouse cursor over a square. You should see a drop-down menu with a series of squares below the Table button; hovering the cursor over a square will cause the pertaining table to appear in your document.
- For example, selecting a section four squares down and eight squares right will create a table with eight columns and four rows.
-
6
Click your preferred square. Doing so will create a table with your selected number of rows and columns.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Word. It’s a blue app with a blue «W» written on a white folder icon.
-
2
Tap New. You’ll see this option at the bottom-left side of the screen.
- If Word opens to a document, tap the «Back» button in the top-left corner of the screen first.
- If you’d rather load a pre-existing document, tap Open in the bottom-right corner of the screen and then tap a document’s name to open it.
-
3
Tap Blank Document. It’s in the top-left corner of the page.
- If you’re opening an existing document, skip this step.
-
4
Tap the «…» button. It’s in the middle-right section of the screen in the toolbar above the keyboard.
-
5
Tap Home. You’ll see this option on the left side of the toolbar.
-
6
Tap Insert. It’s below «Home» in the drop-down menu that appears.
-
7
Tap Table. This option is near the top of the options that are listed at the bottom of the page. Tapping it will insert a three-by-three table into your Word document.
-
8
Tap ▼. It’s on the right side of the toolbar. From here, you can format your table in a few different ways:
- Tap a cell to select it for writing.
- Tap the leftmost button in the toolbar to add a column to the left of your cursor.
- Tap the button to the right of the leftmost button to add a row below your cursor.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Word. It’s a blue app with a blue «W» written on a white folder icon.
-
2
Tap Blank document. It’s at the top of the screen.
- You can also tap a document’s name from the left side of the screen to open it.
-
3
Tap Insert. You’ll see this tab at the top of the screen, to the right of the «Home» tab.
-
4
Tap Table. It’s directly below the «File» tab in the top-left corner of the screen. A table will appear in your Word document.
-
5
Tap a cell in the table. Doing so will place a cursor in your selected cell. From here, you can add columns or rows by tapping the Insert button (below the «Insert» tab) and then tapping one of the following options:
- Insert Above — Add a row above the row in which your cursor sits.
- Insert Below — Add a row below the row in which your cursor sits.
- Insert Left — Add a column to the left of the column in which your cursor sits.
- Insert Right — Add a column to the right of the column in which your cursor sits.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What if I created several cells, but later find I don’t need all of them? How can I make some disappear?
Right-click the cell you don’t want anymore. In the pop up menu, select «Delete» and select which cells you want to delete.
-
Question
How do I download Excel?
If you are using Windows 10, use the Microsoft Store. But if you are using Android (easier) download it on the Google Play Store. The website play.google.com has it for laptops and PCs.
-
Question
How do I increase my row line?
Go to Insert-Table on the main menu. This will open up a Table Tab with sub tabs for Design and Layout. Select Layout. Click in a row immediately above or below where you ant to add one or more rows. On the Table Layout menu, click Insert Below or Insert Above once for each row you want to add.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
If you wish to change the cell formatting or the color of the table, select it and click Design at the top of the Word window to view formatting options.
-
You can use your table to create a custom calendar or a weekly schedule.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Open Microsoft Word.
2. Double-click Blank Document.
3. Click Insert.
4. Click Table.
5. Choose a table size/layout (rows x columns).
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 160,140 times.
Is this article up to date?
You need to copy the content of the cell not the cell itself. This takes a bit of practice and is mightily annoying!
If you see the grey, you’ve selected too much. The easiest way is to click in the cell and press ctrl-a then copy. If the paste doesn’t do what you expect, check what you’ve set the default paste to. You can, of course, control the paste type after you paste or you can do a paste special.
UPDATE: Oops! Never noticed that ctrl-a selects everything and I’ve been using Word for decades!
As an alternative. Click at the start of the cell, then shift-end. Then still holding down shift, use the back arrow to go back one. That last part is important as it changes from selecting the cell to selecting the content. I actually tried it this time so hopefully no more embarrassments.
UPDATE 2: Now that we know you want to copy the format and not the content, we can focus on the best way to do that. Which is to create a style and apply the style to all the cells you want to have the same style. You can also assign a keyboard shortcut to a style to make things even easier.
UPDATE 3: Just to be absolutely clear. The format for a paragraph is contained in the (normally hidden) end paragraph mark. It is this that is selected when you do shift-end, turn on visible paragraph marks to see this more clearly. In a table, this changes to a cell marker rather than a paragraph on. To copy the formatting for a paragraph (or cell), you have to include that mark in your selection.
To Turn a formatted cell into a style, show the style panel, select the cell, click on the «New Style» button. The resulting new style dialogue should already be formatted as per the cell. Give this a name and set the shortcut. Save the style to normal.dot if you want it always available otherwise save it to the document. Now in any cell, simply select your style (no need to select the cell) and the cell will be formatted accordingly.
The «extra thought» is a one-off and need never be repeated if you save the style in normal.dot (the default Word template).
Tables are very useful tools when creating and formatting documents. For example, with a table you can:
- Align Text, Numbers, and Graphics: Many people prefer to use tables for alignment instead of tab stops because text can wrap to multiple lines in a table.
- Create a Form: You can use tables to store lists of telephone numbers, clients, and employee rosters.
- Share Information: You can use tables to share information between programs. For example, you can copy and paste a table’s information into a Microsoft Excel worksheet or Access database.
- Create a Publication: Tables make it easier to create calendars, brochures, business cards, and many other publications.
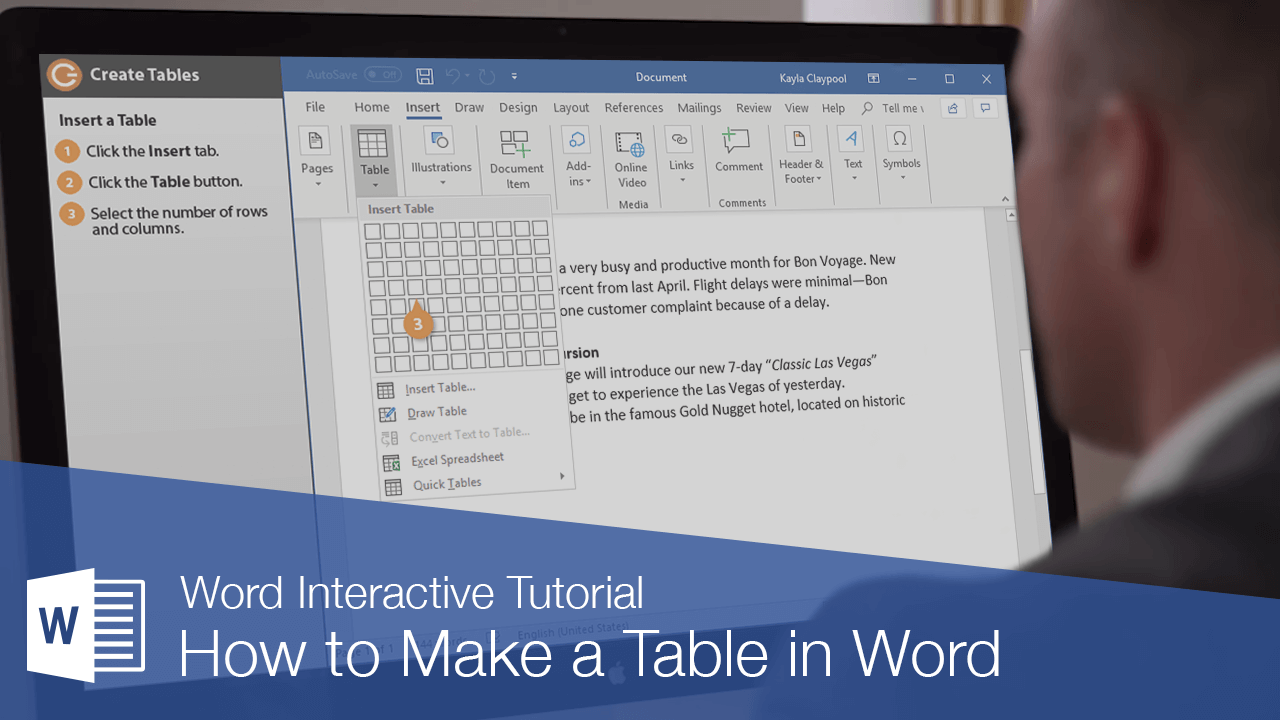
Insert a Table
To create a table, you must first determine how many columns (which run up and down) and rows (which run left to right) you want to appear in your table. Cells are small, rectangular boxes where the rows and columns intersect. The number of columns and rows determines the number of cells in a table.
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click the Table button.
- Use the grid to select how many columns and rows you’d like.
- Enter your content into your newly created table.
The table with the specified number of rows and columns is inserted.
You can use the arrow keys to navigate from cell to cell as you type. You can also press the Tab key to move to the next cell.
Select Cells
You can select a single cell in a table, or you can select multiple cells, entire rows or columns, or the entire table.
Add a Row or Column
You can add more columns and rows to a table after you’ve inserted it. This way, you’re not trapped using a fixed structure if you need to add more data later.
- Select a cell in a row or column adjacent to where you want the new row or column inserted.
- Click the Layout tab in the Table Tools ribbon group.
- Click one of the Insert buttons in the Rows & Columns group.
You can insert a row above or below the selected cell’s row, or a column to the left or right of the selected cell’s column.
Hover your mouse above the line between columns, or to the left of the line between rows, and click the + button that appears to quickly add a new column or row.
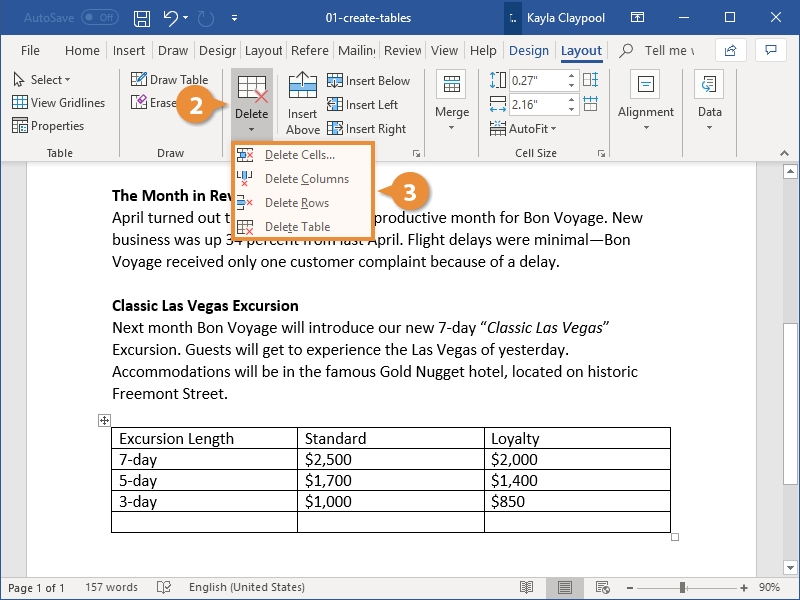
Delete a Row or Column
You can delete rows and columns that you don’t want, in case you made a table that was bigger than you needed.
- Select a cell in a row or column you want to delete.
- Click the Delete button on the Layout tab (in the Table Tools ribbon group).
- Select one of the options.
Here, you have the option to delete the specific cell, the column or row the selected cell is in, or the entire table.
If you decide to delete only the selected cell, you can choose how to move the rest of the cells around to fill the gap. You can shift the rest of the row’s cells to the left or shift the rest of the column’s cells up.
FREE Quick Reference
Click to Download
Free to distribute with our compliments; we hope you will consider our paid training.