- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Pronunciation
- Downloads
- Learning Record
- Mini Phrasebook

→ and →
Click on the words in the correct order.
- Is
- rugby
- popular
- in
- your
- country?
- How
- often
- does
- Carmen
- go
- out?
- Is
- this
- sport
- in
- the
- Olympics?
- How
- do
- you
- go
- to
- work?
- What
- is
- the
- national
- sport
- in
- Japan?
- Where
- do
- you
- meet
- your
- friends?
10000+ результатов для ‘word order in questions be and present simple’
Interview questions in Present Simple and Present Continuos
Случайные карты
от Nadezhda18
Adults
Elementary
Present Simple and Continuous
Speaking
Present Simple General Questions Correct / incorrect
Викторина
от Daryayurievna13
1-й класс
2-й класс
3 класс
4-й класс
5-й класс
English
present simple questions
Present Simple sentences.
Привести в порядок
от Anitagirl98
5-й класс
6 класс
7-й класс
8 класс
Средняя школа
English
Present Simple sentence order
Put these words in the correct order and make questions!
Привести в порядок
от Maxromano
Elementary
Present Simple
Questions
present simple fill out a word
Пропущенное слово
от Nadezhda18
Adults
English
Present Simple and Continuous
Present Simple, word order — questions
Привести в порядок
от Yelena
Word order in questions: to be + present simple (with answers)
Перевернуть плитки
от Hop
Beginner
Grammar
Present Simple drilling affirmative, interrogative and negative sentences
Случайные карты
от Nadezhda18
Adults
English
Present Simple and Continuous
Make questions and answer them
Привести в порядок
от Cathryzh
Adults
English
Present Simple questions
am — is — are / am not — isn’t — aren’t
Пропущенное слово
от Maxromano
be
Elementary
Present Simple
Drill Present Simple vs Present Continuous
Случайные карты
от Nadezhda18
Adults
English
Present Simple and Continuous
TAG questions (present simple)
Викторина
от Laletinakaterin
English
Present Simple
Tag questions
Word order Questions in Present simple
Привести в порядок
от Savelyevaelizav
Word order Present Simple and be
Привести в порядок
от Katyamerk
English
Present Simple. Word order in questions
Привести в порядок
от Margarita178
Word order in questions (Present Simple)
Случайные карты
от Gushinadi
Interview (30 questions)
Случайные карты
от Elenaklinova
past simple
present continuous
present simple
questions
Questions and answers: James
Сопоставить
от Maxromano
Elementary
Present Simple
Questions
present simple questions word order
Привести в порядок
от Mkurkova1
Present Simple Questions Word order
Привести в порядок
от Ria04
English
Present Simple (s-forms driller)
Случайные карты
от Nadezhda18
Adults
English
Present Simple and Continuous
BE Yes/No easy
Сопоставить
от Puchkovadn90
DaryaPuchkova
English
Present Simple
to be
Word order in questions Revision (Present Simple + Continuous, Past Simple)
Привести в порядок
от Hop
Present simple Translate (in on at / city places / jobs)
Случайные карты
от Natalybaldina95
English
in on at
present simple
Present Simple, word order
Привести в порядок
от Yelena
Word order in questions
Привести в порядок
от Natalsamarina
Present Simple Word Order
Привести в порядок
от Smartn7575
Present Simple
Word order in questions
Привести в порядок
от Sahandramedved
new english file elementary
Usually they do, but today they are doing
Случайные карты
от Nadezhda18
Adults
English
Present Simple and Continuous
Beginner Unit 2-2 Present Simple (be and do)
Викторина
от Joy19374
beginner
Adults
English
Outcomes Beginner
Present simple
To be
Fill in the gaps with am,is or are.
Пропущенное слово
от Akatekoroleva
4-6
Present Simple
to be
Present Simple, word order — questions
Привести в порядок
от Magnolya80
3 класс
4-й класс
5-й класс
Present simple questions word order
Привести в порядок
от Alinasem
Present Simple Questions Word Order
Привести в порядок
от Elena463
YEL — Elementary
English
Present Simple questions word order.
Привести в порядок
от Argatova83
Present Simple, word order — questions
Привести в порядок
от Marishenkased93
Present Simple, word order — questions
Привести в порядок
от Markarinar
Verbs with different meaning in present simple and cont. Revision
Случайные карты
от Beawesome3
present simple vs continuous
BE Yes/No hard
Сопоставить
от Puchkovadn90
DaryaPuchkova
English
Present Simple
to be
Verbs with different meanings in present simple and continuous
Случайные карты
от Beawesome3
present simple vs continuous
HW Beginner Unit 5 Pr S Questions
Привести в порядок
от Dinara77
Headway Beginner
Present Simple questions
Unit 6
Word order in questions
Упорядочивание
от Kostyukovaev
Adults
English
Outcomes pre-intermediate
9B_Present Continuous & present Simple
Случайные карты
от Annieg
English File Beginner
Present Simple and present Continuous
Word order (предложения БЕЗ глагола действия)
Привести в порядок
от Babrasin
English
Sentence word order
Word order in to be questions
Привести в порядок
от Oksi1297n
Word order in Present Simple
Привести в порядок
от Buschick
English
Present simple word order
Привести в порядок
от Krafoo
AS2 Present Simple (action verbs and to be)
Викторина
от Joy19374
Начальная школа / начальная
Academy Stars 2
English
Present simple
To be
Word Order in Questions
Привести в порядок
от Anastacey
adults
English
Grammar
SpeakOut Pre-Inter
Word order in questions
Привести в порядок
от Aksanabox
Simple present — Word order
Привести в порядок
от Veronicasiqueira94
Elementary Level
A2 English
Simple present
Speaking
Word order in questions
Present Simple sentence structure
Привести в порядок
от Nadezhda18
Adults
English
Present Simple and Continuous
AS2 U2 to be action verbs
Групповая сортировка
от Joy19374
Начальная школа / начальная
Academy Stars 2
English
Present simple
To be
Present Simple — action verbs+to be — all types of sentences
Викторина
от Abemelizabeth
16-80
Adults
English
Present Simple
to be
Word order in Negative sentences — Present and Past Simple
Привести в порядок
от Elena463
YEL — Elementary
Adults Elementary
English
Word order (предложения с глаголом действия)
Привести в порядок
от Babrasin
English
Sentence word order
HW Beginner Unit 6 Vocabulary
Случайные карты
от Dinara77
Headway Beginner
Present Simple questions
Unit 6
Elementary question word order
Привести в порядок
от Patibready
present simple
Word order in questions 1A
Привести в порядок
от Marinalagun
NEF Pre-Intermediate
TO BE PRESENT SIMPLE POSITIVE WORD ORDER
Привести в порядок
от Englishbrainiacs

Want to create your own interactive worksheets?
Welcome to TopWorksheets, an online platform to create and manage digital exercises.
Save time with interactive worksheets: assign tasks, receive auto-graded submissions and track your students’ progress.
Get started. It’s free!
-
Worksheets -
English -
English language -
Grammar -
Grammar: word order in questions: be and simple present
Language: English
Subject:
English language
> Grammar
Finish worksheet
The time to complete this worksheet is over. Complete the data to send the answers to your teacher
Send answers to teacher
Record your answer
Record your answer
Speak to enter your answer
Play your answer
1. Questions without question words and be
Subject and verb change their position in statement and question.
- Sentence: You are from Germany.
- Question: Are you from Germany?
We always use the short answer, not only Yes or No. That’s why questions without question words are also called YES/NO-questions.
2. Questions with question words and be
| Question word | Verb | Subject | Rest | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Where | are | you | from? | I am from Stuttgart. I‘m from Stuttgart. |
| What | is | your name? | My name is Peter. | |
| How | are | Pat and Sue? | They are fine. They‘re fine. |
Questions with question words are also called WH-questions.
3. Questions without question words and have
| Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Yes/No | Subject | Auxiliary (+ n’t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Have | you | got | a cat? | Yes, | I | have. |
| Have | you | got | a new car? | No, | we | haven’t. |
| Has | your brother | got | a bike? | Yes, | he | has. |
| Do | you | have | a cat? | Yes, | I | do. |
| Do | you | have | a new car? | No, | we | don’t. |
| Does | your brother | have | a bike? | Yes, | he | does. |
4. Questions with question words and have
| Question word | Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Where | have | you | got | your ruler? | I‘ve got it in my pencil case. |
| Where | do | you | have | your ruler? | I have it in my pencil case. |
5. Questions without question words in the Simple Present
| Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Yes/No | Subject | Auxiliary (+ n’t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Do | you | read | books? | Yes, No, |
I I |
do. don’t. |
| Does | Peter | play | football? | Yes, | he | does. |
6. Questions with question words in the Simple Present
| Question word | Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | do | you | play | on your computer? | I play games on my computer. |
| When | does | your mother | go | to work? | She goes to work at 6 o’clock. |
7. Questions without question words in the Simple Past
| Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Yes/No | Subject | Auxiliary (+ n’t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Did | Max | play | football? | Yes, No, |
he he |
did. didn’t. |
BUT:
| to be | Subject | Rest | Yes/No | Subject | Auxiliary (+ n’t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Were | you | in Leipzig last week? | Yes, No, |
I I |
was. wasn’t. |
8. Questions with question words in the Simple Past
| Question word | Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | did | you | play | yesterday evening? | I played computer games. |
BUT:
| Question word | to be | Subject | Rest | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Where | were | you | yesterday? | I was at the cinema. |
9. Subject question
| Question word | Verb | Rest | Subject | Verb | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Who | runs | to the shop? | Peter | runs | to the shop. |
10. Object question
| Question word | Auxiliary | Subject | Verb | Rest | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Who | did | Mandy | phone | last Monday? | Mandy phoned her uncle. |
NOTE!
| Subject question | Object question |
|---|---|
| Who phoned John? | Who did John phone? |
Present Simple (презент симпл) или простое настоящее время употребляется для выражения действий, явлений или процессов, которые происходят постоянно, регулярно, являются правилами или законами, носят непрерывный характер.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим употребление формы глагола to be в Present Simple, расскажем про его спряжение и разберем правила и примеры.
Предложения в настоящем простом времени образуется следующим образом:
Подлежащее + сказуемое + второстепенные члены предложения.
Например:
Я люблю яблоки. I like apples.
Он играет в футбол каждый день. He plays football every day.
Дети идут в школу после завтрака. Children go to school after breakfast.
Она встает в 6 утра. She gets up at 6 o’clock.
В приведенных выше предложениях есть смысловые глаголы-сказуемые, которые в Present Simple не склоняются. За исключением предложений с подлежащими в третьем лице единственного числа (местоимениями он (he), она (she) или их эквивалентам). В этом случае к глаголу добавляется окончание -s (es).
I play chess. Я играю в шахматы.
He plays chess. Он играет в шахматы.
They go to the park on Sunday. Они ходят в парк по воскресеньям.
She goes to the park on Sunday. Она ходит в парк по воскресеньям.
Сейчас мы подробнее остановимся на предложениях, в которых нет сказуемого, выраженного смысловым глаголом, то есть глаголом, обозначающим действие и отвечающим на вопрос «что делать?».
В предложениях, где нет смыслового глагола, появляется вспомогательный глагол to be, который можно перевести как «быть», «существовать», «являться». Но, как правило, на русский язык глагол to be в Present Simple не переводится, а просто опускается.
I am a doctor. Я доктор (т.е. «я являюсь доктором»).
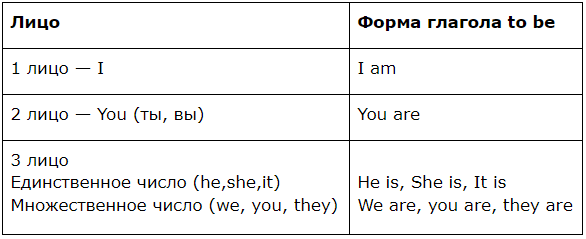
Спряжение глагола to be в Present Simple
В Present Simple глагол to be имеет 3 формы и зависит от подлежащего.
С местоимением I (я) форма глагола to be будет am.
I am a student. Я студент.
С местоимениями he (он), she (она), it (оно, он или она для неодушевленных предметов) и существительными в третьем лице единственном числе форма глагола to be будет is.
He is a good doctor. Он хороший врач.
She is my friend. Она моя подруга.
It is my home town. Это мой родной город.
С местоимениями they (они), we (мы), you (ты, вы) и существительными 2 лица и 3 лица множественного числа форма глагола to be – are.
They are sportsmen. Они спортсмены.
Where are you from? Откуда вы?
We are childhood friends. Мы друзья детства.
Приведем формы глагола to be в Present Simple в виде таблицы:
Случаи употребления глагола to be
- Когда мы говорим о роде деятельности, профессии или о том, кем или чем является действующее лицо.
My mother is a teacher. Моя мама — учитель.
I am a student. Я — ученик.
A water-melon is a berry. Арбуз — это ягода.
This building is our History Museum. Это здание – наш исторический музей.Иногда в такого рода предложениях be в Present Simple может переводиться как «являться». Однако опускание перевода данного глагола не отразится на смысле предложений.
- To be используется для связки в предложениях существительного и прилагательного.
I am happy to be with you. Я счастлив быть с тобой.
Summer is a nice season. Лето – хорошее время года.
These books are interesting. Эти книги интересные.
He is kind. Он добрый.
It is very difficult for me. Это очень трудно для меня.
She is busy. Она занята. - В предложениях о возрасте.
I am twenty (years old). Мне двадцать (лет).
My grandmother is 85 (years old). Моей бабушке 85.
The students are seventeen (years old). Студентам по семнадцать лет.
The oak is about hundred years. Дубу около ста лет. - Для обозначения местоположения или нахождения кого-то или чего-то.
The table is near the window. Стол (стоит) рядом с окном.
Novgorod is between Saint-Petersburg and Moscow. Новгород (находится) между Санкт-Петербургом и Москвой.
My parents are in Paris. Мои родители (находятся) в Париже.
Our university is not far from here. Наш университет (расположен) недалеко отсюда.
Our children are at home. Наши дети дома.Обратите внимание, что в данном случае вспомогательный глагол to be может быть переведен глаголом «находиться».
- Для обозначения национальной принадлежности.
I am Russian. Я русский.
Our partners are Chinese. Наши партнеры — китайцы.
Their friend is American. Их друг американец.
Как определить, что в предложении необходимо употребить вспомогательный глагол to be? Убедиться в том, что в нем нет смыслового глагола или глагола-действия. Особенность конструкции английского предложения такова, что во всех предложениях обязательно должны быть подлежащее и сказуемое. Если сказуемого в привычном нам виде в форме глагола нет, значит, его функции должен выполнять вспомогательный глагол to be. Иногда его еще называют «глагол-помощник».
Очень часто начинающие изучать английский язык строят предложения как в русском языке, то есть без сказуемого, тем самым совершая грубые ошибки. Если в родном языке такие предложения, как «Дерево зеленое», «Ночь», «Я дома» — привычные и грамматически правильные, то при переводе на английский язык обязательно нужно добавить вспомогательный глагол to be в соответствующей для времени Present Simple форме:
A tree is green.
It is night.
I am at home.
Если вам сложно понять смысл глагола-помощника, можете про себя переводить его словом «есть», как употребляли в древней Руси. То есть «Дерево (есть) зеленое», «Я (есть) дома», «Они (есть) дети».
Вопросительные предложения в Present Simple с to be
Теперь давайте разберем, как в настоящем простом времени задавать вопросы к предложениям, где нет смыслового глагола.
В английском языке есть 2 вида вопросительных предложений.
Первый вид — это общие вопросы, которые начинаются со вспомогательного глагола.
Схема общего вопроса в present simple с to be выглядит следующим образом:
Вспомогательный глагол в соответствующей форме (am, is, are) + подлежащее + второстепенные члены предложения.
Например:
Are you a student? Ты студент?
Are your parents at home? Твои родители дома?
Is this his car near the tree? Это его машина около дерева?
Am I ready? Я готов?
Is this pizza tasty? Эта пицца вкусная?
Как правило, общие вопросы подразумевают краткие ответы:
– в случае утвердительного ответа: Yes + подлежащее + вспомогательный глагол to be в нужной форме.
Yes, I am. Yes, he/she/it is. Yes, they/we/you are.
Are you a doctor? Yes, I am. — Вы доктор? Да.
Is it near the market? Yes, it is. — Это рядом с рынком? Да.
Are they Russian? Yes, they are. — Они русские? Да.
– в случае отрицательного ответа: No + подлежащее + вспомогательный глагол to be в нужной форме с отрицательной частицей not.
No, I am not. No, he/she/it is not. No, they/we/you are not.
Или краткие формы:
is not — isn’t
are not — aren’t
Is it Chinese food? No, it isn’t. (It is Russian). — Это китайская еда? Нет (она русская).
Are you from London? No, I am not. (I am from Liverpool). — Ты из Лондона? Нет (я из Ливерпуля).
Is his father a scientist? No, he isn’t. (He is a teacher). — Его отец ученый? Нет (он учитель).
Второй тип вопросов — специальные, то есть вопросы, которые начинаются с вопросительного слова и требуют полного ответа. После вопросительного слова порядок слов в предложениях такой же как в общем вопросе:
Вопросительное слово + вспомогательный глагол в соответствующей форме (am, is, are) + подлежащее + второстепенные члены предложения.
Where are you from? I am from Canada. Откуда ты? Я из Канады.
How is he? He is fine. Как у него дела? У него все в порядке.
How old are they? They are fifteen. Сколько им лет? Им по пятнадцать.
When is the sunset? It is at 8 o’clock. Когда закат? Он в 8 часов.
Отрицательные предложения в презент симпл с to be
У нас остался последний не рассмотренный вид предложений в настоящем простом времени — отрицательные предложения.
Схема отрицаний в английском языке следующая:
Подлежащее + вспомогательный глагол to be в соответствующей форме (am, is, are) + not + второстепенные члены предложения.
В отрицаниях также можно использовать краткие формы am not — aren’t, is not — isn’t, are not — aren’t.
Рассмотрим на примерах.
I am not a dancer. Я не танцор.
December isn’t a summer month. Декабрь — не летний месяц.
He is not at school, he is ill. Он не в школе, он болен.
Their children aren’t adults. They are teenagers. Их дети не взрослые. Они подростки.
My office is not far from here. Мой офис недалеко отсюда.
Устойчивые выражения с глаголом to be
to be glad — радоваться. He is glad to be here. Он рад быть здесь.
to be hungry — быть голодным. She is hungry after the workout. Она голодная после тренировки.
to be ill — болеть, быть больным. He is ill. Он болен.
to be thirsty — хотеть пить. Little children are often thirsty. Маленькие дети часто хотят пить.
to be late — опаздывать. Sorry, I am late. Простите, я опоздал.
to be sure of smth — быть уверенным в чем-то. He is sure of his decision. Он уверен в своем решении.
to be out of place — быть неуместным. I think it’s out of place here. Я думаю, это здесь неуместно.
to be surprised — удивляться чему-либо. They are surprised at meeting us. Они удивлены встрече с нами.
to be for smth — быть за что-то. I am always for sports. Я всегда за спорт.
to be against smth — быть против чего-то. He is against smoking. Он против курения.
to be sorry — сожалеть. I am sorry about the incident. Я сожалею о случившемся.
to be angry – злиться. İ am not angry with you. — Я не злюсь на тебя.
to be afraid of — бояться. Tom is afraid of dogs. — Том боится собак.
to be interested in — интересоваться чем-либо. I am interested in history. — Я интересуюсь историей.
to be good at — хорошо разбираться в чем-то. İ am good at Math. Я хорошо знаю (разбираюсь) математику.
to be bad at — плохо разбираться в чем-то. He is bad at English. Он плохо разбирается в английском.
to be on duty — дежурить. Which class is on duty today? Какой класс сегодня дежурит?
to be proud (of) — гордиться. I am proud to help you. Я горжусь тем, что помогаю тебе.
to be grateful (for) — быть благодарным за что-то. He is grateful for your help. Он благодарен за твою помощь.
to be careful — быть внимательным, осторожным. I am always careful on the road. Я всегда осторожен на дороге.
Обратите внимание, что при употреблении вышеприведенных предложений форма глагола to be определяется в зависимости от подлежащего, которое стоит в начале предложения.
The verb to be in Present Simple is very important. We use to be with this tense all the time. Because there are so many things we can say by using the verb to be!
For example, we can describe the age of a person:
This boy is 8 years old.
My grandfather is 77 years old.
I am six, I am two years older than my brother! Because he is only four!

By using to be we can inform about the profession/occupation of a person:
My mom is a teacher.
I am the best student in my school.
John is an airplane pilot.
We can say that someone or something is in someplace.
My mother is at work.
The book is on the bookshelf.
My bike is in the garage.

We can describe the state, behavior, mood, character of someone or something. And even much more!
This person is suspicious.
This ball is rubber.
My car is red.
The verb to be does not mean action. To be means to exist in some place or some state. We use to be in the Present Simple to connect the subject with an adjective or noun or pronoun.
This book is green.
We are friends.
I am a good man.
My mom is in France.
This is my car.

There are so many things we can say using the verb to be in the Present Simple! That is why it is very important to be able to use this verb correctly.
What are Three Forms of To Be in Present Simple?
To be in the Present Simple has three forms:
- am
- is
- are
Which form we use depends on the subject:
- I am
- He is
- She is
- It is
- We are
- They are
- You are
I am a good person.
We are best friends.
She is beautiful.

What are the Formulas for Sentences with To be in Present Simple?
To form a positive, interrogative (question), or negative sentence with the verb to be, we cannot use the same rules that we use for other verbs in the Present Simple.
The verb to be forms positive, question, and negative sentences according to its own special rules without the help of the auxiliary verbs do or does.
Positive Sentenses
To form an affirmative sentence, we put to be after the subject. Then we put an adjective or a noun or a pronoun.
Subject + am / is / are
I am your friend!
The dog is small.
We are the students of this school.

Negative Sentences
To form a negative sentence, we add the negative not after the to be.
Subject + am / is / are + not
I am not a boy! I am a man!
She is not at all what you think. She is very kind.
Question Sentences
To form a question we put the verb to be before the subject:
am / is / are + Subject
Am I a good friend?
Is he a doctor?
Are those boys your classmates?

Special Questions with To Be in Present Simple
A Special or Wh-Question contains an additional word or phrase in order to get additional information in the answer. Those are words and phrases like:
- How
- Why
- Why
- When
- Since when
In order to form a special question with the verb to be in the Present Simple, we use the same formula that we use for General or Yes/No Questions. Only we add a question word or phrase to the beginning of the question:
Question word or phrase + am / is / are + Subject
Why is he your friend when he’s so rude?
Why is this book on the table?
Who is this man?
Where is your car?
Since when you are so kind to me?
How to Answer Questions using to be in Present Simple?
To answer a question with the verb to be in the Present Simple, we can use two types of answers:
- Short answer
- Full answer
Short Answer with To Be
To form a short positive answer, we use the following formula:
Yes + Subject + am / is / are
Are you a writer?
Yes, I am.Is he your friend?
Yes, he is.
To form a short negative answer, we use the same formula only we put No at the beginning of the sentence. We also add the negative not after the verb to be.
No + Subject + am / is / are + not.
Is he your friend?
No, he is not.

Full answer with To Be
In order to form a full positive answer with the verb to be, we turn the question into a general positive sentence in the Present Simple. We put the affirmative word Yes at the beginning of such a sentence.
Yes + Subject + am / is / are + Rest of the sentence
Are you at work right now?
Yes, I’m at work (right now).
To form a full negative answer, we use the negative word No instead of Yes. We add the negative not after to be.
No + Subject + am / is / are not + Rest of the sentence
Are you at work right now?
No, I’m not at work (right now).
What is the sort form of To Be in Present Simple?
In English, it is customary to use the contracted forms of the verb to be. Therefore, we abbreviate the verb to be in the Present Simple as follows:
Positive:
- I am – I’m
- He is – He’s
- She is – She’s
- It is – It’s
- We are – We’re
- They are – They’re
- You are – You’re
Negative:
- I am not – I’m not
- He is not – He isn’t
- She is not – She isn’t
- It is not – It isn’t
- We are not – We aren’t
- They are not – They aren’t
- You are not – You aren’t
I‘m not your friend!
They‘re classmates.
She‘s a waitress.
When using the short form, you should note that some short forms of to be in the Present Simple look exactly the same as the short form of to be in the Past Simple.
For example:
He’s – He is in the Present Simple.
He’s – He was in the Past Simple.
We’re – We are in the Present Simple.
We’re – We were in the Past Simple.
In some situations, this can confuse your interlocutor. The meaning of such a sentence may be misunderstood.
For example, look at the following sentence:
She’s my friend!
It may not be clear from such a sentence what you are trying to say. That she is my friend now? Or she was my friend in the past?
In order not to confuse your interlocutor, you can use the full form of the verb to be. Or you can add context to such a sentence from which it becomes clear that you are talking about the past or about the present.
She’s my friend, we spend all the time together.
She’s my friend, we spent all the time together when we went to school 10 years ago.
Now, after we have added additional context, we can see that in the first sentence we use to be in the Present Simple. In the second example, this is to be in the Past Simple.

Common Mistakes with To Be in Present Simple
In this part, let’s take a look at the most common mistakes you can come across when you use the verb to be in the Present Simple.
1) One of the main mistakes is the use of an incorrect form of the verb to be. It mainly happens due to the fact that the verb to be has three forms in the present simple.
Remember that we use am with the pronoun I. We use is with the pronouns he, she and it. We use are with the pronouns you, we, they.
We are good friends.
This ball is green.
She is a very kind woman.
Also, students often make mistakes when using pronouns such as:
- anybody
- everyone
- no one
- someone
etc.
These pronouns almost always imply one person. Therefore, we use the form of the verb to be is.
Nobody is perfect.
I feel like someone is here.
Everyone in this room is lucky.

Sometimes students make mistakes using the future or past form of the verb to be in the present simple. Let’s see what all forms of the verb to be look like.
Present:
- I am
- He is
- She is
- It is
- We are
- They are
- You are
Future:
- I will be
- He will be
- She will be
- It will be
- We will be
- They will be
- You will be
Past:
- I was
- He was
- She was
- It was
- We were
- They were
- You were

2) Sometimes students make a mistake using auxiliary verbs with the verb to be to form a question or negative sentence in the Present Simple. Remember that to be is a special verb and does not need auxiliary verbs like do or does.
Incorrect: Does he is your friend?
Incorrect: Does he your friend?
Correct: Is he your friend?Incorrect: They don’t are my classmates.
Incorrect: They don’t my classmates.
Correct: They are not my classmates.Incorrect: I don’t tired.
Incorrect: I am don’t tired.
Correct: I am not tired.

3) Another mistake is when students use incorrect forms of the verb to be when answering questions in Present Simple.
In this case, students are mistakenly guided by the form of the verb to be in the question. Although in some cases we have to change this form because in the answer we can use a different pronoun.
Question: Are you tired?
Answer: Yes, I am. (Not Yes I are).
We used are in the question because we used the pronoun you. But in the answer, we used the pronoun I. We cannot use are with the pronoun I. We use am.
Here are some more examples in which you can see the same error:
Question: Am I your friend?
Answer: Yes, you are my friend! (NOT: Yes, you am my friend!)Question: Am I weird to you?
Answer: No, you are not weird to me! (NOT No, you am not weird to me!)

Take seriously learning the verb to be especially in the Present Simple! Since you will be using this verb very often.
Also, be sure to check out Present Simple: All Rules You Need to Know detailed tutorial that talks about all the nuances of the Present Simple you have to know.
Put the words in the correct order to make Wh-questions.
Hide example
?
How do you relax after school?
-
1.
?
What do you usually have for lunch?
-
2.
?
What time do they have breakfast?
-
3.
?
Where does she usually buy vegetables?
-
4.
?
How much time do you need for revision?
-
5.
?
Where do they usually spend their vacation?
-
6.
?
What time does the match start?
-
7.
?
How well do you know Spanish?
-
8.
?
How does she get to work?
-
9.
?
What do they think of the new film?
-
10.
?
How much does this suit cost?
-
11.
?
How often do you talk to your son?
-
12.
?
Where do they hide their money?
-
13.
?
When do they usually meet for lunch?
-
14.
?
How long do you exercise every day?
-
15.
?
Where does Emma keep her diary?
Next ➔
Try this exercise as a worksheet
- Present Simple — Wh-question — Word order
Similar Exercises
- Present Simple with to be — Positive — Exercise 1
- Present Simple with to be — Positive — Exercise 2
- Present Simple with to be — Negative — Exercise 1
- Present Simple with to be — Negative — Exercise 2
- Present Simple with to be — Negative — Short forms