This is a question about scope.
If you only want the variables to last the lifetime of the function, use Dim (short for Dimension) inside the function or sub to declare the variables:
Function AddSomeNumbers() As Integer
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
intA = 2
intB = 3
AddSomeNumbers = intA + intB
End Function
'intA and intB are no longer available since the function ended
A global variable (as SLaks pointed out) is declared outside of the function using the Public keyword. This variable will be available during the life of your running application. In the case of Excel, this means the variables will be available as long as that particular Excel workbook is open.
Public intA As Integer
Private intB As Integer
Function AddSomeNumbers() As Integer
intA = 2
intB = 3
AddSomeNumbers = intA + intB
End Function
'intA and intB are still both available. However, because intA is public, '
'it can also be referenced from code in other modules. Because intB is private,'
'it will be hidden from other modules.
You can also have variables that are only accessible within a particular module (or class) by declaring them with the Private keyword.
If you’re building a big application and feel a need to use global variables, I would recommend creating a separate module just for your global variables. This should help you keep track of them in one place.
Глобальная переменная в проекте VBA Excel. Объявление глобальной переменной в модуле проекта VBA и обращение к ней из других модулей того же проекта.
Объявление глобальной переменной
Глобальная переменная — это переменная, которая объявлена в одном из модулей проекта VBA и доступна для использования во всех остальных модулях.
Чтобы переменная стала глобальной, она должна быть объявлена в начале модуля перед первой процедурой (раздел Declarations) с помощью оператора Public. Этот способ работает во всех модулях проекта VBA Excel.
Допускается объявление глобальной переменной с помощью оператора Global, но такой способ считается устаревшим и на сайте разработчиков уже не упоминается. Объявить глобальную переменную с оператором Global можно только в стандартном модуле.
Пример объявления глобальных переменных в любом модуле проекта VBA:
|
Public myGlobVar1 ‘по умолчанию — As Variant Public myGlobVar2 As String Public myGlobVar3 As Double |
Объявление глобальных переменных
Обращение к глобальной переменной
Примеры обращения к глобальной переменной, объявленной в разных типах модулей проекта VBA Excel. Актуально для обращения из модуля любого типа данного проекта.
Переменная в стандартном модуле
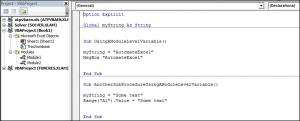
Если глобальная переменная (myGlobVar) объявлена в стандартном модуле (Module1) с уникальным именем, не повторяющимся в других модулях, к ней можно обращаться из других модулей по одному имени (в примере — из модуля формы):
|
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» TextBox1.Text = myGlobVar End Sub |
Стандартное обращение с указанием имени модуля (Module1), в котором объявлена глобальная переменная (myGlobVar):
|
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() Module1.myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» TextBox1.Text = Module1.myGlobVar End Sub |
Переменная в модуле книги
Глобальная переменная (myGlobVar), объявленная в модуле книги, доступна при обращении к ней из других модулей с помощью следующего кода VBA Excel:
|
Sub Primer1() ThisWorkbook.myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» MsgBox ThisWorkbook.myGlobVar End Sub |
Переменная в модуле листа
Обращение к глобальной переменной (myGlobVar), объявленной в модуле рабочего листа (Лист1), из других модулей по имени листа (в проводнике проекта находится без скобок слева от имени ярлыка):
|
Sub Primer2() Лист1.myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» MsgBox Лист1.myGlobVar End Sub |
По имени ярлыка (в проводнике проекта находится в полукруглых скобках справа от имени листа):
|
Sub Primer3() Worksheets(«Лист1»).myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» MsgBox Worksheets(«Лист1»).myGlobVar End Sub |
Переменная в модуле формы
Глобальная переменная (myGlobVar), объявленная в модуле формы (UserForm1), доступна при обращении к ней из других модулей с помощью следующего кода VBA Excel:
|
Sub Primer4() UserForm1.myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» MsgBox UserForm1.myGlobVar End Sub |
Переменная в личной книге макросов
Обращение к глобальной переменной (myGlobVar), объявленной в модуле ЭтаКнига проекта VBAProject (PERSONAL.XLSB) из модуля проекта VBA обычной книги Excel:
|
Sub Primer5() Workbooks(«PERSONAL.XLSB»).myGlobVar = «Глобальная переменная» MsgBox Workbooks(«PERSONAL.XLSB»).myGlobVar End Sub |
Мне не удалось получить доступ из проекта VBA текущей книги Excel к глобальной переменной, объявленной в стандартном модуле личной книги макросов.
Some functions defined inside a function used within the functions. Also, some variables defined outside the functions used by all the functions. Such variables used are global variables. For example, the variables declared under the sub-function are known as “global variables.”
Table of contents
- Global Variable in Excel VBA
- What are Global Variables in Excel VBA?
- How to Declare Global Variable in VBA?
- #1 – Module Variables can be used in any Sub Procedure in the Same Module
- #2 – Global Variables can be used in any Sub Procedure and also in any Module
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Global Variable in Excel VBA
Declaring a variable seems pretty simple. But to have good hands-on experience, we need to understand the scope of those variables. We often declare the variables for each macro inside the subprocedure. But by declaring one variable, we can use it in all the macros in the same module and the other modules of the current VBA project. This article will show you how to declare global variables in Excel VBA.
What are Global Variables in Excel VBA?
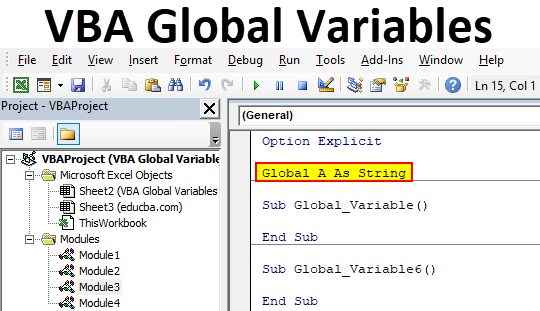
VBA global variables are variables declared before any macro in the module starts. When the variables are declared using either “Public” or “Global,” it becomes a global variable.
Sub Procedure Variables Cannot Use Anywhere.
We usually declare the variable inside the subroutine in VBASUB in VBA is a procedure which contains all the code which automatically gives the statement of end sub and the middle portion is used for coding. Sub statement can be both public and private and the name of the subprocedure is mandatory in VBA.read more by using the word “Dim.”
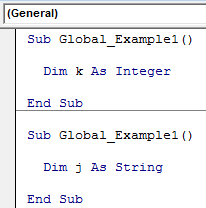
Look at the above image. We have declared the variable “k” as an integer inside the Sub procedure Global_Example1.
Suppose we use this variable inside this Sub procedure at any time. However, we cannot use this variable in another Sub procedure either in the same class module in VBAUsers have the ability to construct their own VBA Objects in VBA Class Modules. The objects created in this module can be used in any VBA project.read more or another module.
As shown in the above image, the variable “k,” declared in the Sub procedure Global_Example1, cannot be used in the Sub procedure Global_Example2.
Similarly, variable “j” declared in the Sub procedure Global_Example2 cannot be used in the Sub procedure Global_Example1 even though both are in the same module.
How to Declare a Global Variable in VBA?
The following are the ways to declare a global variable in Excel VBA.
#1 – Module Variables can be used in any Sub Procedure in the Same Module
As we have seen, we cannot use the Sub procedure variables in any of the modules. Therefore, to make them available for all the Sub procedures in the same module, we need to declare the variables at the top of the module.
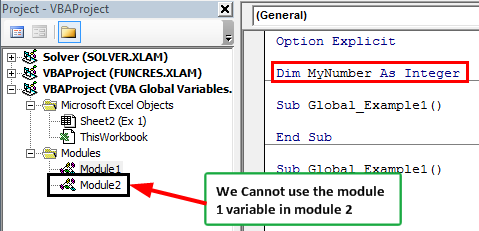
In the above image, we have declared the variable at the start of the module only. I have expressed the variable “MyNumber” as an Integer in Module 1.
Once declared the variable at the top of the module, we can use the same variable for all the other Sub procedures in the same module. In this case, we can use the variable “MyNumber” for all the Sub procedures in Module 1.
We cannot use them in any of the other modules. In this case, the variable “MyNumber,” declared in Module 1, cannot be used in Module 2.
#2 – Global Variables can be used in any Sub Procedure and also in any Module
We have seen two kinds of variable declaration and their scope while using. The exciting thing is we can declare the variable in any one of the modules and use it for all the Sub procedures in all the modules of the same VBA Project.
To make the variable available for all the Sub procedures across all the modules, we need to declare the variable at the top of the module not by using the word “Dim” but by using the name “Public” or “Global.”
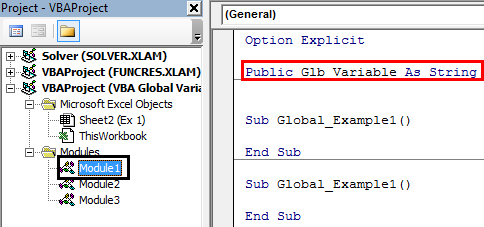
In the above image, we have used the word “Public” to declare the variable instead of our veteran word “Dim.”
In the above screenshot, we have declared the variable in Module 1. However, we have two more modules, Module 2 and Module 3.
Since we have declared the variable using the word “Public” at the top of the module, now we can access these variables in any Sub procedure across any module of the same workbook.
Not only “Public,” but we can also use the word “Global” to declare the variable.
“Global” and “Public” are the keywords to declare the variable and make them available across modules in VBA.
Things to Remember
- Once the excel macroA macro in excel is a series of instructions in the form of code that helps automate manual tasks, thereby saving time. Excel executes those instructions in a step-by-step manner on the given data. For example, it can be used to automate repetitive tasks such as summation, cell formatting, information copying, etc. thereby rapidly replacing repetitious operations with a few clicks.
read more runs with a global variable’s value, the variable is the same across all the Sub procedures. - It is better to maintain a particular module to declare global variables in VBA and have all the variables in one module.
- The only way we can reset the variable’s value is by resetting the macro code by pressing the stop button.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Global Variables. Here, we learn how to declare global variables in Excel VBA, practical examples, and a downloadable template. Below you can find some useful Excel VBA articles: –
- VBA Exit Sub
- VBA ByRef Argument Type Mismatch
- VBA Option Explicit
- VBA Long Data Type
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this tutorial we will cover VBA Global Variables.
In VBA, variables can be declared with different scopes. The scope determines where the variable can be used.
Procedure-level Variable
Typically, you will see variables declared at the procedure-level within Sub Procedures or Functions. Procedure-level variables must be declared using the Dim keyword within the procedure where they will be used.
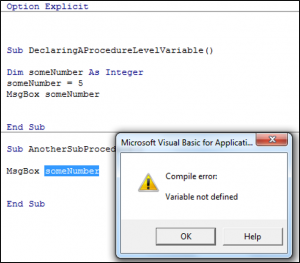
This example declares someNumber as an integer variable within the procedure.
Sub DeclaringAProcedureLevelVariable()
Dim someNumber As Integer
someNumber = 5
MsgBox someNumber
End SubYou can only use this variable within this Sub Procedure. If you call the variable from another Sub Procedure you would get the following Compile Error:
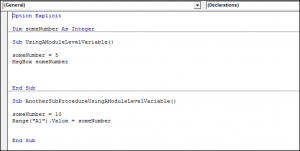
Module Level Variable
A Module-level variable can be used by any Sub Procedure or Function within that module. You need to place the variable declaration at the top of the module in the Declarations section, under the Option Explicit statement, and use the Dim keyword:
Now the variable someNumber can be used in both sub procedures.
Global Level Variable
A global-level variable can be used anywhere within your code, within Modules, Functions, Sub Procedures and Classes. Global variables are declared in the Declarations Section, under the Options Explicit statement and using the keyword Global. The way you declare a Global level variable is shown below. Both of the Sub Procedures in Module1 can use this variable.
Since this variable is a Global level variable, you can also use it in Module2:
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Excel VBA Global Variables
We usually declare any variable by using the word DIM and this is the best direct method of doing this. But the variables declared using DIM can only be used within the same module. If we try to use this variable defined by using DIM, it will be applicable for the module under which it is being declared. What if we want to use a variable in any module or project? Which cannot be possible if we keep on using DIM to define that variable?
In that case, we have a secondary option by defining the variable by word Global or Public in VBA. VBA Global or Public variables are those variables which are declared at the beginning of subcategory with the help of Option Explicit. Whatever things which we don’t or can’t do under subcategories, they are done before that under Option Explicit.
How to Declare Global Variables in VBA?
Below are the different examples to declare a global variable in Excel using VBA code.
You can download this VBA Global Variables Excel Template here – VBA Global Variables Excel Template
VBA Global Variables – Example #1
In this example, we will see how different subcategories can be used as a single module without using Global or Public word for defining any variable. For this, we would need a module.
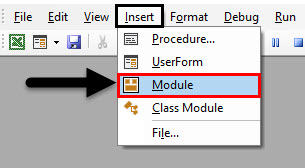
- Go to Insert menu and click on Module as shown below.
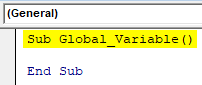
- Now type the subcategory in any name as shown below.
Code:
Sub Global_Variable() End Sub
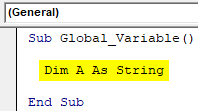
- Now use DIM to define any kind of variable. Here we have chosen alphabet A as String.
Code:
Sub Global_Variable() Dim A As String End Sub
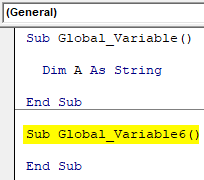
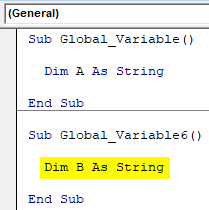
- Now create another subcategory in the same module as shown below.
Code:
Sub Global_Variable() Dim A As String End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() End Sub
- Now in the second subcategory define another variable B using DIM as String.
Code:
Sub Global_Variable() Dim A As String End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() Dim B As String End Sub
As shown above, both the variables A and B defined in both subcategories cannot be used in each other’s region. Those will be applicable in their own subcategory only.
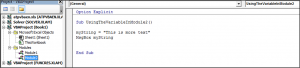
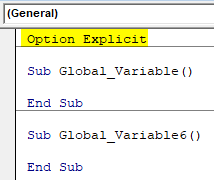
- Now to make this work, write Option Explicit above the first subcategory as shown below.
Code:
Option Explicit Sub Global_Variable() End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() End Sub
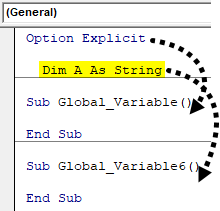
- Now we can define our variable which will be used in both of the subcategories of which we have below. So now consider writing any variable say A as String using DIM.
Code:
Option Explicit Dim A As String Sub Global_Variable() End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() End Sub
As we have defined the variable all the sub-categories will be in that module and this would be applicable to all the code of that module only. And if we try to call the variables defined in this module to some other module, then it would give us the error.
VBA Global Variables – Example #2
In this example, we will see how to use Global or Public word for defining any variable in excel VBA. For this, we will use the code which we have seen in example-1.
We will use below portion of code for Global or Public variable declaration.
Code:
Option Explicit Sub Global_Variable() End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() End Sub
As we did in example-1 where we have declared the common variable which would be used in both the subcategories, below the Option Explicit. In the example, we will declare the Global Variable below the Option Explicit as well.
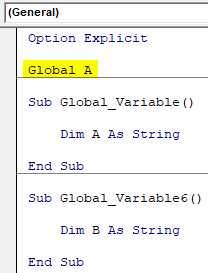
As we already have our code ready so we can directly go on declaring variables using Global. Now in the below Option Explicit write Global the same we used to with DIM and select a variable of choice. Here we are choosing alphabet A as shown below.
Code:
Option Explicit Global A Sub Global_Variable() Dim A As String End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() Dim B As String End Sub
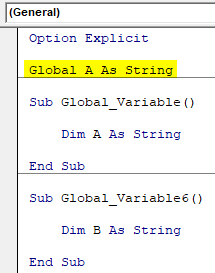
Now we choose any type of variable to be it. As we have already used String in the above example, so we would use the same here as well.
Code:
Option Explicit Global A As String Sub Global_Variable() Dim A As String End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() Dim B As String End Sub
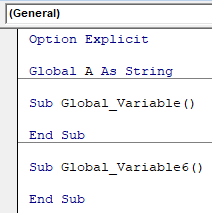
This completes our Global variable declaration process. Now we can use this in any module, any project as String only. Before we use it, delete the previously declared variable, then the code would look like as shown below.
Code:
Option Explicit Global A As String Sub Global_Variable() End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() End Sub
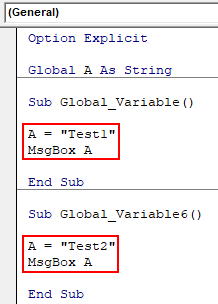
Now let’s assign some text to defined variable A in both subcategories. We are choosing “Test1” and “Test2” for variable A in both subcategories as shown below. And also we have chosen MsgBox to show the values stored in variable A.
Code:
Option Explicit Global A As String Sub Global_Variable() A = "Test1" MsgBox A End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() A = "Test2" MsgBox A End Sub
Now run the code by pressing the F5 key or by clicking on the play button to see the result.
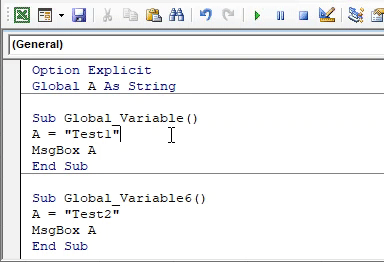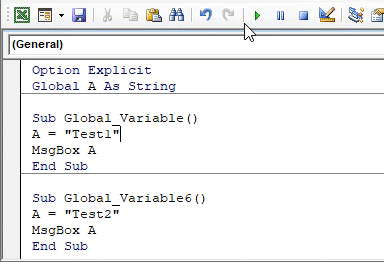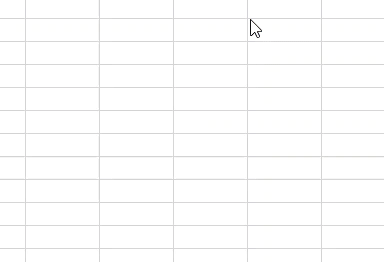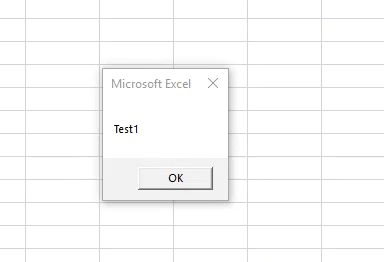
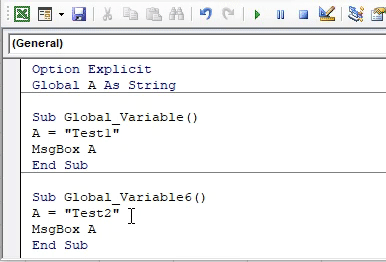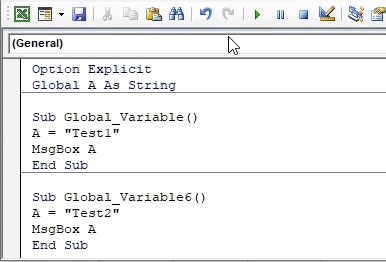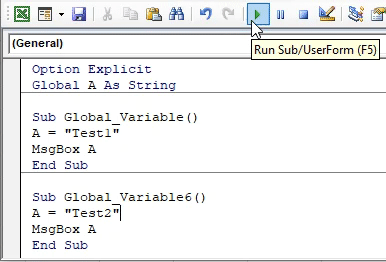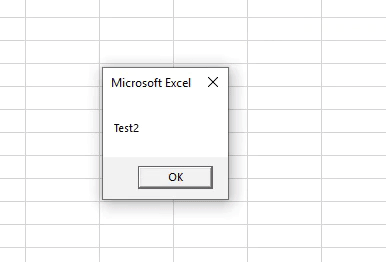
We will get the message as “Test1” as shown above. It is because we had kept our cursor in the first subcategory.
Now put the cursor anywhere in the second subcategory and run the code again. We will now get the message box with message “Test2” as shown below.
This is how we can create and define a variable once with the help of Global and that can be used in any module, any class and in any project. We can use Public as well in place of Global as shown below. And this will give the same result as we got in using Global.
Code:
Option Explicit Public A As String Sub Global_Variable() A = "Test1" MsgBox A End Sub Sub Global_Variable6() A = "Test2" MsgBox A End Sub
Pros of VBA Global Variable
- It saves time in declaring the multiple variables when we know, we may need to define the same type of variable again in different modules or subcategories.
- By using Global or Public in defining a variable process, our code becomes smaller saving time and spaces.
- It reduces the complexity when we are writing the huge code and may get confused among the use of different variables in different modules or subcategories.
Cons of VBA Global Variable
- If we do any changes to the Global variable then that changes will get implemented in all where it is used causing the problem in the functionality of written code.
Things to Remember
- Global and Public can be used interchangeably with the same functionality.
- If we don’t want to use Global variable then we can follow the process as shown in example-1 for defining the variable. But that would be limited to the same module.
- Global variables can be used in any module, any subcategory, any class or in any project.
- A Global variable gives the output of the code where we have kept the cursor. It will not run the complete code at one go giving all the output one by one.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Global Variables. Here we discuss how to declare Global Variables in Excel using VBA code along with some practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA UserForm
- VBA Get Cell Value
- VBA Activate Sheet
- VBA RGB