While the use of a word «Lead» or «Leadership» is contextual, the Etymology of Lead, does assist us in seeing how we have come to perceive a word’s meaning. It also may give us clues as to what concepts societies have attached to it.
Let, then, break down «leadership» by associating a concept to it and then ask the vital questions of whether it is something for you and why. We start by looking at the etymology, since language is the fundamental device by which we convey ideas. There must be agreement on a term before using it. Keep in mind, however, that etymology, and in this case the etymology of lead, isn’t the final verdict on how a term should be used; it only gives an idea of how people have used the term in the past. In other words it helps us place the word in context but is not meant to bind us to that usage.
There are various etymological accounts for the word «lead», from which «leadership» comes. We have:
From Middle English leed, from Old English lēad («lead»), from Proto-Germanic *laudan («lead»), from Proto-Indo-European *lAudh- («lead»). Cognate with West Frisian lead («lead»), Dutch lood («lead»), German Lot («solder, plummet, sounding line»), Swedish lod («lead»), Irish luaidhe («lead»), Lithuanian liudē («plumb, plummet, plumbline»).
Alternative etymology suggests the possibility that Proto-Germanic *laudan may derive from Proto-Celtic *loudhom, from an assumed Proto-Italo-Celtic *ploudhom, from Proto-Indo-European *plou(d)- («to flow»). If so, then cognate with Latin plumbum («lead»). [1]
and —
Origin:
before 900; Middle English leden, Old English lǣdan (causative of līthan to go, travel); cognate with Dutch leiden, German leiten, Old Norse leitha. [2]
and, still —
lead (v.)
«to guide,» O.E. lædan «cause to go with one, lead,» causative of liðan «to travel,» from W.Gmc. *laithjan (cf. O.S. lithan, O.N. liða «to go,» O.H.G. ga-lidan «to travel,» Goth. ga-leiþan «to go»). Meaning «to be in first place» is from late 14c. The noun is first recorded c.1300, «action of leading.» Meaning «the front or leading place» is from 1560s. Johnson stigmatized it as «a low, despicable word.» Sense in card-playing is from 1742; in theater, from 1831; in journalism, from 1927; in jazz bands, from 1934. [3]
Then, there is Webster’s:
Origin of LEAD
Middle English leden, from Old English lǣdan; akin to Old High German leiten to lead, Old English līthan to go
First Known Use: before 12th century [4]
All these commonly accessed sources center on 900 C.E.-onward. There surely was word for the concept of one following the other before this time, but it is interesting to note that there does not seem to a pre-900 B.C.E. history, i.e., there is no Western classical etymology of lead, such as in Latin or Greek, or any roots in Asia, Africa, or the Orient. Even in Europe, «leader» and its antecedents seem to have been looked upon with disfavor in the Renaissance by Johnson. To get more of a personal use of the word, we have to jump to another concept to get the same or similar meaning of «lead». For «conduct», we go back to Classical times and find ducere. [5] Indeed, Benito Mussolini referred to himself as «Duce», comparable to the German «Fuehrer», or, literally, «leader». Now these are personalization’s! One then may wonder that with all the courses and programs, and almost an obsession with persons becoming a «leader», why isn’t a word along the lines of «conductor» used instead to highlight the fact a person is involved? Why not courses in «conductorship», because the Latin seems to be more personalized.
Share your thoughts
Leaders are constantly seeking to exchange their knowledge, because that’s how we increase our leadership skills.
What Other Leaders Have Said
Click below to see contributions from other leaders to this page…
Leaders, Technical Specialist? Not rated yet
I think a leader should lead himself to learn from the team. We can see in this world, the teachers or the Gurus are the real leaders, who learn first …
Click here to write your own.
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lead | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | (led) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | metallic gray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Pb) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lead in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 14 (carbon group) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 600.61 K (327.46 °C, 621.43 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 2022 K (1749 °C, 3180 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 11.34 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 10.66 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 4.77 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 179.5 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 26.650 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −4, −2, −1, 0,[2] +1, +2, +3, +4 (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.33 (in +4), 1.87 (in +2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 175 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 146±5 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 202 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Spectral lines of lead |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc)
a=495.08 pm |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 1190 m/s (at r.t.) (annealed) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 28.9 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 35.3 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 208 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −23.0×10−6 cm3/mol (at 298 K)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young’s modulus | 16 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 5.6 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 46 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.44 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 38–50 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7439-92-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Middle East (7000 BCE) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symbol | «Pb»: from Latin plumbum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Isotopes of lead
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Isotopic abundances vary greatly by sample[5] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| references |
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin plumbum) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children.
Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the group, lead tends to bond with itself; it can form chains and polyhedral structures.
Since lead is easily extracted from its ores, prehistoric people in the Near East were aware of it. Galena is a principal ore of lead which often bears silver. Interest in silver helped initiate widespread extraction and use of lead in ancient Rome. Lead production declined after the fall of Rome and did not reach comparable levels until the Industrial Revolution. Lead played
a crucial role in the development of the printing press, as movable type could be relatively easily cast from lead alloys.[6] In 2014, the annual global production of lead was about ten million tonnes, over half of which was from recycling. Lead’s high density, low melting point, ductility and relative inertness to oxidation make it useful. These properties, combined with its relative abundance and low cost, resulted in its extensive use in construction, plumbing, batteries, bullets and shot, weights, solders, pewters, fusible alloys, white paints, leaded gasoline, and radiation shielding.
Lead’s toxicity became widely recognized in the late 19th century, although a number of well-educated ancient Greek and Roman writers were aware of this fact and even knew some of the symptoms of lead poisoning. Lead is a neurotoxin that accumulates in soft tissues and bones; it damages the nervous system and interferes with the function of biological enzymes, causing neurological disorders ranging from behavioral problems to brain damage, and also affects general health, cardiovascular, and renal systems.
Physical properties[edit]
Atomic[edit]
A lead atom has 82 electrons, arranged in an electron configuration of [Xe]4f145d106s26p2. The sum of lead’s first and second ionization energies—the total energy required to remove the two 6p electrons—is close to that of tin, lead’s upper neighbor in the carbon group. This is unusual; ionization energies generally fall going down a group, as an element’s outer electrons become more distant from the nucleus, and more shielded by smaller orbitals.
The sum of the first four ionization energies of lead exceeds that of tin,[7] contrary to what periodic trends would predict. This is explained by relativistic effects, which become significant in heavier atoms,[8] which contract s and p orbitals such that lead’s 6s electrons have larger binding energies than its 5s electrons.[9] A consequence is the so-called inert pair effect: the 6s electrons of lead become reluctant to participate in bonding, stabilising the +2 oxidation state and making the distance between nearest atoms in crystalline lead unusually long.[10]
Lead’s lighter carbon group congeners form stable or metastable allotropes with the tetrahedrally coordinated and covalently bonded diamond cubic structure. The energy levels of their outer s- and p-orbitals are close enough to allow mixing into four hybrid sp3 orbitals. In lead, the inert pair effect increases the separation between its s- and p-orbitals, and the gap cannot be overcome by the energy that would be released by extra bonds following hybridization.[11] Rather than having a diamond cubic structure, lead forms metallic bonds in which only the p-electrons are delocalized and shared between the Pb2+ ions. Lead consequently has a face-centered cubic structure[12] like the similarly sized[13] divalent metals calcium and strontium.[14][a][b][c]
Bulk[edit]
Pure lead has a bright, shiny gray appearance with a hint of blue.[19] It tarnishes on contact with moist air and takes on a dull appearance, the hue of which depends on the prevailing conditions. Characteristic properties of lead include high density, malleability, ductility, and high resistance to corrosion due to passivation.[20]
A sample of lead solidified from the molten state
Lead’s close-packed face-centered cubic structure and high atomic weight result in a density[21] of 11.34 g/cm3, which is greater than that of common metals such as iron (7.87 g/cm3), copper (8.93 g/cm3), and zinc (7.14 g/cm3).[22] This density is the origin of the idiom to go over like a lead balloon.[23][24][d] Some rarer metals are denser: tungsten and gold are both at 19.3 g/cm3, and osmium—the densest metal known—has a density of 22.59 g/cm3, almost twice that of lead.[25]
Lead is a very soft metal with a Mohs hardness of 1.5; it can be scratched with a fingernail.[26] It is quite malleable and somewhat ductile.[27][e] The bulk modulus of lead—a measure of its ease of compressibility—is 45.8 GPa. In comparison, that of aluminium is 75.2 GPa; copper 137.8 GPa; and mild steel 160–169 GPa.[28] Lead’s tensile strength, at 12–17 MPa, is low (that of aluminium is 6 times higher, copper 10 times, and mild steel 15 times higher); it can be strengthened by adding small amounts of copper or antimony.[29]
The melting point of lead—at 327.5 °C (621.5 °F)[30]—is very low compared to most metals.[21][f] Its boiling point of 1749 °C (3180 °F)[30] is the lowest among the carbon group elements. The electrical resistivity of lead at 20 °C is 192 nanoohm-meters, almost an order of magnitude higher than those of other industrial metals (copper at 15.43 nΩ·m; gold 20.51 nΩ·m; and aluminium at 24.15 nΩ·m).[32] Lead is a superconductor at temperatures lower than 7.19 K;[33] this is the highest critical temperature of all type-I superconductors and the third highest of the elemental superconductors.[34]
Isotopes[edit]
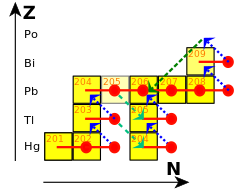
Natural lead consists of four stable isotopes with mass numbers of 204, 206, 207, and 208,[35] and traces of five short-lived radioisotopes.[36] The high number of isotopes is consistent with lead’s atomic number being even.[g] Lead has a magic number of protons (82), for which the nuclear shell model accurately predicts an especially stable nucleus.[37] Lead-208 has 126 neutrons, another magic number, which may explain why lead-208 is extraordinarily stable.[37]
With its high atomic number, lead is the heaviest element whose natural isotopes are regarded as stable; lead-208 is the heaviest stable nucleus. (This distinction formerly fell to bismuth, with an atomic number of 83, until its only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, was found in 2003 to decay very slowly.)[h] The four stable isotopes of lead could theoretically undergo alpha decay to isotopes of mercury with a release of energy, but this has not been observed for any of them; their predicted half-lives range from 1035 to 10189 years[40] (at least 1025 times the current age of the universe).
Three of the stable isotopes are found in three of the four major decay chains: lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208 are the final decay products of uranium-238, uranium-235, and thorium-232, respectively.[41] These decay chains are called the uranium chain, the actinium chain, and the thorium chain.[42] Their isotopic concentrations in a natural rock sample depends greatly on the presence of these three parent uranium and thorium isotopes. For example, the relative abundance of lead-208 can range from 52% in normal samples to 90% in thorium ores;[43] for this reason, the standard atomic weight of lead is given to only one decimal place.[44] As time passes, the ratio of lead-206 and lead-207 to lead-204 increases, since the former two are supplemented by radioactive decay of heavier elements while the latter is not; this allows for lead–lead dating. As uranium decays into lead, their relative amounts change; this is the basis for uranium–lead dating.[45] Lead-207 exhibits nuclear magnetic resonance, a property that has been used to study its compounds in solution and solid state,[46][47] including in the human body.[48]
Apart from the stable isotopes, which make up almost all lead that exists naturally, there are trace quantities of a few radioactive isotopes. One of them is lead-210; although it has a half-life of only 22.2 years,[35] small quantities occur in nature because lead-210 is produced by a long decay series that starts with uranium-238 (that has been present for billions of years on Earth). Lead-211, −212, and −214 are present in the decay chains of uranium-235, thorium-232, and uranium-238, respectively, so traces of all three of these lead isotopes are found naturally. Minute traces of lead-209 arise from the very rare cluster decay of radium-223, one of the daughter products of natural uranium-235, and the decay chain of neptunium-237, traces of which are produced by neutron capture in uranium ores. Lead-210 is particularly useful for helping to identify the ages of samples by measuring its ratio to lead-206 (both isotopes are present in a single decay chain).[49]
In total, 43 lead isotopes have been synthesized, with mass numbers 178–220.[35] Lead-205 is the most stable radioisotope, with a half-life of around 1.73×107 years.[i] The second-most stable is lead-202, which has a half-life of about 52,500 years, longer than any of the natural trace radioisotopes.[35]
Chemistry[edit]
Bulk lead exposed to moist air forms a protective layer of varying composition. Lead(II) carbonate is a common constituent;[51][52][53] the sulfate or chloride may also be present in urban or maritime settings.[54] This layer makes bulk lead effectively chemically inert in the air.[54] Finely powdered lead, as with many metals, is pyrophoric,[55] and burns with a bluish-white flame.[56]
Fluorine reacts with lead at room temperature, forming lead(II) fluoride. The reaction with chlorine is similar but requires heating, as the resulting chloride layer diminishes the reactivity of the elements.[54] Molten lead reacts with the chalcogens to give lead(II) chalcogenides.[57]
Lead metal resists sulfuric and phosphoric acid but not hydrochloric or nitric acid; the outcome depends on insolubility and subsequent passivation of the product salt.[58] Organic acids, such as acetic acid, dissolve lead in the presence of oxygen.[54] Concentrated alkalis will dissolve lead and form plumbites.[59]
Inorganic compounds[edit]
Lead shows two main oxidation states: +4 and +2. The tetravalent state is common for the carbon group. The divalent state is rare for carbon and silicon, minor for germanium, important (but not prevailing) for tin, and is the more important of the two oxidation states for lead.[54] This is attributable to relativistic effects, specifically the inert pair effect, which manifests itself when there is a large difference in electronegativity between lead and oxide, halide, or nitride anions, leading to a significant partial positive charge on lead. The result is a stronger contraction of the lead 6s orbital than is the case for the 6p orbital, making it rather inert in ionic compounds. The inert pair effect is less applicable to compounds in which lead forms covalent bonds with elements of similar electronegativity, such as carbon in organolead compounds. In these, the 6s and 6p orbitals remain similarly sized and sp3 hybridization is still energetically favorable. Lead, like carbon, is predominantly tetravalent in such compounds.[60]
There is a relatively large difference in the electronegativity of lead(II) at 1.87 and lead(IV) at 2.33. This difference marks the reversal in the trend of increasing stability of the +4 oxidation state going down the carbon group; tin, by comparison, has values of 1.80 in the +2 oxidation state and 1.96 in the +4 state.[61]
Lead(II)[edit]
Lead(II) compounds are characteristic of the inorganic chemistry of lead. Even strong oxidizing agents like fluorine and chlorine react with lead to give only PbF2 and PbCl2.[54] Lead(II) ions are usually colorless in solution,[62] and partially hydrolyze to form Pb(OH)+ and finally [Pb4(OH)4]4+ (in which the hydroxyl ions act as bridging ligands),[63][64] but are not reducing agents as tin(II) ions are. Techniques for identifying the presence of the Pb2+ ion in water generally rely on the precipitation of lead(II) chloride using dilute hydrochloric acid. As the chloride salt is sparingly soluble in water, in very dilute solutions the precipitation of lead(II) sulfide is instead achieved by bubbling hydrogen sulfide through the solution.[65]
Lead monoxide exists in two polymorphs, litharge α-PbO (red) and massicot β-PbO (yellow), the latter being stable only above around 488 °C. Litharge is the most commonly used inorganic compound of lead.[66] There is no lead(II) hydroxide; increasing the pH of solutions of lead(II) salts leads to hydrolysis and condensation.[67]
Lead commonly reacts with heavier chalcogens. Lead sulfide is a semiconductor, a photoconductor, and an extremely sensitive infrared radiation detector. The other two chalcogenides, lead selenide and lead telluride, are likewise photoconducting. They are unusual in that their color becomes lighter going down the group.[68]
Lead dihalides are well-characterized; this includes the diastatide[69] and mixed halides, such as PbFCl. The relative insolubility of the latter forms a useful basis for the gravimetric determination of fluorine. The difluoride was the first solid ionically conducting compound to be discovered (in 1834, by Michael Faraday).[70] The other dihalides decompose on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, especially the diiodide.[71] Many lead(II) pseudohalides are known, such as the cyanide, cyanate, and thiocyanate.[68][72] Lead(II) forms an extensive variety of halide coordination complexes, such as [PbCl4]2−, [PbCl6]4−, and the [Pb2Cl9]n5n− chain anion.[71]
Lead(II) sulfate is insoluble in water, like the sulfates of other heavy divalent cations. Lead(II) nitrate and lead(II) acetate are very soluble, and this is exploited in the synthesis of other lead compounds.[73]
Lead(IV)[edit]
Few inorganic lead(IV) compounds are known. They are only formed in highly oxidizing solutions and do not normally exist under standard conditions.[74] Lead(II) oxide gives a mixed oxide on further oxidation, Pb3O4. It is described as lead(II,IV) oxide, or structurally 2PbO·PbO2, and is the best-known mixed valence lead compound. Lead dioxide is a strong oxidizing agent, capable of oxidizing hydrochloric acid to chlorine gas.[75] This is because the expected PbCl4 that would be produced is unstable and spontaneously decomposes to PbCl2 and Cl2.[76] Analogously to lead monoxide, lead dioxide is capable of forming plumbate anions. Lead disulfide[77] and lead diselenide[78] are only stable at high pressures. Lead tetrafluoride, a yellow crystalline powder, is stable, but less so than the difluoride. Lead tetrachloride (a yellow oil) decomposes at room temperature, lead tetrabromide is less stable still, and the existence of lead tetraiodide is questionable.[79]
Other oxidation states[edit]
Some lead compounds exist in formal oxidation states other than +4 or +2. Lead(III) may be obtained, as an intermediate between lead(II) and lead(IV), in larger organolead complexes; this oxidation state is not stable, as both the lead(III) ion and the larger complexes containing it are radicals.[81][82][83] The same applies for lead(I), which can be found in such radical species.[84]
Numerous mixed lead(II,IV) oxides are known. When PbO2 is heated in air, it becomes Pb12O19 at 293 °C, Pb12O17 at 351 °C, Pb3O4 at 374 °C, and finally PbO at 605 °C. A further sesquioxide, Pb2O3, can be obtained at high pressure, along with several non-stoichiometric phases. Many of them show defective fluorite structures in which some oxygen atoms are replaced by vacancies: PbO can be considered as having such a structure, with every alternate layer of oxygen atoms absent.[85]
Negative oxidation states can occur as Zintl phases, as either free lead anions, as in Ba2Pb, with lead formally being lead(−IV),[86] or in oxygen-sensitive ring-shaped or polyhedral cluster ions such as the trigonal bipyramidal Pb52− ion, where two lead atoms are lead(−I) and three are lead(0).[87] In such anions, each atom is at a polyhedral vertex and contributes two electrons to each covalent bond along an edge from their sp3 hybrid orbitals, the other two being an external lone pair.[63] They may be made in liquid ammonia via the reduction of lead by sodium.[88]
Organolead[edit]
Lead can form multiply-bonded chains, a property it shares with its lighter homologs in the carbon group. Its capacity to do so is much less because the Pb–Pb bond energy is over three and a half times lower than that of the C–C bond.[57] With itself, lead can build metal–metal bonds of an order up to three.[89] With carbon, lead forms organolead compounds similar to, but generally less stable than, typical organic compounds[90] (due to the Pb–C bond being rather weak).[63] This makes the organometallic chemistry of lead far less wide-ranging than that of tin.[91] Lead predominantly forms organolead(IV) compounds, even when starting with inorganic lead(II) reactants; very few organolead(II) compounds are known. The most well-characterized exceptions are Pb[CH(SiMe3)2]2 and Pb(η5-C5H5)2.[91]
The lead analog of the simplest organic compound, methane, is plumbane. Plumbane may be obtained in a reaction between metallic lead and atomic hydrogen.[92] Two simple derivatives, tetramethyllead and tetraethyllead, are the best-known organolead compounds. These compounds are relatively stable: tetraethyllead only starts to decompose if heated[93] or if exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet light.[94][j] With sodium metal, lead readily forms an equimolar alloy that reacts with alkyl halides to form organometallic compounds such as tetraethyllead.[95] The oxidizing nature of many organolead compounds is usefully exploited: lead tetraacetate is an important laboratory reagent for oxidation in organic synthesis.[96] Tetraethyllead, once added to gasoline, was produced in larger quantities than any other organometallic compound.[91] Other organolead compounds are less chemically stable.[90] For many organic compounds, a lead analog does not exist.[92]
Origin and occurrence[edit]
| Atomic number |
Element | Relative amount |
|---|---|---|
| 42 | Molybdenum | 0.798 |
| 46 | Palladium | 0.440 |
| 50 | Tin | 1.146 |
| 78 | Platinum | 0.417 |
| 80 | Mercury | 0.127 |
| 82 | Lead | 1 |
| 90 | Thorium | 0.011 |
| 92 | Uranium | 0.003 |
In space[edit]
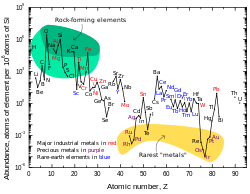
Lead’s per-particle abundance in the Solar System is 0.121 ppb (parts per billion).[97][k] This figure is two and a half times higher than that of platinum, eight times more than mercury, and seventeen times more than gold.[97] The amount of lead in the universe is slowly increasing[98] as most heavier atoms (all of which are unstable) gradually decay to lead.[99] The abundance of lead in the Solar System since its formation 4.5 billion years ago has increased by about 0.75%.[100] The solar system abundances table shows that lead, despite its relatively high atomic number, is more prevalent than most other elements with atomic numbers greater than 40.[97]
Primordial lead—which comprises the isotopes lead-204, lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208—was mostly created as a result of repetitive neutron capture processes occurring in stars. The two main modes of capture are the s- and r-processes.[101]
In the s-process (s is for «slow»), captures are separated by years or decades, allowing less stable nuclei to undergo beta decay.[102] A stable thallium-203 nucleus can capture a neutron and become thallium-204; this undergoes beta decay to give stable lead-204; on capturing another neutron, it becomes lead-205, which has a half-life of around 15 million years. Further captures result in lead-206, lead-207, and lead-208. On capturing another neutron, lead-208 becomes lead-209, which quickly decays into bismuth-209. Bismuth-209 is also radioactive and eventually decays into thallium-205 if left unperturbed. On capturing another neutron, bismuth-209 becomes bismuth-210, and this beta decays to polonium-210, which alpha decays to lead-206. The cycle hence ends at lead-206, lead-207, lead-208, and thallium-205.[103]
In the r-process (r is for «rapid»), captures happen faster than nuclei can decay.[104] This occurs in environments with a high neutron density, such as a supernova or the merger of two neutron stars. The neutron flux involved may be on the order of 1022 neutrons per square centimeter per second.[105] The r-process does not form as much lead as the s-process.[106] It tends to stop once neutron-rich nuclei reach 126 neutrons.[107] At this point, the neutrons are arranged in complete shells in the atomic nucleus, and it becomes harder to energetically accommodate more of them.[108] When the neutron flux subsides, these nuclei beta decay into stable isotopes of osmium, iridium, and platinum.[109]
On Earth[edit]
Lead is classified as a chalcophile under the Goldschmidt classification, meaning it is generally found combined with sulfur.[110] It rarely occurs in its native, metallic form.[111] Many lead minerals are relatively light and, over the course of the Earth’s history, have remained in the crust instead of sinking deeper into the Earth’s interior. This accounts for lead’s relatively high crustal abundance of 14 ppm; it is the 38th most abundant element in the crust.[112][l]
The main lead-bearing mineral is galena (PbS), which is mostly found with zinc ores.[114] Most other lead minerals are related to galena in some way; boulangerite, Pb5Sb4S11, is a mixed sulfide derived from galena; anglesite, PbSO4, is a product of galena oxidation; and cerussite or white lead ore, PbCO3, is a decomposition product of galena. Arsenic, tin, antimony, silver, gold, copper, and bismuth are common impurities in lead minerals.[114]
Lead is a fairly common element in the Earth’s crust for its high atomic number (82). Most elements of atomic number greater than 40 are less abundant.
World lead resources exceed two billion tons. Significant deposits are located in Australia, China, Ireland, Mexico, Peru, Portugal, Russia, and the United States. Global reserves—resources that are economically feasible to extract—totaled 88 million tons in 2016, of which Australia had 35 million, China 17 million, and Russia 6.4 million.[115]
Typical background concentrations of lead do not exceed 0.1 μg/m3 in the atmosphere; 100 mg/kg in soil; 4 mg/kg in vegetation and 5 μg/L in freshwater and seawater.[116]
Etymology[edit]
The modern English word lead is of Germanic origin; it comes from the Middle English leed and Old English lēad (with the macron above the «e» signifying that the vowel sound of that letter is long).[117] The Old English word is derived from the hypothetical reconstructed Proto-Germanic *lauda- (‘lead’).[118] According to linguistic theory, this word bore descendants in multiple Germanic languages of exactly the same meaning.[118]
There is no consensus on the origin of the Proto-Germanic *lauda-. One hypothesis suggests it is derived from Proto-Indo-European *lAudh- (‘lead’; capitalization of the vowel is equivalent to the macron).[119] Another hypothesis suggests it is borrowed from Proto-Celtic *ɸloud-io- (‘lead’). This word is related to the Latin plumbum, which gave the element its chemical symbol Pb. The word *ɸloud-io- is thought to be the origin of Proto-Germanic *bliwa- (which also means ‘lead’), from which stemmed the German Blei.[120]
The name of the chemical element is not related to the verb of the same spelling, which is derived from Proto-Germanic *laidijan- (‘to lead’).[121]
History[edit]
Prehistory and early history[edit]
Metallic lead beads dating back to 7000–6500 BCE have been found in Asia Minor and may represent the first example of metal smelting.[123] At that time lead had few (if any) applications due to its softness and dull appearance.[123] The major reason for the spread of lead production was its association with silver, which may be obtained by burning galena (a common lead mineral).[124] The Ancient Egyptians were the first to use lead minerals in cosmetics, an application that spread to Ancient Greece and beyond;[125] the Egyptians may have used lead for sinkers in fishing nets, glazes, glasses, enamels, and for ornaments.[124] Various civilizations of the Fertile Crescent used lead as a writing material, as coins,[126] and as a construction material.[124] Lead was used in the Ancient Chinese royal court as a stimulant,[124] as currency,[127] and as a contraceptive;[128] the Indus Valley civilization and the Mesoamericans[124] used it for making amulets; and the eastern and southern African peoples used lead in wire drawing.[129]
Classical era[edit]
Because silver was extensively used as a decorative material and an exchange medium, lead deposits came to be worked in Asia Minor from 3000 BCE; later, lead deposits were developed in the Aegean and Laurion.[130] These three regions collectively dominated production of mined lead until c. 1200 BCE.[131] Beginning circa 2000 BCE, the Phoenicians worked deposits in the Iberian peninsula; by 1600 BCE, lead mining existed in Cyprus, Greece, and Sardinia.[132]
Ancient Greek lead sling bullets with a winged thunderbolt molded on one side and the inscription «ΔΕΞΑΙ» («take that» or «catch») on the other side.[133]
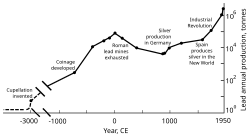
Rome’s territorial expansion in Europe and across the Mediterranean, and its development of mining, led to it becoming the greatest producer of lead during the classical era, with an estimated annual output peaking at 80,000 tonnes. Like their predecessors, the Romans obtained lead mostly as a by-product of silver smelting.[122][134] Lead mining occurred in Central Europe, Britain, the Balkans, Greece, Anatolia, and Hispania, the latter accounting for 40% of world production.[122]
Lead tablets were commonly used as a material for letters.[135] Lead coffins, cast in flat sand forms, with interchangeable motifs to suit the faith of the deceased were used in ancient Judea.[136] Lead was used to make sling bullets from the 5th century BC. In Roman times, lead sling bullets were amply used, and were effective at a distance of between 100 and 150 meters. The Balearic slingers, used as mercenaries in Carthaginian and Roman armies, were famous for their shooting distance and accuracy.[137]
Lead was used for making water pipes in the Roman Empire; the Latin word for the metal, plumbum, is the origin of the English word «plumbing». Its ease of working, its low melting point enabling the easy fabrication of completely waterproof welded joints, and its resistance to corrosion[138] ensured its widespread use in other applications, including pharmaceuticals, roofing, currency, and warfare.[139][140][141] Writers of the time, such as Cato the Elder, Columella, and Pliny the Elder, recommended lead (or lead-coated) vessels for the preparation of sweeteners and preservatives added to wine and food. The lead conferred an agreeable taste due to the formation of «sugar of lead» (lead(II) acetate), whereas copper or bronze vessels could impart a bitter flavor through verdigris formation.[142]
This metal was by far the most used material in classical antiquity, and it is appropriate to refer to the (Roman) Lead Age. Lead was to the Romans what plastic is to us.
Heinz Eschnauer and Markus Stoeppler
«Wine—An enological specimen bank», 1992[143]
The Roman author Vitruvius reported the health dangers of lead[144][145] and modern writers have suggested that lead poisoning played a major role in the decline of the Roman Empire.[146][147][n] Other researchers have criticized such claims, pointing out, for instance, that not all abdominal pain is caused by lead poisoning.[149][150] According to archaeological research, Roman lead pipes increased lead levels in tap water but such an effect was «unlikely to have been truly harmful».[151][152] When lead poisoning did occur, victims were called «saturnine», dark and cynical, after the ghoulish father of the gods, Saturn. By association, lead was considered the father of all metals.[153] Its status in Roman society was low as it was readily available[154] and cheap.[155]
Confusion with tin and antimony[edit]
Since the Bronze Age metallurgists and engineers have understood the difference between rare and valuable tin, essential for alloying with copper to produce tough and corrosion resistant bronze, and ‘cheap and cheerful’ lead. However the nomenclature in some languages is similar. Romans called lead plumbum nigrum («black lead»), and tin plumbum candidum («bright lead»). The association of lead and tin can be seen in other languages: the word olovo in Czech translates to «lead», but in Russian, its cognate олово (olovo) means «tin».[156] To add to the confusion, lead bore a close relation to antimony: both elements commonly occur as sulfides (galena and stibnite), often together. Pliny incorrectly wrote that stibnite would give lead on heating, instead of antimony.[157] In countries such as Turkey and India, the originally Persian name surma came to refer to either antimony sulfide or lead sulfide,[158] and in some languages, such as Russian, gave its name to antimony (сурьма).[159]
Middle Ages and the Renaissance[edit]
Elizabeth I of England was commonly depicted with a whitened face. Lead in face whiteners is thought to have contributed to her death.[160]
Lead mining in Western Europe declined after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, with Arabian Iberia being the only region having a significant output.[161][162] The largest production of lead occurred in South and East Asia, especially China and India, where lead mining grew rapidly.[162]
In Europe, lead production began to increase in the 11th and 12th centuries, when it was again used for roofing and piping. Starting in the 13th century, lead was used to create stained glass.[163] In the European and Arabian traditions of alchemy, lead (symbol ♄ in the European tradition)[164] was considered an impure base metal which, by the separation, purification and balancing of its constituent essences, could be transformed to pure and incorruptible gold.[165] During the period, lead was used increasingly for adulterating wine. The use of such wine was forbidden for use in Christian rites by a papal bull in 1498, but it continued to be imbibed and resulted in mass poisonings up to the late 18th century.[161][166] Lead was a key material in parts of the printing press, and lead dust was commonly inhaled by print workers, causing lead poisoning.[167] Lead also became the chief material for making bullets for firearms: it was cheap, less damaging to iron gun barrels, had a higher density (which allowed for better retention of velocity), and its lower melting point made the production of bullets easier as they could be made using a wood fire.[168] Lead, in the form of Venetian ceruse, was extensively used in cosmetics by Western European aristocracy as whitened faces were regarded as a sign of modesty.[169][170] This practice later expanded to white wigs and eyeliners, and only faded out with the French Revolution in the late 18th century. A similar fashion appeared in Japan in the 18th century with the emergence of the geishas, a practice that continued long into the 20th century. The white faces of women «came to represent their feminine virtue as Japanese women»,[171] with lead commonly used in the whitener.[172]
Outside Europe and Asia[edit]
In the New World, lead production was recorded soon after the arrival of European settlers. The earliest record dates to 1621 in the English Colony of Virginia, fourteen years after its foundation.[173] In Australia, the first mine opened by colonists on the continent was a lead mine, in 1841.[174] In Africa, lead mining and smelting were known in the Benue Trough[175] and the lower Congo Basin, where lead was used for trade with Europeans, and as a currency by the 17th century,[176] well before the scramble for Africa.
Industrial Revolution[edit]
In the second half of the 18th century, Britain, and later continental Europe and the United States, experienced the Industrial Revolution. This was the first time during which lead production rates exceeded those of Rome.[177] Britain was the leading producer, losing this status by the mid-19th century with the depletion of its mines and the development of lead mining in Germany, Spain, and the United States.[178] By 1900, the United States was the leader in global lead production, and other non-European nations—Canada, Mexico, and Australia—had begun significant production; production outside Europe exceeded that within.[179] A great share of the demand for lead came from plumbing and painting—lead paints were in regular use.[180] At this time, more (working class) people were exposed to the metal and lead poisoning cases escalated. This led to research into the effects of lead intake. Lead was proven to be more dangerous in its fume form than as a solid metal. Lead poisoning and gout were linked; British physician Alfred Baring Garrod noted a third of his gout patients were plumbers and painters. The effects of chronic ingestion of lead, including mental disorders, were also studied in the 19th century. The first laws aimed at decreasing lead poisoning in factories were enacted during the 1870s and 1880s in the United Kingdom.[180]
Modern era[edit]
Promotional poster for Dutch Boy lead paint, United States, 1912
Further evidence of the threat that lead posed to humans was discovered in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Mechanisms of harm were better understood, lead blindness was documented, and the element was phased out of public use in the United States and Europe. The United Kingdom introduced mandatory factory inspections in 1878 and appointed the first Medical Inspector of Factories in 1898; as a result, a 25-fold decrease in lead poisoning incidents from 1900 to 1944 was reported.[181] Most European countries banned lead paint—commonly used because of its opacity and water resistance[182]—for interiors by 1930.[183]
The last major human exposure to lead was the addition of tetraethyllead to gasoline as an antiknock agent, a practice that originated in the United States in 1921. It was phased out in the United States and the European Union by 2000.[180]
In the 1970s, the United States and Western European countries introduced legislation to reduce lead air pollution.[184][185] The impact was significant: while a study conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States in 1976–1980 showed that 77.8% of the population had elevated blood lead levels, in 1991–1994, a study by the same institute showed the share of people with such high levels dropped to 2.2%.[186] The main product made of lead by the end of the 20th century was the lead–acid battery.[187]
From 1960 to 1990, lead output in the Western Bloc grew by about 31%.[188] The share of the world’s lead production by the Eastern Bloc increased from 10% to 30%, from 1950 to 1990, with the Soviet Union being the world’s largest producer during the mid-1970s and the 1980s, and China starting major lead production in the late 20th century.[189] Unlike the European communist countries, China was largely unindustrialized by the mid-20th century; in 2004, China surpassed Australia as the largest producer of lead.[190] As was the case during European industrialization, lead has had a negative effect on health in China.[191]
Production[edit]
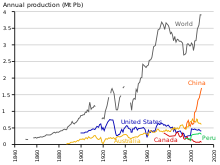
Primary production of lead since 1840
As of 2014, production of lead is increasing worldwide due to its use in lead–acid batteries.[192] There are two major categories of production: primary from mined ores, and secondary from scrap. In 2014, 4.58 million metric tons came from primary production and 5.64 million from secondary production. The top three producers of mined lead concentrate in that year were China, Australia, and the United States.[115] The top three producers of refined lead were China, the United States, and India.[193] According to the International Resource Panel’s Metal Stocks in Society report of 2010, the total amount of lead in use, stockpiled, discarded, or dissipated into the environment, on a global basis, is 8 kg per capita. Much of this is in more developed countries (20–150 kg per capita) rather than less developed ones (1–4 kg per capita).[194]
The primary and secondary lead production processes are similar. Some primary production plants now supplement their operations with scrap lead, and this trend is likely to increase in the future. Given adequate techniques, lead obtained via secondary processes is indistinguishable from lead obtained via primary processes. Scrap lead from the building trade is usually fairly clean and is re-melted without the need for smelting, though refining is sometimes needed. Secondary lead production is therefore cheaper, in terms of energy requirements, than is primary production, often by 50% or more.[195]
Primary[edit]
Most lead ores contain a low percentage of lead (rich ores have a typical content of 3–8%) which must be concentrated for extraction.[196] During initial processing, ores typically undergo crushing, dense-medium separation, grinding, froth flotation, and drying. The resulting concentrate, which has a lead content of 30–80% by mass (regularly 50–60%),[196] is then turned into (impure) lead metal.
There are two main ways of doing this: a two-stage process involving roasting followed by blast furnace extraction, carried out in separate vessels; or a direct process in which the extraction of the concentrate occurs in a single vessel. The latter has become the most common route, though the former is still significant.[197]
Two-stage process[edit]
First, the sulfide concentrate is roasted in air to oxidize the lead sulfide:[198]
- 2 PbS(s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 PbO(s) + 2 SO2(g)↑
As the original concentrate was not pure lead sulfide, roasting yields not only the desired lead(II) oxide, but a mixture of oxides, sulfates, and silicates of lead and of the other metals contained in the ore.[199] This impure lead oxide is reduced in a coke-fired blast furnace to the (again, impure) metal:[200]
- 2 PbO(s) + C(s) → 2 Pb(s) + CO2(g)↑
Impurities are mostly arsenic, antimony, bismuth, zinc, copper, silver, and gold. Typically they are removed in a series of pyrometallurgical processes. The melt is treated in a reverberatory furnace with air, steam, and sulfur, which oxidizes the impurities except for silver, gold, and bismuth. Oxidized contaminants float to the top of the melt and are skimmed off.[201][202] Metallic silver and gold are removed and recovered economically by means of the Parkes process, in which zinc is added to lead. Zinc, which is immiscible in lead, dissolves the silver and gold. The zinc solution can be separated from the lead, and the silver and gold retrieved.[202][203] De-silvered lead is freed of bismuth by the Betterton–Kroll process, treating it with metallic calcium and magnesium. The resulting bismuth dross can be skimmed off.[202]
Alternatively to the pyrometallurgical processes, very pure lead can be obtained by processing smelted lead electrolytically using the Betts process. Anodes of impure lead and cathodes of pure lead are placed in an electrolyte of lead fluorosilicate (PbSiF6). Once electrical potential is applied, impure lead at the anode dissolves and plates onto the cathode, leaving the majority of the impurities in solution.[202][204] This is a high-cost process and thus mostly reserved for refining bullion containing high percentages of impurities.[205]
Direct process[edit]
In this process, lead bullion and slag is obtained directly from lead concentrates. The lead sulfide concentrate is melted in a furnace and oxidized, forming lead monoxide. Carbon (as coke or coal gas[o]) is added to the molten charge along with fluxing agents. The lead monoxide is thereby reduced to metallic lead, in the midst of a slag rich in lead monoxide.[197]
If the input is rich in lead, as much as 80% of the original lead can be obtained as bullion; the remaining 20% forms a slag rich in lead monoxide. For a low-grade feed, all of the lead can be oxidized to a high-lead slag.[197] Metallic lead is further obtained from the high-lead (25–40%) slags via submerged fuel combustion or injection, reduction assisted by an electric furnace, or a combination of both.[197]
Alternatives[edit]
Research on a cleaner, less energy-intensive lead extraction process continues; a major drawback is that either too much lead is lost as waste, or the alternatives result in a high sulfur content in the resulting lead metal. Hydrometallurgical extraction, in which anodes of impure lead are immersed into an electrolyte and pure lead is deposited (electrowound) onto a cathode, is a technique that may have potential, but is not currently economical except in cases where electricity is very cheap.[206]
Secondary[edit]
Smelting, which is an essential part of the primary production, is often skipped during secondary production. It is only performed when metallic lead has undergone significant oxidation.[195] The process is similar to that of primary production in either a blast furnace or a rotary furnace, with the essential difference being the greater variability of yields: blast furnaces produce hard lead (10% antimony) while reverberatory and rotary kiln furnaces produced semisoft lead (3–4% antimony).[207]
The ISASMELT process is a more recent smelting method that may act as an extension to primary production; battery paste from spent lead–acid batteries (containing lead sulfate and lead oxides) has its sulfate removed by treating it with alkali, and is then treated in a coal-fueled furnace in the presence of oxygen, which yields impure lead, with antimony the most common impurity.[208] Refining of secondary lead is similar to that of primary lead; some refining processes may be skipped depending on the material recycled and its potential contamination.[208]
Of the sources of lead for recycling, lead–acid batteries are the most important; lead pipe, sheet, and cable sheathing are also significant.[195]
Applications[edit]
Bricks of lead (alloyed with 4% antimony) are used as radiation shielding.[209]
Contrary to popular belief, pencil leads in wooden pencils have never been made from lead. When the pencil originated as a wrapped graphite writing tool, the particular type of graphite used was named plumbago (literally, act for lead or lead mockup).[210]
Elemental form[edit]
Lead metal has several useful mechanical properties, including high density, low melting point, ductility, and relative inertness. Many metals are superior to lead in some of these aspects but are generally less common and more difficult to extract from parent ores. Lead’s toxicity has led to its phasing out for some uses.[211]
Lead has been used for bullets since their invention in the Middle Ages. It is inexpensive; its low melting point means small arms ammunition and shotgun pellets can be cast with minimal technical equipment; and it is denser than other common metals, which allows for better retention of velocity. It remains the main material for bullets, alloyed with other metals as hardeners.[168] Concerns have been raised that lead bullets used for hunting can damage the environment.[p]
Lead’s high density and resistance to corrosion have been exploited in a number of related applications. It is used as ballast in sailboat keels; its density allows it to take up a small volume and minimize water resistance, thus counterbalancing the heeling effect of wind on the sails.[213] It is used in scuba diving weight belts to counteract the diver’s buoyancy.[214] In 1993, the base of the Leaning Tower of Pisa was stabilized with 600 tonnes of lead.[215] Because of its corrosion resistance, lead is used as a protective sheath for underwater cables.[216]
A 17th-century gold-coated lead sculpture
Lead has many uses in the construction industry; lead sheets are used as architectural metals in roofing material, cladding, flashing, gutters and gutter joints, and on roof parapets.[217][218] Lead is still used in statues and sculptures,[q] including for armatures.[220] In the past it was often used to balance the wheels of cars; for environmental reasons this use is being phased out in favor of other materials.[115]
Lead is added to copper alloys, such as brass and bronze, to improve machinability and for its lubricating qualities. Being practically insoluble in copper the lead forms solid globules in imperfections throughout the alloy, such as grain boundaries. In low concentrations, as well as acting as a lubricant, the globules hinder the formation of swarf as the alloy is worked, thereby improving machinability. Copper alloys with larger concentrations of lead are used in bearings. The lead provides lubrication, and the copper provides the load-bearing support.[221]
Lead’s high density, atomic number, and formability form the basis for use of lead as a barrier that absorbs sound, vibration, and radiation.[222] Lead has no natural resonance frequencies;[222] as a result, sheet-lead is used as a sound deadening layer in the walls, floors, and ceilings of sound studios.[223] Organ pipes are often made from a lead alloy, mixed with various amounts of tin to control the tone of each pipe.[224][225] Lead is an established shielding material from radiation in nuclear science and in X-ray rooms[226] due to its denseness and high attenuation coefficient.[227] Molten lead has been used as a coolant for lead-cooled fast reactors.[228]
Batteries[edit]
The largest use of lead in the early 21st century is in lead–acid batteries. The lead in batteries undergoes no direct contact with humans, so there are fewer toxicity concerns.[r] People who work in lead battery production plants may be exposed to lead dust and inhale it.[230] The reactions in the battery between lead, lead dioxide, and sulfuric acid provide a reliable source of voltage.[s] Supercapacitors incorporating lead–acid batteries have been installed in kilowatt and megawatt scale applications in Australia, Japan, and the United States in frequency regulation, solar smoothing and shifting, wind smoothing, and other applications.[232] These batteries have lower energy density and charge-discharge efficiency than lithium-ion batteries, but are significantly cheaper.[233]
Coating for cables[edit]
Lead is used in high voltage power cables as shell material to prevent water diffusion into insulation; this use is decreasing as lead is being phased out.[234] Its use in solder for electronics is also being phased out by some countries to reduce the amount of environmentally hazardous waste.[235] Lead is one of three metals used in the Oddy test for museum materials, helping detect organic acids, aldehydes, and acidic gases.[236][237]
Compounds[edit]
In addition to being the main application for lead metal, lead-acid batteries are also the main consumer of lead compounds. The energy storage/release reaction used in these devices involves lead sulfate and lead dioxide:
- Pb(s) + PbO
2(s) + 2H
2SO
4(aq) → 2PbSO
4(s) + 2H
2O(l)
Other applications of lead compounds are very specialized and often fading. Lead-based coloring agents are used in ceramic glazes and glass, especially for red and yellow shades.[238] While lead paints are phased out in Europe and North America, they remain in use in less developed countries such as China,[239] India,[240] or Indonesia.[241] Lead tetraacetate and lead dioxide are used as oxidizing agents in organic chemistry. Lead is frequently used in the polyvinyl chloride coating of electrical cords.[242][243] It can be used to treat candle wicks to ensure a longer, more even burn. Because of its toxicity, European and North American manufacturers use alternatives such as zinc.[244][245] Lead glass is composed of 12–28% lead oxide, changing its optical characteristics and reducing the transmission of ionizing radiation,[246] a property used in old TVs and computer monitors with cathode-ray tubes. Lead-based semiconductors such as lead telluride and lead selenide are used in photovoltaic cells and infrared detectors.[247]
Biological effects[edit]
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| GHS labelling: | |
|
Pictograms |
  
|
|
Signal word |
Danger |
|
Hazard statements |
H302, H332, H351, H360Df, H373, H410 |
|
Precautionary statements |
P201, P261, P273, P304, P308, P312, P313, P340, P391[248] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
2 0 0 |
Lead has no confirmed biological role, and there is no confirmed safe level of lead exposure.[249] A 2009 Canadian–American study concluded that even at levels that are considered to pose little to no risk, lead may cause «adverse mental health outcomes».[250] Its prevalence in the human body—at an adult average of 120 mg[t]—is nevertheless exceeded only by zinc (2500 mg) and iron (4000 mg) among the heavy metals.[252] Lead salts are very efficiently absorbed by the body.[253] A small amount of lead (1%) is stored in bones; the rest is excreted in urine and feces within a few weeks of exposure. Only about a third of lead is excreted by a child. Continual exposure may result in the bioaccumulation of lead.[254]
Toxicity[edit]
Lead is a highly poisonous metal (whether inhaled or swallowed), affecting almost every organ and system in the human body.[255] At airborne levels of 100 mg/m3, it is immediately dangerous to life and health.[256] Most ingested lead is absorbed into the bloodstream.[257] The primary cause of its toxicity is its predilection for interfering with the proper functioning of enzymes. It does so by binding to the sulfhydryl groups found on many enzymes,[258] or mimicking and displacing other metals which act as cofactors in many enzymatic reactions.[259] The essential metals that lead interacts with include calcium, iron, and zinc.[260] High levels of calcium and iron tend to provide some protection from lead poisoning; low levels cause increased susceptibility.[253]
Effects[edit]
Lead can cause severe damage to the brain and kidneys and, ultimately, death. By mimicking calcium, lead can cross the blood–brain barrier. It degrades the myelin sheaths of neurons, reduces their numbers, interferes with neurotransmission routes, and decreases neuronal growth.[258] In the human body, lead inhibits porphobilinogen synthase and ferrochelatase, preventing both porphobilinogen formation and the incorporation of iron into protoporphyrin IX, the final step in heme synthesis. This causes ineffective heme synthesis and microcytic anemia.[261]
Symptoms of lead poisoning
Symptoms of lead poisoning include nephropathy, colic-like abdominal pains, and possibly weakness in the fingers, wrists, or ankles. Small blood pressure increases, particularly in middle-aged and older people, may be apparent and can cause anemia.[citation needed] Several studies, mostly cross-sectional, found an association between increased lead exposure and decreased heart rate variability.[262] In pregnant women, high levels of exposure to lead may cause miscarriage. Chronic, high-level exposure has been shown to reduce fertility in males.[263]
In a child’s developing brain, lead interferes with synapse formation in the cerebral cortex, neurochemical development (including that of neurotransmitters), and the organization of ion channels.[264] Early childhood exposure has been linked with an increased risk of sleep disturbances and excessive daytime drowsiness in later childhood.[265] High blood levels are associated with delayed puberty in girls.[266] The rise and fall in exposure to airborne lead from the combustion of tetraethyl lead in gasoline during the 20th century has been linked with historical increases and decreases in crime levels.
Exposure sources[edit]
Lead exposure is a global issue since lead mining and smelting, and battery manufacturing, disposal, and recycling, are common in many countries. Lead enters the body via inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption. Almost all inhaled lead is absorbed into the body; for ingestion, the rate is 20–70%, with children absorbing a higher percentage than adults.[267]
Poisoning typically results from ingestion of food or water contaminated with lead, and less commonly after accidental ingestion of contaminated soil, dust, or lead-based paint.[268] Seawater products can contain lead if affected by nearby industrial waters.[269] Fruit and vegetables can be contaminated by high levels of lead in the soils they were grown in. Soil can be contaminated through particulate accumulation from lead in pipes, lead paint, and residual emissions from leaded gasoline.[270]
The use of lead for water pipes is a problem in areas with soft or acidic water.[271] Hard water forms insoluble protective layers on the inner surface of the pipes, whereas soft and acidic water dissolves the lead pipes.[272] Dissolved carbon dioxide in the carried water may result in the formation of soluble lead bicarbonate; oxygenated water may similarly dissolve lead as lead(II) hydroxide. Drinking such water, over time, can cause health problems due to the toxicity of the dissolved lead. The harder the water the more calcium bicarbonate and sulfate it will contain, and the more the inside of the pipes will be coated with a protective layer of lead carbonate or lead sulfate.[273]
Kymographic recording of the effect of lead acetate on frog heart experimental set up.
Ingestion of applied lead-based paint is the major source of exposure for children:
a direct source is chewing on old painted window sills. Alternatively, as the applied dry paint deteriorates, it peels, is pulverized into dust and then enters the body through hand-to-mouth contact or contaminated food, water, or alcohol. Ingesting certain home remedies may result in exposure to lead or its compounds.[274]
Inhalation is the second major exposure pathway, affecting smokers and especially workers in lead-related occupations.[257] Cigarette smoke contains, among other toxic substances, radioactive lead-210.[275] «As a result of EPA’s regulatory efforts, levels of lead in the air [in the United States] decreased by 86 percent between 2010 and 2020.»[276] The concentration of lead in the air in the United States fell below the national standard of 0.15 μg/m3[277] in 2014.[278]
Skin exposure may be significant for people working with organic lead compounds. The rate of skin absorption is lower for inorganic lead.[279]
Lead in foods[edit]
Lead may be found in food when food is grown in soil that is high in lead, airborne lead contaminates the crops, animals eat lead in their diet, or lead enters the food either from what it was stored or cooked in.[280] Ingestion of lead paint and batteries is also a route of exposure for livestock, which can subsequently affect humans.[281] Milk produced by contaminated cattle can be diluted to a lower lead concentration and sold for consumption.[282]
In Bangladesh, lead compounds have been added to turmeric to make it more yellow.[283] This is believed to have started in the 1980s and continues as of 2019.[283] It is believed to be one of the main sources of high lead levels in the country.[284] In Hong Kong the maximum allowed lead parts per million is 6 in solid foods and 1 in liquid foods.[285]
In December 2022, Consumer Reports tested 28 dark chocolate brands and found that 23 of contained potentially harmful levels of lead, cadmium or both. They have urged the chocolate makers to reduce the level of lead which could be harmful to certain people, specially pregnant women.[286] Lead-containing dust can settle on drying cocoa beans when they are set outside near polluting industrial plants.[287]
Lead in plastic toys[edit]
According to the United States Center for Disease Control, the use of lead in plastics has not been banned. Lead softens the plastic and makes it more flexible so that it can go back to its original shape. It may also be used in plastic toys to stabilize molecules from heat. Lead dust can be formed when plastic is exposed to sunlight, air, and detergents that break down the chemical bond between the lead and plastics.[288]
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for lead poisoning normally involves the administration of dimercaprol and succimer.[289] Acute cases may require the use of disodium calcium edetate, the calcium chelate, and the disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). It has a greater affinity for lead than calcium, with the result that lead chelate is formed by exchange and excreted in the urine, leaving behind harmless calcium.[290]
Environmental effects[edit]
Battery collection site in Dakar, Senegal, where at least 18 children died of lead poisoning in 2008
The extraction, production, use, and disposal of lead and its products have caused significant contamination of the Earth’s soils and waters. Atmospheric emissions of lead were at their peak during the Industrial Revolution, and the leaded gasoline period in the second half of the twentieth century. [291]
Lead releases originate from natural sources (i.e., concentration of the naturally occurring lead), industrial production, incineration and recycling, and mobilization of previously buried lead.[291] In particular, as lead has been phased out from other uses, in the Global South, lead recycling operations designed to extract cheap lead used for global manufacturing have become a well documented source of exposure.[292] Elevated concentrations of lead persist in soils and sediments in post-industrial and urban areas; industrial emissions, including those arising from coal burning,[293] continue in many parts of the world, particularly in the developing countries.[294]
Lead can accumulate in soils, especially those with a high organic content, where it remains for hundreds to thousands of years. Environmental lead can compete with other metals found in and on plants surfaces potentially inhibiting photosynthesis and at high enough concentrations, negatively affecting plant growth and survival. Contamination of soils and plants can allow lead to ascend the food chain affecting microorganisms and animals. In animals, lead exhibits toxicity in many organs, damaging the nervous, renal, reproductive, hematopoietic, and cardiovascular systems after ingestion, inhalation, or skin absorption.[295] Fish uptake lead from both water and sediment;[296] bioaccumulation in the food chain poses a hazard to fish, birds, and sea mammals.[297]
Anthropogenic lead includes lead from shot and sinkers. These are among the most potent sources of lead contamination along with lead production sites.[298] Lead was banned for shot and sinkers in the United States in 2017,[299] although that ban was only effective for a month,[300] and a similar ban is being considered in the European Union.[301]
Analytical methods for the determination of lead in the environment include spectrophotometry, X-ray fluorescence, atomic spectroscopy and electrochemical methods. A specific ion-selective electrode has been developed based on the ionophore S,S’-methylenebis (N,N-diisobutyldithiocarbamate).[302] An important biomarker assay for lead poisoning is δ-aminolevulinic acid levels in plasma, serum, and urine.[303]
Restriction and remediation[edit]
Radiography of a swan found dead in Condé-sur-l’Escaut (northern France), highlighting lead shot. There are hundreds of lead pellets (a dozen is enough to kill an adult swan within a few days). Such bodies are sources of environmental contamination by lead.
By the mid-1980s, there was significant decline in the use of lead in industry.[304] In the United States, environmental regulations reduced or eliminated the use of lead in non-battery products, including gasoline, paints, solders, and water systems. Particulate control devices were installed in coal-fired power plants to capture lead emissions.[293] In 1992, U.S. Congress required the Environmental Protection Agency to reduce the blood lead levels of the country’s children.[305] Lead use was further curtailed by the European Union’s 2003 Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive.[306] A large drop in lead deposition occurred in the Netherlands after the 1993 national ban on use of lead shot for hunting and sport shooting: from 230 tonnes in 1990 to 47.5 tonnes in 1995.[307]
In the United States, the permissible exposure limit for lead in the workplace, comprising metallic lead, inorganic lead compounds, and lead soaps, was set at 50 μg/m3 over an 8-hour workday, and the blood lead level limit at 5 μg per 100 g of blood in 2012.[308] Lead may still be found in harmful quantities in stoneware,[309] vinyl[310] (such as that used for tubing and the insulation of electrical cords), and Chinese brass.[u] Old houses may still contain lead paint.[310] White lead paint has been withdrawn from sale in industrialized countries, but specialized uses of other pigments such as yellow lead chromate remain.[182] Stripping old paint by sanding produces dust which can be inhaled.[312] Lead abatement programs have been mandated by some authorities in properties where young children live.[313]
Lead waste, depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the waste, may be treated as household waste (to facilitate lead abatement activities),[314] or potentially hazardous waste requiring specialized treatment or storage.[315] Lead is released into the environment in shooting places and a number of lead management practices have been developed to counter the lead contamination.[316] Lead migration can be enhanced in acidic soils; to counter that, it is advised soils be treated with lime to neutralize the soils and prevent leaching of lead.[317]
Research has been conducted on how to remove lead from biosystems by biological means: Fish bones are being researched for their ability to bioremediate lead in contaminated soil.[318][319] The fungus Aspergillus versicolor is effective at absorbing lead ions from industrial waste before being released to water bodies.[320] Several bacteria have been researched for their ability to remove lead from the environment, including the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio and Desulfotomaculum, both of which are highly effective in aqueous solutions.[321]
See also[edit]
- Derek Bryce-Smith – one of the earliest campaigners against lead in petrol in the UK
- Thomas Midgley Jr. – discovered that the addition of tetraethyllead to gasoline prevented «knocking» in internal combustion engines
- Clair Patterson – instrumental in the banning of tetraethyllead in gasoline in the US and lead solder in food cans.
- Robert A. Kehoe – foremost medical advocate for the use of tetraethyllead as an additive in gasoline.
Notes[edit]
- ^ The tetrahedral allotrope of tin is called α- or gray tin and is stable only at or below 13.2 °C (55.8 °F). The stable form of tin above this temperature is called β- or white tin and has a distorted face centered cubic (tetragonal) structure which can be derived by compressing the tetrahedra of gray tin along their cubic axes. White tin effectively has a structure intermediate between the regular tetrahedral structure of gray tin, and the regular face centered cubic structure of lead, consistent with the general trend of increasing metallic character going down any representative group.[15]
- ^ A quasicrystalline thin-film allotrope of lead, with pentagonal symmetry, was reported in 2013. The allotrope was obtained by depositing lead atoms on the surface of an icosahedral silver-indium-ytterbium quasicrystal. Its conductivity was not recorded.[16][17]
- ^ Diamond cubic structures with lattice parameters around the lattice parameter of silicon exists both in thin lead and tin films, and in massive lead and tin, freshly solidified in vacuum of ~5 x 10−6 Torr. Experimental evidence for almost identical structures of at least three oxide types is presented, demonstrating that lead and tin behave like silicon not only in the initial stages of crystallization, but also in the initial stages of oxidation.[18]
- ^ British English: to go down like a lead balloon.
- ^ Malleability describes how easily it deforms under compression, whereas ductility means its ability to stretch.
- ^ A (wet) finger can be dipped into molten lead without risk of a burning injury.[31]
- ^ An even number of either protons or neutrons generally increases the nuclear stability of isotopes, compared to isotopes with odd numbers. No elements with odd atomic numbers have more than two stable isotopes; even-numbered elements have multiple stable isotopes, with tin (element 50) having the highest number of isotopes of all elements, ten.[35] See Even and odd atomic nuclei for more details.
- ^ The half-life found in the experiment was 1.9×1019 years.[38] A kilogram of natural bismuth would have an activity value of approximately 0.003 becquerels (decays per second). For comparison, the activity value of natural radiation in the human body is around 65 becquerels per kilogram of body weight (4500 becquerels on average).[39]
- ^ Lead-205 decays solely via electron capture, which means when there are no electrons available and lead is fully ionized with all 82 electrons removed it cannot decay. Fully ionized thallium-205, the isotope lead-205 would decay to, becomes unstable and can decay into a bound state of lead-205.[50]
- ^ Tetraphenyllead is even more thermally stable, decomposing at 270 °C.[91]
- ^ Abundances in the source are listed relative to silicon rather than in per-particle notation. The sum of all elements per 106 parts of silicon is 2.6682×1010 parts; lead comprises 3.258 parts.
- ^ Elemental abundance figures are estimates and their details may vary from source to source.[113]
- ^ The inscription reads: «Made when the Emperor Vespasian was consul for the ninth term and the Emperor Titus was consul for the seventh term, when Gnaeus Iulius Agricola was imperial governor (of Britain).»
- ^ The fact that Julius Caesar fathered only one child, as well as the alleged sterility of his successor, Caesar Augustus, have been attributed to lead poisoning.[148]
- ^ Gaseous by-product of the coking process, containing carbon monoxide, hydrogen and methane; used as a fuel.
- ^ California began banning lead bullets for hunting on that basis in July 2015.[212]
- ^ For example, a firm «…producing quality [lead] garden ornament from our studio in West London for over a century».[219]
- ^ Potential injuries to regular users of such batteries are not related to lead’s toxicity.[229]
- ^ See[231] for details on how a lead–acid battery works.
- ^ Rates vary greatly by country.[251]
- ^ An alloy of brass (copper and zinc) with lead, iron, tin, and sometimes antimony.[311]
References[edit]
- ^ «Standard Atomic Weights: Lead». CIAAW. 2020.
- ^ Pb(0) carbonyls have been observered in reaction between lead atoms and carbon monoxide; see Ling, Jiang; Qiang, Xu (2005). «Observation of the lead carbonyls PbnCO (n=1–4): Reactions of lead atoms and small clusters with carbon monoxide in solid argon». The Journal of Chemical Physics. 122 (3): 034505. 122 (3): 34505. Bibcode:2005JChPh.122c4505J. doi:10.1063/1.1834915. ISSN 0021-9606. PMID 15740207.
- ^ Weast, Astle & Beyer 1983, p. E110.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). «The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties» (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ Meija et al. 2016.
- ^ Theodore Low De Vinne (1899). The Practice of Typography: A Treatise on the Processes of Type-making, the Point System, the Names, Sizes, Styles, and Prices of Plain Printing Types. Century Company. pp. 9–36.
- ^ Lide 2005, p. 10-179.
- ^ Pyykkö 1988, pp. 563–594.
- ^ Claudio, Godwin & Magyar 2002, pp. 1–144.
- ^ Norman 1996, p. 36.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, pp. 226–227, 374.
- ^ Christensen 2002, p. 867.
- ^ Slater 1964.
- ^ Considine & Considine 2013, pp. 501, 2970.
- ^ Parthé 1964, p. 13.
- ^ Sharma et al. 2013.
- ^ Sharma et al. 2014, p. 174710.
- ^ Peneva, Djuneva & Tsukeva 1981.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 372.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, pp. 372–373.
- ^ a b Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 6.
- ^ Lide 2005, pp. 12–35, 12–40.
- ^ Brenner 2003, p. 396.
- ^ Jones 2014, p. 42.
- ^ Lide 2005, pp. 4–13, 4–21, 4–33.
- ^ Vogel & Achilles 2013, p. 8.
- ^ Anderson 1869, pp. 341–343.
- ^ Gale & Totemeier 2003, pp. 15–2–15–3.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 8.
- ^ a b Lide 2005, p. 12-219.
- ^ Willey 1999.
- ^ Lide 2005, p. 12-45.
- ^ Blakemore 1985, p. 272.
- ^ Webb, Marsiglio & Hirsch 2015.
- ^ a b c d e IAEA — Nuclear Data Section 2017.
- ^ University of California Nuclear Forensic Search Project.
- ^ a b Stone 1997.
- ^ de Marcillac et al. 2003, pp. 876–78.
- ^ World Nuclear Association 2015.
- ^ Beeman et al. 2013.
- ^ Radioactive Decay Series 2012.
- ^ Committee on Evaluation of EPA Guidelines for Exposure to Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials et al. 1999.
- ^ Smirnov, Borisevich & Sulaberidze 2012.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 368.
- ^ Levin 2009, pp. 40–41.
- ^ Webb 2000, p. 115.
- ^ Wrackmeyer & Horchler 1990.
- ^ Cangelosi & Pecoraro 2015.
- ^ Fiorini 2010, pp. 7–8.
- ^ Takahashi et al. 1987.
- ^ Thürmer, Williams & Reutt-Robey 2002, pp. 2033–2035.
- ^ Tétreault, Sirois & Stamatopoulou 1998, pp. 17–32.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, pp. 10–11.
- ^ a b c d e f Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 373.
- ^ Bretherick 2016, p. 1442.
- ^ Harbison, Bourgeois & Johnson 2015, p. 132.
- ^ a b Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 374.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, pp. 11–12.
- ^ Polyanskiy 1986, p. 20.
- ^ Kaupp 2014, pp. 9–10.
- ^ Dieter & Watson 2009, p. 509.
- ^ Hunt 2014, p. 215.
- ^ a b c King 1995, pp. 43–63.
- ^ Bunker & Casey 2016, p. 89.
- ^ Whitten, Gailey & David 1996, pp. 904–905.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 384.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 387.
- ^ a b Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 389.
- ^ Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, p. 426.
- ^ Funke 2013.
- ^ a b Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 382.
- ^ Bharara & Atwood 2006, p. 4.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 388.
- ^ Toxicological Profile for Lead 2007, p. 277.
- ^ Downs & Adams 2017, p. 1128.
- ^ Brescia 2012, p. 234.
- ^ Macintyre 1992, p. 3775.
- ^ Silverman 1966, pp. 2067–2069.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 381.
- ^ Yong, Hoffmann & Fässler 2006, pp. 4774–4778.
- ^ Becker et al. 2008, pp. 9965–9978.
- ^ Mosseri, Henglein & Janata 1990, pp. 2722–2726.
- ^ Konu & Chivers 2011, pp. 391–392.
- ^ Hadlington 2017, p. 59.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, pp. 384–386.
- ^ Röhr 2017.
- ^ Alsfasser 2007, pp. 261–263.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 393.
- ^ Stabenow, Saak & Weidenbruch 2003.
- ^ a b Polyanskiy 1986, p. 43.
- ^ a b c d Greenwood & Earnshaw 1998, p. 404.
- ^ a b Wiberg, Wiberg & Holleman 2001, p. 918.
- ^ Toxicological Profile for Lead 2007, p. 287.
- ^ Polyanskiy 1986, p. 44.
- ^ Windholz 1976.
- ^ Zýka 1966, p. 569.
- ^ a b c d Lodders 2003, pp. 1222–1223.
- ^ Roederer et al. 2009, pp. 1963–1980.
- ^ Lochner, Rohrbach & Cochrane 2005, p. 12.
- ^ Lodders 2003, p. 1224.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, pp. 608–615.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, p. 551.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, pp. 608–609.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, p. 553.
- ^ Frebel 2015, pp. 114–115.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, pp. 608–610.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, p. 595.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, p. 596.
- ^ Burbidge et al. 1957, pp. 582, 609–615.
- ^ Langmuir & Broecker 2012, pp. 183–184.
- ^ Davidson et al. 2014, pp. 4–5.
- ^ Emsley 2011, pp. 286, passim.
- ^ Cox 1997, p. 182.
- ^ a b Davidson et al. 2014, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d United States Geological Survey 2017, p. 97.
- ^ Rieuwerts 2015, p. 225.
- ^ Merriam-Webster.
- ^ a b Kroonen 2013, *lauda-.
- ^ Nikolayev 2012.
- ^ Kroonen 2013, *bliwa- 2.
- ^ Kroonen 2013, *laidijan-.
- ^ a b c Hong et al. 1994, pp. 1841–1843.
- ^ a b Rich 1994, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e Winder 1993b.
- ^ History of Cosmetics.
- ^ Chapurukha Kusimba, June 20, 2017. «Making Cents of Currency’s Ancient Rise». Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ Yu & Yu 2004, p. 26.
- ^ Toronto museum explores 2003.
- ^ Bisson & Vogel 2000, p. 105.
- ^ Wood, Hsu & Bell 2021.
- ^ Rich 1994, p. 5.
- ^ United States Geological Survey 1973.
- ^ Lead sling bullet.
- ^ de Callataÿ 2005, pp. 361–372.
- ^ Ceccarelli 2013, p. 35.
- ^ Ossuaries and Sarcophagi.
- ^ Calvo Rebollar 2019, p. 45.
- ^ Rich 1994, p. 6.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, pp. 179–184.
- ^ Bisel & Bisel 2002, pp. 459–460.
- ^ Retief & Cilliers 2006, pp. 149–151.
- ^ Grout 2017.
- ^ Eschnauer & Stoeppler 1992, p. 58.
- ^ Hodge 1981, pp. 486–491.
- ^ Marcus Vitruvius Pollio (1914) [c. 15 BC]. De architectura. Book 8, 10-11 fulltext.
- ^ Gilfillan 1965, pp. 53–60.
- ^ Nriagu 1983, pp. 660–663.
- ^ Frankenburg 2014, p. 16.
- ^ Scarborough 1984.
- ^ Waldron 1985, pp. 107–108.
- ^ Reddy & Braun 2010, p. 1052.
- ^ Delile et al. 2014, pp. 6594–6599.
- ^ Finger 2006, p. 184.
- ^ Lewis 1985, p. 15.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 183.
- ^ Polyanskiy 1986, p. 8.
- ^ Thomson 1830, p. 74.
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary, surma.
- ^ Vasmer 1986–1987, сурьма.
- ^ Kellett 2012, pp. 106–107.
- ^ a b Winder 1993a.
- ^ a b Rich 1994, p. 7.
- ^ Rich 1994, p. 8.
- ^ Ede & Cormack 2016, p. 54.
- ^ Cotnoir 2006, p. 35.
- ^ Samson 1885, p. 388.
- ^ Sinha et al. 1993.
- ^ a b Ramage 1980, p. 8.
- ^ Tungate 2011, p. 14.
- ^ Donnelly 2014, pp. 171–172.
- ^ Ashikari 2003, p. 65.
- ^ Nakashima et al. 1998, p. 59.
- ^ Rabinowitz 1995, p. 66.
- ^ Gill & Libraries Board of South Australia 1974, p. 69.
- ^ Bisson & Vogel 2000, p. 85.
- ^ Bisson & Vogel 2000, pp. 131–132.
- ^ Hong et al. 1994, pp. 1841–43.
- ^ Lead mining.
- ^ Rich 1994, p. 11.
- ^ a b c Riva et al. 2012, pp. 11–16.
- ^ Hernberg 2000, p. 246.
- ^ a b Crow 2007.
- ^ Markowitz & Rosner 2000, p. 37.
- ^ More et al. 2017.
- ^ American Geophysical Union 2017.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 1997.
- ^ Rich 1994, p. 117.
- ^ Rich 1994, p. 17.
- ^ Rich 1994, pp. 91–92.
- ^ United States Geological Survey 2005.
- ^ Zhang et al. 2012, pp. 2261–2273.
- ^ Tolliday 2014.
- ^ Guberman 2016, pp. 42.14–15.
- ^ Graedel 2010.
- ^ a b c Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 56.
- ^ a b Davidson et al. 2014, p. 6.
- ^ a b c d Davidson et al. 2014, p. 17.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 51.
- ^ Davidson et al. 2014, pp. 11–12.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, pp. 51–52.
- ^ Davidson et al. 2014, p. 25.
- ^ a b c d Primary Lead Refining.
- ^ Pauling 1947.
- ^ Davidson et al. 2014, p. 34.
- ^ Davidson et al. 2014, p. 23.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, pp. 52–53.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency 2010, p. 1.
- ^ a b Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 57.
- ^ Street & Alexander 1998, p. 181.
- ^ Evans 1908, pp. 133–179.
- ^ Baird & Cann 2012, pp. 537–538, 543–547.
- ^ California Department of Fish and Wildlife.
- ^ Parker 2005, pp. 194–195.
- ^ Krestovnikoff & Halls 2006, p. 70.
- ^ Street & Alexander 1998, p. 182.
- ^ Jensen 2013, p. 136.
- ^ Think Lead research.
- ^ Weatherings to Parapets.
- ^ Lead garden ornaments 2016.
- ^ Putnam 2003, p. 216.
- ^ Copper Development Association.
- ^ a b Rich 1994, p. 101.
- ^ Guruswamy 2000, p. 31.
- ^ Audsley 1965, pp. 250–251.
- ^ Palmieri 2006, pp. 412–413.
- ^ National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements 2004, p. 16.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 7.
- ^ Tuček, Carlsson & Wider 2006, p. 1590.
- ^ Concordia University 2016.
- ^ Toxicological Profile for Lead 2007, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Progressive Dynamics, Inc.
- ^ Olinsky-Paul 2013.
- ^ Gulbinska 2014.
- ^ Rich 1994, pp. 133–134.
- ^ Zhao 2008, p. 440.
- ^ Beiner et al. 2015.
- ^ Szczepanowska 2013, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Burleson 2001, p. 23.
- ^ Insight Explorer & IPEN 2016.
- ^ Singh 2017.
- ^ Ismawati et al. 2013, p. 2.
- ^ Zweifel 2009, p. 438.
- ^ Wilkes et al. 2005, p. 106.
- ^ Randerson 2002.
- ^ Nriagu & Kim 2000, pp. 37–41.
- ^ Amstock 1997, pp. 116–119.
- ^ Rogalski 2010, pp. 485–541.
- ^ «Lead 695912».
- ^ World Health Organization 2018.
- ^ Bouchard et al. 2009.
- ^ World Health Organization 2000, pp. 149–153.
- ^ Emsley 2011, pp. 280, 621, 255.
- ^ a b Luckey & Venugopal 1979, pp. 177–178.
- ^ Toxic Substances Portal.
- ^ United States Food and Drug Administration 2015, p. 42.
- ^ National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
- ^ a b Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
- ^ a b Rudolph et al. 2003, p. 369.
- ^ Dart, Hurlbut & Boyer-Hassen 2004, p. 1426.
- ^ Kosnett 2006, p. 238.
- ^ Cohen, Trotzky & Pincus 1981, pp. 904–906.
- ^ Navas-Acien 2007.
- ^ Sokol 2005, p. 133, passim.
- ^ Mycyk, Hryhorczuk & Amitai 2005, p. 462.
- ^ Liu et al. 2015, pp. 1869–1874.
- ^ Schoeters et al. 2008, pp. 168–175.
- ^ Tarragó 2012, p. 16.
- ^ Toxicological Profile for Lead 2007, p. 4.
- ^ Bremner 2002, p. 101.
- ^ Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
- ^ Thornton, Rautiu & Brush 2001, p. 17.
- ^ Moore 1977, pp. 109–115.
- ^ Wiberg, Wiberg & Holleman 2001, p. 914.
- ^ Tarragó 2012, p. 11.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2015.
- ^ «Lead (Pb) Air Pollution». epa.gov. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 8 July 2022. Retrieved 22 July 2022.
As a result of EPA’s regulatory efforts, levels of lead in the air nationally decreased by 86 percent between 2010 and 2020.
- ^ «NAAQS Table». epa.gov. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 5 April 2022. Retrieved 22 July 2022.
National Ambient Air Quality Standards (40 CFR part 50) for six principal pollutants
- ^ «Lead Trends». epa.gov. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 1 June 2022.
- ^ Wani, Ara & Usman 2015, pp. 57, 58.
- ^ Castellino N, Sannolo N, Castellino P (1994). Inorganic Lead Exposure and Intoxications. CRC Press. p. 86. ISBN 9780873719971. Archived from the original on 5 November 2017.
- ^ Hesami, Reza; Salimi, Azam; Ghaderian, Seyed Majid (10 January 2018). «Lead, zinc, and cadmium uptake, accumulation, and phytoremediation by plants growing around Tang-e Douzan lead–zinc mine, Iran». Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 25 (9): 8701–8714. doi:10.1007/s11356-017-1156-y. ISSN 0944-1344. PMID 29322395. S2CID 3938066.
- ^ Mielke, Howard W.; Reagan, Patrick L. (February 1998). «Soil Is an Important Pathway of Human Lead Exposure». Environmental Health Perspectives. 106 (Suppl 1): 217–229. doi:10.2307/3433922. ISSN 0091-6765. JSTOR 3433922. PMC 1533263. PMID 9539015.
- ^ a b University, Stanford (24 September 2019). «Lead found in turmeric». Stanford News. Retrieved 25 September 2019.
- ^ «Researchers find lead in turmeric». phys.org. Retrieved 25 September 2019.
- ^ «Maximum Permitted Concentration of Certain Metals Present in Specified Foods». www.elegislation.gov.hk. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ «Consumer Reports urges dark chocolate makers to reduce lead, cadmium levels». www.yahoo.com. Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- ^ Dark chocolate is high in cadmium and lead. How much is safe to eat?
- ^ «Lead in Consumer Products | Sources of Lead | CDC». www.cdc.gov. 1 February 2022. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ^ Prasad 2010, pp. 651–652.
- ^ Masters, Trevor & Katzung 2008, pp. 481–483.
- ^ a b United Nations Environment Programme 2010, p. 4.
- ^ Renfrew, Daniel (2019). Life without lead : contamination, crisis, and hope in Uruguay. Oakland, California. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-520-96824-0. OCLC 1102765674.
- ^ a b Trace element emission 2012.
- ^ United Nations Environment Programme 2010, p. 6.
- ^ Assi et al. 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization 1995.
- ^ UK Marine SACs Project 1999.
- ^ United Nations Environment Programme 2010, p. 9.
- ^ McCoy 2017.
- ^ Cama 2017.
- ^ Layton 2017.
- ^ Hauser 2017, pp. 49–60.
- ^ Lauwerys & Hoet 2001, pp. 115, 116–117.
- ^ «Lead Poisoning: A Historical Perspective».
- ^ Auer et al. 2016, p. 4.
- ^ Petzel, Juuti & Sugimoto 2004, pp. 122–124.
- ^ Deltares & Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research 2016.
- ^ Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry 2017.
- ^ Grandjean 1978, pp. 303–321.
- ^ a b Levin et al. 2008, p. 1288.
- ^ Duda 1996, p. 242.
- ^ Marino et al. 1990, pp. 1183–1185.
- ^ Schoch 1996, p. 111.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency 2000.
- ^ Lead in Waste 2016.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency 2005, p. I-1.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency 2005, p. III-5–III-6.
- ^ Freeman 2012, pp. a20–a21.
- ^ Young 2012.
- ^ Acton 2013, pp. 94–95.
- ^ Park et al. 2011, pp. 162–174.
Bibliography[edit]
This article was submitted to WikiJournal of Science for external academic peer review in 2017 (reviewer reports). The updated content was reintegrated into the Wikipedia page under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 license (2018). The version of record as reviewed is:
Mikhail Boldyrev; et al. (3 July 2018). «Lead: properties, history, and applications» (PDF). WikiJournal of Science. 1 (2): 7. doi:10.15347/WJS/2018.007. ISSN 2470-6345. Wikidata Q56050531.
- Acton, Q. A., ed. (2013). Issues in Global Environment—Pollution and Waste Management: 2012 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. ISBN 978-1-4816-4665-9.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. «Information for the Community: Lead Toxicity» (MP4 webcast, 82 MB). Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2017). «Lead Toxicity. What Are U.S. Standards for Lead Levels?». Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- Alsfasser, R. (2007). Moderne anorganische Chemie [Modern inorganic chemistry] (in German). Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-019060-1.
- American Geophysical Union (2017). «Human Activity Has Polluted European Air for 2000 Years». Eos Science News. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- Amstock, J. S. (1997). Handbook of Glass in Construction. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-001619-4.
- Anderson, J. (1869). «Malleability and ductility of metals». Scientific American. 21 (22): 341–43. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican11271869-341.
- Ashikari, M. (2003). «The memory of the women’s white faces: Japaneseness and the ideal image of women». Japan Forum. 15 (1): 55–79. doi:10.1080/0955580032000077739. S2CID 144510689.
- Assi, M. A.; Hezmee, M. N. M.; Haron, A. W.; et al. (2016). «The detrimental effects of lead on human and animal health». Veterinary World. 9 (6): 660–671. doi:10.14202/vetworld.2016.660-671. ISSN 0972-8988. PMC 4937060. PMID 27397992.
- Auer, Charles M.; Kover, Frank D.; Aidala, James V.; Greenwood, Mark (1 March 2016). Toxic Substances: A Half Century of Progress (PDF) (Report). EPA Alumni Association. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- Audsley, G. A. (1965). The Art of Organ Building. Vol. 2. Courier. ISBN 978-0-486-21315-6.
- Baird, C.; Cann, N. (2012). Environmental Chemistry (5th ed.). W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 978-1-4292-7704-4.
- Becker, M.; Förster, C.; Franzen, C.; et al. (2008). «Persistent radicals of trivalent tin and lead». Inorganic Chemistry. 47 (21): 9965–78. doi:10.1021/ic801198p. PMID 18823115.
- Beeman, J. W.; Bellini, F.; Cardani, L.; et al. (2013). «New experimental limits on the α decays of lead isotopes». European Physical Journal A. 49 (50): 50. arXiv:1212.2422. Bibcode:2013EPJA…49…50B. doi:10.1140/epja/i2013-13050-7. S2CID 119280082.
- Beiner, G. G.; Lavi, M.; Seri, H.; et al. (2015). «Oddy Tests: Adding the Analytical Dimension». Collection Forum. 29 (1–2): 22–36. doi:10.14351/0831-4985-29.1.22. ISSN 0831-4985.
- Bharara, M. S.; Atwood, D. A. (2006). «Lead: Inorganic ChemistryBased in part on the article Lead: Inorganic Chemistry by Philip G. Harrison which appeared in theEncyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry, First Edition». Lead: Inorganic Chemistry. doi:10.1002/0470862106.ia118. ISBN 978-0470860786.
- Bisel, S. C.; Bisel, J. F. (2002). «Health and nutrition at Herculaneum». In Jashemski, W. F.; Meyer, F. G. (eds.). The Natural History of Pompeii. Cambridge University Press. pp. 451–75. ISBN 978-0-521-80054-9.
- Bisson, M. S.; Vogel, J. O. (2000). Ancient African Metallurgy: The Sociocultural Context. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-7425-0261-1.
- Blakemore, J. S. (1985). Solid State Physics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-31391-9.
- Bouchard, M. F.; Bellinger, D. C.; Weuve, J.; et al. (2009). «Blood Lead Levels and Major Depressive Disorder, Panic Disorder, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder in US Young Adults». Archives of General Psychiatry. 66 (12): 1313–9. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.164. ISSN 0003-990X. PMC 2917196. PMID 19996036.
- Bremner, H. A. (2002). Safety and Quality Issues in Fish Processing. Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-85573-678-8.
- Brenner, G. A. (2003). Webster’s New World American Idioms Handbook. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-7645-2477-6.
- Brescia, F. (2012). Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern Introduction. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-323-14231-1.
- Bretherick, L. (2016). Bretherick’s Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards. Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-4831-6250-8.
- Bunker, B. C.; Casey, W. H. (2016). The Aqueous Chemistry of Oxides. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-938425-9.
- Burbidge, E. M.; Burbidge, G. R.; Fowler, W. A.; et al. (1957). «Synthesis of the Elements in Stars». Reviews of Modern Physics. 29 (4): 547–654. Bibcode:1957RvMP…29..547B. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.29.547.
- Burleson, M. (2001). The Ceramic Glaze Handbook: Materials, Techniques, Formulas. Sterling. ISBN 9781579904395.
- California Department of Fish and Wildlife. «Nonlead Ammunition in California». www.wildlife.ca.gov. Retrieved 17 May 2017.
- de Callataÿ, F. (2005). «The Graeco-Roman economy in the super long-run: Lead, copper, and shipwrecks». Journal of Roman Archaeology. 18: 361–72. doi:10.1017/S104775940000742X. S2CID 232346123.
- Cama, T. (2017). «Interior secretary repeals ban on lead bullets». The Hill. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- Cangelosi, V. M.; Pecoraro, V. L. (2015). «Lead». In Roduner, E. (ed.). Nanoscopic Materials: Size-Dependent Phenomena and Growth Principles. Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 843–875. ISBN 978-1-78262-494-3.
- Casciani, D. (2014). «Did removing lead from petrol spark a decline in crime?». BBC News. Retrieved 30 January 2017.
- Calvo Rebollar, Miguel (2019). Construyendo la Tabla Periódica. Zaragoza, Spain: Prames. ISBN 978-84-8321-908-9.
- Ceccarelli, P. (2013). Ancient Greek Letter Writing: A Cultural History (600 BC- 150 BC). OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-967559-3.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1997). «Update: blood lead levels—United States, 1991-1994». Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 46 (7): 141–146. ISSN 0149-2195. PMID 9072671.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2015). «Radiation and Your Health». Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- Christensen, N. E. (2002). «Relativistic Solid State Theory». In Schwerdtfeger, P. (ed.). Relativistic Electronic Structure Theory — Fundamentals. Theoretical and Computational Chemistry. Vol. 11. Elsevier. pp. 867–68. doi:10.1016/s1380-7323(02)80041-3. ISBN 978-0-08-054046-7.
- Claudio, Elizabeth S.; Godwin, Hilary Arnold; Magyar, John S. (2002). «Fundamental Coordination Chemistry, Environmental Chemistry, and Biochemistry of Lead(II)». Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 51. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 1–144. doi:10.1002/0471267287.ch1. ISBN 978-0-471-26534-4.
- Cohen, A. R.; Trotzky, M. S.; Pincus, D. (1981). «Reassessment of the Microcytic Anemia of Lead Poisoning». Pediatrics. 67 (6): 904–906. doi:10.1542/peds.67.6.904. PMID 7232054. S2CID 42146120.
- Committee on Evaluation of EPA Guidelines for Exposure to Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials; Commission on Life Sciences; Division on Earth and Life Studies; National Research Council (1999). Evaluation of Guidelines for Exposures to Technologically Enhanced Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials. National Academies Press. pp. 26, 30–32. ISBN 978-0-309-58070-0.
- Concordia University (2016). Lead acid batteries (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- Considine, D. M.; Considine, G. D. (2013). Van Nostrand’s Scientific Encyclopedia. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-4757-6918-0.
- Copper Development Association. «Leaded Coppers». copper.org. Retrieved 10 July 2016.
- Cotnoir, B. (2006). The Weiser Concise Guide to Alchemy. Weiser Books. ISBN 978-1-57863-379-1.
- Cox, P. A. (1997). The Elements: Their Origin, Abundance and Distribution. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-855298-7.
- Crow, J. M. (2007). «Why use lead in paint?». Chemistry World. Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Dart, R. C.; Hurlbut, K. M.; Boyer-Hassen, L. V. (2004). «Lead». In Dart, R. C. (ed.). Medical Toxicology (3rd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1426. ISBN 978-0-7817-2845-4.
- Davidson, A.; Ryman, J.; Sutherland, C. A.; et al. (2014). «Lead». Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_193.pub3. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- de Marcillac, Pierre; Coron, Noël; Dambier, Gérard; et al. (2003). «Experimental detection of α-particles from the radioactive decay of natural bismuth». Nature. 422 (6934): 876–78. Bibcode:2003Natur.422..876D. doi:10.1038/nature01541. PMID 12712201. S2CID 4415582.
- Delile, H.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Goiran, J.-P.; et al. (2014). «Lead in ancient Rome’s city waters». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (18): 6594–99. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.6594D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1400097111. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4020092. PMID 24753588.
- Deltares; Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research (2016). Lood en zinkemissies door jacht [Lead and zinc emissions from hunting] (PDF) (Report) (in Dutch). Retrieved 18 February 2017.[permanent dead link]
- Dieter, R. K.; Watson, R. T. (2009). «Transmetalation reactions producing organocopper compounds». In Rappoport, Z.; Marek, I. (eds.). The Chemistry of Organocopper Compounds. Vol. 1. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 443–526. ISBN 978-0-470-77296-6.
- Donnelly, J. (2014). Deep Blue. Hachette Children’s Group. ISBN 978-1-4449-2119-9.
- Downs, A. J.; Adams, C. J. (2017). The Chemistry of Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine and Astatine: Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry. Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-4831-5832-7.
- Duda, M. B. (1996). Traditional Chinese Toggles: Counterweights and Charms. Editions Didier Millet. ISBN 978-981-4260-61-9.
- Ede, A.; Cormack, L. B. (2016). A History of Science in Society, Volume I: From the Ancient Greeks to the Scientific Revolution, Third Edition. University of Toronto Press. ISBN 978-1-4426-3503-6.
- Emsley, J. (2011). Nature’s Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- «Encyclopedia Judaica: Ossuaries and Sarcophagi». www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 14 July 2018.
- Eschnauer, H. R.; Stoeppler, M. (1992). «Wine—An enological specimen bank». In Stoeppler, M. (ed.). Hazardous Materials in the Environment. Elsevier Science. pp. 49–72 (58). doi:10.1016/s0167-9244(08)70103-3. ISBN 978-0-444-89078-8.
- Evans, J. W. (1908). «V.— The meanings and synonyms of plumbago». Transactions of the Philological Society. 26 (2): 133–79. doi:10.1111/j.1467-968X.1908.tb00513.x.
- Finger, S. (2006). Doctor Franklin’s Medicine. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-3913-3.
- Fiorini, E. (2010). «2.000 years-old Roman Lead for physics» (PDF). ASPERA: 7–8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2018. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- Frankenburg, F. R. (2014). Brain-Robbers: How Alcohol, Cocaine, Nicotine, and Opiates Have Changed Human History. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-4408-2932-1.
- Frebel, A. (2015). Searching for the Oldest Stars: Ancient Relics from the Early Universe. Princeton University. ISBN 978-0-691-16506-6.
- Freeman, K. S. (2012). «Remediating soil lead with fishbones». Environmental Health Perspectives. 120 (1): a20–a21. doi:10.1289/ehp.120-a20a. PMC 3261960. PMID 22214821.
- Funke, K. (2013). «Solid State Ionics: from Michael Faraday to green energy—the European dimension». Science and Technology of Advanced Materials. 14 (4): 1–50. Bibcode:2013STAdM..14d3502F. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/14/4/043502. PMC 5090311. PMID 27877585.
- Gale, W. F.; Totemeier, T. C. (2003). Smithells Metals Reference Book. Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-048096-1.
- Gilfillan, S. C. (1965). «Lead poisoning and the fall of Rome». Journal of Occupational Medicine. 7 (2): 53–60. ISSN 0096-1736. PMID 14261844.
- Gill, T.; Libraries Board of South Australia (1974). The history and topography of Glen Osmond, with map and illustrations. Libraries Board of South Australia. ISBN 9780724300358.
- Graedel, T. E.; et al. (2010). Metal stocks in Society – Scientific Synthesis (PDF) (Report). International Resource Panel. p. 17. ISBN 978-92-807-3082-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 April 2018. Retrieved 18 April 2017.
- Grandjean, P. (1978). «Widening perspectives of lead toxicity». Environmental Research. 17 (2): 303–21. Bibcode:1978ER…..17..303G. doi:10.1016/0013-9351(78)90033-6. PMID 400972.
- Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1998). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3365-9.
- Grout, J. (2017). «Lead poisoning and Rome». Encyclopaedia Romana. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- Guberman, D. E. (2016). «Lead» (PDF). 2014 Minerals Yearbook (Report). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 8 May 2017.
- Gulbinska, M. K. (2014). Lithium-ion Battery Materials and Engineering: Current Topics and Problems from the Manufacturing Perspective. Springer. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-4471-6548-4.
- Guruswamy, S. (2000). Engineering properties and applications of lead alloys. Marcel Dekker. ISBN 978-0-8247-8247-4.
- Hadlington, T. J. (2017). On the Catalytic Efficacy of Low-Oxidation State Group 14 Complexes. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-51807-7.
- Harbison, R. D.; Bourgeois, M. M.; Johnson, G. T. (2015). Hamilton and Hardy’s Industrial Toxicology. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-92973-5.
- Hauser, P. C. (2017). «Analytical Methods for the Determination of Lead in the Environment». In Astrid, S.; Helmut, S.; Sigel, R. K. O. (eds.). Lead: Its Effects on Environment and Health. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 17. de Gruyter. pp. 49–60. doi:10.1515/9783110434330-003. ISBN 9783110434330. PMID 28731296.
- Hernberg, S. (2000). «Lead Poisoning in a Historical Perspective» (PDF). American Journal of Industrial Medicine. 38 (3): 244–54. doi:10.1002/1097-0274(200009)38:3<244::AID-AJIM3>3.0.CO;2-F. PMID 10940962. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- «A History of Cosmetics from Ancient Times». Cosmetics Info. Archived from the original on 14 July 2016. Retrieved 18 July 2016.
- Hodge, T. A. (1981). «Vitruvius, lead pipes and lead poisoning». American Journal of Archaeology. 85 (4): 486–91. doi:10.2307/504874. JSTOR 504874. S2CID 193094209.
- Hong, S.; Candelone, J.-P.; Patterson, C. C.; et al. (1994). «Greenland ice evidence of hemispheric lead pollution two millennia ago by Greek and Roman civilizations» (PDF). Science. 265 (5180): 1841–43. Bibcode:1994Sci…265.1841H. doi:10.1126/science.265.5180.1841. PMID 17797222. S2CID 45080402.
- Hunt, A. (2014). Dictionary of Chemistry. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-94178-9.
- IAEA — Nuclear Data Section (2017). «Livechart — Table of Nuclides — Nuclear structure and decay data». www-nds.iaea.org. International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- Insight Explorer; IPEN (2016). New Study Finds Lead Levels in a Majority of Paints Exceed Chinese Regulation and Should Not be on Store Shelves (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- Ismawati, Yuyun; Primanti, Andita; Brosché, Sara; Clark, Scott; Weinberg, Jack; Denney, Valerie (2013). Timbal dalam Cat Enamel Rumah Tangga di Indonesia (PDF) (Report) (in Indonesian). BaliFokus & IPEN. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- Jensen, C. F. (2013). Online Location of Faults on AC Cables in Underground Transmission. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-05397-4.
- Jones, P. A. (2014). Jedburgh Justice and Kentish Fire: The Origins of English in Ten Phrases and Expressions. Constable. ISBN 978-1-47211-389-4.
- Kaupp, M. (2014). «Chemical bonding of main-group elements» (PDF). In Frenking, G.; Shaik, S. (eds.). The Chemical Bond: Chemical Bonding Across the Periodic Table. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1–24. doi:10.1002/9783527664658.ch1. ISBN 9783527664658. S2CID 17979350.
- Kellett, C. (2012). Poison and Poisoning: A Compendium of Cases, Catastrophes and Crimes. Accent Press. ISBN 978-1-909335-05-9.
- King, R. B. (1995). Inorganic Chemistry of Main Group Elements. VCH Publishers. ISBN 978-1-56081-679-9.
- Konu, J.; Chivers, T. (2011). «Stable Radicals of the Heavy p-Block Elements». In Hicks, R. G. (ed.). Stable Radicals: Fundamentals and Applied Aspects of Odd-Electron Compounds. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470666975.ch10. ISBN 978-0-470-77083-2.
- Kosnett, M. J. (2006). «Lead». In Olson, K. R. (ed.). Poisoning and Drug Overdose (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 238. ISBN 978-0-07-144333-3.
- Krestovnikoff, M.; Halls, M. (2006). Scuba Diving. Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 978-0-7566-4063-7.
- Kroonen, G. (2013). Etymological Dictionary of Proto-Germanic. Leiden Indo-European Etymological Dictionary Series. Vol. 11. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-18340-7.
- Langmuir, C. H.; Broecker, W. S. (2012). How to Build a Habitable Planet: The Story of Earth from the Big Bang to Humankind. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14006-3.
- Lauwerys, R. R.; Hoet, P. (2001). Industrial Chemical Exposure: Guidelines for Biological Monitoring, Third Edition. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-9383-8.
- Layton, M. (2017). «Lead faces threat of new Euro ban». shootinguk.co.uk. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- «Lead sling bullet; almond shape; a winged thunderbolt on one side and on the other, in high relief, the inscription DEXAI «Catch!»«. The British Museum. Archived from the original on 14 February 2012. Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- «Lead garden ornaments». H. Crowther Ltd. 2016. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- «Lead in Waste Disposal». United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2016. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- «Lead mining». The Northern Echo. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- Levin, H. L. (2009). The Earth Through Time. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-38774-0.
- Levin, R.; Brown, M. J.; Kashtock, M. E.; et al. (2008). «Lead exposures in U.S. children, 2008: Implications for prevention». Environmental Health Perspectives. 116 (10): 1285–93. doi:10.1289/ehp.11241. PMC 2569084. PMID 18941567.
- Lewis, J. (1985). «Lead Poisoning: A Historical Perspective». EPA Journal. 11 (4): 15–18. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (85th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-0484-2.
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Pak, V.; et al. (2015). «Early blood lead levels and sleep disturbance in preadolescence». Sleep. 38 (12): 1869–74. doi:10.5665/sleep.5230. PMC 4667382. PMID 26194570.
- Lochner, J. C.; Rohrbach, G.; Cochrane, K. (2005). «What is Your Cosmic Connection to the Elements?» (PDF). Goddard Space Flight Center. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- Lodders, K. (2003). «Solar System abundances and condensation temperatures of the elements» (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal. 591 (2): 1220–47. Bibcode:2003ApJ…591.1220L. doi:10.1086/375492. ISSN 0004-637X. S2CID 42498829.
- Luckey, T. D.; Venugopal, B. (1979). Physiologic and Chemical Basis for Metal Toxicity. Plenum Press. ISBN 978-1-4684-2952-7.
- Macintyre, J. E. (1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9.
- Marino, P. E.; Landrigan, P. J.; Graef, J.; et al. (1990). «A case report of lead paint poisoning during renovation of a Victorian farmhouse». American Journal of Public Health. 80 (10): 1183–85. doi:10.2105/AJPH.80.10.1183. PMC 1404824. PMID 2119148.
- Markowitz, G.; Rosner, D. (2000). ««Cater to the children»: the role of the lead industry in a public health tragedy, 1900–55″. American Journal of Public Health. 90 (1): 36–46. doi:10.2105/ajph.90.1.36. PMC 1446124. PMID 10630135.
- Masters, S. B.; Trevor, A. J.; Katzung, B. G. (2008). Katzung & Trevor’s Pharmacology: Examination & Board Review (8th ed.). McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 978-0-07-148869-3.
- McCoy, S. (2017). «The End of Lead? Federal Gov’t Order Bans Sinkers, Ammo». GearJunkie. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- Meija, Juris; et al. (2016). «Atomic weights of the elements 2013 (IUPAC Technical Report)». Pure and Applied Chemistry. 88 (3): 265–91. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-0305.
- Merriam-Webster. «Definition of LEAD». www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- Moore, M. R. (1977). «Lead in drinking water in soft water areas—health hazards». Science of the Total Environment. 7 (2): 109–15. Bibcode:1977ScTEn…7..109M. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(77)90002-X. PMID 841299.
- More, A. F.; Spaulding, N. E.; Bohleber, P.; et al. (2017). «Next-generation ice core technology reveals true minimum natural levels of lead (Pb) in the atmosphere: Insights from the Black Death» (PDF). GeoHealth. 1 (4): 211–219. doi:10.1002/2017GH000064. ISSN 2471-1403. PMC 7007106. PMID 32158988.
- Mosseri, S.; Henglein, A.; Janata, E. (1990). «Trivalent lead as an intermediate in the oxidation of lead(II) and the reduction of lead(IV) species». Journal of Physical Chemistry. 94 (6): 2722–26. doi:10.1021/j100369a089.
- Mycyk, M.; Hryhorczuk, D.; Amitai, Y.; et al. (2005). «Lead». In Erickson, T. B.; Ahrens, W. R.; Aks, S. (eds.). Pediatric Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Poisoned Child. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-141736-5.
- Nakashima, T.; Hayashi, H.; Tashiro, H.; et al. (1998). «Gender and hierarchical differences in lead-contaminated Japanese bone from the Edo period». Journal of Occupational Health. 40 (1): 55–60. doi:10.1539/joh.40.55.
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (2004). Structural Shielding Design for Medical X-ray Imaging Facilities. ISBN 978-0-929600-83-3.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. «NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards — Lead». www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 18 November 2016.
- Navas-Acien, A. (2007). «Lead Exposure and Cardiovascular Disease—A Systematic Review». Environmental Health Perspectives. 115 (3): 472–482. doi:10.1289/ehp.9785. PMC 1849948. PMID 17431501.
- Nikolayev, S., ed. (2012). «*lAudh-«. Indo-European Etymology. starling.rinet.ru. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- Norman, N. C. (1996). Periodicity and the s- and p-Block Elements. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-855961-0.
- Nriagu, J. O. (1983). «Saturnine gout among Roman aristocrats — Did lead poisoning contribute to the fall of the Empire?». The New England Journal of Medicine. 308 (11): 660–63. doi:10.1056/NEJM198303173081123. PMID 6338384.
- Nriagu, J. O.; Kim, M-J. (2000). «Emissions of lead and zinc from candles with metal-core wicks». Science of the Total Environment. 250 (1–3): 37–41. Bibcode:2000ScTEn.250…37N. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00359-4. PMID 10811249.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. «Substance data sheet for occupational exposure to lead». www.osha.gov. Archived from the original on 16 March 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- Olinsky-Paul, T. (2013). «East Penn and Ecoult battery installation case study webinar» (PDF). Clean Energy States Alliance. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- Palmieri, R., ed. (2006). The Organ. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-94174-7.
- «surma». Oxford English Dictionary (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. 2009.
- Park, J. H.; Bolan, N.; Meghara, M.; et al. (2011). «Bacterial-assisted immobilization of lead in soils: Implications for remediation» (PDF). Pedologist: 162–74. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 November 2015.
- Parker, R. B. (2005). The New Cold-Molded Boatbuilding: From Lofting to Launching. WoodenBoat Books. ISBN 978-0-937822-89-0.
- Parthé, E. (1964). Crystal Chemistry of Tetrahedral Structures. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-677-00700-7.
- Pauling, L. (1947). General Chemistry. W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9.
- Peneva, S. K.; Djuneva, K. D.; Tsukeva, E. A. (1981). «RHEED study of the initial stages of crystallization and oxidation of lead and tin». Journal of Crystal Growth. 53 (2): 382–396. Bibcode:1981JCrGr..53..382P. doi:10.1016/0022-0248(81)90088-9. ISSN 0022-0248.
- Petzel, S.; Juuti, M.; Sugimoto, Yu. (2004). «Environmental Stewardship with Regional Perspectives and Drivers of the Lead-free Issue». In Puttlitz, K. J.; Stalter, K. A. (eds.). Handbook of Lead-Free Solder Technology for Microelectronic Assemblies. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8247-5249-1.
- Polyanskiy, N. G. (1986). Fillipova, N. A (ed.). Аналитическая химия элементов: Свинец [Analytical Chemistry of the Elements: Lead] (in Russian). Nauka.
- Prasad, P. J. (2010). Conceptual Pharmacology. Universities Press. ISBN 978-81-7371-679-9. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- «Primary Lead Refining Technical Notes». LDA International. Archived from the original on 22 March 2007. Retrieved 7 April 2007.
- Progressive Dynamics, Inc. «How Lead Acid Batteries Work: Battery Basics». progressivedyn.com. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 3 July 2016.
- Putnam, B. (2003). The Sculptor’s Way: A Guide to Modelling and Sculpture. Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-42313-5.
- Pyykkö, P. (1988). «Relativistic effects in structural chemistry». Chemical Reviews. 88 (3): 563–94. doi:10.1021/cr00085a006.
- Rabinowitz, M. B. (1995). «Imputing lead sources from blood lead isotope ratios». In Beard, M. E.; Allen Iske, S. D. (eds.). Lead in Paint, Soil, and Dust: Health Risks, Exposure Studies, Control Measures, Measurement Methods, and Quality Assurance. ASTM. pp. 63–75. doi:10.1520/stp12967s. ISBN 978-0-8031-1884-3.
- «Radioactive Decay Series» (PDF). Nuclear Systematics. MIT OpenCourseWare. 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
- Ramage, C. K., ed. (1980). Lyman Cast Bullet Handbook (3rd ed.). Lyman Products Corporation.
- Randerson, J. (2002). «Candle pollution». New Scientist (2348). Retrieved 7 April 2007.
- Reddy, A.; Braun, C. L. (2010). «Lead and the Romans». Journal of Chemical Education. 87 (10): 1052–55. Bibcode:2010JChEd..87.1052R. doi:10.1021/ed100631y.
- Retief, F.; Cilliers, L. P. (2006). «Lead poisoning in ancient Rome». Acta Theologica. 26 (2): 147–64 (149–51). doi:10.4314/actat.v26i2.52570.
- Rich, V. (1994). The International Lead Trade. Woodhead Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85709-994-5.
- Rieuwerts, J. (2015). The Elements of Environmental Pollution. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-85919-6.
- Riva, M. A.; Lafranconi, A.; d’Orso, M. I.; et al. (2012). «Lead poisoning: Historical aspects of a paradigmatic «occupational and environmental disease»«. Safety and Health at Work. 3 (1): 11–16. doi:10.5491/SHAW.2012.3.1.11. PMC 3430923. PMID 22953225.
- Roederer, I. U.; Kratz, K.-L.; Frebel, A.; et al. (2009). «The end of nucleosynthesis: Production of lead and thorium in the early galaxy». The Astrophysical Journal. 698 (2): 1963–80. arXiv:0904.3105. Bibcode:2009ApJ…698.1963R. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/698/2/1963. S2CID 14814446.
- Rogalski, A. (2010). Infrared Detectors (2nd ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-7671-4. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- Röhr, C. (2017). «Binare Zintl-Phasen» [Binary Zintl Phases]. Intermetallische Phasen [Intermettallic Phases] (in German). Universitat Freiburg. Retrieved 18 February 2017.
- Rudolph, A. M.; Rudolph, C. D.; Hostetter, M. K.; et al. (2003). «Lead». Rudolph’s Pediatrics (21st ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 369. ISBN 978-0-8385-8285-5.
- Samson, G. W. (1885). The divine law as to wines. J. B. Lippincott & Co.
- Scarborough, J. (1984). «The myth of lead poisoning among the Romans: An essay review». Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 39 (4): 469–475. doi:10.1093/jhmas/39.4.469. PMID 6389691.
- Schoch, R. M. (1996). Case Studies in Environmental Science. West Publishing. ISBN 978-0-314-20397-7.
- Schoeters, G.; Den Hond, E.; Dhooge, W.; et al. (2008). «Endocrine disruptors and abnormalities of pubertal development» (PDF). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 102 (2): 168–175. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00180.x. hdl:1854/LU-391408. PMID 18226071.
- Sharma, H. R.; Nozawa, K.; Smerdon, J. A.; et al. (2013). «Templated three-dimensional growth of quasicrystalline lead». Nature Communications. 4: 2715. Bibcode:2013NatCo…4.2715S. doi:10.1038/ncomms3715. PMID 24185350.
- Sharma, H. R.; Smerdon, J. A.; Nugent, P. J.; et al. (2014). «Crystalline and quasicrystalline allotropes of Pb formed on the fivefold surface of icosahedral Ag-In-Yb». The Journal of Chemical Physics. 140 (17): 174710. Bibcode:2014JChPh.140q4710S. doi:10.1063/1.4873596. PMID 24811658.
- Silverman, M. S. (1966). «High-pressure (70-k) synthesis of new crystalline lead dichalcogenides». Inorganic Chemistry. 5 (11): 2067–69. doi:10.1021/ic50045a056.
- Singh, P. (2017). «Over 73% of paints found to have excessive lead: Study». Times of India. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- Sinha, S. P.; Shelly; Sharma, V.; et al. (1993). «Neurotoxic effects of lead exposure among printing press workers». Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 51 (4): 490–93. doi:10.1007/BF00192162. PMID 8400649. S2CID 26631583.
- Slater, J. C. (1964). «Atomic Radii in Crystals». The Journal of Chemical Physics. 41 (10): 3199–3204. Bibcode:1964JChPh..41.3199S. doi:10.1063/1.1725697. ISSN 0021-9606.
- Smirnov, A. Yu.; Borisevich, V. D.; Sulaberidze, A. (2012). «Evaluation of specific cost of obtainment of lead-208 isotope by gas centrifuges using various raw materials». Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering. 46 (4): 373–78. doi:10.1134/s0040579512040161. S2CID 98821122.
- Sokol, R. C. (2005). «Lead exposure and its effects on the reproductive system». In Golub, M. S. (ed.). Metals, Fertility, and Reproductive Toxicity. CRC Press. pp. 117–53. doi:10.1201/9781420023282.ch6. ISBN 978-0-415-70040-5.
- Stabenow, F.; Saak, W.; Weidenbruch, M. (2003). «Tris(triphenylplumbyl)plumbate: An anion with three stretched lead–lead bonds». Chemical Communications (18): 2342–2343. doi:10.1039/B305217F. PMID 14518905.
- Stone, R. (1997). «An Element of Stability». Science. 278 (5338): 571–572. Bibcode:1997Sci…278..571S. doi:10.1126/science.278.5338.571. S2CID 117946028.
- Street, A.; Alexander, W. (1998). Metals in the Service of Man (11th ed.). Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-025776-2.
- Szczepanowska, H. M. (2013). Conservation of Cultural Heritage: Key Principles and Approaches. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-67474-4.
- Takahashi, K.; Boyd, R. N.; Mathews, G. J.; et al. (1987). «Bound-state beta decay of highly ionized atoms» (PDF). Physical Review C. 36 (4): 1522–1528. Bibcode:1987PhRvC..36.1522T. doi:10.1103/physrevc.36.1522. OCLC 1639677. PMID 9954244. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2014. Retrieved 27 August 2013.
- Tarragó, A. (2012). «Case Studies in Environmental Medicine (CSEM) Lead Toxicity» (PDF). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
- Tétreault, J.; Sirois, J.; Stamatopoulou, E. (1998). «Studies of lead corrosion in acetic acid environments». Studies in Conservation. 43 (1): 17–32. doi:10.2307/1506633. JSTOR 1506633.
- «Think Lead research summary» (PDF). The Lead Sheet Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2017. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- Thomson, T. (1830). The History of Chemistry. Henry Colburn and Richard Bentley (publishers). ISBN 9780405066238.
- Thornton, I.; Rautiu, R.; Brush, S. M. (2001). Lead: The Facts (PDF). International Lead Association. ISBN 978-0-9542496-0-1. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- Thürmer, K.; Williams, E.; Reutt-Robey, J. (2002). «Autocatalytic oxidation of lead crystallite surfaces». Science. 297 (5589): 2033–35. Bibcode:2002Sci…297.2033T. doi:10.1126/science.297.5589.2033. PMID 12242437. S2CID 6166273.
- Tolliday, B. (2014). «Significant growth in lead usage underlines its importance to the global economy». International Lead Association. Archived from the original on 28 February 2017. Retrieved 28 February 2017.
Global demand for lead has more than doubled since the early 1990s and almost 90% of use is now in lead-acid batteries
- «Toronto museum explores history of contraceptives». ABC News. 2003. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- «Toxic Substances Portal – Lead». Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011.
- «Toxicological Profile for Lead» (PDF). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry/Division of Toxicology and Environmental Medicine. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 July 2017.
- «Trace element emission from coal». IEA Clean Coal Centre. 2012. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- Tuček, K.; Carlsson, J.; Wider, H. (2006). «Comparison of sodium and lead-cooled fast reactors regarding reactor physics aspects, severe safety and economical issues» (PDF). Nuclear Engineering and Design. 236 (14–16): 1589–98. doi:10.1016/j.nucengdes.2006.04.019.
- Tungate, M. (2011). Branded Beauty: How Marketing Changed the Way We Look. Kogan Page Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7494-6182-9.
- UK Marine SACs Project (1999). «Lead». Water Quality (Report). Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- United Nations Environment Programme (2010). Final review of scientific information on lead (PDF). Chemicals Branch, Division of Technology, Industry and Economics. Retrieved 31 January 2017.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (2010). «Metallurgical Industry:Secondary Lead Processing». AP 42 Compilation of Air Pollutant Emission Factors (5th ed.). Retrieved 20 May 2018.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (2000). «Regulatory Status of Waste Generated by Contractors and Residents from Lead-Based Paint Activities Conducted in Households (August 2000)». Retrieved 28 February 2017.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (2005). «Best Management Practices for Lead at Outdoor Shooting Ranges» (PDF). Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- United States Food and Drug Administration (2015). Q3D Elemental Impurities Guidance for Industry (PDF) (Report). United States Department of Health and Human Services. p. 41. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- United States Geological Survey (1973). Geological Survey Professional Paper. United States Government Publishing Office. p. 314.
- United States Geological Survey (2005). Lead (PDF) (Report). Retrieved 20 February 2016.
- United States Geological Survey (2017). «Lead» (PDF). Mineral Commodities Summaries. Retrieved 8 May 2017.
- University of California Nuclear Forensic Search Project. «Decay Chains». Nuclear Forensics: A Scientific Search Problem. Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- Vasmer, M. (1986–1987) [1950–1958]. Trubachyov, O. N.; Larin, B. O. (eds.). Этимологический словарь русского языка [Russisches etymologisches Worterbuch] (in Russian) (2nd ed.). Progress. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- Vogel, N. A.; Achilles, R. (2013). The Preservation and Repair of Historic Stained and Leaded Glass (PDF) (Report). United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- Waldron, H. A. (1985). «Lead and lead poisoning in antiquity». Medical History. 29 (1): 107–08. doi:10.1017/S0025727300043878. PMC 1139494.
- Wani, A. L.; Ara, A.; Usman, J. A. (2015). «Lead toxicity: A review». Interdisciplinary Toxicology. 8 (2): 55–64. doi:10.1515/intox-2015-0009. PMC 4961898. PMID 27486361.
- Weast, R. C.; Astle, M. J.; Beyer, W. H. (1983). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-0464-4.
- «Weatherings to Parapets and Cornices». The Lead Sheet Association. Archived from the original on 20 February 2017. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- Webb, G. A. (2000). Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-85404-327-9.
- Webb, G. W.; Marsiglio, F.; Hirsch, J. E. (2015). «Superconductivity in the elements, alloys and simple compounds». Physica C: Superconductivity and Its Applications. 514: 17–27. arXiv:1502.04724. Bibcode:2015PhyC..514…17W. doi:10.1016/j.physc.2015.02.037. S2CID 119290828.
- Whitten, K. W.; Gailey, K. D.; David, R. E. (1996). General chemistry with qualitative analysis (3rd ed.). Saunders College. ISBN 978-0-03-012864-6.
- Wiberg, E.; Wiberg, N.; Holleman, A. F. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-352651-9.
- Wilkes, C. E.; Summers, J. W.; Daniels, C. A.; et al. (2005). PVC Handbook. Hanser. ISBN 978-1-56990-379-7.
- Willey, D. G. (1999). «The physics behind four amazing demonstrations — CSI». Skeptical Inquirer. 23 (6). Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- Winder, C. (1993a). «The history of lead — Part 1». LEAD Action News. 2 (1). ISSN 1324-6011. Archived from the original on 31 August 2007. Retrieved 5 February 2016.
- Winder, C. (1993b). «The history of lead — Part 3». LEAD Action News. 2 (3). ISSN 1324-6011. Archived from the original on 31 August 2007. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- Windholz, M. (1976). Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs (9th ed.). Merck & Co. ISBN 978-0-911910-26-1. Monograph 8393.
- Wood, J. R.; Hsu, Y-T.; Bell, C. (2021). «Sending Laurion Back to the Future: Bronze Age Silver and the Source of Confusion» (PDF). Internet Archaeology. 56 (9). doi:10.11141/ia.56.9. S2CID 236973111.
- World Health Organization (1995). Environmental Health Criteria 165: Inorganic Lead (Report). Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- World Health Organization (2000). «Lead» (PDF). Air quality guidelines for Europe. Regional Office for Europe. pp. 149–53. ISBN 978-92-890-1358-1. OCLC 475274390.
- World Health Organization (2018). «Lead poisoning and health». Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- World Nuclear Association (2015). «Nuclear Radiation and Health Effects». Archived from the original on 24 December 2015. Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- Wrackmeyer, B.; Horchler, K. (1990). 207Pb-NMR Parameters. Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy. Vol. 22. Academic Press. pp. 249–303. doi:10.1016/S0066-4103(08)60257-4. ISBN 978-0-08-058405-8.
- Yong, L.; Hoffmann, S. D.; Fässler, T. F. (2006). «A low-dimensional arrangement of [Pb9]4· clusters in [K(18-crown-6)]2K2Pb9·(en)1.5«. Inorganica Chimica Acta. 359 (15): 4774–78. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2006.04.017.
- Young, S. (2012). «Battling lead contamination, one fish bone at a time». Compass. United States Coast Guard. Archived from the original on 14 June 2013. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- Yu, L.; Yu, H. (2004). Chinese Coins: Money in History and Society. Long River Press. ISBN 978-1-59265-017-0.
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. (2012). «Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China». Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 184 (4): 2261–73. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2115-6. PMID 21573711. S2CID 20372810.
- Zhao, F. (2008). Information Technology Entrepreneurship and Innovation. IGI Global. p. 440. ISBN 978-1-59904-902-1.
- Zuckerman, J. J.; Hagen, A. P. (1989). Inorganic Reactions and Methods, the Formation of Bonds to Halogens. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-18656-4.
- Zweifel, H. (2009). Plastics Additives Handbook. Hanser. ISBN 978-3-446-40801-2.
- Zýka, J. (1966). «Analytical study of the basic properties of lead tetraacetate as oxidizing agent». Pure and Applied Chemistry. 13 (4): 569–81. doi:10.1351/pac196613040569. S2CID 96821219. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
Further reading[edit]
- Astrid, S.; Helmut, S.; Sigel, R. K. O., eds. (2017). Lead: Its Effects on Environment and Health. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 17. De Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-044107-9. Table of contents
- Casas, J. S.; Sordo, J., eds. (2006). Lead Chemistry, Analytical Aspects. Environmental Impacts and Health Effects. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-444-52945-9.
- «Toxicologic and epidemiologic clues from the characterization of the 1952 London smog fine particulate matter in archival autopsy lung tissues».
- «Assessing the mechanism of DNA damage induced by lead through direct and indirect interactions».
External links[edit]
Look up lead in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lead.
- The Toxicology of Heavy Metals: Getting the Lead Out, American Society for Clinical Pathology
- COVID-19 to reduce global lead production by 5,2% in 2020 (with a figure showing global lead production, 2010-2024)
What does the word lead mean?
According to Dictionary and Your Dictionary, the word lead has a plethora of different meanings. First, the word lead can be used as a verb, meaning to conduct or escort, usually by holding and guiding, or to show the way. This can also be used as a noun to refer to the person who is in the first or foremost place in advance of others, or the extent to which the person is leading. For example, the person who is to have direction or charge of as in to lead an army, sales team, political party, or an exploring party as a measure of precedence. Lead can also be used as an adjective in many different ways. It most commonly means most important, or principal. It can also be used in football to refer to a forward pass that is thrown ahead of the intended receiver so as to allow him to catch it while running, or baseball to refer to a base runner or batter in an advance position, as well as the timing of ignition relative to the position of the piston in an internal-combustion engine. Lead can also mean the angle between the direction of the firing of a gun is aimed and the position of a moving target which corrects for the flight time of the missile, or a jumper that consists of a short piece of wire.
In chemistry, the word lead is a noun that refers to heavy, comparatively soft, malleable, bluish-gray metal. This metal is sometimes found in its natural state, however it is usually combined as a sulfide, especially in galena. Information on this metal is as follows: Symbol: Pb; atomic weight/atomic wt: 207.19; atomic number/atomic no.: 82; specific gravity: 11.34 at 20°C. Lead is a pliable, heavy, inelastic metal element, which has a bright, bluish color and is an ingredient of solder, but is easily tarnished. It is both malleable and ductile, though with little tenacity. This can also refer to something that is made of this metal or one of its alloys, accumulators, cable sheaths, paints, and as a radiation shield, or some plummet or pass of lead that is suspended by a line. It can also be used as a verb or adjective in this sense, or can be used to refer to a lead weight suspended on a line used to take soundings of the depth of water.
The word lead can also refer to bullets that have been shot, black lead or a mixture of graphite and clay that is used in as the marking substance in pencils, or in the printing industry to refer to a thin strip of metal or brass less than type-high, which is used for increasing the space between lines of type. In stained glass, lead refers to the grooved bar of lead which sections of glass are set in. Finally, imn British English, this refers to a roof that is shallow or flat, and covered with lead. Lead has numerous other definitions that refer to things like the width of port opening, the action of a tooth or the tooth of a wheel, a course of a rope, a release of steam from a valve, the end of its stroke, a distance of haul, a fleet of yachts and the lead of a boat, and more.
What are synonyms and antonyms for the word lead?
SYNONYMS (from Power Thesaurus)
- head
- cause
- control
- leader
- forefront
- leading
- principal
- leading role
- leading man
- track
- show
- star
- superintend
- oversee
- bring
- run
- conduct
- result
- guide
- dispose
- accompany
- head up
- take
- pilot
- administer
- prerogative
- persuade
- leash
- front
- usher
- hint
- leadership
- command
- trail
- clue
- move
- escort
- precede
- carry
- steer
- influence
- shepherd
- rule
- manage
- govern
- supervise
- pass
- drive
- chair
- advantage
- direct
ANTONYMS (from Power Thesaurus)
- put up with
- play it by the book
- agree to
- adhere to
- trail
- ask where to go
- come to heel
- give in to
- give way to
- catch the bus
- keep in step
- be regulated by
- accept
- consent to
- bow to
- ask for the road
- be controlled by
- obey
- accept orders from
- be dutiful to
- yield to
- be governed by
- follow up
- comply with
- take it lying down
- abide by
- do what someone says
- chase
- heed
- stomach
- play by the rules
- submit to
- ask for directions
- observe
- be subject to
- surrender to
- ask for direction
- defer to
- fall into line with
- follow the orders of
- conform to
- brook
- carry out the orders of
- dog
- lump it
- truckle to
- follow
- be ruled by
- take orders from
- ask the way
What is the origin of the word lead?
According to Etymonline, the word lead has been used since the Middle English leden, and comes from the Old English lǣdan, Old English lēad, and Old High German līdan. This word can also be compared to the Scots leid, lede North Frisian lud, luad, West Frisian lead, Dutch lood, German Lot , Swedish lod lead, Icelandic lóð, and Irish luaidhe.
How can the word lead be used in a sentence?
Lead can be used in many sentences in different parts of speech and tenses like the past tense or past participle. Some examples of lead are below.
The conductor leads the orchestra and the lead singer through the piece of music.
The witness played a principal part in the lead story about the diamond. Their information on the time of flight to the next base and the potential customer that entered the store was crucial to the news.
He bet it all when he was in the lead in the round of cards, but found himself in misery after the playing of a card that made him lose it all.
Orators of all ages took numerous leads from the different speakers. They advised them on many topics, from a transaction to admission to college and more. The pupil sat there in shock.
The jockey on the white horse took the reins and the lead in the race to the surprise of many. This was an important entry in the jockey’s career record.
Overall, the word lead means to guide the way or play a principal role. It can also refer to the toxic bluish-white metallic element. This toxic malleable metallic element has a specific melting point and corrosion or tarnishes that are dangerous and different degrees of hardness. A mass of lead has the symbol Pb and a specific valency and relative density, and may be used in electrical connection, or the top position of a roof covering.
Sources:
- lead | Origin and meaning of lead | Online Etymology Dictionary
- Lead synonyms – 2 757 Words and Phrases for Lead | Power Thesaurus
- Lead antonyms – 402 Opposites of Lead | Power Thesaurus
- Lead | Definition of Lead | Dictionary.com
- Lead Meaning | Best 134 Definitions of Lead | Your Dictionary
Kevin Miller is a growth marketer with an extensive background in Search Engine Optimization, paid acquisition and email marketing. He is also an online editor and writer based out of Los Angeles, CA. He studied at Georgetown University, worked at Google and became infatuated with English Grammar and for years has been diving into the language, demystifying the do’s and don’ts for all who share the same passion! He can be found online here.
I recently came across the following quote in a fairly significant leadership book, The Practice of Adaptive Leadership by Ronald Heifetz, Alexander Rashow, and Marty Linsky.
«The word leader comes from the Indo-European root word leit, the name
for the person who carried the flag in front of army going into battle
and usually died in the first enemy attack. His sacrifice would alert
the rest of the army to the location of the danger ahead.» Page 26 of The Practice of Adaptive Leadership
The problem is that I’m having difficulty finding any source that confirms that ‘leit’ referred to the flag bearer in a battle. I’ve found that it means «to leave» and «to die», but I’m not finding where the flag bearer concept came from, and they don’t cite a source.
So I have two questions: Did ‘leit’ refer to the person carrying the flag going into battle? If not, what is a fuller meaning of the word as it was originally used?
Thank you so much. Miguel
The Secret History of Lead
The Secret History of Lead
Research support was provided by the Investigative Fund of The Nation Institute. Follow-ups:
“Amplification,” June 19, 2000 and letters exchanges: “Lead–Balloons and Bouquets,” May 15, and “Lead-Letter Office,” July 3, 2000.
The next time you pull the family barge in for a fill-up, check it out: The gas pumps read “Unleaded.” You might reasonably suppose this is because naturally occurring lead has been thoughtfully removed from the gasoline. But you would be wrong. There is no lead in gasoline unless somebody puts it there. And, a little more than seventy-five years ago, some of America’s leading corporations–General Motors, Du Pont and Standard Oil of New Jersey (known nowadays as Exxon)–were that somebody. They got together and put lead, a known poison, into gasoline, for profit.
Lead was outlawed as an automotive gasoline additive in this country in 1986–more than sixty years after its introduction–to enable the use of emissions-reducing catalytic converters in cars (which are contaminated and rendered useless by lead) and to address the myriad health and safety concerns that have shadowed the toxic additive from its first, tentative appearance on US roads in the twenties, through a period of international ubiquity only recently ending. Since the virtual disappearance of leaded gas in the United States (it’s still sold for use in propeller airplanes), the mean blood-lead level of the American population has declined more than 75 percent. A 1985 EPA study estimated that as many as 5,000 Americans died annually from lead-related heart disease prior to the country’s lead phaseout. According to a 1988 report to Congress on childhood lead poisoning in America by the government’s Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, one can estimate that the blood-lead levels of up to 2 million children were reduced every year to below toxic levels between 1970 and 1987 as leaded gasoline use was reduced. From that report and elsewhere, one can conservatively estimate that a total of about 68 million young children had toxic exposures to lead from gasoline from 1927 to 1987.
How did lead get into gasoline in the first place? And why is leaded gas still being sold in the Third World, Eastern Europe and elsewhere? Recently uncovered documents from the archives of the aforementioned industrial behemoths and the US government, a new skein of academic research and a careful reading of that long-ago period’s historical record, as well as dozens of interviews conducted by The Nation, tell the true story of leaded gasoline, a sad and sordid commercial venture that would tiptoe its way quietly into the black hole of history if the captains of industry were to have their way. But the story must be recounted now. The leaded gas adventurers have profitably polluted the world on a grand scale and, in the process, have provided a model for the asbestos, tobacco, pesticide and nuclear power industries, and other twentieth-century corporate bad actors, for evading clear evidence that their products are harmful by hiding behind the mantle of scientific uncertainty.
This is not just a textbook example of unnecessary environmental degradation, however. Nor is this history important solely as a cautionary retort to those who would doubt the need for aggressive regulation of industry, when commercial interests ask us to sanction genetically modified food on the basis of their own scientific assurances, just as the merchants of lead once did. The leaded gasoline story must also be read as a call to action, for the lead menace lives.
Consider:
§ the severe health hazards of leaded gasoline were known to its makers and clearly identified by the US public health community more than seventy-five years ago, but were steadfastly denied by the makers, because they couldn’t be immediately quantified;
§ other, safer antiknock additives–used to increase gasoline octane and counter engine “knock”–were known and available to oil companies and the makers of lead antiknocks before the lead additive was discovered, but they were covered up and denied, then fought, suppressed and unfairly maligned for decades to follow;
§ the US government was fully apprised of leaded gasoline’s potentially hazardous effects and was aware of available alternatives, yet was complicit in the cover-up and even actively assisted the profiteers in spreading the use of leaded gasoline to foreign countries;
§ the benefits of lead antiknock additives were wildly and knowingly overstated in the beginning, and continue to be. Lead is not only bad for the planet and all its life forms, it is actually bad for cars and always was;
§ for more than four decades, all scientific research regarding the health implications of leaded gasoline was underwritten and controlled by the original lead cabal–Du Pont, GM and Standard Oil; such research invariably favored the industry’s pro-lead views, but was from the outset fatally flawed; independent scientists who would finally catch up with the earlier work’s infirmities and debunk them were–and continue to be–threatened and defamed by the lead interests and their hired hands;
§ confronted in recent years with declining sales in their biggest Western markets, owing to lead phaseouts imposed in the United States and, more recently, Europe, the current sellers of lead additives have successfully stepped up efforts to market their wares in the less-developed world, efforts that persist and have resulted in some countries today placing more lead in their gasoline, per gallon, than was typically used in the West, extra lead that serves no purpose other than profit;
§ faced with lead’s demise and their inevitable days of reckoning, these firms have used the extraordinary financial returns that lead additive sales afford to hurriedly fund diversification into less risky, more conventional businesses, while taking a page from the tobacco companies’ playbook and simultaneously moving to reorganize their corporate structures to shield ownership and management from liability for blanketing the earth with a deadly heavy metal.
You can choose whether to smoke, but you can’t pick the air you breathe, even if it is contaminated by lead particles from automobile exhaust. Seventy-five years ago, well-known industrialists like GM’s Alfred Sloan and Charles Kettering (remembered today for having founded the prestigious Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center) and the powerful brothers Pierre and Irénée du Pont added to their substantial fortunes and did the planet very dirty by disregarding the common-sense truth that no good can come from burning a long-known poison in internal-combustion engines.
The steady emergence of improved methodology and finer, more sensitive measuring equipment has allowed scientists to prove lead’s tragic toll with increasing precision. The audacity of today’s lead-additive makers’ conduct mounts with each new study weighing in against them. Because lead particles in automobile exhaust travel in wind, rain and snow, which know no national boundaries, lead makers and refiners who peddle leaded gasoline knowingly injure not only the local populations using their product but men, mice and fish tens of thousands of miles distant.
GM and Standard Oil sold their leaded gasoline subsidiary, the Ethyl Gasoline Corporation, to Albemarle Paper in 1962, while Du Pont only cleaned up its act recently, but all hope to leave their leaded gasoline paternity a hushed footnote to their inglorious pasts. The principal maker of lead additive today the Associated Octel Company of Ellesmere Port, England) and its foremost salesmen (Octel and the Ethyl corporation of Richmond, Virginia) acknowledge what they see as a political reality: Their product will one day be run out of business. But they plan to keep on selling it in the Third World profitably until they can sell it no longer. They continue to deny lead’s dangers while overrating its virtues, reprising the central tenets of the lead mythology chartered by GM, Du Pont and Standard lifetimes ago.
These mighty corporations should pay Ethyl and Octel for keeping their old lies alive. They’ll need them, in their most up-to-the-minute and media-friendly fashion: Because of the harm caused by leaded gasoline they have been joined to a class-action suit brought in a circuit court in Maryland against the makers of that other product of lead’s excruciating toxic reign: lead paint. Along with the makers of lead paint and the lead trade organizations with whom they both once worked in close concert, suppliers and champions of lead gasoline additives–Ethyl, Du Pont and PPG–have been named as defendants in the suit.
Though the number of cases of lead poisoning has been falling nationwide, the lead dust in exhaust spewed by automobiles in the past century will continue to haunt us in this one, coating our roads, buildings and soil, subtly but indefinitely contaminating our homes, belongings and food.
The Problem With Lead
Lead is poison, a potent neurotoxin whose sickening and deadly effects have been known for nearly 3,000 years and written about by historical figures from the Greek poet and physician Nikander and the Roman architect Vitruvius to Benjamin Franklin. Odorless, colorless and tasteless, lead can be detected only through chemical analysis. Unlike such carcinogens and killers as pesticides, most chemicals, waste oils and even radioactive materials, lead does not break down over time. It does not vaporize, and it never disappears.
For this reason, most of the estimated 7 million tons of lead burned in gasoline in the United States in the twentieth century remains–in the soil, air and water and in the bodies of living organisms. Worldwide, it is estimated that modern man’s lead exposure is 300 to 500 times greater than background or natural levels. Indeed, a 1983 report by Britain’s Royal Commission on Environmental Pollution concluded that lead was dispersed so widely by man in the twentieth century that “it is doubtful whether any part of the earth’s surface or any form of life remains uncontaminated by anthropogenic [man-made] lead.” While lead from mining, paint, smelting and other sources is still a serious environmental problem, a recent report by the government’s Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry estimated that the burning of gasoline has accounted for 90 percent of lead placed in the atmosphere since the 1920s. (The magnitude of this fact is placed in relief when one considers the estimate of the US Public Health Service that the associated health costs from a parallel problem–the remaining lead paint in America’s older housing–total in the multibillions.)
Classical acute lead poisoning occurs at high levels of exposure, and its symptoms–blindness, brain damage, kidney disease, convulsions and cancer–often leading, of course, to death, are not hard to identify. The effects of pervasive exposure to lower levels of lead are more easily miscredited; lead poisoning has been called an “aping disease” because its symptoms are so frequently those of other known ailments. Children are the first and worst victims of leaded gas; because of their immaturity, they are most susceptible to systemic and neurological injury, including lowered IQs, reading and learning disabilities, impaired hearing, reduced attention span, hyperactivity, behavioral problems and interference with growth. Because they often go undetected for some time, such maladies are particularly insidious. In adults, elevated blood-lead levels are related to hypertension and cardiovascular disease, particularly strokes, heart attacks and premature deaths. Lead exposure before or during pregnancy is especially serious, harming the mother’s own body, affecting fetal development and frequently leading to miscarriage. In the eighties the EPA estimated that the health damages from airborne lead cost American society billions each year. In Venezuela, where the state oil company sold only leaded gasoline until 1999, a recent report found 63 percent of newborn children with blood-lead levels in excess of the so-called safe levels promulgated by the US government.
The Search for an Antiknock
On December 9, 1921, a young engineer named Thomas Midgley Jr., working in the laboratory of the General Motors Research Corporation in Dayton, Ohio, reported to his boss, Charles Kettering, that he’d discovered that tetraethyl lead–a little-known compound of metallic lead and one of the alkyl series, also referred to as lead tetraethyl or TEL–worked to reduce “knock” or “pinging” in internal-combustion engines.
Tetraethyl lead was first discovered by a German chemist in 1854. A technical curiosity, it was not used commercially on account of “its known deadliness.” It is highly poisonous, and even casual cumulative contact with it was known to cause hallucinations, difficulty in breathing and, in the worst cases, madness, spasms, palsies, asphyxiation and death. Still unused in 1921, sixty-seven years after its invention, it was not an obvious choice as a gasoline additive.
In the laboratories of Charles Kettering, however, the search for a gasoline additive to cure “knock” had been going on for some years prior to Midgley’s rediscovery of TEL. In 1911 Kettering had invented the electric self-starter–a landmark development in automotive history that eliminated dangerous hand-cranking and enabled many Americans (particularly women) to drive for the first time, arguably killing steam and electric cars in the process. This invention would make “Boss” Kettering rich, famous and beloved to a nation falling in love with its wheels. Thanks to the starter, the folksy inventor’s new firm, Dayton Engineering Laboratories Company, or DELCO, received its first big order, for $10 million, from the upstart General Motors Corporation, founded only three years earlier by William Crapo Durant.
GM’s 1912 Cadillac was equipped with DELCO’s self-starter and battery ignition. When customers reported that the engine of this luxury automobile had an alarming tendency to knock–a sharp, metallic sound hinting at damage being done inside the engine–critics blamed Kettering’s electrical components.
Kettering was convinced, rightly, that knocking was a function of an engine’s fuel rather than ignition problems. When Kettering and his partners sold DELCO to Durant’s GM and its new partner–Alfred Sloan’s Hyatt Roller Bearings–in 1916, his lab was already engaged in a search for the cure. Following the sale, this work was transferred to his new firm, the Dayton Research Laboratories, where a newly hired assistant, Thomas Midgley, was assigned to study the problem of engine knock.
Stabbing in the dark, Midgley got lucky quickly when he added iodine to the fuel, stopping knock in a test engine and establishing for all time that the malady–premature combustion of the fuel/air mixture–was connected to the explosive qualities of the fuel, what would later be called “octane.” Iodine raised octane and cured knock; however, it was corrosive and prohibitively expensive. Inspired by the fundamental breakthrough, Midgley nonetheless carried on with fuel research, testing every substance he could find for antiknock properties, “from melted butter and camphor to ethyl acetate and aluminum chloride.” Unfortunately, “most of them had no more effect than spitting in the Great Lakes.”
The Antiknock That Got Away
Automotive engineers knew by this time that engines that didn’t knock would not only operate more smoothly. They could also be designed to run with higher compression in the cylinders, which would allow more efficient operation, resulting in greater fuel economy, greater power or some harmonious combination of the two. The key was finding a fuel with higher octane. Though octane sufficient for use in high-compression engines had been achievable since 1913 through a process called thermal cracking, the process required added expenditures on plant and equipment, which tightfisted oil refiners didn’t relish. The nation’s fuel supply remained resolutely low grade, a situation that troubled Kettering.
By limiting allowable compression, low-octane fuel meant cars would be burning more gasoline. Like many visionary engineers, Kettering was enamored of conservation as a first principle. As a businessman, he also shared persistent fears at the time that world oil supplies were running out. Low octane and low compression meant lower gas mileage and more rapid exhaustion of a dwindling fuel supply. Inevitably, demand for new automobiles would fade.
By 1917 Kettering and his staff had trained their octane-boosting sights on ethyl alcohol, also known as grain alcohol (the kind you drink), power alcohol or ethanol. In tests supervised by Kettering and Midgley for the Army Air Corps at Wright Field in Dayton, Ohio, researchers concluded that alcohols were among the best antiknock fuels but were not ideal for aircraft engines unless used as an additive, in a blend with gasoline. This undoubtedly led Kettering to concur with an April 13, 1918, Scientific American report: “It is now definitely established that alcohol can be blended with gasoline to produce a suitable motor fuel.”
The story of TEL’s rise, then, is very much the story of the oil companies’ and lead interests’ war against ethanol as an octane-boosting additive that could be mixed with gasoline or, in their worst nightmare, burned straight as a replacement for gasoline. For more than a hundred years, Big Oil has reckoned ethanol to be fundamentally inimical to its interest, and, viewing its interest narrowly, Big Oil might not be wrong. By contrast, GM’s subsequent antipathy to alcohol was a profit-motivated attitude adjustment. Alcohol initially held much fascination for the company, for good reason. Ethanol is always plentiful and easy to make, with a long history in America, not just as a fuel additive but as a pure fuel. The first prototype internal-combustion engine in 1826 used alcohol and turpentine. Prior to the Civil War alcohol was the most widely used illuminating fuel in the country. Indeed, alcohol powered the first engine by the German inventor Nicholas August Otto, father of the four-stroke internal-combustion engines powering our cars today. More important, by the time of Kettering’s antiknock inquiry, alcohol was a proven automotive fuel.
As the automobile era picked up speed, scientific journals were filled with references to alcohol. Tests in 1906 by the Department of Agriculture underscored its power and economy benefits. In 1907 and 1908 the US Geological Survey and the Navy performed 2,000 tests on alcohol and gasoline engines in Norfolk, Virginia, and St. Louis, concluding that higher engine compression could be achieved with alcohol than with gasoline. They noted a complete absence of smoke and disagreeable odors.
Despite many attempts by Big Oil to stifle its home-grown competitor (one time-honored gambit: lobbying legislators to pass punitive taxation thwarting alcohol’s economic viability), power alcohol would number among its adherents several highly regarded inventors and scientists, including Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell. Henry Ford built his very first car to run on what he called farm alcohol. As late as 1925, after the advent of TEL, the high priest of American industry would predict in an interview with the Christian Science Monitor that ethanol–“fuel from vegetation”–would be the “fuel of the future.” Four years later, early examples of his Model A car would be equipped with a dashboard knob to adjust its carburetor to run on gasoline or alcohol.
Ethanol made a lot of sense to a practical Ohio farm boy like Kettering. It was renewable, made from surplus crops and crop waste, and nontoxic. It delivered higher octane than gasoline (though it contained less power per gallon), and it burned more cleanly. By 1920, as Kettering was aware, a US Naval Committee had concluded that alcohol-gasoline blends “withstand high compression without producing knock.”
Higher compression was, after all, what the GM men were after. In February 1920, shortly after joining General Motors’ employ, Thomas Midgley filed a patent application for a blend of alcohol and cracked (olefin) gasoline, as an antiknock fuel. Later that month K.W. Zimmerschied of GM’s New York headquarters wrote Kettering, observing that foreign use of alcohol fuel “is getting more serious every day in connection with export cars, and anything we can do toward building our carburetors so they can be easily adapted to alcohol will be appreciated by all.” Kettering assured him that adaptation for alcohol fuel “is a thing which is very readily taken care of” by exchanging metal carburetor floats for lacquered cork ones. GM was concerned (albeit temporarily) about an imminent disruption in oil supply, and alcohol-powered cars could keep its factories open. An internal GM report that year stated ominously, “This year will see the maximum production of petroleum that this country will ever know.”
Ethanol on the March
In October 1921, less than two months before he hatched leaded gasoline, Thomas Midgley drove a high-compression-engined car from Dayton to a meeting of the Society of Automotive Engineers in Indianapolis, using a gasoline-ethanol blended fuel containing 30 percent alcohol. “Alcohol,” he told the assembled engineers, “has tremendous advantages and minor disadvantages.” The benefits included “clean burning and freedom from any carbon deposit…[and] tremendously high compression under which alcohol will operate without knocking…. Because of the possible high compression, the available horsepower is much greater with alcohol than with gasoline.”
After four years’ study, GM researchers had proved it: Ethanol was the additive of choice. Their estimation would be confirmed by others. In the thirties, after leaded gasoline was introduced to the United States but before it dominated in Europe, two successful English brands of gas–Cleveland Discoll and Kool Motor–contained 30 percent and 16 percent alcohol, respectively. As it happened, Cleveland Discoll was part-owned by Ethyl’s half-owner, Standard Oil of New Jersey (Kool Motor was owned by the US oil company Cities Service, today Citgo). While their US colleagues were slandering alcohol fuels before Congressional committees in the thirties, Standard Oil’s men in England would claim, in advertising pamphlets, that ethanol-laced, lead-free petrol offered “the most perfect motor fuel the world has ever known,” providing “extra power, extra economy, and extra efficiency.”
For a change, the oil companies spoke the truth. Today, in the postlead era, ethanol is routinely blended into gasoline to raise octane and as an emissions-reducing oxygenate. Race cars often run on pure ethanol. DaimlerChrysler and Ford earn credits allowing them to sell additional gas-guzzling sport utility vehicles by engineering so-called flex-vehicles that will run on clean-burning E85, an 85 percent ethanol/gasoline blend. GM helped underwrite the 1999 Ethanol Vehicle Challenge, which saw college engineering students easily converting standard GM pickup trucks to run on E85, producing hundreds of bonus horsepower. Ethanol’s technical difficulties have been surmounted and its cost–as an octane-boosting additive rather than a pure fuel–is competitive with the industry’s preferred octane-boosting oxygenate, MTBE, a petroleum-derived suspected carcinogen with an affinity for groundwater that was recently outlawed in California. With MTBE’s fall from grace, many refiners–including Getty, which took out a full-page ad in the New York Times congratulating itself for doing so–returned to ethanol long after it was first developed as a clean-burning octane booster.
Enter Du Pont
In 1919 GM purchased Kettering’s Dayton research laboratory. The following year the company installed him as vice president of research of the renamed General Motors Research Corporation.
No longer the shambling, anarchic outfit it had been under the inveterate risk-taker W.C. Durant, GM was now to be run in the militarily precise mold of E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Company of Wilmington, Delaware. Awash in a sea of gunpowder profits from World War I, the du Pont family had been increasing its stake in GM since 1914. By 1920 it controlled more than 35 percent of GM shares and moved to pack the board, installing professional management, with the du Pont faction taking control of the corporation’s all-powerful finance committee.
Caught short by a margin call in the recession of 1920, Durant, GM’s colorful founder, lost his stake and was forced by the du Pont family to walk the plank (he would spend his final days running a bowling alley). One of the clan’s craftiest patriarchs, Pierre du Pont, was coaxed from retirement and named GM’s interim president; Alfred Sloan, who had demonstrated the coldhearted allegiance to the bottom line the du Ponts revered, became executive vice president preparatory to assuming the top slot. The pressure on all concerned, including Kettering and his research division, was to make money and to make it fast.
Lest there be any misunderstanding, Sloan wrote to Kettering in September of 1920, alerting him to the du Ponts’ new math: “Although [the Research Corporation] is not a productive unit and a unit that is supposed to make a profit, nevertheless the more tangible result we get from it the stronger its position will be…. It may be inferred at some future time…that we are spending too much money down there [in Dayton] and being in a position to show what benefits had accrued to the corporation would strengthen our position materially.”
That time would come soon enough for Kettering to deliver. An air-cooled engine he’d championed–copper-cooled, he called it–would soon prove a costly disaster for GM. Fortunately for him, immediately after joining GM he had given his trusted assistant Midgley two weeks to find something to ignite the new management’s interest in funding continued fuel research. Though it would take somewhat longer than two weeks to fire their masters’ enthusiasm, “Midge” succeeded.
And the Winner Is…
The effect of this sudden time constraint was striking. As GM researcher and Kettering biographer T.A. Boyd noted in an unpublished history written in 1943, Midgley’s main research in 1919-20 had been to make alcohols out of olefins found in petroleum through reactions with sulfuric acid. (Farm alcohol was one thing, but a patentable process for production of petroleum-derived alcohol–a possible money-maker–was quite another, one of considerably greater interest to the corporation.) “But in view of the verdict setting a time limit on how much further the research for an antiknock compound might continue,” Boyd said, “work was resumed at once in making engine tests of whatever further compounds happened to be available on the shelf of the lab…or which could be gotten readily.”
As noted earlier, Midgley tested many compounds before isolating tetraethyl lead in December 1921. In the early days, he would attribute the discovery of TEL’s antiknock properties to “luck and religion, as well as the application of science.” In a 1925 magazine article, he would recall false trails with iodine, aniline, selenium and tellurium before hitting upon lead. Curiously, his article omitted any reference to the alcohol-gasoline blend he’d patented just five years earlier.
Another oddity: The exact number of compounds tested prior to TEL’s discovery varies dramatically in different accounts. As Professor William Kovarik of Radford University has observed, confusion reigns in part because the lab’s day-to-day test diaries have never been released to the public by the General Motors Institute (GMI) archive. In the words of one archivist there, GM’s lead archives have been “sanitized.” One 1925 article in the Literary Digest put the number at 2,500 compounds tested, while The Story of Ethyl Gasoline, a 1927 pamphlet released by a company Midgley would help found, states that 33,000 were studied. Another time, he claimed 14,991 elements were examined, while a 1980 Ethyl corporation statement set the number at 144. This question is important because GM’s discovery of lead’s antiknock properties, which initially caused little internal excitement, would be hailed in popular media and later cited in polytechnical texts as a model of rational, orderly scientific inquiry that sought the single best answer to the knock question. A more realistic view of events is that TEL’s re-emergence in the twenties was the result of a crude empirical potshot that was understood to promise a landslide of earnings over time.
Apprised of Midgley’s discovery that one part TEL could be used to fortify 1,000 parts of gasoline, Kettering proposed the name “Ethyl” for the new antiknock fluid, a mild irony in light of both men’s longtime–and soon to fade–interest in ethyl alcohol. At researcher Boyd’s suggestion Ethyl was dyed red. There was as yet, however, no plan to market Ethyl. Indeed, in July 1922, seven months after TEL’s discovery, J.W. Morrison of the GM Patent Department would encourage Midgley to “see if the U.S. Industrial Alcohol Co. have opened a valuable line of research. Mr. Clements [the lab manager at GM] stated some time ago that it might be worth our while to carry our investigations further on the problem of utilizing alcohols in motors. I think he mentioned specifically combinations of alcohol and gasoline.”
From the corporation’s perspective, however, the problems with ethyl alcohol were ultimately insurmountable and rather basic. GM couldn’t dictate an infrastructure that could supply ethanol in the volumes that might be required. Equally troubling, any idiot with a still could make it at home, and in those days, many did. And ethanol, unlike TEL, couldn’t be patented; it offered no profits for GM. Moreover, the oil companies hated it, a powerful disincentive for the fledgling GM, which was loath to jeopardize relations with these mighty power brokers. Surely the du Pont family’s growing interest in oil and oil fields, as it branched out from its gunpowder roots into the oil-dependent chemical business, weighed on many GM directors’ minds.
In March 1922, Pierre du Pont wrote to his brother Irénée du Pont, Du Pont company chairman, that TEL is “a colorless liquid of sweetish odor, very poisonous if absorbed through the skin, resulting in lead poisoning almost immediately.” This statement of early factual knowledge of TEL’s supreme deadliness is noteworthy, for it is knowledge that will be denied repeatedly by the principals in coming years as well as in the Ethyl Corporation’s authorized history, released almost sixty years later. Underscoring the deep and implicit coziness between GM and Du Pont at this time, Pierre informed Irénée about TEL before GM had even filed its patent application for it.
The Rise of Tetraethyl Lead
With the application filed, the groundwork was laid for manufacture of TEL. An October 1922 agreement contracted Du Pont to supply GM. Signing for GM was Pierre du Pont; signing for Du Pont: his brother Irénée. Manufacturing began in 1923 with a small operation in Dayton, Ohio, that made 160 gallons of tetraethyl lead a day and shipped it out in one-liter bottles, each of which would treat 300 gallons of gasoline.
In February 1923 the world’s first tankful of leaded gasoline was pumped at Refiners Oil Company, at the corner of Sixth and Main streets, in Dayton, Ohio, from a station owned by Kettering’s friend Willard Talbott. But four months earlier, an agitated William Mansfield Clark, a lab director in the US Public Health Service, had written A.M. Stimson, assistant Surgeon General at the PHS, warning that Du Pont was preparing to manufacture TEL at its plant in Deepwater, New Jersey. It constituted a “serious menace to public health” he stated, with reports already emerging from the plant that “several very serious cases of lead poisoning have resulted” in pilot production.
Clark additionally speculated that widespread use of TEL would mean “on busy thoroughfares it is highly probable that the lead oxide dust will remain in the lower stratum.” Estimating that each gallon of gasoline burned would emit four grams of lead oxide, he worried that this would build up to dangerous levels along heavily traveled roads and in tunnels.
Stimson was troubled enough by Clark’s letter to request that the PHS’s Division of Pharmacology conduct investigations; unfortunately, the division’s director responded, such trials would be too time-consuming. He suggested that the PHS rely upon industry to supply the relevant data, a spectacularly poor plan that would amount to government policy for the next forty years.
Perhaps spurred by Clark’s missive and Stimson’s concern, in December 1922 the US Surgeon General, H.S. Cumming, wrote Pierre du Pont: “Inasmuch as it is understood that when employed in gasoline engines, this substance will add a finely divided and nondiffusible form of lead to exhaust gases, and furthermore, since lead poisoning in human beings is of the cumulative type resulting frequently from the daily intake of minute quantities, it seems pertinent to inquire whether there might not be a decided health hazard associated with the extensive use of lead tetraethyl in engines.”
But the Good News Is…
The year 1923 did not begin well, then, for supporters of tetraethyl lead. In January, on account of lead poisoning, Thomas Midgley was forced to decline speaking engagements at three regional panels of the American Chemical Society, which had awarded him a medal for his discovery. “After about a year’s work in organic lead,” he wrote, “I find that my lungs have been affected and that it is necessary to drop all work and get a large supply of fresh air.” He repaired to Miami.
Before leaving town, Midgley penned a reply to Cumming’s letter, which had been passed on to him by Pierre du Pont. Although the question “had been given very serious consideration,” he wrote, “…no actual experimental data has been taken.” Even so, Midgley assured the Surgeon General, GM and Du Pont believed that “the average street will probably be so free from lead that it will be impossible to detect it or its absorption.” In other words, TEL, the deadly chemical curiosity, was being brought to market without any thought or study as to its public health implications, but rather on the hopeful hunch of a clever mechanical engineer who had just been poisoned by lead.
Around this time, Midgley had also begun to receive letters expressing grave concern over TEL from well-known public health and medical authorities at leading universities, including Robert Wilson of MIT, Reid Hunt of Harvard, Yandell Henderson of Yale (America’s foremost expert on poison gases and automotive exhaust) and Dr. Erik Krause of the Institute of Technology, Potsdam, Germany. Krause called TEL “a creeping and malicious poison,” and he told Midgley it had killed a member of his dissertation committee. Charles Kettering may have been concerned by this growing chorus of TEL critics, but the early months of 1923 saw his mind preoccupied with another matter. In May of that year, after four costly years of development, Kettering’s beloved copper-cooled engine was abandoned as a production program, a high-profile embarrassment within the company and the larger automotive community. “It was then,” wrote Kettering’s research assistant and biographer, T.A. Boyd, some years later, “that his spirits reached the lowest point in his research career.”
The abject failure of the copper-cooled engine led the fiercely proud Kettering to believe his personal capital in the company had been terminally depleted. “Since this thing with the Copper-Cooled Car has come up,” he wrote Alfred Sloan (who became GM’s president in 1923), “the Laboratory has been practically isolated from Corporation activities.” Kettering’s shame was so enormous that he tendered his resignation in a letter to Sloan. “I regret very much that this situation has developed. I have been extremely unhappy and know that I have made you and Mr. du Pont equally unhappy…. work here at the Laboratory, I realize, has been almost 100% failure, but not because of the fundamental principles involved. Enough may come out of the Laboratory to have paid for their existence but no one will care to continue in Research activities as the situation now stands.”
‘My Dear Boss’
Sloan declined to let Kettering go. But America’s most famous automotive engineer after Henry Ford emerged with a renewed sensitivity to the profit-making needs of his corporation. In this regard, TEL held out an immediate lifeline. Writing Kettering from Florida in March 1923, Midgley related a mad brainstorm whose relevance had now become fully clear to Kettering. “My dear boss,” he began, “The way I feel about the Ethyl Gas situation is about as follows: It looks as though we could count on a minimum of 20 percent of the gas sold in the country if we advertise and go after the business–this at three cent gross to us from each gallon sold. I think we ought to go after it as soon as we can without being too hasty.”
Midgley barely scratched the surface of the wealth to come. With a legal monopoly based on patents that would provide a royalty on practically every gallon of gasoline sold for the life of its patent, Ethyl promised to make GM shareholders–among whom the du Ponts, Alfred Sloan and Charles Kettering were the largest–very rich. Profit-free ethanol, indeed. As Kovarik has calculated: “With gasoline sales [in 1923] around six billion gallons per year, 20 percent would come to about 1.2 billion gallons, and three cents gross would represent $36 million. With the cost of production and distribution running less than one cent per gallon of treated gasoline, more than two thirds of the $36 million would be annual gross profit. Of course, within a decade 80 percent of the then 12 billion gallon market used Ethyl, for an annual gross of almost $300 million.”
The fears of excessive hastiness expressed in Midgley’s letter were evidently allayed. In April 1923, one month after he’d performed his riveting calculations, the General Motors Chemical Company was established to produce TEL, with Charles Kettering as president and Thomas Midgley as vice president.
Octane, the Motorist’s Friend
Beginning in 1921, GM’s executive committee began to articulate the first principles that would come to be known as Sloanism–that is, planned obsolescence and product differentiation through speed, power, style and color; “a car for every purse and purpose,” as Sloan was fond of saying.
Between 1922 and the end of the decade, Sloan and his GM associates would devise marketing strategies that would see GM overtake Ford as the world’s largest automobile manufacturer and set the tone for the next fifty years of American automotive consumption. Central to this growth would be an awareness that consumers were no longer looking merely for basic transportation, which was the stock in trade of Ford’s beloved Model T. In addition to consumer financing (which Ford opposed), Sloan was convinced that style, snob appeal and speed would help GM steal its customers away. He was right.
Following the failure of his copper-cooled engine, Kettering rejigged his arguments for TEL for internal–definitely not public–consumption. As it happened, the new additive could be fitted neatly into the Sloanist equation. For while it was initially seen by Kettering and his staff as a way to cure knock and to husband fossil-fuel supplies, the high compression it enabled in motors was just as easily exploited to make cars faster and more powerful, thus easier to sell. Alan Loeb, a former EPA attorney and lead historian who has examined the period closely, has neatly summed up Kettering’s conversion: “By 1923…it was clear that Kettering’s original purpose for the antiknock research had given way to GM’s desire to improve auto performance without regard for its effect on fuel economy…. Kettering did not give up on efficiency and conservation as his own ideals, but ever after he knew better than to try to push a product that would not sell. In later years, even as Kettering’s advocacy of conservation became more and more public, it represented GM’s true motive less and less.”
Tellingly, Ethyl’s earliest advertisements dealt solely with speed and power and invariably neglected to mention its active ingredient: lead. Boasted a September 1927 ad that ran in National Geographic: “As an Ethyl user, you have the benefits of greatly increased speed, more power on hills and heavy roads. Quicker acceleration and complete elimination of ‘knock.’ But the real high compression automobile is here at last! Ethyl gasoline has made it possible! Ride with Ethyl in a high compression motor and get the thrill of a lifetime.”
With the advent of the Depression in the thirties, Ethyl’s advertising nodded to the economic realities of the day but still focused on power. An ad that ran in February 1933 contains a Norman Rockwell-esque portrait of a small boy who is complaining to his embarrassed father, “Gee, Pop–they’re all passing you.” The accompanying text rubs it in. “They didn’t pass you when your car was bright and new–and you still don’t like to be left behind. So just remember this: the next best thing to a brand new car is your present car with Ethyl.”
Liftoff
With the formation of the GM Chemical Company, work on a large-scale Du Pont TEL plant began immediately. Irénée du Pont hailed his company’s technical director, W.F. Harrington: “It is essential that we treat this undertaking like a war order so far as making speed and producing the output, not only in order to fulfill the terms of the contract as to time but because every day saved means one day advantage over possible competition.”
Significantly, GM’s patent on TEL would have covered any threat from competing makers of lead additive. Thus, as Kovarik has reasoned, the competition referred to must have been from those who would have offered a different kind of antiknock. GM, Du Pont and TEL’s other backers would long publicly claim there were no conceivable alternatives to the lead antiknock additive. But the facts were otherwise. Ethanol was still out there. And GM negotiated throughout the twenties with Germany’s I.G. Farben over an additive it made from iron carbonyl. Then, in August 1925, Kettering himself joyously announced “Synthol,” a blended automotive fuel of benzene and alcohol that promised to “double gas mileage.” There was, as we shall see, an unexpected–and momentary–business need for Synthol. The point is, there were alternatives.
In a public relations coup, Ethyl leaded gasoline fueled the top three finishers at the Indianapolis 500 motor race on Memorial Day, 1923. With demand skyrocketing, Kettering signed exclusive contracts with Standard Oil of New Jersey (now Exxon), Standard Oil of Indiana (later Amoco, more lately merged with BP) and Gulf Oil (owned by the Mellon interests) for East Coast, Midwest and Southern distribution, respectively, of leaded gasoline.
Tetraethyl Death
In August, Du Pont’s TEL plant opened at Deepwater, New Jersey, across the Delaware River from Wilmington. Less than thirty days would pass before the first of several TEL poisoning deaths of workers there would occur. Not surprisingly, given Du Pont’s stranglehold on all local media within its domain along the Delaware, the deaths went unreported.
Even so, news of these and similar deaths would inevitably come out. Realizing that its own medical research would be less than credible then, and having been turned down by reputable academics and the Public Health Service in its search for consultants to help “refute any false propaganda,” GM hurriedly contracted the US Bureau of Mines in September 1923 to explore the dangers of TEL. Even by the lax standards of its day, the bureau was a docile corporate servant, with not an adversarial bone in its body. It saw itself as in the mining promotion business, with much of its scientific work undertaken in collaboration with industry. The bureau’s presumptive harmlessness notwithstanding, to its written agreement with GM was nonetheless added a remarkable proviso, that the bureau “refrain from giving out the usual press and progress reports during the course of the work, as [GM] feels that the newspapers are apt to give scare headlines and false impressions before we definitely know what the influence of the material will be.”
Indicative of the bureau leadership’s fundamental outlook was an exchange between the superintendent of its Pittsburgh field station, where the TEL investigation was being conducted, and the bureau’s chief chemist, S.C. Lind. By letter, Lind had objected to the use of the trade name “Ethyl” when referring to tetraethyl lead gasoline.
“Of course their [GM officials] object in doing so is fairly clear, and among other things they are not particularly desirous of having the name ‘lead’ appear in this case. That is alright from the standpoint of the General Motors Company but it is quite a question in my mind as to whether the Bureau of Mines would be justified in adopting this name so early in the game.”
The superintendent replied that omission of “the use of the word ‘lead’ in the interbureau correspondence” was intentional to prevent leaks to the papers. “If it should happen to get some publicity accidentally, it would not be so bad if the word ‘lead’ were omitted as this term is apt to prejudice somewhat against its use.”
Indeed, lead had acquired a bad name by 1920, as scientific and public awareness of its supreme deadliness as an occupational and pediatric hazard was increasing. Then, in April 1924, two GM employees engaged in the manufacture of TEL at a pilot plant in Dayton also died of lead poisoning. Large numbers of nonfatal poisonings were noted at this time. Thomas Midgley was said to be “depressed to the point of considering giving up the whole tetraethyl lead program.” But Kettering, emerging from his copper-cooled funk, wouldn’t slow down. Two months later, he would urge Du Pont to step up production. At the same time, seeking even greater control over Bureau of Mines test results, GM stipulated that “all manuscripts, before publication, will be submitted to the Company for comment and criticism.
By any measure, the TEL constituency had experienced a run of rum luck, and in June 1924 GM president Sloan, “gravely concerned about the poison hazard” and deaths at TEL plants in Dayton and Deepwater, approved the formation of a medical committee, with J. Gilman Thompson, consulting physician to Standard Oil of New Jersey (which had been marketing Ethyl and dabbling in its manufacture), as chairman. Summing up the gloomy feeling all around at this time, Du Pont chairman Irénée du Pont wrote Sloan at GM that TEL “may be killed by a better substitute or because of its poisonous character or because of its [destructive] action on the engine.”
Following its investigation, GM’s medical committee delivered what was apparently a negative and highly cautionary report on TEL. But Irénée du Pont, having undergone some sort of conversion or, possibly, having remembered his family’s lifelong devotion to profit at any cost, wrote Sloan on August 29, 1924, and told him not to worry: “I have read the doctors’ report and am not disturbed by the severity of the findings.” Another product his firm made–nitroglycerin–was even more hazardous to make, du Pont added breezily, while lead dust from car exhaust was but nothing compared to erosion from lead paint. Years later, this would become a major plank of TEL supporters’ defense.
For some unknown reason, the report of Sloan’s blue-ribbon medical committee, like many original documents referenced in GM reports on TEL, is not available in the company’s public archives.
Hello, Ethyl
Meanwhile, Standard Oil of New Jersey had developed a faster, cheaper method of synthesizing TEL. In August 1924 production began in a makeshift works at its Bayway plant in Elizabeth, New Jersey. GM still held the TEL patent, but Standard now had the better manufacturing technology and a patent of its own to prove it.
To the apparent surprise of some at Du Pont, which had not been producing the fluid fast enough for GM’s liking, the oil company (one of twenty-seven companies formed by the 1911 breakup of Rockefeller’s Standard Oil Trust) and the automobile company formed a joint venture, which they called the Ethyl Gasoline Corporation. Why, one wonders, would GM deign to form Ethyl, a new company, with Standard? “In the first place,” Sloan would testify in a 1952 antitrust suit, “I recognized that General Motors’ organization had no competence whatsoever in chemical manufacture. We were mechanical people dealing in metal processing.” The deaths at Dayton would certainly support this modest assessment. Sloan would also later record his view that management should not get sidetracked on noncore businesses. But there were clearly bushels of money to be made. Sloan had by now fully cottoned to an essential fact about his company’s new lead additive patent. As the management expert P.F. Drucker described it many years later, “GM, in effect, made money on almost every gallon of gasoline sold, by anyone.”
In one of its first official acts, the newly formed Ethyl Gasoline Corporation evinced renewed sensitivity to spin (not to mention a justifiably elevated level of paranoia) by insisting that its contract with the Bureau of Mines be modified yet again, to reflect that “before publication of any papers or articles by your Bureau, they should be submitted to them [Ethyl] for comment, criticism, and approval.” Thus, as the public health historians David Rosner and Gerald Markowitz have observed, the newly formed Ethyl Corporation was given “veto power over the research of the United States government.”
Death by Loony Gas
Du Pont would supply most of Ethyl’s TEL requirements for years to come, but, according to a letter written by Alfred Sloan to Irénée du Pont in the fall of 1924, in an accommodation to Standard Oil that firm had been permitted to maintain a small “semiworks” at its Bayway refinery. Later, Du Pont engineers would express serious reservations about the safety of Standard’s facility. An internal 1936 Du Pont history would recount that the company was “greatly shocked at the manifest danger of the equipment and methods [and] at the inadequate safety precautions” at the Standard facility, but their suggestions were “waved aside.” Unfortunate it was.
On October 26, 1924, the first of five workers who would die in quick succession at Standard Oil’s Bayway TEL works perished, after wrenching fits of violent insanity; thirty-five other workers would experience tremors, hallucinations, severe palsies and other serious neurological symptoms of organic lead poisoning. In total, more than 80 percent of the Bayway staff would die or suffer severe poisoning. News of these deaths was the first that many Americans heard of leaded gasoline–although it would take a few days, as the New York City papers and wire services rushed to cover a mysterious industrial disaster that Standard stonewalled and GM declined to delve into.
Confusion and panic marked the headlines, with reporters forced to travel to New Jersey to track a story they’d probably have noted in a lightly rewritten press release if Standard had appeared more forthcoming. On October 30, days after the first Bayway death, the press was at last invited to Standard’s New York City headquarters for an afternoon session of long-overdue, professionally crafted spin control. Thomas Midgley had been rushed to 26 Broadway from Dayton and would address the corps. But first, Standard’s medical consultant, J. Gilman Thompson, presented them with a typewritten statement, supplying the company’s most sculpted telling of recent history yet:
[TEL’s] recently discovered use for greatly promoting the efficiency of gasoline engines has led to its manufacture on a commercial scale through processes still more or less in a stage of development. This has occasioned unforeseen accidents…. One of these has been the sudden escape of fumes from large retorts, and the inhalation of such fumes gives rise to acute symptoms, particularly congestion of the brain, producing a condition not unlike delirium tremens. Although there is lead in the compound, these acute symptoms are wholly unlike those of chronic lead poisoning such as painters often have.
“There is no obscurity whatever about the effects of the poison and characterizing the substance as ‘mystery gas’ or ‘insanity gas’ is grossly misleading.
Asked to assess their liability to families of men who said they were not warned of the dangers, Standard Oil officials said “the rejection of many men as physically unfit to engage in the work of the Bayway plant, daily physical examinations, constant admonitions as to wearing rubber gloves and using gas masks and not wearing away from the plant clothing worn during work hours should have been sufficient indication to every man in the plant that he was engaged ‘in a man’s undertaking.’”
The falsity and cruelty of Standard’s position were manifest, the ironies rife. First, Standard wasn’t in experimental production. It was making TEL to sell. Second, its stony silence alone had led to stories in the press about a “mystery” gas, because reporters learned that TEL had been dubbed “loony gas” from Bayway workers whom they interviewed after being brushed off by the company brass. Finally, the escapes of gas weren’t sudden, as claimed, but ongoing, the poisoning cumulative. The doctors at Reconstruction Hospital had told the Herald Tribune that violent insanity was “brought on by the gradual infiltration of lead in their systems.”
The day’s true highlight, however, would be Midgley’s presentation. The celebrated engineer and Ethyl VP, who had only recently been forced to leave work to recover from lead poisoning, proposed to demonstrate that TEL was not dangerous in small quantities, by rubbing some of it on his hands. Midgley was fond of this exhibition and would repeat it elsewhere, washing his hands thoroughly in the fluid and drying them on his handkerchief. “‘I’m not taking any chance whatever,’ he said. ‘Nor would I take any chance doing that every day.’” The New York World cited unbelievable dispatches from Detroit claiming that Midgley “frequently bathed” in TEL to prove its safety to skeptics within the industry.
Ethyl Adrift
The response of local governments and public health officials to the Bayway disaster was swift and stern. The day of Midgley’s peculiar demonstration, the New York City Board of Health banned the sale of TEL-enhanced gasoline, saying that “such mixtures of gasoline, containing lead or other deleterious substances, may be liable to prove detrimental and dangerous to the health and lives of the community, particularly when released as exhaust from motor vehicles.” Within a matter of days Philadelphia, Pittsburgh and the State of New Jersey would ban gasoline containing the lead additive. Ethyl would continue to be sold in the Midwest, but elsewhere on the East Coast its use was unofficially discouraged by authorities.
In early November 1924, after the fifth Bayway worker died, the Bureau of Mines study on TEL was released (remember that GM and then Ethyl had reserved for themselves the right to approve the timing of its release). Not surprisingly, the bureau’s report, based on limited animal testing it had conducted, gave the substance a clean bill of health. The New York Times, which had decided as editorial policy to support the use of TEL, served up just the sort of front-page headline Ethyl hoped for: “No Peril to Public Seen in Ethyl Gas/Bureau of Mines Reports after Long Experiments with Motor Exhausts/More Deaths Unlikely.”
Yandell Henderson of Yale and others assailed the Bureau of Mines study as a hopelessly shoddy investigation financed by an interested party, Ethyl, and bemoaned Washington’s antiregulatory climate. The bureau had “investigated the danger to the public of acute lead poisoning,” he noted derisively,
and had failed even to take into account the possibility that the atmosphere might be polluted to such an extent along automobile thoroughfares that those who worked or lived along such streets would gradually absorb lead in sufficient quantities to poison them in the course of months….
Perhaps if leaded gasoline kills enough people soon enough to impress the public, we may get from Congress a much-needed law and appropriation for the control of harmful substances other than foods. But it seems more likely that the conditions will grow worse so gradually and the development of lead poisoning will come on so insidiously (for this is the nature of the disease) that leaded gasoline will be in nearly universal use and large numbers of cars will have been sold that can run only on that fuel before the public and the Government awaken to the situation….
This is probably the greatest single question in the field of public health that has ever faced the American public. It is the question whether scientific experts are to be consulted, and the action of Government guided by their advice, or whether, on the contrary, commercial interests are to be allowed to subordinate every other consideration to that of profit.
Echoing the fears of PHS lab director William Clark more than two years earlier, Henderson had clearly isolated the greatest threat of leaded gasoline–not the severe cases of industrial poisoning that had grabbed the headlines but the slow, unrelenting low-level exposure that was sure to occur as the use of leaded gasoline spread. As we shall see, the industry would use this dichotomy–accidental deaths at the plant versus insidious poisoning–to its advantage. The former risk could be acknowledged because it could be prevented, while the latter was doubted, denied and endlessly debated.
In years to come, the federal government would do much to help the lead interests actively across a variety of fields, but the greatest assistance offered was an act of omission: a signal failure to arrange for independent examination of the effects of automotive lead emissions on the public health. By 1924 the government’s allegiance and probity were already in question. As C.W. Deppé, owner of the Lilliputian Deppé Motors, put it in a letter to the Secretary of the Interior, Hubert Work: “May I be pardoned if I ask you frankly now, does the Bureau of Mines exist for the benefit of Ford and the G.M. Corporation and the Standard Oil Co. of New Jersey, and other oil companies parties to the distribution of the Ethyl Lead Dopes, or is the Bureau supposed to be for the public benefit and in protection of life and health?”
Enter the Surgeon General
Three months after the Bayway disaster, a grand jury acquitted Standard Oil of criminal responsibility for the tragedy despite the fact that, as the New York Times stated in summarizing the grand jury’s findings: “The report found that the deaths were directly due to poisoning…[and] recommended that before it resumes operations the company try to perfect some machinery by which ethyl gas can be manufactured without endangering life.”
This was good news for Ethyl’s backers, but strangely at variance with the views of Standard’s own partners. As Du Pont’s internal history of 1936 concluded: “Notwithstanding…foreknowledge at the peril, the precautions taken in the small manufacturing operation at Bayway were grossly inadequate.” And GM took a dim view of the Standard operation as well. Ferris Hurd, a GM attorney testifying in the government’s 1953 antitrust suit against Du Pont, summarized events:
[Standard] put up a plant that lasted two months and killed five people and practically wiped out the rest of the plant. The disaster was so bad that the state of New Jersey entered the picture and issued an order that Standard could never go back into the manufacture of [tetraethyl lead] without the permission of the state of New Jersey. In fact, the furor over it was so great that the newspapers took it up, and they misrepresented it, and instead of realizing that the danger was in the manufacture, they got to thinking that the danger was exposure of the public in the use of it, and the criticism of its use was so great that it was banned in many cities and they had to close down the manufacture and sale of Ethyl.
Of course, there was a danger to the public in the use of Ethyl, but the public wouldn’t know it for decades, thanks in large part to the institutional inability and temperamental disinclination of the federal government at this time to do anything more than smile upon new technologies and corporate incursions into new and lucrative markets. The wave of publicity surrounding the Bayway disaster had left Ethyl on the defensive, however. The company knew it would be up to government to set matters right.
A Gift of God?
Today business school students carefully analyze the corporate response to the scare caused by a small batch of tainted Tylenol and widely hail it as a work of genius. Yet it was nothing compared with Ethyl’s road back from disaster, skillfully negotiated with a product that was a deadly poison from the get-go. Ethyl, to use the modern argot, had an aggressive plan and made it stick. You might say it was one of the most brilliant exercises in co-branded damage control ever.
For on Christmas Eve, 1924, Charles Kettering, Frank Howard of Standard and Du Pont chief engineer W.F. Harrington paid a private visit to Surgeon General Hugh Cumming to request that the Public Health Service hold public hearings on TEL. Cumming readily agreed. As Du Pont’s private history of 1936 would note, “In the prevailing state of strong prejudice and excited fears, the new industry was fortunate in having the question of the health risk in the use of tetraethyl lead actively taken up…by the US Public Health Service.”
On May 4, 1925, in an act exquisitely timed and brilliantly crafted to the right tone of seriousness for the proceedings, Ethyl publicly withdrew its product from the market. On May 20 eighty-seven participants convened in the Butler Building at Third and B Streets, in Washington, DC, along with a dozen reporters, for the Surgeon General’s conference. Conspicuously absent was Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon, whose agency was charged with oversight of the PHS. Nowhere was it reported that Mellon family interests controlled Gulf Oil, which had recently acquired an exclusive Ethyl distributorship.
At the hearing, Standard’s Frank Howard (soon to be an Ethyl director) uttered the memorable pronouncement that TEL was “a gift of God” that conscience and the march of human progress compelled GM to exploit.
Our problem is not that simple. We cannot quite act on a remote probability. We are engaged in the General Motors Corporation in the manufacture of automobiles, and in the Standard Oil Company in the manufacture and refining of oil. On these things our present industrial civilization is supposed to depend. I might refer to the comment made at the end of the war–that the Allies floated to victory on a sea of oil–which is probably true….
Now as a result of some 10 years’ [sic] research on the part of The General Motors Corporation and 5 years’ research by the Standard Oil Co., or a little bit more, we have this apparent gift of God–of 3 cubic centimeters of tetraethyl lead–which will permit that gallon of gasoline…to go perhaps 50 percent further…
What is our duty under the circumstances? Should we throw this thing aside? Should we say, ‘No, we will not use it,’ in spite of the efforts of the government and the General Motors Corporation and the Standard Oil Co. toward developing this very thing, which is a certain means of saving petroleum? Because some animals die and some do not die in some experiments, shall we give this thing up entirely?
Frankly, it is a problem that we do not know how to meet. We cannot justify ourselves in our consciences if we abandon the thing. I think it would be an unheard-of blunder if we should abandon a thing of this kind merely because of our fears. Possibilities cannot be allowed to influence us to such an extent as that in this matter.
(Many years later, Howard would be forced to relinquish his Standard post by the Federal Trade Commission for collaborating with Nazi Germany, but he would retain his seat at Ethyl.)
Ethyl sales manager A.S. Maxwell got even more carried away, telling a reporter that engines would run so efficiently with leaded gas that GM was developing an engine that “will triple the best mileage a gallon of gasoline will give today.” Actually, while the high compression Ethyl permitted–like ethanol or any octane booster–might have offered fuel-economy benefits, average fuel economy in the United States fell steadily from 1925, the year of Ethyl’s introduction, through the seventies, when cars shrank and unleaded fuel became the standard. In 1974 GM’s corporate average fuel economy had fallen to a near-comical 12.2 miles per gallon. By 1987, after unleaded became predominant and catalytic converters a standard, the sales/registered-fleet average for cars sold in the United States had climbed to 27.3 miles per gallon. Yet TEL defenders to this day cite conservation as its key benefit.
The Conference Adjourns
America’s automotive population was multiplying exponentially, yet the Surgeon General’s conference spent six hours and forty-five minutes deliberating on what Yandell Henderson had prophetically called “probably the greatest single question in the field of public health that has ever faced the American public” and reached no conclusion. Instead, it voted unanimously on a motion by Dr. Matthias Nicoll, New York State Commissioner of Health, to place the question of tetraethyl lead in the hands of Cumming and a seven-member committee of experts to be appointed by him, with orders to report back by January 1, 1926. And it commended Ethyl for withdrawing its product while the question of its effect on the public health was still unsettled.
Awkwardly for Ethyl, soon after the conference ended but months before the Surgeon General’s newly impaneled committee could complete its study, details emerged about eight more TEL-related deaths and more than 300 injuries at Du Pont’s sinister Deepwater plant. Six square miles that lit up the sky at night, Deepwater was one of the country’s most active ports, yet it was nowhere to be found on nautical maps. Often referred to publicly by Du Pont as a dye works, it was rather a complex of poison-gas works, producing phosgene and chlorine gases as well as the lethal benzol series. Deepwater had no legal government–just Du Pont and its private police force. Dismissing the deaths, a Du Pont spokesman said at the time, “It is a fact that we have a great deal of trouble inducing the men to be cautious. We have to protect them against themselves.” (You can still see Deepwater today at the southern end of the New Jersey Turnpike, but it stopped producing TEL in the nineties.)
Happily for the du Ponts and the other lead interests, on January 19, 1926, the special committee appointed by Surgeon General Cumming found “no good grounds” for prohibiting the sale of Ethyl gasoline: “So far as the committee could ascertain all the reported cases of fatalities and serious injuries in connection with the use of tetraethyl lead have occurred either in the process of manufacture of this substance or in the procedures of blending and ethylizing.”
The committee reviewed the evidence of studies it had conducted in Ohio on 252 workers exposed to lead in their occupations as chauffeurs and garage men. While the committee noted “a greater storage of lead in the bodies of those exposed to ethyl gasoline” and lead in the dust of garages dispensing ethyl, nothing conclusive could be established in the short time given to it. So, although the newspapers would miss the distinction–the New York Times, for instance, headlined it “Report: No Danger in Ethyl Gasoline”–the committee had merely concluded that TEL could be manufactured without the loss of life. It did not give tetraethyl lead a clean bill of health or settle the question of its effect on the public health. In fact, it cautioned:
It remains possible that if the use of leaded gasolines becomes widespread, conditions may arise very different from those studied by us which would render its use more of a hazard than would appear to be the case from this investigation. Longer experience may show that even such slight storage of lead…may lead eventually in susceptible individuals to recognizable or to chronic degenerative diseases of a less obvious character….
In view of such possibilities the committee feels that the investigation begun under their direction must not be allowed to lapse…. The vast increase in the number of automobiles throughout the country makes the study of all such questions a matter of real importance from the standpoint of public health, and the committee urges strongly that a suitable appropriation be requested from Congress for the continuance of these investigations under the supervision of the Surgeon General of the Public Health Service.
While proposing that the sale of leaded gasoline should go forward, regulated by the Surgeon General, the committee passed a resolution calling on the Public Health Service to conduct further studies. Separately, the president of the Society of Automotive Engineers called for additional investigations concerning lead’s possible relation to sterility. And the American Chemical Society, which might have been supposed a lockstep supporter of Ethyl, proposed around this time that increased governmental regulation over chemicals “is a subject worthy of further discussion.”
Thus, even the industry’s paid scientists were uneasy about the use of lead in gasoline. Yet none of these calls for further government action were ever acted upon, and it was this failure that gave Ethyl its opening. The PHS never conducted the studies, the Surgeon General never lobbied Congress to pay for them and, for the next forty years, all research on TEL’s health impact would be underwritten by GM, Standard Oil, Du Pont, Ethyl and lead-industry trade associations. With the credulity-stretching statement of an Ethyl spokesman that the only purpose of GM and Standard Oil–“two of the largest units in the automobile and oil industry”–was “to conserve a vital natural resource,” the company welcomed the committee’s report as total vindication. “We plan to resume operations,” Ethyl announced without delay the day of the report’s release. In May 1926, one year after the sale of TEL-laced gasoline was suspended, signs appeared in gas stations: “Ethyl is back.”
But There Is No Alternative
Misrepresenting the Surgeon General’s committee report findings and glossing over its call for further study, Ethyl medical consultant Robert Kehoe recalled in a 1928 article the government’s abdication of its charge: “As it appeared from [the committee’s] investigation that there was no evidence of immediate danger to the public health, it was thought that these necessarily expensive studies should not be repeated at present, at public expense, but that they should be continued at the expense of the industry most concerned, subject, however, to the supervision of the Public Health Service.” His own study, Kehoe wrote unsurprisingly, failed to “show any evidence for the existence of such hazards.”
Others were less sanguine about the committee’s report and Kehoe’s summary of the evidence. Committee member Dr. David Edsall, dean of Harvard’s School of Public Health, called the report incomplete and “half-baked.” C.E.A. Winslow of Yale recommended that “the search for an investigation of antiknock compounds be continued intensively with the object of securing effective agents containing less poisonous metals (such as iron, nickel, tin, etc.) or no metals at all.” Winslow unsuccessfully sought to have the committee mention alternatives to TEL in its final report, forwarding this recommendation to the PHS, along with correspondence from the Ford Motor Company. One letter to Winslow, which is missing from the PHS files in the National Archive but present in his Yale University archive, dated August 15, 1925, reads:
Alcohols for motor fuel
Further to my letter of June 19th:
You may probably have observed the production of synthetic alcohol as brought by the Badische Anilin and Soda Fabrik [BASF of I.G. Farben], now being produced in Germany at the rate of 60,000 gallons per month. Such alcohol is reported to be produced for between 10 cents and 20 cents per gallon and has much promise as a mixture with hydrocarbon [gasoline] fuels to eliminate knocking and carbonization.
[signed] Wm. H. Smith, Ford Motor Co.
Surgeon General Cumming was not interested in alternatives to lead, even though proof of their existence ought to have immediately thrown the veracity of all Ethyl utterances into question. Speaking in August 1925, for instance, Thomas Midgley had told a meeting of scientists, “So far as science knows at the present time, tetraethyl lead is the only material available which can bring about these [antiknock] results, which are of vital importance to the continued economic use by the general public of all automotive equipment, and unless a grave and inescapable hazard rests in the manufacture of tetraethyl lead, its abandonment cannot be justified.”
Midgley had conveniently overlooked his earlier, high-profile endorsement of ethanol, as would Kettering and the entire US press corps. Kettering was also forgetting Synthol, the octane-boosting alternative he had publicized just months earlier when it looked like Ethyl might be forced to close shop. With the government’s de facto seal of approval in hand for TEL, Kettering never again mentioned Synthol. Summarizing his remarks before the Surgeon General’s committee, the New York Times reported: “The experience of the company does not offer any promise that any such cheap and efficient anti-knock can be discovered to replace the lead.”
Uncle Sam Lends a Hand
Far from heeding his committee’s call for the initiation of further studies on the effects of widespread use of tetraethyl lead, the Surgeon General thrust himself quickly into the role of international cheerleader for Ethyl’s lead gasoline additive. In 1928 England’s Daily Mail quoted British scientists voicing fear over the potential public health hazard posed by TEL, which was soon to be introduced to the British market by the Anglo-American oil company brand Pratt’s. Ethyl’s new president, Earle Webb, apprised Surgeon General Cumming of this development and received a warm, familiar response. “Your courtesy in keeping us informed of such developments is helpful and I am grateful for its continuance,” Cumming replied, before contacting the British ministry.
Soon thereafter, England’s Ministry of Health would give TEL a clean bill of health, referring to American findings. This would be hard to jibe with a soon-to-be-published report in the British Medical Journal on “the slow, subtle, insidious saturation of the system by infinitesimal doses of lead extending over a long period of time,” but Cumming wasn’t through yet.
Foreshadowing years of sterling service on behalf of Ethyl, the Surgeon General, the nation’s highest-ranking medical officer, would put pen to paper again in 1928, encouraging New York City sanitary officials to lift the city’s ban on the use of TEL-laced gasoline. “There are no good grounds” for the ban, he implored them. In 1931 Cumming would further assist Ethyl’s overseas marketing efforts. Cabling the PHS offices from an international conference in Paris, the Surgeon General directed his minions to send the Swiss minister of health favorable reports on Ethyl.
In 1932 the du Pont family would temporarily shift party allegiance and support to Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s presidential bid with a sizable contribution to his campaign fund. The Democratic Administration was swift to return the favor. A year after FDR’s inauguration, the Surgeon General would busy himself writing letters of introduction for Ethyl officials to public health counterparts in foreign countries.
“This will introduce you to Mr. E.W. Webb, President of the Ethyl Gasoline Corp.” the letters began. Cumming helpfully assured recipients that Webb had consulted with the PHS and that the PHS had found Ethyl an excellent product and given it a clean bill of health. He also fired off missives advancing Ethyl’s cause with pesky state legislatures and public health authorities in the United States who were erecting regulatory hurdles.
By 1936 Ethyl fluid would be added to 90 percent of gasoline sold in America–a resounding commercial success. But even this would not be enough. Responding to a complaint lodged by Ethyl that year, the Federal Trade Commission issued a restraining order preventing competitors from criticizing leaded gasoline in the commercial marketplace. Ethyl gasoline, the FTC order read, “is entirely safe to the health of motorists and the public…and is not a narcotic in its effect, a poisonous dope, or dangerous to the life or health of a customer, purchaser, user or the general public.” The FTC’s action on Ethyl’s behalf came in the wake of an ad by the makers of unleaded Cushing Gasoline, who meekly proposed, “It stands on its own merits and needs no dangerous chemicals–hence you can offer it to your customers without doubt or fear.”
Ethylized Science
Dr. Robert Kehoe of the University of Cincinnati, Ethyl’s chief medical consultant, would express the opinion following the inconclusive 1926 report of the Surgeon General’s committee (of which he was a member) that there was no basis for concluding that leaded fuels posed any health threat whatsoever. And while it is true that tetraethyl lead’s opponents could point in 1924 to no exact scientific test of leaded gasoline emissions as incontrovertible proof of their hazards, there was a large body of evidence, dating back 3,000 years, that lead is poison.
Though the principals must surely have been aware of this historical evidence, it will suffice to recap merely a few of the contemporaneous scientific descriptions of lead’s poisonous effects. In 1910, for instance, Alice Hamilton completed a ground-breaking and widely reported study of the lead industries for the State of Illinois, finding pervasive worker poisoning and conditions markedly worse than in European industry. In 1914 Americans Henry Thomas and Kenneth Blackfan detailed pediatric lead-poisoning death in the case of a boy who ate white-lead paint bitten off a crib railing. By 1921, the year of Midgley’s discovery of TEL as an octane-boosting gasoline additive, the weight of the evidence was such that America’s National Lead Company, sworn enemy of the antilead movement, was forced to admit grudgingly that its product was indeed a poison, in all its many forms (e.g., carbonate of lead, lead oxides and sulfate and sulfide of lead). The following year, the League of Nations would recommend banning white-lead paints for interior use on health grounds, as many European countries had already done. Establishing a pattern of tolerance for this most dangerous element, the United States declined to adopt the league’s resolution.
The bankruptcy of TEL supporters’ medical opinion was exposed at the time by Yandell Henderson and others. Harvard’s Dr. Edsall testified at the Surgeon General’s conference:
For 100 years and more observations have been made as to the effect of having a noteworthy amount of lead dust around in any occupation…. It is not a question, then, whether there is or is not a hazard…. I am disposed to believe that the hazard is a noteworthy one. How severe I am not prepared to say. The only way in which one can determine how serious it is would be through a very large number of extremely carefully carried-out observations as to what the effects are upon a large number of human beings.
By 1928, emboldened by a refreshingly compliant government and TEL’s effective victory before the Surgeon General, National Lead and St. Joseph’s Lead would form the Lead Industries Association to take back the ground ceded with National Lead’s 1921 admission. “Of late the lead industries have been receiving much undesirable publicity,” LIA reminded its members, as if it had forgotten in the intervening years that its product was a deadly poison. For years to come, the LIA, on whose board Du Pont and Ethyl officers served, would carefully gather, fund, support and disseminate propaganda supporting its pro-lead views, fighting all who would stand in its way. This disinformation, along with the lack of an adequate regulatory framework and the expense and difficulty of scientifically proving lead’s insidious impact–bought manufacturers of lead paint and lead gasoline more than fifty years of unjust deserts.
The Kehoe Rule
Ethyl president Earle Webb once listed Robert Kehoe as one of three men without whom Ethyl could not have done what it did, and surely this must be so. Hired by Kettering in 1924 on behalf of GM to study hazards of TEL manufacturing plants, the young toxicologist quickly demonstrated the unerring instinct for pleasing one’s masters that guarantees one employment of a more lasting nature. In 1925 he was appointed chief medical consultant of the Ethyl Corporation and remained in the post until his retirement in 1958. But it was in Kehoe’s day job, as the outspoken director of the Kettering Laboratory–founded with an initial $130,000 gift from GM, Du Pont and Ethyl at the University of Cincinnati, where the lead industry paid Kehoe’s salary for half a century–that he really rose to the challenge of promoting TEL. Against Kehoe’s lab and decades of its pseudo-science, the general and unfunded concerns of the public health community were doomed for close to fifty years.
As Kehoe told a Senate committee with rare accuracy in 1966, “at present, this [Kettering] Laboratory is the only source of new information on this subject [occupational and public health standards for lead] and its conclusions have a wide influence in this country and abroad in shaping the point of view and the activities, with respect to this question, of those who are responsible for industrial and public hygiene.” Working on Ethyl’s behalf and as a consultant to the lead industry until shortly before his death in 1992, at 99, Kehoe put in exceptionally good innings. (His lab would also certify the safety of the refrigerant Freon, subject of another environmentally insensitive GM patent that would earn hundreds of millions before it was outlawed.)
Summing up the findings of a lifetime, Kehoe told Congress that he and his colleagues “had been looking for 30 years for evidence of bad effects from leaded gasoline in the general population and had found none.” The credibility of his research had already been undercut and would soon be destroyed. But for many years, Kehoe’s findings had been vouched for by semi-private organizations, including the American Public Health Association and the American Medical Association. Although they never undertook to investigate or independently verify his findings, their lap-dog approvals served to bulk up the scholarship in a field that was sparsely scholared.
Kehoe’s central belief–criticized by medical authorities from Yale, Harvard and Columbia at the Surgeon General’s original 1925 conference and thoroughly discredited today, though still embraced by the lead-additive industry–was that lead appeared naturally in the human body; that the high blood-lead levels his test subjects exhibited were normal and healthy. In fact, independent researchers later realized, Kehoe’s control patients–the ones who wouldn’t be exposed to leaded gas in his studies–were invariably already saturated with lead, which had the effect of making exposed persons’ high lead load appear less worrisome. Such later findings confirmed the assertions of Yandell Henderson and others who criticized Kehoe’s methodology in 1925 before the Surgeon General’s conference. Harvard’s Dr. Edsall had reminded the Surgeon General, “In spite of what Dr. Kehoe has just said, I think that his work will have to be neglected for the reason that the finding of lead in such a large proportion of control people means that however carefully these observations were made there was something wrong technically.”
Late in his career, Kehoe contended that lead levels in gasoline could–and should–be raised.
In recent years, a new generation of academics has singled out Robert Kehoe as the father of a rule, or paradigm, of profound importance, one that was to govern American industry and its parade of hazardous products for much of the twentieth century. By relying on what Jerome Nriagu of the University of Michigan has called the cascading uncertainty rule (“There is always uncertainty to be found in a world of imperfect information”), the lead industry and makers and marketers of TEL gasoline additives were able to argue in 1925: “You say it’s dangerous. We say it’s not. Prove us wrong.” (Or, as Nriagu prefers, “Show me the data.”) They still do.
As a result, Ethyl had its cake and ate it, several times. If the company’s substance checked out as safe, then it would have been shown to have behaved responsibly. If not, it would take an eternity to prove, during which time the company could keep challenging test results and calling for more data. “Both possible outcomes,” the historian Alan Loeb has written, “accommodated Ethyl. The general public was dealt all the risk and Ethyl and its owners were insulated from responsibility. To the extent that there was a health consequence, the Kehoe rule placed the burden upon the public.”
In the past fifty years, nuclear power, tobacco, chemical, asbestos, coal, pesticide and automobile interests have adopted strategies similar to the one developed by Kehoe. Clutching most of the technology and all of the research capital in their own hands, they’ll say “Prove us wrong, and we’ll change.” But confronted with damning evidence, they’ll repeatedly challenge the methodology of the studies or the bias of researchers. All of which takes time. When these defenses fail, the whole notion of extrapolating from test results on animals might be questioned. As Professor Herbert Needleman of the University of Pittsburgh has observed, because toxins are not tested on humans, this effectively means that no agent can ever be demonstrated as toxic to industry’s satisfaction.
Today, application of the Kehoe Rule has special meaning, as multinational corporations seek to introduce myriad genetically engineered crops and products prior to rigorous independent scientific testing. Once again, the burden of proof is being subtly shifted to the doubters, with the entire world cast in the role of guinea pig. In 1925 Haven Emerson, a Columbia professor of public health and former New York health commissioner, said of the TEL experience, “Up to the present time we have almost invariably got our first inkling of a new industrial chemical hazard by some human catastrophe… it seems rather pitiable in a country of such wealth in means and knowledge that we had to wait for a series of human catastrophes to develop the demand for a series of animal experiments.”
Lead Paint vs. Lead Gas
Working alongside Kehoe at first was the Lead Industries Association. Formed primarily to fight restrictions on the use of lead paint, the LIA was also ready to serve as a sort of all-purpose lead-issue obfuscator. Though it wouldn’t fund much actual research, the LIA would underwrite the original studies at Harvard in the twenties that isolated a new pseudo-psychological malady named “pica,” the so-called unnatural impulse of some small children, mostly nonwhite, to stick lead paint chips in their mouths.
Much to LIA’s chagrin, Kehoe would break ranks with them on the subject of lead paint, judging their product indefensible in light of all small children’s tendency to put things in their mouths. Coming from the lead-happy Kehoe, this was a grim diagnosis indeed. Happily for the doctor, in 1958 LIA and the former American Zinc Institute founded another industry advocacy group, the International Lead Zinc Research Organization, with an eye to promoting global use of the lead additive in fuel and protecting makers of cadmium, the toxic zinc relation often found in batteries. Kehoe and Ethyl would find a happier home at ILZRO, which would fund the occasional scientific study. Dr. Paul Mushak, visiting professor of pediatric toxicology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, told The Nation that the industry has tended to underwrite research toward the margins of relevant issues, so as to avoid discovering something it might not like.
Kehoe’s split with LIA and the lead-paint camp was, oddly, beneficial for both parties. Ever since, the lead-paint and lead-gasoline interests have been able to point the finger at one another when assessing their own responsibility for the global lead-pollution problem, buying more time to sell their products and more time to distance themselves from potential liability.
Ethyl Changes Hand
By the late thirties Ethyl had sewed up the US market, as noted, and was making major inroads in Europe. After World War II, Third World markets would begin to be opened. On the surface things looked pretty good for the company, which by now had blanketed the earth with its “gift of God.” As “The Ethyl Story,” an insert in the Ethyl corporation’s annual report for 1963, observed with enthusiasm, “today, lead alkyl antiknock compounds are used in more than 98 percent of all gasoline sold in the United States and in billions of gallons more sold in the rest of the world. Leaded gasoline is available at 200,000 service stations in this country and thousands of others around the globe.”
Strange it was, then, that in 1962 GM and Standard suddenly dumped the Ethyl Corporation on the market. Even more surprising to many was the buyer, the tiny Albermarle Paper Manufacturing Company of Richmond, Virginia, and the structure of the deal: It was the modern world’s first recorded leveraged buyout. Albemarle, owned by the Gottwald family, had acquired Ethyl, eighteen times its size, with $200 million of borrowed money, making the front page of the New York Times. “It was like a Mom and Pop grocery buying the A&P!” remarked an incredulous Monroe Jackson Rathbone, Standard Oil of New Jersey’s president, after presumably taking a back seat in the negotiations.
No one who’s talking knows why GM wanted out of Ethyl in 1962. Ethyl’s official historian notes dryly that profits were flat in the late fifties. The company’s TEL patents had expired in 1947, and this allowed Nalco, PPG and Houston Chemical to get into the TEL game on the back of Ethyl’s yeoman work. But Ethyl was still the 800-pound gorilla in the tetraethyl arena; overall, profits were pleasingly plump and Ethyl’s annual reports were upbeat. A more important factor may have been the sense that antitrust was in the air, with the du Pont family being ordered by the government during this period to divest billions in GM shares. Ethyl’s incestuous paternity and its unseemly relations with Nazi Germany during World War II were reasons to avoid closer scrutiny by a nosy government. And, just perhaps, GM might have known something heavy was coming.
Ethyl’s new owners would, in fact, soon find themselves staring at more worrisome smoke signals than a patch of duff profits. In July 1943 the Los Angeles Times reported the city’s first major smog episode. In 1950 Dr. Arie Haagen-Smit reported that the interaction of hydrocarbons (HC) and oxides of nitrogen (NOX) caused smog in Los Angeles. By 1953 automobiles would be identified as the region’s largest source of hydrocarbons. Though they may or may not have known it in 1962, the makers of TEL would soon be staring down the barrel of a gun–the anti-air pollution movement.
American auto makers saw the threat that air pollution posed to their business. In the mid-fifties they’d concluded a formal but secret agreement among themselves to license pollution-control technologies jointly and not publicize discoveries in the area without prior approval of all the signatories, a pre-emptive strike against those who would pressure them to install costly emissions controls. The effect of their pact would be to stifle the development of these much-needed devices and technologies. When their agreement came to the Justice Department’s attention in 1969, the fallout from the exposure of their perfidy and mounting awareness of the nation’s out-of-control smog problem would guarantee passage of air-pollution laws that would eventually put lead out of business in America. By this time, the legislative mood had changed as it pertained to the automobile, fueled in large measure by the work–and persecution, by GM–of a young lawyer and Congressional aide named Ralph Nader, who, after raising serious questions about auto safety, had been followed and harassed by GM’s private detectives.
Crucially, too, by 1969 the entire Kehoe view of natural human lead burdens had been knocked out–with one punch–by Dr. Clair Patterson, a California Institute of Technology geochemist. A onetime member of the Manhattan Project, Patterson is widely credited with giving us our most accurate estimate of the earth’s age–4.55 billion years. With the publication in 1965 of his seminal work, “Contaminated and Natural Lead Environments of Man,” in the Archives of Environmental Health, the scientific world had its hardest proof ever that high background lead levels in industrial lands were man-made and endemic. Noticing heavy planetary lead contamination in the process of establishing the age of the planet, Patterson detailed how industrial man had raised his lead burden 100 times and levels of atmospheric lead 1,000 times. Kehoe’s rule of error ended in a flash.
Kehoe held his head high in his remarks to Edmund Muskie’s Congressional clean air subcommittee in 1966, but Patterson had turned him into an academic train wreck. Unlike Kehoe, Patterson utilized state-of-the-art methods to avoid subject contamination with background lead. Analyzing the 1,600-year-old bones of pre-Columbian humans, he showed that the twentieth-century human lead burden was seriously elevated. Though Patterson’s work was widely hailed by the scientific community (it was the reason Kehoe was humored, rather than respected, by the Muskie committee), the paper earned the professor a visit from representatives of the Ethyl corporation, who, in Patterson’s words, tried to “buy me out through research support that would yield results favorable to their cause.”
Instead of joining forces with Ethyl, Patterson delivered a lecture assailing the company’s activities and predicting the demise of their TEL operation. Following these events, his longstanding contract with the Public Health Service was not renewed, nor was a substantial contract with the American Petroleum Institute. Members of the board of trustees at Cal Tech leaned on the chairman of his department to fire him. Others have alleged that Ethyl offered to endow a chair at Cal Tech if Patterson was sent packing.
In January 1969 the four major US auto companies and their trade association–along with seven manufacturers of trucks and cabs, listed as co-conspirators–were accused by the Justice Department of conspiracy to delay development and use of devices to control air pollution from cars, based on their secret agreement. Though they would settle the government’s suit in September by agreeing to terminate their compact as well as all joint research, publicity or lobbying on emissions issues, Detroit’s position vis-à-vis air pollution had been severely compromised. Ethyl was on its own now, and it was fair and easy game to take the fall.
On January 14, 1970, GM president Ed Cole announced to a flabbergasted audience the company’s intention to meet pending clean-air laws with catalytic converters beginning in 1974. Attached to automotive exhaust systems, these devices trap many harmful emissions. However, the catalysts’ active element, platinum, is expensive, a real problem when it is rendered instantly inoperative (and the car undrivable) by the lead in “ethylized” gasoline. Farewell, then, leaded gasoline.
Ethyl was livid. As an authorized corporate biographer wrote some years later, “Here was General Motors, which had fathered the additive, calling for its demise! And it struck some people as incongruous–not to use a harsher word–for General Motors to sell half of what was essentially a lead additive firm for many millions and then to advocate annihilation of the lead antiknock business.”
“‘Get the lead out’ has become a slogan in every household,” Lawrence Blanchard Jr., an Ethyl exec, complained. “I still stay awake some nights trying to figure out how we got into this mess.”
Big Lead Fights Back
Tetraethyl lead was no longer GM’s concern. Nor was it the concern of other auto makers, who followed suit announcing that they too would adopt the catalyst to meet ever-tightening federal emissions standards. Du Pont and Ethyl, on the other hand–along with a ragtag bunch of cheapskate oilmen who hoped to avoid upgrading their refineries to produce unleaded gasoline of sufficiently high octane–still cared a lot about American sales of TEL. When the EPA launched the first of several halfhearted attempts to begin removing lead from gasoline, lead’s corporate affinity group fought back with a ferocity that bespoke major arrogance and even greater desperation. No sooner had the EPA announced a scheduled phaseout, setting a reduced lead content standard for gasoline in 1974, than it was sued by Ethyl and Du Pont, who claimed they had been deprived of property rights. In that same year, a panel of the US Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit set aside the EPA’s lead regulations as “arbitrary and capricious.”
Ethyl had argued that “actual harm” must be shown, not just “significant risk,” before their product could be outlawed, and the panel agreed. That Ethyl could make the argument at all was a troubling reminder that the executive and legislative branches of the United States government had signally failed to heed the Surgeon General’s committee’s original request for funding in 1926 for more independent research, leaving the driving, scientifically speaking, to Robert Kehoe.
In 1976 the full United States Court of Appeals for the DC Circuit overturned the decision against the EPA, finding that “significant risk” was adequate foundation for the agency’s action against lead and within its authority. Supreme Court Justice Lewis Powell, a longtime Ethyl director when he was a Virginia corporate lawyer, didn’t need to recuse himself, as the Court refused to hear an appeal brought by TEL makers Ethyl, Du Pont, Nalco and PPG, as well as the National Petroleum Refiners Association and four oil companies. Ethyl’s excitable Blanchard lashed out, “The whole proceeding against an industry that has made invaluable contributions to the American economy for more than fifty years is the worst example of fanaticism since the New England witch hunts in the Seventeenth Century.”
Fighting on the beaches and fighting on the seas, an impassioned Ethyl wasn’t going to go down easy, urging a reprieve for leaded fuel at a 1979 meeting of the Petrochemical Energy Group. Soon after, the company’s oil industry amigos would sound the alarm for a mysterious “octane crisis” on account of an alleged increase in competition for aromatics, crude oil components that are mainstays of the plastics and synthetics businesses, as well as unleaded gasoline octane boosters. To combat the crisis, they requested an EPA slowdown on the gradual phaseout of lead. The petrochemical industry–led by Du Pont, Monsanto and Dow–would simultaneously launch an intensive lobbying campaign to delay the scheduled lead phaseout, charging, in a reminiscent tack, that the newly discovered dearth of aromatics “threatens the jobs of the 14 million Americans directly dependent and the 29 million Americans indirectly dependent on the petrochemical industry for employment.”
The ever-hopeful lead cabal’s dreams were cruelly dashed in early 1982, after word leaked out of Vice President George Bush’s Task Force on Regulatory Relief that the newly elected Reagan Administration planned to relax or eliminate the US lead phaseout. Recognizing its cue, Du Pont formally called upon the EPA to rescind all lead regulations. EPA Administrator Ann Gorsuch was only too pleased to comply, but she unwittingly launched a firestorm of bad publicity in advance of an announcement by telling a visiting refiner with a big mouth that she would not enforce violations of current lead limits because the regulations would soon be repealed. When Gorsuch’s remarks appeared in the newspapers (and were lampooned in the comic strip Doonesbury), Reagan’s EPA would, under heavy political pressure, strike a compromise that effectively sped up the phaseout. Once again, Ethyl had been let down by old friends.
The New Science of Lead
Ethyl and Octel continued to whine, but by 1984 the health benefits of America’s lead phaseout had become too remarkable to ignore, and it was this fact that ultimately ended lead’s reign in America. The harmful effects of lead at lower and lower concentrations had been shown by independent studies in the late seventies and early eighties, and by now PHS was at long last settling in with the antilead camp. EPA economist Joel Schwartz, assigned by his Reaganaut superiors to examine the impact of the lead phaseout on small refiners preparatory to phasing lead back in, went rogue and reported back instead on the impact of the phaseout’s early years on American blood-lead levels, which the federal Centers for Disease Control in Atlanta had been independently compiling. The CDC’s findings were startling, contradicting everything leadheads of the Kehoe school held dear.
Between 1976 and 1980 the EPA would report, the amount of lead consumed in gasoline dropped 50 percent. Over the same period, blood-lead levels dropped 37 percent. The EPA estimated that the public benefits of the phaseout, which included reduced medical costs and lower maintenance for cars, had already exceeded costs by $700 million. Between 1975 and 1984 lead for gasoline consumption dropped 73 percent, while ambient air lead decreased 71 percent [see graph in printed issue].
The Lead Industries Association was so angry with the data the EPA had corralled that in June 1984 it sued the CDC, which had impaneled its lead experts to prepare an updated statement on childhood lead poisoning for the nation’s medical and public health community (the suit was dismissed on jurisdictional grounds). Schwartz told The Nation that the collection of lead data was hindered by the Reagan Administration, which, early in its term, prohibited the CDC from requiring lead-screening programs to report results to it, figures that it would then publish each quarter in the scientific journal Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Reports. Subsequently, the CDC was prohibited from even inquiring about lead-screening program results.
As more impartial studies were funded, however, the common-sense objections to leaded gas raised by public health campaigners in the twenties only seemed more prescient. Yandell Henderson, Alice Hamilton, David Edsall and numerous other eminent public health scholars had precisely predicted the problem sixty years earlier, before it became a global condition. Sadly, they were ignored. Dispersed into the air in automobile exhaust, lead dust would be no more healthy than it was when lead smelting was identified as a poisonous pastime 3,000 years ago. Moreover, as with many industrial toxins, the perceived acceptable level of exposure fell as further studies were finally carried out.
In the fifties and sixties, blood-lead levels of less than 60 micrograms (a microgram is a millionth of a gram) per deciliter (one-tenth of a liter) of blood (mcg/dl) were considered acceptable by America’s medical establishment, not requiring intervention, because overt symptoms of lead poisoning, such as convulsions, do not typically occur below this level. Prior to that, dating back to the twenties, lead poisoning usually had to be severe enough to cause death or severe brain damage to be considered a diagnosed poisoning event. A corresponding blood-lead level of 80-100 mcg/dl or possibly higher might be imputed. In the intervening years, the acceptable level has dropped steadily from 40 mcg/dl to 30 to 25 and now to 10 or below.
Though the lead industry advocacy groups cling to the old numbers, the CDC, the American Academy of Pediatrics, the EPA and the National Academy of Sciences have agreed that the ill-health effects beginning at 10 mcg/dl are established fact, “an unprecedented coherence of opinion in the field of neurotoxicology.” In 1994 a letter to the editors of the medical journal Pediatrics, several prominent lead research doctors addressing industry naysayers wrote, “If this massive database is not persuasive for lead, then no other chemical can be considered to have been demonstrated to be toxic.”
Completing a sequence familiar to pollution watchers, a recent review of scientific research by the National Research Council has led it to conclude, “There is growing evidence that there is no effective threshold for some of the adverse effects of lead.” Children are especially at risk. Summarizing its study of the relevant science, the Department of Housing and Urban Development wrote, “There does not yet appear to be a discernible threshold for the adverse effects of lead on the young.”
In a 90,000-word 1997 review of all scientific evidence on the subject, Erik Millstone of the Science and Technology Policy Research Unit at Sussex University concluded that children suffer ill effects from lead at especially low exposures–much lower than was thought even recently–including reduced IQ, behavioral and learning difficulties and hyperactivity. Children are 4-5 times more susceptible to the effects of lead than adults. According to the CDC this is because children’s digestive systems absorb more lead than adults–40-50 percent of that ingested versus 10-15 percent. In addition to breathing it in, children will ingest large quantities of airborne lead when it settles on soil, dust, food and playthings, which eventually contact their mouths. Based on research linking the two, in 1998 the Justice Department began studying the impact of childhood lead exposure on juvenile delinquent behavior.
Perhaps the only encouraging news in any discussion of leaded gasoline is how readily blood-lead levels fall when its use is trimmed or eliminated. The US phaseout of lead began in 1975 and was largely complete by 1986. Based on data collected in more than sixty US cities by the CDC, the Department of Health and Human Services reported that blood-lead levels in Americans aged 1-74 had declined 78 percent between 1978 and 1991.
For children aged 1-5, blood-lead levels decreased 76 percent, from 15.0 to 3.6 mcg/dl. The percent of children with blood-lead levels greater than or equal to 10 micrograms declined from 88 percent to 9 percent. The British Medical Journal reported three years ago that since Britain’s lead phaseout began, blood-lead levels there had fallen by two-thirds. In New York City, where the war against tetraethyl lead can be said to have first begun with its ban in 1925, Dr. Sergio Piomelli, a hematologist at Columbia University’s Children’s Hospital, has reported that before the US lead phaseout began, 30,000 out of 100,000 New York City children tested had elevated lead levels; after the phaseout was complete, 1,500 of 100,000 had similarly high levels. In 2000, he told The Nation, the affected population is even smaller.
Still, one of the most telling measures of the extent of human lead contamination–careful measurement of lead levels in the bones of our preindustrial ancestors–argues against too much backslapping. A 1992 article in The New England Journal of Medicine revealed that pre-Columbian inhabitants of North America had average blood-lead levels 625 times lower than the current “safe” level of 10 mcg/dl.
Eastward, Ho!
Foreign custom kept Ethyl in business, and it put Octel on the map. In the seventies, with the auto industry embracing catalytic converters and talk of a lead phaseout circulating, the US market seemed certain to shrink, making foreign profits increasingly important to the lead giants. Casting back over 1972 in its annual report for that year, Ethyl reminded shareholders, “Continued penetration of expanding world markets would lessen any…impact on Ethyl’s total antiknock sales.” The following year, noting growing reservations about the American market, it went on to recall: “Sales of antiknock compounds continued to increase in all overseas markets in 1973. To promote this growth, Ethyl International added antiknock bulk terminals in the Far East, Middle East and South America. Construction of other terminals in various areas of the world is planned in 1974 and 1975.”
Ethyl further elaborated its foreign strategy in 1974: “Most foreign countries have recognized the importance of the role lead antiknocks play in conserving crude oil in this period of shortages…. we believe antiknocks will continue to constitute a major product of the Company for years to come whether or not there is a domestic reduction in use of lead in gasoline.”
By 1979 the company would observe, “It is worth noting that during the second half of 1979, for the first time, Ethyl’s foreign sales of lead antiknock compounds exceeded domestic sales.” Ethyl and Octel both were additionally fortunate in being able to manipulate their prices to keep profit levels high. As Octel reported in a 1998 SEC filing, “From 1989 to 1995, the Company was able to substantially offset the financial effects of the declining demand for TEL through higher TEL pricing. The magnitude of these price increases reflected the cost effectiveness of TEL as an octane enhancer as well as the high cost of converting refineries to produce higher octane grades of fuel.” In other words, they had their customers over a barrel.
Lead for the Poor
The sad, bitter fruit of Ethyl’s and Octel’s missionary work on behalf of leaded gasoline lies in its prevalence in the Third World today. Given the current state of knowledge regarding the hazards of lead, this constitutes a particularly egregious example of environmental racism. While more than 80 percent of the heaviest lead-using countries today are low income, 70 percent of low lead users (those that have phased out lead or allow only very low levels) are high income. While Americans cruise their freeways burning exclusively unleaded gasoline, as of 1996, 93 percent of all gasoline sold in Africa contained lead, 94 percent in the Middle East, 30 percent in Asia and 35 percent in Latin America.
According to the World Bank, 1.7 billion urbanites in developing nations are in danger of lead poisoning, including neurological damage, high blood pressure and heart disease from airborne lead, 90 percent of which is attributable to leaded gasoline. Excessive exposure to lead causes 200,000-500,000 cases of hypertension in the Third World, with 400 deaths per year attributable to lead exposure in the late eighties. In Mexico City, one of the world’s most polluted (and populous) cities, 4 million cars pump an estimated 32 tons of lead each day into the air. In Jakarta, one and a half tons enters the atmosphere every twenty-four hours. A research scientist with the Canadian National Water Research Institute performed roadside-dust analyses in Nigeria that revealed as much as 6,000 parts per million of lead. In the United States, lead dust is considered hazardous to children at 600 ppm [see chart in printed issue].
In Alexandria, Egypt, where gas is heavily leaded, concentrations of TEL and air-lead levels are often double the European Union’s recommended level, and traffic controllers have been found to suffer central nervous system dysfunction. In Cairo more than 800 infants die annually because of maternal exposure to lead. Daytime air-lead levels in Buenos Aires have been measured at 3.9 grams per cubic meter versus the twenty-four-hour EU limit of 1 gram per cubic meter.
The continued use of TEL is especially troubling in light of the fact that the Third World’s car population is multiplying rapidly, a situation that will only intensify if multinational automobile manufacturers have their way. Although the Chinese government has recently expressed its intention to remove lead from its fuel, other nations that haven’t are already seeing vehicular population explosions like that predicted for China.
Prodded by Western lead manufacturers, some countries have even allowed the lead content in their gasoline to be increased. Although it has since moved toward deleading its gasoline, India, for instance, more than doubled the amount of lead permitted in its gasoline (from 0.22 to 0.56 grams per liter) during the seventies and eighties; in Uganda, the number soared from 0.58 to 0.84 grams per liter, higher than was ever typical in the West. Never known for their philanthropy, refiners in poorer nations are disinclined to upgrade their refineries so as to obtain higher octane gasolines without using lead.
Ironically, in the nineties the Venezuelan state oil company, Petroleos de Venezuela, exported unleaded gasoline. But it was importing TEL and adding it to all gasoline sold for domestic use–this in the country with the greatest number of automobiles per capita in Latin America. By way of explanation, it is perhaps not unhelpful to know that several high-ranking officials of the state oil company held consultancies with companies that sell lead additives to the country. Among the consequences of this corrupt arrangement: According to a 1991 study 63 percent of newborns studied had blood-lead levels in excess of US “safe” levels.
Environmental standards in Third World countries tend to be lax. Where clean-air laws and unleaded gasoline do not exist, there is no impetus for automobile manufacturers to install catalytic converters in their cars. With the rapid growth in automobile use and the growing size of these countries’ fleets, coupled with low vehicle-turnover rates (car lives of fifteen years are not at all uncommon in low-income countries) and minimal maintenance, air pollution becomes a much greater hazard. According to the World Health Organization, two-thirds of India’s pollution is generated today by vehicles, compared with only 24 percent in 1971; the WHO estimates that 7,500 deaths in New Delhi each year are related to air pollution.
Finally, because lead ruins catalytic converters and fouls modern engine-management computers, leaded gasoline prevents motorists in these countries from using more efficient, less-polluting modern vehicles even if they want to. Where cars equipped with catalysts are sold as new or used vehicles, a predominantly leaded fuel supply invites motorists to either remove the air-cleansing catalysts or destroy them by filling their cars with leaded fuel.
It’s Cleanup Time
The public health benefits and cost savings to societies of removing lead from gasoline are so vast that the business-friendly World Bank was moved–at a 1996 UN conference in Turkey, where leaded gas still accounts for 82 percent of the market–to call for a complete global phaseout. The bank calculated that the United States had saved more than $10 for every $1 it invested in its conversion to unleaded, by reducing health costs, saving on engine maintenance and improving fuel efficiency with modern engine technologies. Further claiming that no-lead fuel may increase engine life by as much as 150 percent, the bank called for an immediate five-year phaseout. (Buttressing the World Bank’s public-spirited campaign, undoubtedly, is the realization that many of the state-owned oil companies currently producing leaded gasoline will require private investment–and possibly ownership–to finance refinery upgrades to produce high-octane unleaded fuels.)
Unsurprisingly, the industry, which favors phaseouts of twenty-years’ duration and more, responded testily:
“Octel and the World Bank have been discussing the transition from leaded to unleaded gasoline for a long time,” a spokesman told the Chemical Marketing Reporter in 1996. “It isn’t really appropriate for the World Bank to apply US studies and data to the phaseout of lead in Third World countries.”
Ethyl and Octel both have strategies for dealing with Third World nations seeking to go unleaded. In separate interviews with The Nation, they admitted advising their remaining customers to go slow. As Ethyl’s vice president of international sales, Bob Yondola, explained: “As countries have the infrastructure to support unleaded gasoline, have the monies for their people to buy the new cars, etc., etc., it makes sense [to switch to unleaded gas]. But if you’ve got some parts of the world where their infrastructure is still–you know, they need to come up with food and water, and sewers…for their people. And there are still places in the world like that. Then, I mean, getting the lead out of the gasoline, to me, wouldn’t make as much sense as having sewers.”
Associated Octel’s public affairs spokesman Bob Larbey, since retired, said his firm will help Third World refiners clean up their contaminated lead operations, for a fee. “But,” he said, “we talk to developing countries. For example, refiners come to us and say, ‘We want to get the lead out,’ because we’re refinery experts, you see, and we could advise them on how they could best phase lead out, with what strategy. I think if we argue anything at all, we say, ‘Well, if you’re going to go out of lead, fine, let’s talk a bit, but there’s no need, this is the lead in health information, there’s no proven adverse health affect, and so there’s no need for you to do it precipitously. You might not want to take twenty years [as in the European phaseout] but really, there’s no need to rush.’ Because if you replaced it with other components of petrol then there’s a risk from anything…. Petrol itself is a risk without lead.”
The lead industry clutches the alleged dangers of other octane-enhancing gasoline additives near to its bosom. While admitting the hazard of his company’s product, one Octel executive told the New York Times that leaded fuel is an “economic and environmental bargain” for the Third World because it improves fuel economy, which lowers other emissions like benzene, also found in gasoline.
“Getting rid of one environmental risk won’t necessarily improve public health if you replace it with greater risks,” yet another spokesman for Octel’s affiliate told the Chemical Marketing Reporter. Benzene, the hazard to which lead enthusiasts refer most often, can be used by refiners to boost octane cheaply in the absence of lead. But it isn’t mandatory, and any sensible lead-reduction regulation would limit its use. Moreover, while as many as 5,000 Americans died annually from lead-related heart disease prior to the lead phaseout, only forty-seven people developed cancer from the use of benzene as a lead replacement. “The health impacts of aromatics [like benzene] are several orders of magnitude less than that of lead,” said a World Bank spokesperson.
Diversification and Spinoff
Selling lead is an unusually profitable business. As Ethyl’s 1995 report to shareholders blandly observes, lead additive sales accounted for 26 percent of gross revenues, but 74 percent of its profit. In 1995 the New York Times wrote of the profit bonanza Octel’s then-owner, Great Lakes Chemical, had stumbled upon when, searching for sources of bromine for fire retardants, it landed in the TEL business.
Far from petering out, demand for leaded gasoline, while shrinking, has remained far stronger than anyone predicted, especially in the third world. Meanwhile, every other major producer has stopped making the additives, known as tetraethyl lead, or TEL. That has left Great Lakes with an unexpected flood of profits and 90 percent of a market that no one else will enter because of the environmental problems associated with lead and the huge capital costs of building a new plant.
Octel’s old plant, along the Manchester Ship Canal outside Liverpool, bankrolled immense growth for Great Lakes, allowing it to double in size within five years (to $5 billion in annual revenue) following its acquisition of Octel, all the while maintaining a hefty 15 percent annual operating profit. As recently as 1977 Great Lakes had only $50 million in operating revenue.
Years of lead profits have funded major diversification efforts for Ethyl and its owners, led by the Gottwald family of Richmond. The company’s annual report for 1996 revealed “a long-running strategy: namely, using Ethyl’s significant cash flow from lead antiknocks to build a self-supporting major business and earnings stream in the petroleum additives industry.”
By 1983 Ethyl had become “the world’s largest producer of organo-metallic chemicals.” It would expand its production for the petroleum industry (including the purchase of the petroleum additives divisions of Amoco and Texaco), as well as acquire interests in other specialty chemicals, plastics and aluminum products, oil, gas and coal. Ethyl would also invest billions in pharmaceuticals, biotech research, semiconductors and life insurance. At great expense, it would develop a serene corporate campus of seventy acres along the banks of the James River in Richmond.
As the science against TEL mounted and government regulation stiffened, Ethyl began a series of restructurings that today find its TEL business standing suspiciously alone. In 1989 Ethyl spun off Tredegar Industries, a group it created to hold its aluminum, plastics and energy businesses. For every Ethyl share they held, investors would receive prorated shares in the new company. Voilà! Limited liability. Later Ethyl would spin off its billion-dollar insurance company, First Colony Life. In 1994 Ethyl would split up its chemical and petroleum additives division and create a wholly owned subsidiary, Albemarle Corporation, named after the 100-year-old paper company that bought Ethyl (which retained its name) in 1962. One of the main enterprises of Albemarle, ironically, is supplying Ethyl with MMT under a long-term agreement. MMT is another gasoline additive (made of manganese and barely sold in the United States) with suspected health consequences. In 1994 Ethyl and its Albemarle offspring did a rousing $48 million of business together. Oddly, for a company that claims to be proud of its product (so proud that under an obscure provision of NAFTA it sued the Canadian government for outlawing MMT) Ethyl declined to tell Automobile Magazine in 1999 in which countries it sold MMT to refiners, presumably because it fears awakening consumers to the presence of its manganese additive.
Because it was itself spun off to a management team from Great Lakes Chemical, Octel remains highly concentrated in lead, with TEL representing 85 percent of its business in 1996. Although CEO Dennis Kerrison has announced his intention to develop non-TEL businesses into core businesses by 2005, “even the most extreme estimates allow for the continued use of leaded petrol in some parts of the world until at least the year 2010.” Off the record, company officials admit they could be selling lead in 2020 and beyond.
Until then, Octel, “through the specialist facilities of Octel Environmental, provides a range of decontamination, destruction, removal and recycling services to refineries throughout the world to help to reduce the environmental impact of toxic lead residues.” Under its Product Stewardship Programme–“a public service,” Octel calls it–fifty tons of lead alkyl sludge were removed from New Zealand refineries as part of a cleanup beginning in 1996. Octel had supplied the refineries with 4,000 tons of TEL annually for years. So, in a crowning irony, poisoned motorists in New Zealand and around the world will, through higher gasoline prices, pay Octel (and Ethyl) to clean up the mess the TEL barons and their refinery customers made.
Will the Sun Ever Set on Lead?
Associated Octel’s fiftieth-anniversary catalogue affectionately quotes a letter the company received from a former technical services manager in 1982, when Britain’s antilead campaign kicked off in earnest: “Many funerals have been arranged for lead in petrol–1926, 1943, 1954, 1970, etc.–as I can recall. The grave has been dug, the service arranged, the coffin prepared, the parson and mourners instructed, but the body just would not lie down in the coffin.”
Though the catalogue was published in 1988, the sentimental hope that it’s not over yet is secretly still held by Octel and Ethyl, and all the others who continue to push leaded gasoline. But the body of tetraethyl lead must be made to lie down in its coffin. The five-year phaseout of leaded gasoline favored by the World Bank in 1996 makes inarguable moral and business sense–two things that don’t always go together, especially at the World Bank. The only ones arguing otherwise are Octel, Ethyl and the small coterie of self-interested researchers and narrowly trained toxicological technicians who’ve lived on the industry’s tab for the last thirty years, since Robert Kehoe stepped down.
Many European nations have banned leaded gas for 2000. Progress has been made. But somehow Ethyl and Octel will be splitting Third World profits for years to come. If the science was ever in doubt (and it really wasn’t), the facts are now incontrovertible. Leaded gasoline is dangerous. When safer alternatives are available, as they always have been, leaded gasoline’s benefits are nil. It is not good for cars, and it prevents the use of modern emissions reduction equipment, like catalytic converters, which, owing to the greenhouse effect, the world needs more desperately now than ever. TEL’s most crass (and main) historic selling point is no longer valid: It isn’t even cheap.
There is at least one simple lesson to be drawn from the tetraethyl lead story. Industry cannot be trusted to regulate itself, as Clair Patterson–the man who dated the earth and single-handedly deflated ethylized science–once remarked. “It is not just a mistake for public health agencies to cooperate and collaborate with industries in investigating and deciding whether public health is endangered–it is a direct abrogation and violation of the duties and responsibilities of those public health organizations.”
As for General Motors, Du Pont, Standard Oil, Ethyl, Associated Octel and rest of the lead cabal, it’s conceivable they’ll be hauled into court sooner or later, which is one reason these companies all take such an active interest in so-called tort reform legislation. You would too, if you had been a key actor in one of the most tortious episodes of twentieth-century industrial history. We can hope that Congress doesn’t give them a free pass, but no matter what, it will be the citizenry that will pay any financial bills coming due. They’ve already paid with their health. Many of the effects of childhood lead exposure are irreversible.
These businesses should be shut down. And to make sure they don’t forget their heinous experience, all these companies ought to open their archives to independent review, to assist in assembling the information that will help lay TEL down to eternal rest, to help show the world what went wrong when common sense was put on hold in the name of profit. In the face of all that is known today, the leaderships of foreign countries who continue to poison their people with TEL should be harangued to phase out lead from their gasoline–on a daily basis, by the United Nations as well as by governments, agencies and medical officials from around the world. Until then, the merchants of tetraethyl lead–or any other unnecessary additive known to be dangerous–are no better than criminals. They should be dealt with accordingly. Maybe in this new century they will be.
The author wishes to thank for their assistance and to acknowledge the research of Professor William Kovarik, Dr. Herbert Needleman, Professors David Rosner and Gerald Markowitz, Dr. Jerome Nriagu, Dr. Amy Kyle, Richard Merritt, Richard Bremner and Alan Loeb. He would also like to express particular gratitude to his research associate, Bill Krauss, his editor, Richard Lingeman, and his fact-checker, Michael Kunichika.