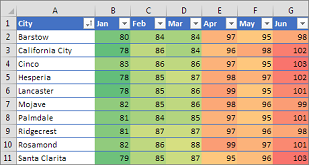
Conditional formatting can help make patterns and trends in your data more apparent. To use it, you create rules that determine the format of cells based on their values, such as the following monthly temperature data with cell colors tied to cell values.
You can apply conditional formatting to a range of cells (either a selection or a named range), an Excel table, and in Excel for Windows, even a PivotTable report.
Conditional formatting typically works the same way in a range of cells, an Excel table, or a PivotTable report. However, conditional formatting in a PivotTable report has some extra considerations:
-
There are some conditional formats that don’t work with fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report. For example, you can’t format such fields based on whether they contain unique or duplicate values. These restrictions are mentioned in the remaining sections of this article, where applicable.
-
If you change the layout of the PivotTable report by filtering, hiding levels, collapsing and expanding levels, or moving a field, the conditional format is maintained as long as the fields in the underlying data are not removed.
-
The scope of the conditional format for fields in the Values area can be based on the data hierarchy and is determined by all the visible children (the next lower level in a hierarchy) of a parent (the next higher level in a hierarchy) on rows for one or more columns, or columns for one or more rows.
Note: In the data hierarchy, children do not inherit conditional formatting from the parent, and the parent does not inherit conditional formatting from the children.
-
There are three methods for scoping the conditional format of fields in the Values area: by selection, by corresponding field, and by value field.
The default method of scoping fields in the Values area is by selection. You can change the scoping method to the corresponding field or value field by using the Apply formatting rule to option button, the New Formatting Rule dialog box, or the Edit Formatting Rule dialog box.
|
Method |
Use this method if you want to select |
|
Scoping by selection |
|
|
Scoping by value field |
|
|
Scoping by corresponding field |
When you conditionally format fields in the Values area for top, bottom, above average, or below average values, the rule is based on all visible values by default. However, when you scope by corresponding field, instead of using all visible values, you can apply the conditional format for each combination of:
|
Note: Quick Analysis is not available in Excel 2010 and previous versions.
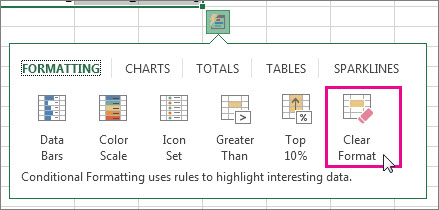
Use the Quick Analysis button 
-
Select the data that you want to conditionally format. The Quick Analysis button appears on the lower-right corner of the selection.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
, or press Ctrl+Q.
-
In the pop-up that appears, on the Formatting tab, move your mouse over the different options to see a Live Preview on your data, and then click on the formatting option you want.
Notes:
-
The formatting options that appear in the Formatting tab depend on the data you have selected. If your selection contains only text, then the available options are Text, Duplicate, Unique, Equal To, and Clear. When the selection contains only numbers, or both text and numbers, then the options are Data Bars, Colors, Icon Sets, Greater, Top 10%, and Clear.
-
Live preview will only render for those formatting options that can be used on your data. For example, if your selected cells don’t contain matching data and you select Duplicate, the live preview will not work.
-
-
If the Text that Contains dialog box appears, enter the formatting option you want to apply and click OK.
If you’d like to watch a video that shows how to use Quick Analysis to apply conditional formatting, see Video: Use conditional formatting.
You can download a sample workbook that contains different examples of applying conditional formatting, both with standard rules such as top and bottom, duplicates, Data Bars, Icon Sets and Color Scales, as well as manually creating rules of your own.
Download: Conditional formatting examples in Excel
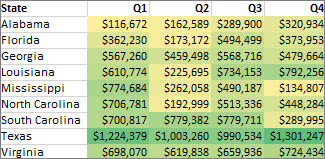
Color scales are visual guides that help you understand data distribution and variation. A two-color scale helps you compare a range of cells by using a gradation of two colors. The shade of the color represents higher or lower values. For example, in a green and yellow color scale, as shown below, you can specify that higher value cells have a more green color and lower value cells have a more yellow color.
Tip: You can sort cells that have this format by their color — just use the context menu.
Tip: If any cells in the selection contain a formula that returns an error, the conditional formatting is not applied to those cells. To ensure that the conditional formatting is applied to those cells, use an IS or IFERROR function to return a value other than an error value.
Quick formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Color Scales.
-
Select a two-color scale.
Hover over the color scale icons to see which icon is a two-color scale. The top color represents higher values, and the bottom color represents lower values.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Formatting Options button that appears next to a PivotTable field that has conditional formatting applied.
Advanced formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a completely new conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Selected cells.
-
All cells for a Value label: Click All cells showing <Value label> values.
-
All cells for a Value label, excluding subtotals and the grand total: Click All cells showing <Value label> values for <Row Label>.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format all cells based on their values (default).
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format Style list box, select 2-Color Scale.
-
To select a type in the Type box for Minimum and Maximum, do one of the following:
-
Format lowest and highest values: Select Lowest Value and Highest Value.
In this case, you do not enter a Minimum and MaximumValue.
-
Format a number, date, or time value: Select Number and then enter a Minimum and MaximumValue.
-
Format a percentage Percent: Enter a Minimum and MaximumValue.
Valid values are from 0 (zero) to 100. Don’t enter a percent sign.
Use a percentage when you want to visualize all values proportionally because the distribution of values is proportional.
-
Format a percentile: Select Percentile and then enter a Minimum and MaximumValue. Valid percentiles are from 0 (zero) to 100.
Use a percentile when you want to visualize a group of high values (such as the top 20thpercentile) in one color grade proportion and low values (such as the bottom 20th percentile) in another color grade proportion, because they represent extreme values that might skew the visualization of your data.
-
Format a formula result: Select Formula and then enter values for Minimum and Maximum.
-
The formula must return a number, date, or time value.
-
Start the formula with an equal sign (=).
-
Invalid formulas result in no formatting being applied.
-
It’s a good idea to test the formula to make sure that it doesn’t return an error value.
Notes:
-
Make sure that the Minimum value is less than the Maximum value.
-
You can choose a different type for the Minimum and Maximum. For example, you can choose a number for Minimum a percentage for Maximum.
-
-
-
-
To choose a Minimum and Maximum color scale, click Color for each, and then select a color.
If you want to choose additional colors or create a custom color, click More Colors. The color scale you select is shown in the Preview box.
Color scales are visual guides that help you understand data distribution and variation. A three-color scale helps you compare a range of cells by using a gradation of three colors. The shade of the color represents higher, middle, or lower values. For example, in a green, yellow, and red color scale, you can specify that higher value cells have a green color, middle value cells have a yellow color, and lower value cells have a red color.
Tip: You can sort cells that have this format by their color — just use the context menu.
Quick formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Color Scales.
-
Select a three-color scale. The top color represents higher values, the center color represents middle values, and the bottom color represents lower values.
Hover over the color scale icons to see which icon is a three-color scale.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Formatting Options button that appears next to a PivotTable field that has conditional formatting applied..
Advanced formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a new conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Just these cells.
-
Corresponding field: Click All <value field> cells with the same fields.
-
Value field: Click All <value field> cells.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format all cells based on their values.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format Style list box, select 3-Color Scale.
-
Select a type for Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum. Do one of the following:
-
Format lowest and highest values: Select a Midpoint.
In this case, you do not enter a Lowest and HighestValue.
-
Format a number, date, or time value: Select Number and then enter a value for Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum.
-
Format a percentage: Select Percent and then enter a value for Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum. Valid values are from 0 (zero) to 100. Do not enter a percent (%) sign.
Use a percentage when you want to visualize all values proportionally, because using a percentage ensures that the distribution of values is proportional.
-
Format a percentile: Select Percentile and then enter a value for Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum.
Valid percentiles are from 0 (zero) to 100.
Use a percentile when you want to visualize a group of high values (such as the top 20th percentile) in one color grade proportion and low values (such as the bottom 20th percentile) in another color grade proportion, because they represent extreme values that might skew the visualization of your data.
-
Format a formula result: Select Formula and then enter a value for Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum.
The formula must return a number, date, or time value. Start the formula with an equal sign (=). Invalid formulas result in no formatting being applied. It’s a good idea to test the formula to make sure that it doesn’t return an error value.
Notes:
-
You can set minimum, midpoint, and maximum values for the range of cells. Make sure that the value in Minimum is less than the value in Midpoint, which in turn is less than the value in Maximum.
-
You can choose a different type for Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum. For example, you can choose a Minimum number, Midpoint percentile, and Maximum percent.
-
In many cases, the default Midpoint value of 50 percent works best, but you can adjust this to fit unique requirements.
-
-
-
To choose a Minimum, Midpoint, and Maximum color scale, click Color for each, and then select a color.
-
To choose additional colors or create a custom color, click More Colors.
-
The color scale you select is shown in the Preview box.
-
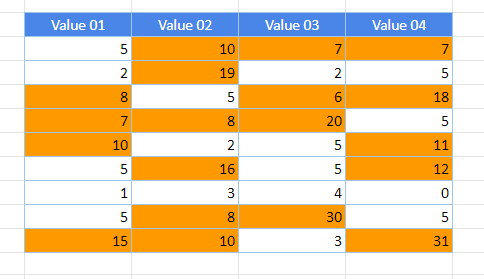
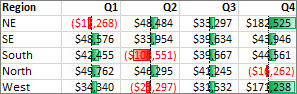
A data bar helps you see the value of a cell relative to other cells. The length of the data bar represents the value in the cell. A longer bar represents a higher value, and a shorter bar represents a lower value. Data bars are useful in spotting higher and lower numbers, especially with large amounts of data, such as top selling and bottom selling toys in a holiday sales report.
The example shown here uses data bars to highlight dramatic positive and negative values. You can format data bars so that the data bar starts in the middle of the cell, and stretches to the left for negative values.
Tip: If any cells in the range contain a formula that returns an error, the conditional formatting is not applied to those cells. To ensure that the conditional formatting is applied to those cells, use an IS or IFERROR function to return a value (such as 0 or «N/A») instead of an error value.
Quick formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Style group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, click Data Bars, and then select a data bar icon.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Apply formatting rule to option button.
Advanced formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Just these cells.
-
Corresponding field: Click All <value field> cells with the same fields.
-
Value field: Click All <value field> cells.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format all cells based on their values.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format Style list box, select Data Bar.
-
Select a Minimum and MaximumType. Do one of the following:
-
Format lowest and highest values: Select Lowest Value and Highest Value.
In this case, you do not enter a value for Minimum and Maximum.
-
Format a number, date, or time value: Select Number and then enter a Minimum and MaximumValue.
-
Format a percentage: Select Percent and then enter a value for Minimum and Maximum.
Valid values are from 0 (zero) to 100. Do not enter a percent (%) sign.
Use a percentage when you want to visualize all values proportionally, because using a percentage ensures that the distribution of values is proportional.
-
Format a percentile Select Percentile and then enter a value for Minimum and Maximum.
Valid percentiles are from 0 (zero) to 100.
Use a percentile when you want to visualize a group of high values (such as the top 20th percentile) in one data bar proportion and low values (such as the bottom 20th percentile) in another data bar proportion, because they represent extreme values that might skew the visualization of your data.
-
Format a formula result Select Formula, and then enter a value for Minimum and Maximum.
-
The formula has to return a number, date, or time value.
-
Start the formula with an equal sign (=).
-
Invalid formulas result in no formatting being applied.
-
It’s a good idea to test the formula to make sure that it doesn’t return an error value.
-
Notes:
-
Make sure that the Minimum value is less than the Maximum value.
-
You can choose a different type for Minimum and Maximum. For example, you can choose a Minimum number and a Maximum percent.
-
-
To choose a Minimum and Maximum color scale, click Bar Color.
If you want to choose additional colors or create a custom color, click More Colors. The bar color you select is shown in the Preview box.
-
To show only the data bar and not the value in the cell, select Show Bar Only.
-
To apply a solid border to data bars, select Solid Border in the Border list box and choose a color for the border.
-
To choose between a solid bar and a gradiated bar, choose Solid Fill or Gradient Fill in the Fill list box.
-
To format negative bars, click Negative Value and Axis and then, in the Negative Value and Axis Settings dialog box, choose options for the negative bar fill and border colors. You can choose position settings and a color for the axis. When you are finished selecting options, click OK.
-
You can change the direction of bars by choosing a setting in the Bar Direction list box. This is set to Context by default, but you can choose between a left-to-right and a right-to-left direction, depending on how you want to present your data.
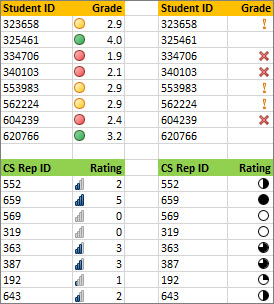
Use an icon set to annotate and classify data into three to five categories separated by a threshold value. Each icon represents a range of values. For example, in the 3 Arrows icon set, the green up arrow represents higher values, the yellow sideways arrow represents middle values, and the red down arrow represents lower values.
Tip: You can sort cells that have this format by their icon — just use the context menu.
The example shown here works with several examples of conditional formatting icon sets.
You can choose to show icons only for cells that meet a condition; for example, displaying a warning icon for those cells that fall below a critical value and no icons for those that exceed it. To do this, you hide icons by selecting No Cell Icon from the icon drop-down list next to the icon when you are setting conditions. You can also create your own combination of icon sets; for example, a green «symbol» check mark, a yellow «traffic light», and a red «flag.»
Tip: If any cells in the selection contain a formula that returns an error, the conditional formatting is not applied to those cells. To ensure that the conditional formatting is applied to those cells, use an IS or IFERROR function to return a value (such as 0 or «N/A») instead of an error value.
Quick formatting
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
On the Home tab, in the Style group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, click Icon Set, and then select an icon set.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Apply formatting rule to option button.
Advanced formatting
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Just these cells.
-
Corresponding field: Click All <value field> cells with the same fields.
-
Value field: Click All <value field> cells.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format all cells based on their values.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format Style list box, select Icon Set.
-
Select an icon set. The default is 3 Traffic Lights (Unrimmed). The number of icons and the default comparison operators and threshold values for each icon can vary for each icon set.
-
You can adjust the comparison operators and threshold values. The default range of values for each icon are equal in size, but you can adjust these to fit your unique requirements. Make sure that the thresholds are in a logical sequence of highest to lowest from top to bottom.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Format a number, date, or time value: Select Number.
-
Format a percentage: Select Percent.
Valid values are from 0 (zero) to 100. Do not enter a percent (%) sign.
Use a percentage when you want to visualize all values proportionally, because using a percentage ensures that the distribution of values is proportional.
-
Format a percentile: Select Percentile. Valid percentiles are from 0 (zero) to 100.
Use a percentile when you want to visualize a group of high values (such as the top 20th percentile) using a particular icon and low values (such as the bottom 20th percentile) using another icon, because they represent extreme values that might skew the visualization of your data.
-
Format a formula result: Select Formula, and then enter a formula in each Value box.
-
The formula must return a number, date, or time value.
-
Start the formula with an equal sign (=).
-
Invalid formulas result in no formatting being applied.
-
It’s a good idea to test the formula to make sure that it doesn’t return an error value.
-
-
-
To make the first icon represent lower values and the last icon represent higher values, select Reverse Icon Order.
-
To show only the icon and not the value in the cell, select Show Icon Only.
Notes:
-
You may need to adjust the column width to accommodate the icon.
-
The size of the icon shown depends on the font size that is used in that cell. As the size of the font is increased, the size of the icon increases proportionally.
-
-
To more easily find specific cells, you can format them by using a comparison operator. For example, in an inventory worksheet sorted by categories, you could highlight products with fewer than 10 items on hand in yellow. Or, in a retail store summary worksheet, you might identify all stores with profits greater than 10%, sales volumes less than $100,000, and region equal to «SouthEast.»
The examples shown here work with examples of built-in conditional formatting criteria, such as Greater Than, and Top %. This formats cities with a population greater than 2,000,000 with a green background and average high temperatures in the top 30% with orange.
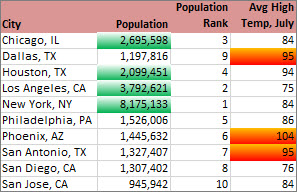
Note: You cannot conditionally format fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by text or by date, only by number.
Quick formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Style group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Highlight Cells Rules.
-
Select the command you want, such as Between, Equal To Text that Contains, or A Date Occurring.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and then select a format.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Apply formatting rule to option button.
If you’d like to watch videos of these techniques, see Video: Conditionally format text and Video: Conditionally format dates.
Advanced formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet or on other worksheets, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Just these cells.
-
Corresponding field: Click All <value field> cells with the same fields.
-
Value field: Click All <value field> cells.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format only cells that contain.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format only cells with list box, do one of the following:
-
Format by number, date, or time: Select Cell Value, select a comparison operator, and then enter a number, date, or time.
For example, select Between and then enter 100 and 200, or select Equal to and then enter 1/1/2009.
You can also enter a formula that returns a number, date, or time value.
-
If you enter a formula, start it with an equal sign (=).
-
Invalid formulas result in no formatting being applied.
-
It’s a good idea to test the formula to make sure that it doesn’t return an error value.
-
-
Format by text: Select Specific Text, choosing a comparison operator, and then enter text.
For example, select Contains and then enter Silver, or select Starting with and then enter Tri.
Quotes are included in the search string, and you may use wildcard characters. The maximum length of a string is 255 characters.
You can also enter a formula that returns text.
-
If you enter a formula, start it with an equal sign (=).
-
Invalid formulas result in no formatting being applied.
-
It’s a good idea to test the formula to make sure that it doesn’t return an error value.
To see a video of this technique, see Video: Conditionally format text.
-
-
Format by date: Select Dates Occurring and then select a date comparison.
For example, select Yesterday or Next week.
To see a video of this technique, see Video: Conditionally format dates.
-
Format cells with blanks or no blanks: Select Blanks or No Blanks.
A blank value is a cell that contains no data and is different from a cell that contains one or more spaces (spaces are considered as text).
-
Format cells with error or no error values: Select Errors or No Errors.
Error values include: #####, #VALUE!, #DIV/0!, #NAME?, #N/A, #REF!, #NUM!, and #NULL!.
-
-
To specify a format, click Format. The Format Cells dialog box appears.
-
Select the number, font, border, or fill format you want to apply when the cell value meets the condition, and then click OK.
You can choose more than one format. The formats you select are shown in the Preview box.
You can find the highest and lowest values in a range of cells that are based on a cutoff value you specify. For example, you can find the top 5 selling products in a regional report, the bottom 15% products in a customer survey, or the top 25 salaries in a department .
Quick formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Style group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Top/Bottom Rules.
-
Select the command you want, such as Top 10 items or Bottom 10 %.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and then select a format.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Apply formatting rule to option button.
Advanced formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Just these cells.
-
Corresponding field: Click All <value field> cells with the same fields.
-
Value field: Click All <value field> cells.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format only top or bottom ranked values.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format values that rank in the list box, select Top or Bottom.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To specify a top or bottom number, enter a number and then clear the % of the selected range box. Valid values are 1 to 1000.
-
To specify a top or bottom percentage, enter a number and then select the % of the selected range box. Valid values are 1 to 100.
-
-
Optionally, change how the format is applied for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report that are scoped by corresponding field.
By default, the conditional format is based on all visible values. However when you scope by corresponding field, instead of using all visible values, you can apply the conditional format for each combination of:
-
A column and its parent row field, by selecting each Column group.
-
A row and its parent column field, by selecting each Row group.
-
-
To specify a format, click Format. The Format Cells dialog box appears.
-
Select the number, font, border, or fill format you want to apply when the cell value meets the condition, and then click OK.
You can choose more than one format. The formats you select are shown in the Preview box.
You can find values above or below an average or standard deviation in a range of cells. For example, you can find the above average performers in an annual performance review or you can locate manufactured materials that fall below two standard deviations in a quality rating.
Quick formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Style group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Top/Bottom Rules.
-
Select the command you want, such as Above Average or Below Average.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and then select a format.
You can change the method of scoping for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by using the Apply formatting rule to option button.
Advanced formatting
-
Select one or more cells in a range, table, or PivotTable report.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by:
-
Selection: Click Just these cells.
-
Corresponding field: Click All <value field> cells with the same fields.
-
Value field: Click All <value field> cells.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format only values that are above or below average.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format values that are list box, do one of the following:
-
To format cells that are above or below the average for all of the cells in the range, select Above or Below.
-
To format cells that are above or below one, two, or three standard deviations for all of the cells in the range, select a standard deviation.
-
-
Optionally, change how the format is applied for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report that are scoped by corresponding field.
By default, the conditionally format is based on all visible values. However when you scope by corresponding field, instead of using all visible values, you can apply the conditional format for each combination of:
-
A column and its parent row field, by selecting each Column group.
-
A row and its parent column field, by selecting each Row group.
-
-
Click Format to display the Format Cells dialog box.
-
Select the number, font, border, or fill format you want to apply when the cell value meets the condition, and then click OK.
You can choose more than one format. The formats you select are displayed in the Preview box.
Note: You can’t conditionally format fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report by unique or duplicate values.
In the example shown here, conditional formatting is used on the Instructor column to find instructors that are teaching more than one class (duplicate instructor names are highlighted in a pale red color). Grade values that are found just once in the Grade column (unique values) are highlighted in a green color.
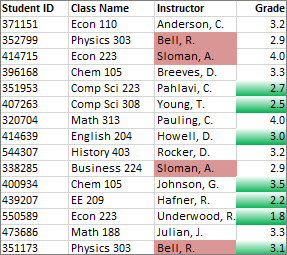
Quick formatting
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
On the Home tab, in the Style group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Highlight Cells Rules.
-
Select Duplicate Values.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and then select a format.
Advanced formatting
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet or table is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet, and then by selecting Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Format only unique or duplicate values.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format all list box, select unique or duplicate.
-
Click Format to display the Format Cells dialog box.
-
Select the number, font, border, or fill format you want to apply when the cell value meets the condition, and then click OK.
You can choose more than one format. The formats you select are shown in the Preview box.
If none of the above options is what you’re looking for, you can create your own conditional formatting rule in a few simple steps.
Notes: If there’s already a rule defined that you just want to work a bit differently, duplicate the rule and edit it.
-
Select Home > Conditional Formatting > Manage Rules, then in the Conditional Formatting Rule Manager dialog, select a listed rule and then select Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule then appears in the list.
-
Select the duplicate rule, then select Edit Rule.
-
Select the cells that you want to format.
-
On the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting > New Rule.
-
Create your rule and specify its format options, then click OK.
If you don’t see the options that you want, you can use a formula to determine which cells to format — see the next section for steps).
If you don’t see the exact options you need when you create your own conditional formatting rule, you can use a logical formula to specify the formatting criteria. For example, you may want to compare values in a selection to a result returned by a function or evaluate data in cells outside the selected range, which can be in another worksheet in the same workbook. Your formula must return True or False (1 or 0), but you can use conditional logic to string together a set of corresponding conditional formats, such as different colors for each of a small set of text values (for example, product category names).
Note: You can enter cell references in a formula by selecting cells directly on a worksheet or other worksheets. Selecting cells on the worksheet inserts absolute cell references. If you want Excel to adjust the references for each cell in the selected range, use relative cell references. For more information, see Create or change a cell reference and Switch between relative, absolute, and mixed references.
Tip: If any cells contain a formula that returns an error, conditional formatting is not applied to those cells. To address this, use IS functions or an IFERROR function in your formula to return a value that you specify (such as 0, or «N/A») instead of an error value.
-
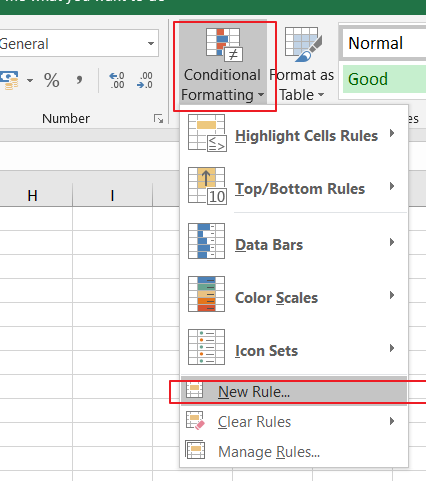
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules.
The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a conditional format, click New Rule. The New Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To add a new conditional format based on one that is already listed, select the rule, then click Duplicate Rule. The duplicate rule is copied and appears in the dialog box. Select the duplicate, then select Edit Rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
To change a conditional format, do the following:
-
-
Make sure that the appropriate worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected in the Show formatting rules for list box.
-
Optionally, change the range of cells by clicking Collapse Dialog in the Applies to box to temporarily hide the dialog box, by selecting the new range of cells on the worksheet or other worksheets, and then by clicking Expand Dialog.
-
Select the rule, and then click Edit rule. The Edit Formatting Rule dialog box appears.
-
-
-
Under Apply Rule To, to optionally change the scope for fields in the Values area of a PivotTable report, do the following:
-
To scope by selection: Click Selected cells.
-
To scope by corresponding field: Click All cells showing <Values field> values.
-
To scope by Value field: Click All cells showing <Values field> for <Row>.
-
-
Under Select a Rule Type, click Use a formula to determine which cells to format.
-
Under Edit the Rule Description, in the Format values where this formula is true list box, enter a formula.
You have to start the formula with an equal sign (=), and the formula must return a logical value of TRUE (1) or FALSE (0).
-
Click Format to display the Format Cells dialog box.
-
Select the number, font, border, or fill format you want to apply when the cell value meets the condition, and then click OK.
You can choose more than one format. The formats you select are shown in the Preview box.
Example 1: Use two conditional formats with criteria that uses AND and OR tests
The following example shows the use of two conditional formatting rules. If the first rule doesn’t apply, the second rule applies.
First rule: a home buyer has budgeted up to $75,000 as a down payment and $1,500 per month as a mortgage payment. If both the down payment and the monthly payments fit these requirements, cells B4 and B5 are formatted green.
Second rule: if either the down payment or the monthly payment doesn’t meet the buyer’s budget, B4 and B5 are formatted red. Change some values, such as the APR, the loan term, the down payment, and the purchase amount to see what happens with the conditionally formatted cells.
Formula for first rule (applies green color)
=AND(IF($B$4<=75000,1),IF(ABS($B$5)<=1500,1))
Formula for second rule (applies red color)
=OR(IF($B$4>=75000,1),IF(ABS($B$5)>=1500,1))
Example 2: Shade every other row by using the MOD and ROW functions
A conditional format applied to every cell in this worksheet shades every other row in the range of cells with a blue cell color. You can select all cells in a worksheet by clicking the square above row 1 and to the left of column A. The MOD function returns a remainder after a number (the first argument) is divided by divisor (the second argument). The ROW function returns the current row number. When you divide the current row number by 2, you always get either a 0 remainder for an even number or a 1 remainder for an odd number. Because 0 is FALSE and 1 is TRUE, every odd numbered row is formatted. The rule uses this formula: =MOD(ROW(),2)=1.
Note: You can enter cell references in a formula by selecting cells directly on a worksheet or other worksheets. Selecting cells on the worksheet inserts absolute cell references. If you want Excel to adjust the references for each cell in the selected range, use relative cell references. For more information, see Create or change a cell reference and Switch between relative, absolute, and mixed references.
-
The following video shows you the basics of using formulas with conditional formatting.
If you want to apply an existing formatting style to new or other data on your worksheet, you can use Format Painter to copy the conditional formatting to that data.
-
Click the cell that has the conditional formatting that you want to copy.
-
Click Home > Format Painter.
The pointer changes to a paintbrush.
Tip: You can double-click Format Painter if you want to keep using the paintbrush to paste the conditional formatting in other cells.
-
To paste the conditional formatting, drag the paintbrush across the cells or ranges of cells you want to format.
-
To stop using the paintbrush, press Esc.
Note: If you’ve used a formula in the rule that applies the conditional formatting, you might have to adjust any cell references in the formula after pasting the conditional format. For more information, see Switch between relative, absolute, and mixed references.
If your worksheet contains conditional formatting, you can quickly locate the cells so that you can copy, change, or delete the conditional formats. Use the Go To Special command to find only cells with a specific conditional format, or to find all cells that have conditional formats.
Find all cells that have a conditional format
-
Click any cell that does not have a conditional format.
-
On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click the arrow next to Find & Select, and then click Conditional Formatting.
Find only cells that have the same conditional format
-
Click any cell that has the conditional format that you want to find.
-
On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click the arrow next to Find & Select, and then click Go To Special.
-
Click Conditional formats.
-
Click Same under Data validation.
When you use conditional formatting, you set up rules that Excel uses to determine when to apply the conditional formatting. To manage these rules, you should understand the order in which these rules are evaluated, what happens when two or more rules conflict, how copying and pasting can affect rule evaluation, how to change the order in which rules are evaluated, and when to stop rule evaluation.
-
Learn about conditional formatting rule precedence
You create, edit, delete, and view all conditional formatting rules in the workbook by using the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box. (On the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules.)
The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
When two or more conditional formatting rules apply, these rules are evaluated in order of precedence (top to bottom) by how they are listed in this dialog box.
Here’s an example that has expiration dates for ID badges. We want to mark badges that expire within 60 days but are not yet expired with a yellow background color, and expired badges with a red background color.
In this example, cells with employee ID numbers who have certification dates due to expire within 60 days are formatted in yellow, and ID numbers of employees with an expired certification are formatted in red. The rules are shown in the following image.
The first rule (which, if True, sets cell background color to red) tests a date value in column B against the current date (obtained by using the TODAY function in a formula). Assign the formula to the first data value in column B, which is B2. The formula for this rule is =B2<TODAY(). This formula tests the cells in column B (cells B2:B15). If the formula for any cell in column B evaluates to True, its corresponding cell in column A (for example, A5 corresponds to B5, A11 corresponds to B11), is then formatted with a red background color. After all the cells specified under Applies to are evaluated with this first rule, the second rule is tested. This formula checks if values in the B column are less than 60 days from the current date (for example, suppose today’s date is 8/11/2010). The cell in B4, 10/4/2010, is less than 60 days from today, so it evaluates as True, and is formatted with a yellow background color. The formula for this rule is =B2<TODAY()+60. Any cell that was first formatted red by the highest rule in the list is left alone.
A rule higher in the list has greater precedence than a rule lower in the list. By default, new rules are always added to the top of the list and therefore have a higher precedence, so you’ll want to keep an eye on their order. You can change the order of precedence by using the Move Up and Move Down arrows in the dialog box.
-
What happens when more than one conditional formatting rule evaluates to True
Sometimes you have more than one conditional formatting rule that evaluates to True. Here’s how rules are applied, first when rules don’t conflict, and then when they do conflict:
When rules don’t conflict For example, if one rule formats a cell with a bold font and another rule formats the same cell with a red color, the cell is formatted with both a bold font and a red color. Because there is no conflict between the two formats, both rules are applied.
When rules conflict For example, one rule sets a cell font color to red and another rule sets a cell font color to green. Because the two rules are in conflict, only one can apply. The rule that is applied is the one that is higher in precedence (higher in the list in the dialog box).
-
How pasting, filling, and the Format Painter affect conditional formatting rules
While editing your worksheet, you may copy and paste cell values that have conditional formats, fill a range of cells with conditional formats, or use the Format Painter. These operations can affect conditional formatting rule precedence in the following way: a new conditional formatting rule based on the source cells is created for the destination cells.
If you copy and paste cell values that have conditional formats to a worksheet opened in another instance of Excel (another Excel.exe process running at the same time on the computer), no conditional formatting rule is created in the other instance and the format is not copied to that instance.
-
What happens when a conditional format and a manual format conflict
If a conditional formatting rule evaluates as True, it takes precedence over any existing manual format for the same selection. This means that if they conflict, the conditional formatting applies and the manual format does not. If you delete the conditional formatting rule, the manual formatting for the range of cells remains.
Manual formatting is not listed in the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box nor is it used to determine precedence.
-
Controlling when rule evaluation stops by using the Stop If True check box
For backwards compatibility with versions of Excel earlier than Excel 2007, you can select the Stop If True check box in the Manage Rules dialog box to simulate how conditional formatting might appear in those earlier versions of Excel that do not support more than three conditional formatting rules or multiple rules applied to the same range.
For example, if you have more than three conditional formatting rules for a range of cells, and are working with a version of Excel earlier than Excel 2007, that version of Excel:
-
Evaluates only the first three rules.
-
Applies the first rule in precedence that is True.
-
Ignores rules lower in precedence if they are True.
The following table summarizes each possible condition for the first three rules:
If rule
Is
And if rule
Is
And if rule
Is
Then
One
True
Two
True or False
Three
True or False
Rule one is applied and rules two and three are ignored.
One
False
Two
True
Three
True or False
Rule two is applied and rule three is ignored.
One
False
Two
False
Three
True
Rule three is applied.
One
False
Two
False
Three
False
No rules are applied.
You can select or clear the Stop If True check box to change the default behavior:
-
To evaluate only the first rule, select the Stop If True check box for the first rule.
-
To evaluate only the first and second rules, select the Stop If True check box for the second rule.
You can’t select or clear the Stop If True check box if the rule formats by using a data bar, color scale, or icon set.
-
If you’d like to watch a video showing how to manage conditional formatting rules, see Video: Manage conditional formatting.
The order in which conditional formatting rules are evaluated — their precedence — also reflects their relative importance: the higher a rule is on the list of conditional formatting rules, the more important it is. This means that in cases where two conditional formatting rules conflict with each other, the rule that is higher on the list is applied and the rule that is lower on the list is not applied.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click the arrow next to Conditional Formatting, and then click Manage Rules.
The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box appears.
The conditional formatting rules for the current selection are displayed, including the rule type, the format, the range of cells the rule applies to, and the Stop If True setting.
If you don’t see the rule that you want, in the Show formatting rules for list box, make sure that the right range of cells, worksheet, table, or PivotTable report is selected.
-
Select a rule. Only one rule can be selected at a time.
-
To move the selected rule up in precedence, click Move Up. To move the selected rule down in precedence, click Move Down.
-
Optionally, to stop rule evaluation at a specific rule, select the Stop If True check box.
Clear conditional formatting on a worksheet
-
On the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting > Clear Rules > Clear Rules from Entire Sheet.
Follow these steps if you have conditional formatting in a worksheet, and you need to remove it.
For an entire
worksheet
-
On the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting > Clear Rules > Clear Rules from Entire Sheet.
In a range of cells
-
Select the cells that contain the conditional formatting.
-
Click the Quick Analysis Lens
button that appears to the bottom right of the selected data.
Notes:
Quick Analysis Lens will not be visible if:-
All of the cells in the selected range are empty, or
-
There is an entry only in the upper-left cell of the selected range, with all of the other cells in the range being empty.
-
-
Click Clear Format.
Find and remove the same conditional formats throughout a worksheet
-
Click on a cell that has the conditional format that you want to remove throughout the worksheet.
-
On the Home tab, click the arrow next to Find & Select, and then click Go To Special.
-
Click Conditional formats.
-
Click Same under Data validation. to select all of the cells that contain the same conditional formatting rules.
-
On the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting > Clear Rules > Clear Rules from Selected Cells.
Tip: The following sections use examples so you can follow along in Excel for the web. To start, download the Conditional Formatting Examples workbook and save it to OneDrive. Then, open OneDrive in a web browser and select the downloaded file.
-
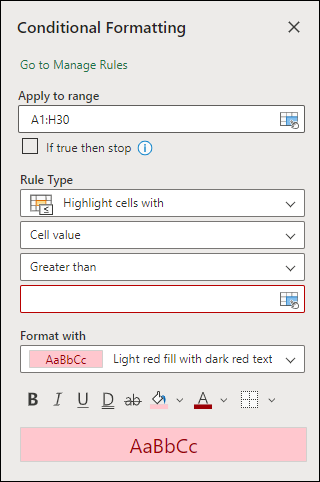
Select the cells you want to format, then select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > New Rule. You can also open the Conditional Formatting pane and create a new rule without first selecting a range of cells.
-
Verify or adjust the cells in Apply to range.
-
Choose a Rule Type and adjust the options to meet your needs.
-
When finished, select Done and the rule will be applied to your range.
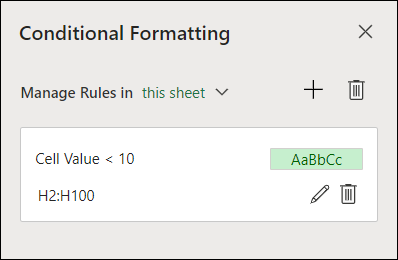
-
Select a cell which has a conditional format you want to change. Or you can select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Manage Rules to open the Conditional Formatting task pane and select an existing rule.
-
The Conditional Formatting task pane displays any rules which apply to specific cells or ranges of cells.
-
Hover over the rule and select Edit by clicking the pencil icon. This opens the task pane for rule editing.
-
Modify the rule settings and click Done to apply the changes.
The Conditional Formatting task pane provides everything you need for creating, editing, and deleting rules. Use Manage Rules to open the task pane and work with all the Conditional Formatting rules in a selection or a sheet.
-
In an open workbook, select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Manage Rules.
-
The Conditional Formatting task pane opens and displays the rules, scoped to your current selection.
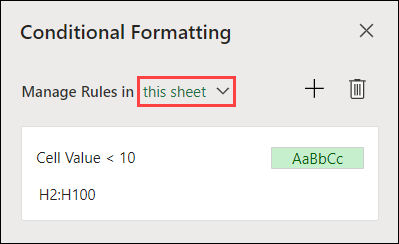
From here, you can:
-
Choose a different scope on the Manage Rules in menu — for example, choosing this sheet tells Excel to look for all rules on the current sheet.
-
Add a rule by selecting New Rule (the plus sign).
-
Delete all rules in scope by selecting Delete All Rules (the garbage can).
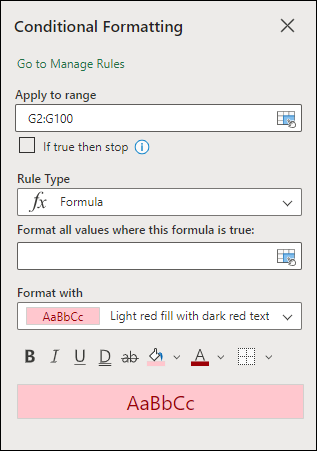
You can use a formula to determine how Excel evaluates and formats a cell. Open the Conditional Formatting pane and select an existing rule or create a new rule.
In the Rule Type dropdown, select Formula.
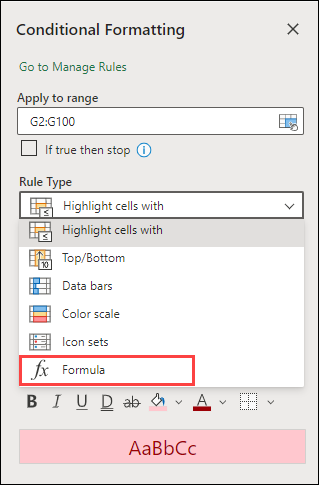
Enter the formula in the box. You can use any formula that returns a logical value of TRUE (1) or FALSE (0), but you can use AND and OR to combine a set of logical checks.
For example, =AND(B3=»Grain»,D3<500) is true for a cell in row 3 if both B3=»Grain» and D3<500 are true.
You can clear conditional formatting in selected cells or the entire worksheet.
-
To clear conditional formatting in selected cells, select the cells in the worksheet. Then Select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Clear Rules > Clear Rules from Selected Cells.
-
To clear conditional formatting in the entire worksheet, select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Clear Rules > Clear Rules from Entire Sheet.
-
To delete conditional formatting rules, select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting >Manage Rules and use the delete (garbage can) on a specific rule or the Delete all rules button.
Color scales are visual guides which help you understand data distribution and variation. Excel offers both two-color scales and three-color scales.
A two-color scale helps you compare a range of cells by using a gradation of two colors. The shade of the color represents higher or lower values. For example, in a green and yellow color scale, you can specify that higher value cells be more green and lower value cells have a more yellow.
A three-color scale helps you compare a range of cells by using a gradation of three colors. The shade of the color represents higher, middle, or lower values. For example, in a green, yellow, and red color scale, you can specify that higher value cells have a green color, middle value cells have a yellow color, and lower value cells have a red color.
Tip: You can sort cells that have one of these formats by their color — just use the context menu.
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format using color scales.
-
Click Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Color Scales and select a color scale.
A data bar helps you see the value of a cell relative to other cells. The length of the data bar represents the value in the cell. A longer bar represents a higher value, and a shorter bar represents a lower value. Data bars are useful in spotting higher and lower numbers, especially with large amounts of data, such as top selling and bottom selling toys in a holiday sales report.
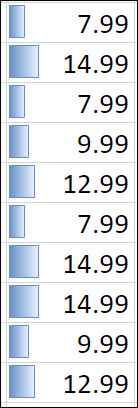
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
Select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Data Bars and select a style.
Use an icon set to annotate and classify data into three to five categories separated by a threshold value. Each icon represents a range of values. For example, in the 3 Arrows icon set, the green up arrow represents higher values, the yellow sideways arrow represents middle values, and the red down arrow represents lower values.
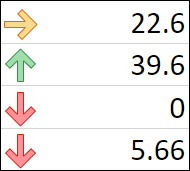
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
Select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Icon Sets and choose an icon set.
This option lets you highlight specific cell values within a range of cells based on their specific contents. This can be especially useful when working with data sorted using a different range.
For example, in an inventory worksheet sorted by categories, you could highlight the names of products where you have fewer than 10 items in stock so it’s easy to see which products need restocking without resorting the data.
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
Select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cell Rules.
-
Select the comparison, such as Between, Equal To, Text That Contains, or A Date Occurring.
You can highlight the highest and lowest values in a range of cells which are based on a specified cutoff value.
Some examples of this would include highlighting the top five selling products in a regional report, the bottom 15% products in a customer survey, or the top 25 salaries in a department.
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
Select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Top/Bottom Rules.
-
Select the command you want, such as Top 10 items or Bottom 10 %.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and select a format (fill, text, or border color).
You can highlight values above or below an average or standard deviation in a range of cells.
For example, you can find the above-average performers in an annual performance review, or locate manufactured materials that fall below two standard deviations in a quality rating.
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
Select Home> Styles > Conditional Formatting > Top/Bottom Rules.
-
Select the option you want, such as Above Average or Below Average.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and select a format (fill, text, or border color).
-
Select the cells that you want to conditionally format.
-
Select Home > Styles > Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cell Rules > Duplicate Values.
-
Enter the values you want to use, and select a format (fill, text, or border color).
If you want to apply an existing formatting style to other cells on your worksheet, use Format Painter to copy the conditional formatting to that data.
-
Click the cell that has the conditional formatting you want to copy.
-
Click Home > Format Painter.
The pointer will change to a paintbrush.
Tip: You can double-click Format Painter if you want to keep using the paintbrush to paste the conditional formatting in other cells.
-
Drag the paintbrush across the cells or range of cells you want formatted.
-
To stop using the paintbrush, press Esc.
Note: If you’ve used a formula in the rule that applies the conditional formatting, you might have to adjust relative and absolute references in the formula after pasting the conditional format. For more information, see Switch between relative, absolute, and mixed references.
Note: You can’t use conditional formatting on external references to another workbook.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Conditional formatting compatibility issues
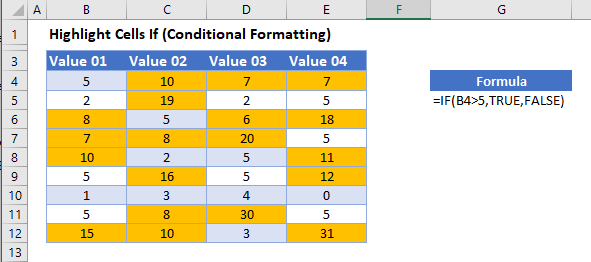
This tutorial will demonstrate how to highlight cells if a condition is met using Conditional Formatting in Excel and Google Sheets.
Highlight Cells – IF Function
To highlight cells depending on the value contained in that cell with conditional formatting, you can use the IF Function within a Conditional Formatting rule.
- Select the range you want to apply formatting to.
- In the Ribbon, select Home > Conditional Formatting > New Rule.
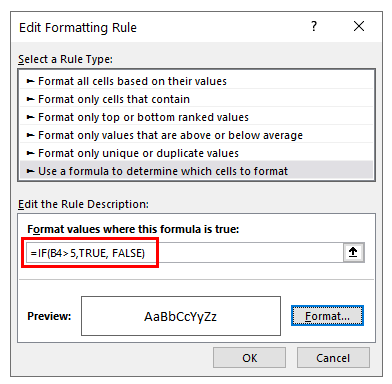
- Select Use a formula to determine which cells to format, and enter the formula:
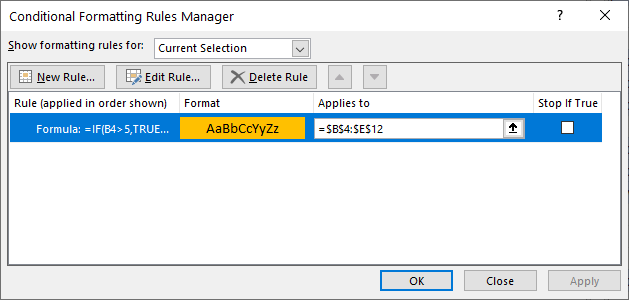
=IF(B4>5,TRUE,FALSE)- Click the Format button and select your desired formatting.
- Click OK, then OK again to return to the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager.
- Click Apply to apply the formatting to your selected range and then click Close.
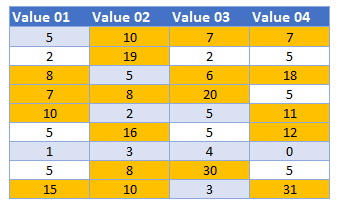
Every cell in the range selected that has a value greater than 5 will have its background color changed to yellow.
Highlight Cells If – Google Sheets
The process to highlight cells based on the value contained in that cell in Google Sheets is similar to the process in Excel.
- Highlight the cells you wish to format, and then click on Format > Conditional Formatting.
- The Apply to Range section will already be filled in.
- From the Format Rules section, select Custom Formula.
- Select the fill style for the cells that meet the criteria.
- Click Done to apply the rule.
This post will guide you how to highlight cell if same value exists in another column in Excel. How do I highlight cell if value is present in any cell in another column in Excel 2013/2016.
Table of Contents
- Highlight Cell If Same Value Exists in Another Column
- Highlight Cell If Same Value Exists in Another Column Using VBA
- Related Functions
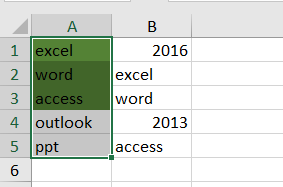
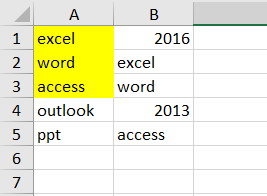
Assuming that you have a list of data in range A1:B5, you want to highlight cell in Column A if the value is found in Column B, how to accomplish it. You can use the Conditional Formatting feature to highlight cell in Excel. Just do the following steps:
Step1: select your range of cells in which you wish to highlight.
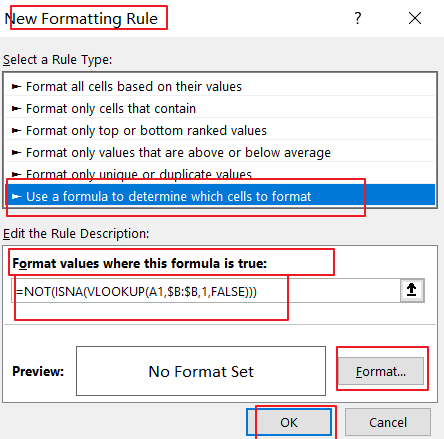
Step2: go to Home tab, and click Conditional Formatting command under Styles group, and select new Rule from the context menu list. and the New Formatting Rule dialog will open.
Step3: click Use a formula to determine which cells to format option in the Select a Rule Type list, and type the following formula into the Format values where this formula is true text box.
=NOT(ISNA(VLOOKUP(A1,$B:$B,1,FALSE)))
Note: the Cell A1 is the first cell of the column that you want to highlight, and $B:$B is another column that you want to be checked)
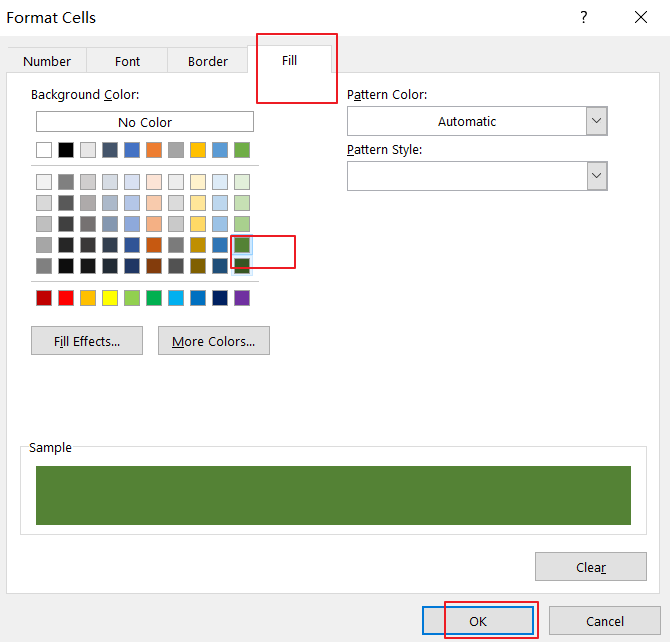
Step4: click Format button in the New Formatting Rule dialog box, and the Format Cell dialog will open.
Step5: switch to Fill tab in the Format Cell dialog box, and choose one color as you need. click Ok button back to the New Formatting Rule dialog box.
Step6: click OK button. You would see that the cells in Column A have been highlighted if those values can be found in column B.
Highlight Cell If Same Value Exists in Another Column Using VBA
You can also use an Excel VBA Macro to highlight cell if value is present in another column. Just do the following steps:
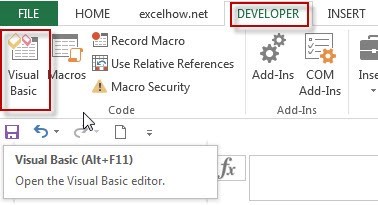
Step1: open your excel workbook and then click on “Visual Basic” command under DEVELOPER Tab, or just press “ALT+F11” shortcut.
Step2: then the “Visual Basic Editor” window will appear.
Step3: click “Insert” ->”Module” to create a new module.
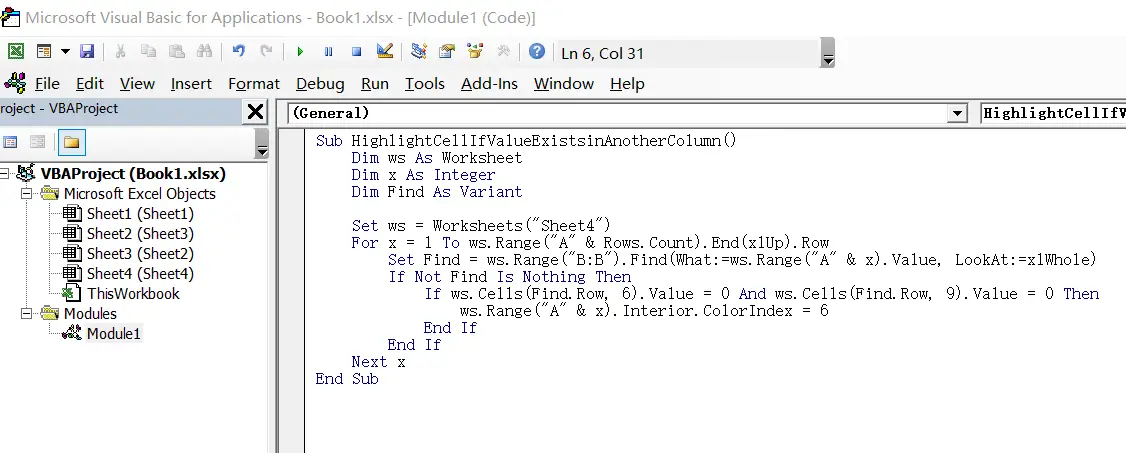
Step4: paste the below VBA code into the code window. Then clicking “Save” button.
Sub HighlightCellIfValueExistsinAnotherColumn()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim x As Integer
Dim Find As Variant
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet4")
For x = 1 To ws.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
Set Find = ws.Range("B:B").Find(What:=ws.Range("A" & x).Value, LookAt:=xlWhole)
If Not Find Is Nothing Then
If ws.Cells(Find.Row, 6).Value = 0 And ws.Cells(Find.Row, 9).Value = 0 Then
ws.Range("A" & x).Interior.ColorIndex = 6
End If
End If
Next x
End Sub
Step5: back to the current worksheet, then run the above excel macro. Click Run button.
Step6: let’s see the result:
- Excel VLOOKUP function
The Excel VLOOKUP function lookup a value in the first column of the table and return the value in the same row based on index_num position.The syntax of the VLOOKUP function is as below:= VLOOKUP (lookup_value, table_array, column_index_num,[range_lookup])…. - Excel ISNA function
The Excel ISNA function used to check if a cell contains the #N/A error, if so, returns TRUE; otherwise, the ISNA function returns FALSE.The syntax of the ISNA function is as below:=ISNA(value)….
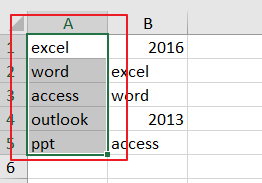
I want to create a conditional formatting rule where the cell will be highlighted if it also appears in a list (column A).
The values are all text (e.g «Apple», «Pear»). It has to be an exact match («Apple Juice» shouldn’t be highlighted if «Apple» is in the list). The result should be this:
Help will be greatly appreciated!
jeranon
4332 silver badges14 bronze badges
asked Oct 28, 2018 at 15:20
1
Select cell b2 in your example
Then from Home Ribbon
Conditional Formatting> New Rule > Classic > Use a formula to determine which cells to format
Then in formula enter:
=countif($A2:$A6,b2)>0
After you’ve done that use format paint brush on remaining b3 and b4 in your image
answered Oct 28, 2018 at 16:06
JGFMKJGFMK
8,2454 gold badges55 silver badges92 bronze badges
I am using the match function. So in your example it would be like this:
=MATCH($A2,$B2:$B4,0)
and then use the Format Painter for the rest of the cells you want to apply it.
answered Jun 16, 2021 at 9:08
Have you ever stared at a spreadsheet looking for the important stuff? The problem with many spreadsheets is that all the cells look the same. So you have to hunt for key or actionable information. In this tutorial, I’ll show how to highlight cells in Excel using built-in conditional formatting criteria. (Includes practice file.)
I routinely see this scenario. You get a spreadsheet from someone with hundreds of data rows that look the same. Everything is formatted in the same boring way. But is the data the same? Are there cell values that are different from the rest? Is something outside the average? These are typical questions users have when they open spreadsheets.
What is Conditional Formatting in Excel?
Instead of having the reader scan each cell, you can have Microsoft Excel do some legwork using some rules. This allows Excel to apply a defined format to a range of cells that meet specific criteria or conditions. These defined rules evaluate a cell value to see if it meets a specific criteria. If the condition is met, certain formatting is applied to the cell.
The goal is to make important information stand out so you can find it easier.
Excel already does some of this for you. For example, when you format numbers, there are options to display negative numbers in red. This is an example of a predefined format.
The program even allows you to use formatting options on individual cells or rows. The simplest method is to have Excel apply conditional formatting if it meets certain conditions or locations. This uses the “Cell Value Is” method.
Cell Value Highlight Examples
Below is a small sampling of ideas for using conditional formatting:
- Apply a red background fill if the cell value is less than 50
- Apply an italic, bold font style if the cell value is between 70 and 90
- Apply a green font color if the cell text contains “Montana.”
- Highlight cells that are equal to 15 with a red border
- Apply a yellow background fill to duplicate values
- Add an Up arrow icon to cell values above 10%
- Highlight all blank cells
Excel also allows you to use formulas for conditional formatting. One benefit to Excel formulas is that you can reference the values elsewhere in your spreadsheet. In the example below, I’m using an Excel IF formula to test if the cell value in B2 is greater than the value in C2. If the formula is TRUE, apply a green background color.
Microsoft has greatly enhanced this feature over the years and now predefines popular examples, so you don’t need to rely on formulas as much. Below are some popular examples.
Adding a new format rule is easy. The hardest part is finding what you want to highlight on your spreadsheet. It helps to think about your audiences’ needs and what actions they might take.
How to Highlight Cells Above a Specific Number
If you wish to follow along, this is Example 1 from the sample worksheet below. Again, I’m going to highlight selected cells if the state’s population exceeds or equals 2% of the US population.
- Open the state-counts-cf.xlsx sample spreadsheet and click the Example 1 tab.
- Click cell F2.
- Select the whole column by pressing Ctrl +Shift + ↓.
- From the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting button.
- From the drop-down menu, select Highlight Cell Rules.
- From the side menu, select Greater Than…
- Adjust the value in the Format cells that are GREATER THAN: field.
Note: Excel will pre-populate this field based on the existing values of your highlighted cells.
- Enter your desired value. In our case, it’s 2.0%. Excel will start highlighting cells for you.
- Click the down triangle ▼ to make your color selection.
✪ Note: You can create a different color scheme by selecting a Custom Format.
- Click OK.
You should now see your results applied.
How to Highlight Top 10 Items
One popular request is to find the top entries, whether they be a set number or percentage. This is an example of one of Excel’s preset or built-in formats. In other words, you don’t need to enter specific values as you did in Example 1. Instead, these presets are built around common items people look for, such as Top 10 or below-average performers. The advantage is that you don’t have to do the math.
In this example, I want to highlight the top 10 states by US House Seats in Column D.
- Open the state-counts-cf.xlsx sample spreadsheet and click the Example 2 tab.
- Click cell D2.
- Select the whole column by pressing Ctrl +Shift + ↓.
- From the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting button.
- From the Conditional Formatting drop-down menu, select Top/Bottom Rules.
- From the side menu, select Top 10 Items…
- In the Top 10 Items dialog box, adjust your count or color scheme if necessary.
- Click OK.
One advantage to using color is that Excel can sort by color too. Additionally, you can also SUM or COUNT colored cells.
How to Use Data Bars Instead of Background Color
Another useful option is to use “Data bars.” This is another type of visualization that you can apply. A key difference with the Data Bar format is that it shows all cells instead of those meeting a specific condition.
By default, Excel will keep the text value background. I find that this can be distracting. In this example, I duplicated the % Change column but told Excel not to put the data value in Column I. The result is just the data bar.
The data bar format doesn’t work well with all data types. This is a good example of trying different formats to see what works best for your data. This is especially true if you have negative values or a tight range.
- Open the state-counts-cf.xlsx sample spreadsheet and click the Example 3 tab.
- Click cell I2.
- Select the whole column by pressing Ctrl +Shift + ↓.
- From the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting button.
- From the Conditional Formatting drop-down list, select Data Bars.
- From the side menu, select More Rules…
- In the Edit the Rule Description: section, check Show Bar Only.
- Click OK.
How to Highlight a Row
Highlighting outlier cells is great, but sometimes if you have a large spreadsheet, you may not see the colored cells because they’re off-screen. In these situations, it helps to highlight the entire row. That way, regardless of which columns you’re viewing, you know which rows are important. This works best when you have 1 conditional.
A key difference here is we won’t be highlighting a column but the entire spreadsheet. That’s how we get the row effect.
- Open the state-counts-cf.xlsx sample spreadsheet and click the Example 4 tab.
- Click cell I2.
- Select all rows by pressing Ctrl +Shift + ↓ + ←.
- From the Home tab, click the Conditional Formatting button.
- Select New Rule…
- In the Edit Formatting Rule dialog box, select Use a formula to determine which cells to format.
- In the Format values where this formula is true: type your criteria.
- Click the Format button to apply your highlight color.
- Click the Fill tab.
- Select your color.
- Click OK to accept your color.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
In the example above, I want to highlight any row where the value in column F (Percent total of US population) is greater than 2%. The highlight color is green. I’m also using a mixed cell reference by placing a $ sign before F2 in the formula.
✪ Tip: If you’re not sure you have the correct formula, you can always test it in another column. For example, I could enter in cell H2, this formula =$F2>20%. The H2 cell would be evaluated as either TRUE or FALSE. You could then copy the formula down the column to make sure you get your expected results.
- Click OK.
Find Existing Conditional Formating Rules
Sometimes we’re given a spreadsheet, and you see highlighted cells or rows. But… where are the conditional rules, or did someone manually format these cells? Fortunately, Excel provides a way to see conditional formatting rules. You can use the example spreadsheet to follow along or use your own.
- Open up your spreadsheet.
- From the Home tab, click Conditional Formatting.
- Select Manage Rules… from the drop-down list.
- In the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager dialog box, select your worksheet.
- Click OK.
In the example above, you can see the rule I applied to highlight the row. From here, you could add a rule, edit the rule, or delete it.
Highlighting Tips & Tricks
This tutorial touched on some of the ways you can use conditional formatting to highlight cell values. The best way to learn is to experiment with some data, whether it’s your own or the sample spreadsheet. Here are some other tips for you:
- You can have multiple rules in the same column. For example, you might want to have different range values, be different colors.
- Play around with different formats to see which type works best for your data.
- If you get unexpected results, check to see if multiple conditions are being run and the rule order. You may need to change the order.
- You can set ranges on data bars. For example, if you have a % Complete column, you may want to set a range of 0 to 1.
- You can remove conditional formatting rules with the Clear Rules option.
- Apply your rules after you’ve entered data. Sometimes duplicate rules are created when you insert rows.
Excel’s conditional formatting can make your spreadsheets more useful if used appropriately. People won’t waste time looking for important changes or that “needle in the haystack.” Play around and create your own custom cell styles and conditional formats.
Show Me How Video
To see the above examples, click the image below to be taken to the accompanying video and transcript.
Excel Practice File
- Beginners Guide to Excel XLOOKUP
- How to Use Excel VLOOKUP
- How to Check Excel Cells for Specific Text
- How to Use Flash Fill in Excel
- How to Create an Excel Pivot Table


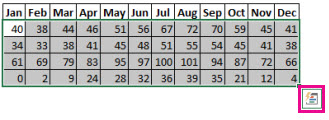

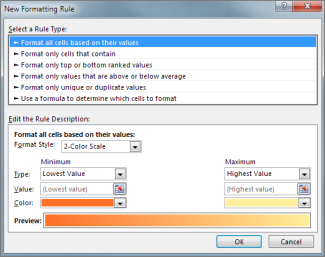
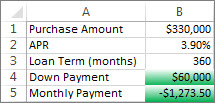

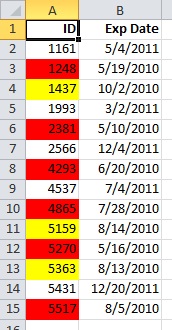
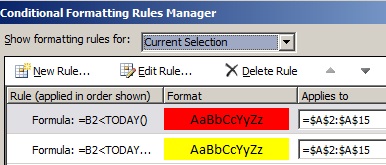
 button that appears to the bottom right of the selected data.
button that appears to the bottom right of the selected data.