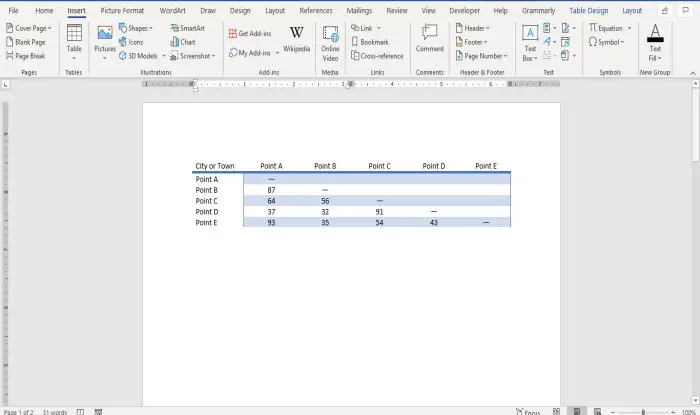
On Microsoft Word, tables are essential formatting tools. Microsoft Office has made it easier to create and format basic tables in Microsoft Word for Office 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, and Word 2013.
We haven’t covered tables as much as we would have liked to. It’s time to correct that, as the number of people asking questions on how to format tables properly is piling up. Maybe these eight table tips can be an appetizer. You just cannot create beautiful Microsoft Word documents by cutting corners on tables—here’s how to format tables in Word.
By the way, it’s possible to get a free copy of Microsoft Word, should you need one.
1. How to Make a Table in Microsoft Word
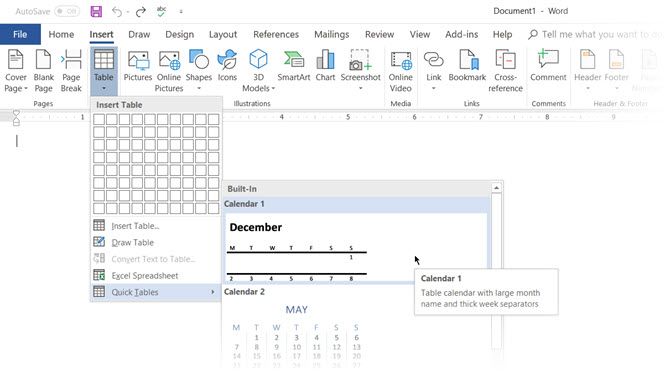
Using tables, and even changing them on the fly according to the data, has become far easier in the newer versions of Word such as Microsoft Word 2019 and Office 365. Intuitive Microsoft Word table formatting features give you finer (and quicker) control over how a table looks. But first head to the Ribbon > Insert > Table > Insert Table for making your first table.
It gives you five options for creating your first table.
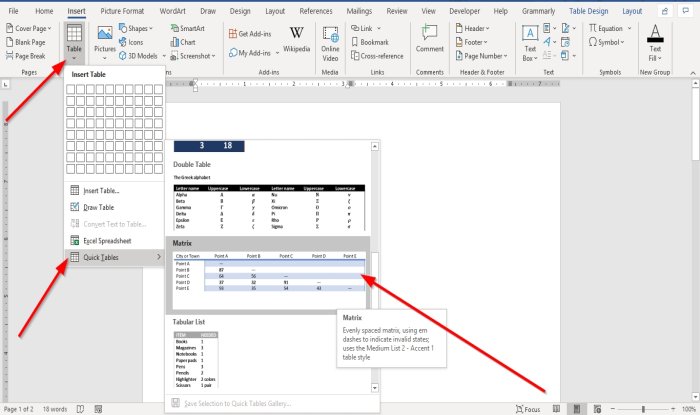
The quickest way to start is with Quick Tables. The built-in designs save you from the lack of design skills. You can modify the designs by adding your own rows and columns or deleting the ones you don’t need.
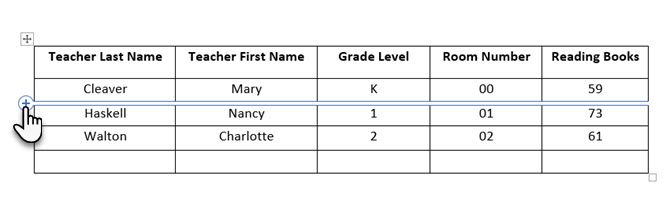
Another quick way to create a table in Word is the Insert Control feature. You can create a new column or row with one click. Hover the mouse over a table. A bar appears right outside your table between two existing columns or rows. Click on it when it appears, and a new column or row will be inserted at that position.
When you want to move or order a row around, use the combination of Alt+Shift+Up Arrow and Alt+Shift+Down Arrow to order the row up or down. Move contiguous rows by selecting them all first.
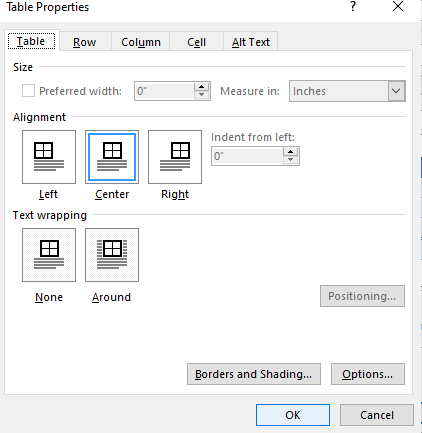
How to Use Table Properties to Position Your Table on the Page
If your tables are overlapping in Word, or you want to stop them from overlaying your text, then you need to learn how to position your tables on the page using the Table Properties feature.
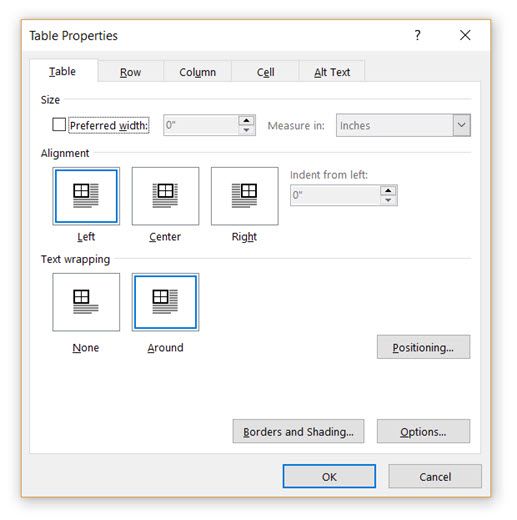
Right-click on the table and select Table Properties from the context menu. The Table Properties dialog box is for precise control over the data and its display. Control the size, alignment, and indentation of the table.
By default, Word aligns a table on the left. If you want to center a table on the page, select the Table tab. Click on Alignment > Center.
The Indent from left figure controls the distance of the table from the left margin.
Position the table according to the text around it for a visually aesthetic look. Wrap text around tables by dragging it by the handle. The text wrapping changes automatically from None to Around. From the Table Positioning dialog box, you can set the Distance from surrounding text for each side of the table.
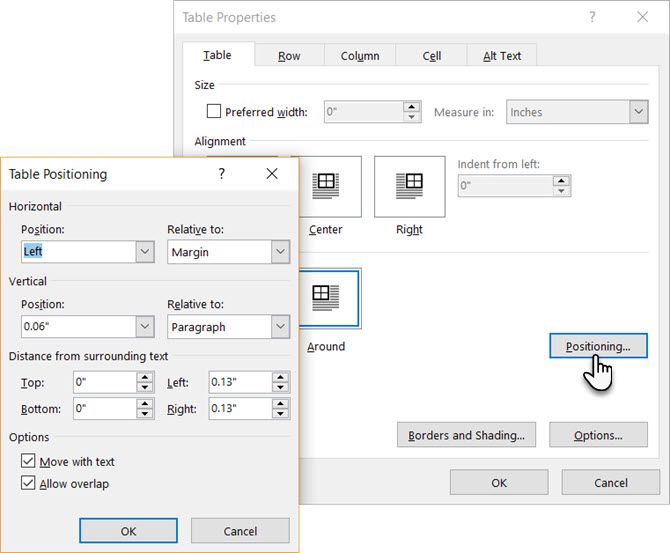
Select Move with Text if the text is directly related to the table data. The table is vertically aligned to the related paragraph around it. If the table data applies to the whole document, you can keep the option unchecked.
You can also control the tables with Microsoft Word keyboard shortcuts.
2. Use the Ruler
If you’re looking for an easy way to make tables look good in Word, then sizing tables and positioning them accurately is an art in itself. If you need precise measurements to size your rows and columns—use the ruler.
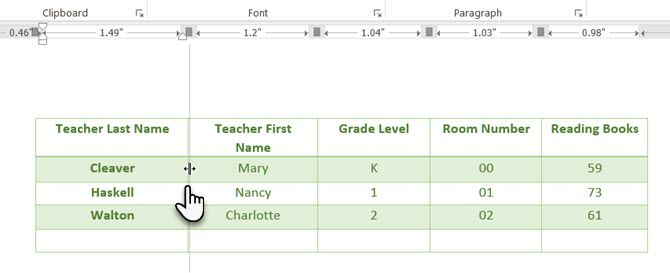
Hover the mouse over a border. When the double-arrow pointer appears, click the border and hold down the ALT key. Move the rows and columns to fit your measurements.
3. Convert Text to Table (and Vice Versa)
Tabular data gives information in its structure. It would have been frustrating if Word didn’t have something to handle non-tabular data. You can convert data to tables instantly from the Insert Table command.
Select the text. Go to Ribbon > Insert > Table > Insert Table.
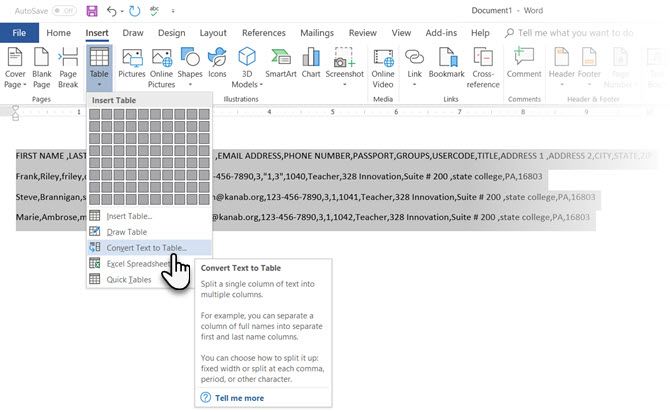
Microsoft Word determines the required number of rows and columns by considering the text separators and then auto-fits the contents. The Convert Text to Table dialog box allows you more control if the previous operation doesn’t work out right. You can also choose how to fit the contents of the table on the page.
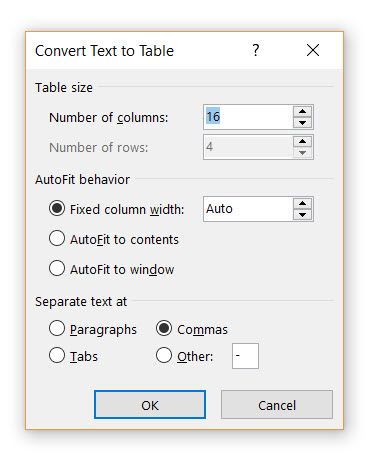
You can specify how Microsoft Word should separate the data into rows and columns. Paragraph, tabs, commas, or any other delimiting character. This allows you to easily import non-tabular data from CSV files or plain TXT files and convert them into formatted tables. Remember, you can also import data from Microsoft Word into an Excel spreadsheet.
Convert Table to Text
Engineer the reverse process if someone asks you to send them files with comma-separated values or any other delineator. Select the entire table by clicking the “move” handle above the table.
Go to Ribbon > Table Tools > Layout > In the Data Group, click Convert to Text.
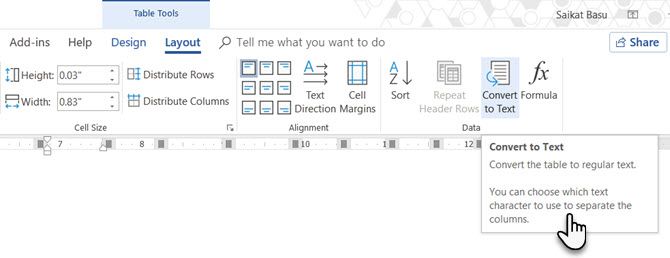
Simple text can be boring. When you have the chance, convert your table of data to a more visual chart instead with one of the underused features in Microsoft Word.
4. Auto-Fill Column Numbers
Microsoft Excel makes auto-filling a sequence of numbers very easy. Microsoft Word does not, and you may have to resort to a manual job. There is a simpler way.
Create a new column for the serial numbers if it does not exist. Select this column by positioning the mouse over the column.
With the column selected, go to Home > Paragraph > Click the Numbering button for inserting a numbered list.
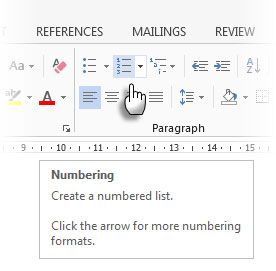
A number sequence is inserted in the column automatically.
5. Freeze Those Tables!
Microsoft Word tables change their dimension to accommodate new data. There may be times when you do not want the table to change size at all, even when new data is inserted. That is—“freeze” the size of cells.
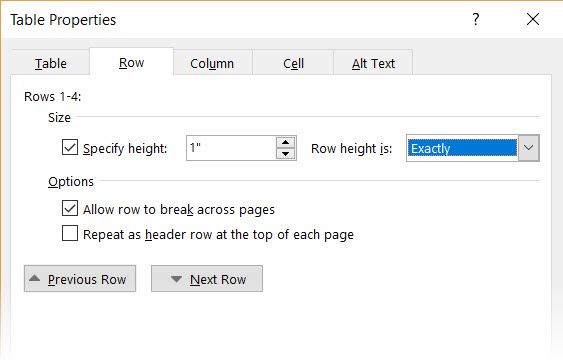
The first step is to specify a fixed size for the cells. Go to Table Properties > Row > Enter a value in the Specify height box. For Row height is select Exactly from the dropdown.
Now, select the Table tab > click the Options button > uncheck the Automatically Resize to Fit Contents check box.
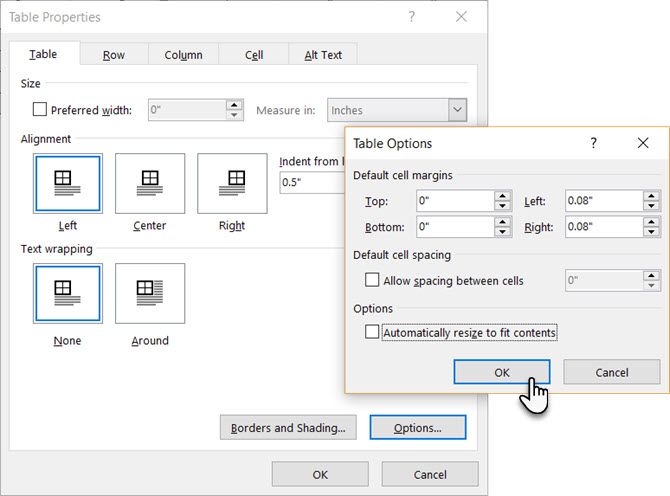
Click OK twice to exit the Table Properties dialog box.
This also solves the problem of inserting an image into a cell without the cell expanding to accommodate the image. If the image is bigger than the available space in the cell, it gets cropped to fit within the cell.
6. Change Rows Into Columns in a Table
There are situations where you have to change rows into columns and columns into rows. One possible scenario is where the number of columns exceeds the page margin. Switching columns around to rows and vice-versa is called transposition.
The bad news is that Word does not have an inbuilt method for handling this yet. Microsoft suggests that you copy-paste your table into Microsoft Excel and use its Transpose command. The transposed table can now be copy-pasted back into Microsoft Word.
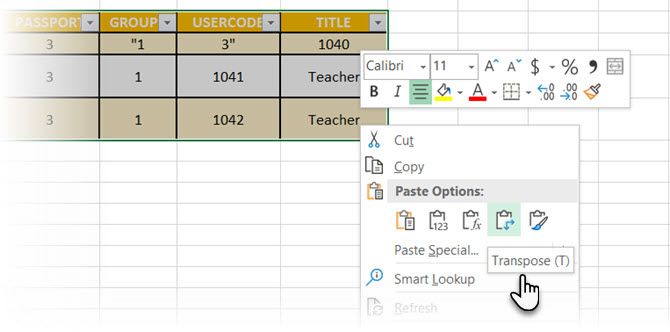
Data shows how easy it is in Excel with this short tutorial on switching rows into columns. Also, take the help of Microsoft’s Support Page if you run into a problem using the Transpose command.
7. Paste Perfect Excel Tables Into Gmail
You will find a use for this simple workaround. By default, Gmail does not retain the spreadsheet format when you paste from Microsoft Excel. To email tabular data without sending it as a separate attachment, use Microsoft Word as a bridge.
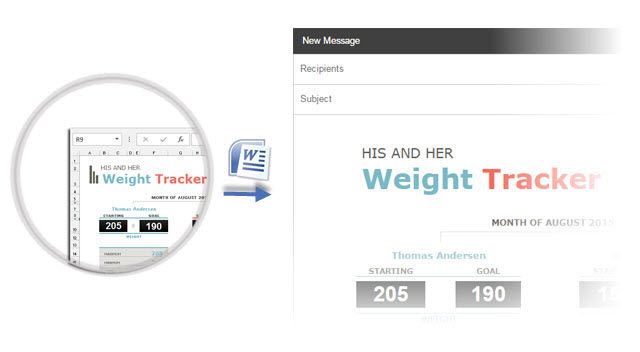
Select and copy-paste the Microsoft Excel table to a Microsoft Word document with the source formatting. Now, copy-paste from Microsoft Word to Gmail. As you can see from the screenshot, the problem is solved. You might have to tweak the more heavily formatted tables slightly, but most of the formatting is retained.
8. Reuse Your Tables to Save Time
You can save a lot of time by re-using tables in your professional Microsoft Word documents. Save empty table formats and insert new data when required. With this quick save, you won’t have to recreate the layout from scratch for new data.
Select a table. Go to Ribbon > Insert > Text group > click Quick Parts > Save Selection to Quick Part Gallery.
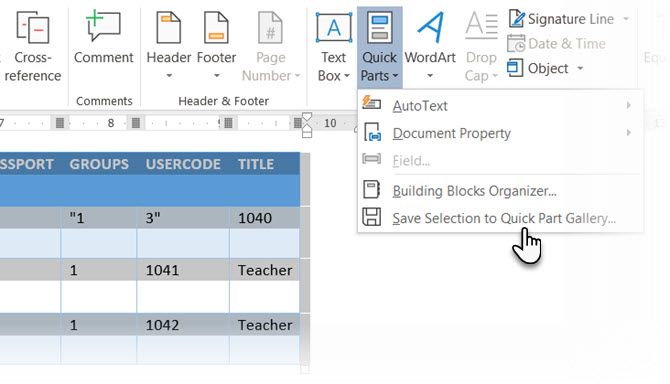
After you save a selection to the Quick Part Gallery, you can reuse the selection by clicking Quick Parts and choosing the selection from the gallery.
Use the Building Blocks Organizer to preview any table you created. You can also edit properties and delete the tables from here.
Do Microsoft Word Tables Confuse You?
These tips aren’t enough to cover the scope of formatting tables in Word. I haven’t talked about the role of the Design tab in creating eye-catching tables. That is a topic in itself. But it is one of the lesser areas to get confused over thanks to the visual help in that tab.
Working with tables in Word can be extremely rewarding. While tables are one common area between Microsoft Word and Excel, Microsoft Excel is more for power managing tabular data. Nonetheless, learning how to format tables well in both applications is an essential Microsoft Office skill. Use them at every opportunity.
Tables in Word are useful in so many situations. In this post you’ll discover how to create tables, then manipulate and design them in the quickest and easiest way to provide that visual punch.
Clickable Table of Contents
Enhance your Word tables with these advanced features
1. What are tables in Word good for?
Tables are useful for 2 distinct reasons.
- To show an actual table of data, or
- To organise and postion text, images and other elements on the page.
Many years ago, typewriters ruled the world. And a feature of a good typewriter was the tab stop, which was a device that essentially let you control indentation.
Over the years many people have continued to use tabs to indent text, because of its convenience, but they are hard work to set up properly.
Tables provide a much easier way to organise content on a page.
1. Select the Insert tab.
2. Click the Tables icon in the Tables group.
3. Move your mouse pointer into the table grid until the required number of rows and columns are highlighted orange, then left-click.
An empty table is inserted into the document.
Two new tabs, Design and Layout are also added to the ribbon area, under the banner of Table Tools.
3. MOVING AROUND A Word TABLE
- While the table is empty, you can use the cursor keys to move around the cells. However, when the cells contain information, using the cursor keys will move through the cell content first before moving to the next cell
- You can left-click in any cell to position the cursor.
- Press Tab to move to the next cell. The cursor will move across and then down the table.
- Press Shift + Tab to move to the previous cell.
NB. Using Tab is better than using the cursors as it will move to the next/previous cell regardless of whether there is information in the cells.
NB2. If you press Tab while you are in the last cell, a new row will be added to the bottom of your table
4. SELECTING A CELL, ROW, COLUMN OR THE ENTIRE TABLE
To select a cell:
1. Position the mouse pointer inside the cell on the bottom-left corner of the cell.
The pointer will change shape to a solid black arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
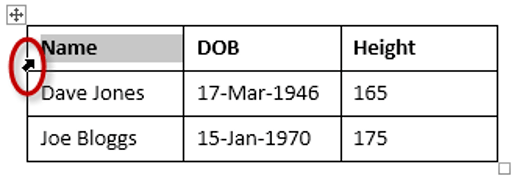
To select a row of a table:
1. Position the mouse pointer in the left margin in line with the row you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a white arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a column
1. Position the mouse pointer so that it rests on the top border of the table, above the column you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a solid black arrow pointing down.
2. Left-click.
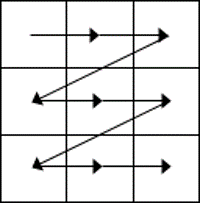
To select the entire table:
1. Position your mouse pointer over the 4-headed arrow icon situated at the top-left of the table.
2. Left-click.
5. INSERTING AN EXTRA ROW OR COLUMN
To insert an extra row:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Above or Insert Below in the Rows and Columns group
Here is a quick way to insert new rows:
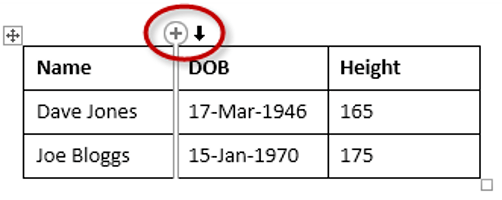
1. Position the cursor to the left of the table, but in close proximity.
2. A plus symbol will appear above or below the mouse pointer indicating where the new row will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer up or down to move the plus sign above or below.
4. Left-click to insert the new row,
To insert an extra column:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Left or Insert Right in the Rows and Columns group
Here is a quick way to insert a new column:
1. Position the cursor above a column, but in close proximity to the table.
2. A plus symbol will appear to the left or right of the mouse pointer indicating where the new column will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer left or right to move the plus sign to the left or the right of the column.
4. Left-click to insert the new column,
6. DELETING A ROW OR COLUMN
To delete the current row or column:
1. Position the cursor in any cell of the row you want to delete.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Delete icon in the Rows and Columns group.
4. Choose Delete Row or Delete Column from the drop-down menu.
7. Quickly fORMATTING tables in Word
Word provides you with a number of pre-set table designs. This means that it formats the headings and the data, applies a variety of borders and colours the cells in a way that makes it look like a professionally produced table. As a beginner this simple technique will give you a good-looking table.
1. Position the cursor in any cell in the table.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
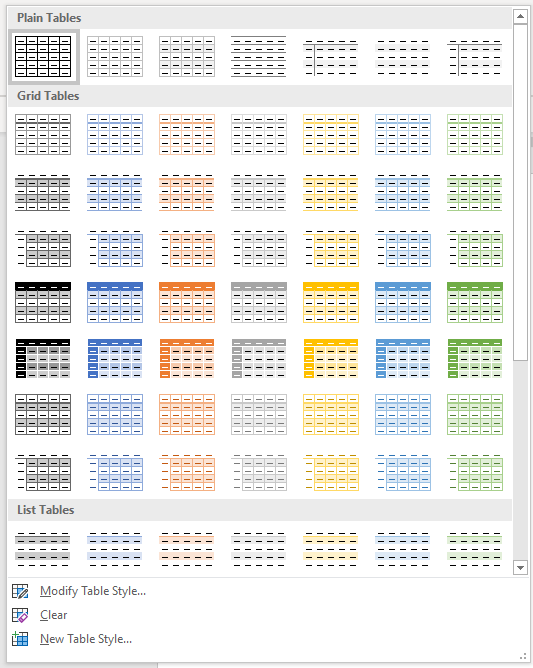
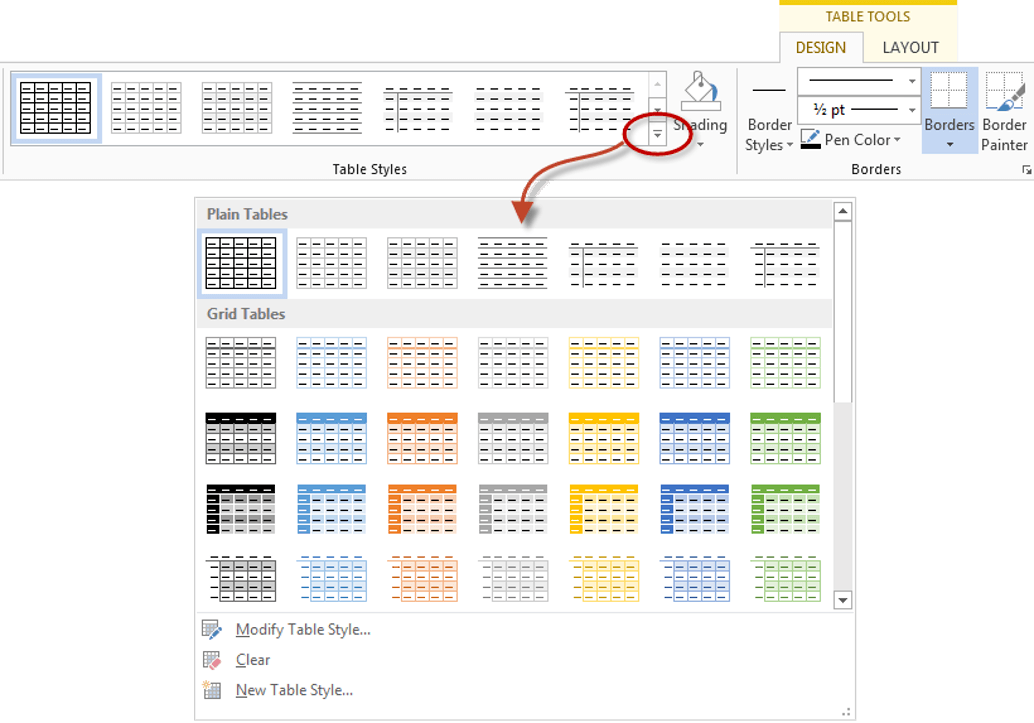
The Table Styles group lists a number of table designs. To get the full list, click the More button beneath the table styles scroll bar
The default table style is Table Grid in the Plain Tables category which adds simple gridlines but no shading to your table.
Live Preview allows you to hover over a design and see it applied to your table. If you like what you see, click to select the table design.
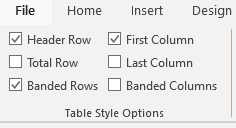
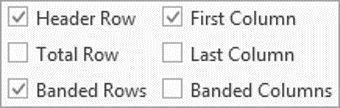
In the Table Style Options group of the Design tab, tick the components that you have in your table. For example, if your table has column headings, tick Header Row. In doing this, the various parts of your table are formatted accordingly
Header Row
This will emphasise the header row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Total Row
This will emphasise the bottom table row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
First Column
This will emphasise the first column (for labels etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Last Column
This will emphasise the last column (for row totals etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Banded Rows
This will make odd rows one colour and even rows a different colour. This helps readability.
Banded Columns
This will make odd columns one colour and even columns a different colour. This helps readability.
8. SETTING THE BORDERS AND SHADING
The Table Styles Gallery allows you to completely format a table with one click. Whereas you used to need some nous, anybody can now create a professional looking design.
However, you will often still need to apply your own border and shading, and manually change a table design. With a little effort can add a lot of flavour to your page and dramatically enhance the overall appearance of the document.
To set the borders for tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to set the borders for. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
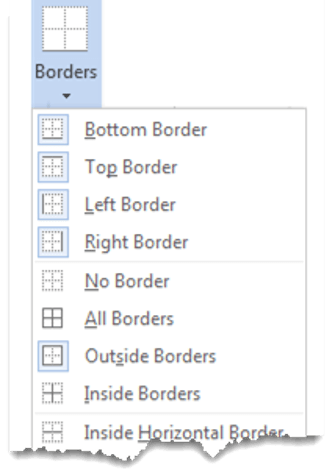
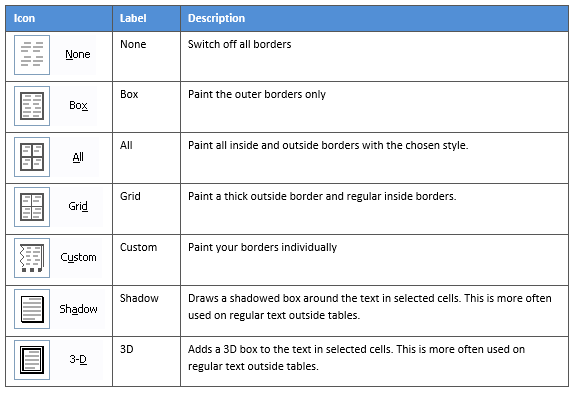
3. Select the Borders icon. A drop-down list appears. This list shows every combination of border that can be turned on or off. The icons with a shaded background are currently switched on. The rest are switched off.
4. Click any icon to switch the border on or off. The border style that is applied is the default style (½ pt solid black line ) or the last style that was used.
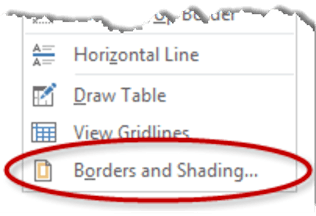
5. To apply customised borders, with different colours, styles and widths, click the Borders & Shading option at the bottom of the list to display the Borders and Shading dialog box.
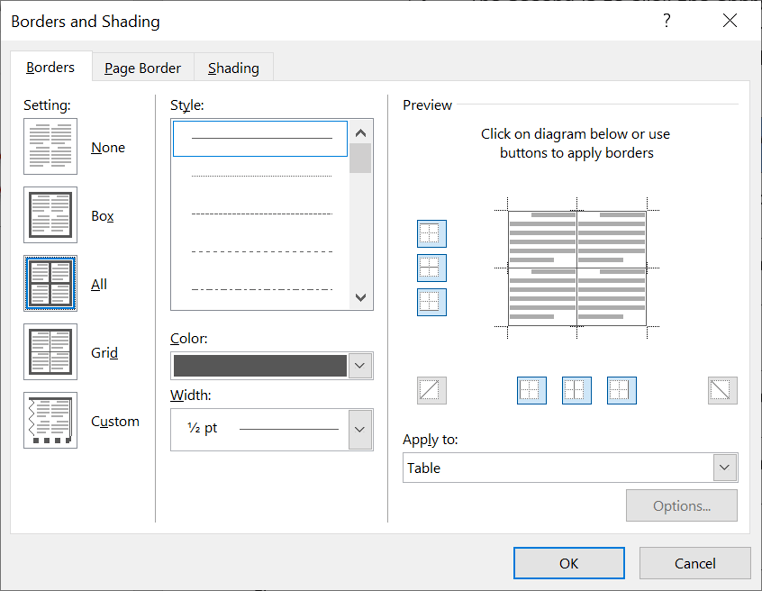
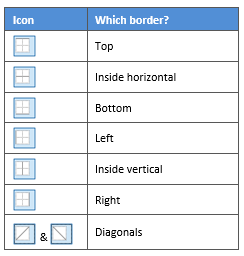
Your selection will always have an outer border, and if you selected more than one cell, you will have some inside borders as well. The easiest way to use the dialog box is to start on the bottom-middle and work your way up and right.
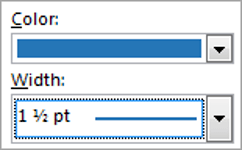
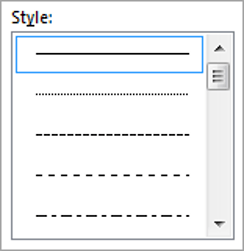
1. Select the colour and width (thickness) that you would like for your border.
2. Choose a style (e.g. dotted, dashed, double, solid etc.)
3. Paint your borders. There are two ways to do this.
- The first way is to click directly on a border in the Preview itself.
- The second way is to click the appropriate icon around the edge of the Preview section that represents each border. Depending on which cells you selected in your table, some of these icons may not be available.
On the left-hand side of the dialog box, there are some pre-defined border combinations which you can use to save yourself some time. Depending on your selection of cells, the pre-defined options may differ. Here’s a run-down:
To shade the cells of tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to shade. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
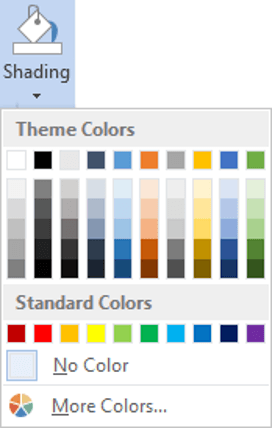
3. Click the Shading icon.
The colours that you see displayed match the current them of the document. Themes were discussed earlier in the course.
4. Click a colour in the palette.
While you can pick any colour, it is recommended to stick with the light colour shades, otherwise your tables will appear very loud and ugly, like they’re shouting in your face. Subtle is the order of the day. The exception to this is column headings or other cells that you wish to differentiate. Under these circumstances, you can use a dark colour, but use a light font with it.
If you cannot find the exact colour you need,
- Click the More Colours link underneath the palette. This displays a larger, more accurate colour palette.
- And if that’s not enough, click the Custom tab and you’ll get a really fine selection of colours (you can even enter your own RGB settings if you know them)
9. REPEATING table HEADINGS ON EVERY PAGE WHEN PRINTING
When you have large tables that occupy two or more pages, many people insert manual page breaks, then copy and paste their table header rows at the top of each page.
When rows are added or removed from tables in Word, the table headers end up half way down the page.
There is a simple tool that will eliminate this problem
1. Ensure that the table is a single table, with no manual page breaks in the middle, and one header at the top. The table header may occupy more than one row, it doesn’t affect the way this feature works.
2. Position the cursor somewhere in the top row of the table.
3. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
4. Click the Repeat Header Rows icon ion the Data group.
Now, it doesn’t matter how many rows tables in Word contain, if the table ever spills across into another page, the header row (which normally displays the column headings) will always appear at the top of the table.
10. All the key points again
- Tables in Word serve 2 distinct purpose: to display a table of data and to organise and position items on the page
- To create table, select 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- There are 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- You can press the TAB key to move direct to the next cell and SHIFT and TAB together to move backwards through a table.
- The four elements of a table are cells, rows, columns and the whole table. Each can be selected.
- Rows can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert Above or Insert Below icons. Alternatively, hover to the left of a row and click the plus symbol that appears above or below the mouse pointer.
- Columns can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert
Left or Insert Right icons. Alternatively, hover above a table column and click the plus symbol that appears to the left or right of the mouse pointer. - Columns and rows and be removed from the table, by positioning the cursor in the row or column to be removed, then clicking the Delete icon on the Layout tab of Table Tools and choosing Delete
Row or Delete Column. - Tables can be formatted using the Table Style gallery or by manually setting the shading and borders manually. Both sets of tools are found on the Design ribbon of the Table Tools.
- When using the Microsoft Table Styles, you can control the behaviour of the formatting by setting the Table Style options – 6 tick boxes that define the structure of your table.
- For long tables that spill across onto subsequent pages, the top row, which normally contains the column headings can be set to repeat automatically. So there is no excuse for cutting and pasting headings midway through your table or taping pages together to make sense of the table!
I hope you found plenty of value in this post. I’d love to hear your biggest takeaway in the comments below together with any questions you may have.
Have a fantastic day.
About the author
Jason Morrell
Jason loves to simplify the hard stuff, cut the fluff and share what actually works. Things that make a difference. Things that slash hours from your daily work tasks. He runs a software training business in Queensland, Australia, lives on the Gold Coast with his wife and 4 kids and often talks about himself in the third person!
SHARE
Are you struggling to get your message across? When your Microsoft Word project contains information, try presenting it in the form of a Word table. Learn how to make tables in Word quickly with a template.
A table is a kind of chart that organizes and presents data in rows and columns. It makes information easier to grasp, understand, and analyze at a glance, compared to explaining the same data through plain text.
Microsoft Word gives you various ways to insert or create a table. And you’ve got granular control over the formatting, layout, and appearance of Microsoft Word tables. Table charts are useful in different types of Word projects, whether for personal, educational, or business use.
This article will show you how to make a table in Word using a template. Then edit and format it to change its appearance.
(Note: The screenshots and instructions that follow are made using Microsoft Word for Mac version 16.4. If you’re using a different version of Word, then the interface and steps may be different.)
How to Make & Edit MS Word Tables (Video)
In this video, you’ll learn how to quickly make tables in Mircosoft Word. Find out how to start with a premium template. Quickly customize it to make an attractive, professional MS Word table you can use and reuse.
To learn even more about MS Word tables and about templates than can be used for tables, study the step-by-step tutorial below:
How to Make Basic Tables in Word
Let’s start by learning how to make a basic table in Microsoft Word:
1. Insert a Table
You can create a basic Microsoft Word table in one of two ways:
Method 1. The Insert Tab
Click on the Insert tab, then click the Table button on the ribbon.
The Insert Table panel appears. Drag the cursor over the squares to specify the number of columns and rows you want to create. Click to apply.
Method 2. The Insert Menu
Go to Insert > Table….
The Insert Table panel opens. Specify the number of columns and rows you need. (You can always add or remove columns and rows later.)
Also select the Autofit Behavior you want the table to have. You’ve got several options:
- Initial column width. The default setting is Auto, which divides the entire width of your page window across the number of columns in the table. Or, you can specify a different column width.
- AutoFit to contents. Resizes the column width based on the width of the content inside the column.
- AutoFit to window. Distributes the columns equally across the entire width of the page window.
- Set as default for new tables. Check this option if you want the settings to be applied globally to all new tables you create.
When you’re happy with the options you’ve selected, click OK.
2. Draw a Table
Or, you can draw a table in MS Word. This is a useful feature if you want to create an irregular or more complicated table with columns and/or rows of varying widths.
To draw a table, click Insert > Table > Draw Table.
With your mouse or trackpad, click and drag the cursor to start drawing your table. You can begin by drawing the outermost boundary of the table first.
Then, click and drag the cursor to create columns and rows inside the table. When you’re done, click anywhere outside the table.
Here’s an example of an “irregular” table you can draw using this feature.
If you make a mistake, click Layout > Eraser to erase a line from the table.
Click and drag the eraser along the line you wish to erase. The line that’ll be erased appears as a thick, red line. Release the mouse or trackpad to erase.
Click outside the table when you’re done.
3. Convert Text to Tables and Vice Versa
Another way to create a table is by converting text into a table. This means you can take non-tabular data from a CSV or plain TXT file and convert them into a table.
First, copy and paste the non-tabular data into your Word document.
With the text selected, go to Insert > Table > Convert Text to Table….
The Convert Text to Table panel opens. Specify the settings you wish to use. Click OK.
The text is then converted into a table.
You can also do the opposite, which is to convert a table into text.
Select the cells or entire table you want to convert. Next, click on the Layout tab then click the Convert Table to Text icon.
The Convert Table to Text panel opens. This is where you’ll decide how you want to separate text that’s currently in different columns. When you’ve made a selection, click OK.
For this example, I chose to separate text with commas. This is what the converted table looks like.
4. Advanced: How to Insert a Table from Excel
If you’ve already created a table in Excel, you can embed it into your Word document.
Open the Excel file. Click and drag the mouse to select the table.
Go back to your Word document. Go to Edit > Paste Special ….
In the Paste Special panel, select Microsoft Excel Binary Worksheet Object, then click OK.
This embeds the Excel table into Word. It’s still an Excel table, which means you can’t edit or format the table in MS Word. You’ve got to do so in Excel.
Double-click anywhere in the table to launch the source file in Excel. When you make any changes to the table in Excel, the table embedded in your Word project automatically updates to reflect those changes.
Now you know how to make a table in MS Word using various options.
How to Edit Tables
At any time after creating your table, you can edit and customize it to look the way you want it to. Here are some steps for editing tables in Microsoft Word:
1. Add a Column or Row
To add a row or column, click inside a table cell. Right-click on the mouse, then click Insert.
Select one of the following:
- Columns to the Left. Adds a column to the left of the current column
- Columns to the Right. Adds a column to the right of the current column
- Rows Above. Adds a row above the current row
- Rows Below. Adds a row below the current row
- Cells … Inserts a cell and shifts the rest of the cells either to the right or down from where the cursor is
- Table … Inserts a table inside the current cell
Or, with the cursor in one of the cells, you can click on the Layout tab.
Then choose of the following buttons on the ribbon:
- Insert Above. Inserts a row above the current cell
- Insert Below. Inserts a row below the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Left. Inserts a column to the left of the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Right. Inserts a column to the right of the current cell
Finally, you can add a new row when you’ve reached the last cell in the last row of your table. Simply press tab and a new row appears.
2. Delete a Column or Row
To delete a cell, column, row, or table, click on the Layout tab > Delete.
Select one of the options that appear:
- Delete Cells …
- Delete Columns
- Delete Rows
- Delete Table
You can use the same steps to edit a table you’ve drawn. Or, you can use the Layout tab to add or delete rows and columns.
Merge Cells
Sometimes you may want to merge cells to present information more clearly. To merge cells, click and drag the cursor to select the cells you wish to merge.
On the Layout tab, click on the Merge Cells button.
Or, after selecting the cells to be merged, right-click on your mouse, then click Merge Cells.
Now the cells have been merged into one.
Split Cells
After merging cells, you can always split them again into separate cells.
Place the cursor in the merged cell, then click Layout > Split Cells.
Or, right-click on your mouse, then click Split Cells….
Either way, the Split Cells panel pops up. Specify the number of columns and rows you want to split the cell into. Click OK.
Split Table
You may decide that it makes more sense to split up a table into two separate tables. Microsoft Word lets you do that easily, too.
In this example, I want to split the table right above the Accessories cell. And so, I’ll place the cursor in that cell. Next, click on the Layout tab, then click the Split Table button.
Now, we’ve got two separate tables.
Table Formatting
When you first create a table, it looks plain and boring. But Microsoft Word has many features so you can format tables to look exactly the way you want them. Here are some common ways to format tables:
1. Table Styles
The easiest way to format a table is by using one of the pre-formatted table styles. Put the cursor in any cell in the table. Click on the Table Design tab. Next, click on the arrow to expand the Table Styles group.
Click on a style you want to use and it’s applied immediately.
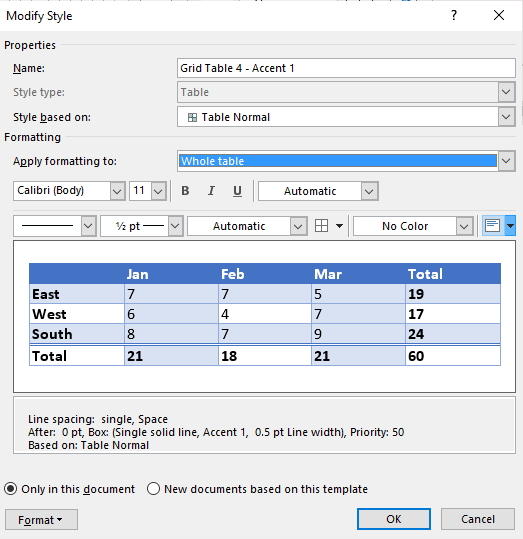
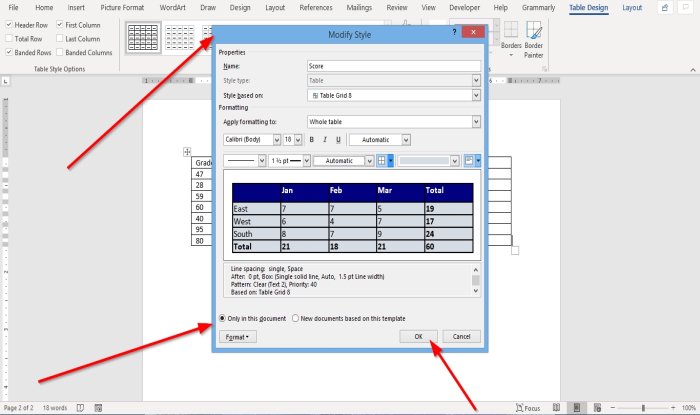
You can change any style you’ve selected. Again, click on Table Design, expand the Table Style group, then click Modify Style.
The Modify Style panel opens. Make the selections you want, then click OK.
2. Use Your Own Formatting
The Table Design tab gives you control over the appearance of every aspect of your table. Click on the Table Design tab and any of the appropriate buttons on the ribbon.
Resize a Table
You can also resize your table. Click on any cell to select the table, then click and drag one of the corners to resize it.
Or, you can use the Layout tab to resize individual cells, specific rows or columns, or the entire table. Select the columns or rows you wish to resize. Specify the height and/or width you wish to apply.
You can also adjust column width by hand by using the Table Ruler. Click inside a column you want to change. Then, drag the sliders in the Table Ruler to set to desired width.
Text Wrapping
If you want text to flow around the table, you can do so by changing its text wrapping.
Click in any cell to select the table. Click Table > Table Properties….
In the Table Properties panel and under Text Wrapping, click Around > OK.
Now the text flows around the table.
Take note that the Table Properties panel allows you to format other qualities of the table, including:
- Size
- Alignment
- Positioning
- Borders and Shading
On the other tabs, you can change:
- Column, Row, and Cell Size
- Allow row to break across pages
- Repeat as header row at the top of each page
- Cell Vertical Alignment
- Alt Text (Title and Description) — more information about the table, to help people with vision or cognitive impairment who may not see the table
Find Great Styles for Microsoft Word
You don’t have to start from scratch to create an impressive and effective Word document — even if you don’t have design skills. You can find great styles by using a template for Word.
One great source for great Microsoft Word templates and professional graphics is Envato Elements. For one low monthly subscription, you get unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, fonts, and other creative tools you need for your project. It’s a terrific option if you create plenty of materials.
For single projects, GraphicRiver is an outstanding source for templates for Word. This marketplace gives you access to thousands of creative elements on a pay-per-use basis.
Learn More
Microsoft Word has many robust features to help you realize the vision you’ve got for your document. But with power comes complexity. That’s why it’s a good idea to learn how to use Microsoft Word.
These articles will help you get started:
Visualize Your Data with Microsoft Word Tables
Make your information clearer and easier to understand by learning how to make a table in Microsoft Word. Tables organize data into rows and columns, which makes them easier to grasp at a glance. Follow the steps in this article to create, format, and customize tables in Word.
You can also use a premium Word template to get a premium design created by designers. Get Word templates from Envato Elements, if you want unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, and other creative tools you need — all for one flat monthly fee.
Or, get premium templates for Word from GraphicRiver if you prefer to pay for each use of an item. Both sources give you access to thousands of design elements created by professionals, so you can save time, energy, and effort while creating an outstanding Word document.
Did you find this post useful?
Marketing & Communications Professional and Lifelong Learner/Canada
Lexi Rodrigo is a marketing and communications professional, copywriter, and course creator who helps remarkable brands and people get seen, heard, and known. Writing for the web since 2008, she has over 100+ blog posts published on Envato Tuts, Acadium, Mirasee, Vero, Copyblogger, FreelanceFolder, Business2Community, and others.
Lexi has supported multimillion-dollar companies and nonprofits in various marketing and communication roles. She has driven results like tripling the organic search traffic of a blog in three months and generating over $65 million in revenues, donations, and sponsorships.
She has a Bachelor of Arts degree in communications. She is also the co-author of «Blog Post Ideas: 21 Proven Ways to Create Compelling Content and Kiss Writer’s Block Goodbye.» When she’s not reading or writing, Lexi bakes bread, grows food, and takes long walks.

What you may not know is how easily you can take your tables from basic (and boring) to impressive and eye-catching.
Transform your tables
Tables in published journals usually look far superior to those in the average business document.
But it is perfectly possible to transform Word’s default tables into ones that are every bit as impressive as those produced by the big publishers. And in doing so, you can really lift your documents, to make them much more engaging.
You can do this without stepping outside of Word. And – here’s the best bit – you don’t need a degree in graphic design or to be a Microsoft Office ninja to do so. Far from it.
Watch the video to see how you can transform your tables, step by step:
This post is taken from a lesson in our online-training programme Emphasis 360, which improves your writing in practical, bite-sized weekly lessons. You can find out more about Emphasis 360 and preview more lessons for free here.
Image credit: Your Design / Shutterstock


Author: Rob Ashton

Rob Ashton (our founder) posts mainly about writing and the brain – a topic he’s been researching for seven years. His personal website includes a free course based on his work.
Comments
Here’s eight better but simple table formatting options not available from Microsoft Word’s Table Style gallery.
Word’s Table Style gallery is a tempting selection of table formats but it doesn’t show you all the options to make your table look good. Some of these variations are right there on the ribbon, others are buried a bit deeper.
All the Office galleries have a problem. They are too easy and greatly overused. Tweaking a Word table style makes your document look different.
The Table Style options are just to the left of the Table Style gallery on the Table | Design ribbon.

Select the options you want and the gallery thumbnails will change to show an example.
Column banding
There are plenty of row banding (alternate shading of rows) in the gallery but default to the column banding choice so it’s not used as often.

You can turn on both row and column banding though the result isn’t usually very helpful.

Last row / column formatting
The other choices on the Table Style options are formatting the last row or column. This will highlight summary or totals.

Vertical Centering
As well as Left, Center and Right formatting there are also vertical options to position items ‘up and down’ within a cell. Choose from Top (default), Bottom or our favorite, Middle.
Look at the data cells in this example where the numbers are at the top of each cell, out of alignment with the row headings.

On the Table | Layout tab there are nine cell layout options to choose from. The middle row has the middle / vertical center options with left, center or right alignment.

Which gives you a nicer look like this:

The middle option is especially good when there’s an extra-large cell (e.g. comments ) which is out of proportion with the rest of the row.

Cell lines
Most of the Table Styles have white lines between cells (top table) but you can change that to another color or the background color (bottom table):

To change that, select the rows or entire table then choose Inside Borders and a Pen Color.

You can also change the border style to a thicker or double line.
Table Width
A default Word table takes up 100% of the page width but that’s not always needed.
Quickly reduce the table width by dragging the table handle at bottom right.
For a more precise adjustment go to Table Properties and change the Preferred Width to either a fixed width or a percentage of the page width.

Table Position
Also on the Table Properties are options to position the table on the left, center or right of the page.

Autofit
Most likely the column widths won’t match the contents since the defaults are equal widths for each column.
Right-click on the table and choose Autofit to see some options.

The problem with autofit contents is that you’ll end up with varying widths for common columns. In this example each autofitted column is a different width due to large variations in the cell values.

More likely you’ll want all the data columns (not label or comments) to have the same width. Do that by selecting the columns then setting a fixed width from the Table Layout Tab or click on the icon to the right of the width field which will autofit by making all the columns the same width within the entire width selected (called ‘Distribute Columns’).

Fonts
The Table Style gallery doesn’t change the font of any cell content.
Consider changing the row/column headings to match the font of document headings. The data cells can use the Normal or regular text font.
After you create a table, Microsoft Office Word 2007 offers you many ways to format that table. If you decide to use Table Styles, you can format your table all at once, and even see a preview of what your table will look like formatted in a particular style before you actually apply the style.
You can create a custom look for tables by splitting or merging cells, adding or deleting columns or rows, or adding borders. If you’re working with a long table, you can repeat the table headings on each page on which the table appears. To prevent awkward page breaks that disrupt the flow of your table, you can also specify just how and where the table should break across pages.
What do you want to do?
-
Use Table Styles to format an entire table
-
Add or remove borders
-
Display or hide gridlines
-
Add a cell, row, or column
-
Delete a cell, row, or column
-
Merge or split cells
-
Repeat a table heading on subsequent pages
-
Control where a table is divided
Use Table Styles to format an entire table
After you create a table, you can format the entire table by using Table Styles. By resting your pointer over each of the preformatted table styles, you can preview what the table will look like.
-
Click in the table that you want to format.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, rest the pointer over each table style until you find a style that you want to use.
Note: To see more styles, click the More arrow
.
-
Click the style to apply it to the table.
-
In the Table Style Options group, select or clear the check box next to each the table element to apply or remove the selected style.
Top of Page
Add or remove borders
You can add or remove borders to format a table the way that you want.
Add table borders
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Select, and then click Select Table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then do one of
the following:-
Click one of the predefined border sets.
-
Click Borders and Shading, click the Borders tab, and then choose the options that you want.
-
Remove table borders from the whole table
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Select, and then click Select Table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click No Border.
Add table borders to specified cells only
-
On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Show/Hide.
-
Select the cells that you want, including their end-of-cell marks.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click the border that you want to add.
Remove table borders from specified cells only
-
On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Show/Hide.
-
Select the cells that you want, including their end-of-cell marks.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click No Border.
Top of Page
Display or hide gridlines
Gridlines show the cell boundaries of a table on the screen wherever the table doesn’t have borders applied. If you hide the gridlines in a table that has borders, you won’t see the change because the gridlines are behind the borders. To view the gridlines, remove the borders.
Unlike borders, gridlines appear only on the screen; they are never printed. If you turn off gridlines, the table is displayed as it will be printed.
Note: Gridlines are not visible when you view a document in a Web browser or in Print Preview.
Display or hide table gridlines in a document
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Table group, click View Gridlines.
Top of Page
Add a cell, row, or column
Add a cell
-
Click in a cell that is located just to the right of or above where you
want to insert a cell. -
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, click the Rows & Columns Dialog Box Launcher.
-
Click one of the following options:
|
Click this |
To do this |
|
Shift cells right |
Insert a cell and move all other cells in that row to the right. Note: This option may result in a row that has more cells than the other rows. |
|
Shift cells down |
Insert a cell and move remaining existing cells in that column down one row each. A new row will be added at the bottom of the table to contain the last existing cell. |
|
Insert entire row |
Insert a row just above the cell that you clicked in. |
|
Insert entire column |
Insert a column just to the right of the cell that you clicked in. |
Add a row
-
Click in a cell that is located just below or above where you want to add a row.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a row just above the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Above.
-
To add a row just below the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Below.
-
Add a column
-
Click in a cell that is located just to the right or left of where you want to add a column.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a column just to the left of the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Left.
-
To add a column just to the right of the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Right.
-
Top of Page
Delete a cell, row, or column
-
Do one of the following:
To select
Do this
A cell
Click the left edge of the cell.
.
A row
Click to the left of the row.
A column
Click the column’s top gridline or top border.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Rows & Columns group, click Delete, and then click Delete Cells, Delete Rows, or Delete Columns, as appropriate.
Top of Page
Merge or split cells
Merge cells
You can combine two or more cells in the same row or column into a single cell. For example, you can merge several cells horizontally to create a table heading that spans several columns.
-
Select the cells that you want to merge by clicking the left edge of a cell and then dragging across the other cells that you want.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Merge Cells.
Split cells
-
Click in a cell, or select multiple cells that you want to split.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Split Cells.
-
Enter the number of columns or rows that you want to split the selected cells into.
Top of Page
Repeat a table heading on subsequent pages
When you work with a very long table, it will be divided wherever a page break occurs. You can make adjustments to the table so that the table headings are repeated on each page.
Repeated table headings are visible only in Print Layout view and when you print the document.
-
Select the heading row or rows. The selection must include the first row of the table.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Data group, click Repeat Header Rows.
Note: Word automatically repeats the table headings on each new page that results from an automatic page break. Word does not repeat a heading if you insert a manual page break within a table.
Top of Page
Control where a table is divided
When you work with a very long table, it must be divided wherever a page break occurs. By default, if a page break occurs within a large row, Microsoft Word allows a page break to divide the row between the two pages.
You can make adjustments to the table to make sure that the information appears as you want it to when the table spans multiple pages.
Prevent a
table row from breaking across pages
-
Click in the table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Properties, and then click the Row tab.
-
Clear the Allow row to break across pages check box.
Force a table to break across pages at a particular row
-
Click in the row that you want to appear on the next page.
-
Press CTRL+ENTER.
Top of Page
Create, Modify and Apply Table Styles in Word Documents
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated August 21, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021 or 365 (Windows)
You can apply table styles to your Word tables to format them quickly and consistently. Word is shipped with several built-in table styles or you can create your own. You can edit table styles by modifying borders, shading, character formatting, paragraph formatting and table properties. If your document includes multiple tables, table styles can save a lot of time.
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For newer versionns of Word, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names. For example, the Table Tools Design tab may appear as Table Design.
Recommended article: How to Keep a Microsoft Word Table Together on One Page
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or live classroom Word courses >
Table styles and themes
Every Word document uses a document theme which includes a font theme and color theme. The colors used in table styles are based on the color theme.
You can select document themes, color themes and font themes using the Themes, Colors or Fonts drop-down menus on the Design tab in the Ribbon:
You can also create your own custom color themes so your tables can be formatted using your organization’s colors.
Display gridlines
When you are working with tables, it’s a good idea to turn gridlines on. Borders, which are a format, will print. Gridlines do not print.
To display gridlines:
- Click in a table.
- Click the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab.
- Click View Gridlines. Gridlines will stay on for all Word documents.
View Gridlines appears on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab when you click in a table:
Apply a table style
If your Word document contains multiple tables that you want to format in a consistent way, it’s best to use table styles rather than applying manual or direct formatting to each table.
To apply a table style to a table:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Hover over the various table styles. The table formatting will change as you move over different table styles in the gallery.
- Click the table style you want to apply.
Below is the Table Styles gallery (the current theme is the Office theme):
Note: Table styles do not include row height, column width or custom cell formatting for individual cells. If a user applies manual or direct formatting to a table (such as fills and borders) on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab, this formatting will override the table style.
Apply Table Style Options
Once you have selected a table style, you can select or check different Table Style Options (which are affected by the formats in the selected table style).
The six Table Style Options that you can apply are: Header Row, Total Row, Banded Rows, First Column, Last Column and Banded Columns. If you have selected a plain table style, you may not notice any changes in the table formatting if you select different Table Style Options.
Table Style Options appear on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab as follows when you click in a table:
To select Table Style Options:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Header Row. If this option is checked, the header row will be formatted differently from the body rows.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Total Row. If this option is checked, the last row will be formatted differently from the body rows.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Banded Rows or Banded Columns for alternate row or column shading.
- In Table Style Options, check First Column or Last Column if you want the first or last column formatted differently from the other columns.
In the following table, Header Row and Banded Rows are checked in Table Style Options:
Modify a table style
You can modify a table style in a Word document and all tables using that table style will change.
To modify a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Modify Table Style. A dialog box appears. You can also right-click a table style and select Modify.
- From the Apply Formatting to drop-down menu, select the element that you want to modify (such as Header row).
- Select the desired formatting such as font, font size, font color, fill and border.
- From the Apply Formatting to drop-down menu, select the next element that you want to modify.
- Select the desired formatting such as font, font size, font color, fill and border.
- Repeat for other elements.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template. If you select Only in this document, the modified style will only be available for the current document. If you select New documents based on this template, then the table style will be modified for future documents based on the current template (usually the Normal template).
- Click OK.
Below is the Modify Style dialog box:
You can also click Format at the bottom of the dialog box and choose other options such as Font or Paragraph.
If you modify a table style and the tables using that style do not change, it’s likely that direct or manual formatting has been applied to the table which then overrides the table style. You may need to clear formatting in the table by selecting the table and clicking Clear Formatting on the Home tab in the Font group.
You can also modify Table Properties in a table style. Table properties include table alignment, row settings and cell margins.
To modify Table Properties in a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Modify Table Style. A dialog box appears. You can also right-click a table style and select Modify.
- Click Format on the bottom left of the dialog box. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Table Properties. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Table tab and select an Alignment.
- Click the Row tab and select the desired options. For example, turn off Allow row to break across pages.
- Select any other formatting options you want to apply to the entire table.
- Click OK.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template.
- Click OK.
Below is the Table Properties dialog box with the Table tab selected:
Create a new table style
You can also create a new or custom table style.
To create a custom table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click a table style to apply it as a base style.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click New Table Style. A dialog box appears.
- Enter a name for the new table style in the Name box.
- Select the desired formatting.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template.
- Click OK.
New Table Style appears at the bottom of the Table Styles gallery:
The new table style will appear in the Table Styles gallery under Custom (at the top of the gallery). If you want to delete it, right-click it in the gallery and select Delete Table Style.
Clear a table style
To clear a table style and remove formatting:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Clear.
Clear appears at the bottom of the Table Styles gallery:
Set a default table style
You can also set a default table style for new tables in the current document or all new documents.
To set a default table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Right-click the table style you want to use as the default style and select Set as Default from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Select This document only or All documents based on the Normal.dotm template (the default template in Word is the Normal template).
- Click OK.
If you are working with documents with multiple tables, formatting with table styles can ensure that your tables are formatted consistently and save a lot of time.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.
More resources
4 Ways to Create a Table in Word
14 Shortcuts to Quickly Select Text in Microsoft Word
How to Create Headings in Word (Using Heading Styles)
How to Quickly Remove Hard Returns in Word Documents
10 Microsoft Word Tips, Tricks and Shortcuts for Selecting in Tables
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
Download PC Repair Tool to quickly find & fix Windows errors automatically
A table is an information systematically arrange in rows and columns. Make Tables in Word look good! Microsoft Word offers features that can format a table, such as the built-in Styles. The built-in Styles provide the user with various colors, shading, borders, text, and other features to give the table a professional and unique look. The table can be preformatted using the Quick Table Tool too.
A Quick Table Is a feature offered by Microsoft Word. The Quick Table defined as a preformatted table that consists of sample data that the user can customize.
1] Using the Built-in Table Styles
Open Microsoft Word.

If you already have an existing table in the document, click the table in the document.
A Table Design tab will appear on the menu bar; click the Table Design tab.
On the Table Design tab in the Table Styles group, you will see a display of Built-in Table Styles samples, click the drop-down arrows, and see more styles and select the style you desire.
In the Built-in Styles drop-down list, you can modify the table by clicking Modifying Table Style.
A Modify Style dialog box will appear.
Inside the Modify Style dialog box, you have options to name, Style, Apply Format, customize the Font and Size of the text, customize the Border Style, Thickness, Alignment, and Color of the table’s border, within the table.
You can choose the Formatted table only in this document or A new document based on this template options at the bottom of the dialog box.
You can further customize the table by clicking the Format button at the bottom left of the dialog box.
Then click Ok.
Now we have a table with style in our document.
In the Built-in Styles drop-down list, you can click Clear to clear out the table or click New Table Styles to open the Modify Style dialog box to customize the table’s style.
2] Using the Quick Table tool
Go to the Insert tab.
In the Table group, click the Table button; in its drop-down list, Point your cursor on Quick Tables, you will find various built-in quick table styles in its gallery. Choose a quick table style from the gallery.
A Preformatted table will appear in the document where you can make changes.
I hope this helps; if you have questions, please comment below.
Read next: How to display and work with multiple windows in Word.
Shantel has studied Data Operations, Records Management, and Computer Information Systems. She is quite proficient in using Office software. Her goal is to become a Database Administrator or a System Administrator.
Note: This article is also available as a download.
By
default, inserting a table into a Word document gets you a grid. Which is fine.
At least Word isn’t second-guessing you and applying its own format or foisting
some overbearing wizard on you. And if you’re after structure rather than
design, that grid is all you need. But when you want to move beyond utility and
create an attractive element on the page, you need to know a few formatting
tricks.
Word
comes well supplied with features for jazzing up tables–maybe too many, in
fact, empowering users to produce some fairly hideous results. Other users
steer clear of table formatting completely after a few failed attempts to put a
border where they want it or change a column width without disrupting the table
dimensions. Here are a few simple techniques that will enable your users to quickly
improve the appearance of their tables without going overboard or wasting time
with confusing options.
#1: Align the
table on the page
Even
if you keep the table formatting simple, its placement can make or break the
overall page layout. The simplest positioning trick involves horizontal
alignment: left, center, or right. And the easiest way to manipulate the
alignment is to select the table (Table | Select | Table) and click the
appropriate button (Align Left, Center, Align Right) on the Formatting toolbar,
just as you would do to align regular text. Or use the keyboard shortcuts:
[Ctrl]L, [Ctrl]E, [Ctrl]R. (The Table Properties dialog box offers the same
options, but this way is quicker.) The key here is to make sure the whole table
is selected. If only certain cells are selected, these options will apply to
the text inside those cells rather than to the table.
#2: Wrap text
around the table
In
the old days, you had to put a table inside a frame to have text wrap around
it. The process is much easier now: Choose Print Layout from the View menu and
click on the table to display its move handle. Then, click on the handle and
drag the table wherever you want it on the page. This type of layout, like the
one shown in Figure A, can make the
page more interesting and less linear in design. It can also save on space.
|
Figure A |
 |
#3: Add space
around the table
Once
you’ve dragged a table to a good spot on the page (“good” means the
table isn’t throwing things off balance by hanging awkwardly into a margin,
sitting too high or low, or creating any funky line breaks in the text), you
can polish it up by adding some space around it. A little breathing room will
enhance readability and reduce that crowded look.
Click
within the table and go to Table | Table Properties. In the Table tab, you’ll
see that the Around option is selected under Alignment. Click Positioning to
access the options shown in Figure B.
Word is already providing a little space to the left and right of the table (0.13″),
but you can increase or decrease that amount if you want. You can also use the
Top and Bottom options to add space above and below your table.
|
Figure B |
 |
#4 Add space
within the table
In
addition to providing space around the table perimeter, it’s a good idea to add
some space within the cells. Nothing looks more slapdash than text crammed into
a table, which is what you get unless you tweak it a little bit. You have a
couple of methods to choose from here.
The
first approach is to manually format the text within the cell. Start by
clicking within the paragraph you want to format (or selecting multiple
paragraphs) and choosing Format | Paragraph. In the Paragraph dialog box, set
the desired right and left margins (which will add space on each side of the
text within the cell). Then, specify a Space Before and Space After setting.
Even 2 or 3 points will improve the appearance of the table text. The advantage
of adding space this way is that you can do it selectively, so you have
granular control over text positioning in the table.
The
second method is to build the extra internal space into the table
itself–probably quicker, but your specifications will apply to all the text in
the table. Click within the table and choose Table | Properties. In the Table
tab, click Options to open the dialog box shown in Figure C. Now, just enter the desired measurements in the Default
Cell Margins fields.
|
Figure C |
 |
#5: Add space
between cells
Another
technique to explore is cell spacing. It’s certainly not an essential step for
creating an attractive table, but it creates an eye-catching effect, especially
if you combine it with shading features. To add cell spacing, click in the
table and go back to the Table Options dialog box (Table | Properties |Table
tab | Options). Click Allow Spacing Between Cells and then enter the amount of
space you want. We’re getting into trial-and-error territory now, and you’ll
need to experiment to see what works best. But here are a couple of possibilities.
Figure D has cell spacing set to 0.04″.
And Figure E has similar
specifications along with shading (blue shading applied to the entire table,
with light yellow shading applied to the table rows).
|
Figure D |
 |
|
Figure E |
 |
#6: Turn off
gridlines to see where your actual borders are
One
thing that’s initially confusing is the difference between the table gridlines
(which are a mere visual guide; they don’t print) and borders. Working with
gridlines turned on is helpful as you build and format a table, but to see what
you’ve produced, choose Hide Gridlines from the Table menu. (You can turn
gridlines back on via the Show Gridlines command.) For instance, in Figure F, we removed all the borders
from a table and then selectively applied a border to the bottom of the two
cells representing signature lines. Turning off gridlines (Figure G) shows whether those borders are formatted properly for
the job they’re supposed to do.
|
Figure F |
 |
|
Figure G |
 |
#7: Turn text
sideways
So
far, we haven’t used the Tables And Borders toolbar, but it offers quick access
to some useful options, and we’re going to use it now. To display it, just
right-click on any visible toolbar and select Tables And Borders from the list
of toolbar choices.
The
sideways text technique isn’t appropriate for all situations, but it’s handy to
know about it. Sometimes, you might just want to produce an effect like the one
in Figure H–a slightly
unconventional way to incorporate labels into a table. Other times, you might
have column headings that are a little too unwieldy to run horizontally, so a
good solution is to turn them sideways, as in Figure I.
|
Figure H |
 |
|
Figure I |
 |
To
rotate your text, select the cell(s) that contain it and click the Change Text
Direction button on the Tables And Borders toolbar twice. The first click will
rotate the text to the right, which isn’t so great for readability. The second
click will rotate it so that it runs from bottom to top, like in the figures.
#8: Manually apply
shading and borders
If
you want to add a little color or definition to a table, shading and borders
are the way to go. The trick is to make sure you’re applying them to the right
table components. Although the Tables And Borders toolbar offers a palette of
border placement options and lets you “draw” borders of various
formats, the Borders And Shading dialog box is probably a little less confusing
to use. For applying shading, the Tables And Borders toolbar works okay, but
the Borders And Shading dialog box offers more options, so that’s what we’ll
use here.
To
demonstrate the process, let’s say you want to add a border to the top and bottom
of a row and apply a light yellow fill color. Start by selecting the row and
going to Format | Borders And Shading. In the Borders tab, you’ll see a little image
of a table cell with a border on all sides. (This is assuming you haven’t
changed any border settings; by default, Word tables are formatted with a grid
border.) Since you selected a group of cells (a row, actually), Word will set
the Apply To dropdown list to Cell (meaning all the cells in the selection).
This is what we want, but bear in mind that you can change this to apply to
text or to the entire table.
To
create the border, click on the left, middle, and right sides of the image to remove those segments, leaving just the
top and bottom borders in place. Figure J
shows how this will look. You can make selections from the Style, Color,
and Width list boxes if you want. If you do, you’ll need to click on the table
cell image to apply those selections to the desired sides. To add color, click
the Shading tab and click in the light yellow square in the palette of options
under Fill.
|
Figure J |
 |
#9: Find your
favorite Table AutoFormat styles (and tweak them, if necessary)
Word
offers 45 AutoFormat styles–prefab sets of formatting that automatically apply
various text and table effects. To see what’s available, click in your table
and choose Table | AutoFormat (or click the corresponding button on the Tables
And Borders toolbar, since we have it displayed now). Word will open the dialog
box shown in Figure K. You can spin
through the selections and try them out, see what you like. One of the options
is Table Normal, which is handy for those occasions when you want to strip all
the formatting from a table (like if you get a little carried away with various
embellishments and you’re embarrassed to even look at them).
|
Figure K |
 |
It’s
important to note that when you apply an AutoFormat style to a table, its specifications
will override any formatting you applied to the table yourself. For example, if
you set cell margins to add space around the text in the table, you’ll lose
that if you apply Table AutoFormat because that formatting isn’t part of those
prefab styles. So apply the AutoFormat style first and then set your cell margins.
The
AutoFormat choices are handy, and you may just want to use them as is. But you
also have a great deal of control over modifying them. For one thing, you’ll
notice the Apply Special Formats To options at the bottom of the dialog box. If
you like everything about a particular style but you want to leave the top row
alone, deselect Heading Rows. You may also want to use a style as a starting
point and then click Modify. You can do just about anything you want here–it’s
like modifying a character or paragraph style, only the choices are table-specific.
One
final note about Table AutoFormat: If there’s a style you want to use all the
time, you can select it and click Default. Word will let you set it as the
default style for the current document or for the current template.
# 10: Create a
custom table style for instant formatting
You
can use Table AutoFormat to create your own set of attributes and save them as
a user-defined style. You can then apply the style whenever you want to create
that particular effect. To build a style, open the Table AutoFormat dialog box
and click New. Enter a name for the style and choose the existing style that
you want to base your new style on. (Word defaults to Table Normal, which is
unformatted, in case you want to start with a blank slate.) Make the formatting
selections you want for the style. If you want the style to be available to
other documents based on the current template, click Add To Template.
Otherwise, the style will belong to the current document only. Click OK and
then click Close.
To
apply the style, click in a table and open the Table AutoFormat dialog box. Choose
User-Defined Table Styles from the Category dropdown list box to display your
custom style(s) as shown in Figure L.
Select the style and click Apply.
|
Figure L |
 |
























































































































































 .
.