Генератор случайных чисел в VBA Excel. Функция Rnd, оператор Randomize, функция рабочего листа RandBetween. Синтаксис, параметры, примеры кода.
Rnd – это функция, которая возвращает значение типа Single, содержащее псевдослучайное число меньшее 1, но большее или равное нулю.
Псевдослучайное число отличается от случайного тем, что оно получено с помощью алгоритма, который, в любом случае, подчиняется какой-либо закономерности. Для решения большинства, а возможно и всех, задач в VBA Excel псевдослучайное число можно считать случайным.
Синтаксис
Rnd[(Число)]
Число – необязательный параметр, определяющий алгоритм вычисления псевдослучайного числа. Зависимость случайного числа от этого параметра:
| Число | Возвращаемое значение |
|---|---|
| Меньше нуля | Одно и то же псевдослучайное число каждый раз, как результат использования параметра Число в качестве начального значения для алгоритма |
| Больше нуля | Каждое следующее число в псевдослучайном порядке |
| Равно нулю | Самое последнее псевдослучайное число, созданное функцией Rnd |
| По умолчанию | Каждое следующее число в псевдослучайном порядке |
Для любого параметра Число создается одна и та же последовательность чисел, так как каждый последующий вызов функции Rnd использует предыдущее значение в качестве начального для следующего псевдослучайного числа в последовательности.
Функция Rnd – это и есть простейший генератор случайных чисел в VBA Excel, возвращающий значения в интервале 0<=Rnd<1.
Чтобы повысить «случайность» псевдослучайных чисел, возвращаемых функцией Rnd, используется оператор Randomize.
Оператор Randomize
Randomize – это оператор, который инициализирует генератор случайных чисел функции Rnd, задавая начальное число для генерации первого псевдослучайного числа.
Синтаксис
Randomize[Число]
Число – необязательный параметр, задающий начальное число для генерации. Если параметр Число опущен, используется значение, возвращенное системным таймером.
При повторном использовании в VBA Excel оператора Randomize с тем же значением аргумента Число предыдущая последовательность не повторяется.
Для повторения предыдущей последовательности случайных чисел необходимо непосредственно перед оператором Randomize с тем же значением аргумента Число вызвать функцию Rnd с отрицательным аргументом.
WorksheetFunction.RandBetween
RandBetween – функция рабочего листа, возвращающая целое случайное число в пределах заданного диапазона значений.
Синтаксис
WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(Arg1, Arg2)
- Arg1 – наименьшее целое число, которое возвращает функция рабочего листа RandBetween (обязательный параметр);
- Arg2 – наибольшее целое число, которое возвращает функция рабочего листа RandBetween (обязательный параметр).
Примеры записи строк с WorksheetFunction.RandBetween в VBA Excel (присвоение случайного числа переменной):
|
a = WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(—65, —15) a = WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(5, 145) |
Если данную функцию вставить в ячейку рабочего листа, например: =СЛУЧМЕЖДУ(25;55), случайное число будет обновляться при каждом пересчете листа.
Примеры с Rnd и Randomize
Пример 1
Запускаем генератор случайных чисел функции Rnd с разными параметрами и выводим результаты на рабочий лист Excel:
|
Sub Primer1() Dim i As Byte Cells(1, 1) = «Rnd(-5)» For i = 2 To 5 Cells(i, 1) = Rnd(—5) Next Cells(1, 2) = «Rnd(3)» For i = 2 To 5 Cells(i, 2) = Rnd(3) Next Cells(1, 3) = «Rnd(0)» For i = 2 To 5 Cells(i, 3) = Rnd(0) Next End Sub |
Получаем следующий результат:
Пример 2
Повторное использование оператора Randomize с тем же значением аргумента Число:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
Sub Primer2() Dim i As Byte Cells(1, 1) = «Последовательность 1» Rnd (—1) Randomize 4 For i = 2 To 5 Cells(i, 1) = Rnd Next Cells(1, 2) = «Последовательность 2» Randomize 4 For i = 2 To 5 Cells(i, 2) = Rnd Next Cells(1, 3) = «Последовательность 3» Rnd (—1) Randomize 4 For i = 2 To 5 Cells(i, 3) = Rnd Next End Sub |
Строка кода Rnd (-1) обеспечивает генерацию последовательности случайных чисел сначала при повторных использованиях оператора Randomize.
Строка кода Randomize 4 перед заполнением второго столбца не влияет на работу функции Rnd, а заполнение последовательности для третьего столбца начинается заново благодаря строке Rnd (-1) перед оператором Randomize.
Пример 3
Создание генераторов случайных чисел для разных диапазонов. Исходим из того, что функция Rnd генерирует псевдослучайную последовательность из чисел меньше 1, но больше или равным 0.
Примеры с положительными случайными числами:
|
‘От 0 (включительно) до 10 10 * Rnd ‘От 6 (включительно) до 7 Rnd + 6 ‘От 5 (включительно) до 10 5 * Rnd + 5 |
Примеры с отрицательными случайными числами:
|
‘От -10 до 0 (включительно) —10 * Rnd ‘От -10 до 10 (включительно) —20 * Rnd + 10 ‘От -10 до -5 (включительно) —(5 * Rnd + 5) |
Пример заполнения ячеек положительными и отрицательными случайными числами на листе Excel:
|
Sub Primer3() Dim i As Byte Cells(1, 1) = «От 1 до 3» For i = 2 To 9 Cells(i, 1) = 2 * Rnd + 1 Next Cells(1, 2) = «От -5 до 5» For i = 2 To 9 Cells(i, 2) = —10 * Rnd + 5 Next Cells(1, 3) = «От -5 до -2» For i = 2 To 9 Cells(i, 3) = —3 * Rnd — 2 Next End Sub |
Результат выполнения кода VBA Excel третьего примера:
We will explore the options to create your own random number generator in an Excel Worksheet or in VBA (Macro). You can generate randoms in 2 ways:
- Using Excel functions i.e. using the RAND or RANDBETWEEN functions
- Using VBA (Visual Basic macro) using the RANDOMIZE and RND functions
Random Number Generator using Excel functions
To create a random number in Excel you have 3 options:
Remember that the RAND and RANDBETWEEN functions are volatile, meaning they will be recalculated on any change to the worksheet regardless if it affects the formula. This may mean you will see constant changes to these numbers. In case it affects your performance be sure to replace your random numbers with static (copy paste as values) or generate them using VBA.
Random Numbers using VBA functions
To generate random numbers in VBA you need to use 2 functions:
- Randomize – that initializes the Rnd function with a provided seed. If you leave the argument blank it will use the actual system timer value. If you provide a certain number e.g. 10 you will always get the same sequence of random numbers. Why? Because computers use pseudo random number generators.
- Rnd – function that generates the actual random decimal numbers between 0-1.
Below a simple example:
Dim myRandom as Double Randomize 'Initialize the Rnd function myRandom = Rnd 'Generate a random number between 0-1 Debug.Print myRandom 'Print the number on console e.g. 0.308616280555725
VBA Generate whole numbers
To generate whole numbers similarly like the RANDBETWEEN Excel function we need to use the VBA CInt function to convert the decimal number to an Integer:
Dim myRandom As Double Randomize 'Initialize the Rnd function myRandom = CInt(Rnd * 100) 'Generate a random number between 0-100 Debug.Print myRandom 'e.g. 25
The above is limited to numbers starting at 0 up to the upper boundry (above 100). We can adjust the lower and upper boundries adjusting the formula above:
Dim myRandom As Double Randomize 'Initialize the Rnd function myRandom = CInt(5 + Rnd * 95) 'Generate a random number between 5-100 Debug.Print myRandom 'e.g. 5
The above will generate numbers between 5 and 100.
VBA Generate decimal numbers
Using similar approach as above and removing the VBA CInt function we can generate decimal numbers between any 2 given numbers:
Dim myRandom As Double Randomize 'Initialize the Rnd function myRandom = 5 + Rnd * 95 'Generate a random decimal number between 5-100 Debug.Print myRandom 'e.g. 5.4242442
Home / VBA / How to Generate Random Numbers in VBA
In VBA, there are different ways that you can use to generate a random number in Excel, and in this post, we will look at all of them one by one.
RND Function
To generate a random number, in VBA, there is a function called RND. This function stands for random and when you use this function in code it returns a random number between 0 to 1. In RND, you don’t need to specify any argument.
Range("A1") = Rnd()The above code uses it to get a random number in the A1 and it has returned 0.705547521.

But when you use it for an entire range it returns the same random number in the entire range and that makes it void for use to generate random numbers more than once.

Now here it doesn’t make sense to use it, right? But there’s a solution that you can use, FOR NEXT LOOP.

In the above code, you have a loop that loops through 10 cells (one by one) from the selected cell and adds a random number.
Here’s the full code:
Sub vba_random_number()
Dim i As Long
i = 10
For i = 1 To i
ActiveCell.Value = Rnd()
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
Next i
End SubRandom Number Between Two Numbers
If you want to generate a random number between two defined numbers, in that case, you need to write code by using two VBA Functions (RND + INT). The code for this formula would be like below.

Sub vba_random_number()
Dim myRnd As Integer
myRnd = Int(2 + Rnd * (45 - 10 + 1))
Range("A1") = myRnd
End SubWhen you run this macro, RND uses the max number and the min number that you have defined to generate the random number and INT removes the decimal from that.

Using Worksheet Functions in a VBA Code to Generate a Random Number
In VBA, you can access worksheet functions and use them to get a result by specifying the arguments. There are two functions from the worksheet that can help you to get a random number in the result.
- RandBetween
- RandArray
Before you use these functions make sure to understand the arguments that you need to define. Now in the below code, you have RANDBETWEEN which generates a random number between two numbers.

Range("A1") = WorksheetFunction.RandBetween(1000, 2000)Here the max number is 2000 and the min number is 1000. In the same way, you can use the RANDARRAY which is dynamic arrays function.
Here’s the code.
Range("A1:B10") = WorksheetFunction.RandArray(10, 2, 1000, 2000, True)
If you look at the syntax of the RANDARRAY, you will find that you can enter random numbers in an entire range which is not possible with all the methods that we have discussed above.

Return to VBA Code Examples
This tutorial will demonstrate how to work with random numbers in VBA.
RND Function
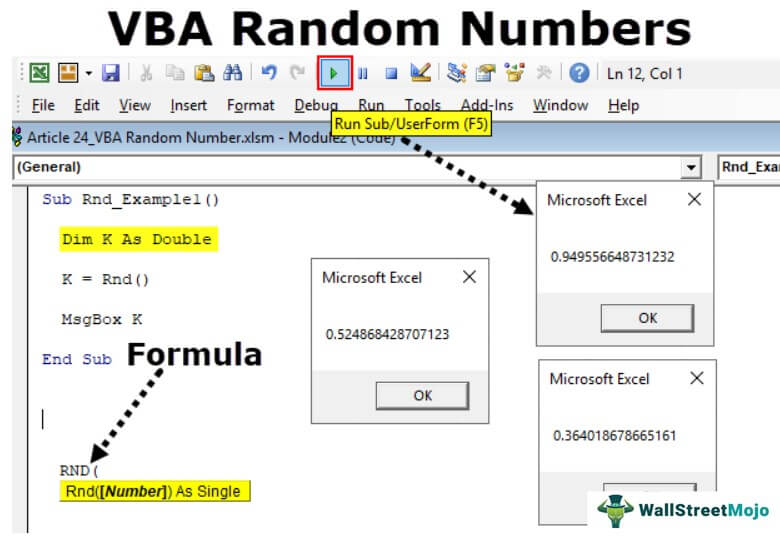
The RND Function generates a number that is between 0 and 1. The syntax of the RND Function is:
Rnd([Number]) where:
- Number (Optional) – This is optional and if <0, the function returns the same random number on each call using [Number] as the seed, if =0, the function returns the most recent random number, if >0 the function returns the next generated random number. If blank the default >0, is used.
Sub RndNum()
MsgBox Rnd()
End SubGenerating a Random Number in VBA
In order to generate a random number between two values, you have to use the RND Function in combination with the INT Function (Integer Function) using the following general formula:
- Int(lowerbound + Rnd * ( upperbound – lowerbound + 1 ) )
So, in order to generate a random number between 2 and 30, you would use the following code:
Sub GeneratingARandomNumber()
Dim randomNumber As Integer
randomNumber = Int(2 + Rnd * (30 - 2 + 1))
Debug.Print randomNumber
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!

VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
(No installation required!)
Free Download
We have an inbuilt function called RND to generate random numbers in VBA. It just takes an argument of a number to generate random numbers. It is also an optional parameter. It will create random numbers greater than 0 and smaller than 1.
It works the same as the Excel function “RAND.” As we said in the worksheet function “RAND” in VBA, too, we can generate random numbers that are greater than 0 but less than 1.
Now, look at the syntax of the RND function.
[Number]: We can pass the argument in three ways.
- If we pass the number as <0, it generates the same random number every time.
- If we pass the number as 0, it will repeat its most recent number.
- If we pass the number >0, it keeps giving you different random numbers, i.e., the next random number in the sequence.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Random Numbers
- How to Generate Random Numbers using VBA Code?
- Example #1
- Example #2 – Get the Same Random Number Every Time
- Example #3 – Generate Whole Random Number
- Recommended Articles
- How to Generate Random Numbers using VBA Code?
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Random Numbers (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Generate Random Numbers using VBA Code?
You can download this VBA Random Numbers Excel Template here – VBA Random Numbers Excel Template
Example #1
We will see a simple example of using the “RND” function. After that, follow the below steps to write the VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more on your own.
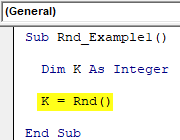
Step 1: Declare the variable as “Integer” in VBA.
Code:
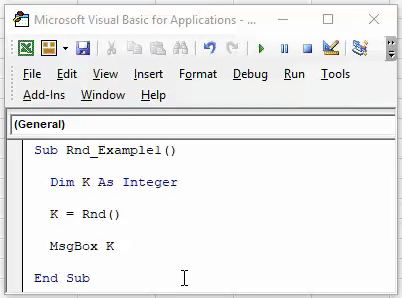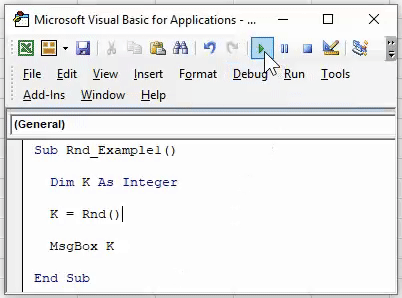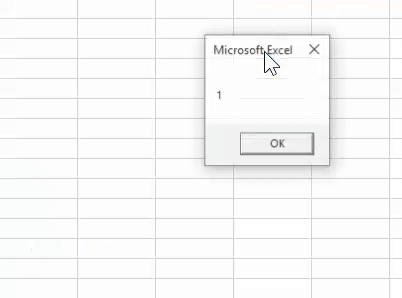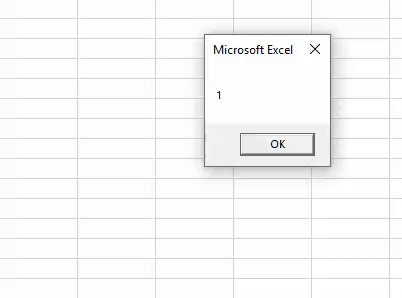
Sub Rnd_Example1() Dim K As Integer End Sub
Step 2: Now, assign the value to the variable “k” through the RND function.
Code:
Sub Rnd_Example1() Dim K As Integer K = Rnd() End Sub
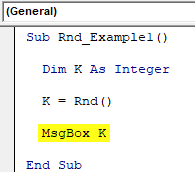
Step 3: Show the value returned by the variable “k” in the message box.
Code:
Sub Rnd_Example1() Dim K As Integer K = Rnd() MsgBox K End Sub
Now, run the excel macroA macro in excel is a series of instructions in the form of code that helps automate manual tasks, thereby saving time. Excel executes those instructions in a step-by-step manner on the given data. For example, it can be used to automate repetitive tasks such as summation, cell formatting, information copying, etc. thereby rapidly replacing repetitious operations with a few clicks.
read more and see what the result is.
Look what has happened.
It shows the result as 1, where the “RND” function can return only numbers greater than zero but less than 1.
You must be thinking about what the wrong thing here is.
The wrong thing here is the kind of data type we have assigned to the variable “k.”
If you look back at the variable we have declared, we have assigned the data type as “Integer.” Since we have assigned the variable as Integer, it can only show the whole numbers between -32768 to 32767.
Whenever RND returns the decimal number, VBA converts the decimal number to the nearest Integer, i.e., 1.
So, to make the formula work properly, declare the variable as “Double.”
“Double” is the data type in VBA that can hold decimal values.
Code:
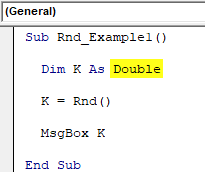
Sub Rnd_Example1() Dim K As Double K = Rnd() MsgBox K End Sub
Now, code and see what the result is.
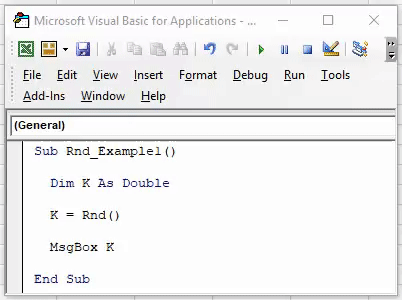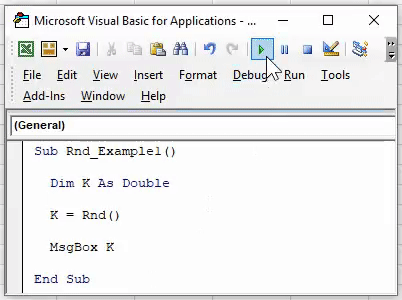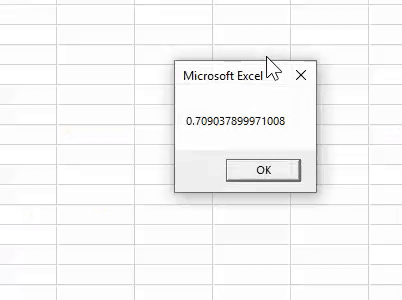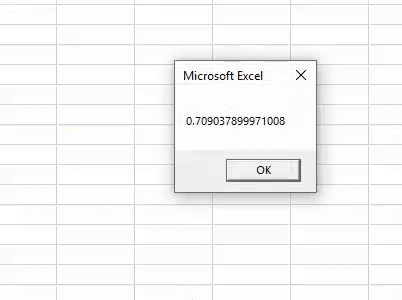
Click on “OK” and run once more to see the result.
This time we got a different result. Since “RND” is a volatile function in nature, it reproduces different results every time you execute the code.
Example #2 – Get the Same Random Number Every Time
As we have seen in the previous example e, the “RND” function reproduces the result every time we execute the code. Therefore, to get the same random number, again and again, we need to pass the argument as zero.
Code:
Sub Rnd_Example2() Dim K As Double K = Rnd(0) MsgBox K End Sub
It will produce the same number repeatedly when we execute the code.
Example #3 – Generate Whole Random Number
We can also generate whole numbers using other VBA functionsVBA functions serve the primary purpose to carry out specific calculations and to return a value. Therefore, in VBA, we use syntax to specify the parameters and data type while defining the function. Such functions are called user-defined functions.read more or input numbers. For example, look at the below code.
Code:
Sub Rnd_Example3() Dim K As Double K = 1 + Rnd * 100 MsgBox K End Sub
This code will generate random whole numbers with decimal points every time we execute the code.
If you are looking at the whole numbers without decimal points, we can use the code below.
Code:
Sub Rnd_Example3() Dim K As Double K = CInt(1 + Rnd * 100) MsgBox K End Sub
It will keep generating the whole numbers from 1 to 100.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Random Numbers. Here, we learned how to generate VBA random numbers using the RND function, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- VBA New Line
- VBA Split
- Generate Random Numbers in Excel
- How to Randomize List in Excel?