Homophone List
We have a full list of English homophones and lots of free homophone worksheets, riddles, jokes & more
- Home
- Homophones Explained
- What Is A Homophone?
- About Our Homophones List
- Homophone Vs Homonym
- Homophone Vs Homograph
- Homophone Vs Homonym Vs Homograph
- Homophone Lists
- Complete A-Z Homophones List
- Homophones Starting With…
- Examples Of Common Homophones
- Worksheets
- Quizzes
- Games
- Sentences
- Riddles
- Jokes
- Contact
The homophone for one is won.
Make sure you check out our complete homophones list.
Homophones Poster
Dear Deer – A Book Of Homophones
How Much Can A Bare Bear Bear?
Two Sets Of Homophone Flashcards
The King Who Rained
Copyright © Stephen Pepper, Homophone List 2013-2023
The English language is hard. Not only does it have many words that look alike, but it also has words that sound exactly alike but have different meanings. This can be very confusing to anyone trying to learn the language.
Words that sound the same but have different definitions are called homophones. They are particularly frustrating to spell if English is not your first language. In fact, many native speakers get them mixed up from time to time as well.
Won and one are perfect examples of a homophone, and below we take a closer look at how they are spelled, what they mean, and how you should use them in writing.
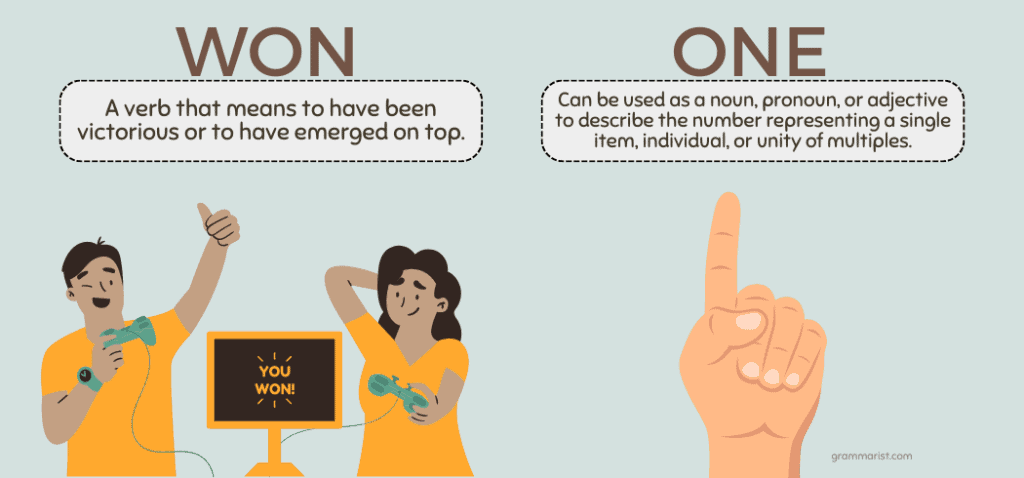
Won vs. One: What’s the Difference?
Won is a verb that means to have been victorious or to have emerged on top. One can be used as a noun, pronoun, or adjective to describe the number representing a single item, individual, or unity of multiples.
Won and one are homophones, or two words that sound exactly the same but have different meanings. Homophones with the same spelling are also called homonyms, but won and one are not homonyms due to their different spellings.
Won Spelling and Use
Won is the past tense and past participle of the verb win, which means to be victorious in a game or contest, to emerge on top, to be the most successful, or to gain someone’s approval or support through persuasion or example.
Win can be used as a noun, but its past tense, won, is always used as a transitive verb – or a verb that takes an object.
For example:
- As the match came to an end, she knew she had won before the referee made it official.
- The soccer team won their district playoff game, advancing them into the state final bracket.
- Although they were surprised to have won the lotto draw, they chose to be humble and donate half their winnings.
Origin of Won
As explained above, won is the past tense and past participle of the word win, a 14th-century combination of the old English winnan, meaning to “work, struggle, or fight for,” and the Proto-Germanic gewinnan, meaning to “gain or succeed by struggling or conquering.”
As a verb, win was used to describe a victorious event. The words won and winning are from the 17th century, meaning to gain the affection or esteem of something.
One Spelling and Use
One is a number that corresponds to a single thing. It is more than zero and less than two and is the lowest cardinal number, or counting numbers that start at one, are not fractions, and continue sequentially (for example, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5…).
For example:
- After my morning, all I need is one more good reason to go home and sleep until tomorrow.
- To get a better grade, add one example to your presentation explaining how you came up with your hypothesis.
- There is only one class to attend tomorrow to finish the training.
One is also used as an unspecified pronoun. One may also mean the same as or identical or to signify two seamlessly joined things.
For example:
- One never knows what the next day will bring.
- A dog and a wolf are technically one and the same species.
Origin of Use
One is from the 13th-century Old English an, meaning the number one. It was originally pronounced as “un,” with the now-standard pronunciation as “wun” not adapted until the 14th century in West England.
Let’s Review
Won and one are homophones, meaning they are pronounced the same despite their different spellings and meanings. Won means to have come out on top or to have been victorious and is the past tense of the word win.
One is the word used to describe a single item, individual, or unity of multiples into one unit.
Омофоны (homophone) – это слова, которые пишутся по-разному, но слышатся одинаково. При этом значения у них тоже разные. Омофоны – излюбленный источник ошибок для русскоязычных пользователей. И без того испытывая трудности в английской грамматике, на омофонах они просто «загибаются». Здесь мы приводим список из 70 самых распространенных омофонов английского языка с транскрипцией и переводом.
Таблица.
| Омофон | Перевод | Омофон | Перевод | Транскрипция |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
air |
воздух |
heir |
наследник |
| eə | |
|
aisle |
проход |
isle |
остров |
| aɪl | |
|
eye |
глаз |
I |
я |
| aɪ | |
|
bare |
голый |
bear |
носить |
| beə | |
|
be |
быть |
bee |
пчела |
| bi: | |
|
brake |
тормоз |
break |
ломать |
| breɪk | |
|
buy |
покупать |
by |
с помощью… |
| baɪ | |
|
cell |
клетка |
sell |
продавать |
| sel | |
|
cent |
цент |
scent |
запах |
| sent | |
|
cereal |
хлопья |
serial |
сериал |
| ‘sɪərɪəl | |
|
coarse |
шероховатый |
course |
блюдо |
| kɔ:s | |
|
complement |
дополнять |
compliment |
комплимент |
| ‘kɒmplɪmənt | |
|
dam |
дамба |
damn |
черт |
| dæm | |
|
dear |
дорогой |
deer |
олень |
| dɪə | |
|
die |
умереть |
dye |
красить |
| daɪ | |
|
fair |
ярмарка |
fare |
тариф |
| feə | |
|
fir |
ель |
fur |
шерсть |
| fɜ: | |
|
flour |
мука |
flower |
цветок |
| ‘flaʊə | |
|
for |
для |
four |
четыре |
| fɔ: | |
|
hair |
волосы |
hare |
заяц |
| heə | |
|
heal |
лечить |
heel |
каблук |
| hi:l | |
|
hear |
слышать |
here |
здесь |
| hɪə | |
|
him |
ему |
hymn |
гимн |
| hɪm | |
|
hole |
дыра |
whole |
целый |
| həʊl | |
|
hour |
час |
our |
наш |
| ‘aʊə | |
|
idle |
ленивый |
idol |
идол |
| ‘aɪdl̩ | |
|
in |
в |
inn |
таверна |
| ɪn | |
|
knight |
рыцарь |
night |
ночь |
| naɪt | |
|
knot |
узел |
not |
не |
| nɒt | |
|
know |
знать |
no |
нет |
| nəʊ | |
|
made |
сделал |
maid |
служанка |
| ‘meɪd | |
|
|
почта |
male |
мужчина |
| meɪl | |
|
meat |
мясо |
meet |
встречать |
| mi:t | |
|
morning |
утро |
mourning |
оплакивание |
| ‘mɔ:nɪŋ | |
|
none |
никто |
nun |
монахиня |
| nʌn | |
|
oar |
весло |
or |
или |
| ɔ: | |
|
one |
один |
won |
выиграл |
| wʌn | |
|
pair |
пара |
pear |
персик |
| peə | |
|
peace |
мир |
piece |
кусок |
| pi:s | |
|
plain |
плоский |
plane |
самолет |
| pleɪn | |
|
poor |
бедный |
pour |
лить |
| pɔ:| |
|
pray |
молить |
prey |
добыча |
| preɪ | |
|
principal |
директор школы |
principle |
принцип |
| ‘prɪnsəpl̩ | |
|
profit |
доход |
prophet |
проповедник |
| ‘prɒfɪt | |
|
real |
реальный |
reel |
катушка |
| ri:l | |
|
right |
правый |
write |
писать |
| ‘raɪt | |
|
root |
корень |
route |
путь |
| ru:t | |
|
sail |
отправиться в плавание |
sale |
распродажа |
| seɪl | |
|
sea |
море |
see |
видеть |
| ‘si: | |
|
seam |
шов |
seem |
казаться |
| si:m | |
|
sight |
вид, зрение |
site |
территория |
| saɪt | |
|
sew |
шить |
so |
так |
| səʊ | |
|
sole |
одинокий |
soul |
душа |
| səʊl | |
|
some |
несколько |
sum |
сумма |
| sʌm | |
|
son |
солнце |
sun |
солнце |
| sʌn | |
|
stair |
лестница |
stare |
глазеть |
| steə | |
|
stationary |
стационарный |
stationery |
канцелярские изделия |
| ‘steɪʃənri | |
|
steal |
украсть |
steel |
сталь |
| sti:l | |
|
suite |
номер повышенной комфортности |
sweet |
сладкий |
| swi:t | |
|
tail |
хвост |
tale |
сказка |
| teɪl | |
|
their |
их |
there |
там |
| ðeə | |
|
to |
к |
too |
тоже |
| tu: | |
|
toe |
большой палец ноги |
tow |
буксировать |
| təʊ | |
|
waist |
талия |
waste |
тратить |
| weɪst | |
|
wait |
ждать |
weight |
вес |
| weɪt | |
|
way |
путь |
weigh |
взвешивать |
| ‘weɪ | |
|
weak |
слабый |
week |
неделя |
| wi:k | |
|
wear |
носить |
where |
где |
| weə | |
Wiki User
∙ 7y ago
Best Answer
Copy
won
won
won
Won is a homophone for one.
Yes.
Won would be a homonym.
Homonym means to sound the same. A homonym for one (a number) is won (the past tense of win).
Wiki User
∙ 7y ago
This answer is:
KUSHARG GARG ∙
Lvl 1
∙ 2mo ago
won
Study guides
More answers
Wiki User
∙ 14y ago
Copy
Won.
This answer is:
Anonymous ∙
Lvl 1
∙ 2y ago
Copy
the desception of «one» is a number.
homophone words sound the same, but mean something different.
so the homophone for one is «won»
because they sound the same. as «one» is a number. but «won» is past tense of «win»
This answer is:
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: What is the homophone for one?
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
Download English Homophones pdf
Would you like a English Homophones Word List pdf download? Here is the full English homphones list of over 100 English homophones. This list includes the most commonly mispronounced English homophones with the International Phonetic Alphabet IPA in a printable .pdf that you can download.
This is the one of the most comprehensive English homphones lists available and it includes the IPA International Phonetic Alphabet for each homophone example. This homophones list includes all the homophones mentioned on this page and is split into sections for short vowels, long vowels, dipthong vowels and longer words.
This English homophones printable list is a great tool for ESL speakers.
You should remember to pay attention to vowels and word stress as you go through the list.
For homophone practice with long vowels (you’ll see /:/ in the IPA), you should check you are making a long vowel and not a short vowel.
For homophones practice that have diphthong vowels, make sure you get two vowels in each diphthong vowel.
And importantly, for the homophones practice for multi-syllable words, pay attention to making good word stress in each homophone pair.
Click the button below to download the English homophones pdf with IPA symbols. This is your full English homophones printable list for revising and improving homophones for clearer spoken English.
Homophones and Your English Speaking Confidence
When people lack confidence with their spoken English it can really hold them back. It’s tiring and exhausting!
Revising areas such as how to pronounce English homophones can really help. The English pronunciation homophones exercises on this page can help people improve their speaking confidence through improved pronunciation skills.
For many ESL students, covering homophones is an eye opener. We say something is an ‘eye-opener’ when it’s surprising. Many of them say to me ‘All these years and I’ve been trying to say those two words differently, and now I know that they are actually pronounced the same way!’
For example, many of my overseas students from non-English speaking backgrounds mispronounce words like ‘pause’ – they use the incorrect vowel sounds. It helps so much when they understand that ‘pause’ is exactly the same as ‘paws’.
It gives people confidence to know that they are pronouncing homophones correctly.
Correcting your pronunciation of homophones with this English homphones list can make your English clearer and build your speaking confidence. You can be confident that you are pronouncing these words clearly and correctly.
Here are answers to questions we’re often asked about English homophones examples:
How to pronounce the word ‘homophone’?
The word ‘homophone’ is pronounced as /ˈhɒ.mə.foʊn/. The word stress is on the first syllable, the vowel in the 2nd syllable is the weak vowel schwa and the last vowel is the diphthong vowel /oʊ/.
Why is English pronunciation and spelling more difficult than other languages?
Spelling and pronunciation is more difficult in English than many other languages because English is not a phonetic language. This means that the way a word is spelled does not tell us exactly how to pronounce it. This makes English pronunciation a challenging area for many learners of English. The spelling and pronunciation are very variable. Words can look very different (eg suite and sweet) and be pronounced the same way! And similarly, words that look similar can be pronounced quite differently, for example, ‘cost’ and ‘post’.
Why are there so many homophones in English?
English has more homophones than many other languages. This is mainly because over many, many year English has borrowed many words from other languages. Another reason is that the pronunciation of English words has changed quite a lot over time, while its spelling has changed very little.
What is the difference between a homophone and a homograph?
Like many ESL speakers, you may have heard of homophones and homographs. Are you wondering what’s the difference between a homophone and a homograph? Here is a clear explanation with some examples.
A homophone is a word that has the same pronunciation as another word but is spelled differently and has a different meaning. For example ‘toe’ and ‘tow’, ‘rows’ and ‘rose’, ‘there’ and ‘their’ and they’re’.
A homograph is a word that has the same spelling as another word but has a different meaning. Homographs may be pronouced the same way or differently.
For example, homographs that are pronounced differently are: the verb ‘to wind’ and the noun ‘the wind’. The ‘i’ letter is pronounced differently in these two words. Homographs that are pronounced the same way are: the verb ‘to contact’ and the noun ‘a contact’. ‘Contact’ is pronounced the same way for both.
Improve your pronunciation of homographs and homophones in sentences and conversations with a full Speech Active Course.
Why is the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) helpful for learning homophones?
The IPA is set of symbols where each symbol represents a speech sound or tells us where the word stress is. The IPA for English has 44 symbols. The dash /ˈ/ indicates that the next syllable is stressed.
The IPA tells us the correct pronunciation of a word so it is very helpful when learning homophones. Look at homophones: crews & cruise – they look very different but if we look at the IPA – /kruːz/ – it tells us that the pronunciation is exactly the same for these homophones.
Here is another example of how the IPA looks for the words ‘moose’ and ‘mousse’. See how this homograph looks in the IPA in the dictionary below.
Do I need to learn all the IPA symbols?
No, I suggest you just learn the IPA symbols for the sounds that you have difficulty with. Try and identify which sounds are difficult for you and learn the IPA symbols for them. Also you remember that the two dots /:/ are a long vowel, when you see two vowel symbols it means it’s a double or diphthong, when you see this dash /’/ it means the next syllable is stressed.
If you want to revise the IPA symbols for all the sounds in English, and also revise the pronunciation of all English vowels and consonants, you can do it here:
English Vowel Sounds with IPA Symbols.
English Consonant Sounds with IPA Symbols.
How can I find out the IPA symbols in words?
The best way to look up the IPA for an English word is using a good online dictionary. So next time you’re looking up how to pronounce a homophone I recommend the Cambridge Online Dictionary, it’s very reliable and easy to use. The IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) in the Cambridge online dictionary is excellent, you can see each IPA symbol and the word stress marked in. You can also click to hear the word pronounced in British and American style English.
Thank you for visiting our homophones practice page. I hope it has helped you correct the English homophones that you use regularly.
Here are some other helpful English Pronunciation resources that might help you:
English Word Stress Exercises: videos, audio and voice recorder exercises to help you improve your word stress and emphasis in English.
Pronounce words like ‘comfortable’ & ‘restaurant’ like a native speaker. Pronouncing words with omitted syllables.
Improve English Schwa Sound.
Improve Consonant Clusters. Speakers of Thai, Vietnamese, Burmese, Cantonese and other south east Asian languages will find this page helpful.
Checklist For Choosing Accent Reduction Training.
Would you like more help with your English Pronunciation? Contact us to find out more about our English Pronunciation Courses. Our training is tailored specifically for speakers of your language background. See more about our course for speakers of your first language here – Speech Active Course List
See our course tour video below.
Keep up the great work on improving your spoken English.
Please contact us at Speech Active to talk more about how we can help you improve : )
Remember, a little bit here and there every day helps.
All the best
Georgie Harding
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What you will learn:
1. What are homophones?
2. 101 English homophones with examples
3. How to learn homophones in English
4. Quiz: Test your understanding of English homophones
What are homophones?
Homophones are two or more words that sound the same (identical pronunciation), but have different meanings. These words are often spelt differently in English too (e.g. pear vs. pair). The term homophone comes from Greek ‘homo-’ (meaning: same) and ‘-phone’ (meaning: sound or voice), so the word literally means: ‘same sound’.
English has more homophones than most languages because its pronunciation has changed a lot over time, while its spelling has changed very little. Many words have been borrowed from other languages through the centuries and this explains why English spelling is so strange (or confusing!). For example: right (Old English: riht) vs. write (Old English: writan) vs. rite (Latin: ritus). In the past, these words would have been pronounced differently, but today they all sound the same in modern English.
In this guide, we will focus on homophones in British English. Most of these are the same in American English too. However, national and regional accents change the way people pronounce words and sometimes this creates different homophones. For example, these words are homophones in American English, but not in British English: hostel/hostile, balm/bomb, caught/cot, halve/have.
Let’s take a look at some homophones!
101 English homophones with examples
In this list of English homophones, you will find simple, intermediate and more advanced level vocabulary. For each pair or set, there are meanings and examples. Some you will know already, but others will certainly be new! Where possible, these homophones have been put into approximate categories to help you organise and learn them.
NUMBER HOMOPHONES
- One, won
One (noun): The number that comes after 0 but before 2.
My son is one year old today.
Won (verb): The past tense of ‘win’.
The football team won two games in a row.
- Two, to, too
Two (noun): The number that comes after 1 and before 3, a pair.
He bought two packets of crisps.
To (preposition): In the direction of a particular location.
I am going to the shop.
Too (adverb): To a higher degree than desired, also.
The girl was too tired to work. I was tired too.
- Four, for
Four (noun): The number that comes after 3 and before 5.
The clock struck four.
For (preposition): If someone receives something, if something is done for a reason.
I bought John some sweets for his birthday (for him to eat).
It is common for native speakers to use numbers in online chat or SMS messages. For example, you can write ‘before’ like ‘b4’ and ‘forget’ as ‘4get’. This is because ‘for’ sounds the same as ‘four’ (4). Another common example is ‘m8’ (mate – friend).
- Eight, ate
Eight (noun): The number that comes after 7 and before 9.
There were only eight days left until Christmas.
Ate (verb): Past tense form of ‘eat’.
We ate dinner together then went home.
FOOD & DRINK HOMOPHONES
- Steak, stake
Steak (noun): Prime cut of meat, usually beef.
My all-time favourite meal is steak and chips.
Stake (noun): A strong wooden post with a sharp point at one end.
Vampires can only be killed with a stake through the heart!
- Bean, been
Bean (noun): Edible seed that grows in pods on leguminous plants.
Baked beans on toast is a traditional British dish!
Been (verb): Past tense form of ‘be’.
Where have you been all night?
- Pear, pair
Pear (noun): Common type of fruit.
Would you like a pear from the garden?
Pair (noun): A set of two things (often used together).
He couldn’t find a matching pair of socks.
- Bread, bred
Bread (noun): Type of food.
Our local bakery sells the best wholemeal bread for miles!
Bred (verb): Past tense form of ‘breed’ – to raise or develop animal stock.
In the past, many farmers bred rabbits for meat and fur.
- Cereal, serial
Cereal (noun): Grain used for food (e.g. wheat), type of dried breakfast eaten with milk.
My favourite cereal is cornflakes.
Serial (noun/adjective): A story or programme delivered in instalments, taking place in series.
The serial killer loved watching serials on TV!
- Flour, flower
Flour (noun): Ingredient used to make bread and cakes.
This recipe uses two cups of flour and 1/4 cup of sugar.
Flower (noun): Seed-bearing part of a plant.
Her husband gave her a nice bunch of flowers on her birthday.
- Meat, meet
Meat (noun): Food from the flesh of an animal.
The hotel guests got food poisoning because the meat wasn’t cooked properly.
Meet (verb): Arrange or happen to cross paths with somebody.
I’m going to meet my friend at the train station this evening.
- Chilli, chilly
Chilli (noun): Small spicy pepper or pod used in cooking.
I ordered the Mexican Hot Pizza, but couldn’t eat the chilli on top!
Chilly (adjective): A bit cold, not warm.
Don’t forget your coat! It’s a bit chilly out today.
- Mussel, muscle
Mussel (noun): Mollusc with purple-brown shell.
I had the mussels as a starter and they were delicious!
Muscle (noun): Type of human body tissue.
What do you prefer in a boyfriend – brains or muscles?!
- Wine, whine
Wine (noun): Alcoholic drink made from fermented grapes.
Chilled white wine goes well with fish.
Whine (noun/verb): Long high-pitched cry, complain.
The little dog shivered by the door and let out a whine.
- Bite, byte
Bite (noun/verb): Tear something apart with teeth.
Let’s grab a bite to eat in town after work!
Byte (noun): Unit of measurement of digital information.
How many bytes are there in each character in MS Word?
- Grate, great
Grate (verb): Shred into small pieces using a food grater.
The recipe says we need to grate the cheese into the sauce.
Great (adjective): Large, prominent, very good.
The Great White Shark is a great hunter!
- Berry, bury
Berry (noun): Small pulpy fruit.
Did you know that watermelons are a type of large berry?
Bury (verb): Put or hide underground.
You shouldn’t bury your head in the sand each time there’s an argument.
- Currant, current
Currant (noun): Type of berry, also of dried berry variety.
We have lots of currant bushes at the bottom of our garden – both red- and blackcurrants.
Current (noun/adjective): Strong flow of water, present or up-to-date.
Surfers should be aware of the strong currents along the south coast of England.
Even native speakers get confused by the way words are pronounced vs. written! Here are some examples of commonly confused homophones: compliment/complement, practice/practise, principle/principal, lightning/lightening, insight/incite, miner/minor.
- Leek, leak
Leek (noun): Long white and green stick-like vegetable in the onion family.
Wales is famous for its rainy weather and its giant leeks!
Leak (noun/verb): Hole through which fluid can escape accidentally, drip out.
Our roof has got a leak so we need to fix it before winter comes.
- Maize, maze
Maize (noun): Corn.
It is common for manufacturers to use maize as an ingredient in many processed foods.
Maze (noun): Labyrinth.
Chatsworth House has a maze that is made up of a network of paths and hedges.
- Thyme, time
Thyme (noun): Type of aromatic herb.
What goes best with roast chicken – thyme or rosemary?
Time (noun): Period, measure of seconds/minutes/hours/days/etc.
How much time does it take to cook a roast chicken?
- Sauce, source
Sauce (noun): Liquid used to add flavour to food.
This Chinese cooking sauce uses a variety of citrus fruits.
Source (noun): Origin, cause of something.
Citrus fruits are a good source of vitamin C.
- Sweet, suite
Sweet (noun/adjective): Candy, food with a sugary taste.
If you eat up all your vegetables, I’ll let you have one more sweet!
Suite (noun): Set of rooms or technical instruments.
The journalist interviewed the rock star in his London hotel suite.
- Mousse, moose
Mousse (noun): Light and fluffy dessert.
The French restaurant opposite our office sells the best chocolate mousse in town!
Moose (noun): Large animal in the deer family.
Do people eat moose in Canada? They certainly have a lot of them!
ANIMAL HOMOPHONES
- Hare, hair
Hare (noun): Animal that looks like a large rabbit.
The hare hopped through the woodland.
Hair (noun): Growing from the skin of humans and other animals.
Her hair was so long that she had to wear a large hat to work!
- Bear, bare
Bear (noun): Type of large hairy animal.
Our local pub is called The Brown Bear.
Bare (adjective): Naked, without clothes/covering, plain.
If you walk around with bare feet you might cut yourself!
NOTE: The word ‘bear’ is also a verb that literally means ‘to carry a load’. This is not often used in modern English, although you will find it in expressions like ‘I’ll bear that in mind’ (remember) or ‘I can’t bear it!’ (tolerate, put up with).
- Deer, dear
Deer (noun): Large animal with antlers, similar to a small elk or moose.
Some UK farmers keep deer and breed them for their meat (venison).
Dear (noun/adjective): Beloved person, expensive.
The wedding ring you’ve chosen is a bit too dear, my Dear!
- Gorilla, guerrilla
Gorilla (noun): Large ground-dwelling ape.
African gorillas live in mountainous forests in the west of the country.
Guerrilla (adjective/noun): Unauthorised and irregular (military) action, partisan fighter.
The Colombian guerrillas lived in the jungle and sometimes attacked government troops.
- Sole, soul
Sole (noun): Variety of marine flatfish.
I really love grilled sole with a touch of lemon!
Soul: Spirit, immortal part of a human.
For my philosophy course, I have to write an essay about the human soul.
NOTE: The word ‘sole’ is also a noun that refers to the underside of a person’s foot or shoe, and the word ‘soul’ can be used as an adjective to describe the musical genre.
- Flea, flee
Flea (noun): Small jumping parasitic insect that often lives on dogs or cats.
I caught a flea on our cat today so we’ll need to wash him with special shampoo.
Flee (verb): Run away or escape from danger.
After 3 months of bombing, the family decided to flee the conflict in their war-torn city.
- Boar, bore
Boar (noun): Wild pig.
We saw a boar and a tiger when we visited the local zoo.
Bore (verb/noun): Make someone bored or disinterested, a boring person.
John‘s such a bore! All the guy talks about is golf and work!
NOTE: In technical contexts, the word ‘bore’ can also mean ‘make a hole using a tool’. Therefore, ‘borehole’ would be an engineering word for a drill hole, and not a hole made by a wild pig!
- Horse, hoarse
Horse (noun): Four-legged animal often used for riding or work.
When my grandfather was young, he went to school on a horse and cart.
Hoarse (adjective): Describes a rough or husky voice due to a sore throat.
I was feeling hoarse before the concert, but managed to sing when I got up on stage.
- Lynx, links
Lynx (noun): Type of medium-sized wild cat.
In American Indian mythology the lynx is considered a ‘keeper of secrets’.
Links (noun): Plural form of ‘link’, connections or points of contact.
Our company has links to suppliers all over the world.
- Whale, wail
Whale (noun): Largest (marine) mammal on Earth.
Thanks to the work of conservationists, most species of whale are now protected.
Wail (noun/verb): High-pitched cry of pain, anger or sadness.
I heard a patient wail in agony from the neighbouring (hospital) ward.
- Mare, mayor
Mare (noun): Adult female horse.
Children often came from the village to feed apples to the old mare.
Mayor (noun): Elected leader of regional government.
The mayor cut the ribbon at the museum opening ceremony.
- Toad, towed, toed
Toad (noun): Type of large brown frog.
There’s a toad living in our garden pond and my daughter has named it ‘Freddy’!
Towed (verb): Past tense of ‘tow’, when one vehicle pulls another.
When our car broke down, a neighbour kindly towed it home for us.
Toed (adjective): Having toes.
The three-toed sloth lives in the jungles of Borneo.
PRONOUN HOMOPHONES (+ contractions & determiners)
- I, eye
I (pronoun): Used by a speaker to refer to himself/herself.
I did not enjoy the film.
Eye (noun): The pair of organs that allow us to see.
He is blind in one eye.
- I’ll, isle, aisle
I’ll (contraction): Short form of ‘I will’.
I’ll get to school on time if there is no traffic today.
Isle (noun): A small island.
We go on holiday every year to the Isle of Wight.
Aisle (noun): Passage between two rows of seats.
Passengers must not leave their bags in the aisle at any time.
NOTE: While ‘isle’ and ‘aisle’ are always homophones in British English, the contracted form ‘I’ll’ is pronounced differently in many regional accents (isle vs. aal). The same is true for similar contractions like ‘you’ll’ (yule vs. yorl) and ‘we’ll’ (wheel vs. wirl).
- You, ewe, yew
You (pronoun): Used to refer to the person or people being addressed.
Would you like to come round for dinner sometime next week?
Ewe (noun): Female sheep.
The little lamb followed its mother as the ewe crossed the field.
Yew (noun): Type of evergreen tree.
Traditional English longbows were often made from yew (wood).
- You’ll, Yule
You’ll (contraction): Short form of ‘you will’.
I think you’ll improve your piano playing with practice.
Yule (noun): Old word for Christmas.
The word ‘Yule’ is still used in old Christmas songs and religious hymns.
- You’re, your
You’re (contraction): Short form of ‘you are’.
You’re my best friend.
Your (determiner): Belonging to the person the speaker is addressing.
Hi, I’m Jack! What’s your name?
- Our, hour
Our (determiner): Belonging to the speaker and one or more other person.
We both got our hair cut at the same place!
Hour (noun): Period of 60 minutes.
The queue for the roller coaster was over an hour so we didn’t go on it.
NOTE: In many regional accents of British English, ‘our’ and ‘are’ will be homophones. For example, in the sentence ‘Our (ar) friends are (ar) coming to stay’ the words ‘our’ and ‘are’ can be pronounced in exactly the same way.
- They’re, their, there
They’re (contraction): Short form of ‘they are’.
My brother and his girlfriend got engaged because they’re really in love.
Their (determiner): Belonging to a person or thing being mentioned.
Parents are often keen to help their children with their homework.
There (adverb): In, at, or to a given place.
I threw the ball and now it’s over there.
- Theirs, there’s
Theirs (pronoun): Refers to something that belongs to two or more people.
I think that white football is theirs.
There’s (contraction): Short form of ‘there is’.
There’s a good film on at the cinema tonight. Fancy it?
- We’ve, weave
We’ve (contraction): Short form of ‘we have’.
We’ve been digging all day and we haven’t found any treasure!
Weave (verb): Make fabric/baskets by crossing threads over and under.
My grandmother taught me how to weave cloth and make my own clothes.
- We’d, weed
We’d (contraction): Short form of ‘we would/had’.
If we’d got the bus, then we’d be home by now!
Weed (noun): A wild plant that is not wanted.
The gardener pulled up all the weeds in the flowerbed.
- We’ll, wheel
We’ll (contraction): Short form of ‘we will’.
We’ll have to run; otherwise we’ll miss the bus!
Wheel (noun): A circular object used to move things over the ground.
The back wheel of my bike is bent and needs to be replaced.
- We’re, weir
We’re (contraction): Short form of ‘we are’.
When do you think we’re going to get our exam results?
Weir (noun): Low barrier to control the flow of water in a river.
I saw some boys fishing down by the weir.
- Him, hymn
Him (pronoun): Refers to a male object in a sentence.
His face looks familiar, but I don’t really know him.
Hymn (noun): Religious song to praise God.
The church congregation stood up to sing a hymn.
- He’ll, heel, heal
He’ll (contraction): Short for ‘he will’.
He’ll win the tennis match if he scores the next point.
Heel (noun): Back part of a foot or shoe below the ankle.
He stood on a nail and cut his heel.
Heal (verb): (Cause to) become healthy again.
The cut on your foot will heal by itself, but you must keep it clean.
- He’d, heed
He’d (contraction): Short for ‘he would/had’.
He’d better not be late or I’ll kill him!
Heed (verb): Pay attention to.
He should have heeded the warnings. Now he’s in trouble!
- It’s, its
It’s (contraction): Short form of ‘it is’.
It’s not my fault. It’s yours!
Its (possessive determiner): Belonging to a thing being mentioned.
Lay the baby on its side if it starts crying.
In English you can say ‘it’ about a small baby without being impolite. Native speakers often do this if they do not know the gender of the child. In most other languages grammatical gender dictates that separate words must be used for male vs. female babies.
- Who’s, whose
Who’s (contraction): Short form of ‘who is’.
Who’s coming to your birthday party tomorrow?
Whose (pronoun): Belonging to or associated with which person.
Let’s get on with the game! Whose turn is it to roll the dice?
- What’s, watts
What’s (contraction): Short form of ‘what is’.
What’s the capital of France?
Watts (noun): Unit of power in electrical items (plural form).
How many watts are in an amp?
- Which, witch
Which (pronoun/determiner): Used when asking for information about people or things.
Which of these shirts do you like best?
Witch (noun): Woman with magic powers, usually evil ones.
I’m dressing up as a witch for Halloween this year.
COLOUR HOMOPHONES
- Blue, blew
Blue (adjective): Colour between green and violet (e.g. like the sky).
Elvis was a fan of blue suede shoes!
Blew (verb): Past tense form of ‘blow’.
The storm blew down several trees on our street!
- Red, read
Red (adjective): Colour at the end of the spectrum (e.g. like blood).
Little Red Riding Hood is a popular children’s fairytale.
Read (verb): Past tense form of ‘read’.
How many Harry Potter books have you read?
- Greys, graze
Greys (noun): Two or more shades of the colour grey.
I really like how the artist has used the greys in this painting.
Graze (verb): Eat grass in a field (of cows, sheep, etc.).
Early each morning, the farmer took his cattle out to graze.
FAMILY HOMOPHONES
- Son, sun
Son (noun): A boy or man in relation to his parents.
My son is only eight years old, but he thinks he is 18!
Sun (noun): Star round which the Earth orbits, light/warmth from this star.
The sun rises in the morning and sets in the evening.
- Aunt, aren’t
Aunt (noun): The sister of someone’s father or mother.
My mum’s sister is my aunt.
Aren’t (contraction): Short form of ‘are not’.
We aren’t going on holiday this year.
NOTE: In American English and many UK regional accents, the words ‘aunt’ and ‘ant’ are homophones. In Britain, ‘ant’ (aunt) would be the usual pronunciation in the north of the country.
- Father, farther
Father (noun): Dad.
My father used to play rugby for England.
Farther (adverb): Comparative form of ‘far’.
How much farther do we have to walk?
NATURE HOMOPHONES
- Root, route
Root (noun): Underground part of a plant or tree, source or origin.
A weed may grow again if you don’t remove the root.
Route (noun): Way, course or path.
Our route took us through the Alps and then on to Italy.
- Wood, would
Wood (noun): Small forest, material from trees.
There used to be badgers in the wood, but they are gone now.
Would (verb): Past tense form of ‘will’, expresses conditional.
Where would you like to spend the summer holidays?
- Sea, see
Sea (noun): Expanse of salt water that covers most of our planet.
Julie’s hometown is by the sea.
See (verb): Action of perceiving with the eyes.
If you climb to the top of that hill, you can see for miles!
- Tide, tied
Tide (noun): Alternate rising and falling of the sea.
When it’s low tide you have to walk a long way before you can swim.
Tied (verb): Past tense form of ‘tie’.
She tied the hook to the end of the fishing line.
- Shore, sure
Shore (noun): The land along the edge of the sea or a body of water.
We walked along the shore and found some pretty shells.
Sure (adjective): Confident that one is right.
I’m sure that I locked the door.
- Weather, whether
Weather (noun): Relates to sunshine, rain, wind etc.
The weather in April is usually showery.
Whether (conjunction): Expressing a doubt or choice between alternatives.
I don’t know whether to go to work or call in sick.
Whether the weather is cold
or whether the weather is hot,
we’ll weather the weather,
whatever the weather,
whether we like it or not.
- Mist, missed
Mist (noun): Light fog.
The morning mist covered the fields.
Missed (verb): Past tense form of ‘miss’.
We missed the train so had to get to London by coach.
- Dew, due
Dew (noun): Tiny drops of water that form on cool surfaces at night.
The grass was wet with dew.
Due (adjective): Expected at a certain time.
My sister’s baby is due in 3 weeks!
- Reed, read
Reed (noun): A tall plant which grows in water or marshy ground.
There were reeds growing along the side of the canal.
Read (verb): Look at and comprehend the meaning of words.
She loved books so much that she would read them all day long.
- Air, heir
Air (noun): Mix of gases that we breathe.
The air was moist after the storm.
Heir (noun): A person entitled to the property or rank of another after death.
He was the King’s only son, and so was heir to the throne.
- Night, knight
Night (noun): The period from sunset to sunrise.
The stars come out at night.
Knight (noun): An old term for a mounted soldier in armour.
He was my knight in shining armour.
VERB HOMOPHONES
- Sew, sow, so
Sew (verb): Join or repair with needle and thread.
There’s a hole in my sock, but I don’t know how to sew.
Sow (verb): Plant by scattering seeds on the ground.
Each year the local farmers sow wheat in their fields.
So (adverb/conjunction): To the same or greater extent, therefore, in order that.
I’d never seen so many people in the shop, so I decided to come back later.
- Pause, paws, pours, pores
Pause (verb): Interrupt an action briefly.
I think we should pause the meeting for a short break at 12.00.
Paws (noun): Plural form of ‘paw’, animal foot with pads and claws.
The cat got its paws trapped under the carpet.
Pours (verb): 3rd person form of ‘pour’, flow quickly in a steady stream.
If John pours the tea, then you can offer our guests a biscuit.
Pores (noun): Plural form of ‘pore’, tiny holes in the skin.
When you do physical exercise, sweat comes out through the pores in your skin.
- Wrap, rap
Wrap (verb): Cover in paper or soft material.
My mum likes to use colourful paper to wrap the Xmas presents.
Rap (noun/verb): Hip-hop music, singing style involving quick rhymes.
When I was in my teens I used to love rap, but now I’m more into rock.
- Wear, where, ware
Wear (verb/noun): Have clothing on one’s body, damage over time through use/friction.
Where (adverb): In, to, or in which place or situation.
I have no idea where the nearest petrol station is.
Ware (noun): Manufactured items of a certain type.
John Lewis is a good department store if you want to buy kitchenware.
- Steal, steel
Steal (verb): Take (illegally) without permission.
If you steal goods from a shop, this is called ‘shoplifting’.
Steel (noun): Common type of metal use in construction.
The new art museum is made entirely from glass and steel.
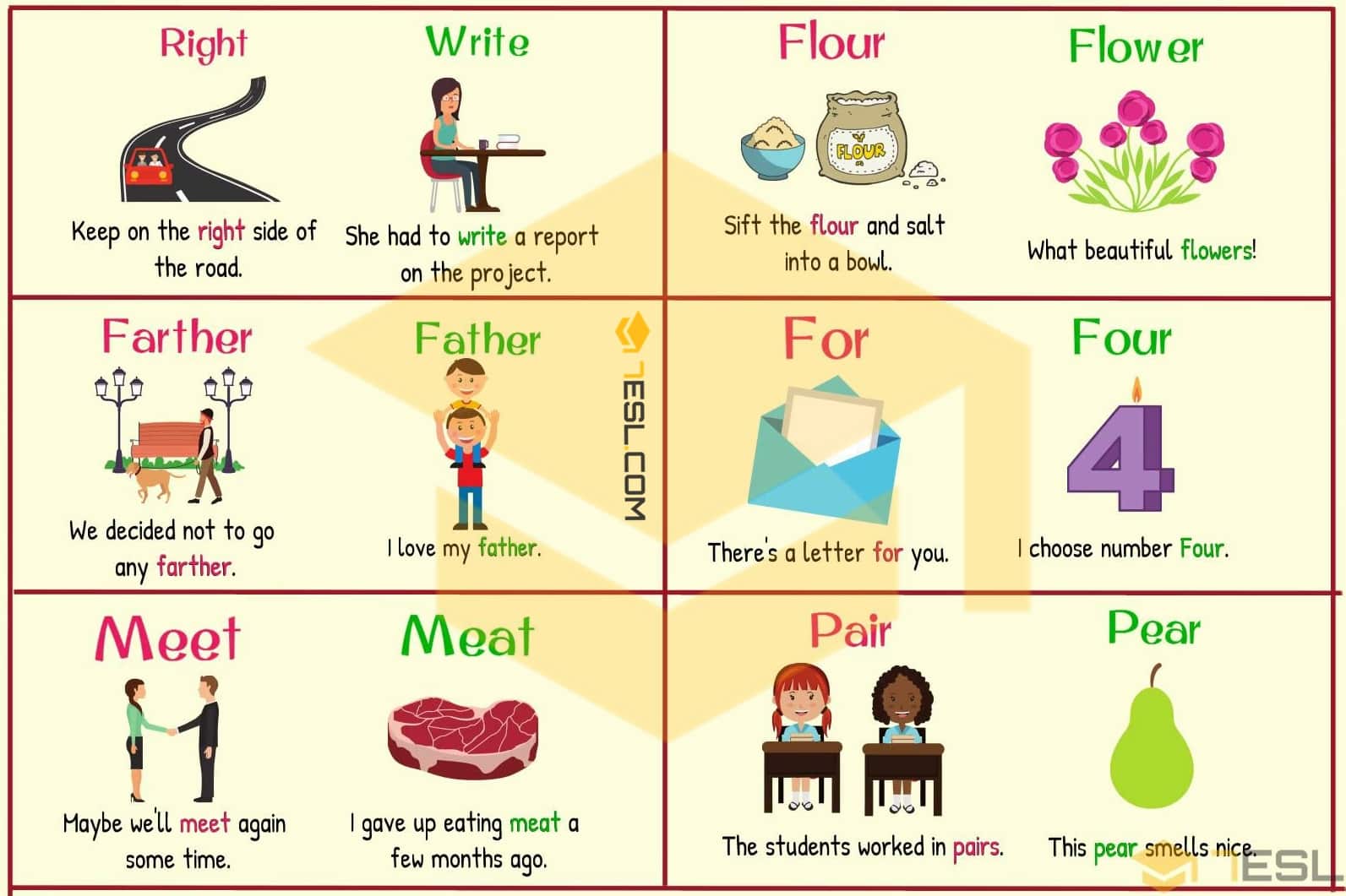
- Write, right, rite
Write (verb): Mark letters, words or symbols on paper with a pen or pencil.
Please remember to write to Santa Claus before Xmas!
Right (adjective): Correct, just, opposite of left.
I answered all the test questions, but only got half right.
Rite (noun): Ritual.
In many cultures, older boys must complete a rite of passage to become ‘men’.
- Buy, by, bye
Buy (verb): Get something in exchange for payment.
I am going to buy some food from the Supermarket.
By (preposition): Identifying who performed an action, near to, using.
My homework gets checked by my teacher.
Bye (exclamation): Informal way of saying ‘goodbye’.
“Bye mum! I’ll see you when I get home from school.”
- Sell, cell
Sell (verb): Give or hand over something for money.
I want to sell my car and buy a new one.
Cell (noun): Small room for a prisoner.
The police kept the thief in a cell overnight.
- Hear, here
Hear (verb): Perceive sound with the ears.
I could hear people laughing in the next room.
Here (adverb): In, at, or to this place or position.
We’ve lived here for most of our lives.
- Break, brake
Break (verb): Smash or separate into pieces.
Be careful not to break a window with that football!
Brake (noun): A device used to slow down a moving vehicle.
When you want to slow the car down, remember to use the brake.
- Affect, effect
Affect (verb): Influence, cause to change.
The Brexit vote will certainly affect the UK economy.
Effect (noun): A change which is a result of an action or other cause.
No one knows what the effects of this political decision will be.
- Die, dye
Die (verb): Stop living.
When sailors die they are sometimes ‘buried’ at sea.
Dye (verb/noun): To colour something, substance that adds colour.
My sister would like to dye her hair pink, but I think green would look better!
- Waste, waist
Waste (verb/noun): Use or expend carelessly, rubbish or unwanted material.
Let’s go. I don’t want to waste any more time!
Waist (noun): Part of the body or measurement around the hips.
I need a pair of jeans with a 36-inch waist.
- Know, no
Know (verb): Be aware of.
Most men know how to boil an egg, but some don’t!
No (exclamation and determiner): A negative response, not any.
No, I don’t want to mow the lawn today.
- Accept, except
Accept (verb): Agree to receive or undertake something.
I said the dog had eaten my homework, but the teacher didn’t accept my excuse!
Except (preposition): Not including, other than.
I invited everyone to my birthday party except Jamie.
- Wait, weight
Wait (verb): Stay where you are until a particular time or event.
I didn’t want to wait any longer, so I left the cafe.
Weight (noun): The heaviness of a person or thing.
My wife often worries about her weight, but she’s actually quite slim!
- Weigh, way, whey
Weigh (verb): Use scales to determine the weight of something.
Match officials have to weigh each boxer before a professional fight.
Way (noun): Method of doing something, road or route.
We got lost and I had to admit that I didn’t know the way home.
Whey (noun): Watery component of milk after the formation of curds.
Whey is produced as part of the cheese-making process.
- Flew, flu, flue
Flew (verb): Past tense form of ‘fly’.
The beautiful eagle flew high above the trees.
Flu (noun): Influenza.
Many people suffer from flu during autumn and winter.
Flue (noun): Duct or pipe for smoke.
When we got a wood-burning stove, we had a flue and liner installed in the chimney.
A flea and a fly flew up in a flue.
Said the flea, “Let us fly!”
Said the fly, “Let us flee!”
So they flew through a flaw in the flue.
- Threw, through
Threw (verb): Past tense form of ‘throw’.
He threw his dirty clothes into the laundry basket and put on a clean t-shirt.
Through (preposition): Moving in one side and out of the other.
He walked through the door and went straight upstairs.
ADJECTIVE & ADVERB HOMOPHONES
- Male, mail
Male (adjective): A man.
The survey was conducted with equal numbers of male and female participants.
Mail (noun): Letters and parcels sent by post.
The postman put the mail through the letterbox.
- Vain, vein, vane
Vain (adjective): Inflated sense of self or appearance, producing no result.
I think a lot of fashion models are vain.
Vein (noun): Type of blood vessel.
The patient needed an injection, but the trainee nurse couldn’t find a vein.
Vane (noun): Weathervane, broad blade attached to rotating wheel/axis.
The weathervane moved from side to side in the wind.
- Weak, week
Weak (adjective): Opposite of strong.
I like my tea weak, with milk and one sugar.
Week (noun): 7 days.
I can meet tomorrow, but I’m around all next week.
- Whole, hole
Whole (adjective): Full, entire.
I can’t eat a whole pizza to myself. Would you like to share?
Hole (noun): Gap or space in the ground or a surface.
There’s a hole in my pocket. That’s how I lost my key!
- Bored, board
Bored (adjective): Lacking interest or engagement.
The girl looked bored and half-asleep in class.
Board (noun/verb): Long and flat piece of wood, get onto transport (plane, ship, etc.).
The window was broken and a board had been nailed across it.
- Coarse, course
Coarse (adjective): Rough, rude.
The surface of the stone was coarse and scratched his fingers.
Course (noun): Study programme.
A friend of mine is doing an online English course.
- Higher, hire
Higher (adjective): Comparative form of ‘high’.
Our company sales figures are higher this year.
Hire (verb): Rent, borrow for money.
There’s no need to take bicycles because we can hire them at the park.
- Plain, plane
Plain (adjective/noun): Simple, without flavour, large flat area of land with few trees.
I usually have plain yoghurt and muesli for breakfast.
Plane (noun): Aeroplane.
Our plane landed at 2 o’clock sharp.
- Aloud, allowed
Aloud (adverb): Not silently.
He read the letter aloud so that everyone could hear.
Allowed (verb): Past tense form of ‘allow’.
The museum staff allowed us to take several photographs.
- Principal, principle
Principal (adjective): Main, number one.
The government’s principal concern is immigration.
Principle (noun): Fundamental truth or proposition.
You can trust Rob. He’s a man of principle.
How to learn homophones in English
There is no secret formula when it comes to learning homophones. Try several different approaches and see what works best for you! To get you started, check out the 5 study tips below:
1) Always learn homophones in context
This is basically a fancy way of saying “in a real sentence or situation”. Context helps us understand the intended meaning behind the usage of a word. This becomes even more important when learning homophones because words like pause/paws/pours/pores all have identical pronunciation! You can only work out which meaning is intended by looking at the context.
2) Have a laugh with English homophones!
Many English jokes use homophones to confuse the listener and create puns. You have already seen several jokes in this study guide, but you can find more on Homophonelist.com. At higher levels, exploring English humour can be a really good way of developing your understanding of vocabulary and culture.
3) Use mobile apps anytime, anywhere
The best way to learn vocabulary is to repeat it regularly. Mobile apps offer a quick solution for learning homophones on the move! You can download apps like Homophones Free or go online to play the BBC’s homophone game.
4) Write nonsense sentences with homophones
Another good way to learn homophones is to practise them in your writing. Take a set of homophones and write one sentence that includes ALL of them. It does not matter if the sentence is nonsense! The main aim of the exercise is to compare the different meanings of the homophones. For example: I said “bye” to my friend and went to buy a coat in a shop by the river.
5) Play spelling games with homophones
Native speakers often make spelling mistakes because of homophones! This shows the importance of learning the correct meanings AND spellings of words that have the same pronunciation. Try this game: Make flashcards with x1 homophone on each side and the translation in your language in brackets. Ask a friend to choose random cards and read out the homophones and/or translations. Try to write down the correct spelling of the word, and then check to see if you are right!
Quiz: Test your understanding of English homophones
Now that you have been through the homophone list, it is time to test your knowledge! Try each of the exercises in this quiz and then check your answers at the end.
EXERCISE A
Put the follow homophones into the sentences: pause, paws, pours, pores.
- Whenever it rains, the water _____ off the roof into the drain.
- If you feel nervous during the presentation, then just _____ for a moment.
- A facial scrub helps clean the _____ and prevent spots.
- Could you please keep your dirty _____ off the biscuits!
EXERCISE B
Write down the correct homophone for each of the jokes.
Q: Why was the mortgage sad?
A: Because it was a loan!
Q: Why will you never starve to death in a desert?
A: Because of all the sandwiches there!
Q: Why does a milking stool only have three legs?
A: Because the cow’s got the udder!
EXERCISE C
Choose the correct homophone in each of the following sentences.
- Our company’s guiding principal/principle is trust.
- Its/it’s forecast to rain all next week.
- If you’re going swimming in the sea, be careful of the current/currant!
- I’ve decided to except/accept the new job at Google.
EXERCISE D
Find the errors in the following text and correct the spelling of the homophones.
I went to sea the doctor on Thursday because I thought I’d caught flue. When I arrived, I wasn’t shore wear the waiting room was sow I asked at reception. They told me witch doctor to see and ware to go. Their were few patients sew I went straight in. The doctor took a pencil to rite down my symptoms. He said I didn’t have flew, but that stress could be the sauce of my headaches. He gave me some aspirin, which soon took affect. I was pleased that my visit had not been in vein.
Answers:
A = pours, pause, pores, paws
B = alone, sand which is there, other (regional pronunciation)
C = principle, it’s, current, accept
D = see, flu, sure, where, so, which, where, there, so, write, flu, source, effect, vain
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Liam G.
— Staff Writer.
Find this post useful? Share it with friends!
Read more
-
-
-
-
10 ways to get conversational English practice every day
Ever lost in conversation? You are not alone! Spoken English can be a hard skill to master, especially if you do not have regular opportunities to gain practice. In this study guide, we will give you 10 great ways to practise your conversational English, both face-to-face and online. Ready? Let’s jump right in! Continue reading →
What are homophones? How do you comfort a distraught grammar teacher? You say, there, their, they’re! This old joke is an example of a homophone.
In speaking, we seldom need to worry about homophone mistakes because the person you are speaking to understands what you are saying due to the context of the conversation. It is with writing that homophone confusion makes a difference because, with identically sounding words, it is easy to use the wrong word. To help untangle the confusion, let’s look at some commonly confused homophones.
What Is A Homophone?
In English, a homophone is a word that is pronounced exactly or nearly the same as another word but differs in meaning and is spelled differently. A homophone is a linguistic situation in which two words have the same pronunciation but have different spellings and meanings. This can be confused with homographs and homonyms. Let’s define all three.
As we saw, homophones are words with different meanings that sound the same. A homograph is a group of words that are spelled the same, but have different meanings and usually have different pronunciations. A homonym, on the other hand, is a word in a group of words that are spelled the same and pronounced the same but have different meanings. It can be confusing to know which word or spelling to use to convey the correct meaning. Adding to the potential confusion is that all homonyms are homophones because they are pronounced the same. But, not all homophones are homonyms because not all homophones are spelled the same.
Common Examples of Homophones
Homophones are the most confusing words in the English language.
- Rode — Road
- Sauce — Source
- Scene — Seen
- See — Sea
- Side — Sighed
- Soar — Sore
- Sole — Soul
- Some — Sum
- Sort — Sought
- Stare — Stair
- Stationary — Stationery
- Steal — Steel
- Stile — Style
- Sun — Son
- Tail — Tale
Interesting examples of homophones used in sentences.
- I ate eight apples for breakfast.
- The flower grew in the flour that spilled on the kitchen counter.
- He left his hair in the hare‘s lair.
- The sea is a great place to see a cee.
- The woodcutter used an ax to chop down aks trees.
- The sun is shining bright and I can see the son playing outside
Homophones examples illustrated with pictures – Image 1

Homophones examples illustrated with pictures – Image 2

Most Commonly Confused Homophones
| Meaning | Examples | |
| Brake | To brake is to slow something down | Use the parking brake to keep the car from rolling backward. |
| Break | To break is to shatter something into pieces | If you don’t hold the vase firmly you might drop it and it will break. |
| By | By is a preposition meaning next to | Come over and sit by me |
| Buy | Buy means to purchase | Use the money I gave you to buy the toy |
| Bye | Bye is the shortened version of goodbye | He said to her, “Bye for now!” |
| Carat | Carat is a unit of weight to measure the size of gemstones (karat is a unit of measurement for the purity of gold) |
The man bought his lady a 2-carat diamond ring |
| Caret | Caret is a mark placed below the line to indicate an insertion in the text | Use a caret to show what you are adding to the sentence |
| Carrot | Carrot is a garden vegetable | Bugs Bunny is always munching on a carrot |
| For | For indicates purpose | I will do this for you |
| Four | Four is the word for the number after 3 and before 5 | There are four possible solutions |
| Fore | Fore means in, toward, or near the front | The doors on the airplane are located fore and aft |
| Its | Its indicates ownership | It’s strange that the bird built its nest where it did |
| It’s | It’s is a contraction for it is | |
| Know | Know is related to knowledge | Did you know I liked apple pie? |
| No | No is the opposite of yes | No, I did not |
| Our | Our indicates what belongs to or is associated with the speaker | Our child wants to study to be a doctor |
| Hour | Hour is a unit of time equaling sixty minutes | The conductor said we will arrive in about an hour |
| There | There means location | The group waiting is over there |
| Their | Their is possessive, referring to them or themselves | What is their reason for waiting? |
| They’re | They’re is a contraction for they are | They’re waiting to come in when the store opens |
| To | To is a preposition indicating motion or direction | I will come to your house |
| Too | Too means also | My friend will come too |
| Two | Two is the word for the number after 1 and before 3 | This way, the two of us will be able to see you |
| Your | Your indicates what belongs to or is associated with the person or people the speaker is addressing | Is your child studying to be a doctor? |
| You’re | You’re is a contraction for you are | I bet you’re proud of them |
We’ve looked at some frequently confused homophones to distinguish how to tell them apart. This will help to use the correct word when writing. As always, the best way to use the correct word is with its context, based on the meaning you wish to convey.
Homophones Examples
Homophones (A)
Ad —– Add
- We put an ad in the local paper.
- Do you want to add your name to the list?
Ail —– Ale
- Make a kind of grand tour on my own, take the waters and cure what ails me.
- Deglaze pan with nut-brown ale and reduce liquid by half.
Air —– Heir
- Let’s go out for some fresh air.
- John was the sole heir to a vast estate.
All —– Awl
- All horses are animals, but not all animals are horses.
- An awl is an iron instrument used for piercing leather, but the word has been in punning use since time immemorial.
Allowed —– Aloud
- Smoking is not allowed here.
- The pain made him cry aloud.
Alms —– Arms
- Parish priests were feeling the pinch through reduced income from alms and tithes.
- He had a pile of books in his arms.
Altar —– Alter
- The groom left the bride standing at the altar.
- I can’t alter the plans.
Ant —– Aunt
- Ants work hard all summer.
- My aunt lives in Canada.
Arc —– Ark
- The beach swept around in an arc.
- The ark is vast, designed to float, not sail – and there were no launching problems!
Ate —– Eight
- I ate three hot dogs.
- My parents died when I was eight.
Auger —– Augur
- These have parallel sides and an auger along which the excess wood escapes.
- Conflicts among the various groups do not augur well for the future of the peace talks.
Aural —– Oral
- The sound track gives us the aural before the visual cue; it is as if the thunder arrives before the lightning.
- Like our oral culture, our society is atomized, disparate and largely obsessed with trivia.
Homophones (B)
Baize —– Bays
- At the same time, away from the competitive baize, she was a loyal and warm-hearted personality.
- He just crouches on the corner at lunchtime and occasionally bays, like a wolf or coyote.
Bald —– Bawled
- He combed his hair and tried to hide his bald patch.
- If you didn’t, you were bawled out, and that took an awful lot of getting used to.
Ball —– Bawl
- Tom caught the ball with one hand
- I couldn’t help it, I just started bawling.
Band —– Banned
Homophones examples:
- They formed a band when they were still at school.
- Leaders of the banned party were arrested last night.
Bard —– Barred
- I can be a bard, a philosopher, an actor.
- The gates are barred, the grass grows long, the paint peels.
Bare —– Bear
- The trees are already bare.
- I am afraid of bears.
Baron —– Barren
- Hariri is not the first political baron to have risen without the benefit of family connections.
- Thousands of years ago the surface was barren desert.
Be —– Bee
- Be quiet!
- A bee is buzzing around.
Beach —– Beech
- It’s a nice day for going to the beach.
- Copses of beech and alder appeared, straggling along the banks with their roots lost in a tangle of briars and bracken.
Bean —– Been
- Tom doesn’t like green beans.
- I’ve never been to Japan.
Beer —– Bier
- He opened the fridge and got out a can of ice-cold beer.
- She made an effort to compose her mind to do just that, and kept her eyes firmly on the bier.
Berry —– Bury
- If you are determined to cultivate fruits, then the safest bets are berry bushes and nut trees.
- We hope to bury any speculation that there was a conspiracy.
Berth —– Birth
- You see them in dedicated lanes, hopefully being given a wide berth by cars.
- What’s your date of birth?
Billed —– Build
- You will be billed monthly for the service.
- They’re going to build on the site of the old power station.
Blue —– Blew
- They failed to put clear blue water between themselves and their competitors.
- She blew onto her coffee to cool it down.
Bored —– Board
- After a while, I got bored and left.
- The plan of the new building is displayed on a board at the back of the room.
Braid —– Brayed
- A worn braid feels rough and is best cut away and the line joined by a blood knot.
- The fisherman brayed laughter, pleased with his joke, and delighted to see the boy had composed himself.
Break —– Brake
- I need a break.
- She stopped with a squeal of the brakes.
Brews —– Bruise
- In the days when most types of beer were dark, wheat brews were seen as being relatively pale and often cloudy.
- Jenny looked as though she’d been crying, and there was a nasty bruise on her cheek.
Bridal —– Bridle
- She went to House of Design, a new Boston bridal house specializing in couture-quality gowns.
- The boy walked up to it and pulled its head up with the bridle, leading it out of the trees.
Broach —– Brooch
- He decided not to broach the subject of divorce until his wife had recovered from her illness.
- Mrs. or Mme Wyatt wore patent-leather shoes and a smart brownish suit with a gold brooch.
Buy —– By / Bye
- I want to buy a new coat.
- The telephone is by the window.
- Bye, Dave.
Homophones Examples – Image 1
Homophones Examples (C)
Capital —– Capitol
- The government is eager to attract foreign capital.
- This same senator also once got lost in a Capitol Hill garden after leaving a conference committee on the House side.
Cellar —– Seller
- We don’t use our coal cellar anymore.
- She is a flower seller.
Census —– Sense
- A national census is taken every ten years.
- He felt an overwhelming sense of loss.
Cereal —– Serial
- Eaten with milk or cream, they made an acceptable breakfast cereal.
- Their letters of planning went back and forth like installments of a serial.
Chili —– Chilly
- The sauce needs more chili.
- I was feeling chilly.
Choral —– Coral
- The third and final section of the evening was choral.
- They spent $ 2 million on environmental measures, he said, and hired biologists to replant coral that would be damaged.
Cite —– Sight / Site
- He was cited for bravery.
- Anne’s sight is very good for someone of her age.
- A site has been chosen for the new school.
Coarse —– Course
- The coarse sand was hot.
- Andy’s doing a one-year journalism course.
Complement —– Compliment
- The dark red walls complement the red leather chairs.
- Being compared to Abba is a great compliment.
Council —– Counsel
- He sent a letter to the council to complain about the noise.
- The judge asked counsel for the defence to explain.
Homophones Examples (D)
Deer —– Dear
- A deer makes tracks in the snow.
- Congratulations to you my dear brother on all your fine accomplishments in school.
Die —– Dye
- Do you believe in anything enough to die for it?
- Carbonless paper coated with chemicals and dye which will produce copies without carbon paper.
Discreet —– Discrete
- He assured her that he would be discreet.
- The change happens in a series of discrete steps.
Doe —– Dough
Homophones examples:
- Ezra waited for the doe to open its eyes and look at him.
- Mix lemon juice and milk; stir into flour mixture until dough leaves side of bowl and forms a ball.
Done —– Dun
- As soon as I’m done, I’ll give you a call.
- The claret dun nymph is at home in slow, peaty streams.
Draft —– Draught
- This is only the first draft of my speech.
- A cold draught of air blew in from the open window.
Dual —– Duel
- The piece of furniture serves a dual purpose as a cupboard and as a table.
- The officer challenged him to a duel.
Homophones (E)
Earn —– Urn
- He did all sorts of jobs to earn a living.
- The soup urn had a lonely look.
Ewe —– You
- He’s helping to drive in the ewes for a mass ante natal clinic
- I have some news for you.
Homophones Examples (F)
Farther —– Father
- We decided not to go any farther.
- I love my father.
Faze —– Phase
- John was embarrassed, but it didn’t faze Mike a bit.
- The first phase of renovations should be finished by January.
File —– Phial
- Mendoza read over the file on the murders.
- The door irised open and he reached inside, drawing out the tiny phial before the door closed up again.
Find —– Fined
- I can’t find the car keys.
- The company was fined £20 000 for breaching safety regulations.
Fir —– Fur
- You always clear away the soft topsoil till you get a fir base.
- There was cat fur all over the chair.
Flaw —– Floor
- There is a fundamental flaw in Walton’s argument.
- We are located on the seventh floor of the building.
Flea —– Flee
- A water flea that is starving in a crowded pond is the victim not of food shortage but of competition.
- He gathered what money he had just in case Gallagher was forced to flee.
Flew —– Flu/ Flue
- A bird flew by and saw one of the half-eaten calves that I had dug up.
- Steven’s still in bed with flu.
- You may prefer central heating, and more controllable ventilation than permanently open flue.
Flex —– Flecks
- She watched him raise one hand to rub the nape of his neck, then flex his shoulder muscles.
- Only a few flecks of gray could be seen in his full head of hair.
Flour —– Flower
- Sift the flour and salt into a bowl.
- What beautiful flowers!
For —– Four
- There’s a letter for you.p
- I choose number Four.
Foreword —– Forward
- He was asked if he would consider writing a foreword for her book.
- They ran forward to welcome her.
Fort —– Fought
- Just the three of you going to be holding the fort tonight.
- He fought many battles with the early Labor party in Lancaster and discrimination against socialist employees was alleged.
Foul —– Fowl
- He woke up with a foul taste in his mouth.
- Fish, fowl and meat, most with a decidedly Southwestern treatment, are represented on the menu.
Homophones Examples (G)
Gait —– Gate
- He was round and fat, he had an energetic gait, a bright, lively face, and laughing eyes.
- We went through the gate into the orchard.
Gamble —– Gambol
- Their religion forbids them to drink or gamble.
- Now, at seventeen, I could gambol in the forbidden delights of Elysium with no one tugging at my hand.
Genes —– Jeans
- The actual number of human genes is still in dispute.
- Her hair looked dishevelled, as did the sweatshirt and jeans she was wearing.
Gored —– Gourd
- He was attacked and gored by a bull.
- I felt hollow, like a dried gourd, a few loose seeds shaking uselessly inside me.
Great —– Grate
- The movie was a great success.
- She took the two halves of the letter away, tore them in fragments, and burned them in her grate.
Groan —– Grown
- Richard’s jokes make you groan rather than laugh.
- He had been a grown man with a small but independent income when he had taken Minnie instead of her to wife.
Homophones Examples – Image 2

Homophones (H)
Hart —– Heart
- Whoever slew a hart or hind was to be blinded.
- Regular exercise is good for the heart.
Hear —– Here
- I could hear the sound of traffic.
- This switch here controls the lights.
Heel —– Heal
- The sergeant clicked his heels and walked out.
- This will help to heal your cuts and scratches.
Hi —– High
- Hi guys!
- The house has a high wall all the way round it.
Him —– Hymn
- He took the children with him.
- The service began with a rousing hymn.
Hoard —– Horde
- They dug up a hoard of Roman coins.
- The elves defeated a huge horde of goblins.
Hole —– Whole
- The bomb blew a huge hole in the ground.
- She wasn’t telling the whole truth.
Holy —– Wholly
- The priest puts some holy water on the child’s head.
- The report claimed that the disaster was wholly unavoidable.
Hour —– Our
- The interview lasted half an hour.
- We showed them some of our photos.
Homophones (I)
I —– Eye
- I moved to this city six years ago.
- Ow! I’ve got something in my eye!
Idle —– Idol
- I cannot afford to leave the land lying idle.
- She is the idol of countless teenagers.
Incite —– Insight
- Republicans have complained that Democrats are using Social Security scare tactics to incite seniors groups and others to oppose the constitutional amendment.
- The article gives us a real insight into the causes of the present economic crisis.
Homophones (K)
Knead —– Need
- On a lightly floured board, knead the dough for a couple of minutes.
- You don’t really need a car.
Knew —– New
- I wonder if he knew of the plan?
- The hardest part of this job is understanding the new technology.
Knight —– Night
- She’s still waiting for a knight in shining armor to come and rescue her.
- The accident happened on Friday night.
Knot —– Not
- Tie the two ropes together with a knot.
- She did not see him.
Know —– No
- I know people’s handwriting changes as they get older.
“It was Tony.” - “‘No, you’re wrong. It was Ted.”
Homophones (L)
Leak —– Leek
- Water had started to leak into the cellar.
- For a first course, there is a potato leek soup.
Lessen —– Lesson
- They gave her an injection to lessen the pain.
- Our first lesson on Tuesdays is French.
Levee —– Levy
- The last four of these sub-deltas were formed by levee breaches in 1839,1860,1874 and 1891.
- If the government wishes to raise tax revenue in order to subsidize the poor, it should levy a tax on films.
Links —– Lynx
- A love of nature links the two poets.
- They may be eagle-eyed or watch like a lynx.
Loan —– Lone
- I had to take out a loan to buy my car.
- He was by no means a lone voice criticizing the government.
Loot —– Lute
- He refused to let his army enter and loot the city.
- Here too he started to write hymns which he would sing to his own accompaniment on a lute.
Homophones examples illustrated with pictures – Image 3

Homophones examples illustrated with pictures – Image 4
Homophones (M)
Made —– Maid
- The sky was clear and the sunlight had a brilliance and intensity that made her head reel.
- A maid pushed her cleaning cart down the path toward the cottages out back.
Mail —– Male
- He found a mountain of mail waiting for him.
- Many women earn less than their male colleagues.
Main —– Mane
- The main reason for living in Spain is the weather.
- She tossed back her mane of chestnut hair.
Manna —– Manner
- There is no mention in the story of the giving of water, or of food beyond the manna.
- I had hoped you would behave in a more responsible manner.
Marshal —– Martial
- Heston has been named grand marshal of the parade.
- He’d heard rumors that the military were planning to declare martial law.
Mask —– Masque
- Her sarcasm is a mask for her insecurity.
- Comus is a masque in which a young lady’s chastity is tried and not vanquished.
Maw —– More
- Millions of dollars were poured into the maw of defense spending.
- Children generally feel much more confident working in groups.
Medal —– Meddle
- She won a gold medal at the last Olympics.
- Church leaders shouldn’t meddle in politics.
Meet —– Meat
- Maybe we’ll meet again some time.
- I gave up eating meat a few months ago.
Might —– Mite
- I might be a few minutes late.
- Some teachers take everything a mite too serious.
Mist —– Missed
- We could just see the outline of the house through the mist.
- He missed 20 games after breaking a bone in his wrist.
Moose —– Mousse
- The team already knew that moose exposed to new predator populations are more vulnerable.
- She would bake a chocolate mousse torte.
Muscle —– Mussel
- Rooney has pulled a muscle in his thigh and won’t play tomorrow.
- You can also try beef heart, mussel, chicken, liver prawn and the like.
Homophones (N)
None —– Nun
- I wish I could offer you some cake but there’s none left.
- Georgiana later marries, and Eliza becomes a nun.
Homophones (O)
Oar —– Or
- We took one oar each and rowed quickly to the shore.
- It can be black, white or grey.
Overdo —– Overdue
- Don’t overdo the salt in the food.
- Her baby is two weeks overdue.
Homophones (P)
Pail —– Pale
- They filled their pail and container, and started the return journey.
- He looked very pale and drawn.
Pain —– Pane
- She felt a sharp pain in her leg.
- Omite peers through the pane, shakes her head and steps back.
Pair —– Pear
- She felt as if every pair of eyes in the room was on her.
- This pear smells nice.
Passed —– Past
- We passed a group of students outside the theatre.
- Study some past exam papers to get an idea of the questions.
Peace —– Piece
- I wish she would just leave me in peace.
- He broke off a piece of bread and gave it her.
Peak —– Peek
- Sales this month have reached a new peak.
- Shut your eyes and don’t peek!
Pedal —– Peddle
- She put her foot down on the accelerator pedal.
- Farmers come to Seoul to peddle rice.
Plane —– Plain
- She slept on the plane.
- The advantages were plain to see.
Principal —– Principle
- His principal reason for making the journey was to visit his family.
- The general principle is that education should be available to all children up to the age of 16.
Profit —– Prophet
- The shop’s daily profit is usually around $500.
- He sent for Teiresias, the old blind prophet, the most revered of Thebans.
Homophones (R)
Rain —– Reign
- There will be heavy rain in most parts of the country.
- A higher synthesis, one ushering in a new reign of peace and harmony, under a benign and ever just science.
Red —– Read
- We painted the door bright red.
- I was shocked when I read of his death.
Right —– Write
- Keep on the right side of the road.
- She had to write a report on the project.
Ring —– Wring
- She left a dirty ring around the bath.
- They are always trying to wring additional funds from the government.
Rode —– Road
- He rode away across the marshes.
- I ran down the road to see what was happening.
Role —– Roll
- They want to limit the role of government.
- I tried to roll him onto his side.
Rouse —– Rows
- We don’t want to rouse any suspicions.
- There were always rows when my dad got home.
Rung —– Wrung
- I have rung the world from these boxes and feel a great affection and gratitude towards them.
- Sally wrung out the socks and hung them on the towel rack.
Homophones List – Image 3

Homophones (S)
Sail —– Sale
- She always wanted to sail around the world.
- The use and sale of marijuana remains illegal.
Sauce —– Source
- Stir in fish sauce, coconut milk, sugar, and lime juice and bring to a simmer.
- Beans are a very good source of protein.
Scene —– Seen
- The police soon arrived at the scene of the crime.
- He crouched down so he couldn’t be seen.
Scull —– Skull
- You didn’t scull too badly today.
- Her skull was crammed with too many thoughts.
See —– Sea
- She looked for him but couldn’t see him in the crowd.
- The waste was dumped in the sea.
Shoe —– Shoo
- What’s your shoe size?
- You shoo the dog out of the kitchen.
Side —– Sighed
- They crossed from one side of London to the other.
- He sighed deeply at the thought.
Slay —– Sleigh
- Those old movies still slay me!
- Alternatives to skiing include a leisure pool, curling and skating on the nearby lake, indoor tennis and sleigh rides.
Soar —– Sore
- She watched the dove soar above the chestnut trees.
- I had a sore throat and aching limbs.
Sole —– Soul
- Griffiths is the sole survivor of the crash.
He is really quite a sensitive soul.
Some —– Sum
- I need some apples for this recipe.
- Bill wants to spend a large sum on modernizing the farm.
Sort —– Sought
- He wondered if Rosa was in some sort of trouble.
- He sought revenge against Surkov for separating him from his wife and son.
Staid —– Stayed
- The museum is trying to get rid of its staid image.
- She stayed at home while the children were young.
Stalk —– Stork
- He ate the apple, stalk and all.
- We always used to say the guys on the Ridge were lucky, the stork brought their babies.
Stare —– Stair
- It’s not polite to stare, you know.
- The second stair creaks when you step on it.
Stationary —– Stationery
- It is called a sinker because it sinks beneath you when you are stationary.
- You could say the same for luggage and stationery.
Steal —– Steel
- Inventors know that someone is always going to try to steal their designs.
- Sheffield is a major steel town.
Stile —– Style
- Continue on a clear path up the hillside to reach a stile on the ridge.
- The paintings are in an expressionistic style.
Sun —– Son
- The sun was shining and birds were singing.
- We have two daughters and a son.
Homophones (T)
Tail —– Tale
- The male has beautiful tail feathers.
- His latest book is a delightful children’s tale about talking animals.
Team —– Teem
- We have a team of eight working on product development.
- With luck, in a year the place should begin to teem with federal workers.
Than —– Then
- Natalie was prettier than her sister.
- I wish I had known then what I know now.
Their —– There
- They washed their faces and went to bed.
- We could go back to my cottage and have lunch there.
Throne —– Thrown
- Queen Elizabeth came to the throne in 1952.
- The boat was thrown onto the rocks.
Tide —– Tied
- The body was washed up on the beach by the tide.
- She tied the newspapers in a bundle.
To —– Too / Two
- I walked to the office.
- The dress was too tight for me.
- I was in two minds about the book.
Toe —– Tow
- He kicked the earth with the toe of his boot.
- The car broke down and we had to get somebody to give us a tow.
Homophones (V)
Vain —– Vein
- She closed her eyes tightly in a vain attempt to hold back the tears.
- The nurse was having trouble finding a vein in his arm.
Vary —– Very
- Class numbers vary between 25 and 30.
- The new building has been very much admired.
Homophones (W)
Wail —– Whale
- Somewhere behind them a child began to wail.
- We saw a whale blowing a jet of spray high in the air.
Waste —– Waist
- Why waste money on clothes you don’t need?
- He put his arm around her waist.
Way —– Weigh
- I’m not happy with this way of working.
- The young birds weigh only a few grams.
Weak —– Week
- She is still weak after her illness.
- He comes to see us once a week.
Weather —– Whether
- The weather is very changeable at the moment.
- I asked him whether he had done it all himself or whether someone had helped him.
Where —– Wear
- I wonder where they will take us to.
- I always wear black.
Which —– Witch
- Which of the applicants has got the job?
- He wants me to be a witch.
Who’s —– Whose
- Who’s the money for?
- Whose house is that?
Won —– One
- Britain won five gold medals.
- There’s only room for one person.
Would —– Wood
- He said he would be here at eight o’clock.
- All the furniture was made of wood.
Homophones (Y)
You’re —– Your
- You’re a good person.
- Dentists advise you to have your teeth checked every six months.
Homophones List | Images
Homophones List | Image 1

Useful Homophones List | Image 2

Homophones List | Image 3

Homophones | Pictures
Commonly Confused Homophones in English | Image 1

Examples of Homophones in English | Image 2

Commonly Confused Homophones in English | Image 3

Examples of Homophones in English | Image 4

Homophone Video
Learn common homophones examples illustrated with pictures and pronunciation video.
Learn a list of homophones in English with American English pronunciation.
To conclude, let’s enjoy a homophonic limerick:
Whether the weather be cold,
Or whether the weather be hot,
We’ll weather the weather,
Whatever the weather,
Whether we like it or not.
Resources Related to Homophones
- Commonly Confused Words
- Most Difficult Words
- Commonly Mispronounced Words
- Commonly Misspelled Words
- Homographs, Homophones, Homonyms
- Homonyms
- Homographs
- Grammatical Errors
Homophones List
Last Updated on March 3, 2023
ОМОФОНЫ — это слова, которые произносятся одинаково, но пишутся по-разному, например, be и bee (см. картинку). И таких слов достаточно много в английском языке. Особенно они вызывают трудности при понимании, так как об их написании остается только догадываться.
English Confusing Words
(Английские слова, которые часто путают)
Проверьте себя, хорошо ли вы знаете омофоны в английском языке? Например, какое слово надо употребить в этом предложении?
Загрузка …
* * *
Часть 1. Homophones. ОМОФОНЫ
Содержание:
- Список омофонов для изучения
- Упражнения для закрепления омофонов
Упражнение 1 (вводное). Найдите 19 орфографических ошибок в письме Джека.
Deer Jane,
Hear I am in Siberia. We’ve been hear for too weaks now, and I can’t bare the thought of staying in this country any longer.
What dreadful whether! It’s bitterly cold out. When I’m chilled to the bone, I think I’ll never warm up.
We live in a wooden house. It is surrounded with a huge would. The hunter, who lives with us, says that the would is full of beasts- You can walk their and meat a dear or a bare. As for me, once I saw a hair.
Do you think, it is fare to leave me hear! I can’t even sleep in piece. Can’t you come and stay with me? The fair is really not very expensive.
Hope to sea you soon.
Best wishes,
Your Jack
Вы можете проверить себя в конце статьи даны ОТВЕТЫ.
Английские омофоны. Список для изучения
A. Самые распространенные омофоны в английском языке. Список №1
- son — sun (солнце – сын)
- hour – our (час – наш)
- there — their (там – их)
- hear — here (слышать – здесь)
- write – right (писать – правый)
- tale – tail (сказка – хвост)
- sea — see (море – видеть)
- meet — meat (встречать – мясо)
- dear — deer (дорогой – олень)
- two — too (два – тоже)
- buy – bye (купить – до свидания)
- new – knew (новый – знал)
- hair – hare (волосы – заяц)
- be — bee (быть — пчела)
B. Менее распространенные английские омофоны. Список №2
- made — maid (сделанный – горничная)
- knight – night (рыцарь – ночь)
- flower – flour (цветок – мука)
- berry — bury (ягода – погребать)
- week – weak (неделя – слабый)
- bare – bear (голый – терпеть)
- bare – bear (голый – медведь)
- weather – whether (погода – ли)
- wood – would (лес – бы)
- whole – hole (целый – дыра)
- fair – fare (справедливый — плата)
- piece – peace (кусок – мир, спокойствие)
- pair – pear (пара – груша)
- sail – sale (парус – распродажа)
- through – threw (через – бросил)
- fool — full (дурак — полный)
Омофоны в английском языке. Упражнения
Упражнение 1. Выучите омофоны из списка №1 и №2 и подготовьтесь к диктанту.
Диктант на омофоны: наш час, дорогой олень, быть пчелой, тоже два, видеть море, слышать здесь, полный дурак, бросил через, пара груш, часть спокойствия, целая дыра, справедливая плата, голый медведь, цветок в муке, ночной рыцарь, горничная сделала (16).
Упражнение 2. Вставьте омофоны из списка №1 и №2.
- The … is becoming warmer. Spring is coming. — Your sister’s …. is your nephew.
- It was a big house and so there was a…. who helped to clean it. — Is your new sweater ….of wool?
- It usually takes me just one…. to do my homework in English. — We like it when foreign guests come to …. school.
- They are nice boys, besides everybody knows …. devotion to ….friends. — Have you been to the UK? How long did you stay ….?
- Don’t forget to ….. me a letter when you go away on holiday. — I’m sure you are ….when you try to learn as much as you can…
- At ….. Moscow looks rather beautiful. — How much do you know about King Arthur? Was he a ….?
- I didn’t know that this …. grows only on tops of high rocks. — Take the ….. and the eggs and mix them.
- The fox has a long bushy …. — That’s the best …. I’ve ever heard.
- They decided to….. Shakespeare in the church.- Do you know that the tomato is a ….?
- We didn’t enjoy our holidays because of bad… — I don’t know …. the story is true.
Упражнение 3. The Haunted house
A few months ago I bought this very old mansion. But it’s a complete 1) … of money. Now it’s on 2) … again and I’m looking for a 3)… house. Why? Every evening I would 3)… strange noises as if someone was walking in the attic. I was scared stiff as I 4)… there was nobody else at home but me. Then, one 5)… I saw the ghost of a 7)… . I 8)… him bumping around the house till two o’clock in the 9)…. The other day someone kept knocking at the door all 10)… long. But when I looked outside, there was nobody 11)…. Another thing is, somebody is constantly opening my 12)…. No, I can’t 13 ) … it any longer! I am determined to get away from that haunted house. I have to find a less spooky place to live.
ПОДСКАЗКА: слышать здесь, их дом там, погода ли плохая, паруса в продаже, знал новое, ночной рыцарь, голые медведи, пара груш, напиши справа, целая дыра, бросил через.
ОТВЕТЫ
Здравствуйте! Для получения доступа к ответам необходимо оформить подписку. Ссылка в боковом меню — ОТВЕТЫ.
The term «homonyms» in its broad meaning includes homonyms, homophones, and homographs. In more specific sense, homonyms are words with the same pronunciation and spelling but different in meaning. Homophones have the same pronunciation but are different in meaning and spelling. Homographs are identical in spelling but differ in meaning and pronunciation. Homophones present the most difficulty for learners of English.
The list below is mostly for intermediate and advanced learners. It includes common homonyms and less frequently used homonyms, with examples illustrating their use. A shorter list of homonyms for beginners is provided in Homonyms Short List in the section Writing.
Note: In many cases, homonyms are words of different origin (i.e., derived from different words). Depending on the definition this or that dictionary provides for the word «homonym» (and definitions of «homonym» may differ), some words in the list below, for example, «chord, cord; discreet, discrete; plain, plane; toast, toast; train, train; trunk, trunk», may or may not be considered homonyms as they were derived from one and the same word. For example, «plain» and «plane» were derived from Latin «planus» meaning «flat, level»; «trunk» was derived from Latin «truncus» meaning «truncated, lopped».
Термин «homonyms» в широком смысле включает в себя омонимы, омофоны и омографы. В более определённом смысле, омонимы – это слова с одинаковым произношением и написанием, но разные по значению. Омофоны имеют одинаковое произношение, но различаются в значении и написании. Омографы пишутся одинаково, но имеют разное значение и произношение. Омофоны представляют наибольшую трудность для изучающих английский язык.
Список ниже в основном для изучающих среднего и продвинутого уровня. Он включает в себя распространённые омонимы и менее употребительные омонимы, с примерами, иллюстрирующими их употребление. Более краткий список омонимов для начинающих дан в материале «Homonyms Short List» в разделе Writing.
Примечание: Во многих случаях, омонимы – это слова разного происхождения (т.е. образованные от разных слов). В зависимости от определения, которое тот или иной словарь даёт для слова «homonym» (а определения слова «homonym» могут отличаться), некоторые слова в списке ниже, например, «chord, cord; discreet, discrete; plain, plane; toast, toast; train, train; trunk, trunk», могут или не могут считаться омонимами, т.к. они были образованы от одного и того же слова. Например, «plain» и «plane» были образованы от латинского «planus» (плоский, ровный); «trunk» был образован от латинского «truncus» (усечённый, отрубленный).
The same pronunciation, different meaning
(Одинаковое произношение, разное значение)
AIR – HEIR (воздух, проветрить – наследник): fresh air; to air the room; the heir to the throne;
AISLE – ISLE (проход – остров): an aisle seat; to sit on the aisle; the British Isles;
ALTAR – ALTER (алтарь – изменить): to lead to the altar; to alter course; to alter a coat;
AURAL – ORAL (слуховой – устный, ротовой): aural perception; aural surgeon; oral examination; oral cavity;
BAIL – BALE (залог, освобождать под залог – кипа, тюк, связка): he was out on bail; he was bailed out for 1000 dollars; a bale of cotton; a bale of hay;
BALL – BALL (шар, мяч – бал): a ball of fire; to play ball; a ball gown; to open a ball;
BAND – BAND (отряд, группа – тесьма, завязка): a rock band; a rubber band;
BANK – BANK (насыпь, берег – банк): the bank of the river; the Bank of England; a bank account;
BARE – BEAR – BEAR (голый – нести ношу, родить – медведь): with bare hands; I can’t bear it; bear in mind; the polar bear;
BARK – BARK – BARK, BARQUE (лай, лаять – кора – парусное судно): the dog barked at me; the bark of a tree; a bark is a sailing ship;
BASE – BASE (основа, основание, база, базовый, основывать на – низкий, подлый): the base of a mountain; the story is based on real facts; base ingratitude; base conduct;
BAT – BAT – BAT (летучая мышь – бита – моргнуть): blind as a bat; a baseball bat; not to bat an eyelid;
BAY – BAY – BAY – BAY – BAY (бухта, залив – ниша, отсек – положение загнанного зверя – лавр – гнедой): Hudson Bay; bay window; an animal at bay; bay leaf; several bay horses;
BE – BEE (быть – пчела): to be or not to be; to be as busy as a bee; a bee in one’s bonnet;
BEAT – BEET (бить – свекла): to beat the drums; beets and carrots;
BERRY – BURY (ягода – хоронить): strawberry jam; to bury the dead; to bury the hatchet;
BERTH – BIRTH (койка – рождение): a single-berth compartment; birth certificate; to give birth to; she is French by birth;
BILL – BILL (счёт, банкнот – клюв): to pay the bill; a ten-dollar bill; a bill is the beak of a bird;
BIT – BIT – BIT (кусочек, немного – удила (часть уздечки), режущий край инструмента, бур, сверло – бит): a bit of butter; wait a bit; this drill has removable bits; the computer term «bit» is a contraction of «binary digit»;
BITE – BYTE (кусать, укус – байт): to bite one’s tongue; his dog bites; a deep bite; insect bites; one kilobyte is 1024 bytes;
BLOCK – BLOC (колода, квартал, преграда, блокировать – блок, объединение): a wooden block; walk two blocks; they blocked the exit; a military bloc;
BORE – BORE – BOAR (бурить – наскучить – кабан): to bore a hole; I’m bored; a wild boar;
BOUGH [bau] – BOW [bau] – BOW [bau] (сук, ветка – поклон, наклонить – корма судна): the boughs of a tree; to take a bow; to bow one’s head; the ship’s bow;
BOW [bou] – BEAU [bou] (лук для стрельбы, дуга, смычок, галстук-бабочка – кавалер): a bow and arrows; a rainbow; the bow of a violin; a bow tie; he is her new beau;
BRAKE – BREAK (тормоз, тормозить – перерыв, сломать, разбить): car brakes; let’s take a break; don’t break it;
BUY – BY – BYE (покупать – около, у – Пока!): to buy a car; to sit by the window; Bye-bye!
CACHE – CASH (тайник, запас – наличные деньги): cache memory; to pay cash; I have no cash;
CAN – CAN (мод. гл.: мочь, быть в состоянии – консервная банка, консервировать): I can do it; a can of beer; canned olives;
CANNON – CANON (пушка – правило, закон): water cannon; cannon ball; the canons of taste;
CANVAS – CANVASS (холст, брезент – предвыборная агитация): a painter’s canvas; to canvass a district;
CAPE – CAPE (накидка, плащ – мыс): he was wearing a dark gray cape; the Cape of Good Hope;
CARAT – CARROT (карат – морковь): a two-carat diamond; grated carrots;
CASE – CASE (случай, обстоятельство, положение дел, судебное дело, пример, довод – ящик, коробка, контейнер, футляр, чехол): in case of fire; a criminal case; two cases of wine; a jewel case;
CAST – CASTE (бросать, бросок – каста): to cast a glance; the cast of actors; high caste;
CELL – SELL (отсек, камера, ячейка, клетка – продавать): a prison cell; my cell phone; red blood cells; to buy and sell; to sell books;
CENSOR – SENSOR (цензор – датчик, чувств. элемент): to censor a document; acoustic sensor;
CENT – SCENT (цент – запах): 100 cents in a dollar; a faint scent of roses;
CEREAL – SERIAL (крупа – серийное издание): to eat breakfast cereal; to watch TV serials;
CHASE – CHASE (преследовать, погоня – паз, оправа, гравировать): to chase butterflies; to chase a thief; a wild-goose chase; metal chasing;
CHORD – CHORD – CORD (струна, хорда – аккорд – верёвка, шнур): to strike a deep chord; dissonant chords; electric cord; vocal cords;
CHUTE – SHOOT (скат, жёлоб – стрелять, делать съёмки): down the chute; to shoot a gun; to shoot a film;
CLIP – CLIP (подрезать – зажим, скрепка): to clip the hedge; a paper clip;
COARSE – COURSE (грубый – курс): coarse fabric; a course of lectures;
COLON – COLON (двоеточие – ободочная кишка): put a colon before a long list; colon cancer;
COLONEL – KERNEL (полковник – ядро, суть): lieutenant colonel; almond kernels; the kernel of the question;
COMPLEMENT – COMPLIMENT (комплемент, дополнение – комплимент): verb complement; give a compliment;
COUNCIL – COUNSEL (совет, собрание – совет, адвокат, дать совет): city council; legal counsel;
CREAK – CREEK (скрип, скрипеть – ручей): the floor creaks; a narrow creek;
CUE – CUE – QUEUE (намёк, подсказка – кий – очередь): give a cue; billiard cue; stand in a queue;
CURRANT – CURRENT (смородина – текущий, течение): red currant; current month; ocean current;
DAM – DAMN (плотина – проклятие): to build a dam; damn it; I don’t give a damn;
DEAR – DEER (дорогой – олень): Dear Sir; dear friend; a young deer; several deer;
DESERT [di’zərt] – DESSERT [di’zərt] (покидать – десерт): to desert the village; apple pie for dessert;
DEW – DUE (роса – должный): morning dew; When is the train due? with due respect;
DIE – DYE (умереть – краситель, окрашивать): He died two years ago. She dyed her hair red.
DISCREET – DISCRETE (осмотрительный – разрозненный): discreet silence; discrete parts;
DOE – DOUGH (самка оленя – тесто): a young doe; to roll the dough;
DUAL – DUEL (двойной – дуэль): dual citizenship; dual ownership; to fight a duel; verbal duel;
EARN – URN (зарабатывать – урна): to earn money; to earn a living; to earn respect; cremation urn;
EVE – EAVE, EAVES (канун – карниз, свес крыши): Christmas Eve; on the eve of their wedding; under the eaves;
FAIR – FAIR – FARE (справедливый – ярмарка – плата за проезд): that’s fair; book fair; bus fare;
FAST – FAST (быстрый, прочный – пост, поститься, ничего не есть): he drives too fast; hard-and-fast rules; to observe the fast;
FAUN – FAWN – FAWN (фавн – оленёнок (до одного года), жёлто-коричневый – подлизываться): in mythology, a faun is half man and half goat; fawn color is light yellowish brown; he is fawning on them;
FINE – FINE (прекрасный – штраф): one fine day; fine wine; to pay a fine for speeding;
FIR – FUR (ель – мех): pines and fir trees; a fir cone; a fur coat; natural fur;
FIT – FIT (годиться, подходить по размеру, подходящий – припадок, приступ): this dress fits you perfectly; it is a perfect fit; the food was fit for a king; a fit of coughing; a fit of anger;
FLAIR – FLARE (способность, чутьё – вспыхивать, вспышка): a flair for fashionable clothes; to flare up; a flare of anger;
FLEA – FLEE (блоха – спасаться бегством): a flea market; to flee the country;
FLAT – FLAT (плоский, плоская поверхность – квартира): flat roof; the flat of the hand; a block of flats;
FLOUR – FLOWER (мука – цветок): two cups of flour; a bunch of flowers;
FOREWORD – FORWARD (предисловие – вперёд): a foreword in a book; to move forward;
FORT – FORTE (форт – сильная сторона): a military fort; good spelling is her forte;
FOUL – FOWL (отвратительный, грязный – птица, дичь): foul smell; foul words; domestic fowl;
GAIT – GATE (походка – ворота): heavy gait; slow gait; to open the gate;
GILD – GUILD, GILD (золотить – гильдия): to gild the pill; gilded youth; the guild of merchants;
GILT – GUILT (позолота, позолоченный – вина): to cover with gilt; we have no proof of his guilt;
GRATE – GRATE – GREAT (решётка – скрести, тереть – большой, великий, замечательный): metal grate; to grate cheese; a great opportunity;
GRAVE – GRAVE (могила – серьёзный, тяжёлый, важный, мрачный): to dig a grave; grave situation; grave illness; his face was grave;
GROUND – GROUND (земля – молотый): to fall to the ground; freshly ground coffee;
HAIR – HARE (волосы – заяц): she has dark hair and green eyes; he ran like a hare;
HALL – HAUL (коридор, зал – тянуть, тащить): down the hall; a concert hall; to haul the boat;
HANGAR – HANGER (ангар – вешалка): a plane hangar; a coat hanger;
HAY – HEY (сено – эй): to make hay; hay fever; Hey!
HEAL – HEEL (излечивать – пятка, каблук): to heal the wounds; high heels;
HEAR – HERE (слышать – здесь): Did you hear what he said? She doesn’t live here.
HI – HIGH (привет – высокий): Hi, how are you? high walls; high speed; high temperature;
HOARSE – HORSE (хриплый – лошадь): a hoarse voice; to ride a horse;
HOLE – WHOLE (дыра – целый): a small hole in my sock; as a whole; the whole world;
I – EYE (я – глаз): I can see it clearly. My left eye itches.
IDLE – IDOL (неработающий, праздный – идол): idle machinery; idle talk; a teenage idol;
ILLICIT – ELICIT (незаконный – извлечь): illicit access; illicit trade; to elicit the truth; to elicit a reply;
JAM – JAM – JAMB (затор, сдавливать – джем – косяк, стойка): a traffic jam; to jam one’s finger in the door; strawberry jam; a door jamb;
KIND – KIND (сорт, вид – добрый): several kinds of apples; What kind of job are you looking for? it is very kind of you;
KNAP – NAP (дробить – лёгкий сон, дремать): to knap a stone; to take a nap;
KNEAD – NEED (месить, массировать – нужда, нуждаться в): to knead the dough; there is no need to worry; he needs rest;
KNIGHT – NIGHT (рыцарь – ночь): the Knights of the Round Table; a dark night; days and nights;
KNIT – NIT (вязать – гнида, яйцо блохи): to knit a sweater; a knitted cap; nit-picking;
KNOT – NOT (узел – не, нет): a tight knot; not a word; he is not a doctor;
KNOW – NO (знать – не, нет): Do you know him? No, I don’t. I have no time.
LAP – LAP – LAP (место от талии до колен в сидячем положении – один круг, оборот, один этап дистанции – лакать, лакание, плеск): the baby sat in his mother’s lap; a computer on his lap; he does six laps a day in the swimming pool; the dog lapped up the water; the sound of the waves lapping at the shore;
LEAK – LEEK (утечка, давать течь, протекать – лук-порей): a leak in the ship; the roof leaks; wild leek;
LESSEN – LESSON (уменьшить – урок): to lessen pain; to give a lesson; to learn a lesson;
LICHEN – LIKEN (лишайник – уподоблять): lichens are plants; he likens her to a rose;
LIE – LIE – LYE (ложь, лгать – лежать – щёлок): to tell a lie; don’t lie to me; to lie on the floor; a lye solution;
LIGHT – LIGHT – LIGHT (свет, светлый – лёгкий – натолкнуться, опускаться на): bright light; light blue; as light as a feather; light rain; a bird lighted on a branch;
LIME – LIME – LIME (известь – лайм – липа): burnt lime; lime juice; lime tree;
LOAN – LONE (ссуда, дать взаймы – одинокий): a bank loan; she loaned him some money; a lone house; a lone traveler; a lone wolf;
LOOP – LOUPE (петля – лупа): to make a loop; a loophole; a loupe is a magnifying glass;
MAIL – MAIL – MALE (почта, отправить почтой – кольчуга, броня – мужского пола, мужчина): Is there any mail for me? to send by mail; a coat of mail; a male child; a male dog;
MAIN – MANE (главный – грива): the main reason; a horse’s mane;
MAIZE – MAZE (маис, кукуруза – лабиринт): maize oil; a maze of streets; a maze is a labyrinth;
MALL – MAUL (пешеходная аллея – кувалда, калечить): shopping mall; to be badly mauled;
MANTEL – MANTLE (каминная полка – накидка, мантия): mantelpiece; mantelshelf; a silk mantle; the mantle of darkness;
MARSHAL – MARTIAL (маршал, выстроить – военный): air marshal; to marshal facts; martial law;
MATCH – MATCH (спичка – ровня, пара, подходить под пару, состязание, матч): to strike a match; a perfect match of colors; these two things don’t match; a football match;
MEAN – MEAN – MEAN (значить – плохой, скудный, низкий, подлый – средний, средняя величина): What do you mean? a mean trick; it was mean of him; mean time; mean speed;
MEAT – MEET (мясо – встретить): meat and potatoes; to meet a girl; to meet with friends;
MEDAL – MEDDLE (медаль – вмешиваться): a gold medal; to meddle in someone’s affairs;
METAL – METTLE (металл – характер): a metal door; to show one’s mettle; full of mettle;
MIGHT – MIGHT – MITE – MITE (мощь – мод. гл.: быть возможным – клещ – чуточка, капелька): with all his might; it might be true; the itch mite; a mite of consolation;
MISS – MISS (промахнуться, промах, пропускать, скучать по – мисс): he fired twice and missed; a near miss; she missed her bus; he misses his family; Miss Smith; Miss, can you help me?
MOLE – MOLE (родинка – крот): a black mole on the chin; as blind as a mole;
MOOR – MOOR (заболоченная местность – пришвартовать): moorlands have bad soil; to moor a ship;
MOOSE – MOUSSE (лось – мусс): to hunt moose; chocolate mousse;
MORNING – MOURNING (утро – скорбь, траур): on Monday morning; from morning till night; to be in deep mourning;
MUSCLE – MUSSEL (мускул – мидия): strong muscles; a man of muscle; mussels are mollusks;
NAVAL – NAVEL (военно-морской – пупок): naval academy; naval officer; navel infection;
NONE – NUN (ни один – монахиня): none of them; I have none; nuns and monks; she is a nun;
OAR – OR – ORE (весло – или – руда): a four-oar boat; one or two; iron ore;
PAIL – PALE (ведро – бледный): a pail of water; his face is pale; pale gray;
PAIN – PANE (боль – оконное стекло): dull pain; a pain in the chest; to take pains; window pane;
PAIR – PARE – PEAR (пара – очищать от кожуры – груша): a pair of gloves; to pare an apple; apples and pears;
PAT – PAT (шлепок, хлопок, похлопать, погладить – подходящий, уместный): a pat on the back; to pat a dog; a pat answer;
PEA – slang: PEE (горох – моча, мочиться): green peas; pea soup; to take a pee;
PEACE – PIECE (мир, покой – кусок): peace and quiet; a piece of bread; a piece of paper;
PEAK – PEEK – PIQUE (пик – заглянуть, взглянуть – уязвить, возбудить): a mountain peak; to peek into the hole; his curiosity was piqued;
PEAL – PEEL (звон колоколов, звонить в колокола – кожица, корка, чистить фрукты, овощи): to peal the bells; apple peel; to peel potatoes;
PEDAL – PEDDLE (педаль – торговать вразнос, мелочами): the gas pedal; to peddle goods from door to door;
PEER – PEER – PIER (сверстник, ровня – вглядываться – причал, пирс): peer group; to be judged by one’s peers; she peered into the dark room; the boat is at the pier;
PINE – PINE (сосна – чахнуть, тосковать): pines grow in many regions of the world; a pine forest; to pine with grief; she is pining for home;
PIT – PIT (яма – косточка фрукта, вынимать косточки): to dig a pit; air pit; orchestra pit; the pit of the stomach; a cherry pit (BrE: a cherry stone); to pit cherries (peaches, plums); to remove the pits;
PITCH – PITCH (бросок, высота/уровень/степень, бросать, сооружать – смола): a high-pitched voice; a high pitch of anxiety; to pitch a baseball; to pitch a tent; as black as pitch;
PLACE – PLAICE (место – камбала европейская): it is a good place for a picnic; plaice is European flatfish;
PLAIN – PLANE (ясный, очевидный, простой, равнина – плоскость, плоский): plain answer; plain food; the Great Plains; horizontal plane; plane geometry;
PLANE – PLANE – PLANE (самолёт – рубанок – платан): to go by plane; an airplane; a plane is a tool for smoothing wooden surfaces; a plane tree, or plane, is a large tree with broad leaves;
PLUM – PLUMB (слива – отвес): plums and peaches; to pick the plums; plumb line; plumb bob;
POLE – POLE – POLL (столб, шест – полюс – список избирателей, подсчет голосов, опрос): a telegraph pole; the North Pole; public opinion poll; exit poll;
PORE – PORE – POUR (обдумывать, изучать – пора (в коже) – лить): to pore over a problem; pores in the skin; to pour water into a glass;
POUND – POUND (фунт – колотить): a pound of cheese; to change dollars for pounds; to pound on the door;
PRAY – PREY (молиться – жертва, добыча): to pray to God; easy prey; birds of prey;
PRINCIPAL – PRINCIPLE (главный, начальник – принцип): principal cause; the school principal; a man of principle; on principle;
PROFIT – PROPHET (выгода, прибыль – пророк): profit and loss; he sold his house at a profit; the word «prophet» meant «speaker» in Greek;
PRUNE – PRUNE (чернослив – обрезать ветви, убирать лишнее): prunes are dried plums; to prune trees; to prune costs;
PRY – PRY (любопытствовать, совать нос – с силой / с трудом сдвинуть, открыть, вырвать): to pry into other people’s affairs; to pry the door open;
RACE – RACE (раса – скачки, гонка): the human race; horse racing; a race horse; race cars;
RACK – RACK – WRACK (вешалка, подставка, полка – пытка, пытать, мучить – разрушение, гибель): dish rack; luggage rack; to rack one’s brains; to go to wrack and ruin (also: to go to rack and ruin);
RAIN – REIGN – REIN (дождь – царствование – вожжа): it looks like rain; during his reign; a pair of reins;
RAP – WRAP (лёгкий удар, слегка/быстро ударять, стучать – шаль, шарф, обёртывать, завернуть): he rapped at the door; she wrapped the package in brown paper;
READ – REED (читать – тростник): to read a book; reed grows near water;
REEK – WREAK (вонь, вонять – излить на): to reek of alcohol; to wreak havoc on the enemy;
REST – REST – WREST (отдых, отдыхать – остаток, остальное – вырвать силой): rest a little; leave the rest of them here; to wrest a knife from someone’s hands;
RETCH – WRETCH (вызывать рвоту – жалкий человек, негодяй): it made her retch; a poor wretch;
REVIEW – REVUE (обзор, рецензия, рассматривать – ревю): to write a review; theatrical revue;
RIGHT – RITE – WRITE (правильный, правый, право – обряд – писать): that’s right; my right hand; civil rights; funeral rites; write a letter;
RING – RING – WRING (кольцо – звонить – скручивать): a wedding ring; to ring a bell; to wring one’s hands;
ROCK – ROCK (скала, камень – качать, качаться, качание): as firm as a rock; to rock the cradle; to rock the boat;
ROLE – ROLL (роль – рулон, катить): to play a role; a roll of toilet paper; the ball rolled away;
ROOT – ROUTE (корень – маршрут): the roots of the tree; Route 10; bus route;
ROW [rou] – ROW [rou] – ROE [rou] – ROE [rou] (ряд – грести – косуля – икра рыб): to sit in the first row; to stand in a row; to row the boat; a roe deer is also called a roe; the roe of sturgeon is called caviar;
RYE – WRY (рожь – кривой): rye bread; rye whiskey; a wry smile; a wry look;
SAIL – SALE (парус, плыть – распродажа): to sail on a ship; I bought it on sale;
SAW – SAW (пила, пилить – старинная пословица, изречение): to saw a log; an old saw;
SEA – SEE (море – видеть): the Black Sea; I want to see the sea. Have you ever seen the sea at sunrise? Did you see it?
SEAL – SEAL (печать, ставить печать, запечатывать – тюлень): the seal of fate; to seal an envelope; seals are sea mammals;
SEAM – SEEM (шов – казаться): Please take it in at the seams. She seems to be a little nervous.
SERF – SURF (крепостной, раб – прибой, плыть на гребне волны, заниматься серфингом): liberation of the serfs; the sound of the surf; to ride a surfboard; surfing;
SEW – SO – SOW (шить – так – сеять): to sew a dress; be so kind; to sow the seeds;
SHEAR – SHEER – SHEER (срезать, ножницы – прозрачный, абсолютный – отклониться от курса): to shear sheep; a pair of shears; sheer stockings; sheer nonsense; the ship was able to sheer off to avoid the collision;
SIGHT – SITE – CITE (вид, зрение – место – цитировать): a beautiful sight; to see the sights; good eyesight; construction site; website; to cite from a book;
SLAY – SLEIGH (сразить, умертвить – сани): slain by a bullet; a horse-drawn sleigh; sleigh bells;
SLEIGHT – SLIGHT – SLIGHT (ловкость – небольшой – пренебрежение, пренебрегать): a sleight of hand; a slight fever; to slight one’s duties;
SOAR – SORE (парить, взмывать – болячка, воспалённый): prices soared; a cold sore; a sore throat;
SOLE – SOLE – SOLE – SOUL (единственный – подошва – камбала – душа): sole heir; shoe sole; fillet of sole; body and soul;
SOME – SUM (какой-то, некоторый – сумма): I need some money; a large sum of money;
SON – SUN (сын – солнце): he is my son; she has three sons; the sun is shining;
SOUND – SOUND – SOUND – SOUND (звук – здоровый – зонд, щуп, измерять глубину, зондировать – узкий пролив): the sounds of music; a sound mind in a sound body; to sound the depth; the Long Island Sound;
STABLE – STABLE (конюшня – стабильный, прочный): a stable full of horses; a stable position;
STAIR – STARE (ступенька – пристально смотреть): go down the stairs; don’t stare at people;
STAKE – STAKE – STEAK (кол, столб – ставка – бифштекс): to pull up stakes; the stakes are high; I’d like a steak for dinner;
STALK – STALK (стебель – выслеживать, подкрадываться): corn stalk; to stalk a deer;
STATIONARY – STATIONERY (неподвижный – писчая бумага и др. канц. товары): stationary bicycle; letterhead stationery;
STEAL – STEEL (красть – сталь): to steal money; to steal a kiss; stainless steel; a heart of steel;
STEP – STEPPE (шаг, шагнуть – степь): the next step; to step forward; alpine steppe;
STICK – STICK (палка, палочка – воткнуть, проколоть, вставить, высунуть, приклеить): he struck him with a stick; to stick a needle into one’s finger; to stick a stamp on an envelope;
STRAIGHT – STRAIT (прямой – узкий пролив): a straight road; the Strait of Gibraltar;
SUITE – SWEET (комплект, номер-люкс, сюита – сладкий): a hotel suite; this cake is too sweet;
TAIL – TALE (хвост – рассказ): a bird with a long tail; a long and interesting tale;
TEA – TEE – TEE (чай – T-образный – метка для мяча в гольфе): a cup of tea; a tea party; a tee joint; to a tee; to tee off;
TEAM – TEEM (команда, объединяться – изобиловать): a football team; to teem with fish;
TEAR – TIER (слеза – ярус): tears in her eyes; the second tier;
THYME – TIME (тимьян – время): thyme is used for seasoning; I need more time;
TIC – TICK – TICK – TICK (тик – тикать, тиканье, галочка – клещ – чехол для матраца): to suffer from tic; the ticking of the clock; to mark with a tick; tick fever; bedtick;
TIP – TIP – TIP – TIP (кончик – наклонить – чаевые – намёк, совет, предупредить): the tip of the tongue; to tip the scales; a one-dollar tip; to give a tip; useful tips on gardening; to tip off;
TOAST – TOAST (тост, гренок – тост за): a piece of toast; I’d like to propose a toast to Alan’s health;
TOE – TOW (палец ноги – буксир, буксировать): I stubbed my toe; a tow truck; to tow a car;
TOO – TWO (тоже – два): I like it too. I spent two days at the lake.
TRAIN – TRAIN (поезд – учить, тренировать): to go by train; to train nurses; to train for the championship;
TRUNK – TRUNK (ствол дерева, туловище, хобот слона – сундук, багажник): the trunk of a tree; an elephant’s trunk; a wooden trunk; the trunk of a car;
VAIN – VANE – VEIN (тщетный, тщеславный – флюгер, лопасть – вена): in vain; she is vain; a weather vane; the vanes of a turbine; veins carry blood to the heart;
VICE – VISE, VICE (порок – тиски): vice squad; organized vice; table vise; vise clamp;
WAIL – WHALE (вопль, вой, вопить, выть – кит): a wail of grief; to wail with pain; killer whales;
WAIST – WASTE (талия – излишняя трата): a slender waist; a waste of time; to waste money;
WAIT – WEIGHT (ждать – вес): to wait for an hour; her weight is 65 kilograms;
WAIVE – WAVE (отказаться от требования – волна, качаться, махать): to waive a claim; ocean waves; a wave of emotion; to wave a flag;
WARE – WEAR – WHERE (изделия – одежда, носить одежду – где): glassware; kitchenware; women’s wear; sportswear; she is wearing a suit; Where is Mike?
WAY – WEIGH – WHEY (путь – взвесить – молочная сыворотка): to find a way; the shortest way; to weigh potatoes; she weighs 65 kilograms; curd and whey;
WEAK – WEEK (слабый – неделя): weak eyes; weak will; next week; for two weeks;
WEATHER – WHETHER (погода – ли): nice weather; ask her whether she wants to go;
WELL – WELL (хорошо – колодец): very well; to feel well; a deep well;
WET – WHET (мокрый – обострить): wet hands; wet floor; to whet a knife; to whet the appetite;
WHICH – WITCH (который – ведьма, колдунья): which of these; Which bag is yours? She is a real witch.
WHINE – WINE (скулить – вино): my dog often whines; stop whining; red wine; French wines;
WILL – WILL (вспом. и мод. гл.: будет – воля, желание, завещание): he will see you tomorrow; he has the will to succeed;
YOKE – YOLK (ярмо, хомут, иго – желток): the yoke of slavery; the yolk of an egg.
The same spelling, different pronunciation, different meaning
(Одинаковое написание, разное произношение, разное значение)
BOW [bou] – BOW [bau] – BOW [bau] (лук для стрельбы, дуга, смычок, бант, галстук-бабочка – поклон, наклонить – корма судна): a bow and arrows; a rainbow; the bow of a violin; a bow tie; to take a bow; to bow one’s head; the ship’s bow;
DESERT [‘dezərt] – DESERT [di’zərt] (пустыня – покидать): the Sahara Desert; he deserted her;
FORTE [fo:rt] – FORTE [‘fo:rtei], [‘fo:rti] (сильная сторона – муз.: форте): good spelling is her forte; forte-piano;
LEAD [li:d] – LEAD [led] (вести – свинец): this road leads to the lake; as heavy as lead;
ROW [rou] – ROW [rau] (ряд – ссора): Please stand in a row. My neighbors had a row yesterday.
SOW [sou] – SOW [sau] (сеять – свинья): to sow the seeds; to raise sows;
TEAR [tiər] – TEAR [teər] (слеза – рвать): tears in her eyes; to tear up his letter;
WIND [wind] – WIND [waind] (ветер – извиваться, заводить): a cold wind; to wind the clock.
Note: Homonyms in the form of proper names are not included in the list because there may be hundreds of them. Examples: bet – Bette; bell – Belle; bill – Bill; may – May – Mae; cliff – Cliff; penny – Penny; capital – Capitol; grease – Greece; main – Maine. (Омонимы в виде имён собственных не включены в список, т.к. их могут быть сотни.)
Homonyms with certain word forms
Many other homonyms occur when verbs, nouns, or pronouns are used in certain forms showing person, number, or tense. Word order and meaning help us to distinguish between such homonyms aurally. Examples: He left the house to his son. The house on the left belongs to my aunt. The list below provides examples of word forms that have the same pronunciation as some other words.
Многие другие омонимы возникают, когда глаголы, существительные или местоимения употреблены в некоторых формах, показывающих лицо, число или время. Порядок слов и значение помогают нам различить такие омонимы на слух. Примеры: He left the house to his son. (Он оставил дом своему сыну.) The house on the left belongs to my aunt. (Дом слева принадлежит моей тёте.) Список ниже дает примеры словоформ, которые имеют одинаковое произношение с некоторыми другими словами.
Third person singular:
sees – seize – seas (видит – схватить – моря); knows – nose (знает – нос); brews – bruise (варит – синяк); adds – ads (добавляет – объявления); links – lynx (соединяет – рысь); means – means (значит – средство); pries – prize (суёт нос в чужие дела – приз); prays – praise (молится – похвала, хвалить);
Past Indefinite:
allowed – aloud (разрешил – вслух); banned – band (запретил – отряд, группа); bored – board (заскучавший – доска); fined – find (оштрафовал – найти); leased – least (арендовал – наименьший); missed – mist (пропустил – туман); passed – past (прошёл – прошлое); owed – ode (был должен – ода); mowed – mode (скосил – способ); towed – toad (буксировал – жаба); mustered – mustard (собрал – горчица); tied – tide (связал – прилив);
led – lead [led] (вёл – свинец); read [red] – red (прочитал – красный); rode – road (ехал – дорога); made – maid (сделал – девушка); saw (увидел) – saw (пила); sent – cent (послал – цент); blew – blue (подул – синий); flew – flu (летел – грипп); knew – new (знал – новый); threw – through (бросил – сквозь); ate – eight (ел – восемь); won – one (выиграл – один); heard – herd (слышал – стадо); left – left (ушёл – левый); wore – war (был одет в – война); would – wood;
Past Participle:
ground – ground (молотый – земля); grown – groan (выращенный – стон); mown – moan (скошенный – стон); thrown – throne (брошенный – трон); seen – scene (увиденный – сцена); lain – lane (пролежавший – узкая дорога);
Plural nouns:
rays – raise (лучи – поднять); days – daze (дни – оцепенение); rows – rose – rose (ряды – роза – поднялся); brows – browse (брови – просматривать); claws – clause (когти – статья, пункт); seas – seize (моря – схватить); feet – feat (ступни, ноги – достижение, подвиг, мастерство);
Pronouns:
him – hymn (его – гимн); mine – mine (мой – рудник, мина); our – hour (наш – час); their – there (их – там);
Contractions:
who’s – whose (кто есть – чей); it’s – its (это есть – её); there’s – theirs (там есть – их); I’ll – aisle (я буду – проход); he’ll – heel (он будет – пятка); we’ll – wheel (мы будем – колесо); we’d – weed (мы бы – сорняк); he’d – heed (он бы – внимание);
Words with suffixes:
fourth – forth (четвёртый – вперёд); higher – hire (выше – нанимать); miner – minor (шахтёр – небольшой); chilly – chili (холодный – перец чили); wholly – holy (целиком – святой);
Two-word combination – one word:
all ready – already (всё готово – уже); all together – altogether (все вместе – вполне, совсем); any way – anyway (любой путь – во всяком случае); he may be there – maybe he is there (он может быть там – возможно он там); mean time (среднее время) – meantime (тем временем).
Note: In British English, homonyms (homophones) may also occur in some of those cases where the sound [r] is not pronounced in words. For example: arms – alms; pour – paw; sore – saw; sort – sought; court – caught, etc. Such words are not homophones in American English where the sound [r] is pronounced in all cases. Note that «ant» and «aunt», pronounced [ænt], are homophones in American English.
Homonymous constructions
In English, not only words but whole constructions can be homonymous in their structure. Due to the limited number of different grammatical forms, the same form is used in different functions. For example, there are only two case forms for personal pronouns (I — me, he – him, we – us, etc.) and only one case form for nouns (i.e., in fact there are no case forms for nouns); the ending ING is used for gerund, present participle, and some adjectives; IT is used as a pronoun in the third person singular for inanimate objects and as a grammatical subject in impersonal sentences. As a result, homonymous constructions appear. Compare these examples:
В английском языке не только слова, но и целые конструкции могут быть омонимичными по своему построению. Из-за ограниченного числа разных грамматических форм, одна и та же форма используется в разных функциях. Например, есть только две формы падежей для личных местоимений (I — me, he – him, we – us и т.д.) и только одна форма падежей для существительных (т.е. фактически нет форм падежей существительных); окончание ING используется для герундия, причастия настоящего времени и некоторых прилагательных; IT используется как местоимение в 3 лице ед. числа для неодушевлённых предметов и как грамматическое подлежащее в безличных предложениях. Как результат, появляются омонимичные конструкции. Сравните эти примеры:
She called him a taxi. (Она вызвала ему такси.) – She called him an idiot. (Она назвала его идиотом.)
They made him a hero. (Они сделали его героем.) – They made him a sandwich. (Они сделали ему бутерброд.)
I see a moving ‘truck. (Я вижу движущийся грузовик.) – I see a ‘moving truck. (Я вижу грузовик для перевозки мебели.)
He is reading. (Он читает.) – He is interesting. (Он интересный.)
It’s water. (Это вода.) – It’s Monday. (Понедельник. – т.е. Сегодня понедельник.)
It’s cold. (Оно холодное. – о предмете) – It’s cold. (Холодно. – о погоде)