What is the Greek term for earth?
Gaea also called Ge Greek personification of the Earth as a goddess.
What is the Ancient Greek word for universe?
The philosopher Pythagoras first used the term cosmos (Ancient Greek: κόσμος) for the order of the universe.
What is the meaning of Greek word Eorthe?
Answer: earth ground soil dryland.
Which Greek word means water?
The Greek cognate húdōr (‘water’) is the basis of numerous English words with the prefix hydr- including hydrate hydrant hydrangea hydraulic hydrogen (the element that generates water when oxidised) hydrocarbon hydroelectric hydrofoil and a whole host of more specialized scientific words.
Is earth a Greek word?
Greek prefix geo- ( – gaio-) from gē (again meaning “earth”). Earth as “Terra Firma”. The English word “earth” has cognates in many modern and ancient languages. … The root has cognates in extinct languages such as ertha in Old Saxon and ert (meaning “ground”) in Middle Irish derived from the Old English eorðe.
Is Terra another name for earth?
Terra is the Latin/Italian/Portuguese term for Earth or land.
What is Greek cosmos?
Cosmos is originally a Greek word meaning both “order” and “world ” because the ancient Greeks thought that the world was perfectly harmonious and impeccably put in order.
What is cosmos Latin?
In the general sense a cosmos is an orderly or harmonious system. … Today the word is generally used as a synonym of the Latin loanword “Universe”. The word cosmetics originates from the same root. In many Slavic languages such as Russian Bulgarian and Serbian the word Космос also means “outer space”.
What is space physics?
space a boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction.
What does Hydro mean in Greek?
They hail from Greek (hydro) and Latin (aqua) and mean “water”.
See also what is the meaning of burrow
What Greek root means life?
Quick Summary. The Greek root word bio means ‘life. ‘ Some common English vocabulary words that come from this root word include biological biography and amphibian. One easy word that is helpful in remembering bio is biology or the study of ‘life.
What is Hudor?
Hydrosphere comes from the word ‘hudor’ meaning water.
What is earth’s real name?
Earth
| Designations | |
|---|---|
| Alternative names | Gaia Terra Tellus the world the globe |
| Adjectives | Earthly terrestrial terran tellurian |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch J2000 |
What God is earth named after?
Earth is the only planet not named after a Roman god or goddess but it is associated with the goddess Terra Mater (Gaea to the Greeks). In mythology she was the first goddess on Earth and the mother of Uranus. The name Earth comes from Old English and Germanic.
Is earth a God?
An Earth god is a deification of the Earth associated with a male figure with chthonic or terrestrial attributes. In Greek mythology the Earth is personified as Gaia corresponding to Roman Terra. Egyptian mythology have the sky goddesses Nut and Hathor with the earth gods Osiris and Geb.
What is Earth’s code name?
Since there is only one planet Earth it is known simply as “the Earth.” “Terra” is not a correct name for Earth nor are “Sol” and “Luna.” These are simply the Latin for Earth Sun and Moon.
Is Earth called Blue planet?
Planet Earth has been called the “Blue Planet” due to the abundant water on its surface. Here on Earth we take liquid water for granted after all our bodies are mostly made of water. However liquid water is a rare commodity in our solar system. … Liquid water covers most of the surface of our planet.
See also how to make a spear out of wood
What is the Egyptian word for Earth?
In Egyptian art Geb as a portrayal of the earth was often depicted lying by the feet of Shu the air god with Nut the goddess of the sky arched above them.
What does prefix tele mean?
Definition of tele- (Entry 2 of 2) 1 : distant : at a distance : over a distance telegram. 2a : telegraph teletypewriter. b : television telecast. c : telecommunication telemarketing.
What is the meaning of Tele in Greek?
Tell students that the Greek root tele means “distant or far away.” Then print the following mathematical sentence on the board and read it aloud: tele + phone = telephone. Say:The other Greek root in telephone is phone it means “sound.” So if tele means “distant” and phone means “sound ” the word.
Is there a god of space?
Aether. Primordial god of the upper air light the atmosphere space and heaven.
What’s bigger than a universe?
No the universe contains all solar systems and galaxies. Our Sun is just one star among the hundreds of billions of stars in our Milky Way Galaxy and the universe is made up of all the galaxies – billions of them.
What is bigger universe or cosmos?
The words “cosmos” and “universe” are used synonymously as they refer to the same concept which is the world or nature. “Universe” seems to have a narrower or smaller scope than “cosmos ” though and “cosmos” signifies a larger and more complex system.
How do you say universe in Latin?
The universe (Latin: universus) is all of space and time and their contents including planets stars galaxies and all other forms of matter and energy.
How many planets are there in space?
There are eight planets in the Solar System according to the IAU definition. In order of increasing distance from the Sun they are the four terrestrials Mercury Venus Earth and Mars then the four giant planets Jupiter Saturn Uranus and Neptune.
See also Where Can Continental Glaciers Be Found Today?
Is space a vacuum?
A vacuum is an empty place which space nearly achieves. Space is an almost perfect vacuum full of cosmic voids. … By definition a vacuum is devoid of matter. Space is almost an absolute vacuum not because of suction but because it’s nearly empty.
Can time be defined?
Physicists define time as the progression of events from the past to the present into the future. … Time can be considered to be the fourth dimension of reality used to describe events in three-dimensional space. It is not something we can see touch or taste but we can measure its passage.
What does bio mean in Greek?
bio- a combining form meaning “life” occurring in loanwords from Greek (biography) on this model used in the formation of compound words (bioluminescence).
What does Hypo prefix mean?
Definition of hypo- (Entry 5 of 5) 1 : under : beneath : down hypoblast hypodermic. 2 : less than normal or normally hypesthesia hypotension. 3 : in a lower state of oxidation : in a low and usually the lowest position in a series of compounds hypochlorous acid hypoxanthine.
What does prefix hyper mean?
hyper- prefix. Definition of hyper- (Entry 2 of 2) 1 : above : beyond : super- hypermarket. 2a : excessively hypersensitive.
Is bio root Greek or Latin?
The Greek root word bio means ‘life. ‘ Some common English vocabulary words that come from this root word include biological biography and amphibian.
What is the meaning of Pend?
pend. / (pɛnd) / verb (intr) to await judgment or settlement. dialect to hang depend.
Is bio a prefix?
The prefix bio- implies of or related to life or living organisms.
What is Hudor Greek?
hydr- From the Greek hudor hudatos meaning ‘water’ a prefix that means ‘pertaining to water’. A Dictionary of Ecology.
How to Pronounce EARTH – American English Pronunciation
When Japanese Voice Actor Pronounces “The Earth”
How the Ancient Greeks Proved that the Earth was Round
Carl Sagan’s explanation of how the Ancient Greek knew Earth was Round
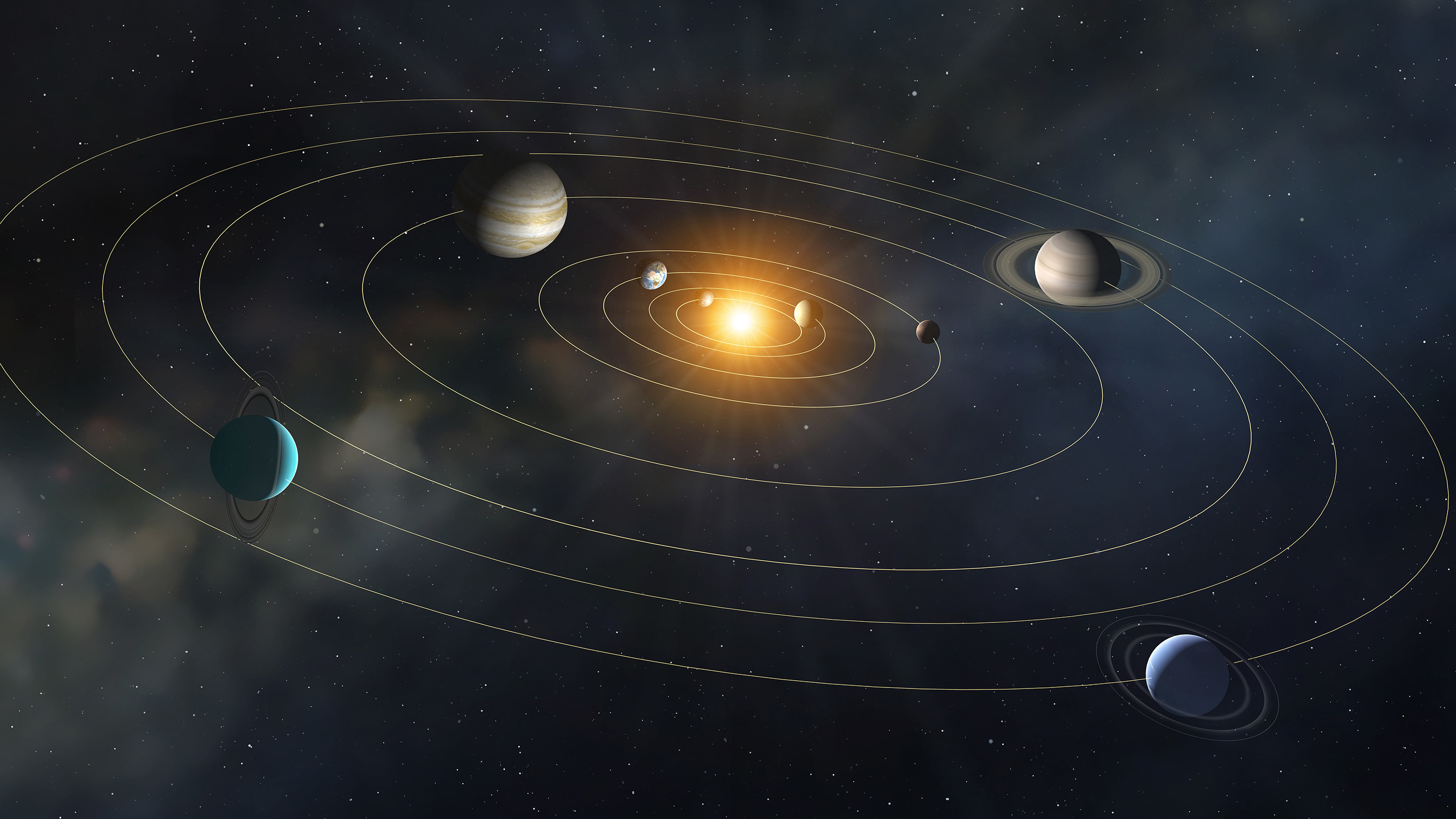
Do you know the Greek names of the Planets? The names of the planets are given by more or less famous astronomers who discovered them throughout the years.
The planets in our solar system got their names mostly from the Greek Mythology and the Roman nomenclature.
Here we will present the Greek names of the planets, as they were given by the ancient Greeks and modern astronomers.
There are also several astronomical terms with a Greek origin. For instance, the word Galaxy comes from the Greek Galaxias, the Greek name for Chaos is Haos, while the word planet comes from the Greek word Planitis.
The names of planets in the Roman and Greek Language
We chose to present the planets according to their distance from the sun.
Sun – Helios
Helios is the Greek name of the Sun, the center of our solar system.
Earth – Ge (from the ancient Greek name Gaia or Gaea)
Gaia was the great mother of all, creator and giver of birth to the Earth and all the Universe, the heavenly gods, the Titans, and the Giants. The gods were born from her union with Uranus (the sky), while the sea-gods were born from her union with Pontus (the sea).
Mercury – Ermis
Ermis is the Greek name of the planet Mercury, which is the closest planet to the sun. It is named after the Greek God of commerce, Ermis or Hermes, who was also the messenger of the Ancient Greek gods.
Venus – Aphrodite
Aphrodite is the Greek name of the planet Venus, which is named after Aphrodite, the goddess of Love.
Mars – Aris
Aris is the Greek name of the planet Mars, the fourth planet from the sun, also known as the Red planet. Aris or Ares was the Greek god of War.
Jupiter – Dias
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the sun, is the largest planet in our solar system. In Greek the name of the planet Jupiter is Dias, the Greek name of god Zeus.
Jupiter has many moons orbiting around the planet. The largest one is Ganymede and it is named after Ganymedes, the hero of the Greek mythology.
Saturn – Kronos
Saturn is the second largest planet of our system and the sixth planet from the sun. The Greek name of the planet Saturn is Kronos. The Titan Cronus was the father of Zeus, while Saturn was the Roman God of agriculture.
Uranus – Ouranos
Ouranos is the Greek name of the planet Uranus, the seventh planet from the sun. This planet is named after the creator of the sky, God Uranus or Ouranos, which means sky in the Greek language. He was the father of Cronus and the Titans, as well as of the Cyclopes.
Neptune – Poseidon
Neptune or Poseidon as is its Greek name, was the God of the Seas. It is the eight planet from the sun, and its predominant color is blue, which makes its name a rather excellent choice.
Pluto – Pluton
The god of the Underworld, Pluto or Pluton in Greek is the farthest planet from the sun and one of the least observed planets in our solar system.
Other Greek names in our galaxy
Greek names were given also to several stars and planetary features in our Galaxy. The names of stars are chosen by their discoverers as well. Some of them are:
Cerberus. The three headed dog – guardian of the gates of the Underworld, known with the name Kerveros in Greek, is given to the large black spot on the surface of planet Mars.
On Mars, there is also the Olympus Mons, the largest volcano of the planet, referring to Mount Olympus or Olympos in Greek, the mountain of the gods in the Greek mythology.
Planet Venus also has its volcano, named Rhea Mons, after Rhea or Rea, the mother of Zeus, daughter of Uranus and Gaia.
Read more:
- Learn Greek words for stars and zodiacs

(Image credit: NASA)
Whether you call our planet the Earth, the world or a terrestrial body, all of these names have an origin story deep in history.
Like many names of solar system objects, Earth’s original namer is long lost to history. But linguistics provide a few clues. Ertha is an approximate spelling for «the ground» (meaning, the ground upon which we stand) in Anglo-Saxon, one of many ancestor languages to English.
«Anglo-Saxon» is a modern term to refer to a cultural group who lived within modern-day England and Wales shortly after the Roman Empire collapsed, between the fifth century and the Norman Conquest of 1066.
The identities of people were complex, and different individuals likely had different associations depending on their family, their history and the land upon which they lived, scientists say. Ertha, like the other names to represent our planet and other ones, must be understood in this context.
Related: What would happen if Earth suddenly stopped spinning?
(opens in new tab)
Ertha in Anglo-Saxon «means the ground on which you walk, the ground in which you sow your crops,» said freelance archaeologist and historian Gillian Hovell, who is known as «The Muddy Archaeologist (opens in new tab).»
Ertha also links to a place in which life emerges and perhaps even to the ancestors who are buried in the ground, Hovell said. But sometimes the name can change its meaning depending on the culture.
(opens in new tab)
Other modern popular terms for «Earth» come from Latin. Terra means land — again, the land on which you are standing, farming or otherwise interacting with, Hovell said. That’s where we get the modern-day English words «terrestrial,» «subterranean,» «extraterrestrial» and so forth.
Orbis was used when authors wanted to talk about Earth as a globe. «They knew it was a globe,» Hovell said of the ancient Romans, who closely followed Greek science; the Greek Eratosthenes measured our planet’s circumference in 240 B.C.
«It was a globe of lands,» Hovell said of the orbis meaning; orbis is the root word of the modern-day «orbit.» There was yet another term, mundus, which was meant to describe the whole of the universe.
(opens in new tab)
«The world is everything that contains us [humans], but it was quite obviously separate from the planets,» Hovell said of mundus. Mundus is reflected in the modern-day French term monde (world), the Italian mondo, the Spanish mundo and the Portuguese mundo, among other «Romance language» ancestors of Latin.
The Roman author Pliny the Elder (Gaius Plinius Secundus), who wrote a large set of volumes on natural history in the first century, used mundus quite a bit in his observations, Hovell said. It is also from Pliny that we get a lot of the terminology used to name planets through the International Astronomical Union, although each culture has its own traditions and monikers.
(opens in new tab)
The tradition of planet naming used by the Romans dates as far back as the Babylonians at least. Babylonia was a complex state in parts of modern-day Iraq and Syria best remembered for its king, Hammurabi, who today is closely associated with a law code created under his reign.
Babylonia persisted from about 1900 through 539 B.C.; the region was then taken over by the Persians (then the Achaemenid Empire). The Persians became the great enemy of the Greeks, but the two empires also shared a lot of intercultural knowledge. This is how the Greeks incorporated some of the gods from Persia, Hovell explained.
Then when the Romans came to the fore, they integrated traditions from the regions they touched — including Greece — into their own pantheon of gods. This allowed for a goddess of love from Babylonia, Ishtar, to become Aphrodite under the Greeks and Venus under the Romans, for example. (This is a very simplified chronology, however, as Roman gods and goddesses had attributes based on their location, celestial timings and other factors, and the same is likely true of other traditions they integrated, historians say.)
The Greek term for planets means something like «wandering ones» or «wanderer,» according to the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum (opens in new tab). The Romans gave these planets names based on how they appeared to the naked eye in the sky, centuries before telescopes were available. But these names aren’t always universal, either.
Pliny the Elder sometimes called Mercury by another god’s name, Apollo, because Apollo was closely associated with the sun, Hovell said. Mercury himself was a messenger of the gods and associated with travelers, among many other connotations.
The planet named after Venus — whose associations include the goddess of love — was sometimes called Lucifer, the «light-bringer» (light is lux in Latin). This was the name the planet might take in the morning, when it rises at dawn. The Romans, Hovell said, understood Venus rises in the morning or the evening, but the planet’s name could change depending on the attributes on display.
Mars, Pliny once wrote, is «burning with fire.» Pliny thought that Mars was very close to the sun, as he and other Romans of the day were following Ptolemy’s geocentric model that put Earth at the center of the universe.
Jupiter’s bright appearance was associated with the king of the gods, and Saturn (who came after Jupiter in the geocentric model) is Jupiter’s father under Roman mythology, which again borrows from older traditions, Hovell said.
Incidentally, the people who named Uranus, Neptune and Pluto centuries later, in the early telescopic age, tried to carry on this tradition of godly associations to be consistent with how the Romans did it. But even this practice was not universal. For example: Uranus was almost named after George III when its discoverer, German-born British astronomer William Herschel, sought a way to thank his financial backer, according to NASA (opens in new tab).
Originally published on Live Science.
Elizabeth Howell is a regular contributor to Live Science and Space.com, along with several other science publications. She is one of a handful of Canadian reporters who specializes in space reporting. Elizabeth has a Bachelor of Journalism, Science Concentration at Carleton University (Canada) and an M.Sc. Space Studies (distance) at the University of North Dakota. Elizabeth became a full-time freelancer after earning her M.Sc. in 2012. She reported on three space shuttle launches in person and once spent two weeks in an isolated Utah facility pretending to be a Martian.
Most Popular
Subjects>Jobs & Education>Education
Wiki User
∙ 12y ago
Best Answer
Copy
Γη = Earth
gaia
or the prefix geo- is also used, for example, geopolis is city
of earth, the -polis suffix being city.
Wiki User
∙ 12y ago
This answer is:
Study guides
More answers
Wiki User
∙ 11y ago
Copy
γη (gi) or
γαία (gea) or
υδρόγειος (idrogios), when speaking for the planet.
This answer is:
Anonymous ∙
Lvl 1
∙ 2y ago
Copy
Spectacle
This answer is:
Add your answer:
Earn +
20
pts
Q: What is the Greek word for Earth?
Write your answer…
Submit
Still have questions?
Related questions
People also asked
The Greek root word ge and English prefix geo- mean “earth.” Soon you’ll be saying “golly gee whiz” when you find out the number of words in English that contain this Greek root!
Since Earth is our home, it would make sense for humans to study that home. Geology is the study of the physical or solid “Earth.” Geologists are those scientists who study that solid “Earth.” The study of geography, on the other hand, deals with the lands of our “Earth,” including the boundaries between and features of those lands and the people who inhabit all of Earth’s different countries.
The measurement of the “Earth” or geometry was born when the Greek mathematician Euclid decided he needed a way to measure his planet. Not to be outdone by Euclid, Greek astronomers such as Aristarchus proposed a heliocentric model of the Universe which radically stated that the Earth revolved around the sun, which went completely against the commonly held belief of a geocentric model where the “Earth” was the center of the Universe around which all other celestial bodies revolved. The notions of perigee and apogee came later, when it was discovered that the “Earth” does not revolve around the sun in a perfect circle, but rather travels through space in an ellipse; this advancement enabled astronomers to realize that “Earth” has a perigee in its orbit when it is closest to the sun, and a corresponding apogee, or point in “Earth’s” orbit when it’s furthest away from the sun.
Mother “Earth” was known as Gaia to the ancient Greeks. Her name was made popular in the 1970s via the Gaia Hypothesis, which suggests that living organisms and inorganic matter interact to keep planet “Earth” healthy. Ironically, a man named George Wald spoke at the first Gaia conference; the name George, which comes from the Greek word “farmer,” was so formed because a “farmer” is someone who works with the “earth” to grow things. The state of Georgia, or etymologically an area on the map for “farmers,” was named after King George the II of Britain, who most likely was never a “farmer!”
And so here ends our exploration of the Greek root word ge and English prefix geo-, a linguistic journey which has taken us around the “Earth” and beyond!
- geology: study of the physical or solid “Earth”
- geologist: one who studies the solid parts of the “Earth”
- geography: study of the nations and peoples of the “Earth”
- geometry: mathematics which measures the features of the “Earth”
- geocentric: of an “Earth”-centered Universe
- Gaia: in Greek mythology, the original “Earth” Mother
- George: from the Greek word for “farmer,” or worker in the “earth”
- Georgia: land of “farmers,” an eponym based upon King George II of Britain