Hide or show rows or columns
Hide or unhide columns in your spreadsheet to show just the data that you need to see or print.
Hide columns
-
Select one or more columns, and then press Ctrl to select additional columns that aren’t adjacent.
-
Right-click the selected columns, and then select Hide.
Note: The double line between two columns is an indicator that you’ve hidden a column.
Unhide columns
-
Select the adjacent columns for the hidden columns.
-
Right-click the selected columns, and then select Unhide.
Or double-click the double line between the two columns where hidden columns exist.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Unhide the first column or row in a worksheet
Need more help?
Download Article
Download Article
Hiding rows and columns you don’t need can make your Excel spreadsheet much easier to read, especially if it’s large. Hidden rows don’t clutter up your sheet, but still affect formulas. You can easily Hide and Unhide rows in any version of Excel by following this guide.
Things You Should Know
- Highlight the rows you wish to hide. Then, right click them and select «Hide».
- Create a group by highlighting the rows you wish to hide and going to Data > Group. A line and a box with a (-) should appear. Click the box to hide the grouped rows.
- Unhide by highlighting the rows above and below the hidden cells, right clicking, and choosing «Unhide». Alternatively, hit the (+) sign next to the rows if it is available.
-
1
Use the row selector to highlight the rows you wish to hide. You can hold the Ctrl key to select multiple rows.
-
2
Right-click within the highlighted area. Select “Hide”. The rows will be hidden from the spreadsheet.
Advertisement
-
3
Unhide the rows. To unhide the rows, use the row selector to highlight the rows above and below the hidden rows. For example, select Row 4 and Row 8 if Rows 5-7 are hidden.
- Right-click within the highlighted area.
- Select “Unhide”.
Advertisement
-
1
Create a group of rows. With Excel 2013, you can group/ungroup rows so that you can easily hide and unhide them.
- Highlight the rows you want to group together and click «Data» tab.
- Click «Group» button in the «Outline» Group.
-
2
Hide the group. A line and a box with a (-) minus sign appears next to those rows. Click the box to hide the «grouped» rows. Once the rows are hidden the small box will display a (+) plus sign.
-
3
Unhide the rows. Click (+) box if you want to unhide the rows.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What if the hidden rows were 123 in Excel?
Just select the cell or cells, then go to Home, and in Cells group, click Format. Then under Visibility, point to HideUnhide, and then click Hide Rows or Hide Columns. This will hide the Rows or Columns of the selected cell or cells.
-
Question
How do I hide non-consecutive rows containing a specific word in a given column?
Highlight the entire spreadsheet. Go to Data then click on Filter. This will add a drop-down box in the header of each column. Click on the drop-down box in the column where the specified words you want to hide is located. De-select all of the items you wish to hide, and click OK.
-
Question
What is the purpose of hiding rows?
Hiding rows you don’t need can make your Excel spreadsheet much easier to read, especially if it’s large. For example, if you want to input data that is used for multiple formulas, a hidden row will still contain that information but will not be shown.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Select rows to hide.
2. Right-click the highlighted area.
3. Click Hide.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 218,122 times.
Is this article up to date?
- You can hide and unhide rows in Excel by right-clicking, or reveal all hidden rows using the «Format» option in the «Home» tab.
- Hiding rows in Excel is especially helpful when working in large documents or for concealing information you won’t need until later.
- Visit Business Insider’s homepage for more stories.
Just as you can quickly hide and unhide columns, you can hide or reveal hidden rows in your Excel spreadsheet as well.
In addition to freezing rows, you may find it helpful to conceal rows you are no longer using without permanently deleting the data from your spreadsheet. To later reveal the hidden cells, you can right-click to unhide individual rows.
You can also navigate to the «Format» option to unhide all hidden rows. This feature is especially helpful if you’ve hidden multiple rows throughout a large spreadsheet.
Here’s how to do both.
Check out the products mentioned in this article:
Microsoft Office (From $139.99 at Best Buy)
MacBook Pro (From $1,299.99 at Best Buy)
Microsoft Surface Pro X (From $999 at Best Buy)
How to hide individual rows in Excel
1. Open Excel.
2. Select the row(s) you wish to hide. Select an entire row by clicking on its number on the left hand side of the spreadsheet. Select multiple rows by clicking on the row number, holding the «Shift» key on your Mac or PC keyboard, and selecting another.
3. Right-click anywhere in the selected row.
4. Click «Hide.»
Marissa Perino/Business Insider
How to unhide individual rows in Excel
1. Highlight the row on either side of the row you wish to unhide.
2. Right-click anywhere within these selected rows.
3. Click «Unhide.»
Marissa Perino/Business Insider
4. You can also manually click or drag to expand a hidden row. Hidden rows are indicated by a thicker border line. Move your cursor over this line until it turns into a double bar with arrows. Double click to reveal or click and drag to manually expand the hidden row or rows. (If you’ve hidden multiple rows, you may have to do this multiple times.)
How to unhide all rows in Excel
1. To unhide all hidden rows in Excel, navigate to the «Home» tab.
2. Click «Format,» which is located towards the right hand side of the toolbar.
3. Navigate to the «Visibility» section. You’ll find options to hide and unhide both rows and columns.
4. Hover over «Hide & Unhide.»
5. Select «Unhide Rows» from the list. This will reveal all hidden rows, a feature especially helpful if you’ve hidden multiple rows throughout a large spreadsheet.
Marissa Perino/Business Insider
Related coverage from How To Do Everything: Tech:
-
How to make a line graph in Microsoft Excel in 4 simple steps using data in your spreadsheet
-
How to add a column in Microsoft Excel in 2 different ways
-
How to hide and unhide columns in Excel to optimize your work in a spreadsheet
-
How to search for terms or values in an Excel spreadsheet, and use Find and Replace
Marissa Perino is a former editorial intern covering executive lifestyle. She previously worked at Cold Lips in London and Creative Nonfiction in Pittsburgh. She studied journalism and communications at the University of Pittsburgh, along with creative writing. Find her on Twitter: @mlperino.
Read more
Read less
Insider Inc. receives a commission when you buy through our links.
Working with large datasets that contain rows after rows of data can be quite painful.
In such cases, looking for data that match particular criteria can be like looking for a needle in a haystack.
Thankfully, Excel provides some features that let you hide certain rows based on the cell value so that you only see the rows that you want to see. There are two ways to do this:
- Using filters
- Using VBA
In this tutorial, we will discuss both methods, and you can pick the method you feel most comfortable with.
Using Filters to Hide Rows based on Cell Value
Let us say you have the dataset shown below, and you want to see data about only those employees who are still in service.
This is really easy to do using filters. Here are the steps you need to follow:
- Select the working area of your dataset.
- From the Data tab, select the Filter button. You will find it in the ‘Sort and Filter’ group.
- You should now see a small arrow button on every cell of the header row.
- These buttons are meant to help you filter your cells. You can click on any arrow to choose a filter for the corresponding column.
- In this example, we want to filter out the rows that contain the Employment status = “In service”. So, select the arrow next to the Employment Status header.
- Uncheck the boxes next to all the statuses, except “In service”. You can simply uncheck “Select All” to quickly uncheck everything and then just select “In service”.
- Click OK.
You should now be able to see only the rows with Employment Status=”In service”. All other rows should now be hidden.
Note: To unhide the hidden cells, simply click on the Filter button again.
Using VBA to Hide Rows based on Cell Value
The second method requires a little coding. If you are accustomed to using macros and a little coding using VBA, then you get much more scope and flexibility to manipulate your data to behave exactly the way you want.
Writing the VBA Code
The following code will help you display only the rows that contain information about employees who are ‘In service’ and will hide all other rows:
Sub HideRows() StartRow = 2 EndRow = 19 ColNum = 3 For i = StartRow To EndRow If Cells(i, ColNum).Value <> "In service" Then Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = True Else Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = False End If Next i End Sub
The macro loops through each cell of column C and hide the rows that do not contain the value “In service”. It should essentially analyze each cell from rows 2 to 19 and adjust the ‘Hidden’ attribute of the row that you want to hide.
To enter the above code, copy it and paste it into your developer window. Here’s how:
- From the Developer menu ribbon, select Visual Basic.
- Once your VBA window opens, you will see all your files and folders in the Project Explorer on the left side. If you don’t see Project Explorer, click on View->Project Explorer.
- Make sure ‘ThisWorkbook’ is selected under the VBA project with the same name as your Excel workbook.
- Click Insert->Module. You should see a new module window open up.
- Now you can start coding. Copy the above lines of code and paste them into the new module window.
- In our example, we want to hide the rows that do not contain the value ‘In service’ in column 3. But you can replace the value of ColNum number from “3” in line 4 to the column number containing your criteria values.
- Close the VBA window.
Note: If your dataset covers more than 19 rows, you can change the values of the StartRow and EndRow variables to your required row numbers.
If you can’t see the Developer ribbon, from the File menu, go to Options. Select Customize Ribbon and check the Developer option from Main Tabs.
Finally, Click OK.
Your macro is now ready to use.
Running the Macro
Whenever you need to use the above macro, all you need to do is run it, and here’s how:
- Select the Developer tab
- Click on the Macros button (under the Code group).
- This will open the Macro Window, where you will find the names of all the macros that you have created so far.
- Select the macro (or module) named ‘HideRows’ and click on the Run button.
You should see all the rows where Employment Status is not ’In service’ hidden.
Explanation of the Code
Here’s a line by line explanation of the above code:
- In line 1 we defined the function name.
Sub HideRows()
- In lines 2, 3 and 4 we defined variables to hold the starting row and ending row of the dataset as well as the index of the criteria column.
StartRow = 2 EndRow = 19 ColNum = 3
- In lines 5 to 11, we looped through each cell in column “3” (or column C) of the Active Worksheet. If a cell does not contain the value “Inservice”, then we set the ‘Hidden’ attribute of the entire row (corresponding to that cell) to True, which means we want to hide the entire corresponding row.
For i = StartRow To EndRow If Cells(i, ColNum).Value <> "In service" Then Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = True Else Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = False End If Next i
- Line 12 simply demarcates the end of the HideRows function.
End Sub
In this way, the above code hides all the rows that do not contain the value ‘In service’ in column C.
Un-hiding Columns Based On Cell Value
Now that we have been able to successfully hide unwanted rows, what if we want to see the hidden rows again?
Doing this is quite easy. You only need to make a small change to the HideRows function.
Sub UnhideRows() StartRow = 2 EndRow = 19 ColNum = 3 For i = StartRow To EndRow Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = False Next i End Sub
Here, we simply ensured that irrespective of the value, all the rows are displayed (by setting the Hidden property of all rows to False).
You can run this macro in exactly the same way as HideRows.
Hiding Rows Based On Cell Values in Real-Time
In the first example, the columns are hidden only when the macro runs. However, most of the time, we want to hide columns on-the-fly, based on the value in a particular cell.
So, let’s now take a look at another example that demonstrates this. In this example, we have the following dataset:
The only difference from the first dataset is that we have a value in cell A21 that will determine which rows should be hidden. So when cell A21 contains the value ‘Retired’ then only the rows containing the Employment Status ‘Retired’ are hidden.
Similarly, when cell A21 contains the value ‘On probation’ then only the rows containing the Employment Status ‘On probation’ are hidden.
When there is nothing in cell A21, we want all rows to be displayed.
We want this to happen in real-time, every time the value in cell A21 changes. For this, we need to make use of Excel’s Worksheet_SelectionChange function.
The Worksheet_SelectionChange Event
The Worksheet_SelectionChange procedure is an Excel built-in VBA event
It comes pre-installed with the worksheet and is called whenever a user selects a cell and then changes his/her selection to some other cell.
Since this function comes pre-installed with the worksheet, you need to place it in the code module of the correct sheet so that you can use it.
In our code, we are going to put all our lines inside this function, so that they get executed whenever the user changes the value in A21 and then selects some other cell.
Writing the VBA Code
Here’s the code that we are going to use:
StartRow = 2
EndRow = 19
ColNum = 3
For i = StartRow To EndRow
If Cells(i, ColNum).Value = Range("A21").Value Then
Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Else
Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = False
End If
Next i
To enter the above code, you need to copy it and paste it in your developer window, inside your worksheet’s Worksheet_SelectionChange procedure. Here’s how:
- From the Developer menu ribbon, select Visual Basic.
- Once your VBA window opens, you will see all your project files and folders in the Project Explorer on the left side.
- In the Project Explorer, double click on the name of your worksheet, under the VBA project with the same name as your Excel workbook. In our example, we are working with Sheet1.
- This will open up a new module window for your selected sheet.
- Click on the dropdown arrow on the left of the window. You should see an option that says ‘Worksheet’.
- Click on the ‘Worksheet’ option. By default, you will see the Worksheet_SelectionChange procedure created for you in the module window.
- Now you can start coding. Copy the above lines of code and paste them into the Worksheet_SelectionChange procedure, right after the line: Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range).
- Close the VBA window.
Running the Macro
The Worksheet_SelectionChange procedure starts running as soon as you are done coding. So you don’t need to explicitly run the macro for it to start working.
Try typing the ‘Retired’ in the cell A21, then clicking any other cell. You should find all rows containing the value ‘Retired’ in column C disappear.
Now try replacing the value in cell A21 to ‘On probation’, then clicking any other cell. You should find all rows containing the value ‘On probation’ in column C disappear.
Now try removing the value in cell A21 and leaving it empty. Then click on any other cell. You should find both rows become visible again.
This means the code is working in real-time when changes are made to cell B20.
Explanation of the Code
Let us take a few minutes to understand this code now.
- Lines 1, 2, and 3 define variables to hold the starting row and ending row of the dataset as well as the index of the criteria column. You can change the values according to your requirement.
StartRow = 2 EndRow = 19 ColNum = 3
- Lines 4 to 10, loop through each cell in column “3” (or column C) of the worksheet. If the cell contains the value in cell A21, then we set the ‘Hidden’ attribute of the entire row (corresponding to that cell) to True, which means we want to hide the entire corresponding row.
For i = StartRow To EndRow
If Cells(i, ColNum).Value = Range("A21").Value Then
Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = True
Else
Cells(i, ColNum).EntireRow.Hidden = False
End If
Next i
In this way, the above code hides the rows of the dataset depending on the value in cell A21. If A21 does not contain any value then the code displays all rows.
In this tutorial, I showed you how you can use Filters as well as Excel VBA to hide rows based on a cell value.
I did this with the help of two simple examples – one that removes required rows only when the macro is explicitly run and another that works in real-time.
I hope that we have been successful in helping you understand the concept behind the code so that you can customize it and use it in your own applications.
Other Excel tutorials you may also like:
- How to Hide Columns Based On Cell Value in Excel
- How to Delete Filtered Rows in Excel (with and without VBA)
- How to Highlight Every Other Row in Excel (Conditional Formatting & VBA)
- How to Unhide All Rows in Excel with VBA
- How to Set a Row to Print on Every Page in Excel
- How to Paste in a Filtered Column Skipping the Hidden Cells
- How to Select Multiple Rows in Excel
- How to Select Rows with Specific Text in Excel
- How to Move Row to Another Sheet Based On Cell Value in Excel?
- How to Compare Two Cells in Excel?
Working in Excel, sometimes there is a need to hide part of displayed data.
The most handy way — is to hide individual columns or rows. For example, during the presentation or before preparing document to print.
How to hide columns and rows in Excel?
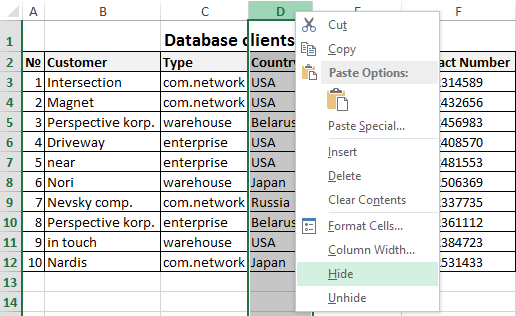
Let’s say you have the table in what you need to display only the most significant data for better reading of performance. In order to do this, we will do the following:
- Select the column data of what you need to hide – for instance, the column C.
- On a selected column to right-click of mouse and select the option «Hide» CTRL+0 (for columns) CTRL+9 (for rows).
The column was hidden, but not deleted. This is evidenced by the priority of the alphabet`s letters in the names of columns (A; B; D; E).
Remark. If you want to hide multiple columns, highlight them before hiding. You can selectively highlight multiple columns with CTRL key pressed. In a similar way, you can hide the rows.
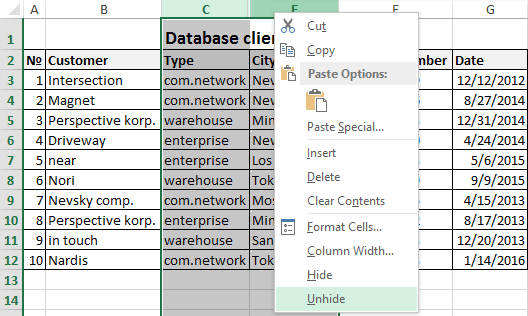
How to display hidden columns and rows in Excel?
To redisplay to the hidden column, you must select 2 of its contiguous (contiguous) columns. Then to generate the context menu, right-click and choose the option «Unhide».
The similar actions are performed in order to open the hidden rows in Excel.
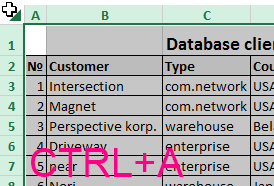
If the sheet is hidden many rows and columns and you want to display all at once, you must highlight the whole worksheet by pressing CTRL+A. Further a separate call to the context menu for the columns to choose the option «Show» and then for the rows, or in reverse order (for rows then for columns).
To select the entire sheet you can by clicking in the intersection of column headings and rows.
About these and other methods to select of an entire sheet and bands you have already known from the previous lessons.