Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
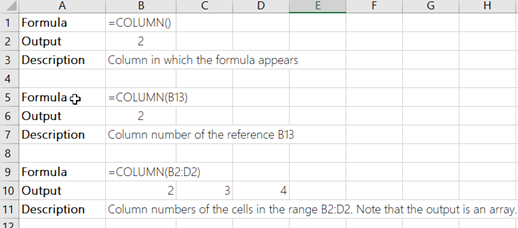
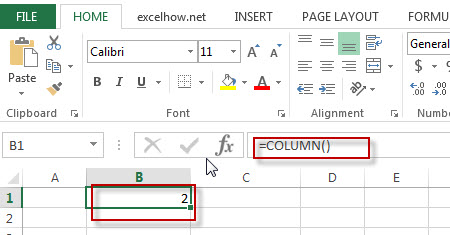
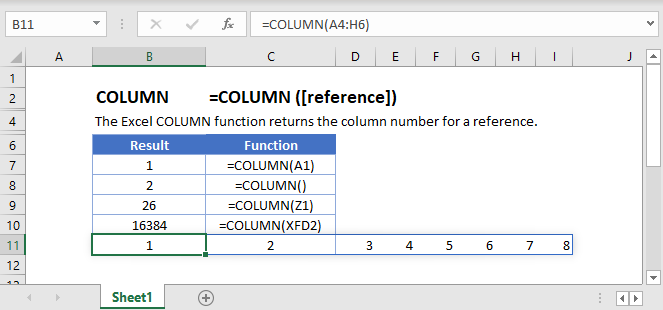
The COLUMN function returns the column number of the given cell reference. For example, the formula =COLUMN(D10) returns 4, because column D is the fourth column.
Syntax
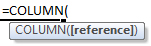
COLUMN([reference])
The COLUMN function syntax has the following argument:
-
reference Optional. The cell or range of cells for which you want to return the column number.
-
If the reference argument is omitted or refers to a range of cells, and if the COLUMN function is entered as a horizontal array formula, the COLUMN function returns the column numbers of reference as a horizontal array.
Notes:
-
If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
-
-
If the reference argument is a range of cells, and if the COLUMN function is not entered as a horizontal array formula, the COLUMN function returns the number of the leftmost column.
-
If the reference argument is omitted, it is assumed to be the reference of the cell in which the COLUMN function appears.
-
The reference argument cannot refer to multiple areas.
-
Example
Need more help?
How to get the row or column number of the current cell or any other cell in Excel.
This tutorial covers important functions that allow you to do everything from alternate row and column shading to incrementing values at specified intervals and much more.
We will use the ROW and COLUMN function for this. Here is an example of the output from these functions.
Though this doesn’t look like much, these functions allow for the creation of powerful formulas when combined with other functions. Now, let’s look at how to create them.
Get a Cell’s Row Number
Syntax
This function returns the number of the row that a particular cell is in.
If you leave the function empty, it will return the row number for the current cell in which this function has been placed.
If you put a cell reference within this function, it will return the row number for that cell reference.
This example would return 1 since cell A1 is in row 1. If it was =ROW(C24) the function would return the number 24 because cell C24 is in row 24.
Examples
Now that you know how this function works, it may seem rather useless. Here are links to two examples where this function is key.
Increment a Value Every X Number of Rows in Excel
Shade Every Other Row in Excel Quickly
Get a Cell’s Column Number
Syntax
This function returns the number of the column that a particular cell is in. It counts from left to right, where A is 1 and B is 2 and so on.
If you leave the function empty, it will return the column number for the current cell in which this function has been placed.
If you put a cell reference within this function, it will return the column number for that cell reference.
This example would return 1 since cell A1 is in row 1. If it was =COLUMN (C24) the function would return the number 3 because cell C24 is in column number 3.
Examples
The COLUMN function works just like the ROW function does except that it works on columns, going left to right, whereas the ROW function works on rows, going up and down.
As such, almost every example where ROW is used could be converted to use COLUMN based on your needs.
Notes
The ROW and COLUMN functions are building blocks in that they help you create more complex formulas in Excel. Alone, these functions are pretty much worthless, but, if you can memorize them and keep them for later, you will start to find more and more uses for them when working in large data sets. The examples provided above in the ROW section cover only two of many different ways you can use these functions to create more powerful and helpful spreadsheets.
Similar Content on TeachExcel
Sum Values from Every X Number of Rows in Excel
Tutorial: Add values from every x number of rows in Excel. For instance, add together every other va…
Formulas to Remove First or Last Character from a Cell in Excel
Tutorial: Formulas that allow you to quickly and easily remove the first or last character from a ce…
Formula to Delete the First or Last Word from a Cell in Excel
Tutorial:
Excel formula to delete the first or last word from a cell.
You can copy and paste the fo…
Reverse the Contents of a Cell in Excel — UDF
Macro: Reverse cell contents with this free Excel UDF (user defined function). This will mir…
Excel Function to Remove All Text OR All Numbers from a Cell
Tutorial: How to create and use a function that removes all text or all numbers from a cell, whichev…
Get the First Word from a Cell in Excel
Tutorial: How to use a formula to get the first word from a cell in Excel. This works for a single c…
Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
In this article, we will learn about how to Count table rows & columns in Excel.
In simple words, while working with large data in Excel we need to find the number of rows or columns in excel table.
The ROWS function in excel returns the number of rows in an array.
Syntax:
The COLUMNS function in excel returns the number of columns in an array.
Syntax:
Let’s understand this function using it in an example.
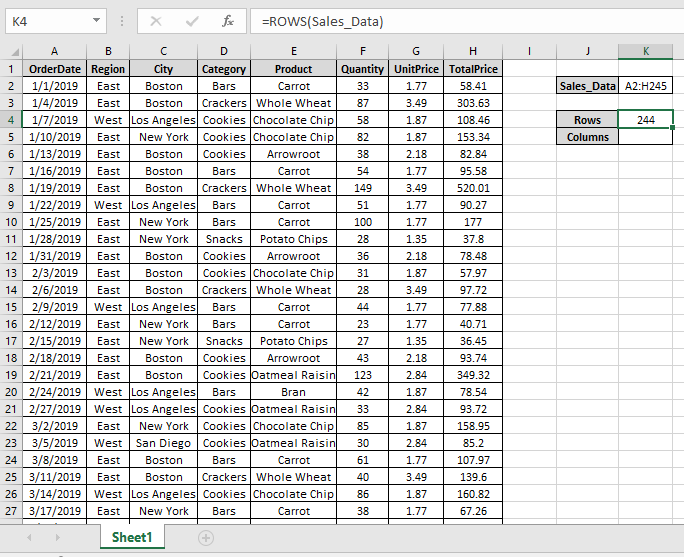
Here we have large data A2:H245 named Sales_Data
Here we need to find out the number of rows & columns of Sales_Data table in Excel.
Use the formula to get the number of rows
A2:H245 : Sales_Data table as an array.
We got the number of rows of the Sales_Data.
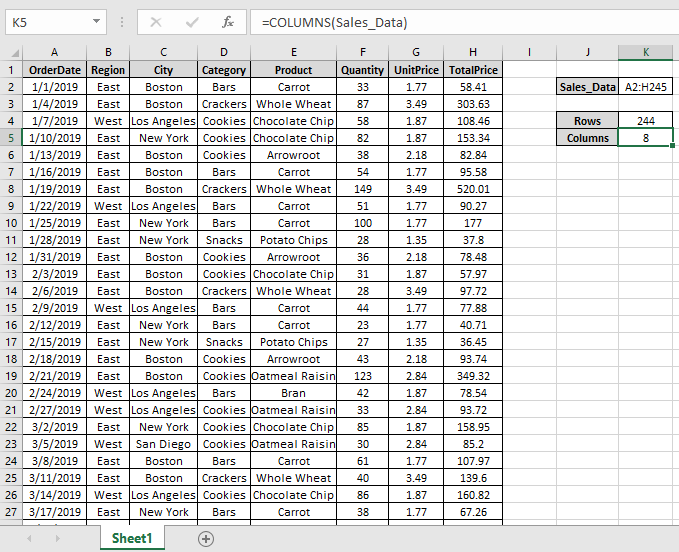
Use the formula to get the number of rows
A2:H245 : Sales_Data table as an array.
As you can see the ROWS & COLUMNS functions returns the number of rows & columns of table.
Hope you understood how to use ROWS function and COLUMNS function in Excel. Explore more articles on Excel cell info function functions here. Please feel free to state your query or feedback for the above article.
Related Articles :
How to use the CELL function in Excel
How to use the ROW function in Excel
How to use the COLUMN Function in Excel
Popular Articles :
50 Excel Shortcut to Increase Your Productivity : Get faster at your task. These 50 shortcuts will make you work even faster on Excel.
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel : This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
How to use the COUNTIF function in Excel : Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel : This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
This post will guide you how to use Excel COLUMN function with syntax and examples in Microsoft excel.
Description
The Excel COLUMN function returns the first column number of the given cell reference.
The COLUMN function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Lookup and Reference Function.
The COLUMN function is available in Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000, Excel 2011 for Mac.
Syntax
The syntax of the COLUMN function is as below:
=COLUMN ([reference])
Where the COLUMN function arguments is:
Reference -This is an optional argument. A reference to a cell or a range of cells for which you want to get the first column number.
Note: If the Array argument is omitted, the Excel COLUMN function will return the column number of the cell that the function is entered in.
Example
The below examples will show you how to use Excel COLUMN Lookup and Reference Function to return the column number of a cell reference.
#1 To get the number of column in B1 Cell, just using the following excel formula: =COLUMN ( )
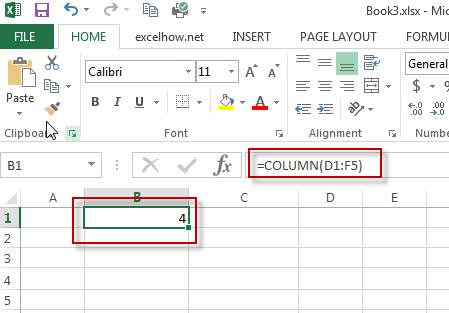
#2 To get the number of column in the reference D1:F5, just using the following excel formula: =COLUMN(D1:F5)
More Excel Column Function Examples
- VLOOKUP Return Multiple Values Horizontally
You can create a complex array formula based on the INDEX function, the SMALL function, the IF function, the ROW function and the COLUMN function to vlookup a value and then return multiple corresponding values horizontally in Excel.… - Sum Every Nth Row or Column
If you want to sum every nth rows in Excel, you can create an Excel Array formula based on the SUM function, the MOD function and the ROW function..….
Purpose
Get the column number of a reference.
Return value
A number representing the column.
Usage notes
The COLUMN function returns the column number of a reference. For example, COLUMN(C5) returns 3, since C is the third column in the spreadsheet. COLUMN takes just one argument, called reference, which can be empty, a cell reference, or a range. When no reference is provided, COLUMN returns the column number of the cell which contains the formula.
Examples
With a single cell reference, COLUMN returns the associated column number:
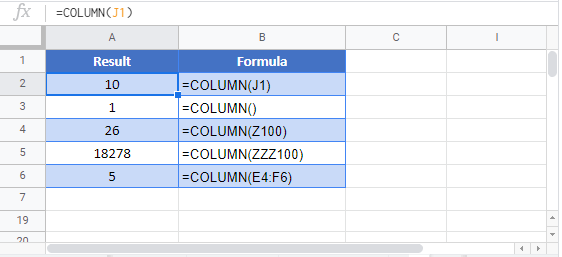
=COLUMN(A1) // returns 1
=COLUMN(C1) // returns 3
When a reference is not provided, COLUMN returns the column number of the cell the formula resides in. For example, if the following formula is entered in cell D6, the result is 4:
=COLUMN() // returns 4 in D6
When COLUMN is given a range, it returns the column numbers for that range:
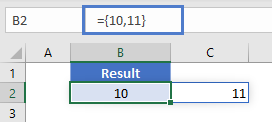
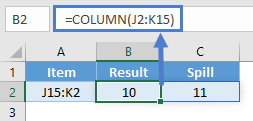
=COLUMN(E4:G6) // returns {5,6,7}
In Excel 365, which supports dynamic array formulas, the result is an array {5,6,7} that spills horizontally into three cells, starting with the cell the formula resides in. In earlier Excel versions, the first item of the array (5) will display in one cell only.
To get Excel 365 to return a single value, you can use the implicit intersection operator (@):
=@COLUMN(E4:G6) // returns 5
This @ symbol disables array behavior and tells Excel you want a single value.
Notes
- Reference can be a single cell address or a range of cells.
- Reference is optional and will default to the cell in which the COLUMN function exists.
- Reference cannot include multiple references or addresses.
- To get row numbers, see the ROW function.
- To count columns, see the COLUMNS function.
- To lookup a column number, see the MATCH function.
Содержание
- COLUMN function
- Syntax
- COLUMN Function
- Related functions
- Summary
- Purpose
- Return value
- Arguments
- Syntax
- Usage notes
- Examples
- Premium Excel Course Now Available!
- Build Professional — Unbreakable — Forms in Excel
- 45 Tutorials — 5+ Hours — Downloadable Excel Files
- Get the Row or Column Number of a Cell in Excel
- Get a Cell’s Row Number
- Syntax
- Examples
- Get a Cell’s Column Number
- Syntax
- Examples
- Notes
- Question? Ask it in our Excel Forum
- VBA Course — Beginner to Expert
- Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
- BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
- COLUMN Function Examples – Excel & Google Sheets
- COLUMN Function Overview
- COLUMN function Syntax and inputs:
- COLUMN Function – Single Cell
- COLUMN Function with no Reference
- COLUMN Function with a Range
- Excel 2019 or older
- Excel 365
- COLUMN Function in Google Sheets
- Additional Notes
- Excel column number from column name
- 7 Answers 7
COLUMN function
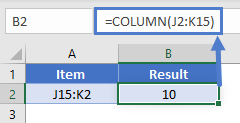
The COLUMN function returns the column number of the given cell reference. For example, the formula = COLUMN( D10) returns 4, because column D is the fourth column.
Syntax
The COLUMN function syntax has the following argument:
reference Optional. The cell or range of cells for which you want to return the column number.
If the reference argument is omitted or refers to a range of cells, and if the COLUMN function is entered as a horizontal array formula, the COLUMN function returns the column numbers of reference as a horizontal array.
If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
If the reference argument is a range of cells, and if the COLUMN function is not entered as a horizontal array formula, the COLUMN function returns the number of the leftmost column.
If the reference argument is omitted, it is assumed to be the reference of the cell in which the COLUMN function appears.
The reference argument cannot refer to multiple areas.
Источник
COLUMN Function
Summary
The Excel COLUMN function returns the column number for a reference. For example, COLUMN(C5) returns 3, since C is the third column in the spreadsheet. When no reference is provided, COLUMN returns the column number of the cell which contains the formula.
Purpose
Return value
Arguments
- reference — [optional] A reference to a cell or range of cells.
Syntax
Usage notes
The COLUMN function returns the column number of a reference. For example, COLUMN(C5) returns 3, since C is the third column in the spreadsheet. COLUMN takes just one argument, called reference, which can be empty, a cell reference, or a range. When no reference is provided, COLUMN returns the column number of the cell which contains the formula.
Examples
With a single cell reference, COLUMN returns the associated column number:
When a reference is not provided, COLUMN returns the column number of the cell the formula resides in. For example, if the following formula is entered in cell D6, the result is 4:
When COLUMN is given a range, it returns the column numbers for that range:
In Excel 365, which supports dynamic array formulas, the result is an array <5,6,7>that spills horizontally into three cells, starting with the cell the formula resides in. In earlier Excel versions, the first item of the array (5) will display in one cell only.
To get Excel 365 to return a single value, you can use the implicit intersection operator (@):
This @ symbol disables array behavior and tells Excel you want a single value.
Источник
Premium Excel Course Now Available!
Build Professional — Unbreakable — Forms in Excel
45 Tutorials — 5+ Hours — Downloadable Excel Files
Get the Row or Column Number of a Cell in Excel
BLACK FRIDAY SALE (65%-80% Off)
Excel Courses Online
Video Lessons Excel Guides
How to get the row or column number of the current cell or any other cell in Excel.
This tutorial covers important functions that allow you to do everything from alternate row and column shading to incrementing values at specified intervals and much more.
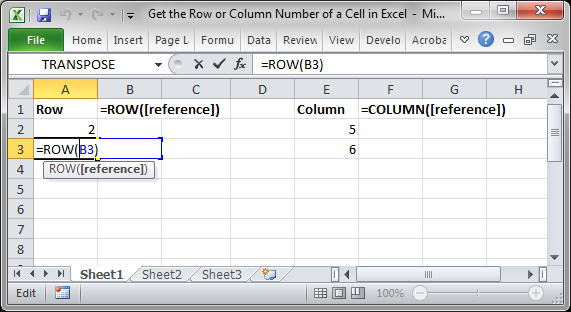
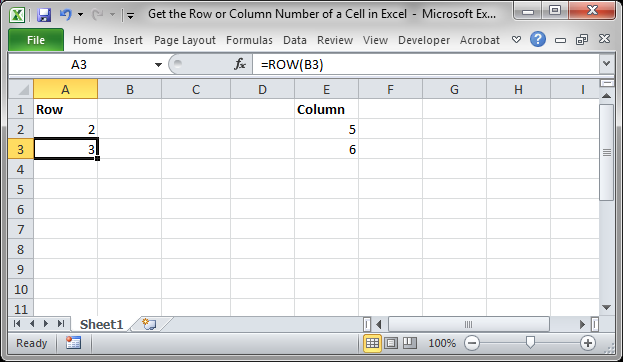
We will use the ROW and COLUMN function for this. Here is an example of the output from these functions.
Though this doesn’t look like much, these functions allow for the creation of powerful formulas when combined with other functions. Now, let’s look at how to create them.
Get a Cell’s Row Number
Syntax
This function returns the number of the row that a particular cell is in.
If you leave the function empty, it will return the row number for the current cell in which this function has been placed.
If you put a cell reference within this function, it will return the row number for that cell reference.
This example would return 1 since cell A1 is in row 1. If it was =ROW(C24) the function would return the number 24 because cell C24 is in row 24.
Examples
Now that you know how this function works, it may seem rather useless. Here are links to two examples where this function is key.
Get a Cell’s Column Number
Syntax
This function returns the number of the column that a particular cell is in. It counts from left to right, where A is 1 and B is 2 and so on.
If you leave the function empty, it will return the column number for the current cell in which this function has been placed.
If you put a cell reference within this function, it will return the column number for that cell reference.
This example would return 1 since cell A1 is in row 1. If it was =COLUMN (C24) the function would return the number 3 because cell C24 is in column number 3.
Examples
The COLUMN function works just like the ROW function does except that it works on columns, going left to right, whereas the ROW function works on rows, going up and down.
As such, almost every example where ROW is used could be converted to use COLUMN based on your needs.
Notes
The ROW and COLUMN functions are building blocks in that they help you create more complex formulas in Excel. Alone, these functions are pretty much worthless, but, if you can memorize them and keep them for later, you will start to find more and more uses for them when working in large data sets. The examples provided above in the ROW section cover only two of many different ways you can use these functions to create more powerful and helpful spreadsheets.
Question? Ask it in our Excel Forum
Excel VBA Course — From Beginner to Expert
200+ Video Lessons 50+ Hours of Instruction 200+ Excel Guides
Become a master of VBA and Macros in Excel and learn how to automate all of your tasks in Excel with this online course. (No VBA experience required.)
VBA Course — Beginner to Expert
Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
The link to our top 15 tutorials has been sent to you, check your email to download it!
(If you don’t see the email, check your Spam or Promotions folder and make sure to add us as a contact so you get our emails in the future.)
Excel VBA Course — From Beginner to Expert
200+ Video Lessons
50+ Hours of Video
200+ Excel Guides
Become a master of VBA and Macros in Excel and learn how to automate all of your tasks in Excel with this online course. (No VBA experience required.)
Источник
COLUMN Function Examples – Excel & Google Sheets
Download the example workbook
This Tutorial demonstrates how to use the Excel COLUMN Function in Excel to look up the column number.
COLUMN Function Overview
The COLUMN Function Returns the column number of a cell reference.
To use the COLUMN Excel Worksheet Function, select a cell and type:
(Notice how the formula inputs appear)
COLUMN function Syntax and inputs:
reference – Cell reference that you want to determine the column # of.
COLUMN Function – Single Cell
The COLUMN Function returns the column number of the given cell reference.
COLUMN Function with no Reference
If no cell reference is provided, the COLUMN Function will return the column number where the formula is entered
COLUMN Function with a Range
You can also input entire ranges of cells into the COLUMN Function. When doing so, the COLUMN Function behaves differently in Excel 2019 (or earlier) vs. Excel 365 or newer version of Excel.
Excel 2019 or older
In previous versions of Excel, the COLUMN Function returns an array containing the column values of all the cells in the range, but only displays the first result in the cell.
If you click the cell containing the formula and press F9, all the results are displayed in curly brackets as an array.
Excel 365
However, Excel 365 (and newer versions of Excel, presumably) comes with a spill range feature. Here, the COLUMN Function will return the columns of all cells in the range, “spilled” into the next cells.
COLUMN Function in Google Sheets
The COLUMN Function works exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel:
Additional Notes
Use the COLUMN Function to return the column number of a cell reference. What if you want the column letter of a cell reference? Use this complicated formula instead:
This formula calculates the column number with the COLUMN Function and calculates the address of a cell in row 1 of that column using the ADDRESS Function. Then it uses the SUBSTITUTE Function to remove the row number (1), so all that remains is the column letter.
Источник
Excel column number from column name
How to get the column number from column name in Excel using Excel macro?
7 Answers 7
I think you want this?
Column Name to Column Number
Edit: Also including the reverse of what you want
Column Number to Column Name
FOLLOW UP
Like if i have salary field at the very top lets say at cell C(1,1) now if i alter the file and shift salary column to some other place say F(1,1) then i will have to modify the code so i want the code to check for Salary and find the column number and then do rest of the operations according to that column number.
In such a case I would recommend using .FIND See this example below
While you were looking for a VBA solution, this was my top result on google when looking for a formula solution, so I’ll add this for anyone who came here for that like I did:
Excel formula to return the number from a column letter (From @A. Klomp’s comment above), where cell A1 holds your column letter(s):
As the indirect function is volatile, it recalculates whenever any cell is changed, so if you have a lot of these it could slow down your workbook. Consider another solution, such as the ‘code’ function, which gives you the number for an ASCII character, starting with ‘A’ at 65. Note that to do this you would need to check how many digits are in the column name, and alter the result depending on ‘A’, ‘BB’, or ‘CCC’.
Excel formula to return the column letter from a number (From this previous question How to convert a column number (eg. 127) into an excel column (eg. AA), answered by @Ian), where A1 holds your column number:
Note that both of these methods work regardless of how many letters are in the column name.
Источник
Excel COLUMNS Function (Example + Video)
When to use Excel COLUMNS Function
Excel COLUMNS function can be used when you want to get the number of columns in a specified range or array.
What it Returns
It returns a number that represents the total number of columns in the specified range or array.
Syntax
=COLUMNS(array)
Input Arguments
- array – it could be an array, an array formula or a reference to a contiguous range of cells.
Additional Notes
- Even if the array contains multiple rows and columns, only the columns are counted. For example:
-
COLUMNS(A1:B1) returns 2.
-
COLUMNS(A1:B100) also returns 2.
-
- This formula can be useful when you want to get a sequence of numbers as you go to the right in your worksheet.
- For example, if you want 1 in A1, 2 in B1, 3 in C1 and so on, use the following formula =COLUMNS($A$1:A1). As you would drag this to the right, the reference inside it would change and the number of columns in the reference would get incremented by one. For example, when you drag it to column B1, the formula becomes COLUMNS($A$1:B1) which then returns 2.
Excel COLUMNS Function – Examples
Here are two examples of using the Excel COLUMNS function.
Example 1: Finding the number of Columns in an Array
In the example above, =COLUMNS(A1:A1) returns 1 as it covers one row (which is A1). Similarly, =COLUMNS(A1:C1) returns 3 as the array A1:C1 covers four columns in it.
Also, note that it only counts the number of columns. Hence, whether the array is A1:C1, or A1:C5, it would return 3 in both the cases.
Example 2: Getting a Sequence of Numbers in a Column
Excel COLUMNS function can be used to get a sequence of numbers. Since the first reference is fixed, as you copy the formula down, the second reference changes and so does the row numbers in the array.
Excel COLUMNS Function – Video Tutorial
Related Excel Functions:
- Excel COLUMN Function.
- Excel ROW Function.
- Excel ROWS Function
Other articles you may also like:
- Row vs Column in Excel – What’s the Difference?
Column Letter to Number in Excel
Figuring out which row you are in is as easy as you like. But, how do you tell which column you are in now? Excel has 16,384 columns, represented by alphabetic characters in Excel. So, suppose you want to find the column CP. How do you tell?
Yes, it is almost impossible to figure out the column number in Excel. However, nothing to worry about because we have a built-in function called COLUMN in excelColumn function finds out the column numbers of the target cells in excel. It takes one argument which is the target cell as reference. Note that this function does not give the value of the cell as it returns only the column number of the cell. read more, which can tell the exact column number we are in right now or find the column number of the supplied argument.
Table of contents
- Column Letter to Number in Excel
- How to Find Column Number in Excel? (with Examples)
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- How to Find Column Number in Excel? (with Examples)
How to Find Column Numbers in Excel? (with Examples)
You can download this Column to Number Excel template here – Column to Number Excel template
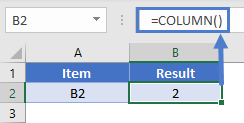
Example #1
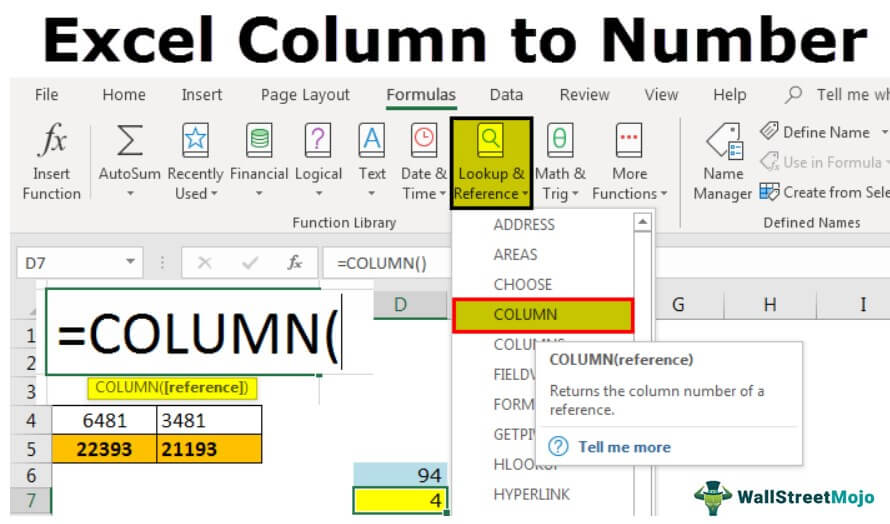
We can get the current column number by using the COLUMN function in Excel.
- We have opened a new workbook and typed some of the values in the worksheet.
- Let us say we are in cell D7, and we want to know the column number of this cell.
- To find the current column number, we must write the COLUMN function in the Excel cell and do not pass any argument; close the bracket.
- Press the “Enter” key. As a result, we will have a current column number in Excel.
Example #2
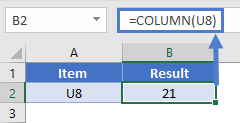
We can get the column number of the different cells by using the COLUMN function in Excel.
Getting the current column is not the toughest task at all. Suppose we want to know the column number of the cell CP5 and how we get that column number.
- We can write the COLUMN function and pass the specified cell value in any cells.
- Then press the “Enter” key. It will return the column number of CP5.
We have applied the COLUMN formula in cell D6 and passed the argument as CP5, i.e., cell referenceCell reference in excel is referring the other cells to a cell to use its values or properties. For instance, if we have data in cell A2 and want to use that in cell A1, use =A2 in cell A1, and this will copy the A2 value in A1.read more of CP5 cell. However, unlike normal cell reference, it will not return the value in the cell CP5. Rather, it will return the column number of CP5.
So, the column number of the cell CP5 is 94.
Example #3
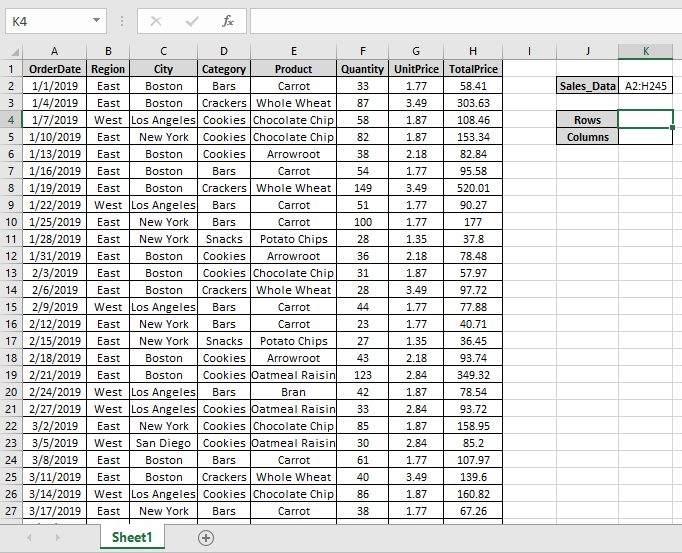
We can get how many columns are selected in the range by using the COLUMNS function in Excel.
We have learned how to get the current cell column number and specified cell column number in Excel. But, how do you tell how many columns are selected in the range?
We have another built-in function called the COLUMNS function in excelThe COLUMNS function returns the total number of columns in the given array or collection of references.read more, which can return the number of columns selected in the formula range.
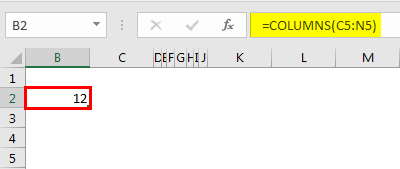
Assume we want to know how many columns are from the range C5 to N5.
- We can open the formula COLUMNS in any cell and select the range as C5 toN5.
- Press the “Enter” key to get the desired result.
So totally, we have selected 12 columns in the range C5 to N5.
In this way, by using the COLUMN and COLUMNS function in Excel, we can get the two different kinds of results, which can help us calculate or identify the exact column when dealing with huge datasets.
Example #4
We can change the cell reference form to R1C1 references in Excel.
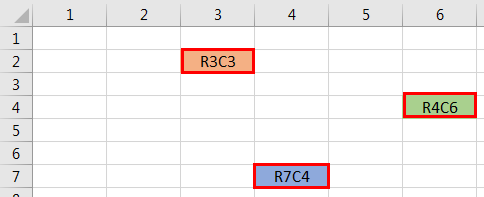
By default, we have cell references, all the rows are represented numerically, and all the columns are represented alphabetically.
It is the usual spreadsheet structure we are familiar with. The cell reference is started with the column alphabet and then followed by row numbers.
As we learned earlier in the article, we need to use the COLUMN function to get the column number. How about changing the column headers from the alphabet to numbers like our row headers? Like the image below.
It is called ROW-COLUMN reference in Excel. Now, take a look at the below image and the reference type.
Unlike our standard cell reference, reference starts with a row number followed by a column number, not an alphabet.
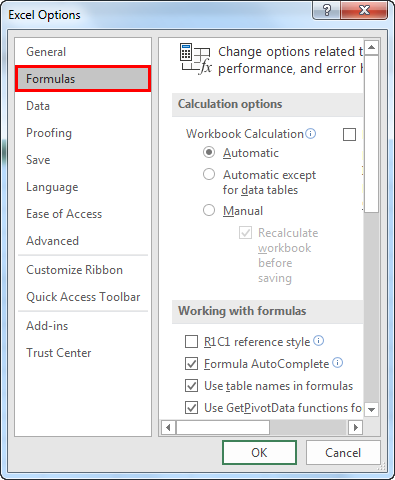
Follow the below steps to change it to the R1C1 reference style.
- We must first go to the “File” and “Options.”
- Next, go to “Formulas” under “Options.”
- Working with “Formulas,” select the checkbox “R1C1 reference style” and click “OK.”
Once we click “OK,” cells will change to R1C1 references.
Things to Remember
- The R1C1 cell reference is the rarely followed cell reference in Excel. As a result, we may get confused easily at the start.
- We see column alphabet first and row number next in normal cell references. But in R1C1 cell references, the row number will come first and the column number.
- The COLUMN function can return the current column number and the supplied column number.
- The R1C1 cell reference makes it easy to find the column number easily.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Column Letter to Numbers in Excel. We discuss finding column numbers in Excel using the COLUMN and COLUMNS functions. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Excel Rows Function
- Excel Rows vs. Columns
- Excel Rows and Columns
- Concatenate Excel Columns