Manytimes, we want to extract month from a date. Extracting them manually not a good idea. Excel provides special MONTH function to get month number from a date. Sum times we want to get month name, like Jan, January, etc. That can be done too.
In this article, we will learn How to get numeric month from date and how to get text month from a date.
Context:
Here I have a list of dates. In the columns adjacent to it I want to get numeric month and text month.
Getting Month Number From Date In Excel
Excel has MONTH function that retrieves retrieves month from a date in numeric form.
Generic Formula
=MONTH(date)
Date: It is the date from which you want to get month number in excel.
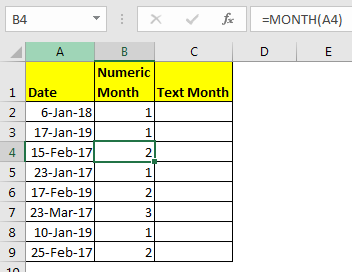
In cell B2, write this formula and copy it down the cells.
=MONTH(A2)
We have our month number in column B.
Getting Text Month From Date In Excel
If you want to get month name in excel from a date than use excel TEXT function.
Generic Formula
=TEXT(date, “mmm”)
=TEXT(date, “mmmm”)
The TEXT function is used to specially formate given values. Now let’s see how we can get month names from date in above example.
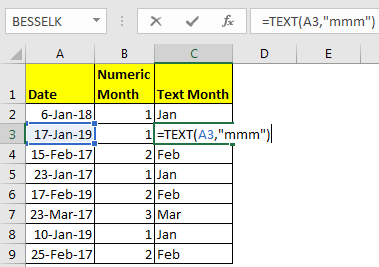
Write this formula in cell C2 and drag it down the cells.
This will return the name short month’s name from given date.
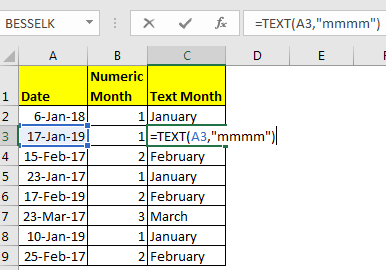
If you want full month name then write this formula.
=TEXT(A2, “mmmm”)
Simple, wasn’t it? So yeah guys these are the ways to extract month from date. If you have any query regarding this article or any other excel function, feel free to ask in the comment section below. We are a large community, there’s always someone to solve your Excel/VBA query.
Related Articles:
Calculate Months Between dates in Excel
Get day name from Date in Excel
Vlookup by Date in Excel
SUM if date is between
Popular Articles
50 Excel Shortcut to Increase Your Productivity: Get faster at your task. These 50 shortcuts will make you work even faster on Excel.
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel: This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
How to use the COUNTIF function in Excel: Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel: This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
To get detailed information about a function, click its name in the first column.
Note: Version markers indicate the version of Excel a function was introduced. These functions aren’t available in earlier versions. For example, a version marker of 2013 indicates that this function is available in Excel 2013 and all later versions.
|
Function |
Description |
|
DATE function |
Returns the serial number of a particular date |
|
DATEDIF function |
Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. This function is useful in formulas where you need to calculate an age. |
|
DATEVALUE function |
Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number |
|
DAY function |
Converts a serial number to a day of the month |
|
DAYS function |
Returns the number of days between two dates |
|
DAYS360 function |
Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
|
EDATE function |
Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date |
|
EOMONTH function |
Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months |
|
HOUR function |
Converts a serial number to an hour |
|
ISOWEEKNUM function |
Returns the number of the ISO week number of the year for a given date |
|
MINUTE function |
Converts a serial number to a minute |
|
MONTH function |
Converts a serial number to a month |
|
NETWORKDAYS function |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates |
|
NETWORKDAYS.INTL function |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
|
NOW function |
Returns the serial number of the current date and time |
|
SECOND function |
Converts a serial number to a second |
|
TIME function |
Returns the serial number of a particular time |
|
TIMEVALUE function |
Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number |
|
TODAY function |
Returns the serial number of today’s date |
|
WEEKDAY function |
Converts a serial number to a day of the week |
|
WEEKNUM function |
Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year |
|
WORKDAY function |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays |
|
WORKDAY.INTL function |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days |
|
YEAR function |
Converts a serial number to a year |
|
YEARFRAC function |
Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date |
Important: The calculated results of formulas and some Excel worksheet functions may differ slightly between a Windows PC using x86 or x86-64 architecture and a Windows RT PC using ARM architecture. Learn more about the differences.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Summary
If you need to extract the month from a date, you can use the MONTH function. In the generic form of the formula above, the date must be in a form that Excel recognizes as a valid date.
Generic formula
Explanation
The MONTH function takes just one argument, the date from which to extract the month. In the example shown, the formula is:
=MONTH(B4)
where B4 contains the dateJanuary 5, 2016. The MONTH function returns the number 1 representing the month( January) of the date.
Note that you can use MONTH to extract the month from a day entered as text:
=MONTH("1/5/2016")
However, using text for dates can produce unpredictable results on computers using different regional date settings. It’s better (and more flexible) to supply an address to a cell that already contains a valid date.
Get month name
To extract the month name from a date, you can use the TEXT function, as described in this example.
Author
Dave Bruns
Hi — I’m Dave Bruns, and I run Exceljet with my wife, Lisa. Our goal is to help you work faster in Excel. We create short videos, and clear examples of formulas, functions, pivot tables, conditional formatting, and charts.
There are hundreds and hundreds of Excel sites out there. I’ve been to many and most are an exercise in frustration. Found yours today and wanted to let you know that it might be the simplest and easiest site that will get me where I want to go.
Get Training
Quick, clean, and to the point training
Learn Excel with high quality video training. Our videos are quick, clean, and to the point, so you can learn Excel in less time, and easily review key topics when needed. Each video comes with its own practice worksheet.
View Paid Training & Bundles
Help us improve Exceljet
Excel allows you to format dates in many different ways. You can choose to show the date in a short date format or in a long date format.
You can also only show the day number, the month name, or the year from a given date.
In this short Excel tutorial, I will show you some easy methods to get the month name from a date in Excel.
So, let’s get started!
Getting the Month Name from the Date
There are multiple different ways to get monthly from a date in Excel.
The method you choose would depend on how you want the result (i.e., whether you want it as a text string or have the entire date but only show the name of the month)
Let’s see a couple of methods to do this that you can use in different scenarios.
Custom Formatting
Using custom number formatting to get the month name is the best method out of all those covered in this tutorial.
This is because it does not change the underlying date. It only changes the way the date is being displayed in the cell – which is by showing only the month name from the date.
The benefit of using this method is that you can still use the date in calculations.
Suppose you have the dates as shown below and you want to only display the month name and not the entire date.
Below are the steps to do this:
- Select all the cells that have the dates for which you want to show the month name
- Click the Home tab
- In the Number group, click on the dialog box launcher icon (or you can use the keyboard shortcut Control +1). This will open the Format Cells dialog box
- In the Category options, click on Custom
- In the type field, enter – ‘mmmm’. you should see one of the month names in the Sample preview.
- Click OK
The above steps would convert all the dates into their respective full month names (as shown below).
As I mentioned, the good thing about this method is that even though you are seeing the month names in the cell, the underlying value is still a date (which means that the underlying value is still a number that represents the date).
So, if you want to use these dates in calculations, you can easily do that.
You can also use custom number formatting to show the month name or the month value in different ways. To do this, you will have to give custom number formatting the right code to display the month name.
Below are the different month codes that you can use:
- m – this will show the month number. For example, a date in January would be shown as 1, a date in February would be shown as 2, and so on
- mm – this will also show the month number, but it will also make sure that there are always two digits that are displayed. For example, a date in January would be shown as 01, a date in February would be shown as 02, and a date in November would be shown as 11
- mmm – this will show the month name in a three-letter code. For example, a date in January would be shown as Jan, a date in August would be shown as Aug, and so on
- mmmm – this is the option that we used in the above example, and it would show the complete month name
- mmmmm – this option shows only the first alphabet of the month name. For example, January is shown as J and February is shown as F, and so on. I’ve never seen this being used because it’s confusing as January would also show J and July would also show J
TEXT Function
TEXT function allows us to convert a date into any permissible format that we want and gives the result as a text string.
For example, we can use the TEXT function to show the month name from a date.
Now if you’re wondering how is it different from the custom number formatting we used earlier, the big difference here is that with the TEXT function, you can combine the result with other functions or text strings.
Don’t worry if you are a little lost as of now, the next few examples will make it clear.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below and you want to show the month name instead of the full date.
Below is the TEXT formula will give you the month name:
=TEXT(A2,"mmmm")
The above text formula takes the date as the input and applies the specified format to it (which is “mmmm” in this formula).
Unlike the Custom Number Formatting method, when you use the TEXT function, the result is a text value. This means that you cannot use the result as a date or number in calculations.
But a good thing about using the TEXT function is that you can combine the result of the function with other text strings.
Let me explain using an example.
Suppose you have the same data set and in this case, instead of just getting the month name, you want to get the month name followed by the quarter number (such as January – Quarter 1).
The below formula would do this for you:
=TEXT(A2,"mmmm")&" - Quarter "&ROUNDUP(MONTH(A2)/3,0)
The above formula uses the ROUNDUP and the MONTH function to get the quarter number of the calendar year, and then it is combined with the month name which is given by the TEXT function.
Since the result of the TEXT function is a text string, I can combine it with other text strings or formula results.
CHOOSE Function
Another formula that you can use to quickly get the month name from the month number is using the CHOOSE formula.
While it ends up being a long formula, the choose formula technique is useful when you want to get the result which you cannot get with custom number formatting or the text function.
For example, if you want to return custom month names (such as month names in any other language or only five alphabets for each month name), you can do that using the CHOOSE formula.
Suppose you have a data set as shown below and you want to get the month name for each of these dates.
Below is the formula that will do that:
=CHOOSE(MONTH(A2),"Jan","Feb","Mar","Apr","May","Jun","Jul","Aug","Sep","Oct","Nov","Dec")
CHOOSE formula takes an index number (which is given by the month formula in our example) and then uses that index number to decide what value to return.
In this example, I have kept the month names to standard three-letter names, but you can change this and use whatever name you want.
Also read: Get Days in Month in Excel
Using Power Query
I have started using Power Query a lot more in my work as I find it a lot easier to clean the data using it.
It has an inbuilt feature that allows you to quickly convert a date into the month name.
The real value of using Power Query in such a scenario would be when you’re importing the data from other Excel files (or consolidating data from multiple Excel files into one file), and while doing it you want to convert your dates into month names.
You can check out my Power Query course on YouTube if you want to learn more about it.
For this technique to work, your data needs to be in an Excel table. While you can still use Power Query with named ranges, if your data is not in an Excel table I recommend you use any of the above methods.
Suppose you have the below data and you want to convert these dates into month names.
Below are the steps to do this:
- Select any cell in the dataset
- Click the Data tab
- In the Get & Transform Data tab, click on From Table/Range
- In the Power Query editor that opens up, right-click on the Date column header
- Go to Transform >> Month >> Name of Month
- Click on Close and Load
The above steps would insert a new worksheet and give you the resulting table in that new sheet.
Now, if you’re wondering why do all this when you can simply use custom number formatting or the text function, you need to understand the real value of Power Query trying to automate work.
If you need the month name from the date just once, feel free to use the methods shown above.
But if you’re using Power Query already to manage data from multiple different sources or combined files or sheets, then knowing that you can easily get the month name from the date can save you a lot of time.
So these are some of the methods that you can use to quickly get the month name from a date in Excel.
I hope you found this tutorial useful.
Other Excel tutorial’s you may also like:
- Calculate the Number of Months Between Two Dates in Excel
- Calculate Time in Excel (Time Difference, Hours Worked, Add/ Subtract)
- How to Change Date Format In Excel?
- How to Get the First Day of the Month in Excel
- How to Add or Subtract Days to a Date in Excel (Shortcut + Formula)
- How to Convert Serial Numbers to Dates in Excel)
- How to Stop Excel from Changing Numbers to Dates Automatically
- How to Make an Interactive Calendar in Excel? (FREE Template)
Dates are an important part of data. There are a few times when we need to use only a part from a date. Take an example of the month. Sometimes you only need a month from a date.
A month is one of the useful components of a date that you can use to summarize data and when it comes to Excel we have different methods to get a month from a date.
I’ve found a total of 5 methods for this. And today, in this post, I’d like to share with you all these methods to get/extract a month from a date. So let’s get down to the business.
1. MONTH Function
Using the MONTH function is the easiest method to extract a month from a date. All you need to do is just refer to a valid date in this function and it will return the number of the month ranging from 1 to 12.
=MONTH(A2)
You can also insert a date directly into the function using the correct date format.
| Pro | Con |
|---|---|
| It’s easy to apply and there is no need to combine it with other functions. | Month number has limited use, most of the time it’s better to present the month name instead of numbers and if you want the month name then you need a different method. |
2. TEXT Function
As I said, it’s better to use a month name instead of a month number. Using the TEXT function is a perfect method to extract the month name from a date. The basic work of the text function here is to convert a date into a month by using a specific format.
=TEXT(A2,"MMM")

By default, you have 5 different date formats which you can use in the text function. These formats will return the month name as a text. All you need to do is refer to a date in the function and specify a format. Yes, that’s all. And, make sure the date you are using should be a valid date as per Excel’s date system.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| You have the flexibility to choose a format among 5 different formats and the original date column will remain the same. | It will return the month name which will be a text and using a custom abbreviation for the month name is not possible. |
3. CHOOSE Function
Let’s say you want to get a custom month name or maybe a name in a different language instead of a number or a normal name. In that situation, CHOOSE function can help you. You need to specify a custom name for all 12 months in the function and need to use the month function to get the month number from the date.
=CHOOSE(MONTH(A1),"Jan","Feb","Mar","Apr","May","Jun","Jul","Aug","Sep","Oct","Nov","Dec")

When the month function returns a month number from the date, choose function will return the custom month name instead of that number.
Related: Formula Bar
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| It allows you more flexibility and you can specify a custom month name for each month. | It’s a time-consuming process to add all the values in the function one by one. |
4. Power Query
If you want to get a month’s name from a date in a smart way then power query is your calling. It can allow you to convert a date into a month and extract a month number or a month name from a date as well. Power Query is a complete package for you to work with dates. Here you have the below data and here you need months from dates.
- First of all, convert your data into a table.
- After that, select any of the cells from the table and go to the data tab.
- From the data tab, click on “From Table”.

- It will load your table in the power query editor.
From here, you have two different options one is to add a new column with the month name or month number or convert your dates into a month name or month number. Skip the next two steps if you just want to convert your dates into months without adding a new column.
- First of all, right-click on the column heading.
- And after that, click “Duplicate Column”.

- Select the new column from the heading and right-click on it.
- Go to Transform ➜ Month ➜ Name of Month or Month.

- It will instantly convert dates into months.

- Just one more thing, right-click on the column heading and rename the column to “Month”.
- In the end, click on “Close & Load” and it will load your data into a worksheet.

| Pro | Con |
|---|---|
| It’s a dynamic and one-time set-up. Your original data will not get impacted. | You should have a power query in your Excel version and the name of the month will be as a full name. |
5. Custom Formatting
If you don’t want to get into any formula method, the simple way you can use it to convert a date into a month is by applying custom formatting. Follow these simple steps.
- Select the range of cells or the column.
- Press the shortcut key Ctrl + 1.
- From the format option, go to “Custom”.
- Now, in the “Type” input bar enter “MM”, “MMM”, or “MMMMMM”.
- Click OK.

| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| It’s easy to apply and doesn’t change the date but its format. | As the value is a date, when you copy and paste it somewhere else as a value it will be a date, not text. If someone changes the format, the month’s name will be lost. |
Conclusion
All the above methods can be used in different situations. But some of them are more frequently used.
TEXT function is applicable in most situations. On the other hand, you also have a power query to get months in a few clicks. If you ask me, I use the text function but these days I am more in love with power query so I would also like to use it.
In the end, I just want to say, you can use any of these methods according to your need. But you need to tell me one thing.
Which one is your favorite method?
Please share with me in the comment section, I’d love to hear from you. And, don’t forget to share this with your friends.
Given a date value in Excel, is it possible to extract the month name?
For example, given the 2020-04-23 can you return the value April?
Yes, of course you can! Excel can do it all.
In this post you’ll learn 8 ways you can get the month name from a date value.
Long Date Format
You can get the month name by formatting your dates!
Good news, this is super easy to do!
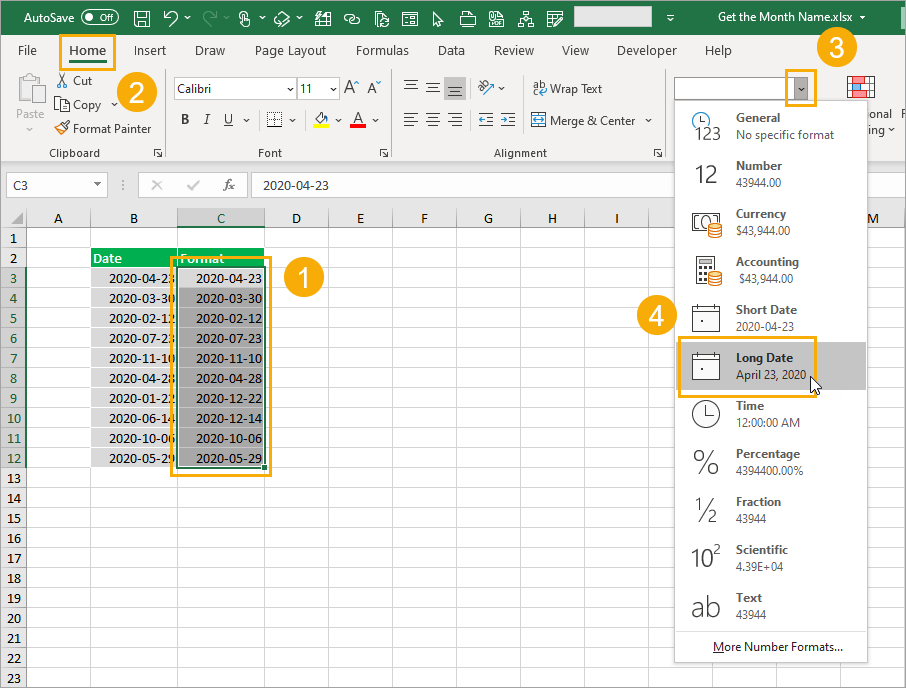
Format your dates:
- Select the dates you want to format.
- Go to the Home tab in the ribbon commands.
- Click on the drop-down in the Numbers section.
- Select the Long Date option from the menu.
This will format the date 2020-04-23 as April 23, 2020, so you’ll be able to see the full English month name.
This doesn’t change the underlying value in the cell. It is still the same date, just formatted differently.
Custom Formats
This method is very similar to the long date format, but will allow you to format the dates to only show the month name and not include any day or year information.
Select the cells you want to format ➜ right click ➜ select Format Cells from the menu. You can also use the Ctrl + 1 keyboard shortcut to format cells.
In the Format Cells dialog box.
- Go to the Number tab.
- Select Custom from the Category options.
- Enter mmmm into the Type input box.
- Press the OK button.
This will format the date 2020-04-23 as April, so you’ll only see the full month name with no day or year part.
Again, this formatting won’t change the underlying value, it will just appear differently in the grid.
You can also use the mmm custom format to produce an abbreviated month name from the date such as Apr instead of April.
Flash Fill
Once you’ve formatted a column of date values in the long date format shown above, you’ll be able extract the name into a text value using flash fill.
Start typing a couple examples of the month name in the adjacent column to the formatted dates.
Excel will guess the pattern and fill its guess in a light grey. You can then press Enter to accept these values.
This way the month names will exist as text values and not just formatted dates.
TEXT Function
The previous formatting methods only changed the appearance of the date to show the month name.
With the TEXT function, you’ll be able to convert the date into a text value.
= TEXT ( B3, "mmmm" )The above formula will take the date value in cell B3 and apply the mmmm custom formatting. The result will be a text value of the month name.
MONTH Functions
Excel has a MONTH function which can extract the month from a date.
MONTH and SWITCH
This is extracted as a numerical value from 1 to 12, so you will also need to convert that number into a name somehow. To do this you can use the SWITCH function.
= SWITCH (
MONTH(B3),
1,"January",
2,"February",
3,"March",
4,"April",
5,"May",
6,"June",
7,"July",
8,"August",
9,"September",
10,"October",
11,"November",
12,"December"
)The above formula is going to get the month number from the date in cell B3 using the MONTH function.
The SWITCH function will then convert that number into a name.
MONTH and CHOOSE
There’s an even more simple way to use the MONTH function as Wayne pointed out in the comments.
You can use the CHOOSE function since the month numbers can correspond to the choices of the CHOOSE function.
= CHOOSE (
MONTH(B3),
"January",
"February",
"March",
"April",
"May",
"June",
"July",
"August",
"September",
"October",
"November",
"December"
)The above formula is will get the month number from the date in cell B3 using the MONTH function, CHOOSE then returns the corresponding month name based on the number.
Power Query
You can also use power query to transform your dates into names.
First you will need to convert your data into an Excel table.
Then you can select your table and go to the Data tab and use the From Table/Range command.
This will open up the power query editor where you’ll be able to apply various transformation to your data.
Transform the date column to a month name.
- Select the column of dates to transform.
- Go to the Transform tab in the ribbon commands of the power query editor.
- Click on the Date button in the Date & Time Column section.
- Choose Month from the Menu.
- Choose Name of Month from the sub-menu.
This will transform your column of dates into a text value of the full month name.
= Table.TransformColumns ( #"Changed Type", {{"Date", each Date.MonthName(_), type text}} )This will automatically create the above M code formula for you and your dates will have been transformed.
You can then go to the Home tab and press Close & Load to load the transformed data back into a table in the Excel workbook.
Pivot Table Values
If you have dates in your data and you want to summarize your data by month, then pivot tables are the perfect option.
Select your data then go to the Insert tab and click on the Pivot Table command. You can then choose the sheet and cell to add the pivot table into.
Once you have your pivot table created, you will need to add fields into the Rows and Values area in the PivotTable Fields window.
Drag and drop the Date field into the Rows area and the Sales field into the Values area.
This will automatically create a Months field that summarizes the sales by month in you pivot table and the abbreviated month name will appear in your pivot table.
Power Pivot Calculated Column
You can also create calculated columns with pivot tables and the data model.
This will calculate a value for each row of data and create a new field for use in the PivotTable Fields list.
Follow the same steps as above to insert a pivot table.
In the Create Pivot Table dialog box, check the option to Add this data to the Data Model and press the OK button.
After creating the pivot table, go to the Data tab and press the Manage Data Model command to open the power pivot editor.
= FORMAT ( Table1[Date], "mmmm" )Create a new column with the above formula inside the power pivot editor.
Close the editor and your new column will be available for use in the PivotTable Fields list.
This calculated column will show up as a new field inside the PivotTable Fields window and you can use it just like any other field in your data.
Conclusions
That’s 8 easy ways to get the month name from a date in Excel.
If you just want to display the name, then the formatting options might be enough.
Otherwise, you can convert the dates into names with flash fill, formulas, power query or even inside a pivot table.
What is your favourite method?
About the Author
John is a Microsoft MVP and qualified actuary with over 15 years of experience. He has worked in a variety of industries, including insurance, ad tech, and most recently Power Platform consulting. He is a keen problem solver and has a passion for using technology to make businesses more efficient.
Содержание
- Date and time functions (reference)
- MONTH Function
- Related functions
- Summary
- Purpose
- Return value
- Arguments
- Syntax
- Usage notes
- Examples
- How to Get Month Name from Date in Excel (4 Easy Ways)
- Getting the Month Name from the Date
- Custom Formatting
- TEXT Function
- CHOOSE Function
- Using Power Query
Date and time functions (reference)
To get detailed information about a function, click its name in the first column.
Note: Version markers indicate the version of Excel a function was introduced. These functions aren’t available in earlier versions. For example, a version marker of 2013 indicates that this function is available in Excel 2013 and all later versions.
Returns the serial number of a particular date
Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. This function is useful in formulas where you need to calculate an age.
Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number
Converts a serial number to a day of the month
DAYS function
Returns the number of days between two dates
Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year
Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date
Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months
Converts a serial number to an hour
ISOWEEKNUM function
Returns the number of the ISO week number of the year for a given date
Converts a serial number to a minute
Converts a serial number to a month
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates
NETWORKDAYS.INTL function
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days
Returns the serial number of the current date and time
Converts a serial number to a second
Returns the serial number of a particular time
Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number
Returns the serial number of today’s date
Converts a serial number to a day of the week
Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays
WORKDAY.INTL function
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays using parameters to indicate which and how many days are weekend days
Converts a serial number to a year
Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date
Important: The calculated results of formulas and some Excel worksheet functions may differ slightly between a Windows PC using x86 or x86-64 architecture and a Windows RT PC using ARM architecture. Learn more about the differences.
Источник
MONTH Function
Summary
The Excel MONTH function extracts the month from a given date as number between 1 to 12. You can use the MONTH function to extract a month number from a date into a cell, or to feed a month number into another function like the DATE function.
Purpose
Return value
Arguments
- serial_number — A valid Excel date.
Syntax
Usage notes
The MONTH function extracts the month from a given date as a number between 1 to 12. For example, given the date «June 12, 2021», the MONTH function will return 6 for June. MONTH takes just one argument, serial_number, which must be a valid Excel date.
Dates can be supplied to the MONTH function as text (e.g. «13-Aug-2021») or as native Excel dates, which are large serial numbers. To create a date value from scratch with separate year, month, and day inputs, use the DATE function.
The MONTH function will «reset» every 12 months (like a calendar). To work with month durations larger than 12, use a formula to calculate months between dates.
The MONTH function returns a number. If you need the month name, see this example.
Examples
To use the MONTH function, supply a date:
With the date «September 15, 2017» in cell A1, MONTH returns 9:
You can use the MONTH function to extract a month number from a date into a cell, or to feed a month number into another function like the DATE function. The formula below extracts the month from the date in cell A1 and uses the TODAY and DATE functions to create a date on the first day of the same month in the current year.
See below for more examples of formulas that use the MONTH function.
Note: dates are serial numbers in Excel, and begin on January 1, 1900. Dates before 1900 are not supported. To display date values in a human-readable date format, apply the number format of your choice.
Источник
How to Get Month Name from Date in Excel (4 Easy Ways)
Excel allows you to format dates in many different ways. You can choose to show the date in a short date format or in a long date format.
You can also only show the day number, the month name, or the year from a given date.
In this short Excel tutorial, I will show you some easy methods to get the month name from a date in Excel.
So, let’s get started!
This Tutorial Covers:
Getting the Month Name from the Date
There are multiple different ways to get monthly from a date in Excel.
The method you choose would depend on how you want the result (i.e., whether you want it as a text string or have the entire date but only show the name of the month)
Let’s see a couple of methods to do this that you can use in different scenarios.
Custom Formatting
Using custom number formatting to get the month name is the best method out of all those covered in this tutorial.
This is because it does not change the underlying date. It only changes the way the date is being displayed in the cell – which is by showing only the month name from the date.
The benefit of using this method is that you can still use the date in calculations.
Suppose you have the dates as shown below and you want to only display the month name and not the entire date.
Below are the steps to do this:
- Select all the cells that have the dates for which you want to show the month name
- Click the Home tab
- In the Number group, click on the dialog box launcher icon (or you can use the keyboard shortcut Control +1). This will open the Format Cells dialog box
- In the Category options, click on Custom
- In the type field, enter – ‘mmmm’. you should see one of the month names in the Sample preview.
- Click OK
The above steps would convert all the dates into their respective full month names (as shown below).
As I mentioned, the good thing about this method is that even though you are seeing the month names in the cell, the underlying value is still a date (which means that the underlying value is still a number that represents the date).
So, if you want to use these dates in calculations, you can easily do that.
You can also use custom number formatting to show the month name or the month value in different ways. To do this, you will have to give custom number formatting the right code to display the month name.
Below are the different month codes that you can use:
- m – this will show the month number. For example, a date in January would be shown as 1, a date in February would be shown as 2, and so on
- mm – this will also show the month number, but it will also make sure that there are always two digits that are displayed. For example, a date in January would be shown as 01, a date in February would be shown as 02, and a date in November would be shown as 11
- mmm – this will show the month name in a three-letter code. For example, a date in January would be shown as Jan, a date in August would be shown as Aug, and so on
- mmmm – this is the option that we used in the above example, and it would show the complete month name
- mmmmm – this option shows only the first alphabet of the month name. For example, January is shown as J and February is shown as F, and so on. I’ve never seen this being used because it’s confusing as January would also show J and July would also show J
TEXT Function
TEXT function allows us to convert a date into any permissible format that we want and gives the result as a text string.
For example, we can use the TEXT function to show the month name from a date.
Now if you’re wondering how is it different from the custom number formatting we used earlier, the big difference here is that with the TEXT function, you can combine the result with other functions or text strings.
Don’t worry if you are a little lost as of now, the next few examples will make it clear.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below and you want to show the month name instead of the full date.
Below is the TEXT formula will give you the month name:
The above text formula takes the date as the input and applies the specified format to it (which is “mmmm” in this formula).
Unlike the Custom Number Formatting method, when you use the TEXT function, the result is a text value. This means that you cannot use the result as a date or number in calculations.
But a good thing about using the TEXT function is that you can combine the result of the function with other text strings.
Let me explain using an example.
Suppose you have the same data set and in this case, instead of just getting the month name, you want to get the month name followed by the quarter number (such as January – Quarter 1).
The below formula would do this for you:
The above formula uses the ROUNDUP and the MONTH function to get the quarter number of the calendar year, and then it is combined with the month name which is given by the TEXT function.
Since the result of the TEXT function is a text string, I can combine it with other text strings or formula results.
CHOOSE Function
Another formula that you can use to quickly get the month name from the month number is using the CHOOSE formula.
While it ends up being a long formula, the choose formula technique is useful when you want to get the result which you cannot get with custom number formatting or the text function.
For example, if you want to return custom month names (such as month names in any other language or only five alphabets for each month name), you can do that using the CHOOSE formula.
Suppose you have a data set as shown below and you want to get the month name for each of these dates.
Below is the formula that will do that:
CHOOSE formula takes an index number (which is given by the month formula in our example) and then uses that index number to decide what value to return.
In this example, I have kept the month names to standard three-letter names, but you can change this and use whatever name you want.
Using Power Query
I have started using Power Query a lot more in my work as I find it a lot easier to clean the data using it.
It has an inbuilt feature that allows you to quickly convert a date into the month name.
The real value of using Power Query in such a scenario would be when you’re importing the data from other Excel files (or consolidating data from multiple Excel files into one file), and while doing it you want to convert your dates into month names.
You can check out my Power Query course on YouTube if you want to learn more about it.
For this technique to work, your data needs to be in an Excel table. While you can still use Power Query with named ranges, if your data is not in an Excel table I recommend you use any of the above methods.
Suppose you have the below data and you want to convert these dates into month names.
Below are the steps to do this:
- Select any cell in the dataset
- Click the Data tab
- In the Get & Transform Data tab, click on From Table/Range
- In the Power Query editor that opens up, right-click on the Date column header
- Go to Transform >> Month >> Name of Month
- Click on Close and Load
The above steps would insert a new worksheet and give you the resulting table in that new sheet.
Now, if you’re wondering why do all this when you can simply use custom number formatting or the text function, you need to understand the real value of Power Query trying to automate work.
If you need the month name from the date just once, feel free to use the methods shown above.
But if you’re using Power Query already to manage data from multiple different sources or combined files or sheets, then knowing that you can easily get the month name from the date can save you a lot of time.
So these are some of the methods that you can use to quickly get the month name from a date in Excel.
I hope you found this tutorial useful.
Other Excel tutorial’s you may also like:
Источник
This post will guide you how to extract month and year from a date in excel. How do I get month and year from date cells with a formula in Excel. How to convert date to month and year in Excel.
Table of Contents
- Extract Month and Year from Date
- Related Functions
If you want to extract month and year from a date in Cell, you can use a formula based on the TEXT function.
Assuming that you have a list of data in range B1:B4 that contain dates, and you want to convert the normal excel date into year and month format (yyyymm), How to achieve it. You can use the following format:
=TEXT(B1,"yyyymm")
Type this formula into a blank cell and then press Enter key in your keyboard. and drag the AutoFill Handle over other cells to apply this formul.
This formula will get a date with the year and month only from the orignial date in Cells.
If you only want to extract month from a date, and you can use the following formula:
=TEXT(B1,"mmm")
If you want to convert date to year format only, you can use the following formula:
=TEXT(B1,"yyyy")
- Excel Text function
The Excel TEXT function converts a numeric value into text string with a specified format. The TEXT function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as a Text Function. The syntax of the TEXT function is as below: = TEXT (value, Format code)…
How to Use Excel > Excel Formula > How to Extract Day, Month and Year from Date in Excel
How to Extract Day, Month and Year from Date in Excel
Table of contents :
- Extract Day from Date in Excel
- Extract Month from Date in Excel
- Extract Year from Date in Excel
Excel provides three different functions to extract a day, month, and year from date. The following is an explanation of each function to extract each value.
Extract Day from Date in Excel
The formula
=DAY(A2)
The result
If you want to extract the day from the date, you can use the DAY function. The DAY function requires only one argument, fill it with valid excel date value.
The result, there are four days value and one error #VALUE!. An error occurred because 2/29/2006 is not a valid Excel date value. Why? Because 2006 is not a leap year, so there is no February 29th.
The DAY function result is a number between 1 and 31.
Extract Month from Date in Excel
The formula
=MONTH(A2)
The result
To extract month from the date you need the MONTH function. Like the DAY function, the MONTH function has only one argument, filled with a valid Excel date value.
There is a #VALUE error. The error appearance is the same place as the #VALUE error in DAY function result. The cause of the error is the same; the date value in cell A5 is not a valid Excel date value. This error will still appear in all excel functions related to the date.
The MONTH function result is a number between 1 and 12.
Extract Year from Date in Excel
The formula
=YEAR(A2)
The result
To extract the year from date, Excel provides the YEAR function. There is an argument that must be filled with a valid Excel date value.
The results of the DAY and MONTH functions are a number with a narrow range. Instead, the YEAR function is a wide range of numbers between 1900 and 9999.
For years less than 1900 or more than 9999, it will be considered an invalid excel date value. If used by an Excel function (related to the date function) returns a #VALUE! Error.
The DAY, MONTH and YEAR functions extract day, month and year from a date. To do the opposite, converting day, month and year in number to date value, you need the DATE function.
Related Function
Function used in this article